1. Introduction
Combustion is a fundamental process extensively utilized in various industrial applications, ranging from power generation to transportation [
1]. With the increasing demand for cleaner and more efficient energy sources, there is a growing interest in understanding the combustion behavior of alternative fuels such as hydrogen [
2,
3]. In the context of premixed combustion systems, the design of the combustor plays a critical role in determining flame characteristics and overall combustion performance [
4,
5,
6]. Recently, studies have been conducted to investigate the flame behavior and shape changes due to hydrogen mixing due to the combustion rate of hydrogen seven times faster than methane [
7,
8,
9]. The targets to be overcome in hydrogen-methane combustion are the large amount of NOx generated due to high-temperature flames [
10,
11,
12]. In addition, the application of ultra-lean burn technology as a means to solve this problem may additionally cause flame stabilization problems [
13,
14]. In order to solve these problems of hydrogen combustion, it is necessary to design a combustor that can reduce the flame temperature.
As a good alternative, there are slit flame combustors with thin flames and multiple flame combustors with fire holes. These combustors can reduce the flame temperature by increasing the surface area of the flame or by splitting the flame into smaller pieces. This is effective in reducing thermal NOx emissions during combustion reactions. Somers and Goy [
15] proposed a slit burner capable of forming a thin flame using a slit structure. The shape of the slit flame was simulated and compared experimentally. Guo et al. [
16] studied ways to improve flame stability while increasing the mixing flow rate in a micro-combustor where a thin flame is formed. The stable flame, transient oscillating flame, extinction, flame with repetitive extinction and ignition, and quenching were analyzed experimentally. Liu et al. [
17] conducted a study on the dynamic behavior and stability of a slit flame through a model of fluid perturbation. The flame aspect ratio significantly affected the time-averaged slit flame front surface area, while the mean flow velocity played an important role in the response of the slit flame heat release rate to transverse disturbance. Raghavan et al. [
18] investigated the impact of slit width on exhaust gas temperature. As the slit width decreased, the exhaust gas temperature tended to decrease. These studies on slit flames offer valuable data regarding flame shape and temperature, but they somewhat lack in the quantification of NOx. In multiple flame combustors, Chen et al. [
19] experimentally investigated the effect of multi-layer slit structures on flame speed reduction in premixed flames. They suggested that the maximum flame length decreases as the number of slits increases, and the shear layer between flames can cause flame surface distortion due to vortex action. Tyagi et al. [
20] conducted an experimental study of local flame-fire interaction in turbulent premixed flames. They suggested that when there is high shear flow between adjacent flames, a local interaction occurs in which the flame structure bends toward the flame center. However, the influence of slit-type combustor design on the combustion behavior of hydrogen, particularly in comparison to methane, remains an area of active research.
This study aims to investigate the influence of thin flame combustor design on hydrogen flame characteristics and combustion performance through numerical simulations. By analyzing variations in flame shape and combustibility between 100% methane and 100% hydrogen combustions, insights can be gained into the optimal design parameters for achieving efficient hydrogen combustion. To achieve this objective, three combustor header shapes (flat, concave, and convex) are modeled to study their effects on flame behavior. Through comprehensive analyses of flow patterns, pressure drops, turbulence premixing, temperature fields, and combustion product compositions, this study seeks to elucidate the impact of combustor design on hydrogen combustion performance and emissions, with a particular focus on NOx emissions.
2. Simulation Methods
2.1. Governing Equation
The flame characteristics of hydrogen and methane were simulated by numerical analysis of the internal flow and flame shape. The numerical analysis program is Simcenter FloEFD (Siemens, Germany), which calculates the combustion reaction based on chemical equilibrium. It also had a method of calculating combustion products mixed with fuel and oxidizing agents to the molecular level until chemical equilibrium is reached. Therefore, the parameters of the fuel mixture are calculated according to the chemical equilibrium equation and expressed as the molar fraction of the product by pressure, density, and temperature. The governing equation for calculating the generation and flow of combustion products (
) at a constant mass fraction is written as follows.
Here, the reaction rate (
) is defined as a function of the mass fraction of residual fuel (
) and oxidizing agent (
) and the molar mass of fuel (
) and oxidizing agent (
) by the mass transport equation as follows.
K is a function dependent on temperature as the reaction rate, which is defined as follows.
Here, is 1x105, is 0.2, T is the current temperature, and is the ignition temperature. Therefore, it can be understood that the combustion process of the fuel-air mixture is determined by the mass fraction of the equilibrium combustion product.
The majority of NOx in combustion byproducts consists of thermal NOx at a flame temperature of 1300℃. Since NO is the primary chemical species in NOx, NOx is represented solely by considering NO in combustion analysis. The mass transport equation for NO can be written as follows.
NO represents the mass fraction of the gas phase, and the reaction is described by the Zeldovich mechanism as follows.
Since the thermal NO is produced at high temperatures, most of the reactions occur immediately after the combustion reaction until heat is transferred from the flame. To determine the concentration of nitrogen atoms, a metastable state is considered, which is consumed as rapidly as free nitrogen atoms are generated based on oxygen involved in the oxidation reaction under lean combustion conditions. This assumption is valid for most combustions except for rich combustion conditions. Therefore, the NO reaction rate can be written as follows.
Here, R is the one-way reaction rate, and the amount of NO is derived from the transport equation as follows.
2.2. Design Parameters
A pre-mixed combustor of 40,000 kcal/h was designed to find out the variations in flame shape and combustibility in 100% methane and 100% hydrogen. Since hydrogen has about three times lower calorific value per unit volume than methane, the fuel flow rate was set at 4.5 Nm
3/h for methane and 13.8 Nm
3/h for hydrogen to match the same calorific value of 40,000 kcal/h. The air volume corresponding to the fuel flow rate is set to a lean combustion condition that is 1.3 times higher than the theoretical air volume. The flow rate of the mixed gas from the final combustor surface is 59.5 for methane-air and 56.6 for hydrogen-air. The design parameters are listed in
Table 1.
2.3. Simulation Models
In
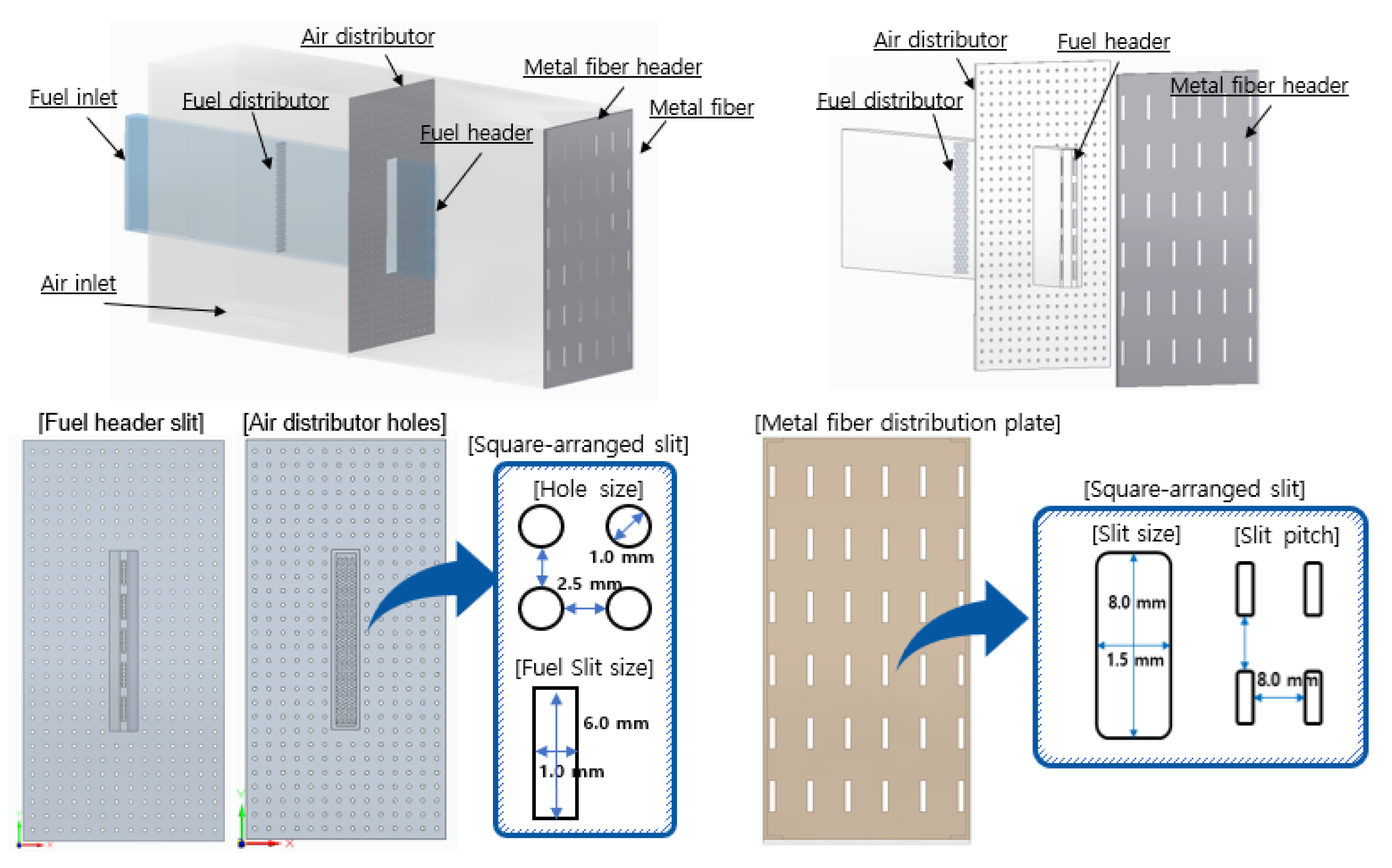
Figure 1, the combustor configurations include fuel heads, metal fiber plates, and distribution plates. Fuel and air are individually injected into each inlet and passed through the fuel distribution panel and the air distribution panel, respectively. After that, the fuel and the air are mixed and flow toward the metal fiber distribution panel. Finally, flames are formed on the metal fiber surface to complete premixed combustion. In detail view of design, the fuel and the air distribution plates for flow uniformity are designed as perforated plates with rectangular holes of 1.0 x 6.0 mm and circular holes of 1.0 mm. The metal fiber distribution plates for flame shape uniformity are designed as perforated plates with holes of 1.5 x 8.0 mm in a square arrangement with 8.0 mm pitch.
