1. Introduction
The problems of involving production waste as secondary raw materials into economic circulation in order to replace natural raw materials are relevant and require an urgent solution [
1]. Utilization of carbon-containing sludge will improve the environmental situation and reduce the consumption of natural energy resources by processing waste into cheap fuel and for the metallurgical industry.
The whole difficulty in the disposal of liquid waste from metallurgical production, which includes flotation waste, during wet processes of coal enrichment lies in the fineness and high humidity, which requires the use of expensive and complex pre-dehydration systems and preparation technologies.
Flotation waste, due to the lack of simple and cost-effective technologies for preparing it for disposal, as well as due to the instability of its chemical and granulometric composition, remains unclaimed and is stored in tailings ponds. To date, a total of more than 45 million tons of flotation waste have been accumulated in tailings ponds No. 2 and No. 3 of ArcelorMittal Temirtau JSC (now Qarmet JSC).
On the other hand, the intensification of the production of ferrous metals requires an increase in the production of sinter and pellets necessary for the production of cast iron and steel [
2,
3,
4]. The sintering fuel, which traditionally is coke breeze, also contributes to the reduction in the quality of the sinter.
The problem of coke breeze deficiency is becoming increasingly urgent and there is a need to search for new types of sinter fuel. Experiments with the introduction of alternative types of solid fuels into the mixture revealed both their advantages and disadvantages [
2].
An alternative option for partial replacement of coke breeze can be coal flotation waste (CFW). However, their physicochemical properties and technological features of its use in the agglomeration of iron ore materials have not been studied. It is necessary to develop optimal compositions of sinter fuel mixtures and technological regulations for the production of sinter using OFU.
Technogenic reserves of sludge are, on the one hand, valuable carbon-containing raw materials for generating thermal and electrical energy, and on the other hand, they are a source of environmental pollution. Sludge dumps occupy large areas around enterprises, take land out of economic use, and pollute the environment.
Utilization of flotation waste in metallurgical production as fuel, carbon and slag-forming materials can provide significant savings in cast iron and lime, improve the quality of the steel produced, and reduce the consumption of basic and auxiliary materials in the plant.
2. Literature Review
Numerous studies show that coal processing waste can be effectively used in various industries: energy, ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, construction industry, etc. [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
In world practice, the main promising consumers of flotation waste have already been identified, and recommendations have been drawn up for the use of waste in various fields of industry. Alternative methods for recycling dewatered flotation waste are known, including use as: a backfill component for filling empty mine workings [
8]; raw materials for the production of building materials [
9,
10,
11]; raw materials for the production of germanium, rare, trace and other potentially valuable elements [
11]; raw materials for the production of sorbents [
12].
A technology has been developed for the dehydration of high-moisture OPC and a method of agglomeration to produce coal-mineral briquettes, which can be used as a deoxidizing and refining flux [
13,
14].
Promising areas include the use of coal flotation waste as fuel for metallurgical units. The thermal energy reserve of the OFU is sufficient to ensure the operation of a power plant with a capacity of 20 MW. Such waste can be burned in combustion devices operating in a layer mode [
3,
4,
5].
An analysis of literature sources showed the absence of any experience in the use of flotation waste at ferrous metallurgy enterprises. Disposal of dewatered flotation tailings can be carried out in a manner similar to existing carbonaceous materials utilization methods.
Currently, there is scientific and technical information on the use of lean coals in metallurgical production, which are similar in their characteristics to flotation waste. For example, JSC ArcelorMittal Temirtau has developed an optimal pelletizing method using a mixture of coke and lean coal as fuel. In order to reduce the cost of sinter and improve its quality, for every percent increase in lean coal, the ratio of the height of the lower layer to the height of the upper layer increases by 0.07-0.10. The results of studies on the use of lean coals during the agglomeration of Lisakovsky roasting magnetic concentrate (LOMC) showed that the replacement of coke breeze with lean coal in the range from 0 to 100% has virtually no effect on the performance of the sintering process and the quality of the resulting sinter [
7,
8]. As a result, significant savings were obtained from reducing fuel costs.
The most widely used coal is anthracite coal, which differs from other natural fuels in its low content of volatile components (on average about 5%) and high carbon content. Anthracite chips do not require additional heat treatment, and their cost is lower than the cost of coke breeze [
4].
