1. Introduction
Inflammation is a natural response of the body following external stress. It is a response of the immune system that is induced by various stimuli, especially pathogens, toxins, lesions, etc... Many diseases involve inflammatory mechanisms such as autoimmune diseases, certain cancers, some neurological disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, bowel, and cardiovascular diseases [
1,
2]. The first aim of the inflammatory response is to eliminate or minimize the impact of infection or injury. After an acute inflammatory response, immune cells and different molecular events are involved in different interactions to restore tissue homeostasis, resolve the acute process, and induce regeneration [
3]. However, the uncontrolled acute inflammatory response can induce chronic inflammation, which can contribute to a variety of chronic inflammatory diseases [
4].
Many drugs are used to help control and resolve inflammatory responses. Amongst these, there are two major types of widely used anti-inflammatory drugs; corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Corticosteroids are used to treat chronic inflammatory diseases such as autoimmune diseases, asthma, and rheumatic arthritis. They suppress the various inflammatory genes activated in chronic inflammatory diseases: cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, inflammatory enzymes, receptors, and others [
5]. NSAIDs are widely used for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-pyretic effects, and are amongst the most prescribed class of medications, representing approximately 5–10% of all medications prescribed each year [
6]. They inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes and subsequently induce a decrease in different anti-inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins [
7]. However, the use of these two anti-inflammatory drug classes has significant disadvantages: corticosteroids can cause long-term adverse effects like hypertension, metabolic disorders, or gastric ulcers [
8] and NSAIDs, although they act effectively during the acute inflammation phase, are not curative and their chronic use could lead to adverse effects, especially at gastric, renal, and hepatic levels [
9]. Moreover, the efficacy of these two anti-inflammatory drug families diminishes along the application time.
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are cyclic glucose chain oligomers that are made up of different numbers of α-1-4-linked glucose residues and they present a cone-like cavity into which compounds like active ingredients, cholesterol, and derivatives may enter to form a water-soluble complex [
10]. Cyclodextrins derived from native β-cyclodextrins (β-CD) show different biological and physical properties, mainly depending on their degree of substitution. Among these cyclodextrin derivatives, a particular methylated cyclodextrin differs from the randomly methylated β-CD (RAMEB): KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB displaying less methylated group substitution than RAMEB.
Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease that is linked to high blood concentrations of small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (sdLDL-C) [
11]. Therapies using cyclodextrin (e.g. KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB) as a cholesterol-sequestrating agent have demonstrated an impact in atherosclerosis [
12]. Moreover, the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis was investigated with KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB, where the authors demonstrated that T lymphocyte content was reduced in atherosclerotic plaques with the mode of action being immunomodulation and Th1 polarization [
13]. In addition, other cyclodextrins such as hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin (HPβ-CD) were able to inhibit atherosclerosis, not only by increasing the efflux of cholesterol, but by involving anti-inflammatory mechanisms [
14]. They can also induce atherosclerosis regression via macrophage reprogramming to improve cholesterol efflux and exert anti-inflammatory effects [
15]. In addition, HPβ-CD and α-CD inhibited cholesterol crystal formation and the activation of complement on monocytes, and HPβ-CD reduced the Immunoglobulin G (IgG) deposition [
16,
17]. This anti-inflammatory effect of CDs is linked to a specific effect against cholesterol crystals [
14]. Moreover, CDs may potentially be useful as active agents for the treatment of neurological disorders: first for diseases involving cholesterol depletion such as Niemann Pick type C disease and second, as anti-aggregative effect compounds for amyloid-related disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease or α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease [
18]. However, this has yet to be fully evaluated as clinical testing for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease is ongoing.
All of the effects induced by CDs were linked to cholesterol complexation. Nevertheless, the potential effect of these compounds and their potential impact on cellular metabolism, interactions between cells from different tissues, and pro- and anti-inflammatory cascade pathways was not clear.
In the present study, we investigated the impact of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB on various pharmacological targets using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in physiologically normal and inflammatory conditions, followed by screening against a panel of twelve human primary cell-based systems designed to model complex human tissue and disease biology of the vasculature, skin, lung, and inflammatory tissues using the BioMAP® Diversity PLUS® Panel. Finally, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB was investigated on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to evaluate anti-inflammatory or pro-resolving properties.
Human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) were chosen as a first primary cell type model. Indeed, endothelial cells: (i) participate in immune-modulation through various processes such as chemokine secretion, co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptor expression, leukocyte recruitment, and phagocytic capabilities[
19], (ii) are valuably placed as a first-line defense system to contribute to immune responses [
19], and (iii) process exogenous peptides through HLA-DR after IFN-γ stimulation [
20]. They were thus considered as a relevant model with which to specifically evaluate the effects of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB in a first-line immunomodulation screening strategy. In this method, cells were treated in the presence (“inflammatory condition”) or absence (“non-inflammatory condition”) of TNF-α or IFN-γ.