In
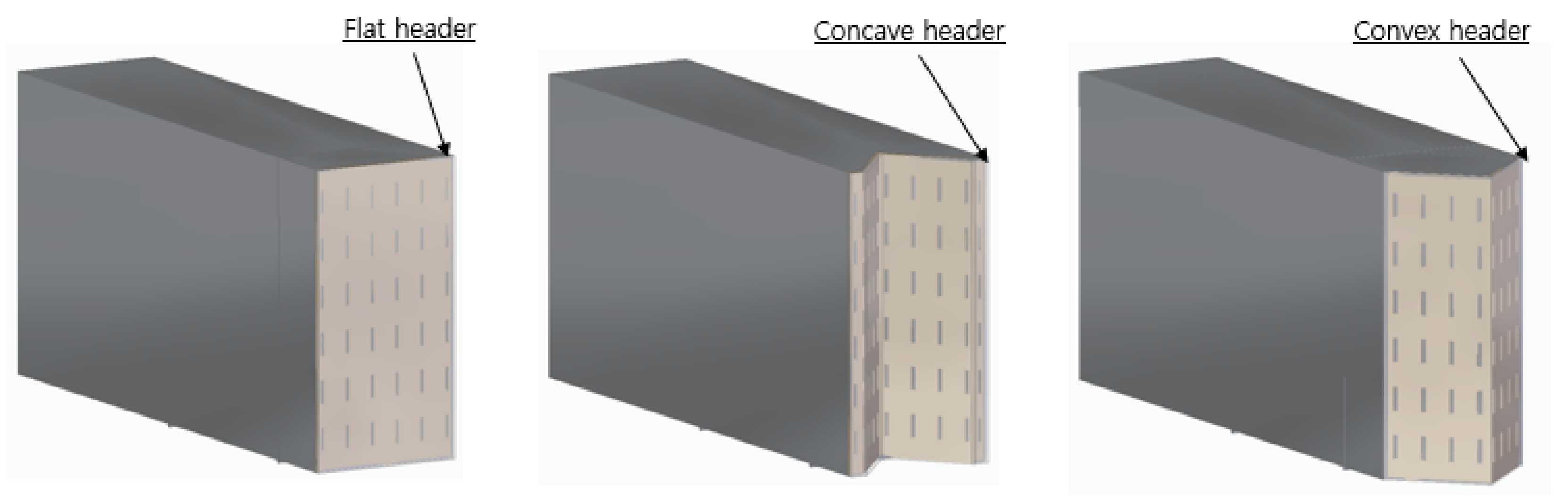
Figure 2, three different combustor headers were modeled to analyze the flame effects according to the combustor header shapes. The headers are designed to form a thin flame to prevent the flame overheating. The combustor headers are designed to be flat, concave, and convex. The concave and convex headers are each folded about 90°, so they have a larger surface combustion area than the flat header.
In
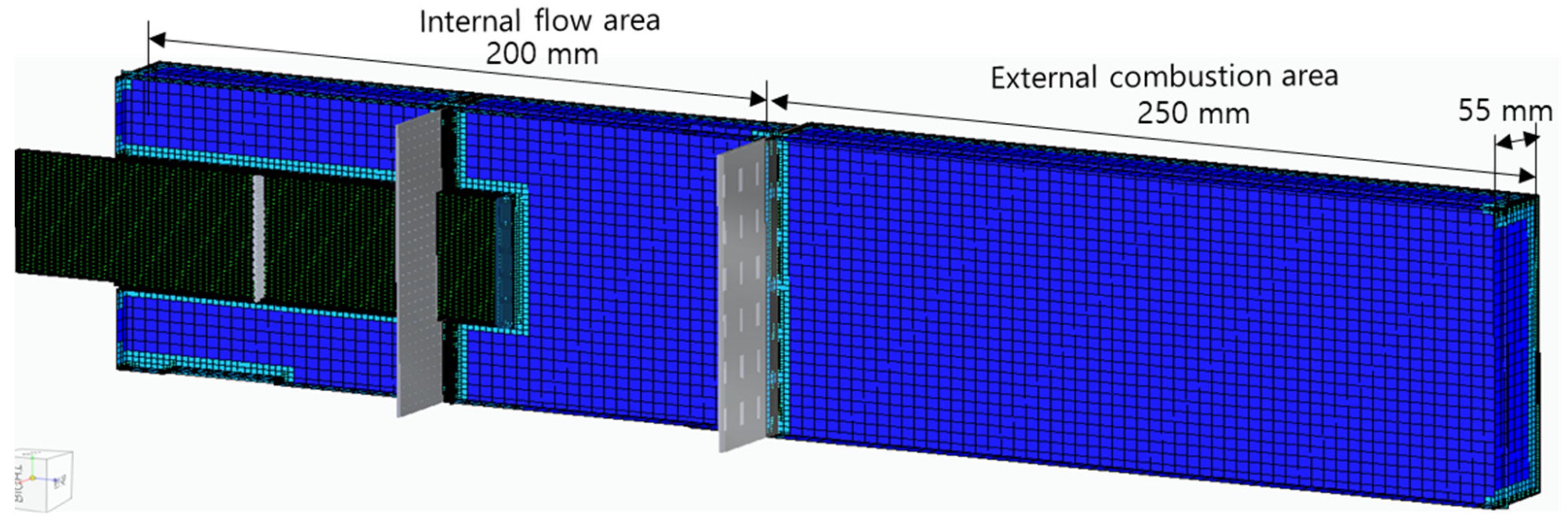
Figure 3, the analysis area of the combustor model is 550 mm long and 55 mm wide, and it is divided into an internal flow area and an external combustion area. The flow area has complex flow paths and narrow perforated holes, so it is necessary to densely form the analysis grid. Here, one grid was set to have a size of less than 0.1 mm by dividing the minimum diameter of a 1.0 mm perforated hole into at least 10 equal parts. The number of grids used in the three combustor header models in total ranges from 2,240,000 to 2,690,000. The outer wall boundary of the combustion area was set to atmospheric pressure.