However, the replacement of coke breeze from coal flotation waste is not equivalent. Under the conditions of the layer process, the calorific value of the OPC does not make a significant contribution to the input part of the heat balance of the agglomeration process due to its lower flammability.
The goal of the work is to find the optimal ratio of coke and BCP in the fuel mixture of the sintering charge.
2. Research Methodology
Semi-quantitative analysis was carried out on an ARL QUANT’X energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer; the main mineralizing components of flotation waste were determined.
The thermoanalytical study was carried out on a synchronous thermal analyzer STA 449 NETZSCH in dynamic mode with a heating rate of 10 °C/min in an air flow of 30 cm3/min in the temperature range 30–1000 °C. We determined: the lower heat of combustion of the carbon-containing material, the change in mass during ignition (IMPP), the change and rate of change in the mass of the sample (TG and DTG curves), the thermal effect of the process (DSC curve), the temperatures of the beginning, end and maximum development of thermal effects. Determination of the particle size distribution of coal slurry by sieve analysis was carried out in accordance with GOST 27562-87 “Iron ores, concentrates, agglomerates and pellets. Determination of particle size distribution by sieve analysis.”
Work on partial replacement of coke with flotation waste during agglomeration was carried out both in laboratory and in pilot industrial conditions.
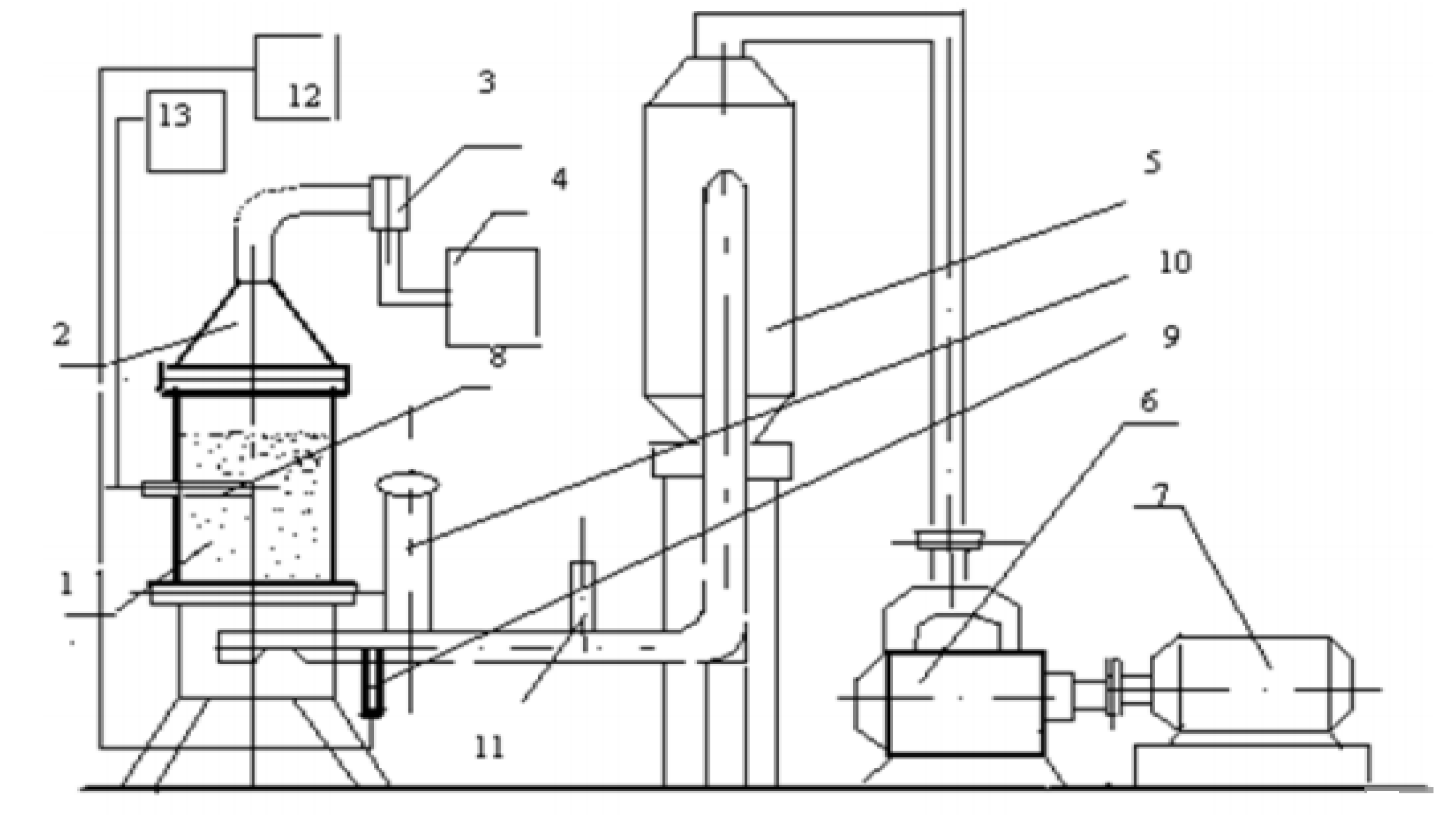
Experimental sintering was carried out on a laboratory sintering installation with a bowl diameter of 250 mm (
Figure 1). In a laboratory sintering plant, the charge from sintering plant No. 2 with different contents of coal flotation waste in the fuel mixture was subjected to agglomeration. Materials for sintering (LGMC and SSGPO concentrate, combined flux, coke breeze) were taken from current production.
