1. Introduction
Distributed: being a computer network in which at least some of the processing is done by the individual workstations and information is shared by and often stored at the workstations, [
1].
Database: usually large collection of data organized especially for rapid search and retrieval (as by a computer), [
1].
Database "
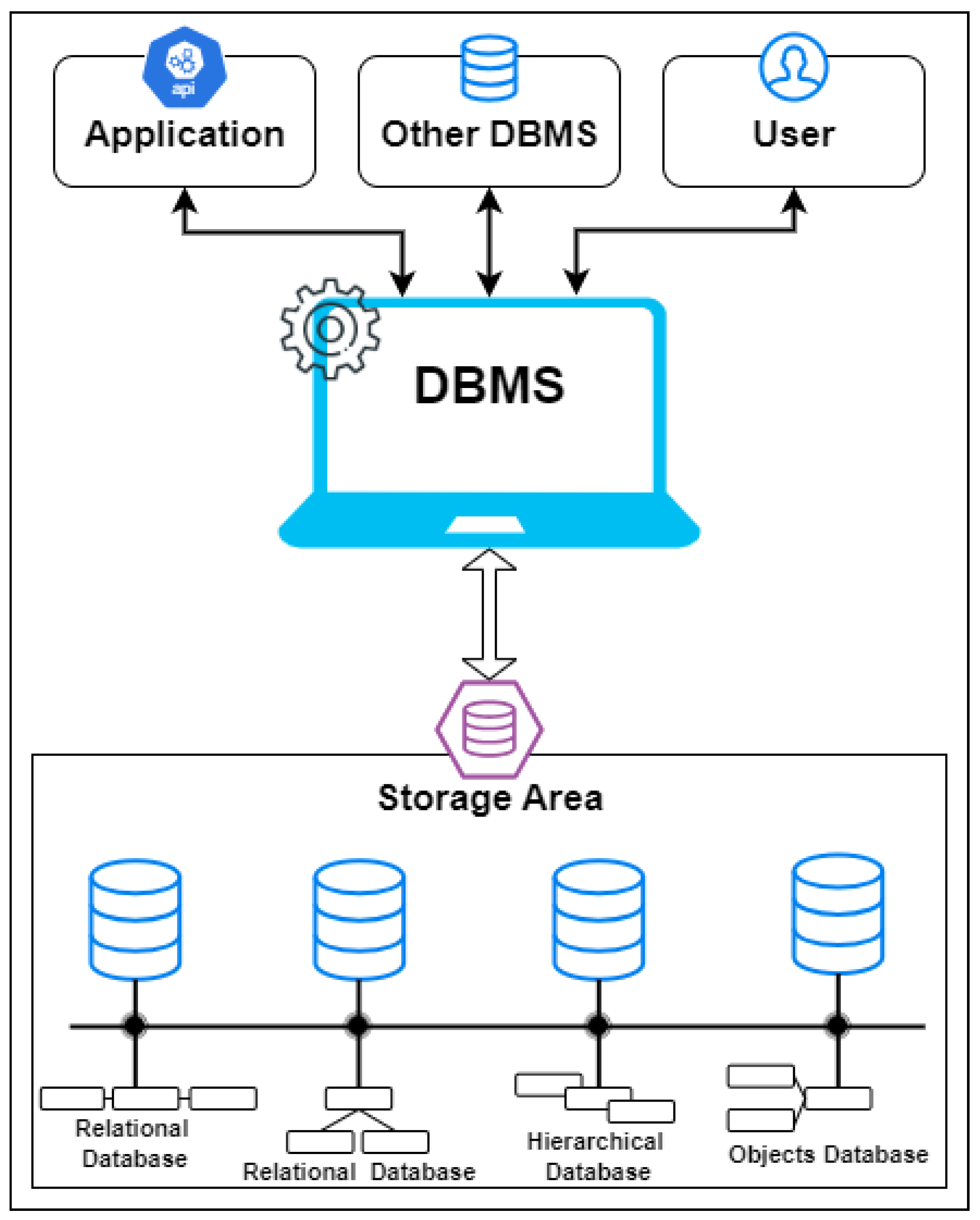
DB" is a collection of vast volumes of permanent data or complicated data structures. The magnitude and complexity make human verification challenging. To correct any potential issues, we will need to use specialized software. This specialized software might be deployed by the database provider as a library, a standalone program, or a combination of both. Regardless of deployment, this specialized software is known as a database management system (
DBMS). Vendors often install a DBMS as a collection of distinct programs and libraries, [
2].
A software system called a distributed database management system (DBMS) where responsible for overseeing a distributed database and providing users with transparency. The phrase "distributed database system" (DDBS) can be used to describe either the distributed database or the distributed database management system. A few instances of DBMS application areas are student information systems, employee management systems, automated teller machines, and train reservation systems. Packages for database management systems (DBMS) include FoxPro, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
According to [
3], a distributed system is a collection of autonomous computing elements that appear to users as a single coherent system.
Figure 1 shows the the schematic of a DBMS system.
Distribution Transparency enables management of physically dispersed databases as if centralized. A DDBMS designer may fragment and replicate a system’s fragments or tables; however, users should be unaware of these details. This is referred to as
distribution transparency. One of the most sought-after characteristics of a distributed database is its transparency. This transparency makes the system easy to use by keeping distribution details hidden from users. Distribution transparency includes three aspects: location, fragmentation, performance, replication, concurrency, migration, and failure. DDBMS transparency levels will be addressed in detail in
Section 3.