3. Results and Discusstion
3.1. Internal Flow Characteristics
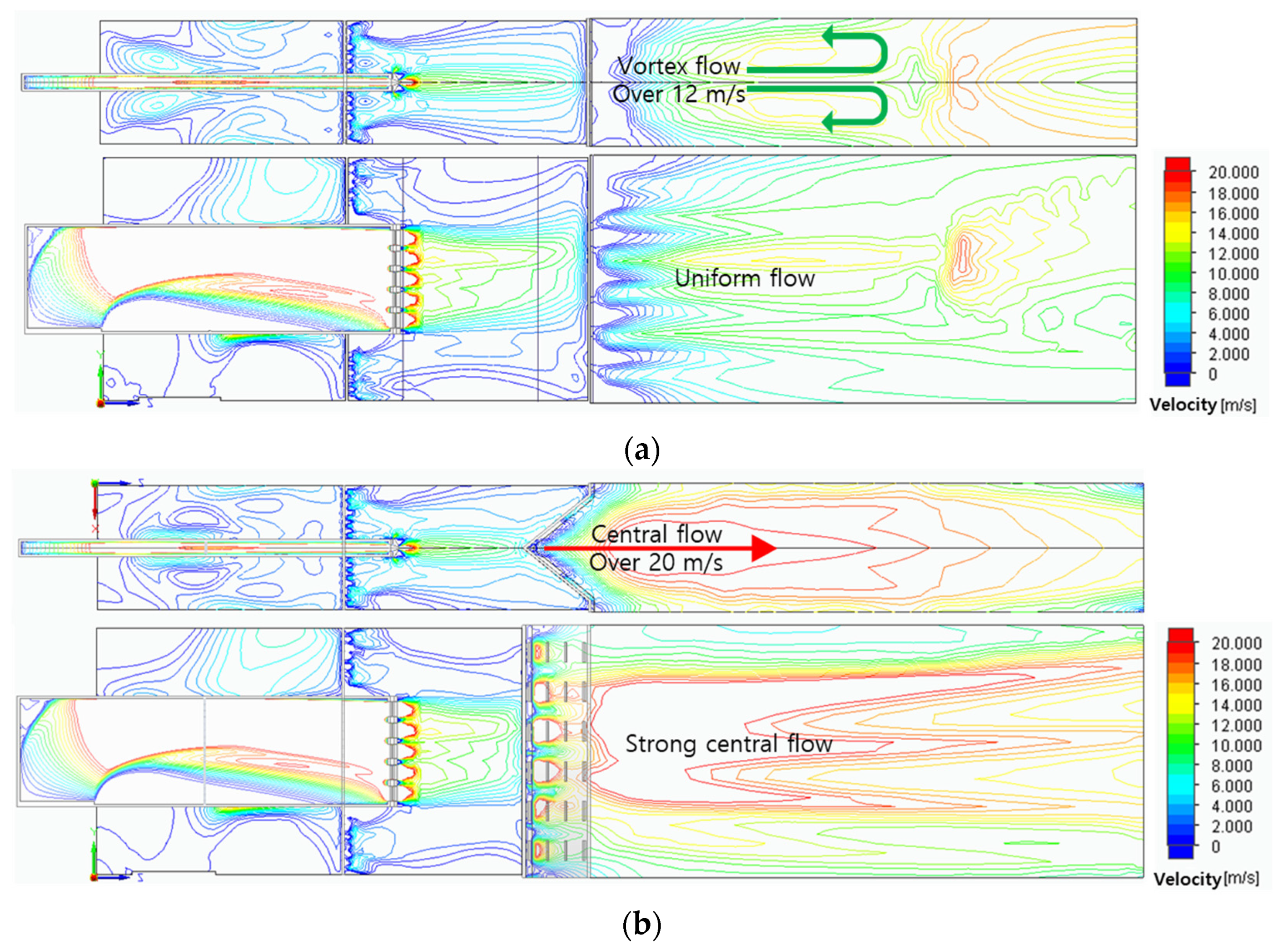
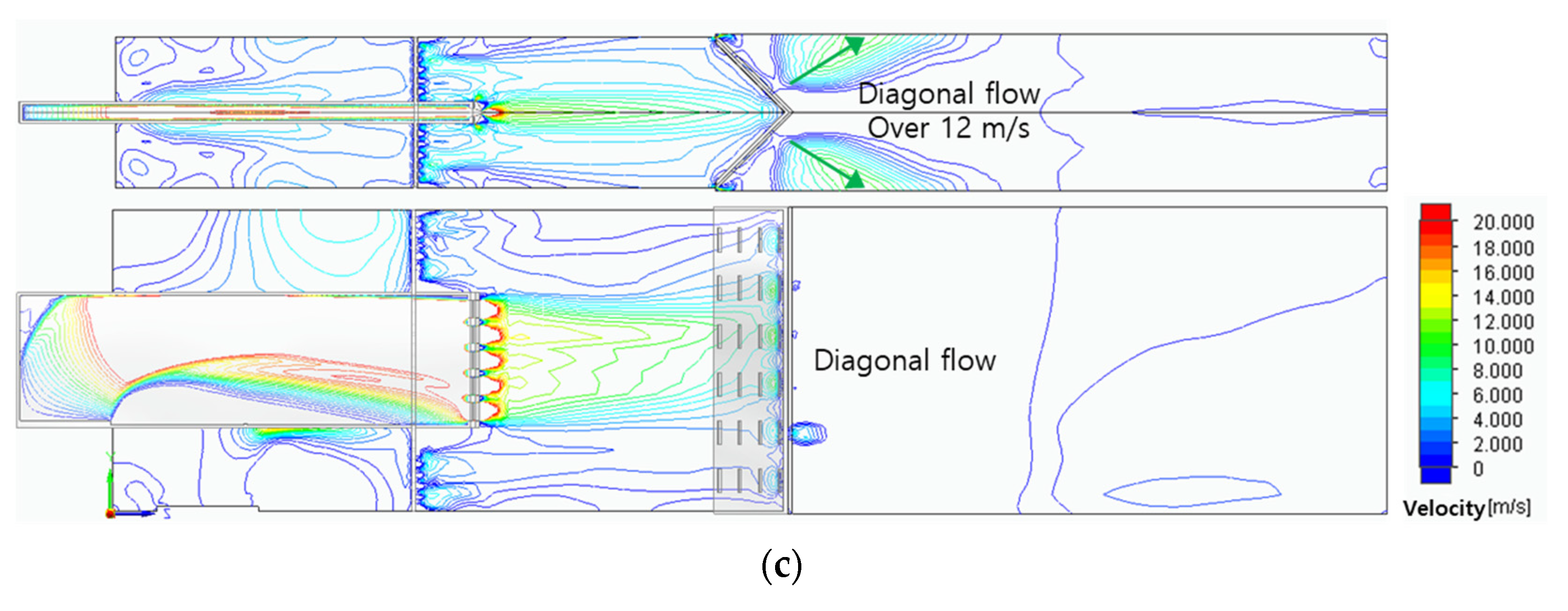
Figure 4 shows the variations of the velocity fields according to the three header shapes. Because the combustor models have the same fuel slit, the fuel passed through this narrow slit to form the same axial flow of about 20 m/s. After that, the fuel was mixed with air and showed various flow fields due to different header shapes. In the case of a flat header, vortex flow was formed, and it has a relatively uniform flow field of about 12m/s in the combustion area. In the case of a concave header, a flow field with central velocity of about 20m/s was formed to form a strong central flow. In the case of a convex header, the flow was concentrated in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the header, and the flow was dispersed diagonally.