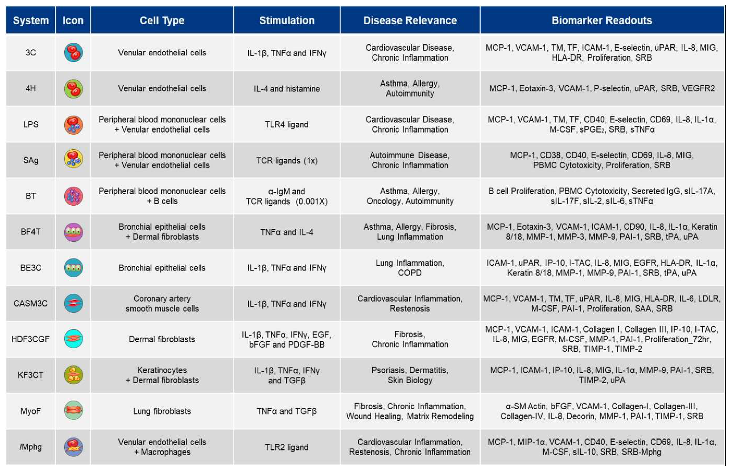
Human primary cell-based models within the BioMAP® Diversity PLUS® Panel represent a broad set of tissue and disease biology, including: vascular biology, adaptive and innate immune responses, respiratory biology, fibrosis, and skin-relevant biology [
21,
22]. The BioMAP® systems used in this study (
Table 1) are constructed with one or more primary cell types pooled from three or more healthy human donors, with stimuli (such as cytokines or growth factors) added to stimulate relevant signaling networks that naturally occur in human tissues or under pathological conditions.
BioMAP® profiling creates a unique signature of changes in protein biomarker readouts when normalized to vehicle controls within individual system environments. Biomarker readouts [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17] per system) are therapeutically and biologically relevant, are predictive of disease outcomes or specific drug effects, and have been validated using agents with known mechanisms of action [
22,
23]. These diverse readouts include cell surface receptors, cytokines, chemokines, matrix molecules, and enzymes. In total, the Diversity PLUS® Panel contains 148 biomarker readouts, which are measured quantitatively by immune-based methods that detect proteins (e.g., ELISA) or functional assays that measure proliferation and viability.
Vascular biology is modeled in both a Th1 (3C system) and a Th2 (4H system) inflammatory environment, as well as in a Th1 inflammatory state specific to arterial smooth muscle cells (CASM3C system). Additional systems recapitulate aspects of the systemic immune response including monocyte-driven Th1 inflammation (LPS system) or T cell stimulation (SAg system), chronic Th1 inflammation driven by macrophage activation (
lMphg system), and the T cell-dependent activation of B cells that occurs in germinal centers (BT system). The BE3C system (Th1) and the BF4T system (Th2) represent airway inflammation of the lung, while the MyoF system models myofibroblast-lung tissue remodeling. Lastly, skin biology is addressed in the KF3CT system by modeling Th1 cutaneous inflammation and the HDF3CGF system by modeling wound healing [
23,
24].
The inflammation process is divided into three steps: initiation, amplification, and resolution, which in sum lead to the complete restoration of the initial state. When correctly controlled, inflammation is supposed to end and lead to the complete restoration of the targeted tissue. Various cell and biochemical effectors from innate and adaptive systems are involved throughout the process and tightly regulated. The metabolism of pro-inflammatory mediators into inactive compounds is not sufficient to allow the tissue to come back to the initial state. Resolution is an active process, involving specific mediators that are biologically active and can be monitored in a Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell model as biomarkers of homeostasis. These biomarkers are issued from omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) metabolism and are termed lipoxins, resolvins, maresins, and protectins, which are collectively referred to as SPMs (Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators) [
