1. Introduction
Water is essential for human survival, making the availability and quality of freshwater a critical concern. In the 21st century, the rapid advancement of modern industry and agriculture has escalated environmental pollution to a global challenge, with water pollution standing out as a particularly severe issue. This pollution stems from various sources, including indiscriminate industrial wastewater discharge, urban sewage, and uncontrolled pesticide and fertilizer use, leading to widespread contamination of water bodies. Such pollution poses a significant threat to both aquatic life and human health. Among the pollutants, heavy metals are especially concerning due to their toxicity and persistence in the environment; they are non-biodegradable and accumulate in the ecosystem, magnifying their impact through the food chain [
1,
2,
3]. Even at low initial concentrations, heavy metals can eventually endanger human health. Given these challenges, there is a pressing need for effective water purification methods. Membrane separation technology, known for its low energy requirements, small footprint, and high efficiency, has become a preferred solution in water treatment efforts [
4,
5,
6].
Electrospinning has emerged as a prominent method for fabricating nanofiber materials, gaining significant attention for its role in creating adsorbent membranes. This technique offers distinct advantages over traditional spinning methods, including ultra-high porosity, extensive specific surface area, and consistent fiber diameter distribution, making it highly suitable for membrane processing applications. As a versatile and efficient technology, electrospinning allows for the use of varied raw materials tailored to specific targets. Its applications extend across filtration and separation, composite reinforcement, tissue engineering, biocatalysis, and controlled drug release [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The theoretical foundations of electrospinning were first established in the late 19th century by Lord Rayleigh. In 1882, Lord Rayleigh investigated the behavior of liquid droplets on charged surfaces and described the conditions under which these droplets would become unstable and disintegrate, which is a fundamental aspect of electrospinning. This work laid the groundwork for understanding how electric forces can deform and disperse liquids, which is central to the process of electrospinning, where electrically charged jets of polymer solutions or melts are used to produce fibers. Further deepening their understanding, researchers established the core principles of electrostatic spinning. By applying high-voltage electrostatic forces to a polymer melt or solution, a strong electric field is created between the polymer in the capillary tube and the grounding device. This setup imparts a uniform positive charge to the polymer, forming suspended charged droplets at the capillary's end. These droplets are then drawn into a conical shape, known as the Taylor cone. When the electric field strength surpasses the surface tension, the droplets are propelled from the capillary tip, stretch towards the grounding device under the electric forces, and form nanofibers.
Electrospun nanofibers have proven to be exceptional nanomaterials with significant potential for removing heavy metal ions. Yang et al. developed amino-functionalized chitosan (CS) electrospun membranes by sequentially grafting poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA) and polyethyleneimine (PEI) onto CS fibers, with the successful incorporation of amino groups verified using XRD, ATR-FTIR, and XPS techniques [
12]. The CS-PGMA-PEI membrane rapidly reached adsorption equilibrium within 60 minutes, demonstrating maximum adsorption capacities for Cr(VI), Cu(II), and Co(II) at 138.96, 69.27, and 68.31 mg/g, respectively, according to the Langmuir model. This study highlights the membrane's potential for efficient water purification, showing notable reproducibility and stability in removing heavy metal ions. In our previous research, we developed carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) composite nanofiber membranes through electrostatic spinning, utilizing CMC and PVA with glutaraldehyde as a cross-linker, and characterized them using techniques such as SEM, FTIR, TGA, UV, and energy spectrum analysis [
13]. The optimized spinning parameters (23 KV and 2 µL/min) resulted in fibers with a reduced diameter of 183 nm, indicating finer and more uniformly distributed fibers. The membranes demonstrated high chemical adsorption efficiencies for Cu
2+ and Cr
6+ with retention rates of 97.2% and 98.8%, respectively, and adsorption capacities were 26.34 mg·g
−1 for Cu
2+ and 28.93 mg·g
−1 for Cr
6+, consistent with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm. At the same time, our team successfully synthesized a chitosan (CS)/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hollow nanofiber membrane (CS/PVP/PVA-HNM) via coaxial electrospinning [
10]. This membrane demonstrated remarkable permeability and adsorption separation. Specifically, the CS/PVP/PVA-HNM had a pure water permeability of 4367.02 L·m
−2·h
−1·bar
−1. The hollow electrospun nanofibrous membrane exhibited a continuous interlaced nanofibrous framework structure with the extraordinary advantages of high porosity and high permeability. The rejection ratios of CS/PVP/PVA-HNM for Cu
2+, Ni
2+, Cd
2+, Pb
2+, malachite green (MG), methylene blue (MB) and crystal violet (CV) were 96.91 %, 95.29 %, 87.50 %, 85.13 %, 88.21 %, 83.91 % and 71.99 %, and the maximum adsorption capacities were 106.72, 97.46, 88.10, 87.81, 53.45, 41.43, and 30.97 mg·g
−1, respectively. This work demonstrates a strategy for the synthesis of hollow nanofibers, which provides a novel concept for the design and fabrication of highly efficient adsorption and separation membranes.