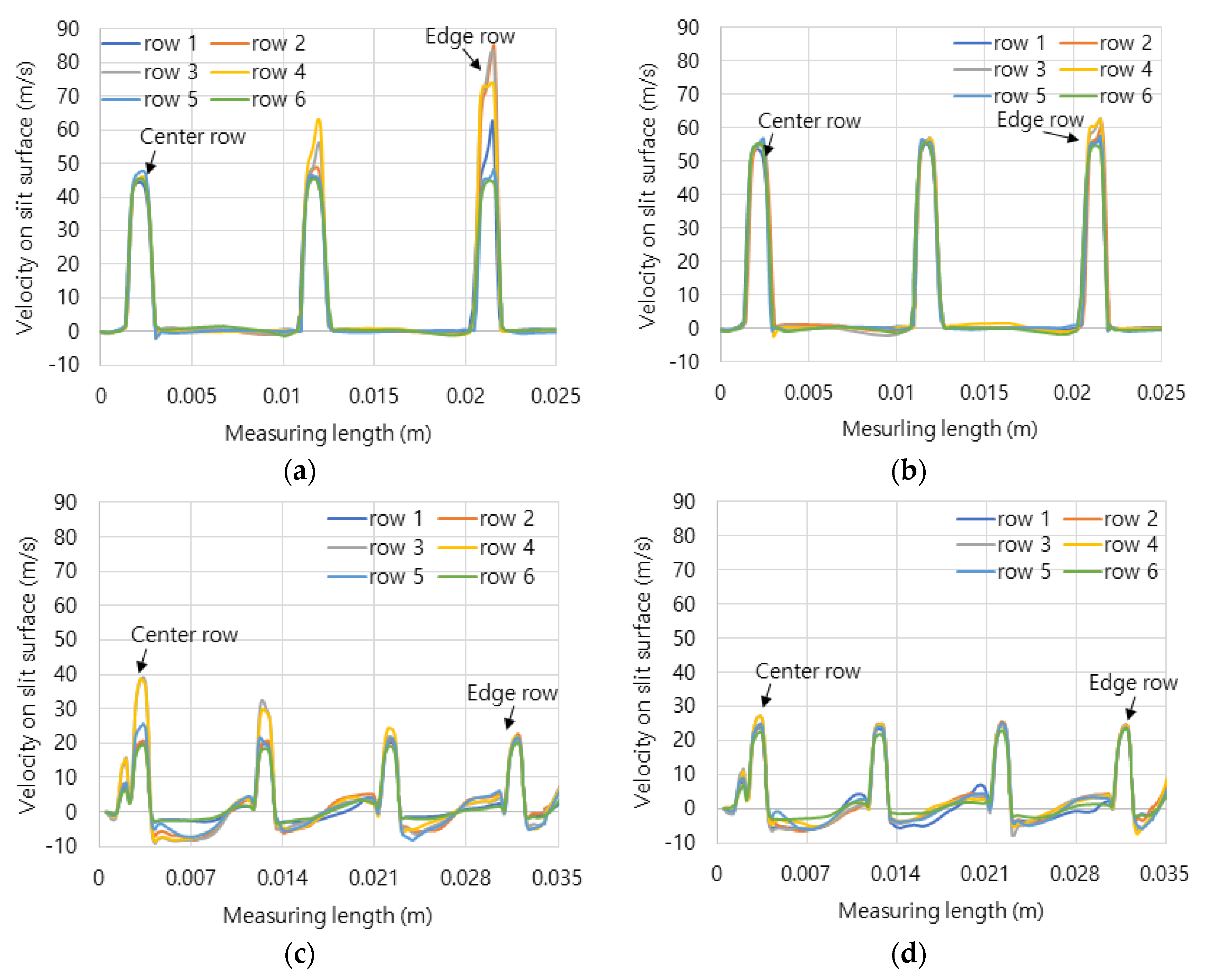
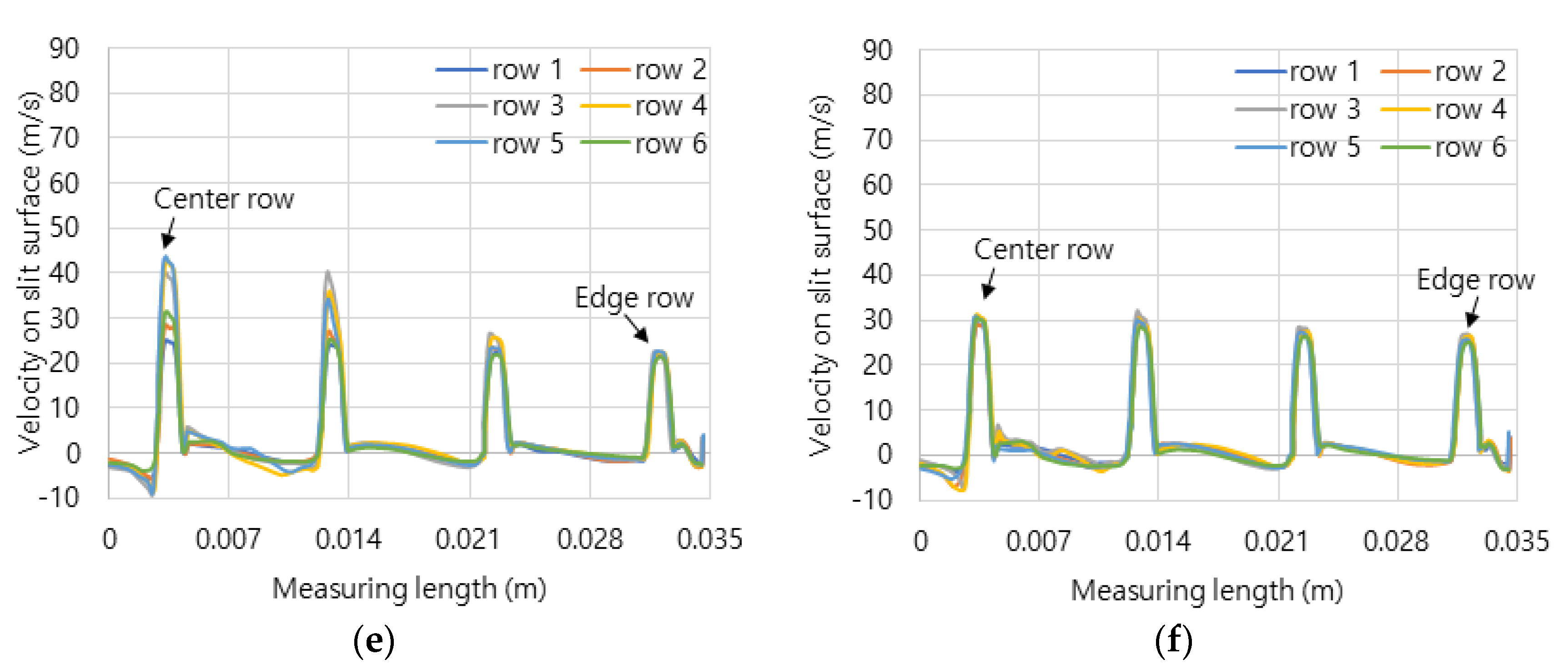
Figure 5 shows the axial velocity distribution from the central line to the edge line on dividing six rows of combustion surface.
Figure 5a,b shows the velocity of hydrogen-air mixed gas and methane-air mixed gas on the flat header surface. Because the flat header has the smallest combustion area than the other header shapes, it has the highest velocity distribution.
Figure 5c–f show the surface velocities of the concave header and the convex header in hydrogen-air mixed gas and methane-air mixed gas. The flow velocities were average 20 m/s, and the central flow of hydrogen-air mixed gas is more developed than that of the methane-air mixed gas. Here, the development of central flow on the concave header causes the flame to form in the center, and conversely, on the convex header, it has the effect of dispersing the flame outward.
3.2. Pressure Drop of Distribution Plates
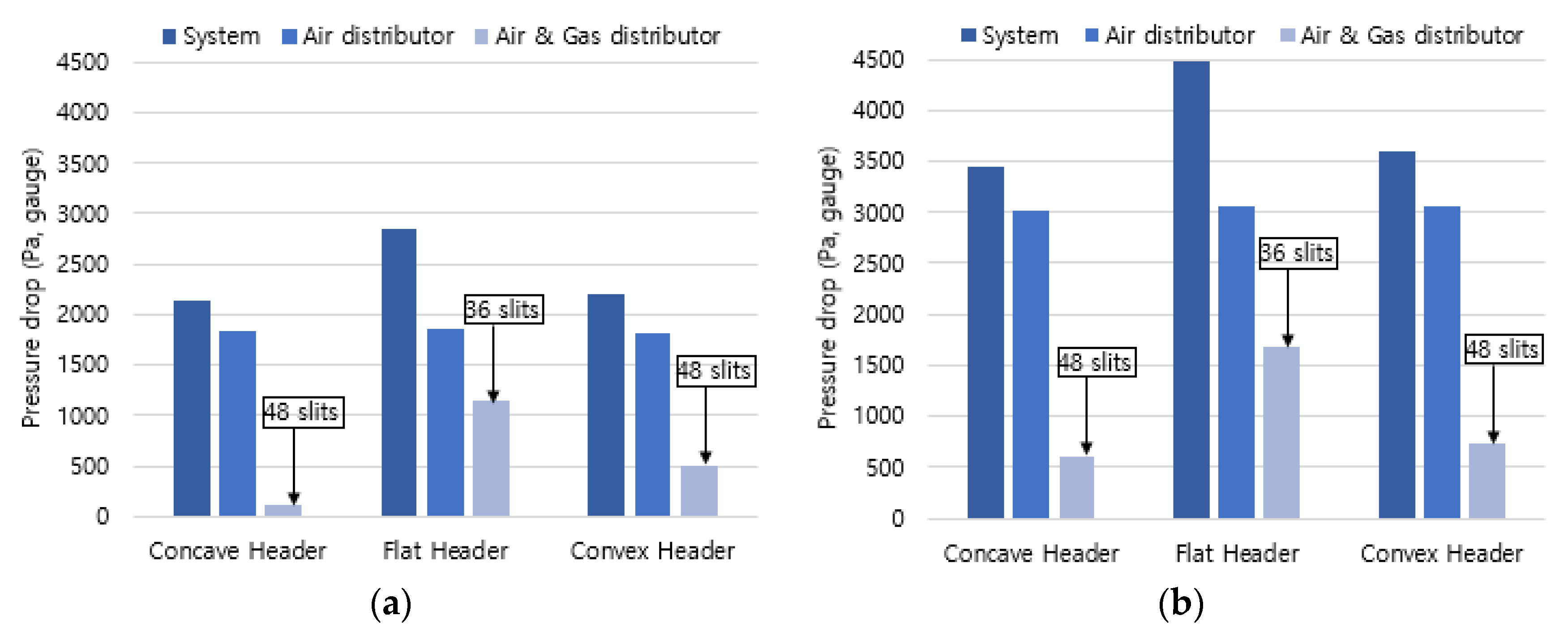
Since the combustor supplies the premixed gas using a blower, a differential pressure analysis was performed on the distribution plate with high pressure drop. The differential pressures for the air distribution plate and the mixed gas distribution plate of air and fuel gas were analyzed along the air flow path, and the pressure drop of the entire system was compared and analyzed in
Figure 6. As a result of the analysis, the differential pressure in the air distribution plate was 1,750 Pa for hydrogen combustion and calculated as 3,000 Pa for methane combustion. Regarding pressure drops for different header types, the flat header showed the highest differential pressure due to the smallest number of slit openings, while the concave header had the lowest differential pressure due to a large number of slit openings and its shape. Concerning the differential pressure of the entire system, the flat header, the convex header, and the concave header were 2700 Pa, 2300 Pa, and 2150 Pa, respectively, in hydrogen combustion. In the same order, the required pressure appeared in methane combustion, with the average pressure being 1500 Pa higher than that of hydrogen combustion. From these results of the pressure drop, the concave header is considered advantageous for the blower due to its lowest pressure drop.
