1. Introduction
The concept of intelligent and portable products has become deeply entrenched in the public imagination [
1,
2], signifying that concomitant with the rapid growth of the internet, there is an accelerated demand for integrated systems, intelligence, and miniaturization, hastening the research into multifunctional sensors [
3,
4,
5]. Moreover, as the standard of living rises, so does the public interest in health and sports activities, leading to a greater focus on the effectiveness of monitoring both the methods and outcomes of physical exercise. In particular following the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a quickened pace in research into multifunctional sensors, due to the heightened demand for system integration, intelligent capability, and compact design [
6,
7,
8]. Collecting real-time data depends on distributed sensors, leveraging many detection mechanisms, including optical [
2,
4], capacitive [
9,
10], resistive [
11,
12,
13], geomagnetic [
14,
15,
16], chemical [
17,
18], and thermal sensitivity [
19,
20,
21]. In the arena of intelligent sports, various sensor technologies have been reported, that are noted for their high sensitivity and diverse functionalities. However, a standard limitation is their dependency on external power sources, necessitating continuous replacement. Even as technological progress has reduced power consumption for each sensor, the number of such units in sports applications might be significant. Given the limited lifespan, high replacement costs, and environmental pollution concerns associated with battery use, developing a maintenance-free and sustainable sensor technology for monitoring motion data during sporting activities is imperative [
22,
23,
24,
25].
Extensive research has shown that, due to the combined effects of contact electrification and electrostatic induction, TENGs have proven to be an effective method for converting environmental mechanical energy into electrical energy [
26,
27]. TENGs possess numerous advantages, such as high efficiency, straightforward architecture, low cost, small size, a wide selection of materials, easy scalability, and a self-powering system that operates without needing an external power source [
28,
29,
30,
31,
32]. TENGs, based on four fundamental operational modes, have been demonstrated and extensively applied to a variety of forms of mechanical energy, including wind [
33,
34,
35], hydro [
36,
37,
38,
39], and kinetic energy [
40,
41,
42], providing a sustainable power source for electronic devices [
43] that consume low energy.
In this study, we present a self-powered acceleration sensor based on TENGs to predict the distance a golf ball travels before reaching the hole. We systematically explored the performance of the acceleration and distance monitoring sensor from both theoretical and experimental perspectives. Attaching the sensor to the bottom of a golf practice mat results in the generation of varying voltage signals when an object moves over the hidden sensors. The object’s acceleration and the predicted distance to its stopping point are automatically calculated based on the time difference between these voltage signals. The sensors utilized a slim film design with a thickness of 1.5 μm and a weight of 4.316 g, guaranteeing that discrepancies in the distance predicted through the waveform signal stay within a 5 % margin of the actual distance achieved by