Benefits of Distributed Database Management System DDBMS
In centralized database systems, expanding to new sites or units entails significant effort and disturbance to present operations. However, in distributed databases, the job only requires transferring additional computers and local data to the new site and finally connecting them to the distributed system, without interrupting present activities, [
4].
More Reliable When a database fails, the whole centralized database system comes to a complete stop. Distributed systems, on the other hand, could still work, although with reduced performance, in the event that one of its components fails. A distributed database management system is thus more reliable.
A Better Response User requests may be fulfilled directly from local data if data is given effectively, which will speed up the response time. In contrast, all inquiries in centralized systems have to go via the central computer for processing, which lengthens the response time.
Lower Communication Cost Data change in a distributed database system may be accomplished with lower transmission costs if the data is kept locally, where it is most often accessed. Centralized systems make this impossible.
Enhanced performance Because the data is situated near the point of greatest demand, and considering the inherent parallelism of distributed database management systems, database access may be faster than that of a remote centralized database.
Enhanced share ability and local autonomy The geographical spread of an organization can be seen in the distribution of data, as users at one place can access data held at another. Data can be stored on-site near the users who use it most frequently. This gives users local authority over the data, allowing them to define and enforce local standards for its use.
2. Literature Review
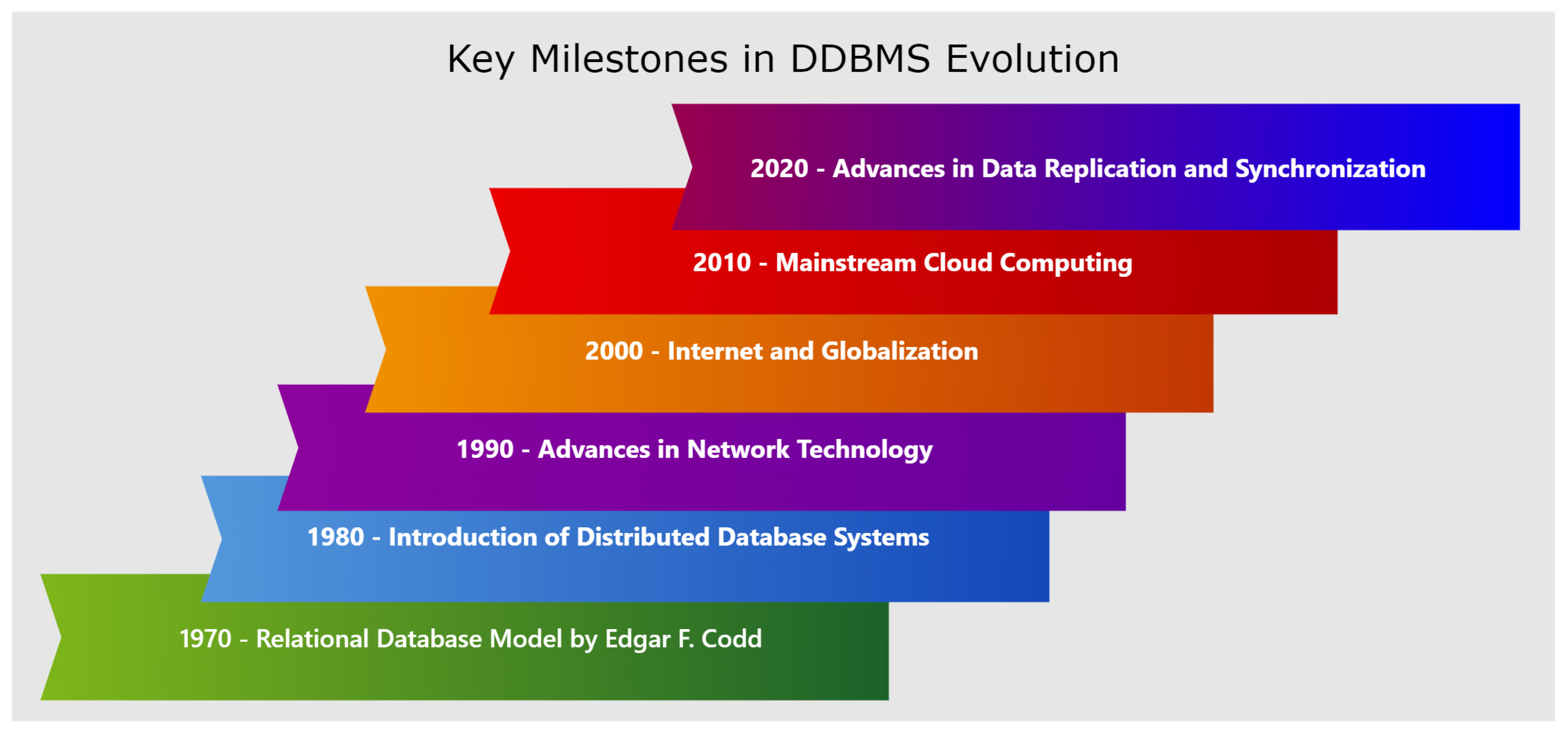
Several distributed database prototype systems were built in the 1980s and 1990s to solve difficulties like as data dissemination, replication, distributed query and handling of transactions, and management of metadata, [
5]. Recently, several new technologies have evolved that mix distributed and database technology. These technologies and systems are being created to deal with the storage, analysis, and mining of the massive amounts of data that are being generated and collected, and they are collectively known as big data technologies. Big data technologies evolved from distributed systems and database systems, in addition to data mining and machine learning algorithms capable of processing massive amounts of data to extract necessary knowledge.