3.3. Fuel and Air Mixing Performance and Turbulence Intensity
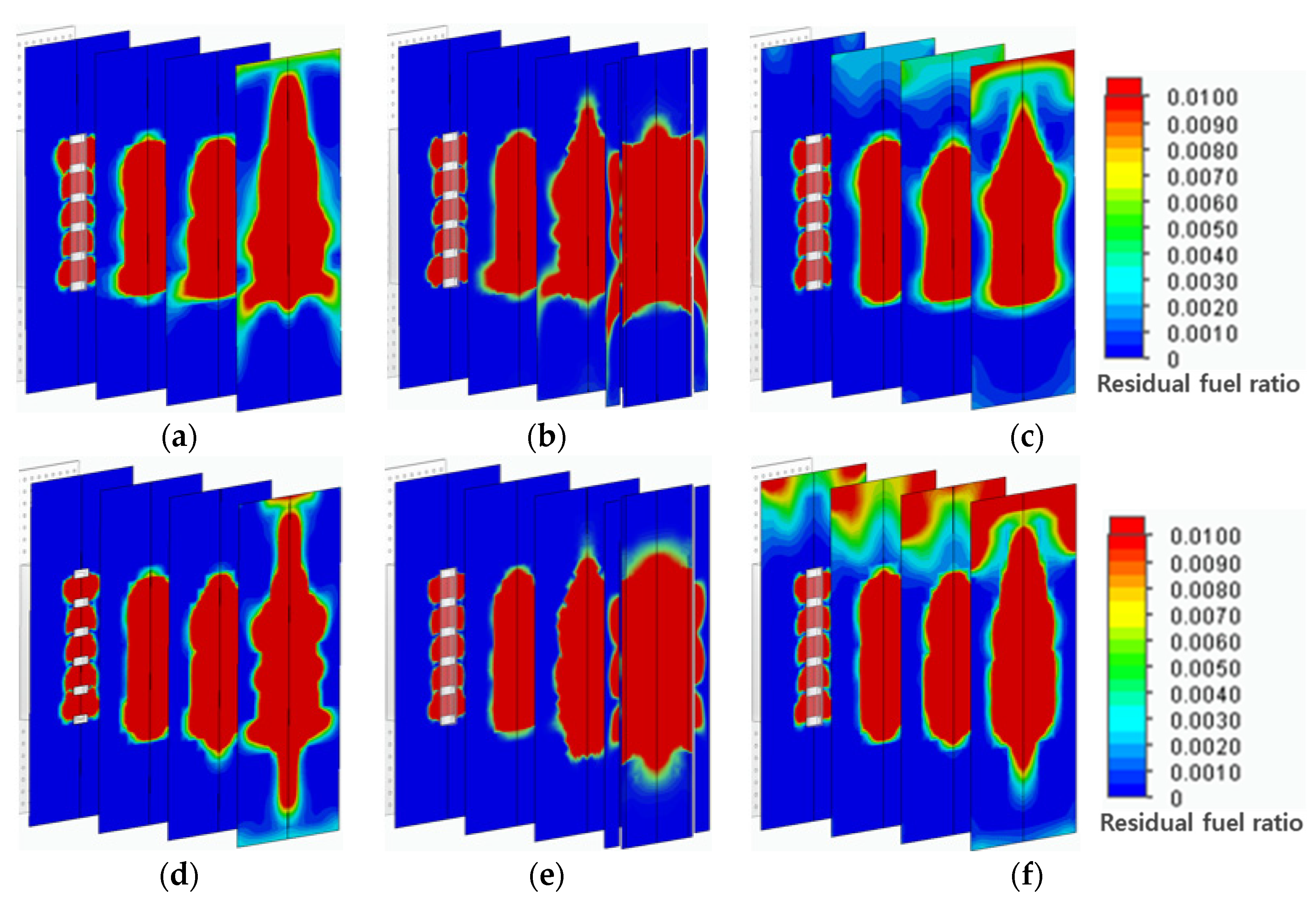
To investigate the premixing performance of fuel and air, the mixing efficiency was analyzed using the mass fraction of residual fuel. In
Figure 7, the mass fraction of residual fuel ranged from the maximum value of 1% to the minimum value of 0.1% for residual fuel diluted in air. Therefore, a higher residual fuel ratio indicates better mixing. The results showed that the distribution of residual fuel widened as it approached the flame. In terms of residual fuel distribution among the different header types, although the convex header showed a relatively wide distribution and the concave header showed a narrower one, it is considered that all of them display a similar residual fuel distribution, suggesting they will exhibit appropriate mixing performance.
