Submitted:
25 April 2024
Posted:
25 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
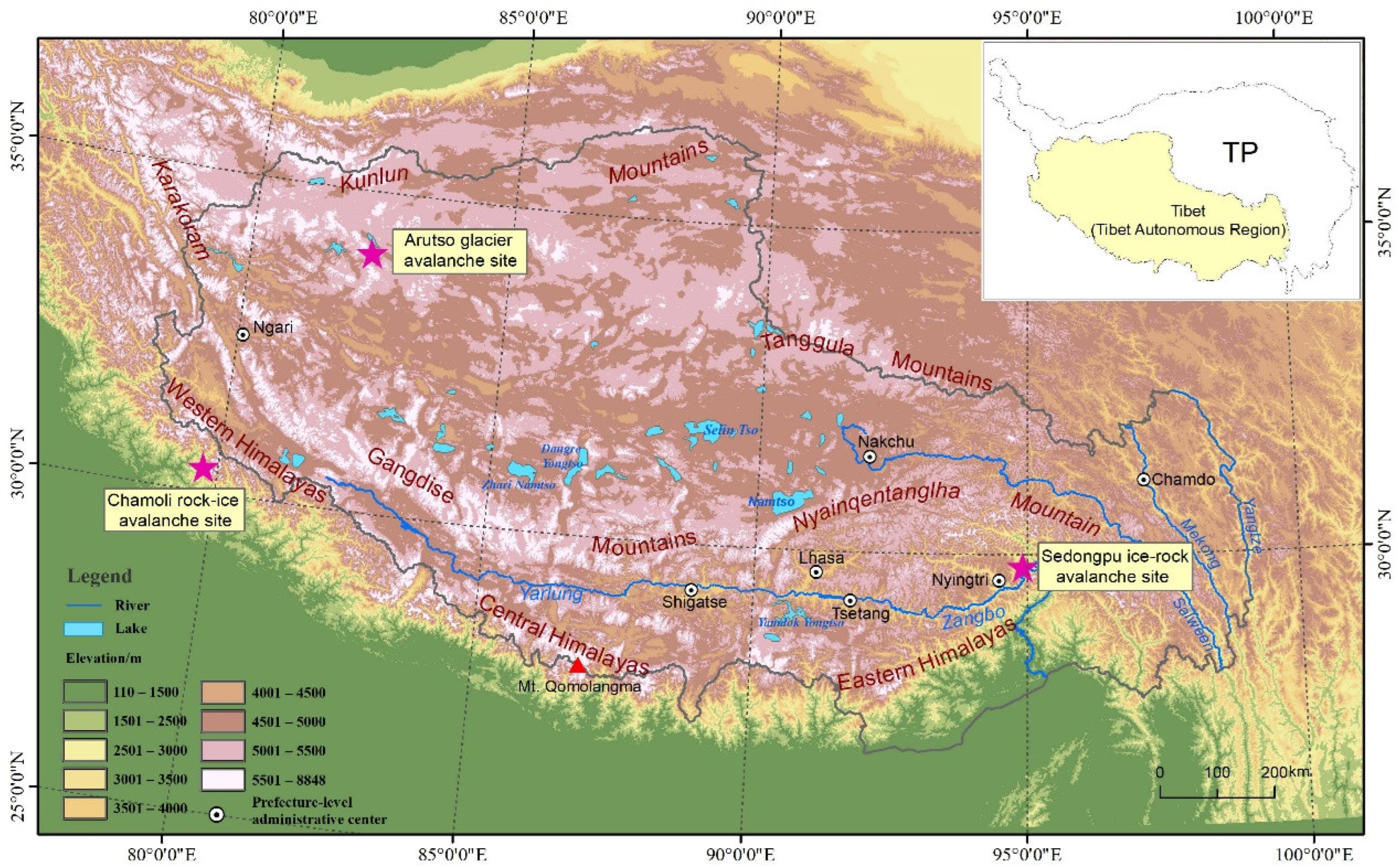
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Methods
3. Results
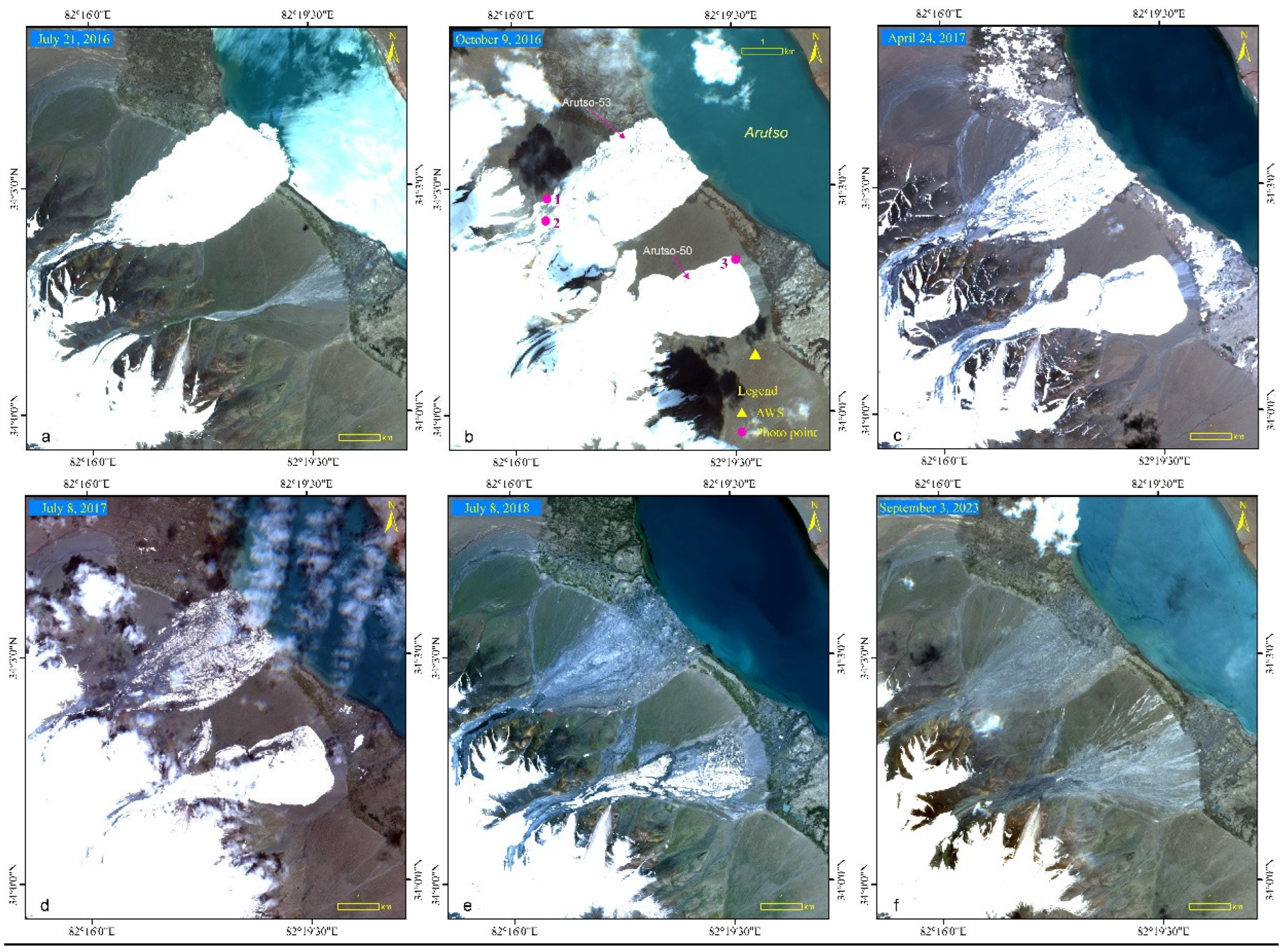
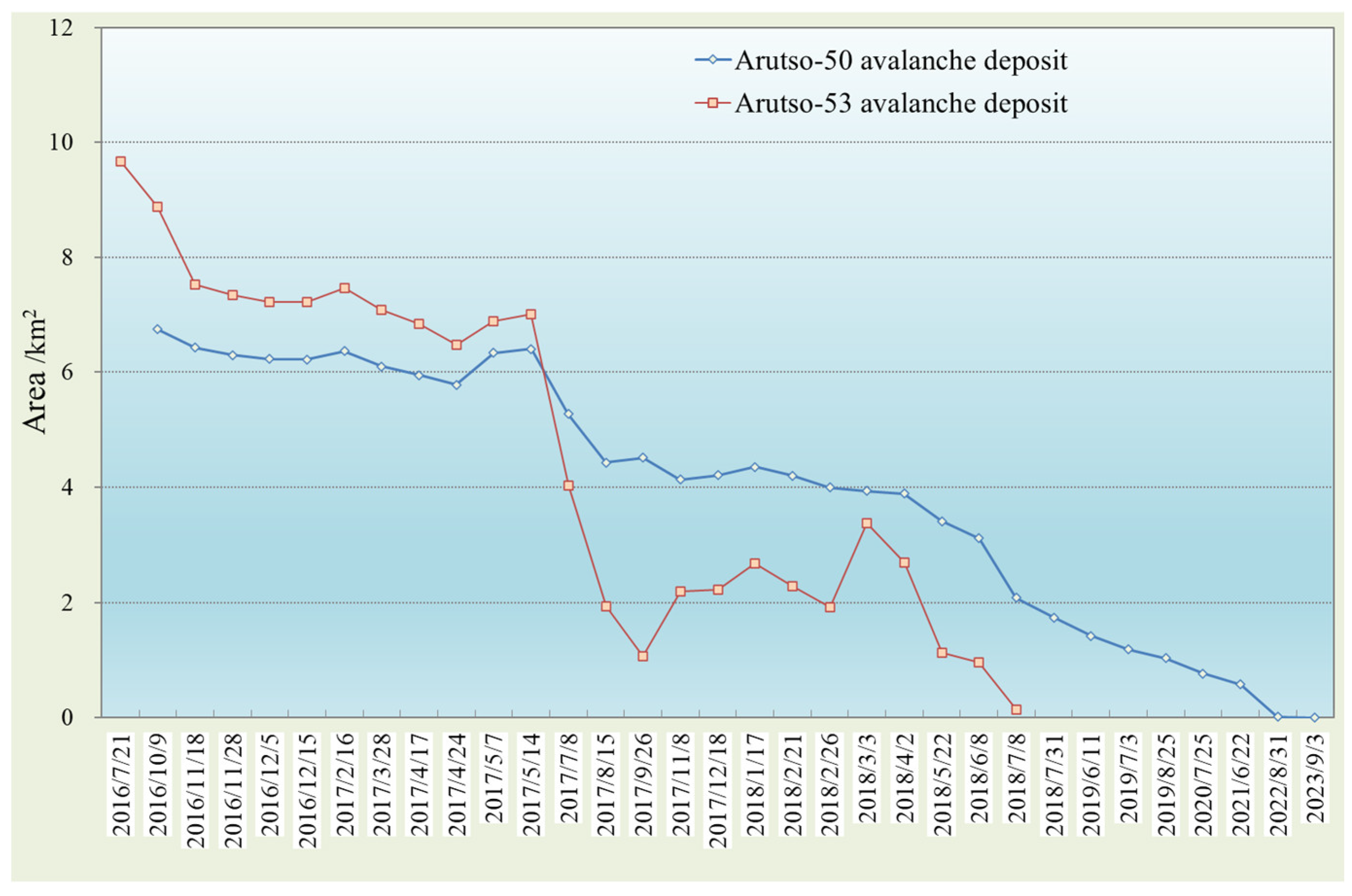
3.1. Arutso Glacier Avalanche
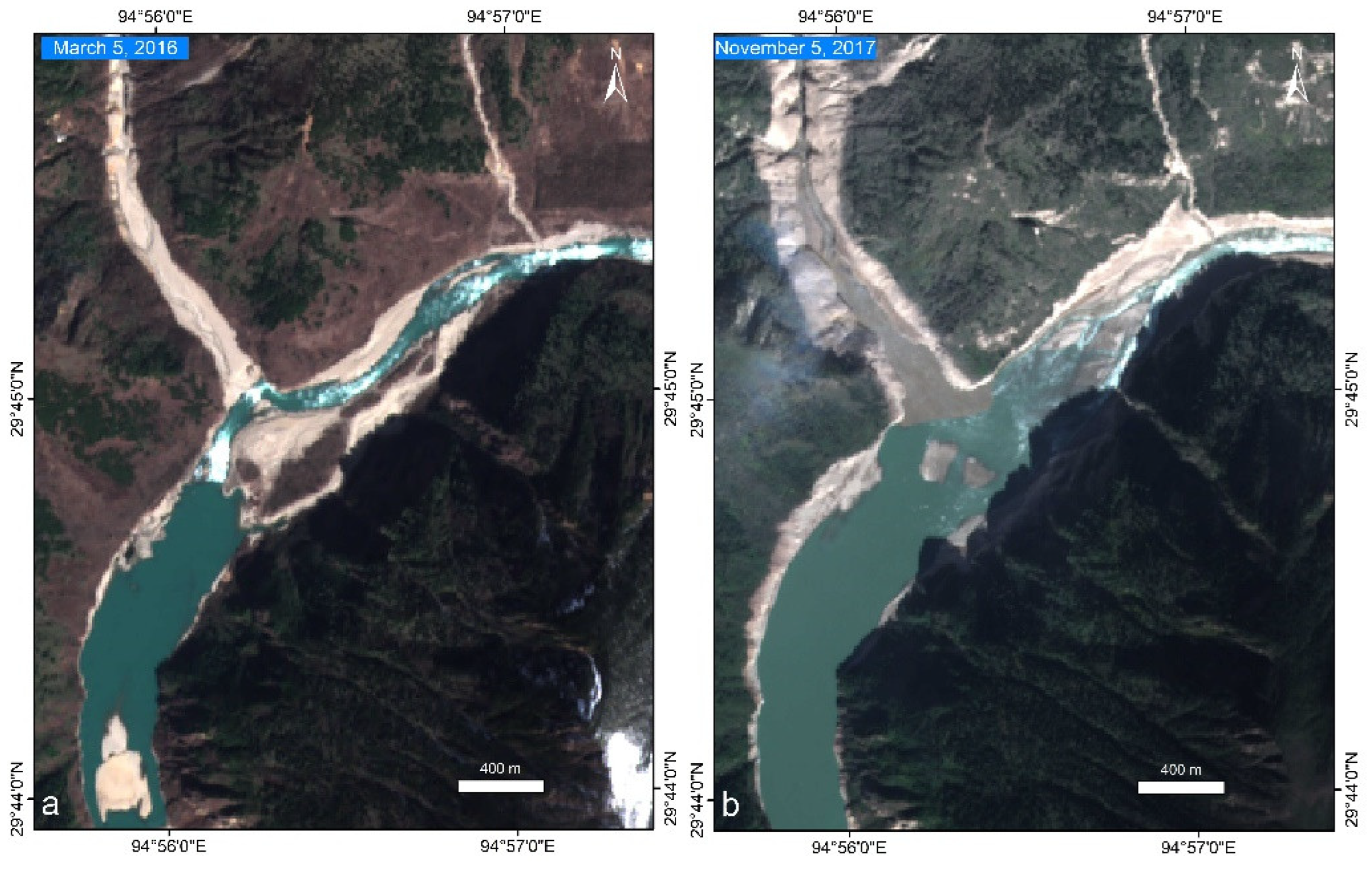
3.1.1. Satellite Observation
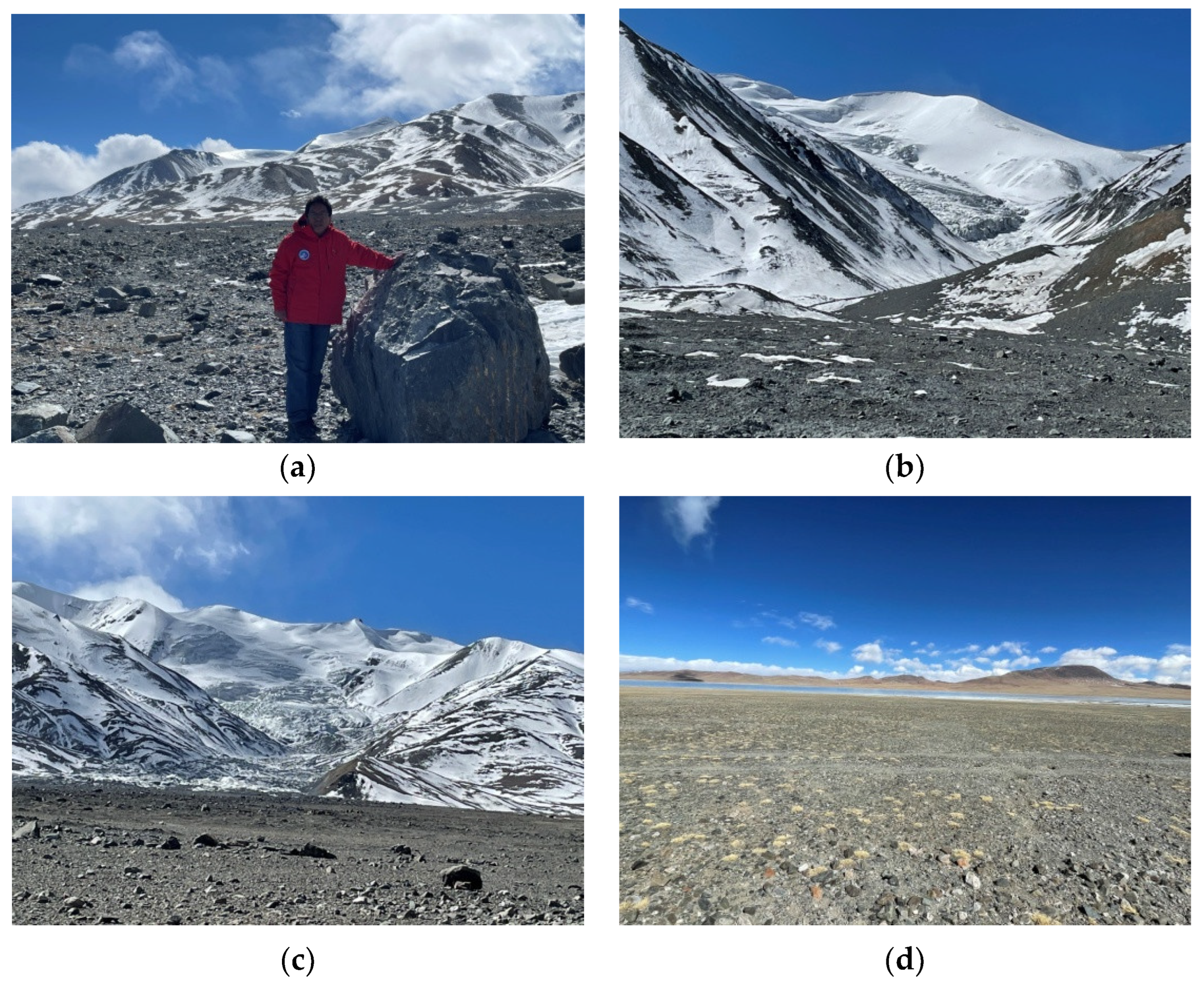
3.1.2. Field Investigation
3.1.3. Analysis on Driving Factors
3.2. Sedongpu Ice-Rock Avalanches
3.2.1. Satellite Observation
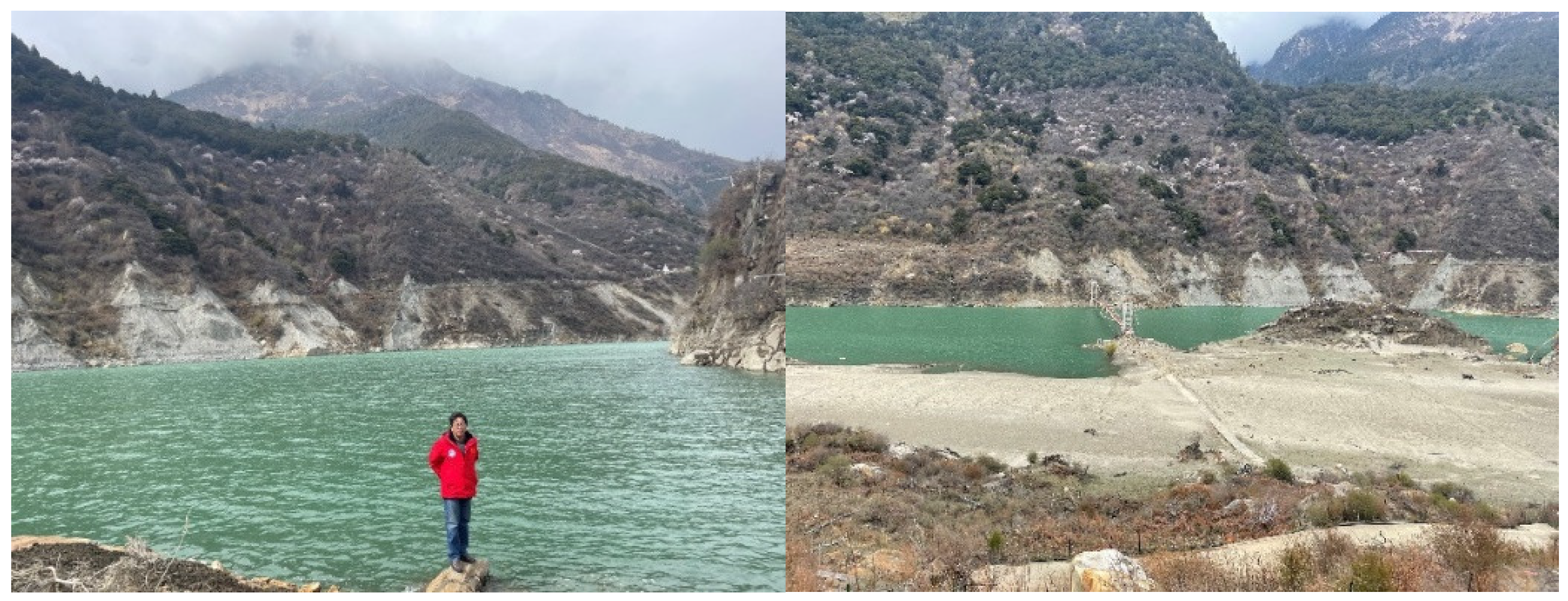
3.2.2. Field Investigation
3.2.3. Analysis on Possible Drivers
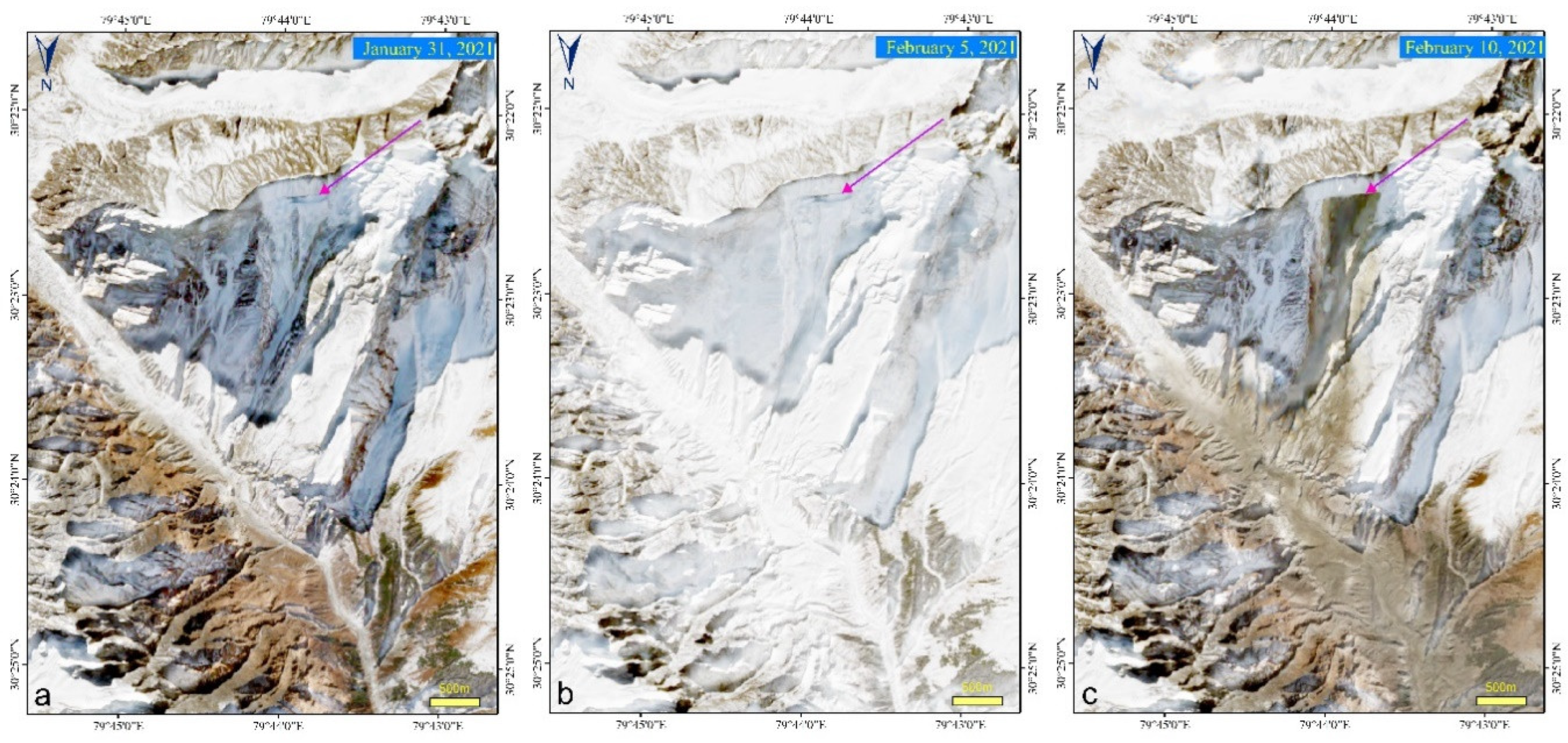
3.3. Chamoli Rock-Ice Avalanche
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Shugar, D.H.; Jacquemart, M.; Shean, D.; Bhushan, S.; Upadhyay, K.; Sattar, A.; Schwanghart, W.; McBride, S.; de