Submitted:
05 April 2024
Posted:
23 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadri, D. and R. Hasanzadeh, Assessment of Spiritual Intelligence and its Association with Teaching Ability in the Faculty Members of the School of Dentistry. Journal of Mashhad Dental School, 2018. 42(2): p. 159-166.
- karimi mounaghi, H. , et al., The Relationship between Spiritual Intelligence / Quotient (SQ) and Teaching Competency in Medical Faculty Members. Iranian Journal of Medical Education, 2012. 12(8): p. 554-563.
- Valente, S. and A.A. Lourenço, Conflict in the Classroom: How Teachers’ Emotional Intelligence Influences Conflict Management. Frontiers in Education, 2020. 5(5).
- Asrar-ul-Haq, M., S. Anwar, and M. Hassan, Impact of emotional intelligence on teacher׳s performance in higher education institutions of Pakistan. Future Business Journal, 2017. 3(2): p. 87-97.
- Haghani, F. , et al., Development and Psychometric Evaluation of a Tool for Assessing Emotional Intelligence in Teaching. Iranian Journal of Medical Education, 2014. 13(12): p. 1127-1137.
- Suleman, Q. , et al., Association between emotional intelligence and academic success among undergraduates: A cross-sectional study in KUST, Pakistan. PLOS ONE, 2019. 14(7): p. e0219468.
- Haghani, F., B. Aminian, and T. Changiz, Do the Teachers Who Are Selected by Students Have a Higher Emotional Intelligence? Strides in Development of Medical Education, 2012. 8(2): p. 132-140.
- Bar-On, R. , The Bar-On Model of Emotional-Social Intelligence. Psicothema, 2006. 18 Suppl: p. 13-25.
- Petrides, K., A. Furnham, and N. Frederickson, Emotional intelligence. Psychologist, 2004. 17: p. 574-577.
- McEnrue, M. and K. Groves, Choosing among tests of emotional intelligence: What is the evidence? Human Resource Development Quarterly, 2006. 17: p. 9-42.
- Sohrabi, Z. , et al., The effects of group blogging on the attitude towards virtual education in nursing students. Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic Of Iran, 2017. 31(1): p. 877-881.
- Darkivandi, R.M. , Emotional Intelligence, Its History and Approaches in the View of Religion and Psychology %J Ravanshenasi Va Din. 2012. 4(3): p. 97-.
- Ashrafi, K. , Kavousian, J., Kadivar, P., karimi, K. The role of emotional intelligence and five personality factors in Predicting Components of goal achievement. Knowledge & Research in Applied Psychology, 2019; 20(4): 101-112. [CrossRef]
- Qualter, P., K. Gardner, and H. Whiteley, Emotional Intelligence: Review of Research and Educational Implications. Pastoral Care in Education, 2007. 25: p. 11-20.
- Moosapoor,N, (STRIDES IN DEVELOPMENT OF MEDICAL EDUCATION). 1383 [cited 2021August03];1(1):48-56. Available from: https://www.sid.ir/fa/journal/ViewPaper.aspx? 5448.
- Bagheri, R., Z. Sohrabi, and E.h. Moradi, Psychometric properties of Persian version of the multifactor leadership questionnaire (MLQ). Medical journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 2016. 29: p. 256.
- Amin Khandaghi M, Saifi G A. Effective capabilities and skills needed for college teaching. IRPHE. 2013; 19 (3) :121-147 URL: http://journal.irphe.ac.ir/article-1-2052-fa.
- Adib-Hajbaghery, M. and M.S. Lotfi, The Association of Emotional Intelligence with Academic Achievement and Characteristics of Students of Kashan University of Medical Sciences. Iranian Journal of Medical Education, 2013. 13(9): p. 703-710.
- Ayiro, L.P. , An Analysis of Emotional Intelligence and the Performance of Principals in Selected Schools in Kenya. 2009. 11(6): p. 719-746.
- Malekmohammadi,M.Noori,H.Ebnesharie,M Emotional intelligence, dimensions, features and models, The Second International Conference on New Research in Management, Economics and Accounting. Available from: https://civilica.com/doc/439944 https://scholar.conference.ac:443/index.
- Sadegh Maleki Avarsin, Mirmohammad Siedkalan, (2008). A survey on the relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Effectiveness among academic staff in Islamic Azad university of Parsabad Moghan, Quarterly Journal Of Educational Leadership & Administration, 2(2), 115. magiran. 8714.
- Omid, A., F. Haghani, and P. Adibi, Clinical teaching with emotional intelligence: A teaching toolbox. J Res Med Sci, 2016. 21: p. 27.
- cherniss, C.G., Daniel Bringing Emotional Intelligence to the Workplace: A Technical Report Issued by the Consortium for Research on Emotional Intelligence in Organizations. 1998, Fetzer Institute.: The Consortium for Research on Emotional Intelligence in Organizations (CREIO).
- Bates, A.W. , Teaching in a digital age, in Open Educational Resources Collection. 2015, Tony Bates Associates Ltd: Porterfield, Michael David - EDTECH 5340.