25,
26].
2. Materials and Methods
All tested samples were of pharmaceutically active substance quality: methylated cyclodextrin Crysmeb (KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB) and Isosorbide (ISOSORBIDE C PHARMA®) were supplied by Roquette Frères (Lestrem, France).
2.1. HUVEC Immuno-Profiling
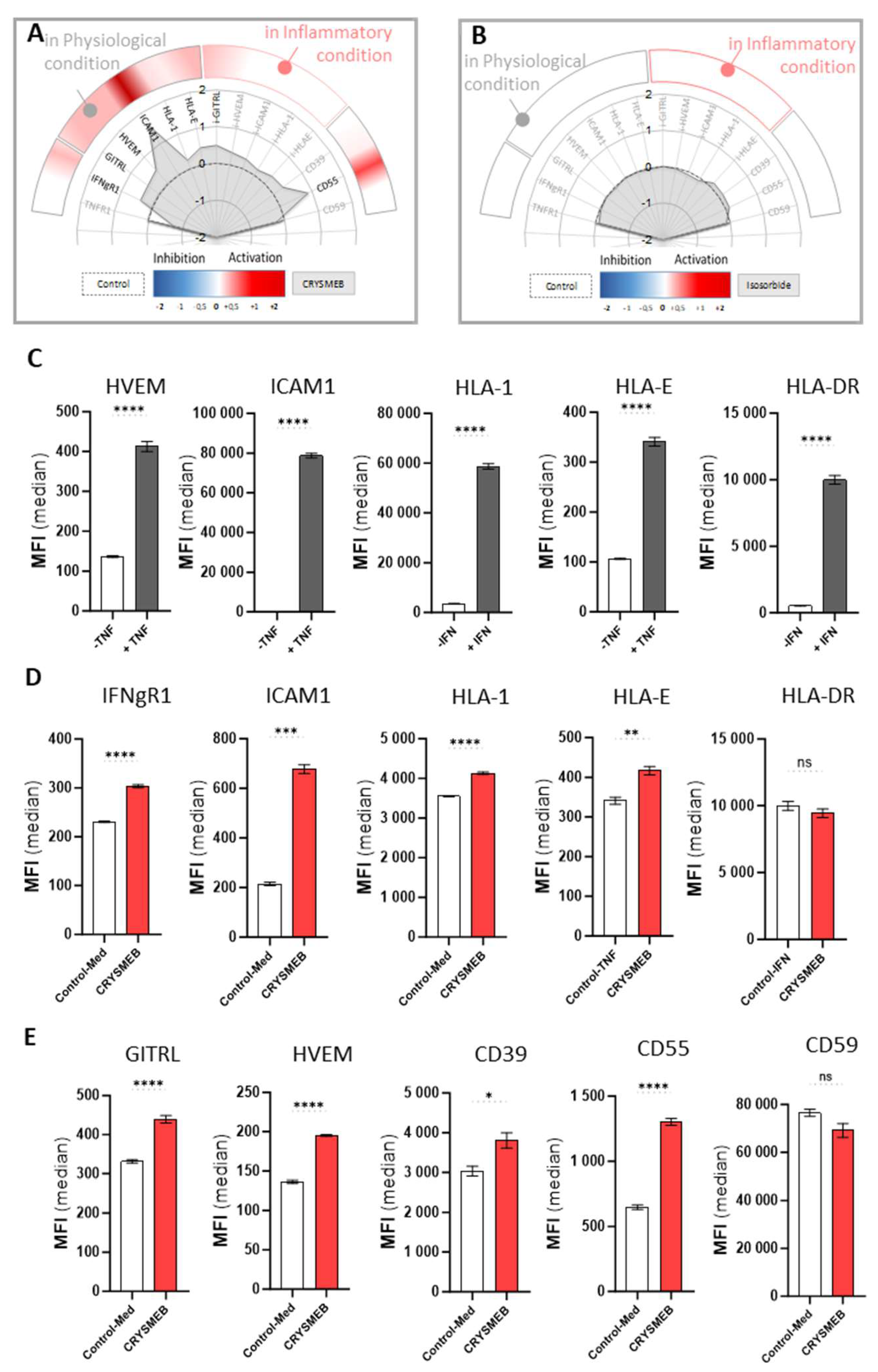
Primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC, PromoCell) (passage 4) were seeded at 5000 cells/well in 96-well plates in ECGM medium (PromoCell) supplemented with 2% FBS and grown for 4 days before adding KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB or ISOSORBIDE C PHARMA® (a polyol used as a humectant and in medicine as an osmotic diuretic without known pharmacological effects) to the medium at non-cytotoxic concentrations of 2.5 mg/mL (evaluated by cell counts / well on a flow cytometer, data not shown). The cells were treated for 48 hours in the presence (“inflammatory condition”) or absence (“non-inflammatory condition”) of 10 ng/mL TNF-α or 20 ng/mL IFN-γ before multi-parametric immunostaining and flow cytometry analysis. Briefly, detached cells were immunolabelled in FACS buffer (PBS / BSA 1% / EDTA 2 mM) with the following antibodies directed against multiple targets for 30 minutes on ice (ICAM-1, GITRL, HLA-E, CD55, CD59, CD39, VCAM-1, E/Psel, HVEM, IFN-γR1, TNFR1, all purchased from BioLegend). Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry at day 2, on a BD FACS Canto II, configuration 4/2/2. One experiment was performed in triplicate for each condition.
2.2. Phenotypic Profiling in Human Primary Cell-Based BioMAP® Systems
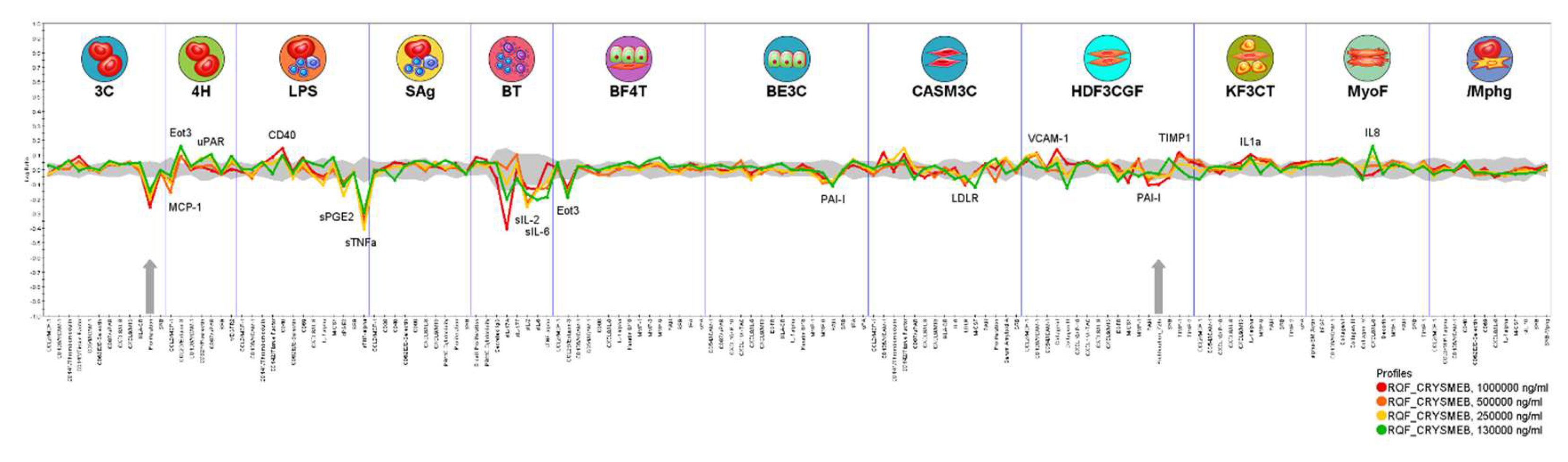
Phenotypic profiling with the BioMAP® Diversity PLUS® Panel was conducted by Eurofins Discovery (USA) as described previously [
21], with doses of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB of 1000 µg/mL, 500 µg/mL, 250 µg/mL, and 130 µg/mL
Human primary cells
All studies follow the guidelines for human subject research under United States HHS human subject regulations (45 CFR Part 46). Preparation and culture of primary human cell types and methods for the systems were as previously described [
22]. All primary human cells used in this work were obtained via commercial sources, cultured according to the supplier’s recommendation, and used at early passage (≤P4) to minimize adaptation to cell culture conditions and to preserve physiological signaling responses. Furthermore, cells were pooled from multiple (three or more) donors in this study to minimize the effect of donor-to-donor variation.