the object. This highlights their considerable potential for practical application. Our developed sensors maintain the simplest structure, lightest weight, highest detection range, integration, and excellent stability compared to recent reports. Furthermore, the sensor has been experimentally proven to predict the final putt distance of a golf ball, detecting the acceleration, and rolling distance, thereby aiding athletes in adjusting their force during golf play. This research further expands the commercial application of TENG as a self-powered sensor in the sports domain.
3. Results and Discussion
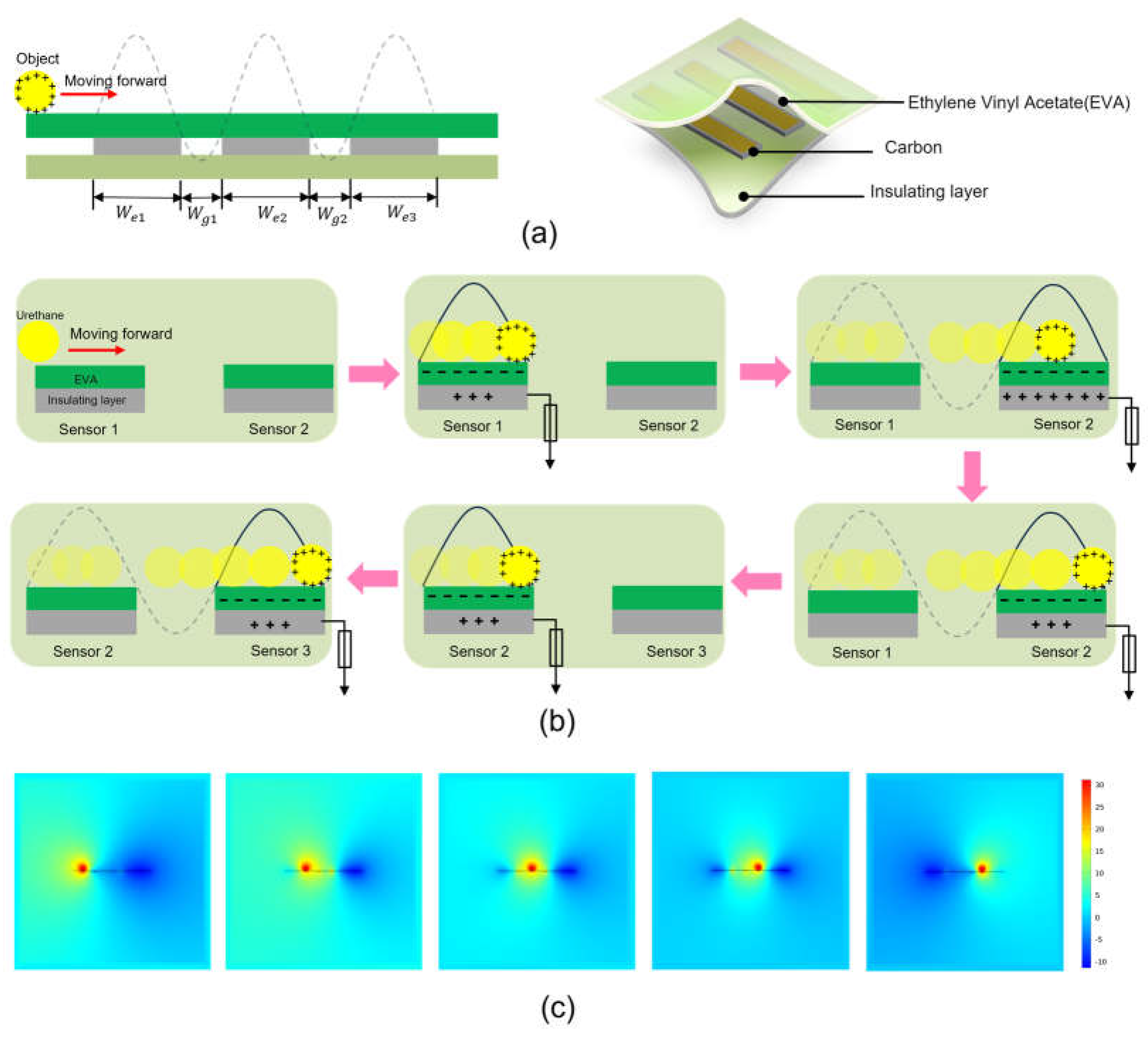
Figure 1a shows the schematic of the main structure of an acceleration sensor based on a single-electrode TENG. The three sensors are embedded equidistantly beneath a mat composed of carbon material, and cut to equal size using a laser cutter (C30 Laser Machine, CORYART, Korea). The three sensors are adhered equidistantly under the pad with leads, as shown in
Figure 1a at left. Note that the signal generation method of the TENG here is a single-electrode mode, so one end of the sensor needs to be in contact with the ground. Since the environment is indoors, an insulating layer is added below the sensor to ensure the efficient transmission of electrons.
Figure 1a at right shows a structural diagram of the sensor, with three sensors equidistantly embedded in the mats and insulating materials. The mat material consists of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), the sensor is made of carbon material, and the bottom insulation material is plastic film. The carbon material of the accelerometer produced is easy to obtain, has a rectangular structure of 210
length × 60
width, and weighs 1.407
.
The proposed acceleration sensor is designed by embedding multiple sensor units into a flexible substrate according to different needs.
Figure 1b shows the working principle. In the initial state, when the object is in contact with the mat, it is located above the sensor electrodes. Electrostatic induction due to the difference in electron affinity between object and surface causes electrons to transfer from the object to the carbon surface of the sensor, resulting in a negative charge on the carbon film and a positive charge on the surface film of the object. Triboelectric charges cannot be conducted or neutralized for some time. At this stage, the positive tribocharges are fully compensated by the opposite ones, so there is no electrical output produced on the electrode. Once the target ball moves forward and rubs against the film below, the equilibration of the electric field is broken. To balance the potential generated by the system, the potential difference initiates a flow of electrons from the carbon electrode to the ground to balance the potential until a new electrical balance is established (when the object ball rolls to the far right of sensor 1). In a similar manner, the object rolls past sensors 2 and 3. COMSOL simulation shows the potential distribution between two adjacent electrodes on a two-dimensional plane under different conditions. Obviously, the change in the spatial position of the charged object relative to the carbon sensor results in a time-varying spatial potential distribution, thereby generating a potential difference. This drives current to flow in the external circuit, as shown in
Figure 1c and the Supporting Movie S1.