The ore mixture was made up of sinter screenings and mine ore of fractions 5-10 mm and 0-5 mm in a ratio of 80:10:10. The charges were sintered in a layer 400 mm high at a vacuum under a grate of 1100 mm water column. Charges with a constant ratio in the iron ore part of the LGMK charge, ore mixture and SSGPO concentrate - 70:20:10, respectively, were subjected to agglomeration. The combined flux was taken from the condition for obtaining an agglomerate with a basicity (CaO/SiO) of 1.23 units. and magnesium oxide - 2.35%. The chemical composition of the charge materials is given in
Table 1. The charge was sintered in a layer 400 mm high at a vacuum under a grate of 1100 mm. water Art.
From the output parameters, we controlled the specific productivity of the installation, the vertical sintering speed, the conditional cooling rate of the sinter, the yield, the mechanical strength of the agglomerate to impact and abrasion according to GOST 15137-77, and the chemical composition of the agglomerate.
Determination of the amount of nitrogen oxide and dioxide in emissions from a laboratory sintering plant was carried out by the photocolorimetric method using the Griess-Ilosva reagent [
17]. The essence of the method is as follows. The gas sampling tube is inserted into the gas outlet pipeline and purged with the analyzed gas using a pump. Then the pump is disconnected and an evacuated vessel with an absorption solution is connected. The gas was withdrawn by changing the position of the valve on the vessel. Based on the measured optical density of the test solution and the calibration dependence, the content of nitrite ion in the analyzed sample was found.
The determination of sulfur dioxide in exhaust gases was carried out using the formaldehyde-parazaniline method [
17]. When taking samples, the absorption device is connected to an electric aspirator and the gas flow under study is aspirated. Then, using the photocolorimetric method, the optical density of the solutions under study is measured and the content of sulfur dioxide in the sample is determined using the corresponding calibration characteristic.
In all sintering options carried out, samples were also taken and analyzed for dust content in the exhaust gases. The dust content was determined by the gravimetric method [
17].
3. Research Results and Discussions
3.1. Physico-Chemical Properties of Coal Flotation Waste
Coal flotation wastes have high dispersion, soakability, swelling ability, etc. Flotation wastes from coal enrichment mineralogically consist of an organic part (carbonaceous substances) and mineral impurities (clay minerals, carbonates, sulfates, etc.). The main clay component is kaolinite. Inorganic substances are represented mainly by the clayey-hydromica complex, the share of which is 55-65%. The content of combustible mass (carbon) in waste is 35-50%. Density varies in a wide range from 1400 to 1800 kg/m
2, bulk density by dry weight is 0.65-0.85 kg/m
3. The sulfur content on a dry weight basis is 0.66% (
Table 2 and
Table 3).
A technical analysis of the waste from the flotation department of ArcelorMittal Temirtau JSC showed that the sulfur content in them is 0.50–0.66%, they have a high humidity of 11.77–20.0%, the yield of volatile substances reaches 22.95–34, 3%, ash content 30.95–60.9% and therefore high organic matter content.