Vries, M.V.W.; Mergili, M.; et al. A massive rock and ice avalanche caused the 2021 disaster at Chamoli, Indian Himalaya. Science 2021, 373, 300–306. [CrossRef]
- Kargel, J.S.; Leonard, G.J.; Shugar, D.H.; Haritashya, U.K.; Bevington, A.; Fielding, E.J.; Fujita, K.; Geertsema, M.; Miles, E.S.; Steiner, J.; et al. Geomorphic and geologic controls of geohazards induced by Nepals 2015 Gorkha earthquake. Science 2015, 351, aac8353. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.; Purves, R.S.; Huggel, C.; Noetzli, J.; Haeberli, W. On the influence of topographic, geological and cryospheric factors on rock avalanches and rockfalls in high-mountain areas. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 241–254. [CrossRef]
- Hock, R.; Rasul,G., Adler, C.; et al. High Mountain Areas. In: IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2019, 131–202.
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.-M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; et al. Recent Third Pole’s Rapid Warming Accompanies Cryospheric Melt and Water Cycle Intensification and Interactions between Monsoon and Environment: Multidisciplinary Approach with Observations, Modeling, and Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate change will affect the Asian Water Towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385.
- Mukherji, A.; Sinisalo, A.; Nüsser, M.; Garrard, R.; Eriksson, M. Contributions of the cryosphere to mountain communities in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: a review. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 1311–1326. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Allen, S.K.; Bao, A.; Ballesteros-Cánovas, J.A.; Huss, M.