Sodium alginate (SA), a natural polysaccharide extracted from various species of brown algae including macroalgae and kelp, is a linear block copolymer consisting of β-D-mannuronic acid and α-L-glucuronic acid, with the molecular formula (C
6H
7NaO
6)
n. It is characterized by a high density of carboxyl (-COOH) and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups along its molecular chain[
14,
15,
16]. These groups enable sodium alginate to effectively bind with divalent or higher-valency metal ions M
n+ (n≥2), facilitating the ion-exchange processes where H
+ and Na
+ are replaced, forming a complex three-dimensional gel network enriched with M
n+. This property makes sodium alginate an ideal candidate for use as an investment material in a variety of applications [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Sodium alginate is non-toxic, has excellent film-forming ability, and has excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability, and is widely used in various industries. These include food production as thickeners and stabilizers; pharmaceuticals, for use in drug delivery systems; cosmetics, for their moisturizing properties; and the textile industry, especially in dyeing processes. Its versatility and environmental friendliness underscore its growing importance in sustainable industrial practices, reflecting a shift toward more environmentally friendly materials in technology and product development.
Polyethyleneimine (PEI), also known as polyazacyclopropane, is a water-soluble macromolecule with the highest known cationic charge density among organic polymers. PEI excels in water treatment applications due to its dense amine groups—primary, secondary, and tertiary[
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. These groups facilitate the binding of heavy metal ions in wastewater through mechanisms like ion-exchange, electrostatic interactions, chelation, and coordination, leading to high adsorption capacity. PEI's effectiveness is highlighted in various studies, including those by Gao et al., who immobilized soluble PEI using polydopamine (PDA) polymerization, facilitating effective Pb
2+ removal through a cooperative adsorption mechanism that leverages charged SO
3H groups within a polystyrene matrix and in-situ PDA formation at room temperature [
27]. This hybrid adsorbent demonstrated exceptional selectivity and efficiency, achieving rapid lead removal kinetics, excellent sorption-regeneration properties, and an outstanding capacity for treating Pb-contaminated water with potential applicability to other metals like Fe
3+, Cu
2+, and Ni
2+. For instance, Bucatariu et al. modified spherical silica microparticles with linear and branched poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI) chains through layer-by-layer deposition involving a copper complex and poly(acrylic acid), followed by selective cross-linking and removal of copper and PAA, to create functional silica/(PEIL)
10 and silica/(PEIB)
10 composites [
28]. These composites demonstrated effective sorption of heavy metals like Cu
2+, Ni
2+, Co
2+, and Cd
2+ in batch and column experiments under noncompetitive conditions. Additionally, Tofighy et al. developed a positively charged membrane using hyperbranched polyethyleneimine (HPEI) as a crosslinking agent through a vacuum-filtration method, aimed at efficiently removing divalent heavy metal ions from contaminated water [
29]. The resulting HPEI crosslinked membrane demonstrated excellent performance, highlighted by its ability to selectively reject heavy metal ions and maintain effectiveness over multiple regeneration cycles, indicating its potential for repeated use in water purification applications.
In this study, we aimed to fabricate multilayer composite nanofibrous membranes using three polymer raw materials: SA, PEI, and PVA. SA and PEI were chosen for their effective functional groups that facilitate Cu2+ adsorption, while PVA served as a co-spinning solution and carrier, enhancing the filament-forming properties essential for electrospinning. The spinning process involved the preparation of two hybrid spinning solutions, SA/PVA and PEI/PVA, which were alternately and cyclically spun using electrospinning to create nanofiber membranes with sufficient thickness for filtration. The resulting nanofiber membranes, theoretically insoluble in water, exhibited significant hydrogen bonding interactions within SA and PVA as well as between PEI and PVA, and interlayer hydrogen bonding between SA and PEI, enhancing the structural integrity. These multilayer membranes were subjected to both single and repeated Cu(II) filtration tests, with their performance and structural characteristics analyzed using SEM, EDS, FTIR, UV-vis, XRD, and TG. The objective of this study was to explore the feasibility and efficiency of using electrospun multilayer composite nanofibrous membranes for the adsorption and removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Sodium alginate, polyethyleneimine, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium diethyldithiocarbamate trihydrate (copper reagent) and copper chloride dihydrate produced by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co.
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.2.1. SA Solution Preparation
97.00 g of deionized water was added to a 250 mL conical flask and set aside on a magnetic stirrer. 3.00 g of sodium alginate solid powder was dissolved into deionized water. When all the sodium alginate powder has been added, seal the bottle with plastic wrap. The stirring speed was then adjusted to 500 rpm and stirring was continued for 8 h at room temperature to ensure complete dissolution of sodium alginate. Once completed, label the solution, and set aside for later use.
2.2.2. PEI Solution Preparation
In the preparation of PEI solution, a quantity of PEI was first removed using a syringe. Subsequently, a 50 ml beaker was placed on an analytical balance and the balance was adjusted to zero. Next, 3.00 g of PEI was accurately weighed and added to the beaker. Thereafter, 47.00 g of deionised water was added to the beaker to dissolve the PEI. This solution was transferred to a 250 ml conical flask, and again using the beaker in which the PEI had been dissolved, 50.00 g of deionised water was weighed and added to the conical flask. After completing all additions, the conical flask was sealed with cling film to avoid contamination. Finally, the sealed conical flask was placed in an ultrasonic cleaner and sonicated for 15 minutes at room temperature to ensure that the PEI was completely dissolved and evenly distributed. After treatment, the conical flasks were labelled and set aside.
2.2.3. PVA Solution Preparation
95.00 grams of deionized water were added to a 250 ml conical flask, which was then equipped with a magnetic stir bar for later use. Using precise measurements, 5.00 grams of PVA solid particles were weighed and added to the flask containing the deionized water. To avoid any contamination during the process, the flask’s opening was securely sealed with cling film. The PVA pellets were then left to soak at room temperature for 4 h, allowing them to fully absorb the water and swell. The flask was placed on a heated stirrer, with the temperature set to 90°C and the stirring speed set to medium. Continuous heating and stirring for 6 h ensured complete dissolution of the PVA granules into a uniform solution. Once the process was completed, the flasks were labeled and set aside for further use in subsequent experiments.