Material selection plays a critical role in the structural design and electrical output of sensors based on TENGs. In this work, the object is a golf ball with a urethane surface material, which is known to carry a positive charge according to the triboelectric series. Therefore, for the triboelectric layer, we selected a well-performing carbon film. As the object rolls over the sensor, it forms a corresponding voltage waveform signal based on the amount of charge transferred. Here, the three sensors will generate three corresponding voltage waveform signals. The time it takes for the object to move from the peak of the first voltage to the peak of the second voltage is
, and the time it takes to move from the peak of the second voltage to the peak of the third voltage is
. The distance from the first peak to the second peak is equal to the distance from the second peak to the third peak. From this, the following formula can be derived:
In the above equation, represents the initial velocity of the ball. By applying the distance-acceleration relationship, the formula for and can be derived, thereby obtaining the acceleration .
The acceleration a is known, and can be calculated by the formula:
Equation (4) can then be obtained:
Finally, the distance S from the ball rolling to the stopping position can be obtained, as shown in
Figure 2a as:
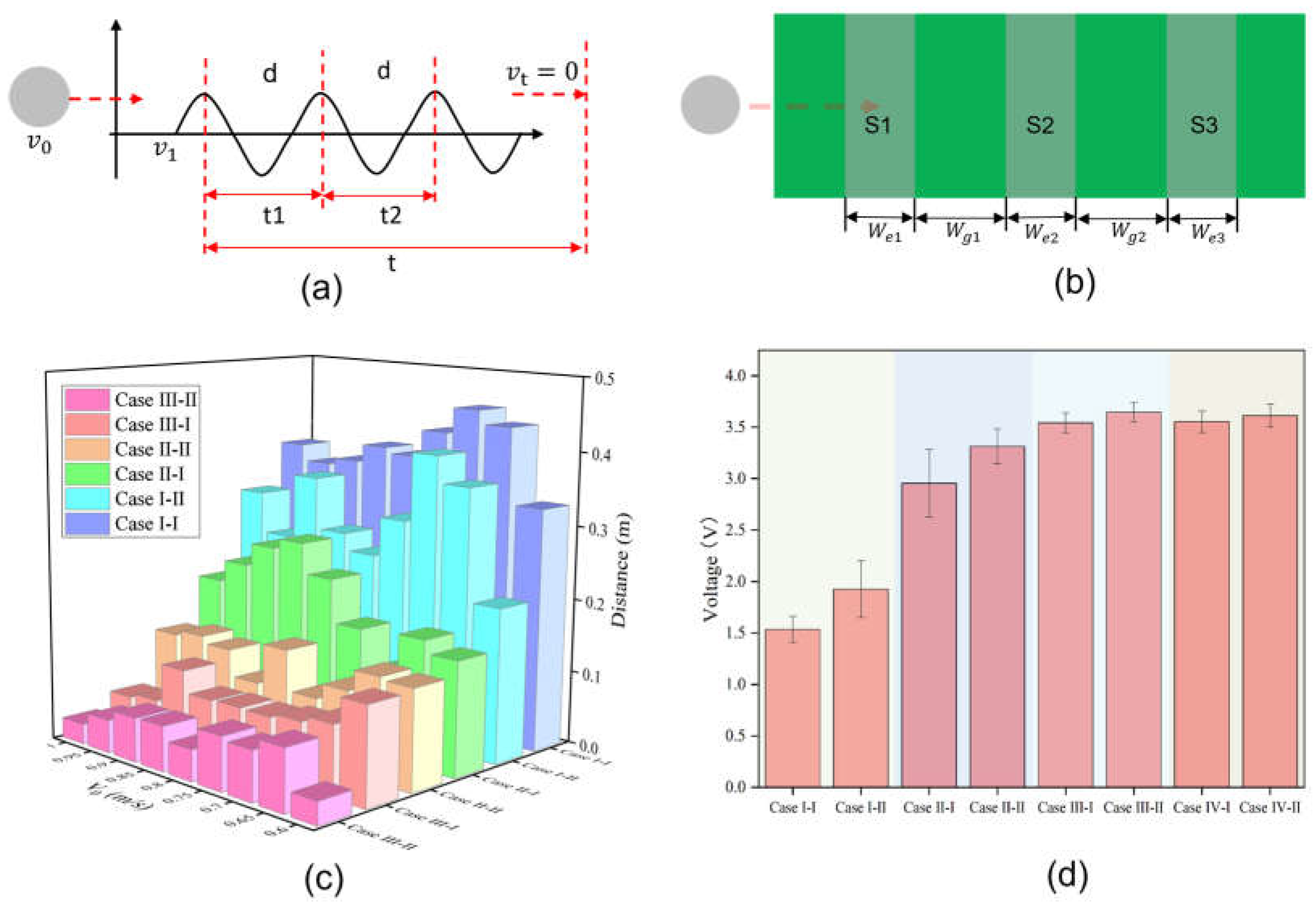
and space
. (c) Errors between the theoretical distance and the actual measured distance for different sensors at various speeds. (d) The maximum voltage generated by the object when passing over different sensors.
The 2D top view in
Figure 2b displays the ball passing over sensors with varying widths
and spacings
.