Using a semi-quantitative method, the main mineralizing components of flotation waste were determined, %: quartz 40.3-55.95; oxides of aluminum 12.3–21.5, calcium 1.3–3.9 and iron oxides 2.2–3.9.
Table 3 presents a semi-quantitative analysis of flotation waste.
Sieve analysis of the waste showed that the particles are unevenly distributed and their ash content is heterogeneous, with the highest ash content observed in the -0.008 mm class.
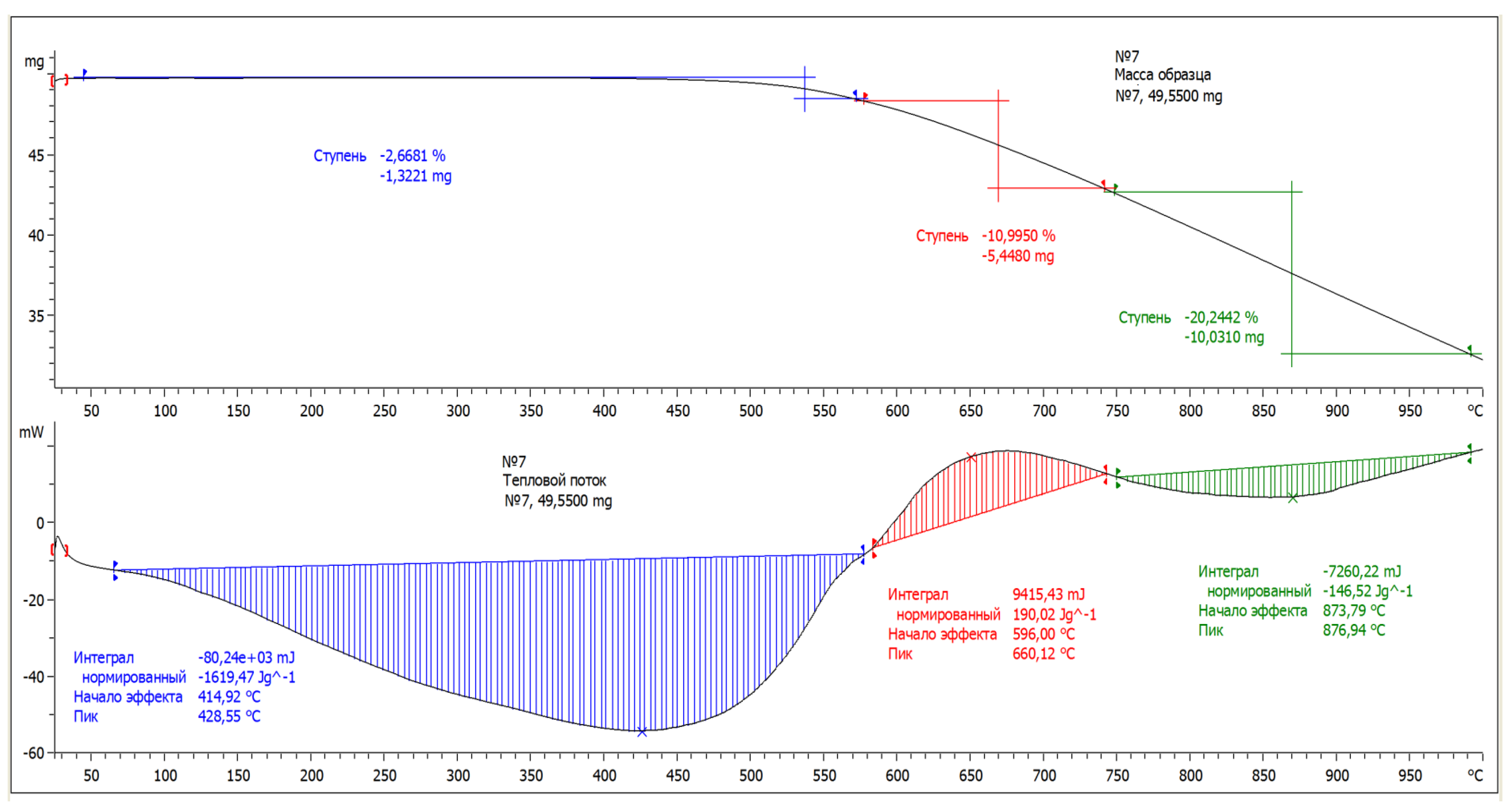
The thermoanalytical study was carried out on a synchronous thermal analyzer STA 449 NETZSCH in dynamic mode with a heating rate β equal to 10, 20 and 30 °C/min in an air flow of 30 cm
3/min in the temperature range 30–1000 °C. [
16,
17]. In
Figure 2 the thermal effect curve (HEC) of coal preparation waste is presented. Thermal effects that occur when heating a sample of coal slurry - changes in weight and heat flow of the heating process were also carried out at the heating rate. Since there is less moisture in coal slurry and virtually no volatile substances, the mass loss in the first stage is 2.66%, at temperatures from 66 °C to 570 °C. At this temperature an endothermic reaction occurs. It is clear from the graphs that there is a noticeable loss in sample weight starting only from a temperature of ≈ 580 °C at the second stage - from 580 °C to 610 °C, weight loss ≈ 10%. An exothermic reaction is observed. The third stage is from a temperature of 750 °C to 1000 °C, an endothermic reaction is observed. Weight loss of sample ≈ 20%. The lowest calorific value of the studied waste was 15.9 MJ/kg, which allows its use as fuel.