With the turn of the century, the convergence of distributed and database technologies increased, resulting in what is today known as big data technology. These developments are essentially the result of the combination of traditional database management concepts with revolutionary data mining and machine learning techniques designed to manage and extract value from massive amounts of data. This evolution highlights a critical change from just maintaining data to strategically exploiting data at scale for a competitive edge.
There are four classifications of databases [
4]. Hierarchical database management systems, These are incredibly fast and simple, with parent-child relationships and a "tree" data structure.
Network DBMS refers to a database with many-to-many relationships represented by a network. The structure is often complex due to the presence of several many-to-many links. The most extensively implemented database management system is
RDBMS, which stands for "
Relational Databases." A collection of relations constitutes the database. Based on the object-oriented programming paradigm, object-oriented database management systems (DBMS) are constructed. Constant data stored in databases and transient data encountered during application execution can both be effectively represented by them. They utilize objects, which are easily reusable and basic components. A collection of operations that manipulate the data constitutes the data portion of each object. Because pointers are utilized instead of relational table structures, access to the object and its attributes is achieved. Spread DBMS is an abbreviation for a collection of interconnected databases that are distributed across the internet or computer network. In addition to managing distributed databases, a Distributed Database Management System (DDBMS) offers mechanisms for granting users visibility into them. For the organization’s computational resources to be utilized to their maximum capacity, data is intentionally distributed across a large number of nodes within these systems.
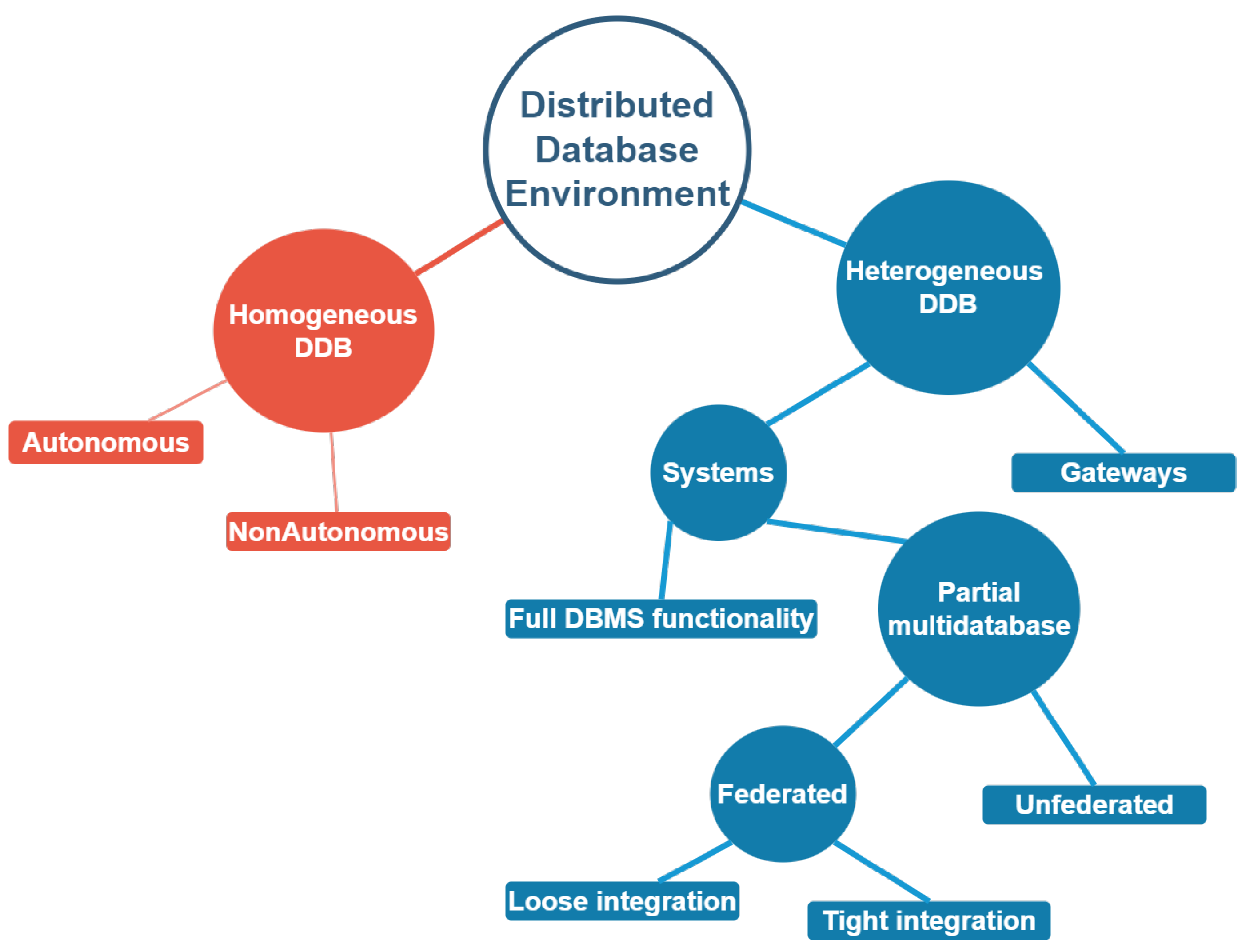
According to [
6], there are two types of distributed database management systems (DDBMS): homogeneous DDB and These database systems typically run on the same operating system, use the same application process, and have the same hardware components. Every site uses the same sort of DBMS. Each node uses the same database management system (DBMS). There are two types of homogeneous databases: autonomous and non-autonomous.