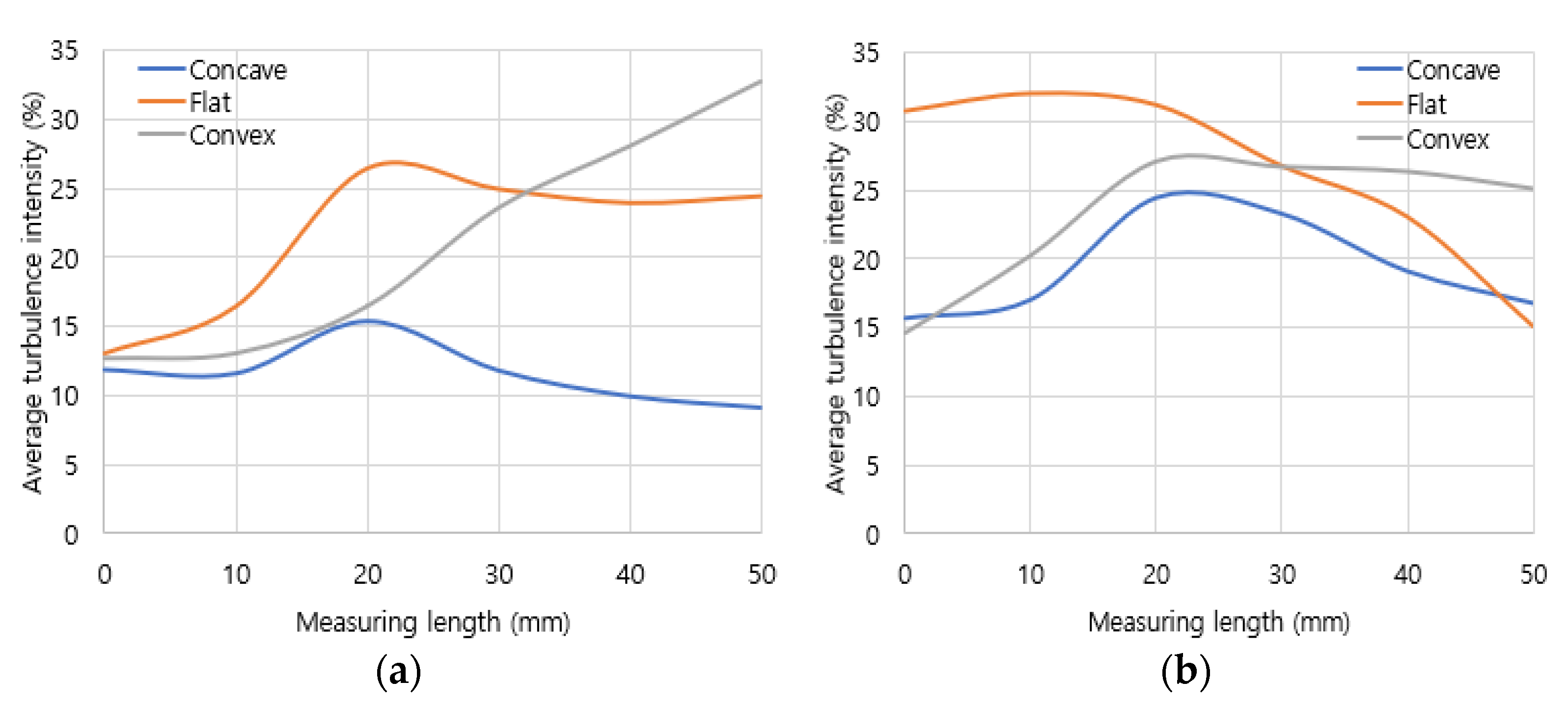
Turbulence intensity analysis was conducted in the mixing area to quantitatively evaluate the mixing performance in the air and fuel mixing zone. Turbulence intensity represents the deviation of the actual flow rate compared to the average flow rate. The total interval of the mixing area was divided into six equal parts at 10 mm intervals to distribute the turbulence intensity according to distance. As the results in
Figure 8, in hydrogen combustion, the turbulence intensity was the lowest in the concave header. Conversely, turbulence intensity increased with distance in the flat header and the convex header. In methane combustion, turbulence intensity was lowest in the concave header, while the flat header and the convex header exhibited a tendency to gradually decrease. From these turbulence intensity results, it was confirmed that the flow in the concave header was the most stable, whereas the flow in the convex header and the flat header was less stable.
3.4. Flame Shape with Temperature and Residual Fuel Ratio
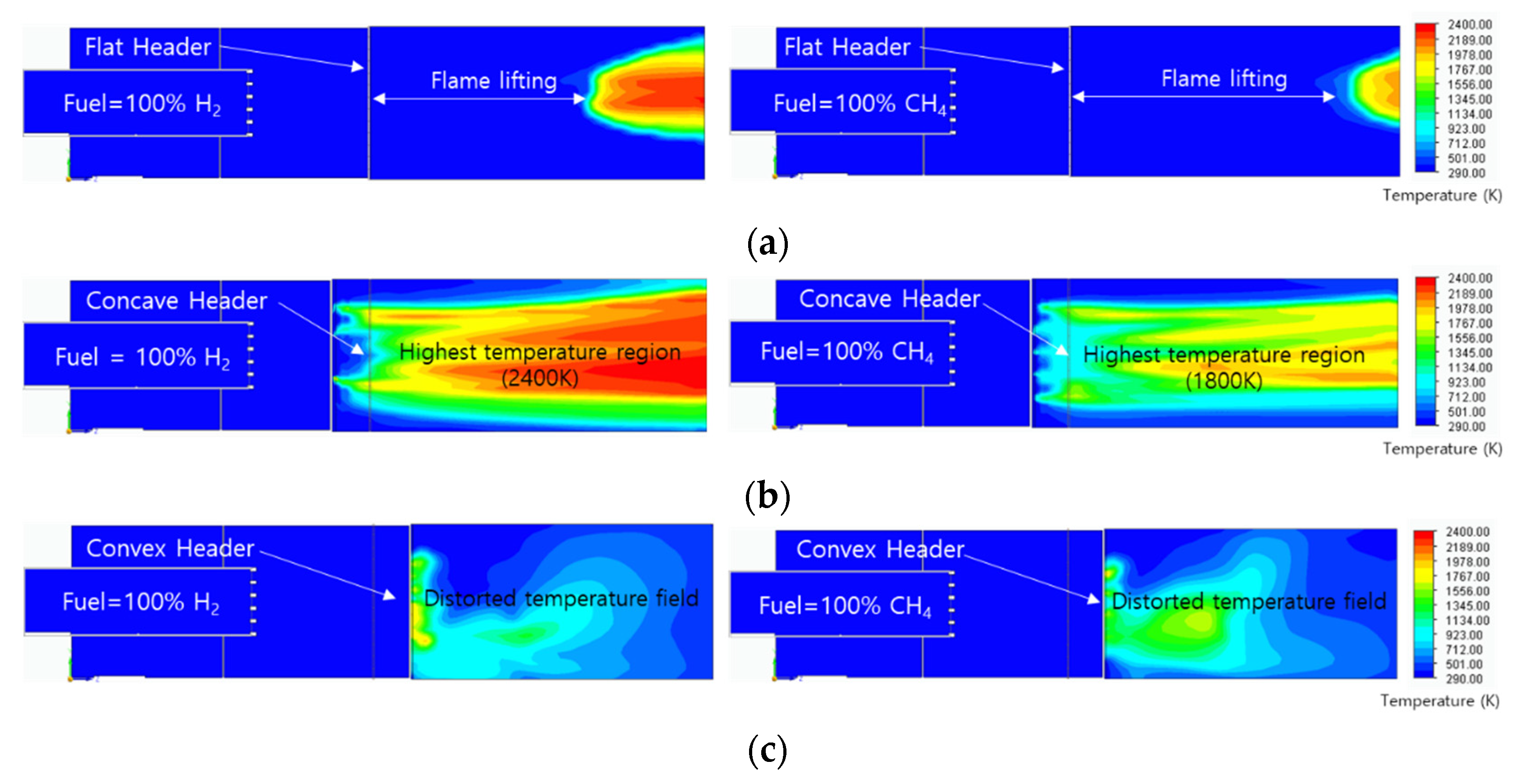
A temperature field analysis was performed to predict the flame shape of 100% hydrogen and 100% methane. The temperature field in
Figure 9 has the temperature range of 293K to 2400K, with red at high temperature and blue at low temperature. In the flat header, the flame was formed by floating from the combustor surface. This means that a lifting flame can be formed on the flat header with the fast surface flow velocity of 50 m/s. At the lifting distance, due to the fast diffusion velocity of hydrogen, the hydrogen flame had a shorter lifting distance than methane flame. In the concave header, the hydrogen flame and the methane flame were stably attached to the combustor surface. The temperature of the hydrogen flame was 600°C higher than that of the methane flame. The convex header is considered unsuitable for use as a combustor because it was dispersed outside the required axial flame region.