Primary human cell types used in BioMAP® systems and their stimuli include the following: 3C System (HUVEC / IL-1β, TNF-α and IFN-γ), 4H System (HUVEC / IL-4 and histamine), LPS System (PBMC and HUVEC / LPS), SAg System (PBMC and HUVEC / TCR ligands), BT System (CD19+ B cells and PBMC / anti-IgM + TCR ligands), BE3C System (bronchial epithelial cells / IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ), BF4T System (bronchial epithelial cells and human dermal fibroblasts / TNF-α and IL-4), HDF3CGF System (human dermal fibroblasts / IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ, EGF, basic-FGF, and PDGF-BB), KF3CT System (keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts / IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ), CASM3C System (coronary artery smooth muscle cells / IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ), MyoF System (differentiated lung myofibroblasts / TNF-α, and TGF-β), /Mphg System (HUVEC and macrophages / TLR2 ligands). Concentrations of stimuli were as previously published [
21]. Adherent cells were cultured to confluence prior to assay initiation. The numbers of lymphocytes used were as previously published. Assays were initiated by the addition of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB , followed by the addition of appropriate stimuli. Assay plates were then incubated at 37°C in 5% CO
2 for 24 hours, or as otherwise indicated. KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB solution prepared in DMSO (final concentration ≤ 0.1%) was added at the previously indicated concentrations 1 hour before stimulation and remained in culture for 24 hour or as otherwise indicated (48 hour - MyoF system; 72 hour- BT system soluble readouts; 168 hour - BT system secreted IgG). The MyoF system was stimulated for 48 hours, and the BT system was stimulated for either 72 hours (soluble readouts) or 7 days (secreted IgG). Cell proliferation was determined by Sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay for adherent cell types or AlamarBlue™ for PBMC and B cells. For proliferation assays, individual cell types were cultured at sub-confluence and were read at specific times for different primary cell types (48, 72, or 96 hours). After stimulation, plates and supernatants were harvested and biomarkers were measured by ELISA and other methodologies: the levels of biomarker endpoints were measured by ELISA as described [
22,
27,
28]. Proliferation of PBMC (T cells) was quantified by AlamarBlue™ reduction and proliferation of adherent cell types was quantified by SRB staining [
22]. The SRB assay was performed by staining cells with 0.1% sulforhodamine B after fixation with 10% TCA and reading of wells at 560 nm [
22]. PBMC viability was assessed by adding AlamarBlue™ to PBMC that had been cultured for 24 hours in the presence of activators and compounds, and subsequent measurement of its reduction after 8 hours.
Each plate contained drug controls (e.g., legacy control test agent colchicine at 1.1 μM), negative controls (e.g., non-stimulated conditions), and vehicle controls (e.g., 0.1% DMSO) appropriate for each system.
Raw data values for each readout for KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB were divided by the raw mean vehicle control and then log
10-transformed as previously described [
29]. Significance prediction envelopes (95%) calculated from historical controls were used to determine activity at each assay endpoint. Biomarker activities were considered modified when two or more consecutive concentrations changed in the same direction relative to the vehicle controls, were outside of the significance envelope, and had at least one concentration with an effect size >20% (|log
10 ratio| > 0.1). The four concentration profiles were compared against the reference profile library generated by Eurofins Discovery (with over 4500 substances), with a correlation metric comprised of a combination of similarity metrics in addition to a Pearson’s correlation as previously described [
22,
29]. Cluster analysis (function similarity map) used the results of pairwise correlation analysis to project the “proximity” of agent profiles from multi-dimensional space into two dimensions. Profiles that are similar with a Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) ≥ 0.7 are connected by lines.
2.3. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Model for Cytokine Secretion and Resolution Assays
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) from healthy volunteers were obtained from l’Etablissement Français du Sang (EFS). After isolation, the PBMCs were frozen until use in experiments. Cell culture medium Macrophage-SFM (M-SFM) was purchased from Gibco. LPS from the Escherichia coli K12 strain was bought from Invivogen. Antibiotics, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), and A23187 (calimycin) were bought from Millipore Sigma. Multipexed kits for cytokine quantification (IL-1ß, IL-10, and TNF-α) were bought from Millipore Sigma. Inhibitors (dexamethasone, ibuprofen, and paracetamol) were purchased from Millipore Sigma.