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yu, T.; et al. Increasing risk of glacial lake outburst floods from future Third Pole deglaciation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 411–417. [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, W.; Qiu, B.; Xue, Y.; Hsu, P.-C.; Wei, J. Influence of Tibetan Plateau snow cover on East Asian atmospheric circulation at medium-range time scales. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4243. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Yu, W.; Yao, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, N.; Yang, W.; You, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Glacier anomalies and relevant disaster risks on the Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2770–2782. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yao, T.; Wang, W.; et al. Glacial hazards on Tibetan Plateau and surrounding alpines. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019,34(11),1285–1292. (In Chinese).
- Lutz, A.F.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Shrestha, A.B.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Consistent increase in High Asia's runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 587–592. [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z. Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau and Topographic Controls. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 4044. [CrossRef]
- Nazir A.; Cui, P.; Paul A. C.; et al. Increasing glacial lake outburst flood hazard in response to surge glaciers in the Karakoram. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 212,103432.
- Chu, D. Remote Sensing of Land Use and Land Cover in Mountain Region; Springer Nature, Singapore. 2020.
- Wang, S.; Xiao, C. Global cryospheric disaster at high risk areas: Impacts and trend. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 891–901. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, B.; Gao, Y.; et al. Remote sensing interpretation of development characteristics of high-position geological hazards in Sedongpu gully, downstream of Yarlung Zangbo River. Chin. J. Geol. Haz. Control. 2021, 32(3),33–41. (In Chinese).
- Chai, B.; Tao, Y., Du, J.; et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow triggered by outburst of Jialong glacial lake in Nyalam County, Tibet. Earth Sci. 2020, 45(12), 4630–4639. (In Chinese).
- Tang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Distribution and risk of ice avalanche hazards in Tibetan Plateau. Earth Sci. 2022, 47(12),4447–4462. (In Chinese).