- Golamali, A., j. negin, and n. kioumars, Professional empowerment of teachers in the future perspective along with a model. Quarterly Journal of Educational Innovations, 2019. 18(69): p. 7-32.
- Unnikrishnan, B. , et al., Association of emotional intelligence with academic performance among medical students in South India. Asian J Pharm Clin Res, 2015. 8: p. 300-302.
- Eslamian, H. , et al., Study the relationship between emotional intelligence and how to apply the standards of effective teaching by faculty Medical Sciences. Iranian Journal of Medical Education, 2014. 14(8): p. 685-694.
- Hassan, N. , et al., The Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Teaching Effectiveness among Lecturers at Universiti Teknologi MARA, Puncak Alam, Malaysia. International Journal of Social Science and Humanity, 2015. 5: p. 1-5.
| Variable | Condition | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | female | 56.9 |
| male | 43.1 | |
| marital status | Married | 84.5 |
| Single | 15.5 | |
| age ( year ) Mean ± SD ( min- max ) | ( 68 – 31)9.3± 45.75 | |
| teaching experience | Up to 10 years | 58.6 |
| 20-10 | 15.5 | |
| More than 20 years | 25.9 | |
| teaching experience ( year )( Mean ± SD ( min- max | (31 –1) 9.8± 12.31 | |
| Scientific degree | Instructor | 1.7 |
| Assistant Professor | 67.2 | |
| Associate Professor | 16.8 | |
| Professor | 17.2 | |
| University of study | State university | 93.1 |
| Overseas University | 6.9 | |
| Passing a training course on teaching to adults | Yes | 72.4 |
| No | 27.6 | |
| questionnaire | Number of questions | Points earned Mean ±SD | Scope range obtained | Range of achievable scores | Percentage of points earned Mean ±SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional intelligence in teaching | 31 | 9.3± 111.51 | 124-87 | 124-0 | 7.5± 89.93 |
| Variable | Condition | Number | Scores obtained from the questionnaire Mean ± SD | Statistical estimation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | female | 33 | 9.57± 112.15 | P=0.556 |
| male | 25 | 9.06± 110.68 | ||
| marital status | Married | 49 | 10.04 ±111.36 | P=0.778 |
| Single | 9 | 3.24 ± 112.33 | ||
| age ( year) | less than 40 years | 22 | 9.53± 111.81 | P=0.178 |
| 50-41 | 17 | 10.88± 108.29 | ||
| More than 50 years | 19 | 6.81± 114.05 | ||
| teaching experience(year) | Up to 10 years | 34 | 10.42± 109.64 | P=0.19 |
| 20-10 | 9 | 5.87± 113.77 | ||
| More than 20 years | 16 | 7.54± 114.4 | ||
| Scientific degree | Instructor | 1 | 113 | P=0.396 |
| Assistant Professor | 39 | 9.44± 110.61 | ||
| Associate Professor | 8 | 10.25± 110 | ||
| Professor | 10 | 7.82± 116.1 | ||
| University of study | State university | 54 | 9.39± 111.11 | P=0.225 |
| Overseas University | 4 | 68/6 ± 117 | ||
| Passing a training course on teaching to adults | Yes | 42 | 44/9 ± 111.57 | P=0.943 |
| No | 16 | 23/9 ± 11.37 |
| The maximum teaching abilities were teaching based on an organized syllabus, class managementArea | number of questions |
Points earned Mean ±SD | Scope range obtained | Range of achievable scores | Percentage of points earned Mean ±SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-teaching planning | 3 | 1.61± 10.29 | 12-6 | 12-0 | 13.42 ± 85.77 |