Cell Isolation and Culture
PBMCs were obtained from healthy blood donor buffy coats by a standard Ficoll-Hypaque gradient method. PBMCs were seeded in macrophage-SFM with antibiotics, at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. PBMCs were exposed to compounds and inhibitors for 24 hr. Medium was then changed to perform the resolution assay.
Lipidomic Analysis for Resolution Assay
HBSS +/+ buffer was used for the resolution assay with renewal of the compounds and inhibitors. Cells were exposed to the inflammatory stimulus (PMA/A23187) for 1 hr. Culture supernatants were then collected for subsequent analysis of lipid mediators. The extraction protocol and LC-MS/MS analysis were performed as adapted from Le Faouder et al [
26]. Briefly, samples were extracted using oasis HLB 96-well solid phase extraction (Waters). LC-MS/MS analysis was performed on a UHPLC system (EXION LC AD, SCIEX) coupled to a QTrap 6500+ MS (SCIEX) instrument equipped with electro-spray ionization operating in negative mode.
Cytokine Secretion Assay
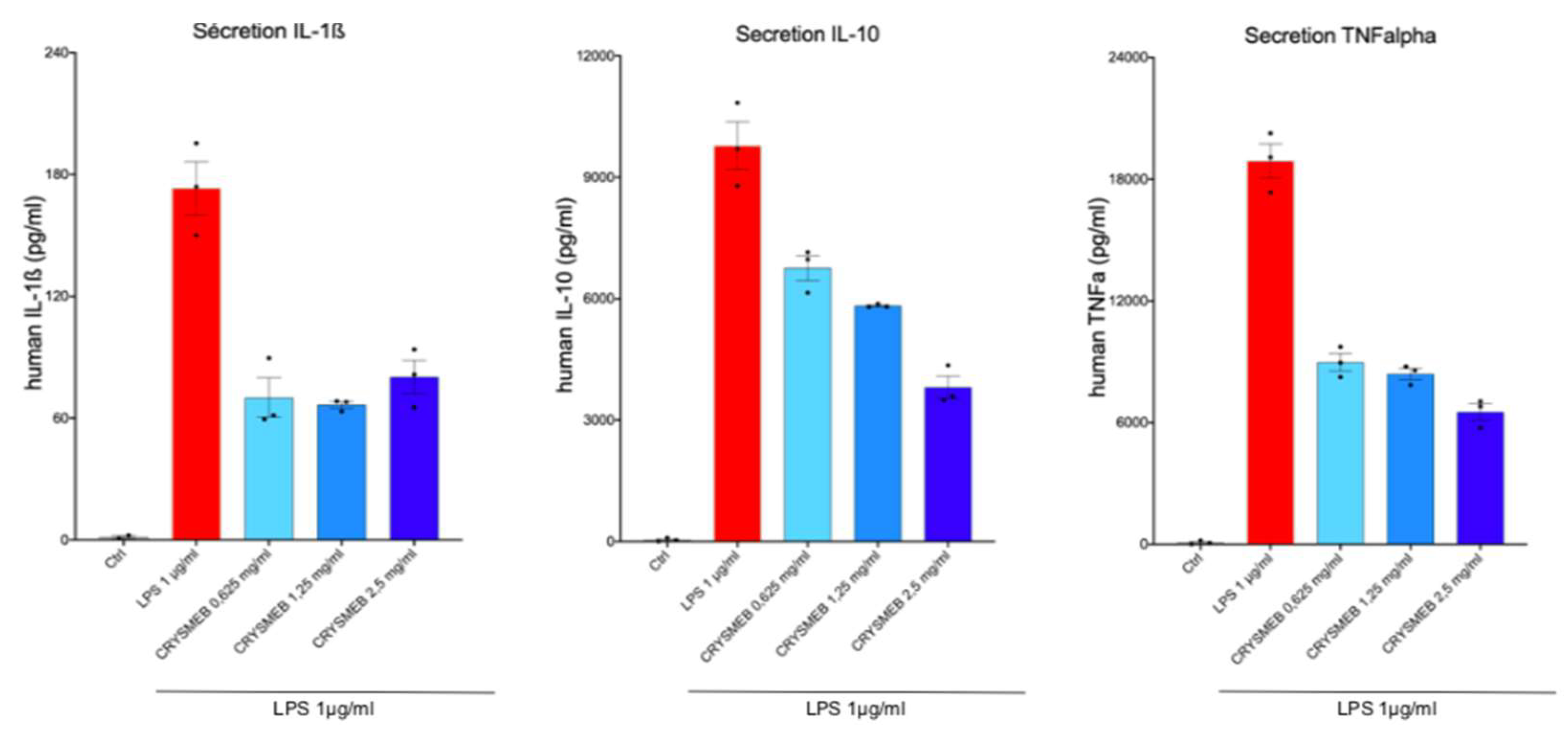
PBMCs were incubated with KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB for 24 hr in the presence of antibiotics. Culture medium with KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB was then renewed, and the PBMCs were stimulated with LPS 1 µg/ml for 24 hr. The supernatants were then collected and frozen until analysis. Cytokines (IL-1β, IL-10, and TNF-α) were analyzed with a with a MILLIPLEX® Multiplex assay kit and measured on a Luminex MAGPIX® reader.