3.2. Laboratory Studies
With single-layer sintering, partial replacement of coke breeze with coal flotation tails leads to a decrease in the vertical sintering rate, deterioration in the quality of the sinter and a general excess fuel consumption. The introduction of 1% flotation waste reduces the vertical sintering speed by 0.1 mm/min, the specific productivity by 0.007 t/m3 h. With the introduction of up to 11% flotation waste, the yield increases by 0.56% for every 1% waste, and then decreases with the same ratio.
Table 2 presents the test results: Option I - 100% coke breeze; II, III, IV options - partial replacement of coke breeze with coal enrichment flotation tailings - 6.1; 11.5 and 23.1% respectively.
Analysis of fuel consumption shows that when up to 10% of waste is added to the fuel mixture, it is constant (95 kg/t of agglomerate), then increases sharply with a ratio of 1.09 kg/t of agglomerate per 1% of waste.
During two-layer sintering, agglomeration was carried out on charges with the same content in the upper and lower layers in the iron ore part of the LGMK charge, ore mixture and SSGPO concentrate - 70:20:10, respectively.
The combined flux was taken from the condition of obtaining an agglomerate with a basicity (CaO/SiO) of -1.12 units. and magnesium oxide - 2.30%. Flotation waste was introduced as additional fuel into the upper layer at the rate of 5, 10, 20% of the total coke consumption for sintering. The return balance, which characterizes laboratory studies, was maintained by changing the height of the top layer with a total height of the charge layer of 400 mm.
The results of two-layer tests are presented in
Table 5: option I - 100% coke breeze; II, III, IV options - introducing 5,10 and 20% of flotation waste from the total coke consumption into the upper layer.
With two-layer sintering, the introduction of 5% flotation waste into the charge leads to an increase in the vertical sintering speed by 1.3 mm/min, specific productivity by 0.08 t/m3 h, the yield of usable agglomerate - 0.1%, mechanical impact strength and abrasion -1.7 and 0.2%, respectively. A further increase in the proportion of waste leads to a decrease in the height of the top layer by 1.5 mm by 1% of waste and yield.
During laboratory tests, it was found that the concentrations of SO2 and NOx in the exhaust gases, compared with conventional charging during single-layer sintering, remained almost at the same level, and with double-layer sintering, a slight increase was observed. Involving flotation waste in production does not significantly change the environmental parameters of the process.
It was found that dust was present in all samples and was released during the first 6 - 8 minutes of the sintering process. During the combustion of solid fuel, the release of volatiles has a “jet” character. When burning flotation waste, the temperature in the sintering zone is insufficient for complete ignition of volatile substances on the surface of the charge materials. As a result, one part of the volatiles ignites together with the coke breeze, and the other part, without having time to interact with the oxidizing components of the gas phase, leaves the reaction zone with the exhaust gases.
3.3. Industrial Tests
Pilot research on replacing part of the coke breeze with flotation waste at the 5th sintering machine of sinter plant No. 2 with an environmental assessment of such replacement. as well as comparative measurements with conventional blending. The composition of the charge from sinter plant No. 2 during experimental and comparative measurements is given in
Table 6.