Table 1 lists the different conditions of the sensors. Sensors with different widths at the same spacing or the same sensor at different spacings produce different voltage waveform signals. Error comparison of the theoretical and actual sensor values under different conditions in
Figure 2c show that as the width of sensors or their spacing increases, the error between the calculated and actual measured values of the object rolling to the stop position decreases. More interestingly, as the width of the sensors or their spacing increases, voltage generated by the object rolling pass the sensors gradually increases, and then stabilizes, eventually maintaining around 3.5 V, as shown in
Figure 2d.
According to the explanation in
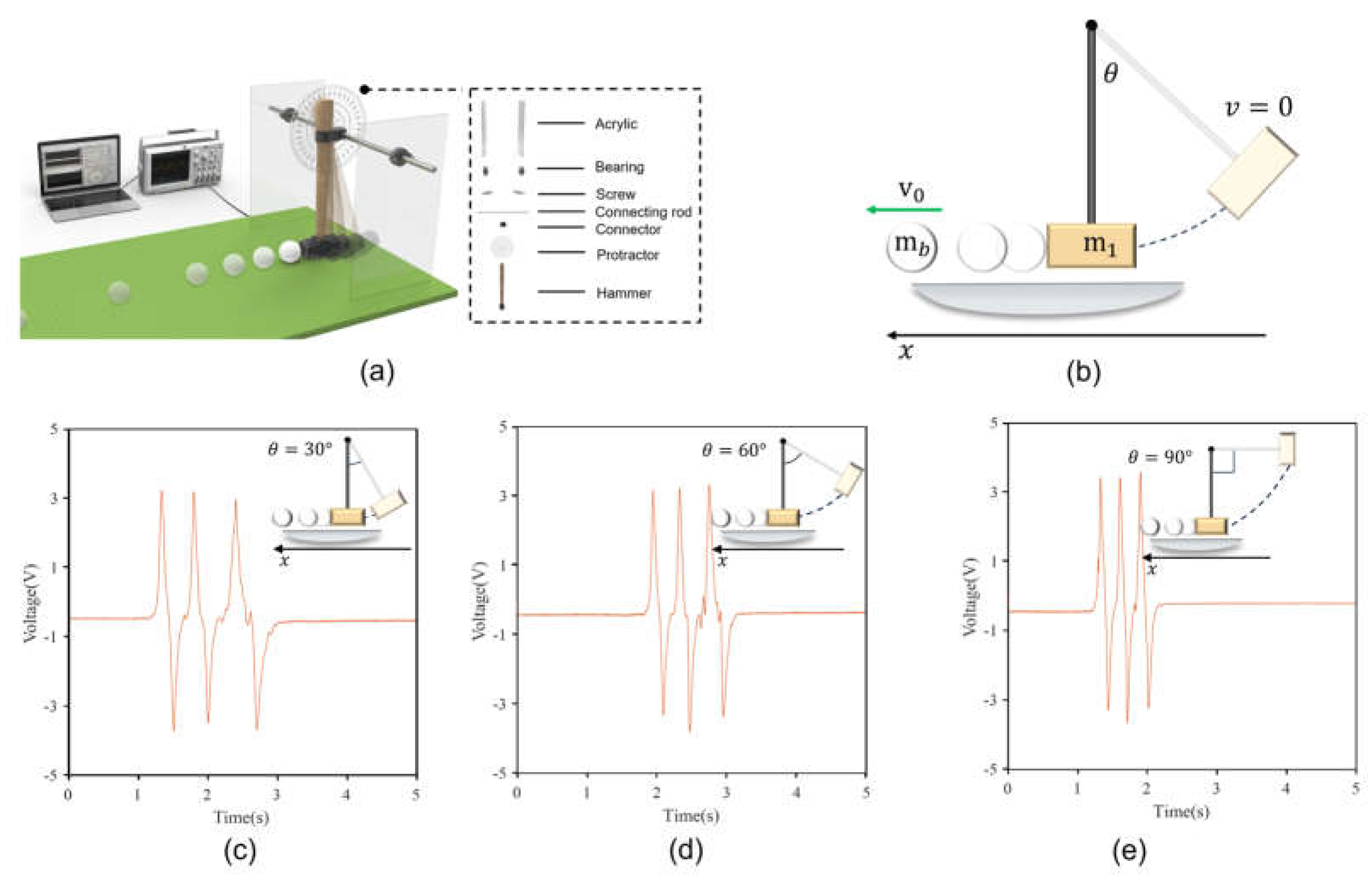
Figure 2, time is the crucial parameter when the ball passes through the three sensors. To verify the working principle of the sensors, we designed and constructed a device that allows the object to roll over a mat with different initial kinetic energies. This device mainly consists of an acrylic board, roller bearings, protractor boards, and a hammer, as shown in
Figure 3a. The hammer is raised to a certain angle and then falls to hit the object, imparting initial kinetic energy for the object to move in a straight line forward. We selected bearings to drive the hammer’s vertical motion, significantly reducing the friction during the hammer’s movement, so the friction is negligible. The object rolls horizontally forward and passes sequentially through three sensors located beneath the mat, when it gains initial kinetic energy. Voltage waveforms with three peaks and troughs can be clearly seen on the oscilloscope. The voltage signal can also be transmitted to a laptop. Our developed program can automatically read the voltage wave signal and quickly analyze and calculate the acceleration, velocity, and the predicted distance of the object. The hammer is raised to a certain angle
θ, and drops from a fixed point to generate kinetic energy for the object, causing it to move horizontally, as shown in
Figure 2b. The kinetic energy generated by the hammer dropping from different angles can be calculated using a formula. Here, we have derived the kinetic energy generated by the hammer’s movement, initial velocity, and the linear distance the ball can roll after being struck by the hammer. The angle between the hammer and the plumb bob is
, and the radius of the hammer’s circular path is
. Assuming the center of mass of the hammer is at the vertex of the circle, the gravitational potential energy of the hammer when it is pulled up is
, where
is the weight of the hammer.