Statistical Evaluation
The results were evaluated by comparing the variance according to Student’s t-test.
4. Discussion
Endothelial cells share common innate immune functions with macrophages such as cytokine secretion, antigen presentation, pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) sensing, or even phagocytosis. Their plasticity allows them to regulate immune surveillance over the different tissues of the organism [
30].
Interestingly, we report here that KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB can upregulate the expression of molecules that are involved in the crosstalk between immune cells and surrounding cells like endothelial cells. Indeed, the increase in HLA-1 expression elicited by this drug may be linked to immune cell recruitment, as HLA-1 signaling was reported to impact leukocyte tethering or neutrophil adherence for instance [
30]. This finding is supported by the drug-induced increase of ICAM-1, a protein that is implicated in the firm adhesion of activated T cells to the endothelium and their trans-endothelial migration [
32], and GITRL, a molecule that is also involved in cell adhesion / migration / activation of innate cells [
33,
34,
35]. Furthermore, the increase of GITRL on the surface of HUVEC (
Figure 1E) may potentially facilitate GITR / GITRL signaling, thus resulting in T cell activation and proliferation [
36,
37]. GITR interaction stimulates antiviral responses through enhanced TNF-α and IFN-γ production in vivo [
38] and GITR is expressed on numerous activated immune cell types such as Treg, macrophages, and natural killer (NK) cells, giving the opportunity for KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB to also interact with cells that are involved in mediating innate immunity [
39]. To support this finding, we confirmed that HLA-E was constitutively expressed on endothelial cells, and it is well established that HLA-E and NK receptor interaction is crucial for NK cell activation [
40,
41]. Moreover, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB induced an increase in IFN-γR1. IFN-γ binds to IFN-γR1 with a very high affinity to induce signaling via the JAK / STAT pathway and is constitutively expressed on endothelial cells. KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB induced an overexpression of this receptor, which can lead to stronger sensitization of cells to IFN-γ and can lead to better activation of these cells. IFN-γ is secreted by immune cells during the early phase of the immune response (NK, LT CD4 helper, and LT CD8), allowing dedicated antigen-presenting cells (
e.g., dendritic cells, macrophages) to increase the presentation of peptides from pathogens on HLA class II molecules. Moreover, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB increased both HLA-E and GITRL, a mechanism that can probably serve to help the immune system to boost immunosurveillance upon infection [
38]. Activation and proliferation of T cells can also be supported by HVEM expression in an HVEM / LIGHT receptor / ligand context [
42].
This first body of data supports the fact that KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB tends to stimulate the expression of endothelial cell markers triggering the recruitment, migration, co-stimulation, and activation of T cells and NK cells. However, it is also interesting to highlight vascular protection. Indeed, complement deposition at the cell surface level is a mechanism that is often used to protect the human body from pathogens by inducing a lysis that is specific to the pathogen’s membrane with a complement-dependent cytotoxicity [
43]. Different pathways are involved in this system (classical, alternative, and lectin pathways) [
44] and CD55 is ideally placed at the beginning of the process to inhibit the complement cascade deposition. Indeed, the increase of CD55 in HUVEC when treated with KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB (
Figure 1E) can protect endothelial cells from lysis by accelerating the degradation of C3 convertase, a central enzyme that regulates the complement cascade at the initial step, CD59 interfering only at the terminal step (preventing the formation of Membrane Attack Complex C5b9) [
45].
Another way to protect endothelial cells from injuries is to modulate platelet aggregation, a natural mechanism that occurs during bleeding. Interestingly, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB demonstrated the capability to increase levels of CD39, an endopeptidase that prevents excessive platelet aggregation and vascular leakage [
46,
47]. Moreover, CD39 is also described as a new immunomodulatory protein and is compared now with a new checkpoint inhibitor [
48], a dual role that can very well illustrate KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB bioactivity in vascular cells.
Montecucco et al [
12] showed that KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB has an impact on atherosclerosis in mouse models of disease. In this disease, platelet accumulation induces the recruitment of inflammatory cells towards the lesion sites [
49]. The impact of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB on different markers and pathways that are involved in the modulation of platelet aggregation, preventing excessive platelet aggregation, cell lysis, and vascular leakage, could explain in part the observed in vivo impact of this cyclodextrin on atherosclerosis.
The first screening strategy using a primary endothelial cell model (HUVEC) demonstrated the potential of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB in vitro to modulate the immune system and to potentially manage vascular issues.