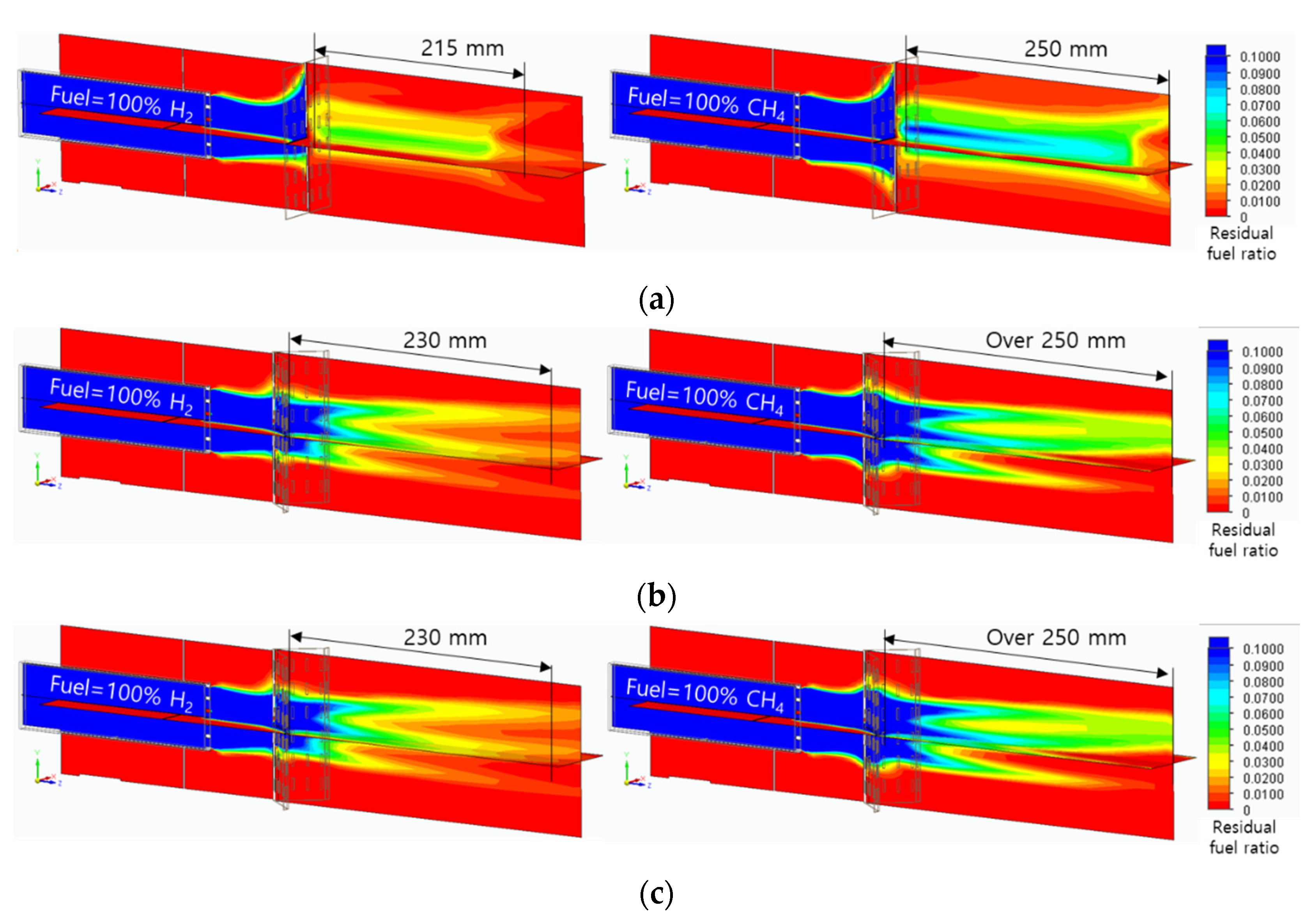
Figure 10 shows the amount of residual fuel for the flame quenching distance analysis. The mass fraction of residual fuel was set from 1% to 10%, and the high fraction was blue, and the low fraction was red. In the flat header, long residual fuel was shown in the axial direction, however, due to the lifting flame, it cannot be regarded as an actual quenching distance. In the concave header, the residual fuel fraction is high on the combustor surface and then decreases toward the axial direction. The flame quenching distances were 230mm and over 250mm in hydrogen flame and methane flame, respectively. The flame quenching distance of the convex header could not be calculated due to the flame dispersion. Therefore, it was found that the hydrogen flame had a shorter quenching distance than the methane flame.
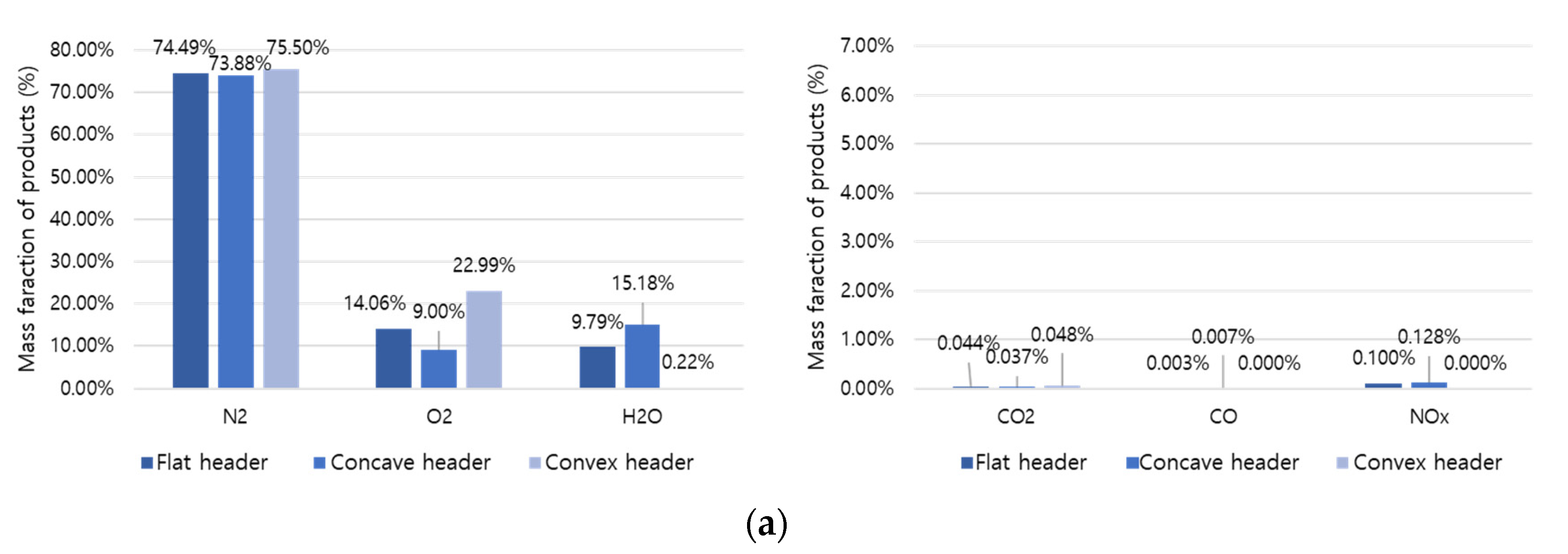
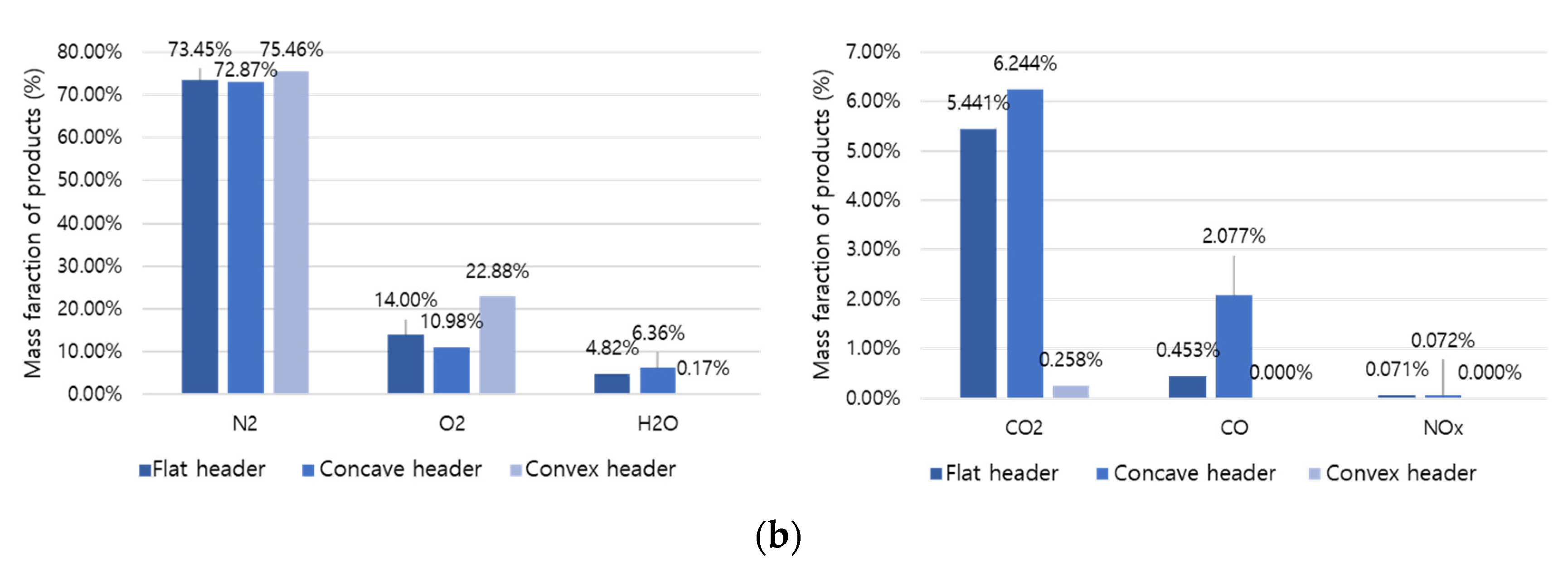
3.5. Exhaust Gas Composition
A comparative analysis was performed on the combustion products at the final outlet based on the shape, temperature, and mass fraction of the flame.