The assumption is made that during the hammer’s fall. There is no energy loss. Then all the gravitational potential energy of the hammer when it reaches the lowest point is converted into kinetic energy, and the speed at this time can be obtained:
Equation (7) can be thus be obtained:
Then, assuming that the collision between the hammer and the golf ball satisfies the conservation of momentum, the initial speed of the golf ball after the collision can be obtained:
Where,
where
is the mass of the golf ball, and
is the initial speed of the golf ball.
Assuming that the friction force on the rolling golf ball is constant, the moving distance of the golf ball can be obtained:
Where, is the friction force, is the friction coefficient, and is the moving distance.
The hammer was raised to (30, 60, and 90)
, respectively, generating three kinetic energies of
,
, and
. The object was hit by the three different kinetic energies of the hammer, and rolled forward at high speed. The object rolled past the three sensors, and obtained three different voltage signal waveforms. We selected the sensor with a width of 60 mm and spacing of 400 mm.
Figure 3c
e show the voltage signal waveforms obtained by the object passing through the sensor in the three cases. Interestingly, because the sensor is fixed, the maximum voltage of the voltage waveform can reach about 3.5 V. The time intervals
and
of the three voltage signals generated can be clearly seen to differ under the different initial kinetic energies. As the kinetic energy increases, the interval between
and
shortens.
Figure 3c
e show the corresponding voltage signal graphs under the three kinetic energy conditions.
To evaluate the performance of the acceleration sensor, we selected sensors of the same length but different widths and measured them under different gravitational potential energy conditions. This process entailed monitoring the initial velocity and acceleration of a rolling object. The sensors were strategically positioned beneath the mat, maintaining a consistent 200mm gap between the various sensor types. By dropping a hammer from distinct angles, we imparted different initial kinetic energies to the ball, designated as
,
, and