Autonomous DDBs operate autonomously, delivering messages back and forth to communicate data updates.
Non autonomous: A centralized, or master, DBMS manages database access and updates across all nodes. The second form of DDBMS is
Heterogeneous DDB. Heterogeneous distributed DB systems use multiple operating systems, application methods, and hardware devices. Different sites use different RDBMSs, including non-relational DBMSs. Each node may utilize a different database management system.
Figure 2.
Distributed Database Environments.
Figure 2.
Distributed Database Environments.
Amidst these technological advancements, the concept of transparency in DDBMS has become a cornerstone for system design and evaluation. Transparency in distributed systems is multifaceted, encompassing several dimensions that collectively enhance usability and system management. At its core, transparency in a DDBMS masks the system’s complexity from the end-user, facilitating a simpler and more effective interaction with the technology.
One of the primary aspects of transparency is replication transparency, which ensures data consistency and system reliability without the user’s awareness of underlying replication processes. The management of replicas, crucial for high availability and fault tolerance, involves sophisticated synchronization mechanisms that operate seamlessly behind the scenes. Studies such as those by Bernstein and Newcomer (2009) highlight how DDBMS manage these complexities invisibly, ensuring user operations remain unaffected by the intricacies of data consistency across distributed nodes, [
7].
Equally critical is fragmentation transparency, which deals with the division of data across multiple physical locations. Effective data fragmentation enhances performance by localizing data interactions and minimizing unnecessary data transmissions across the network. This not only improves response times but also optimizes network bandwidth usage, a critical factor in large-scale distributed environments.
The role of performance transparency in DDBMS cannot be understated. It involves optimizing and balancing loads across the distributed system without user intervention. Techniques for query optimization and load balancing are essential for maintaining an efficient operational state, as noted by Rahimi and Haug (2010). These mechanisms ensure that the DDBMS can handle large-scale operations and complex queries efficiently, crucial for environments such as cloud computing platforms where resources are dynamically allocated, [
2].
Failure transparency involves maintaining continuous service operation despite system failures. The strategies for achieving this include implementing redundancy and establishing robust fail over processes, which are essential for ensuring that system failures do not disrupt user transactions or data accessibility.
Transaction transparency is particularly challenging in a distributed environment, where maintaining The ACID characteristics (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) of transactions between many nodes are critical. Advanced transaction processing techniques that uphold these properties across distributed architectures are critical for ensuring data integrity and operational consistency.
Recent research, including that by Özsu and Valduriez (2020), emphasizes the importance of location transparency in supporting seamless queries across multiple databases without requiring users to be aware of the physical locations of data. This aspect is pivotal in modern DDBMS, where data might span across multiple data centers or cloud regions, [
8] .
As DDBMS continue to evolve, integrating these transparency levels with emerging technologies such as cloud computing and big data frameworks is becoming increasingly important. These integrations are necessary to handle the growing data volumes and the distributed nature of modern computing infrastructures, demanding robust management of distributed data to leverage the full potential of DDBMS technologies.
Recent scholarly works and foundational texts continue to inform and guide the development of these systems, ensuring that as new challenges arise, DDBMS are well-equipped to handle them, thereby maintaining their critical role in the data-driven landscape of the 21st century,
Figure 3 presents the evolution of DDBMS.
3. Transparency Levels in DDBMS
Transparency is the act of distinguishing the abstract concepts and principles of a system from the specific technical details of its execution. Put simply, a transparent system conceals the intricacies of its implementation from consumers. A fully transparent DBMS offers a significant benefit in terms of its extensive support for the creation of intricate applications. We aim to achieve complete transparency in all DBMSs, whether they are centralized or distributed.
The concept of transparency expands upon the overarching notion of concealing the intricacies of implementation from end users. An exceptionally transparent system provides significant flexibility to the end user/application developer as it necessitates minimal or no understanding of the underlying intricacies on their part. In the context of a conventional centralized database, transparency refers specifically to the ability of application developers to achieve logical and physical data independence. In a distributed database (DDB) situation, the data and software are spread among numerous nodes that are linked by a computer network. This introduces various forms of transparencies. The user should not be aware of the ability of a DDBE designer to partition a table, duplicate the partitions, and store these duplicates at distant locations. This feature ensures full distribution transparency, allowing the user to query the table as if it were stored locally, without any fragmentation or replication.
Figure 4 illustrates various degrees of transparency in DDBMS.