These impacts of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB on cellular interactions between immune cells and vascular cells, as well as other cells such as those from respiratory, muscle, and skin tissues, were elucidated using phenotypic profiling in human primary cell based BioMAP® systems. The observed decrease in prostaglandin E2 (PGE
2) in the LPS system, which models monocyte activation, is shared by KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB and several NSAIDs when tested in this platform. This activity is a sentinel biomarker for COX inhibition and suggests KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB to have similar anti-inflammatory properties. Furthermore, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB treatment led to decreases in tissue inflammation and immunomodulatory biomarkers such as IL-2, IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α. These effects on Th1 inflammation (LPS system) or the T cell-dependent activation of B cells that occurs in germinal centers (BT system) can be compared with the systemic effect of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB on Th1-mediated immunity that was observed in mice in an atherosclerotic context and in human T lymphocytes in vitro [
12]. Indeed, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB dose-dependently inhibited the proliferation of Th1 CD4+ cells and methyl β-cyclodextrins can switch off the pro-inflammatory effects of IFN-γ on the vascular endothelium. The inhibition of Th1 immune responses has been described as a potential strategy to inhibit chronic inflammation and atherogenesis in mice [
50,
51]. Nevertheless, in the BioMAP® T cell activation model (T cell driven Th1 vascular inflammation model), no impact of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB on T cell proliferation was observed. Moreover, according to Montecucco et al [
12], methyl β-cyclodextrins can modulate the immune response, switching off the pro-inflammatory effects of IFN-γ on the endothelium since IFN-γ can enhance the expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells that are needed for leukocyte–endothelial cell interaction. However, our results on human umbilical vein endothelial cells showed that KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB induced an increase in IFN-γ receptors. So, the anti-inflammatory effects of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB seem to be driven by pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion inhibition and not at the cellular level on different receptors such as IFN-γR1, or on the expression of molecules that are involved in the crosstalk of immune cells and endothelial cells such as HLA-1, ICAM-1, GITRL.
In another way, some of the observed activities of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB are related to pro-inflammatory activities in the acute phase such as increased amounts of IL-8, which is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is involved in the recruitment of neutrophils into acute inflammatory sites, as well as the increase of VCAM-1, a cell adhesion molecule that mediates the adhesion of monocytes and T cells into sites of inflammation. Eotaxin 3 was found to be context-dependently modulated: it was increased in a Th2-type vascular inflammation model (4H) but decreased in a Th2-type lung inflammation model (BF4T). Whilst the stimulation environments of these two systems are relatively similar, the cell types are different, suggesting that KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB can have different impacts on different tissue types. Eotaxin-3 is a chemokine that mediates the recruitment of eosinophils and basophils into sites of tissue inflammation. This finding confirms the results on human umbilical vein endothelial cells regarding the impact of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB on the modulation on the expression of molecules that are involved in the crosstalk between immune and endothelial cells.
This effect of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB on immune responses seems to be at two distinct levels: affecting cytokine secretion and on the levels of cellular proteins that are involved with immune cell communication, recognition, etc.
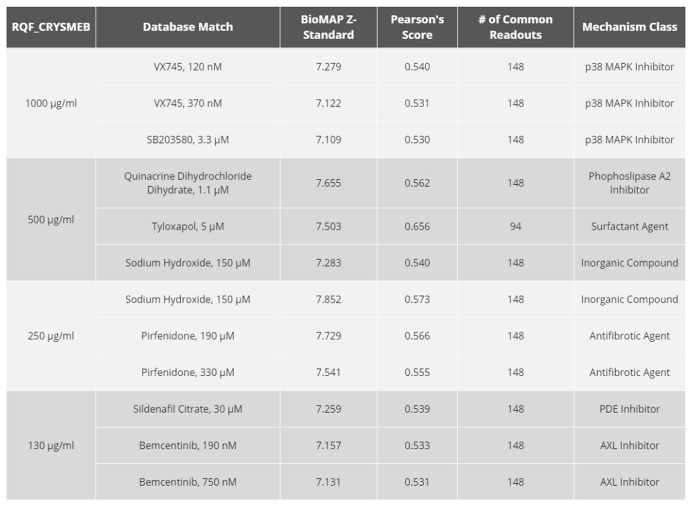
A Similarity Search analysis against the whole BioMAP® reference database, with thousands of molecules and reference agents previously profiled, revealed no significantly similar profile matches, suggesting that the mechanism of action of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB is not shared with any molecule that has been tested as part of the reference database. This could potentially represent a unique mechanism of action, although the exact nature of that would need to be confirmed in a follow-up study of a more detailed mechanistic nature.