, corresponding to angles of (30, 60, and 90)
, respectively (
Figure 3c–e, Insets). The acceleration and velocity of the object rolling forward after the hammer hit were recorded.
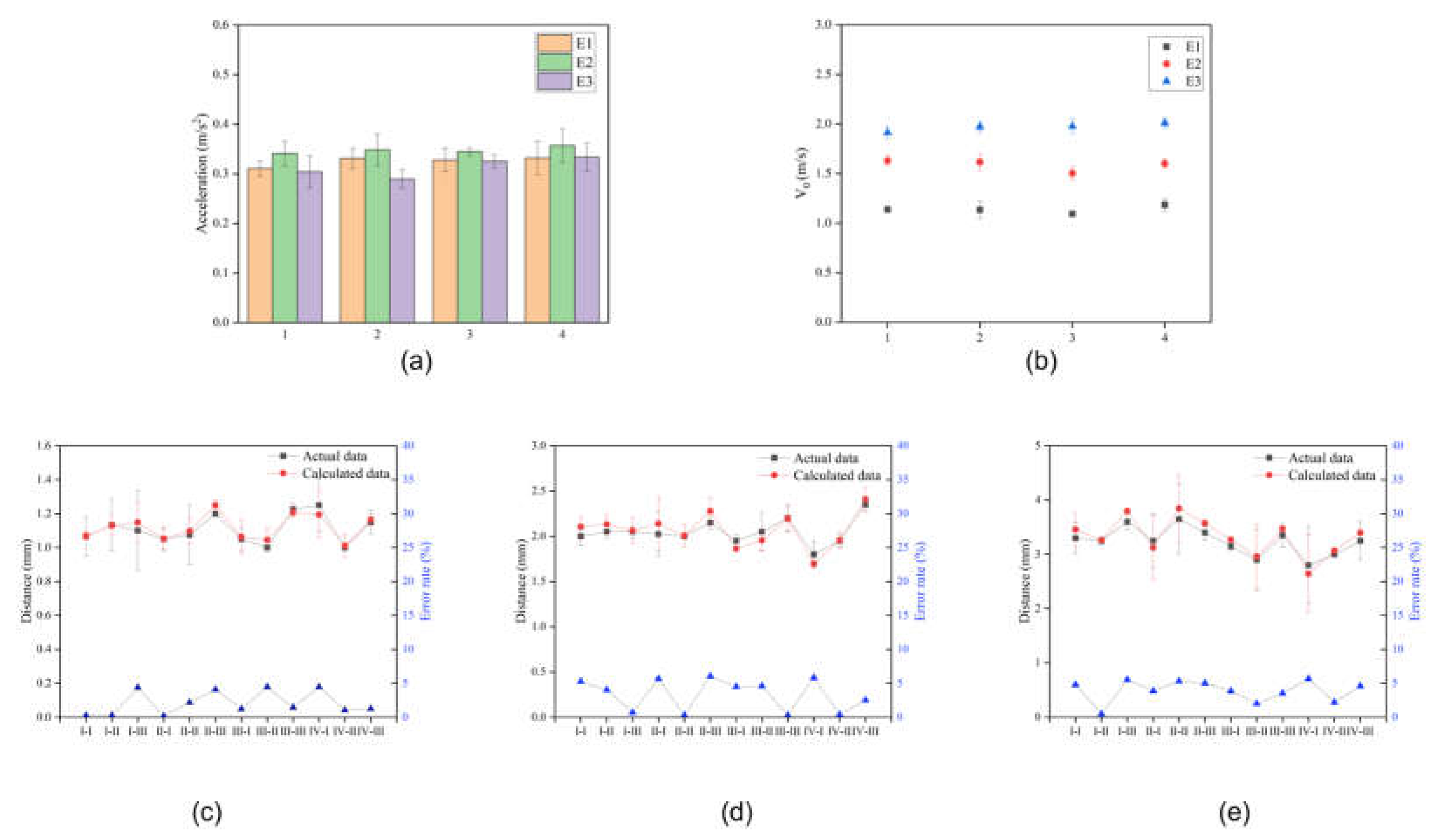
Figure 4a,b show the acceleration and velocity of the object when driven by the three amounts of kinetic energy, and passing through acceleration sensors of widths (60, 80, 100, and 120) mm. As the width of the acceleration sensor increases or the initial kinetic energy increases, the acceleration of the object during rolling can be observed to remain roughly constant at about 0.3 m/s². It can also be clearly seen that as the initial kinetic energy of an object increases the speed of the object increases; but under the same initial kinetic energy conditions, the initial speed of the object is basically the same. Experiments show that the acceleration of the object in this study has nothing to do with the initial kinetic energy, and the amount of kinetic energy affects the velocity
of the object.
The distance after the object rolls past the acceleration sensor can be automatically caculated. Three different kinetic energies , , and , were used, and after the hammer hitting the object, the estimated stopping distance past different sensors from case II to case IVIII was recorded, and compared with the actual measured distance. In this study, to compare the calculated values of the object’s moving distance with the actual measured values, the calculated values were found to be almost consistent with the actual measured distances of the object’s movement, with an error margin of around 5 %. This indicates that the acceleration sensor based on the nanogenerator for frictional electricity demonstrates significant accuracy in distance prediction functionality.
Compared to other rigid-structured acceleration sensors, we further explored the functionalities of sensors based on the nanogenerator for frictional electricity by embedding simple sensor units into a flexible golf practice mat. To demonstrate the capability of the acceleration sensor in predicting distances, we proposed a scenario where the fabricated acceleration sensors predict the travel distance of a golf ball.