| Curriculum teaching | 6 | 1.94± 21.94 | 24-16 | 24-0 | 7.97 ± 91.45 |
| Measuring student performance | 4 | 2.34± 13.3 | 16-7 | 16-0 | 14.66 ± 81.46 |
| class management | 2 | 1.04± 7.29 | 8-3 | 8-0 | 13.03± 91.16 |
| Favorable learning atmosphere | 4 | 1.52±14.29 | 16-11 | 16-0 | 9.51 ± 89.33 |
| Relationship | 2 | 0.89± 7.27 | 8-5 | 8-0 | 11.17± 90.94 |
| Professional development and leadership | 3 | 1.68 ± 9.79 | 12-6 | 12-0 | 14.02 ± 81.60 |
| Performance of professional responsibilities | 5 | 1.69± 17.96 | 20-11 | 20-0 | 8.47± 89.82 |
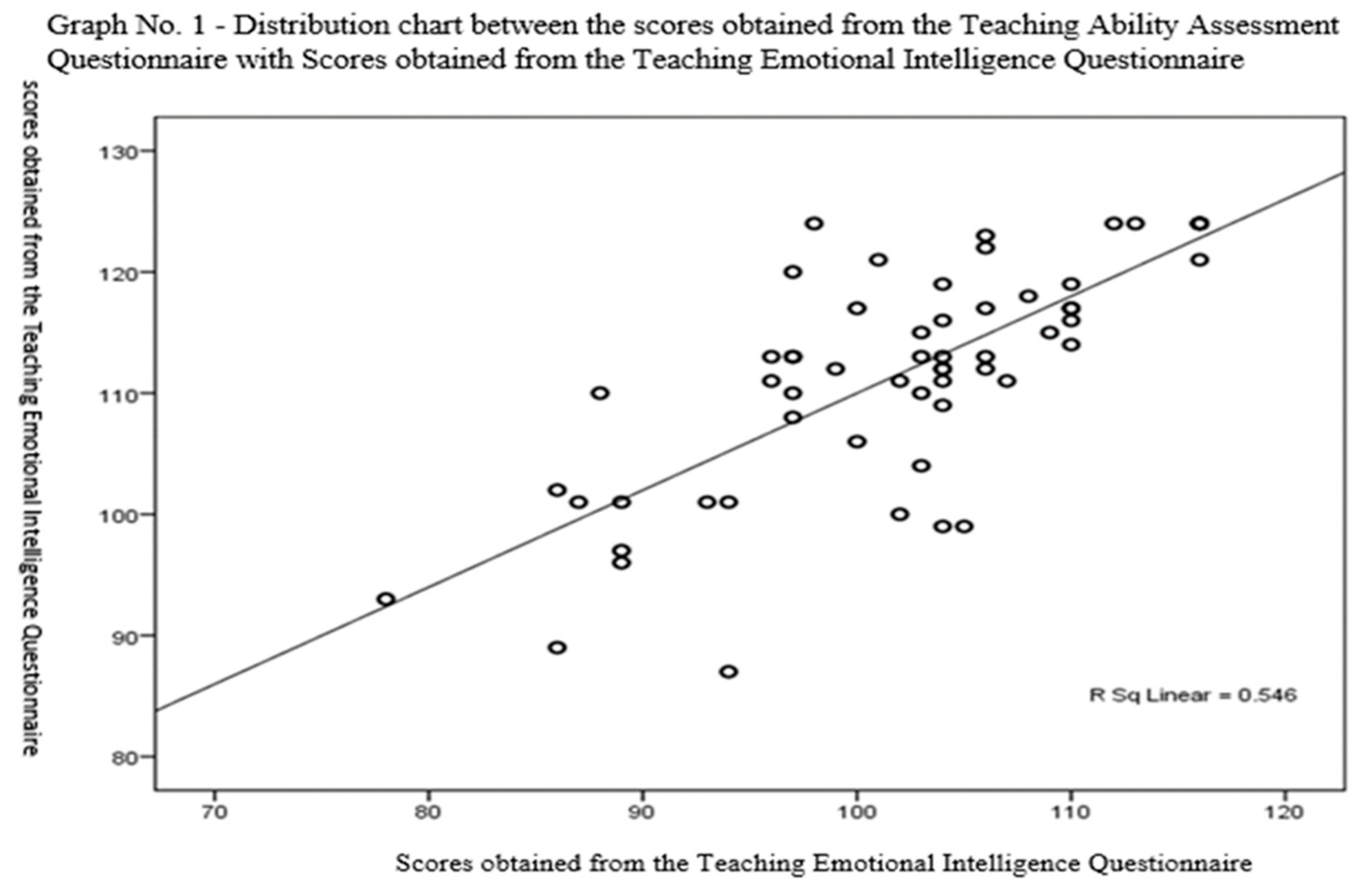
| The whole questionnaire of teaching ability | 29 | 8.59± 101.89 | 116-78 | 116-0 | 7.4± 87.84 |
| Areas of Teaching Ability Questionnaire | Scores obtained from the Teaching Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire | |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-teaching planning | Spearman’s Rho | 0.544 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Curriculum teaching | Spearman’s Rho | 0.542 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Measuring student performance | Spearman’s Rho | 0.587 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation | |
| class management | Spearman’s Rho | 0.393 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Favorable learning atmosphere | Spearman’s Rho | 0.302 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Relationship | Spearman’s Rho | 0.510 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Professional development and leadership | Spearman’s Rho | 0.413 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Performance of professional responsibilities | Spearman’s Rho | 0.602 |
| P-value | P=0.0001 | |
| Type of correlation | Positive correlation |
| Variable | Condition | The correlation coefficient Spearman’s Rho | Statistical estimation | Type of correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| marital status | female | 0.634 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation |
| male | 0.832 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation | |
| marital status | Married | 0.773 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation |
| Single | 0.374- | P=0.364 | No correlation | |
| age ( year ) | less than 40 years | 0.627 | P=0.002 | Positive correlation |
| 50-41 | 759 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation | |
| More than 50 years | 657 | P=0.002 | Positive correlation | |
| teaching experience(year) | Up to 10 years | 0.751 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation |
| 20-10 | 0.462 | P=0.21 | No correlation | |
| More than 20 years | 0.684 | P=0.005 | Positive correlation | |
| Scientific degree | Assistant Professor | 0.716 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation |
| Associate Professor | 0.898 | P=0.002 | Positive correlation | |
| Professor | 0.423 | P=0.223 | No correlation | |
| University of study | State university | 0.746 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation |
| Overseas University | 0.2 | P=0.8 | No correlation | |
| Passing a training course on teaching to adults | Yes | 0.57 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation |
| No | 0.874 | P=0.0001 | Positive correlation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