- Huggel, C.; Zgraggen-Oswald, S.; Haeberli, W.; et al. The 2002 rock/ice avalanche at Kolka /Karmadon, Russian Caucasus: assessment of extraordinary avalanche formation and mobility, and application of QuickBird satellite imagery. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5(2),173–187.
- Kääb, A.; Wessels, R.; Haeberli, W.; et al. Rapid imaging facilitates timely assessment of glacier hazards and disasters. Eos Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union. 2003, 84(13),117–124.
- Pandey, P. Inventory of rock glaciers in Himachal Himalaya, India using high-resolution Google Earth imagery. Geomorphology 2019, 340, 103–115. [CrossRef]
- Bhambri, R.; Hewitt, K.; Kawishwar, P.; Pratap, B. Surge-type and surge-modified glaciers in the Karakoram. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15391. [CrossRef]
- Farinotti, D.; Immerzeel, W.W.; de Kok, R.J.; Quincey, D.J.; Dehecq, A. Manifestations and mechanisms of the Karakoram glacier Anomaly. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 8–16. [CrossRef]
- Goerlich, F.; Bolch, T.; Paul, F. More dynamic than expected: an updated survey of surging glaciers in the Pamir. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3161–3176. [CrossRef]
- Bhambri, R.; Watson, C.S.; Hewitt, K.; et al. The hazardous 2017–2019 surge and river damming by Shispare Glacier, Karakoram. Sci. Rep. 2020,10, 4685.
- Lhakpa, D.; Fan, Y.; Cai, Y. Continuous Karakoram Glacier Anomaly and Its Response to Climate Change during 2000–2021. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 6281. [CrossRef]
- Bazai, N.A.; Cui, P.; Carling, P.A.; Wang, H.; Hassan, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Jin, W. Increasing glacial lake outburst flood hazard in response to surge glaciers in the Karakoram. Earth-Science Rev. 2021, 212, 103432. [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A. Monitoring high-mountain terrain deformation from repeated air- and spaceborne optical data: examples using digital aerial imagery and ASTER data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2002, 57, 39–52. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; An, B.; Wei, L. Enhanced glacial lake activity threatens numerous communities and infrastructure in the Third Pole. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8250. [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yao, T.; Tian, L.; Sheng, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhao, H.; Yang, W.; Yang, K.; Berthier, E.; Brun, F.; et al. Response of downstream lakes to Aru glacier collapses on the western Tibetan Plateau. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 199–214. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Shangguan, D.; Yao, X.; Wei, J.; Bao, W.; Yu, P.; Liu, Q.; et al. The second Chinese glacier inventory: data, methods and results. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 357–372. [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Kulkarni, A.; Kääb A.; et al. The state and fate of Himalayan Glaciers. Science 2012,336(6079), 310–314.
- Yao, T.D.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.S.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.J.; Yang, X.X.; Duan, K.Q.; Zhao, H.B.; Xu, B.Q.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lü, J.; Tong, L.; et al. Research on glacial/rock fall-landslide-debris flows in Sedongpu basin along Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet. Geol. Chin. 2019, 46(2),219–234.
- An, B.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Wu, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, H.; Gao, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, C.; et al. Process, mechanisms, and early warning of glacier collapse-induced river blocking disasters in the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 816, 151652. [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Tu, J.; Pei, L.; et al. Preliminary discussion of the frequently debris flow events in Sedongpu Basin at Gyalaperi peak,Yarlung Zangbo River. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26(6),1552–1561.
- Bhardwaj, A.; Sam, L. Reconstruction and Characterisation of Past and the Most Recent Slope Failure Events at the 2021 Rock-Ice Avalanche Site in Chamoli, Indian Himalaya. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 949. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mehta, M.; Mishra, A.; Trivedi, A. Temporal fluctuations and frontal area change of Bangni and Dunagiri glaciers from 1962 to 2013, Dhauliganga Basin, central Himalaya, India. Geomorphology 2017, 284, 88–98. [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA's Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [CrossRef]
- Aschbacher, J.; Milagro-Pérez, M.P. The European Earth monitoring (GMES) programme: Status and perspectives. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 3–8. [CrossRef]
- Baetens, L.; Desjardins, C.; Hagolle, O. Validation of Copernicus Sentinel-2 Cloud Masks Obtained from MAJA, Sen2Cor, and FMask Processors Using Reference Cloud Masks Generated with a Supervised Active Learning Procedure. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 433. [CrossRef]
- Richter, R.; Louis, J.; Berthelot, B. Sentinel-2 MSI–Level 2A Products Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. VEGA Space GmbH, 2011, 1.8.
- Berger, M.; Moreno, J.; Johannessen, J.A.; Levelt, P.F.; Hanssen, R.F. ESA's sentinel missions in support of Earth system science. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 84–90. [CrossRef]
- Hagolle, O.; Huc, M.; Pascual, D.V.; Dedieu, G. A multi-temporal method for cloud detection, applied to FORMOSAT-2, VENµS, LANDSAT and SENTINEL-2 images. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1747–1755. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [CrossRef]
- Hall, D. K.; Riggs, G. A.; Salomonson, V. V. Theoretical Basic Document (ATBD) for the MODIS Snow and Sea Ice-Mapping Algorithms, 2001, NASA.