3.1. Data Independence
Data independence is a vital aspect of transparency that we aim in a DBMS. It is also the only type relevant in the framework of a centralized DBMS. It relates to the ability of user applications to withstand changes in data definition and arrangement, as well as the reverse. As is commonly known, data definition occurs on two levels. The data structure is provided at two levels: logical and physical. The former is often referred to as the schema definition, and the latter as the physical data description.
Two distinct forms of data independence can be examined: logical data independence and physical data independence. "Logical data independence" pertains to the resistance of user applications to modifications in the logical structure (schema) of the database. Constraint-free updating of the conceptual schema; not impacted by external schemas or application programs. In order to expand the database (through the addition of a record type or data item), modify the constraints, or reduce the database (through the elimination of a record type or data item), it is possible to modify the conceptual schema.
The Physical independence of data obscures from user applications the specifics of storage architecture. Physical data organization should not be a concern during the development of a user application. Consequently, modifications to data organization implemented for performance purposes should not necessitate adjustments to the user application. The capability to modify the internal schema without impacting the conceptual schema is another way in which it is described. As a result, there is no need for modifications to external schemas. Potential modifications to the internal schema may be necessary due to the reorganization of specific physical files, which may have been accomplished by implementing new access structures, with the intention of enhancing the efficiency of retrieval or updates. In the event that the database retains its existing data, there is no necessity to revise the conceptual framework. By incorporating an access path, for instance, the retrieval efficiency of SECTION documents can be increased.
Physical data independence is generally present in most databases and file environments, where physical details such as the specific position of data on disk, as well as hardware aspects of storage encoding, placement, compression, record splitting, merging, and so on, are hidden from the user. Applications are unaware of these details. On the other side, logical data independence is more difficult to establish since it allows structure and constraint changes without affecting application programs, which is a much stricter requirement. When we have a multiple-level DBMS, the catalog must be enhanced to contain information on how to map requests and data between the levels. The DBMS performs these mappings using additional software that refers to the mapping information in the catalog. Data independence happens when a schema is modified at one level but the schema at the next higher level remains unaltered; only the mapping between the two levels changes. As a result, application programs that use the higher-level schema do not need to be altered.
Example Use Case of Data Independence: Biomedical Research Database by Ira J. [
14] provides a detailed overview of how data independence is employed in biomedical research databases. These databases hold and handle a significant amount of clinical, research, and genomic data that is essential for clinical decision support systems and research projects.
-
Logical Data Independence
Consider a situation in which a biomedical research database needs to be updated to include new genomic biomarkers that are becoming useful for personalized medicine approaches.
The database structure has been changed to integrate the additional genetic biomarkers as new characteristics. Logical data independence ensures that existing programs used by researchers and clinicians to query patient genetic information or track treatment outcomes do not need to be upgraded or made aware of schema changes unless they are specifically modified to accommodate the new data. This ensures that the clinical decision support systems will continue to work properly even if the database schema evolves to include increasingly detailed genetic data.
-
Physical Data Independence
Due to the growing number of complicated genomic data, database managers decide to move the data storage to a more powerful database system designed for large-scale genetic sequences and structured clinical data.
Physical data independence enables the IT team to complete the migration and optimization of data storage without disrupting the frontend apps used by researchers and physicians. This modification comprises the implementation of new data compression algorithms and the use of more efficient indexing systems to accelerate data retrieval. Applications continue to execute data queries without modification, and users do not perceive any service disruptions or changes in how they interact with the system.
3.2. Network Transparency
In centralized database management systems, the only available resource that must be protected from the user is the data (such as., the storage system). In a distributed database environment, actually there is another resource that must be managed in the same way: the network. Preferably, the user should be shielded from the network’s functioning details, even if it means concealing its existence. Then there would be no distinction between database applications running on centralized and distributed databases. This type of transparency is called network transparency as well as distribution transparency.
An analysis of network transparency could be conducted with respect to the data or the services provided. From the perspective of the former, it is advantageous to have a conventional means of accessing services. From the perspective of a database management system, distribution transparency requires that users not specify the location of data storage. There are two distinct categories of distribution transparency: naming transparency and location transparency.
The term
location transparency indicates the fact that the command used to complete a job is independent of both the location of data as well as the system on which the operation is carried out.
Naming transparency implies that each object in the database is assigned a unique name. In the lack of naming transparency, users must include the location name (or identifier) as part of the object name. In
Example Use Case from Reference: Cloud-Based Document Storage Service by [
15], the authors provide a detailed discussion on how cloud-based services, such as Google Drive or Dropbox, implement network transparency to provide a seamless user experience. This example is very useful for seeing how sophisticated underlying network processes are abstracted from the user.
-
Location Transparency
The cloud-based document storage solution enables users to save, view, and manage documents without knowing their physical location. Users interact with the system using a simple interface, which allows them to upload and retrieve documents. Underneath the scenes, the service may distribute and store documents in several data centers around the world, increasing accessibility and redundancy. However, the user can access these documents as if they were all stored on their local device, demonstrating location transparency.
-
Naming Transparency
In the same cloud service, each document is assigned a unique identification that does not correspond to its physical storage location or the server on which it is hosted. This identity enables users to view their files from any internet-connected device, regardless of where the document is really stored in the backend systems. This configuration ensures that even if the service provider reorganizes the data across its servers or relocates it to multiple data centers to improve load balancing and performance, the user experience stays consistent and unaffected.