2.2.4. Hybrid Electrospinning Solution Preparation
In the preparation of spinning solution, the first step was the mixing of SA and PVA. The steps were as follows: 8 g of SA solution was accurately weighed into a 50 ml centrifuge tube according to the mass ratio of SA to PVA of 1:3, and then 24 g of PVA solution was added. Mixing was carried out using a vortex mixer to ensure that the two solutions were well incorporated. Afterwards, the mixture was shaken at room temperature for 5 min to further promote homogeneous mixing. To eliminate air bubbles from the mixture, the mixture was sonicated for 10 minutes using an ultrasonic cleaner. After treatment, the tube was labelled "No. 1" and set aside.
Next, a mixture of PEI and PVA was prepared. The mixing ratio of PEI to PVA was 1:4. First, 7 g of PEI solution was accurately weighed into another 50 ml centrifuge tube, followed by 28 g of PVA solution. Mix using the same vortex mixer to ensure that the solution is well mixed. After 5 minutes of shaking at room temperature, the same was carried out for 10 minutes using an ultrasonic cleaner to remove air bubbles from the mixture. After completing these steps, the centrifuge tubes were labelled "No. 2" for subsequent use.
2.2.5. Preparation of Cu2+ Solutions with Copper Reagents
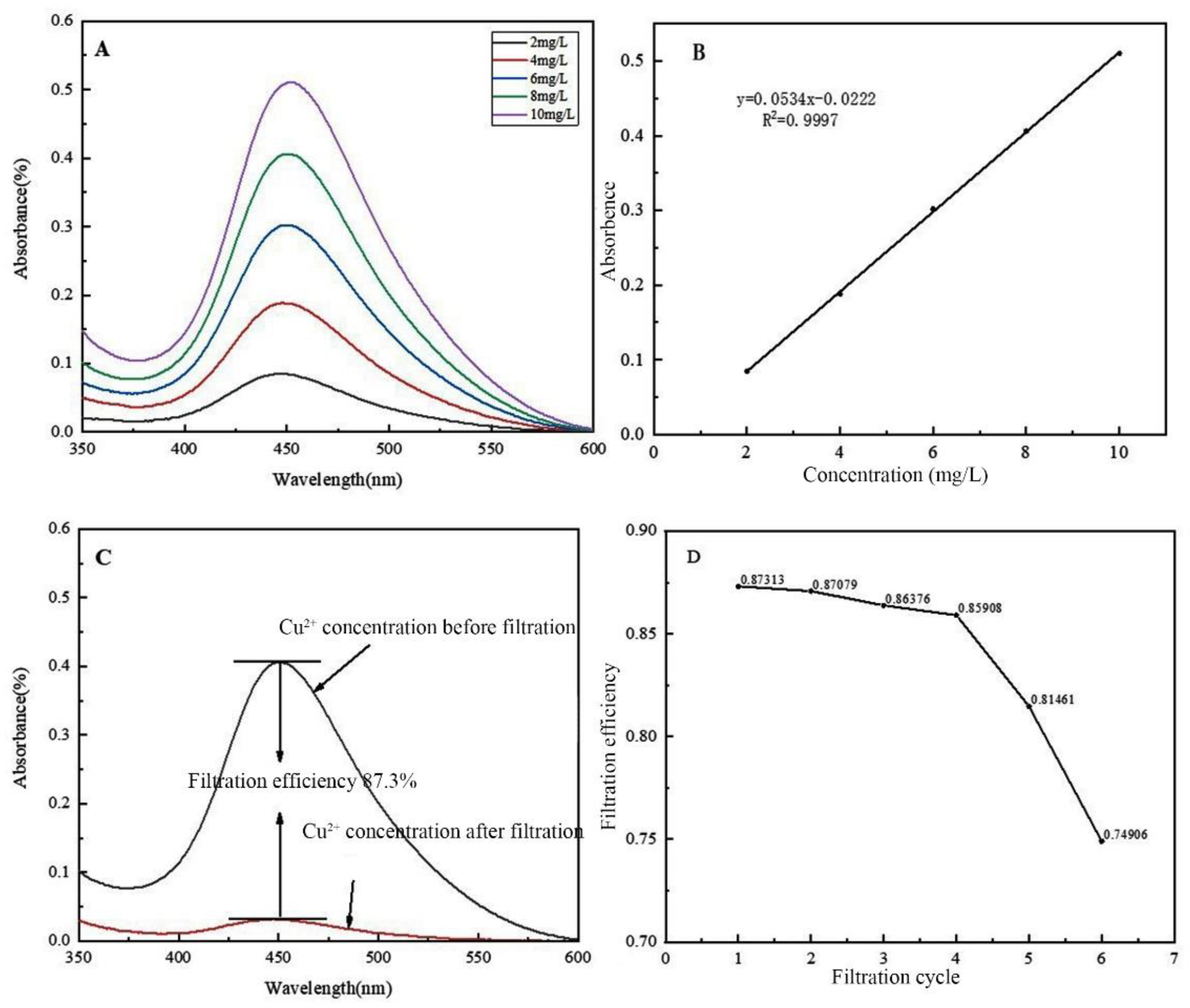
To prepare the Cu2+ solution, 1.00 g of CuCl2 was first precisely weighed and dissolved in a small volume of deionised water, then transferred to a 1-liter volumetric flask. The original beaker was rinsed three times with deionised water to ensure all residues were transferred. Deionised water was then added to the flask up to the 1 L mark to create a base solution of 1 g/L Cu2+. This solution was further diluted to obtain concentrations of 10 mg/L, 8 mg/L, 6 mg/L, 4 mg/L, and 2 mg/L, with 300 mL prepared for each concentration, all properly labelled.