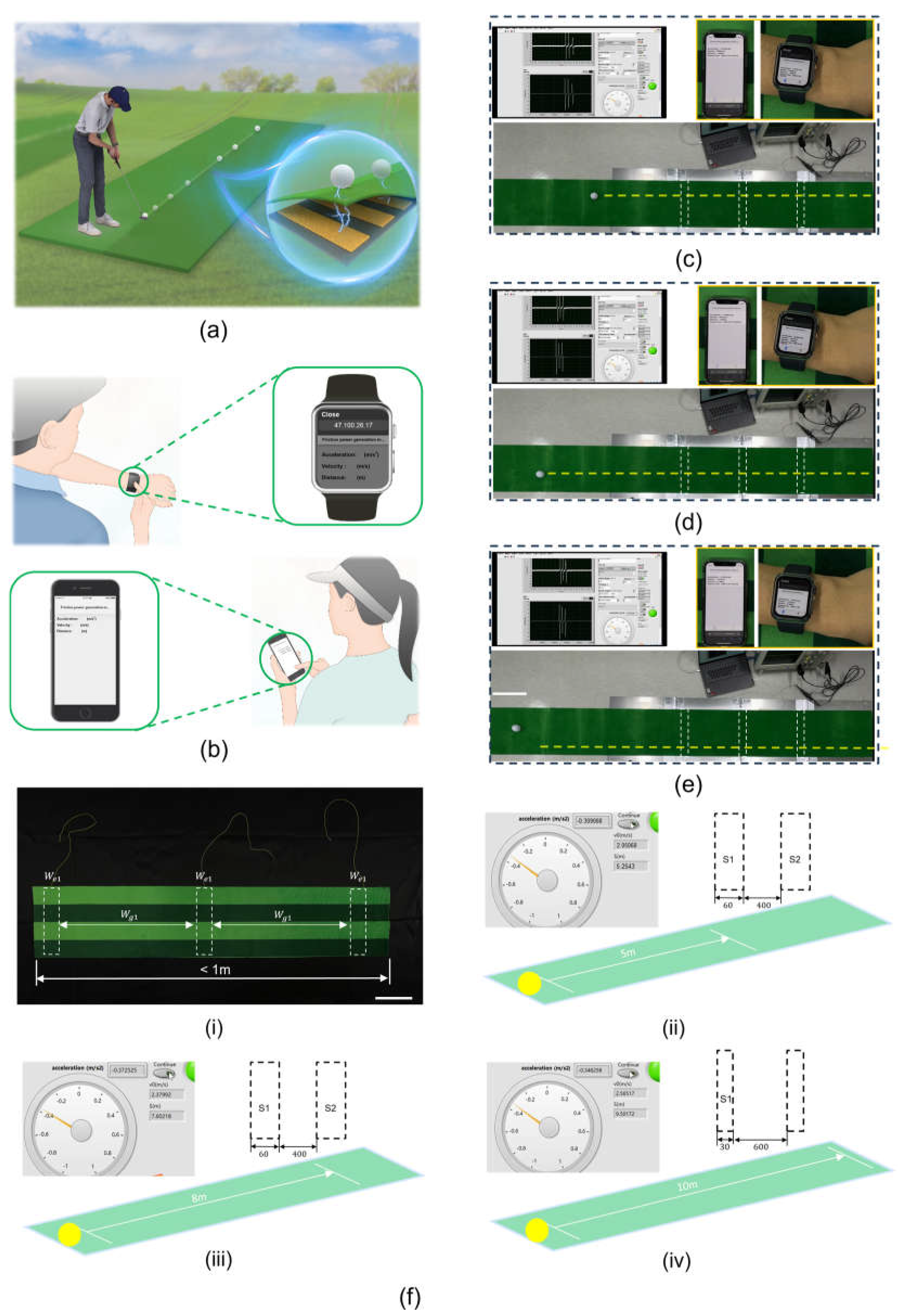
First,
Figure 5a illustrates the motion of a golfer hitting the ball into the hole, with an inset showing the principle of TENG as the golf ball passes over the sensor beneath the mat. As the golf ball rolls forward, passing over the TENG sensor, three distinct voltage waveforms are visible on the oscilloscope. Then, by analyzing the time interval of these voltage waveform signals, the motion acceleration and rolling distance of golf the golf ball can be calculated and transmitted in real time to smartphones and smartwatches, allowing players or referees to quickly obtain data results, as shown in
Figure 5b. Last, tests were conducted on a 3 m long golf practice mat with the golf ball struck with varying force in three scenarios. As depicted in Figures 5c
e, and Supporting Movies
,
, and
, the golf ball rolled distances of (1.489, 1.948, and 2.189) m under three different force conditions. The initial velocity, rolling acceleration, and rolling distance of the golf ball were clearly displayed on a computer interface, with smartphones and smartwatches also able to simultaneously receive the same data. We continued to increase the force of hitting golf ball, the acceleration sensor based on the TENG can predict the distance to about 5m or even 8m. As the predicted distance extends, achieving a clear and stable waveform time
and
, we need to change the size and spacing of the acceleration sensors. When we change the width of the acceleration sensors to 30mm and the spacing to 600mm, the acceleration sensors can predict distances up to about 10m, as shown in
Figure 5f
i, f
ii, and f
iii. We successfully produced a mat containing a sensor that is less than 1m in length and can predict the linear movement distance of an object up to about 10m. This length of distance prediction is sufficiently comprehensive for golf swing training before the ball enters the hole. This prototype of the TENG-based embedded acceleration sensor demonstrates the potential of creating sensitive and effective commercial sensors for real-time monitoring and assessment in golf sports.