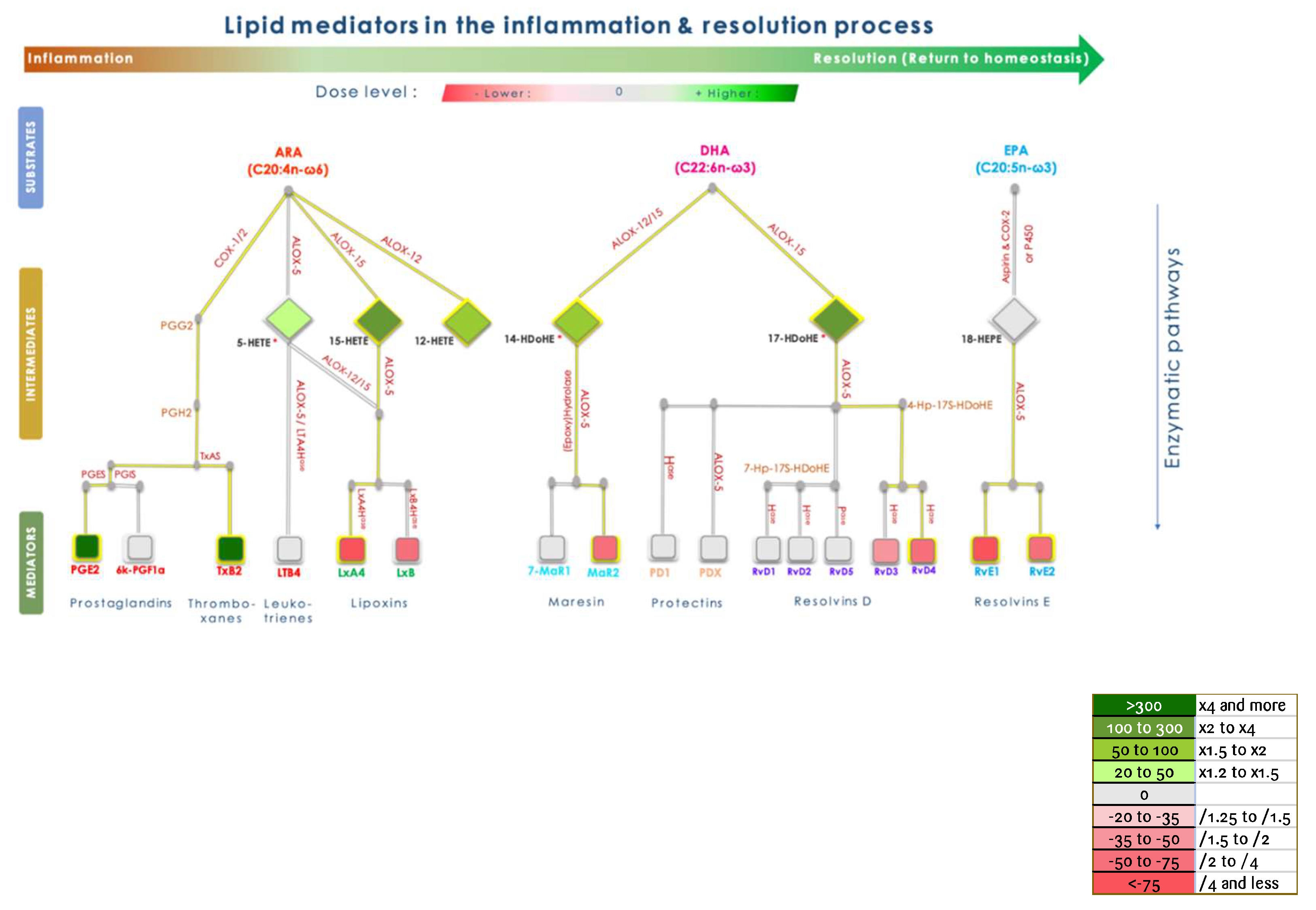
In addition, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB inhibited the secretion of IL-1β, IL-10, and TNF-α in PBMCs when stimulated by LPS. This suggests that this compound has anti-inflammatory capabilities. The mechanism of action of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB was then investigated by studying the inflammatory and resolving lipid mediator metabolism pathways on PBMCs when stimulated by PMA/A23187. Surprisingly, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB activated the COX enzyme as well as the 5-LOX, 12-LOX, and 15-LOX pathways, and induced an increase in pro-inflammatory mediators (metabolic pathway modulations corresponding to these results are represented in
Figure 6). This result observed with PBMCs alone is the opposite of the one found with the BioMAP® LPS system, with which a diminution of PGE
2 levels was observed. However, various experimental conditions in those studies were different and could explain this apparent contradiction: first, the stimulation used was PMA/A23187 (versus LPS), which induces a much stronger inflammatory response. Then, the lipid mediators were measured at 1 hr after PMA/A23187 stimulation (versus at 48 hr and 24 hr for the assays in HUVECs and 24, 48;72 or 168 hours in BioMAP® models respectively), and finally, the PBMCs were not in contact with HUVECs (as was the case in the BioMAP® system). KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB could indeed demonstrate a better efficacy at a later time point and also on milder inflammation (as is the case with LPS stimulation). Additionally, the presence of vascular endothelial cells could influence the response to KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB exposure and the impact on the crosstalk between immune cells and other cell types.
Moreover, we did not observe production of specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPM) despite the production of pro-resolving lipid intermediates such as 14-HDoHe and 17-HDoHe. One reason that could explain these observations is that inflammation is a kinetic process, characterized by the sequential production of pro-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediators. We thus suggest that the quantification of SPMs at other time points would allow for a better deciphering of the mechanisms of action of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB.
In addition, KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB induced a decrease in low-density lipoprotein receptors, which are involved in cholesterol regulation. This is due to the well-known membrane cholesterol-extracting effect of cyclodextrins and derivatives on cholesterol levels and thus their impact on lipid raft disruption, as well as changes in biophysical parameters and organization of membrane bilayers, which can also induce an indirect modulation of protein function [
17]. In summary, this also represents another facet of KLEPTOSE® CRYSMEB activity that would warrant further evaluation and potential confirmation in follow-up studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Damien Truffin; methodology, Damien Truffin, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King; software, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King, ; validation, Damien Truffin, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King; formal analysis Damien Truffin, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King; investigation, Damien Truffin, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King; resources, Damien Truffin.; data curation, Damien Truffin, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King; writing—original draft preparation, Damien Truffin, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King; writing—review and editing, Damien Truffin, Flora Marchand, Mathias Chatelais, Frauke Herbst, Justin Lipner, Alastair J. King; visualization, Damien Truffin; supervision Damien Truffin.; project administration, Damien Truffin.; funding acquisition, Damien Truffin. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.