Similarly, for the copper reagent, 1.00 g of sodium diethylthiocarbamate trihydrate was weighed, dissolved, and transferred into a 1 L volumetric flask. The beaker used was washed three times and the flask was filled to the 1-liter mark to produce a 1 g/L solution of the copper reagent. These meticulous steps ensured the accurate preparation of the Cu2+ solution and copper reagent, making them ready for further experimental use.
2.3. Preparation of SA/PEI/PVA Multilayer Composite Nanofiber Membrane
The experiment involved the electrospinning of two mixed liquids, designated as No. 1 and No. 2. Initially, the liquids were drawn into syringes and spun under controlled conditions. The process began by wrapping a circle of tin foil around the receiving drum to aid in the removal of the nanofiber membrane. A zero wire connected the voltage device to the drum, and the ground wire was accessed. After verifying the connections, the experiment commenced. Using the No. 1 syringe, the liquid was injected at a rate of 4-10μL/min using an automatic liquid supply pump. The needle-to-drum distance was maintained between 5-15cm, and the voltage was set between 17-20kV. After injecting 0.5ml, spinning was paused to switch to the No. 2 syringe. This syringe was used to inject liquid at a rate of 8-12μL/min under the same distance and voltage settings. This process was repeated, alternating between the two syringes, until a total volume of more than 10mL was spun. Once complete, the nanofiber film was carefully removed from the tin foil, sealed in a bag, labeled, and stored in a desiccator for future use. The resultant nanofibrous membranes, characterized by their multilayer structure and appropriate thickness, are suitable for filtering heavy metal ions and various assay characterizations.
2.4. Cu2+ Filtration
The setup of the filtration apparatus begins with assembling the necessary components: a top cover, a funnel filter cup, a sand core filter head, and an Erlenmeyer flask. These are arranged vertically from top to bottom and held securely in place by stainless steel clamps to maintain stability throughout the process. The lower section of the sand core funnel is attached to a conduit that directs the filtrate straight into the Erlenmeyer flask.