Figure 11a,b represent the combustion products of hydrogen and methane, respectively. Hydrogen combustion products have high H
2O and NOx fractions, and methane combustion products have high CO
2 and CO fractions. Here, hydrogen causes an increase in temperature and thermal NOx generation and an increase in conversion to H
2O. In addition, the concave header had the lowest O
2 fraction compared to other headers. Therefore, it can be evaluated that the concave header has the highest combustibility. In the concave header, NOx is 0.128% in hydrogen combustion and 0.072% in methane combustion, and the NOx emission rate of hydrogen combustion can be about 1.78 times higher than methane combustion.
4. Conclusions
This study suggests that the thin flame combustor design significantly influences hydrogen flame characteristics and combustion performance. The flame characteristics of hydrogen and methane were investigated using numerical simulations. Variations in flame shape and combustibility were observed in 100% methane and 100% hydrogen combustions. Three combustor header shapes (flat, concave, and convex) were modeled to analyze their effects on flame behavior. Different header shapes resulted in distinct flow patterns, affecting flame behavior. Concave headers promoted strong central flows, while convex header dispersed the flow outward. In the temperature field and residual fuel field, hydrogen flames showed higher temperatures and shorter quenching distances compared to methane flames. Concave header forms a stable flame, with lower residual fuel fractions and higher flame stability. In the comparative analysis of combustion products, hydrogen combustion led to increased temperatures and higher NOx fraction compared to methane combustion. The concave header had complete combustibility with lower O2 emission, particularly in hydrogen combustion. These findings provide valuable insights for optimizing hydrogen combustor design in industrial applications, particularly in enhancing combustion efficiency and minimizing emission.
Acknowledgments
This work supported by the Carbon Innovation Stars Project (20018190, development of 0.5 ton/hr-Hybrid Hydrogen Burner with Slit flame) funded By the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy(MOTIE, Korea)
References
- Kadowaki, S.; Hasegawa, T. Numerical simulation of dynamics of premixed flames: flame instability and vortex–flame interaction. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 2005, 31, 193–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarli, V.D.; Benedetto, A.D. Laminar burning velocity of hydrogen–methane/air premixed flames. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Duan, Q.; Sun, J. Premixed flame propagation in hydrogen explosions. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 81, 1988–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, G.K.; Gatzoulis, A.; Frouzakis, C.E.; Matalon, M.; Tomboulides, A.G. Consistent definitions of ‘‘Flame Displacement Speed’’ and ‘‘Markstein Length’’ for premixed flame propagation. Combustion and Flame 2015, 162, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, K.; Kido, H.; Takeda, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Shentsov, V.; Makarov, D.; Molkov, V. Flame stabilisation mechanism for under-expanded hydrogen jets. J. Fire 2024, 7, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, N.; Dopazo, C. Timescales associated with the evolution of reactive scalar gradient in premixed turbulent combustion: a direct numerical simulation analysis. J. Fire 2024, 7, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shen, X.; Wen, J.X.; Xiu, G. The behavior of methane/hydrogen/air premixed flame in a closed channel with inhibition. J. Fuel 2020, 265, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halter, F.; Chauveau, C.; Gokalp, I. Characterization of the effects of hydrogen addition in premixed methane/air flames. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, C.E.; Hayakawa, A.; Nagano, Y.; Kitagawa, T. Effects of hydrogen concentration on premixed laminar flames of hydrogen-methane-air. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, H.H.W.; Beckmann, N.; Abanteriba, S. An overview on dry low NOx micromix combustor development for hydrogen-rich gas turbine applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 6978–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Lyu, Y.; Peng, J.; Qiu, P.; Liu, L.; Yang, C.; Yu, Y.; Chang, G.; Yan, B.; Sun, S.; Yu, X. Experimental study of flame evolution, frequency and oscillation characteristics of steam diluted micro-mixing hydrogen flame. J. Fuel 2021, 301, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Lee, H.; Hwang, S. Low NOX combustion characteristics by hydrogen micro jet flame in cross flow. J. Mechanical Science and Technology 2023, 37, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Kheirkhah, S.; Bergthorson, J.; Yun, S.; Hwang, J.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, M.K.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Vena, P. Flame stabilization mechanisms and shape transitions in a 3D printed, hydrogen enriched, methane/air low-swirl burner. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 14764–14779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schefer, R.W. Hydrogen enrichment for improved lean flame stability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2003, 28, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, L.M.T.; Goey, L.P.H. A numerical study of a premixed flame on a slit burner. Combustion Science and Technology 1995, 108, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhai, M.; Shen, Q.; Qi, H.; Dong, P.; Zhu, J. Methane-air partially premixed flame behaviors in a micro plate slit. Chem. Eng. and Proc.-Process Intensification 2020, 158, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yang, L.; Qin, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, J. Models of the time-averaged heat release rate of the two-dimensional laminar premixed slit flame subjected to the transverse disturbance. Aerospace Science and Technology 2023, 132, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, K.A.S.; Rao, S.S.; Raju, V.R.K. Numerical investigation of the effect of slit-width on the combustion characteristics of a micro-combustor with a centrally slotted bluff body. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 5696–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Luo, G.; Sun, Y.; Lv, Q. Impacts of plate slits on flame acceleration of premixed methane/air in a closed tube. J. the Energy Institute 2018, 91, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Boxx, I.; Peluso, S.; O’Connor, J. The role of flow interaction in flame–flame interaction events in a dual burner experiment. Proc. of the Combustion Institute 2019, 37, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Combustor configuration and distribution plates design.
Figure 1.
Combustor configuration and distribution plates design.
Figure 2.
Three types of combustor headers.
Figure 2.
Three types of combustor headers.
Figure 3.
Analysis area of combustor model.
Figure 3.
Analysis area of combustor model.
Figure 4.
Flow velocity fields: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header.
Figure 4.
Flow velocity fields: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header.
Figure 5.
Velocity distributions from the center line to the end line of the combustor surface: (a) hydrogen flat header, (b) methane flat header, (c) hydrogen concave header, (d) methane concave header, (e) hydrogen convex header, and (f) methane convex header.
Figure 5.
Velocity distributions from the center line to the end line of the combustor surface: (a) hydrogen flat header, (b) methane flat header, (c) hydrogen concave header, (d) methane concave header, (e) hydrogen convex header, and (f) methane convex header.
Figure 6.
Pressure drops on various distribution plates: (a) hydrogen combustion, (b) methane combustion.
Figure 6.
Pressure drops on various distribution plates: (a) hydrogen combustion, (b) methane combustion.
Figure 7.
Mass fractions of residual fuel in mixing zone: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header based on hydrogen combustion, (d) flat header, (e) concave header, and (f) convex header based on methane combustion.
Figure 7.
Mass fractions of residual fuel in mixing zone: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header based on hydrogen combustion, (d) flat header, (e) concave header, and (f) convex header based on methane combustion.
Figure 8.
Turbulence intensities in mixing zone: (a) hydrogen combustion, (b) methane combustion.
Figure 8.
Turbulence intensities in mixing zone: (a) hydrogen combustion, (b) methane combustion.
Figure 9.
Temperature field of hydrogen flame and methane flame: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header.
Figure 9.
Temperature field of hydrogen flame and methane flame: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header.
Figure 10.
Residual fuel ratio field in the range from 1% to 10%: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header.
Figure 10.
Residual fuel ratio field in the range from 1% to 10%: (a) flat header, (b) concave header, and (c) convex header.
Figure 11.
Mass fraction of combustion products: (a) hydrogen combustion and (b) methane combustion.
Figure 11.
Mass fraction of combustion products: (a) hydrogen combustion and (b) methane combustion.
Table 1.
Design parameters at methane-air mixed gas and hydrogen-air mixed gas.
Table 1.
Design parameters at methane-air mixed gas and hydrogen-air mixed gas.
| Design Parameter |
CH4
|
H2
|
| Required heat input |
40,000 kcal/hr |
40,000 kcal/hr |
| Fuel flow rate |
4.5 Nm3/h |
13.8 Nm3/h |
| Calorific value HHV |
8698 kcal/Nm3
|
2796 kcal/Nm3
|
| Fuel inlet temperature |
15 ℃ |
15 ℃ |
| Combustion air flow rate |
55.0 Nm3/h |
42.8 Nm3/h |
| Mixture flow rate |
59.5 Nm3/h |
56.6 Nm3/h |
| Excess air ratio |
1.3 |
1.3 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).