3.3. Mobility (Migration) Transparency
Mobility Transparency enables the relocation of resources or systems with minimal impact on software or user processes. Additionally, it improves the load balancing for any overloaded consumer. Web pages and the Network File System (NFS) are a few examples. Transparency regarding mobility enables clients and resources to circulate within a system without impacting the functionality of users or programs. An example that exemplifies the concept of mobility transparency is mobile phones. Consider that the receiver and the callee are transiting from one environment (cell) to another while traveling by train through various regions of the country. The caller’s phone is considered the client’s and the callee’s phone is considered a resource. The two individuals engaged in the conversation are not cognizant of the resource and client phones’ ability to transition between frequencies.
3.4. Replication Transparency
To achieve optimal performance, dependability, and availability, it is typically advantageous to distribute data in a duplicated manner across the devices inside a network. Replication improves performance by facilitating the accommodation of inverted and conflicting user demand. For instance, data that is often accessed by one user can be stored both on that person’s local system and on the machine of another user who has the same access needs. This enhances the proximity of the reference. In addition, in the event of a machine failure, redundant copies of the data are stored on other machines within the network. Naturally, this is an overly simplistic portrayal of the problem. The decision of whether to replicate a database object and how many copies to have depends significantly on the user applications.
The issue of data duplication raises the question of whether users ought to be notified of the existence of multiple copies or whether the system should handle copy management and permit users to interact with the data as if there is a single copy. (Please note that the presence of duplicates is the only point under discussion; their arrangement or location are unrelated.) As perceived by the user, the solution is self-evident. It is preferable to evade the obligation of duplicate management and clearly indicate the necessity for action regarding multiple copies. A systems perspective reveals that the circumstance is more complex. Providing the user with the responsibility of specifying which instances should undergo a particular operation facilitates transaction management for distributed database management systems. Nevertheless, partaking in such behaviors inevitably results in a reduction of adaptability. The determination regarding the quantity and necessity of duplicates is left to the discretion of the user application, not the system. Any modification to these assessments as a result of various factors unquestionably affects the user application and, as a result, substantially reduces data independence. In the event that In light of the aforementioned considerations, replication transparency should be a standard feature of database management systems. Transparency regarding replication refers more precisely to the existence of replicas than to their precise locations. Noting that the dissemination of these duplicates in an imperceptible or concealed manner is the duty of network transparency is essential.
Data replication is the procedural undertaking of establishing duplicate copies of data across multiple interconnected locations via a computer network. Fragment duplicates may be maintained in various locations in order to satisfy particular information requirements. Data duplication can reduce communication and overall inquiry expenses, whereas fragment duplication can enhance data accessibility and response time.
To illustrate, suppose database A is divided into two distinct sections, denoted as A1 and A2. Within a distributed replica database. At Sites S1 and S2, fragment A1 is maintained, while fragment A2 is kept at Sites S2 and S3. It is imperative that replicated data conforms to the mutual consistency rule, which stipulates that every duplicate of a data item must be exact. It is the responsibility of the Distributed Database Management System (DDBMS) to ensure that all staging areas where database copies are stored are updated in real time whenever modifications are made to the database. This is essential for maintaining data consistency throughout all replicas. Pull Replication and Push Replication are the two fundamental types of replication.
-
Push Replication
After a modification is made to the data, the originating DP node notifies the replica nodes of the modifications to ensure that the data is immediately updated. This type of replication prioritizes data consistency. However, due to the latency required to assure data consistency across all nodes, data availability is diminished.
-
Pull Replication
After updating data, the originating DP node notifies the replica nodes via "messages" that the update has occurred. The replica nodes are responsible for determining when updates are applied to their local fragment. This replication method delays the propagation of data modifications to replicas. Priority is given to guaranteeing data availability. Nevertheless, this form of replication permits momentary inconsistencies in the data. Replication offers numerous benefits, including enhanced data availability, increased tolerance for data failures, improved load distribution, and reduced query costs. However, it also contributes to the processing overhead of DDBMSes as the system is required to maintain each data clone.
The choice as to whether to use data replication is influenced by several factors, including database size. The amount of data copied will affect storage and transmission costs. Usage frequency. The frequency with which data is used determines how often it needs to be updated. Frequently used data needs to be updated more frequently, particularly huge data sets that are only utilized once every quarter. Replication transparency is also associated with concurrency transparency and failure transparency. Whenever a user makes changes to a data item, the modifications are immediately applied to all copies of the table. Nevertheless, it is imperative that the user remains unaware of this operation.
3.5. Concurrency Transparency
Both applications and users should be able to use shared data or objects without interfering with one another. This necessitates extremely complicated processes in a distributed system, as genuine concurrency exists rather than the simulated concurrency of a central system. Shared objects are accessible simultaneously [
16]. Concurrency control and implementation are difficult tasks. The
examples include NFS and ATM networks. Concurrency transparency allows many processes to run concurrently on shared resources without interfering with one other.