(e) The golf ball passing through the TENG sensor to obtain its actual acceleration, speed, and distance, and th on mobile phones and smartwatches. Scale bar: 20cm. (fi) The fabricated 1m sensorcontaining mat of 60 mm width × 400 mm spacing. Scale bar: 10 cm. (fii) and (fiii) The sensor in (i) can predict ball rolling to about 5 m and 8 m, respectively. (fiii) A sensor with a width of 30 mm and a spacing of 600 mm can predict the ball rolling to the distance of about 10 m.
Figure 1.
Structural design and working principle of the acceleration sensors. (a) Structural diagram of the acceleration sensor. (b) When an object moves horizontally above the sensor, electrostatic induction occurs between the object and the three sensors, charge transfer takes place between the object and the sensor material, and the corresponding voltage signal is shown on the oscilloscope. (c) Simulation of the potential difference between the object and the sensor material during the contact electrification phase using COMSOL.
Figure 1.
Structural design and working principle of the acceleration sensors. (a) Structural diagram of the acceleration sensor. (b) When an object moves horizontally above the sensor, electrostatic induction occurs between the object and the three sensors, charge transfer takes place between the object and the sensor material, and the corresponding voltage signal is shown on the oscilloscope. (c) Simulation of the potential difference between the object and the sensor material during the contact electrification phase using COMSOL.
Figure 2.
Measurements and performance analysis of the acceleration sensors. (a) Calculation of the acceleration and distance based on the voltage signals generated by TENG. (b) The object passing over sensors of different widths
Figure 2.
Measurements and performance analysis of the acceleration sensors. (a) Calculation of the acceleration and distance based on the voltage signals generated by TENG. (b) The object passing over sensors of different widths
Figure 3.
Experimental platform and response characteristics. (a) Schematic of the ball motion test under different initial kinetic energies. (b) The object acquires different initial kinetic energies by falling through different angles. (c–e) Graphs of the VoltageTime relationship of the object rolling forward across the mat after gaining kinetic energy from the hammer falling from angles of (30, 60, and 90), respectively, as shown in each Inset.
Figure 3.
Experimental platform and response characteristics. (a) Schematic of the ball motion test under different initial kinetic energies. (b) The object acquires different initial kinetic energies by falling through different angles. (c–e) Graphs of the VoltageTime relationship of the object rolling forward across the mat after gaining kinetic energy from the hammer falling from angles of (30, 60, and 90), respectively, as shown in each Inset.
Figure 4.
Comparison of different performances of the TENG-based acceleration sensors. (a) and (b) The acceleration and speed display, respectively, of the object passing through different types of sensors under different initial kinetic energies. (c), (d), and (e) The predicted distance, and actual distance that the object can roll under different initial kinetic energies, and the error involved, respectively.
Figure 4.
Comparison of different performances of the TENG-based acceleration sensors. (a) and (b) The acceleration and speed display, respectively, of the object passing through different types of sensors under different initial kinetic energies. (c), (d), and (e) The predicted distance, and actual distance that the object can roll under different initial kinetic energies, and the error involved, respectively.
Figure 5.
Practical application of the acceleration sensor based on TENG in golf sports. (a) Schematic of an athlete hitting a golf ball. (b) Schematic showing that the data read by the acceleration sensor can be automatically transmitted to mobile phones and smartwatches. (c)
Figure 5.
Practical application of the acceleration sensor based on TENG in golf sports. (a) Schematic of an athlete hitting a golf ball. (b) Schematic showing that the data read by the acceleration sensor can be automatically transmitted to mobile phones and smartwatches. (c)
Table 1.
Three sensors with the same width, with widths of 20 mm, 40 mm, 60 mm, and 80 mm, respectively, with different spacing between sensors (200 mm, 400 mm, 600 mm).
Table 1.
Three sensors with the same width, with widths of 20 mm, 40 mm, 60 mm, and 80 mm, respectively, with different spacing between sensors (200 mm, 400 mm, 600 mm).
| Case |
(mm) |
(mm) |
| II |
20 |
200 |
| III |
400 |
| III |
40 |
200 |
| IIII |
400 |
| IIII |
60 |
200 |
| IIIII |
400 |
| IVI |
80 |
200 |
| IVII |
400 |
Table 2.
Four sensors with the same width, with widths of 60 mm, 80 mm, 100 mm, and 120 mm, respectively, with different spacing between sensors (200 mm, 400 mm, 600 mm).
Table 2.
Four sensors with the same width, with widths of 60 mm, 80 mm, 100 mm, and 120 mm, respectively, with different spacing between sensors (200 mm, 400 mm, 600 mm).
| Case |
(mm) |
(mm) |
| II |
60 |
200 |
| III |
400 |
| IIII |
600 |
| III |
80 |
200 |
| IIII |
400 |
| IIIII |
600 |
| IIII |
100 |
200 |
| IIIII |
400 |
| IIIIII |
600 |
| IVI |
120 |
200 |
| IVII |
400 |
| IVIII |
|
600 |