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. Development of methods for mapping global snow cover using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 127–140. [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Bayr, K.J. MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 181–194. [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yao, T.; Gao, Y.; Thompson, L.; Mosley-Thompson, E.; Muhammad, S.; Zong, J.; Wang, C.; Jin, S.; Li, Z. Two glaciers collapse in western Tibet. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 194–197. [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A.; Leinss, S.; Gilbert, A.; Bühler, Y.; Gascoin, S.; Evans, S.G.; Bartelt, P.; Berthier, E.; Brun, F.; Chao, W.-A.; et al. Massive collapse of two glaciers in western Tibet in 2016 after surge-like instability. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 114–120. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Glacier variations at Arutso in western Tibet from 1971 to 2016 derived from remote-sensing data. J. Glaciol. 2018,64, 397–406.
- Li, W.; Zhao, B.; Xu, Q.; Scaringi, G.; Lu, H.; Huang, R. More frequent glacier-rock avalanches in Sedongpu gully are blocking the Yarlung Zangbo River in eastern Tibet. Landslides 2022, 19, 589–601. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, T.; He, J. Barrier lake bursting and flood routing in the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon in October 2018. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124603. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, W.; Westoby, M.; et al. An approximately 50 M m3 ice-rock avalanche on 22 March 2021 in the Sedongpu valley, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Cryosphere, 2022,16, 1333–1340.
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Dynamic processes of 2018 Sedongpu landslide in Namcha Barwa–Gyala Peri massif revealed by broadband seismic records. Landslides 2020, 17, 409–418. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Study on the barrier lake event for landslide⁃river blocking of Sedongpu valley on Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet of China. J. Hebei Geo Univ. 2020, 43(3),31–37.
- Nie, Y.; Pritchard, H.D.; Liu, Q.; Hennig, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Nepal, S.; Samyn, D.; Hewitt, K.; et al. Glacial change and hydrological implications in the Himalaya and Karakoram. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 91–106. [CrossRef]
- Delaney, K.B.; Evans, S.G. The 2000 Yigong landslide (Tibetan Plateau), rockslide-dammed lake and outburst flood: Review, remote sensing analysis, and process modelling. Geomorphology 2015, 246, 377–393. [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.L.; Rittger, K.; Brodzik, M.J.; Racoviteanu, A.; Barrett, A.P.; Khalsa, S.-J.S.; Raup, B.; Hill, A.F.; Khan, A.L.; Wilson, A.M.; et al. Runoff from glacier ice and seasonal snow in High Asia: separating melt water sources in river flow. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 19, 1249–1261. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Tian, L. Changes in the ablation zones of glaciers in the western Himalaya and the Karakoram between 1972 and 2015. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 505–512. [CrossRef]
- Kraaijenbrink, P.D.A.; Stigter, E.E.; Yao, T.; Immerzeel, W.W. Climate change decisive for Asia’s snow meltwater supply. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 591–597. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X. Increase in occurrence of large glacier-related landslides in the high mountains of Asia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1635. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Yang, X.; et al. Glaciers in Tibet. Beijing: Science Press, 1986. (In Chinese).
- Zhang, W. J. Identification of glaciers with surge characteristics on the Tibetan Plateau, Ann. Glaciol. 1992, 16, 168–172.
- Kääb, A.; Jacquemart, M.; Gilbert, A.; et al. Sudden large-volume detachments of low-angle mountain glaciers–more frequent than thought? Cryosphere, 2021,15, 1751–1785.
- Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Yin, Y. Massive glacier-related geohazard chains and dynamics analysis at the Yarlung Zangbo River downstream of southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 426. [CrossRef]




| Band number | Central wavelength /nm | Bandwidth /nm | Spatial resolution /m | Main applications |
| Band 1-Coastal and aerosol | 443 | 20 | 60 | Atmospheric correction |
| Band 2-Blue | 490 | 65 | 10 | Sensitive to vegetation and aerosol scattering |
| Band 3-Green | 560 | 35 | 10 | Green peak, sensitive to total chlorophyll in vegetation |
| Band 4-Red | 665 | 30 | 10 | Max chlorophyll absorption |
| Band 5-Vegetation red edge 1 | 705 | 15 | 20 | Vegetation detection |
| Band 6-Vegetation red edge 2 | 740 | 15 | 20 | Vegetation detection |
| Band 7-Vegetation red edge 3 | 783 | 20 | 20 | Vegetation detection |
| Band 8-NIR | 842 | 115 | 10 | Leaf Area Index (LAI) |
| Band 8a-Narrow NIR | 865 | 20 | 20 | Used for water vapour absorption reference |
| Band 9-Water vapour | 940 | 20 | 60 | Water vapour absorption atmospheric correction |
| Band 10 SWIR-cirrus | 1375 | 30 | 60 | Detection of thin cirrus for atmospheric correction |
| Band 11 SWIR1 | 1610 | 90 | 20 | Snow and cloud detection |
| Band 12 SWIR2 | 2190 | 180 | 20 | AOT(aerosol optical thickness) determination |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