3.6. Failure Transparency
Facilitates the concealment of malfunctions, enabling users and application programs to carry out operations notwithstanding the failure of hardware or software components. Access transparency mechanisms ensure tolerance for faults (18). Distributed systems are more susceptible to failure due to the fact that any of the components may malfunction, leading to a complete or degraded service interruption. Differing between a malfunctioning and a sluggish operation is a difficult task due to the obscured complexities. Database management systems serve as exemplary instances. Failure transparency is a feature that obscures flaws, enabling users and application programs to carry out tasks despite the failure of hardware or software components. It can also be demonstrated through the use of electronic correspondence, which remains operational despite failures of communication networks or servers. Errors are concealed by retransmitting messages until they are transmitted successfully, a process that may require multiple days. Network and process failures are converted to programming-level exceptions by middleware.
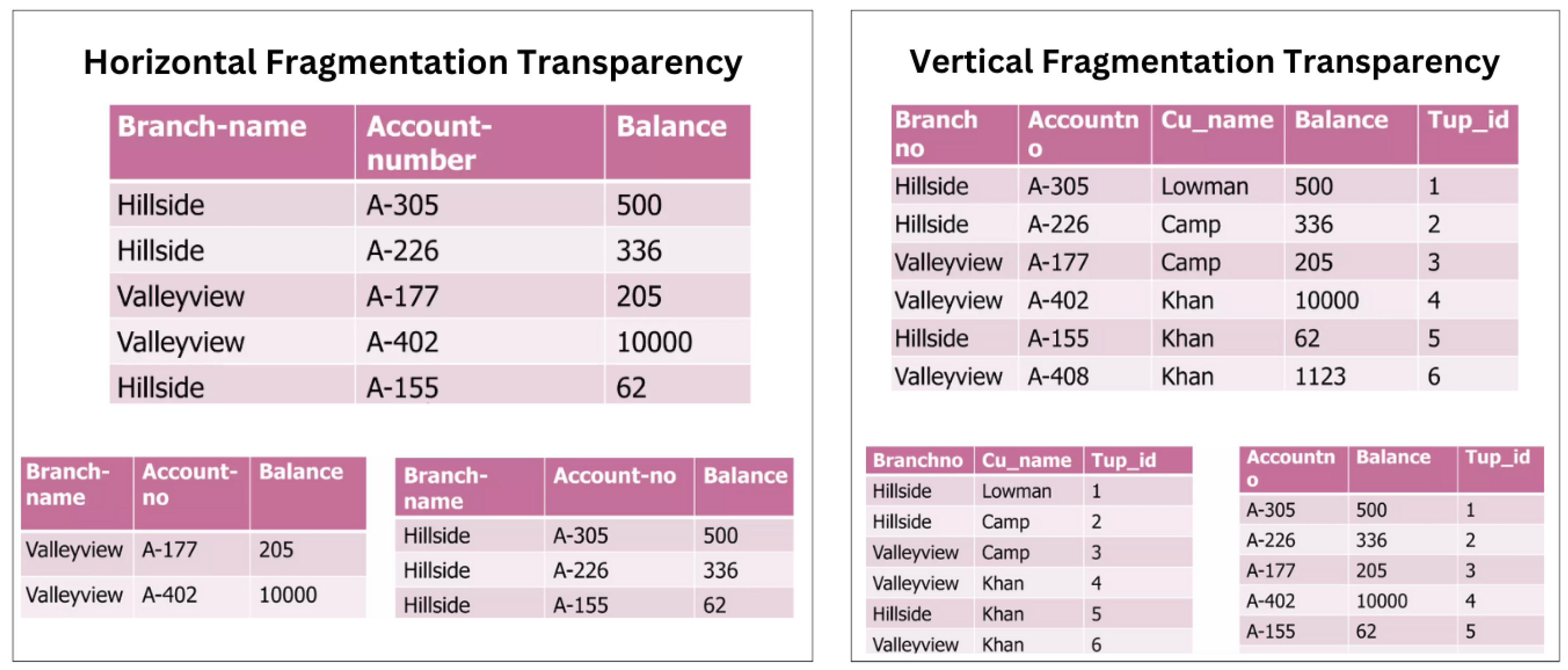
3.7. Fragmentation Transparency
It is usual practice to break each database relation into smaller fragments and use each fragment as a separate database object. This is often done for reasons of efficiency, accessibility, and dependability. Furthermore, fragmentation might mitigate the detrimental consequences of replication. Each replica is a portion of the full relation, requiring less space and fewer data items to manage.
Figure 5 shows two sorts of fragmentation alternatives. Horizontal fragmentation involves partitioning a relation into sub-relations, each with a subset of the original relation’s tuples (rows). The second option is vertical fragmentation, which defines each sub-relation based on a subset of the original relation’s properties (columns).
Goebel V. (2011) mentions a third sort of fragmentation transparency,
Mixed fragmentation, which combines horizontal and vertical techniques. For example, a table can be divided into horizontal subsets (rows), each with a subset of the attributes (columns), [
17].
We face the challenge of managing user queries that are provided for complete relations but require execution on subrelations when database objects are fragmented. Put simply, the challenge lies in developing a query processing approach that utilizes fragments instead of relations, even though the inquiries are specified in the latter. This process generally entails converting a "global query" into "several fragment queries."
3.8. Performance Transparency
Performance transparency in a DDBMS indicates to the system’s capacity to dynamically adapt to changing workload needs. This level of openness ensures that the system may be adjusted, optimized, or scaled to handle changing loads without requiring manual intervention or causing noticeable downtime for end users.