To prepare the filter membrane, a nanofiber membrane is first sized by tracing and cutting out a circle that matches the diameter of the sand core funnel using a compass and scissors. This membrane is then sandwiched between two filter papers of the same size to prevent any damage from the filtration hardware. This assembly is then placed on the sand core funnel. The setup is completed by connecting a through-hole beaker to the sand core funnel with a sealing film and a clamp to ensure a tight, leak-free connection.
Before initiating the filtration, 100 mL of a pre-prepared 8 mg/L Cu2+ solution is added to the through-hole beaker. After securing the top cap, the system is left to allow the solution to gradually pass through the nanofiber membrane into the Erlenmeyer flask below. Once filtration is complete, the filtrate is collected and prepared for UV analysis. For assessing the membrane's reusability and durability, several filtration cycles are performed. Each cycle uses 80 mL of the 8 mg/L Cu2+ solution, and after each use, the nanofiber membrane is carefully sealed and stored. The cycles are conducted every 8 h, totaling six repetitions. The filtrate from each cycle is gathered and marked for subsequent evaluation and testing. This procedure not only evaluates the membrane's filtration capabilities but also tests its stability and reliability for repeated use.
2.5. Membrane Characterization
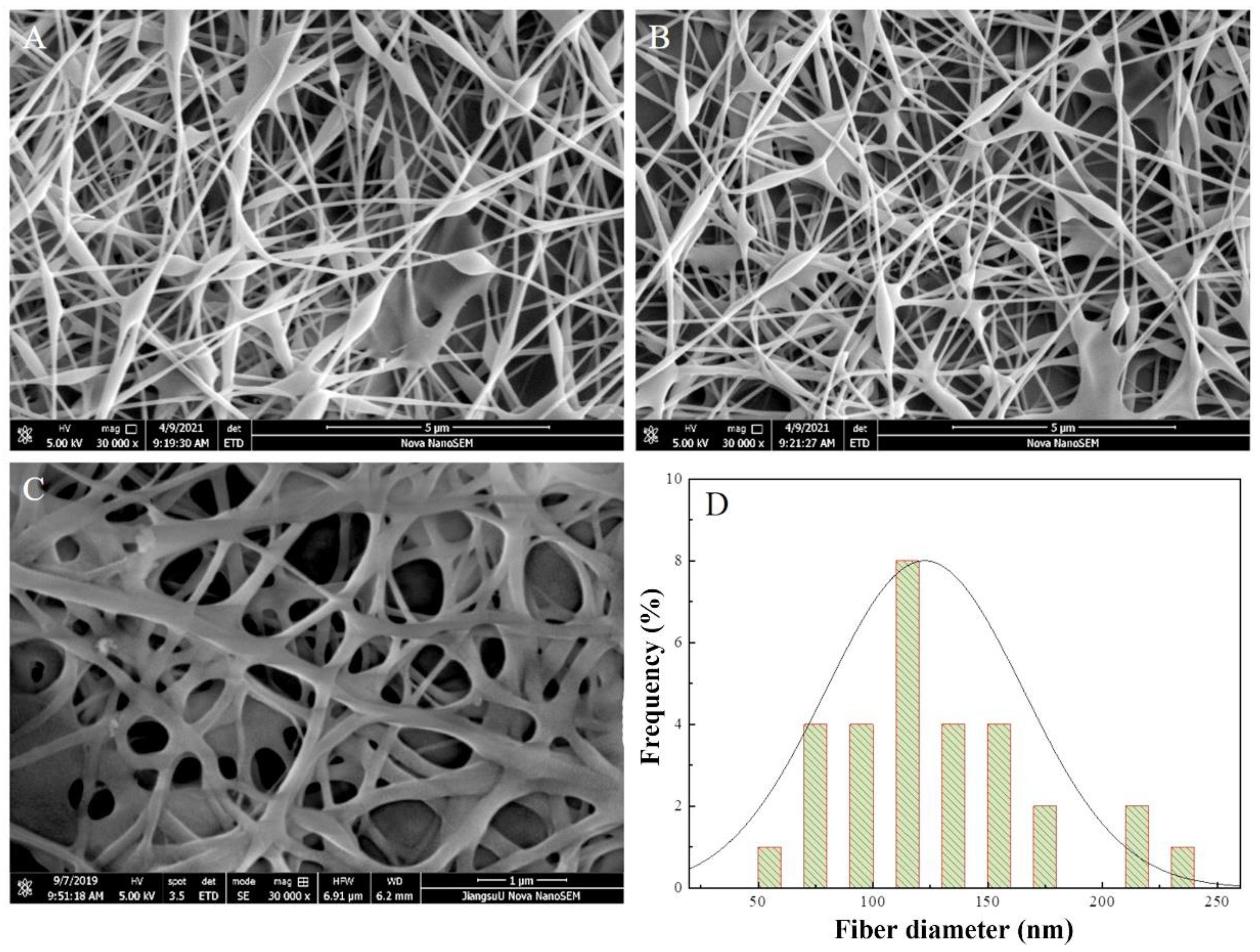
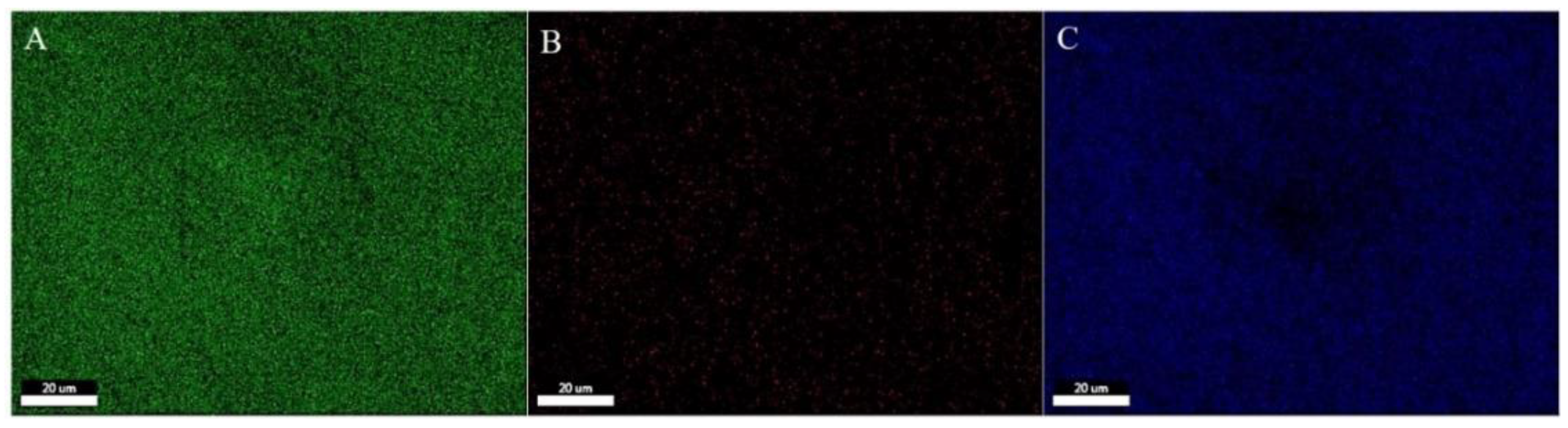
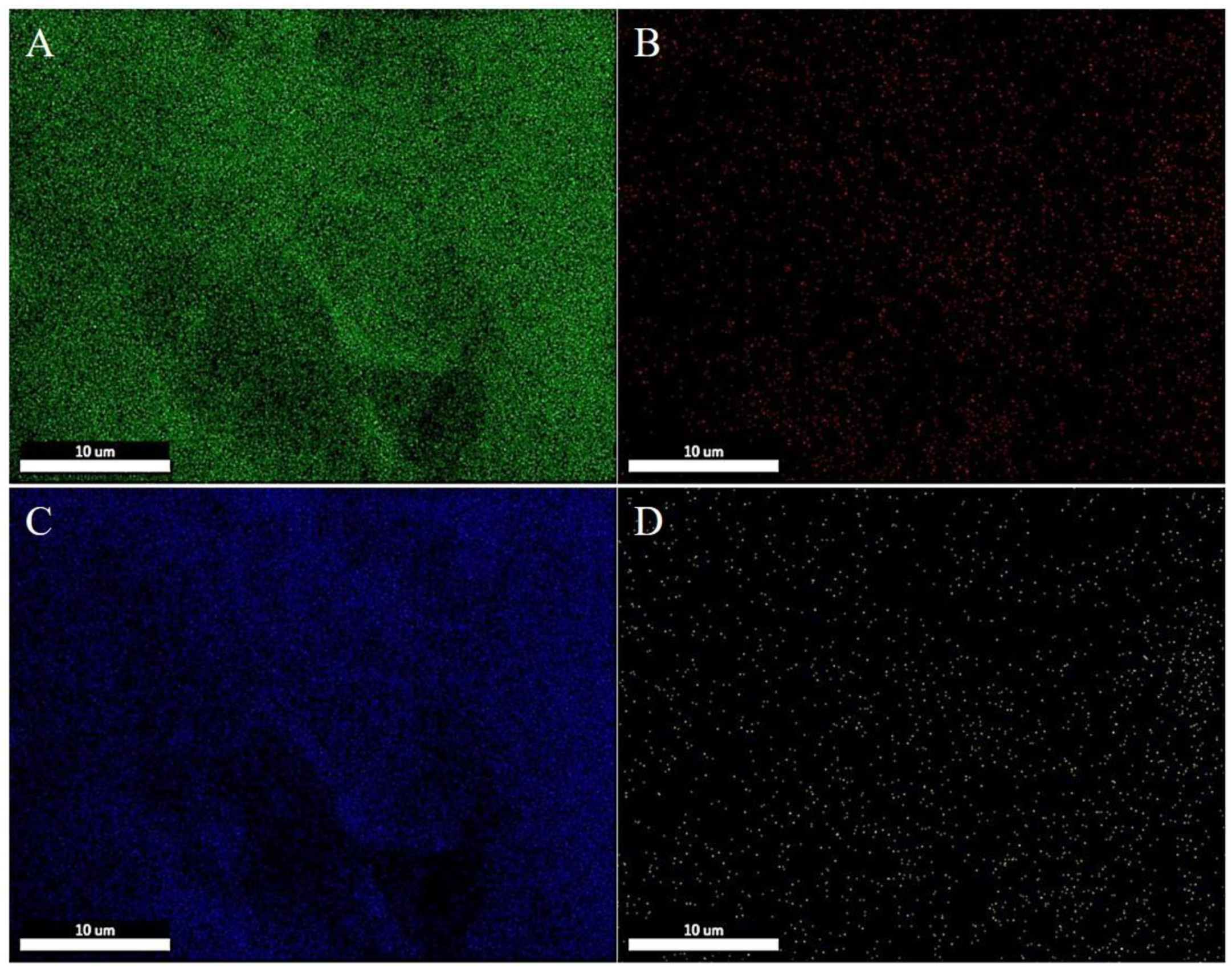
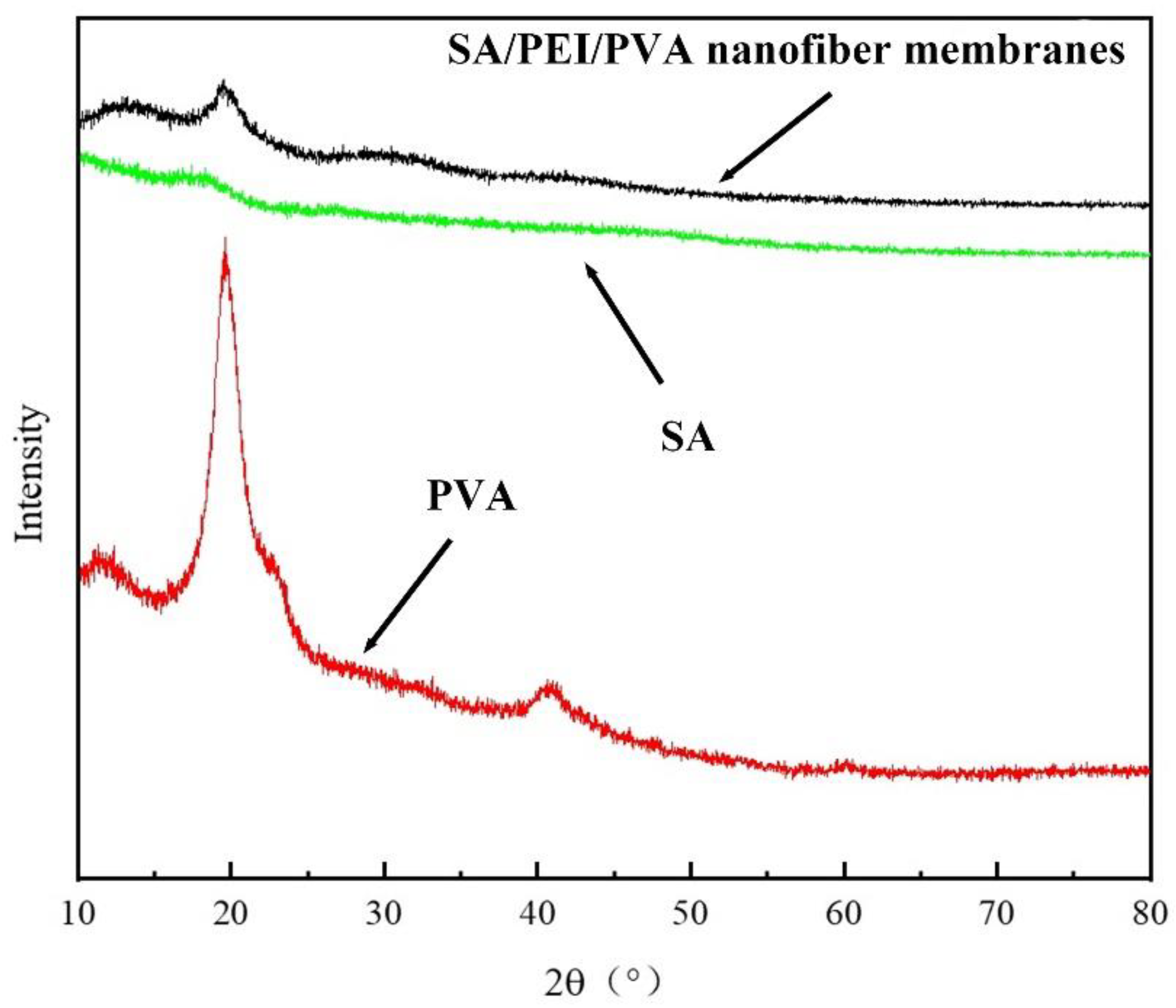
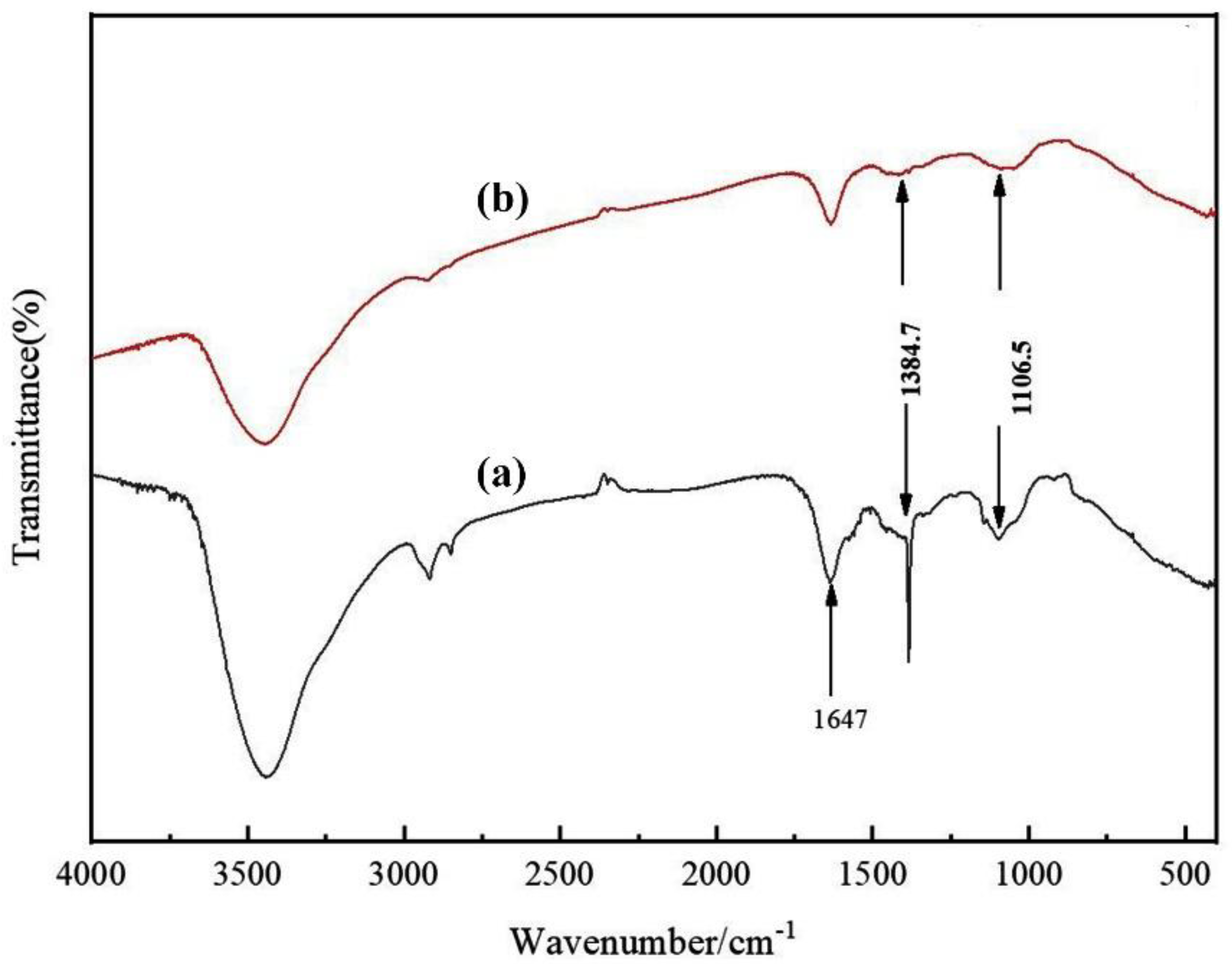
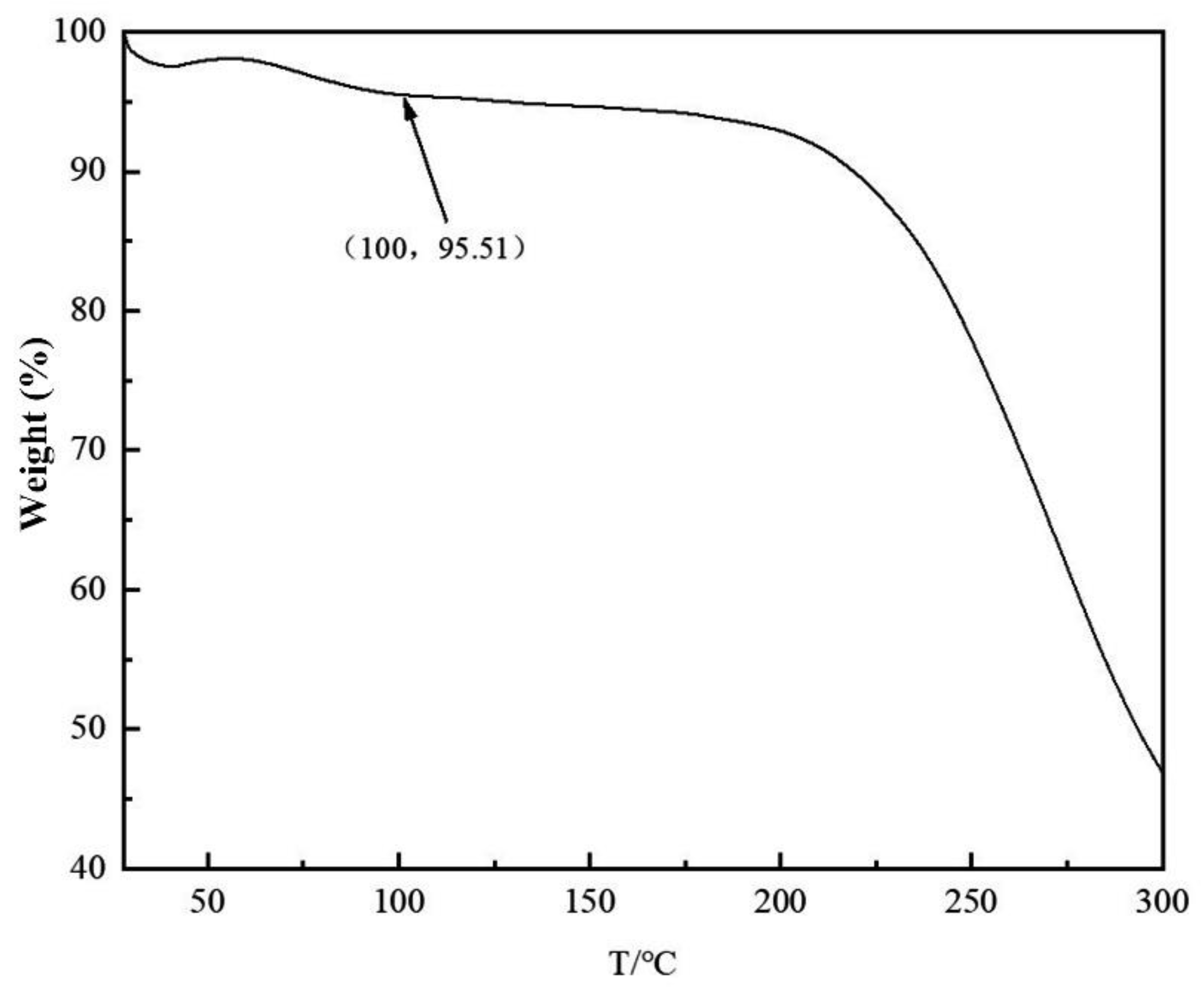
The morphology of the multilayer composite nanofiber membranes was observed using a field emission scanning electron microscope (NovaNano450, FEI, USA). The membrane surface was analyzed for elements using an X-ray spectrometer (Octane Plus, EDAX, USA). The nanofiber membranes, SA solid powder and PVA solid powder were characterized on an X-ray diffraction analyzer with a scanning range of 10-80° (2θ). The prepared SA/PEI/PVA multilayer composite nanofiber membranes were placed in a standard thermogravimetric analyzer (STA449F3, NETZSCH, Germany) with an atmosphere of air, a ramp rate of 10 K/min, and a test temperature range of 20-300°C. The nanofiber membranes were then analyzed in a standard thermogravimetric analyzer (STA449F3, NETZSCH, Germany). The prepared SA/PEI/PVA multilayer composite nanofiber membrane samples were oven-dried, ground and pressed with potassium bromide, and then scanned and analyzed in the infrared with a Fourier Transform infrared absorption spectrometer (FTIR, Nicolet iS10, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) in the wavelength range of 4000-500cm-1. The 10 mg/L, 8 mg/L, 6 mg/L, 4 mg/L, and 2 mg/L Cu2+ solutions configured were detected with a UV-visible spectrophotometer, and the absorbance-concentration relationship was analyzed by the five-point fitting method. Six cuvettes were prepared and 3 ml of 10mg/L, 8mg/L, 6mg/L, 4mg/L, 2mg/LCu2+ solution was measured in a cylinder and added into five quartz cuvettes, and the sixth quartz cuvette was filled with 3 ml of deionized water to serve as the baseline and control. Two drops of copper reagent configured were added to the quartz cuvettes with Cu2+ solution, and scanned and analyzed by UV-visible spectrophotometer to plot absorbance versus concentration for the next step of filtration detection. The assay method for the filtrate to be tested is the same as above, which is to take 3 ml of filtrate and add two drops of copper reagent. The detection method for recirculation filtration is the same as above.