During experimental measurements on vacuum chambers in the filters of the sampler, the presence of mainly agglomeration dust was noted, in which resinous substances are contained in small quantities and are found on the filters in the form of a yellow coating. Comparative measurements in vacuum chambers did not reveal any agglomeration dust on the filters. Resinous substances, both in experimental and comparative measurements, were detected in sufficient quantities in the exhaust gases in the collector and in the exhauster (
Table 7).
When conducting comparative measurements, there was a decrease in the proportion of oily scale in the sintering machine charge from 70 to 40 tons (or from 2.15 to 1.51% of the charge composition), which apparently had some impact on the comparative results. The content of resinous substances when using flotation waste in the sinter plant charge increased from 0.63 to 1.14 mg/nm3 (or by 45%) in the collector and from 0.95 to 1.33 mg/nm3 (or by 29%) at the exhauster.
Removal of volatile and resinous substances occurs at low temperatures (up to 300 0C) and the equilibrium temperature of their condensation is 78 0C.
As a result, when using flotation waste, most of the volatile and tarry substances are removed from the combustion zone, captured by the waterlogging zone and, moving through the layer, removed in the last vacuum chambers.
The gas temperature in these vacuum chambers is 250-300 0C and in the collector 100-150 0C, therefore no deposits of tarry substances were found in this section of the gas exhaust tract. After the second stage of gas purification, the temperature of the exhaust gas decreases and ranges from 70 to 90 0C, i.e., decreases to a temperature close to the equilibrium deposition of resinous substances.
As a result, the formation of a layer of deposits consisting of a mixture of dust (up to 50%) and resin containing up to 80% organic compounds was revealed on the exhauster blades. After exhausters, as a result of adiabatic compression, the temperature of the exhaust gases increases by 15-20 0C and further deposition of tarry substances stops. Increasing the temperature to 90-120 0C sharply reduces resin condensation and with a further increase in temperature to 180-260 0C, condensation practically stops. The high yield of volatiles in flotation waste changes the composition of the exhaust gases. Nitrogen oxides on eshauster increase on average from 248.2 to 309 mg/nm3 (by 20%).
Based on the results of laboratory and semi-industrial studies on the partial replacement of coke breeze in the charge of sinter plants with flotation waste, the main production and technological features, technical and economic indicators of the sintering process were determined.
Conclusions
Thus, the work determined the material composition of waste from the flotation department of ArcelorMittal Temirtau JSC (now Qarmet JSC) and proposed options for their effective use as a fuel-containing additive in the fuel mixture of the sintering charge. The possibilities of using coal flotation waste as an alternative substitute for coke breeze have been studied after the regimes for its preparation for sintering have been developed and a rational mode of layer-by-layer combustion in the sintering layer has been organized. Based on the results of laboratory and industrial studies, the possibility of using flotation waste mixed with coke breeze as a fuel mixture for the agglomeration of iron ore materials has been substantiated.
The use of flotation waste as fuel in its pure form is impractical due to high humidity and ash content. Therefore, fuel mixtures of various compositions were compiled. Analyzes have shown that for the conditions of the sinter plant of Qarmet JSC, it is possible to partially replace coke breeze with coal enrichment flotation waste in an amount of 5.10 % of the fuel consumption for the process. In this case, the best conditions are achieved with two-layer sintering of the sinter charge and the environmental parameters of the sintering process do not change significantly.
With two-layer sintering, the introduction of 5% flotation waste leads to an increase in the vertical sintering speed by 1.33 mm/min, specific productivity by 0.08 t/m h, the yield of suitable agglomerate - 0.1%, mechanical strength to impact and abrasion - 1 .78 and 0.2%, respectively. A further increase in the proportion of waste leads to a decrease in the height of the top layer by 1.5 mm per 1% of the waste, the yield.
The use of this fuel mixture on sintering machines will reduce the consumption of coke breeze while increasing specific productivity and the yield of usable sinter, as well as reduce the irrational alienation of land resources and, with an effective smoke emission treatment system, ensure a reduction in environmental pollution.
References
- Shpirt, M.Ya. , Rainbow A.K.M. Ecological problems caused by coal mining and processing with suggestions for remediation. ― Millpress Roterdam Netherlands. 2006. ― 162 p.
- Alex Acquah Wang Shijie Hongming Fang Hongming Fang Show all 7 authors Zhen Xu. Review on alternative fuel application in iron ore sintering. Ironmaking & Steelmaking Processes, Products and Applications. Volume 48, 2021 - Issue 10: STEEL WORLD ISSUE Pages 1211-1219 | Received 02 Feb 2021, Accepted 29 Jun 2021, Published online: 25 Jul 2021. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W (Yang, W); Yang, KK (Yang, KK); Choi, S.M. (Choi, S.M.). Effect of fuel characteristics on the thermal processes in an iron ore sintering bed. JSME INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL SERIES B-FLUIDS AND THERMAL ENGINEERING Volume48Issue2Page316-321. [CrossRef]
- M Sikora, P Janík, P Pustějovská, S Jursová. The anthracite as sinter fuels. New Trends in Production Engineering, 92019;2(2): 232-240. [CrossRef]
- Behera Sahu, H. Coal mine waste characterization and defluoridation property.February. 2023. e13244. Heliyon 9(6):e13244. [CrossRef]
- Behera Sahu, H. Characteristics of coal mine waste and defluoridation properties. February. 2023. e13244. Helion 9(6):e13244. [CrossRef]
- Kharionovsky A., A. , Grishin V. Yu., Kolikov K. S., Udalova N. P. Problems of using coal mining waste // Mining Information and Analytical Bulletin. - 2021. - No. 10-1. — P. 45-55. [CrossRef]
- A.A. Lavrinenko, N. Yu. A.A. Lavrinenko, N. Yu. Svechnikova, E.A. Igumensheva, N.S. Konovnitsyna Use of coal flotation waste as non-conventional fuel for low-temperature fluidized bed furnaces ISSN 0236-1493. Gornyy informatsionno-analiticheskiy byulleten’. 2017. No. 9, pp. 123–130. [CrossRef]
- Svechnikova, N.Yu. , Petukhov V.N., Yudina S.V., Kuklina O.V., Puzina A.S., Akhmetzyanov T.N., Gavryushina Ya.V. Study of physical and chemical properties of coal concentration wastes with a purpose of their utilization as secondary raw materials. Chernaya metallurgiya. Byulleten’ scientific and economic information = Ferrous metallurgy. Bulletin of scientific, technical and economic information, 2019, vol. 75, no. 11, pp. 1225–1230. (In Russ.). [CrossRef]
- Rankine, R. , Pacheco M., Sivakugan N. Underground Mining with Backfills // Soils and Rocks. 2007, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 93-101.
- Recycling of coal mine waste for coal extraction and production of environmentally friendly bricks / Taha Y., Benzaazua M., Hakkou R., Mansori M. // Minerals Engineering. 2017, vol. 107, pp. 123-138.
- Thang N.C., Tuan N.V., Hiep D.N. The Potential Use of Waste Rock from Coal Mining for the Application as Recycled Aggregate in Concrete. October. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Use of coal beneficiation tailings as solid sorbents in the treatment of nitrate-contaminated real wastewater / Nunes K.G.P. Illi J.C., Dávila I.V.J., Feris L.A. // Applied Water Science. 2020, vol. 10, no. 4, p. 14.
- K.M. Shaimerdenova, K.E. K.M. Shaimerdenova, K.E. Sakipov, N.T., Abdirova, S.E. Suleimenova, IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF EKIBASTUZ COAL USING THE DRY ENRICHMENT METHOD, Eurasian Physical Technical Journal: Vol. 21 No. 1(47) (2024).
- Ibraev, E.K. , Ibraeva O.T., Sakipov K.E., UNBURNED WASTE COAL FLOTATION AGGLOMERATION. Eurasian Physical Technical Journal, 2018, Vol.15, No.1(29).
- Yuxing Zhang, Zhiqiang Xu, Yanan Tu, Jinyu Wang, Jie Li. Study on properties of coal-sludge-slurry prepared by sludge from coal chemical industry // Pow der Technology Volume 366, 15 апреля 2020, Pages 552- 559. [CrossRef]
- An investigation into the enrichment of coal wastes of Western Lignite Company (WLC) by physical and physico-chemical methods / A. Ucara, O. An investigation into the enrichment of coal wastes of Western Lignite Company (WLC) by physical and physico-chemical methods / A. Ucara, O. Sahbaza, N. Ediz et al. February, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Methodological manual for analytical control of emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere - St. Petersburg, OJSC “NII Atmosfera”, 2012.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).