In practice, performance transparency entails automatic load balancing, effective data replication mechanisms, and real-time monitoring of system performance to prompt changes. A DDBMS can divide query loads over many servers or dynamically allocate resources to performance-critical jobs in response to rising demand. Examples of Performance Transparency in DDBMS Techniques Dynamic resource allocation, Computing resources are automatically adjusted based on real-time workload and performance indicators. Automatic load balancing. Data and query requests are distributed efficiently over the network to improve response times and reduce latency. Query Optimization. Changing query execution plans based on the current system status and data distribution.
3.9. Scaling Transparency
The system and applications can scale without affecting the structure or algorithms ,[
8]. Scaling transparency enables a DDBMS to grow or contract its size, both in terms of data volume and user count, without requiring adjustments to the system’s design or application algorithms. This kind of openness is critical for systems that must handle data or user growth seamlessly.
Scaling transparency is achieved using strategies that enable the system to scale horizontally (add more nodes) or vertically (add additional resources to existing nodes) without interfering with the application’s activities. It ensures that when the system scales, the applications operating on top of it are not required to be rewritten or substantially modified, keeping a consistent interface and behavior, [
18].
Scaling transparency relies on automatic data partitioning across numerous databases to efficiently manage huge datasets. Elastic Scalability refers to the system’s ability to dynamically add or remove resources and nodes based on current needs without stopping service. Distributed Query Processing optimizes query processing in a distributed architecture to prevent system expansion from degrading performance.
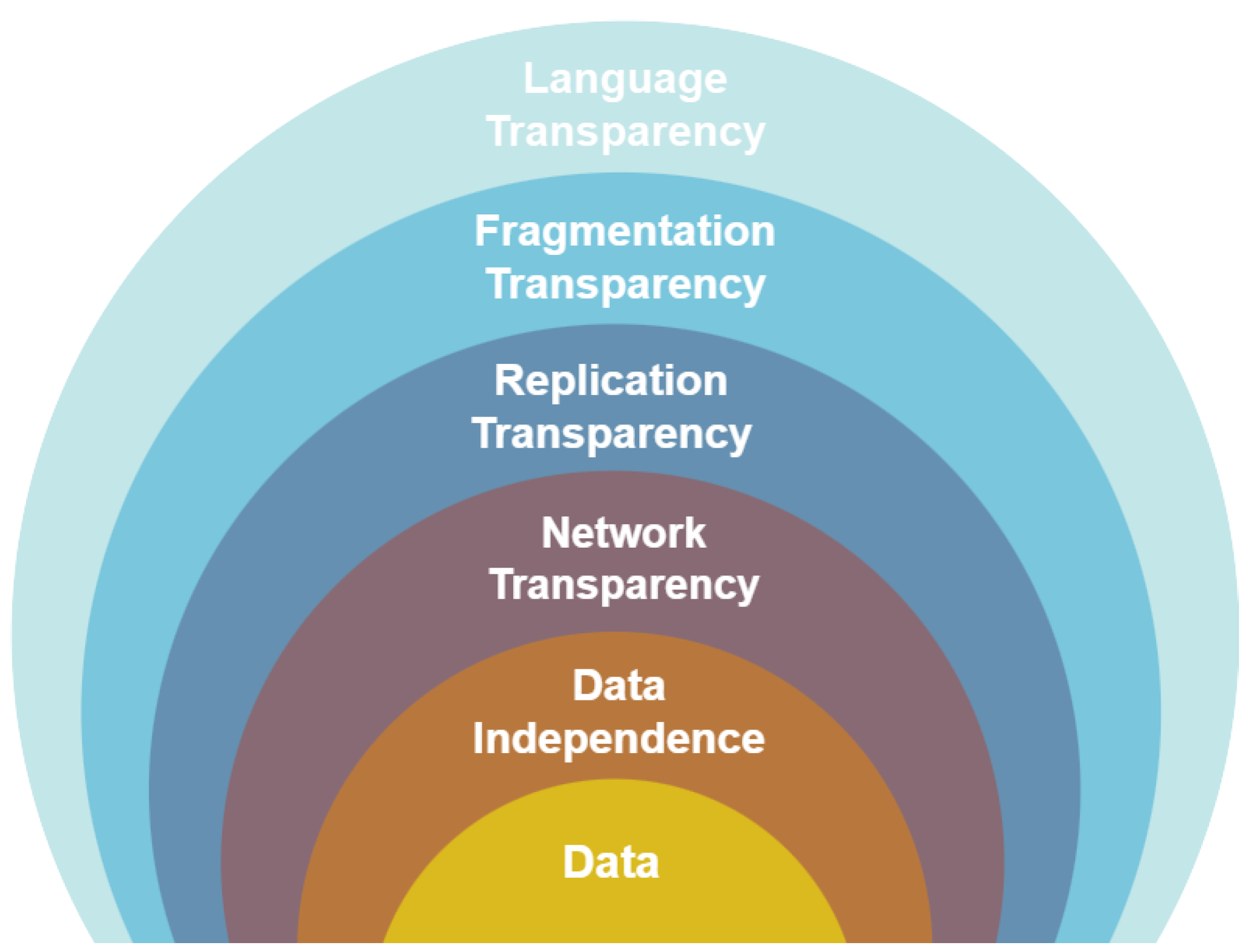
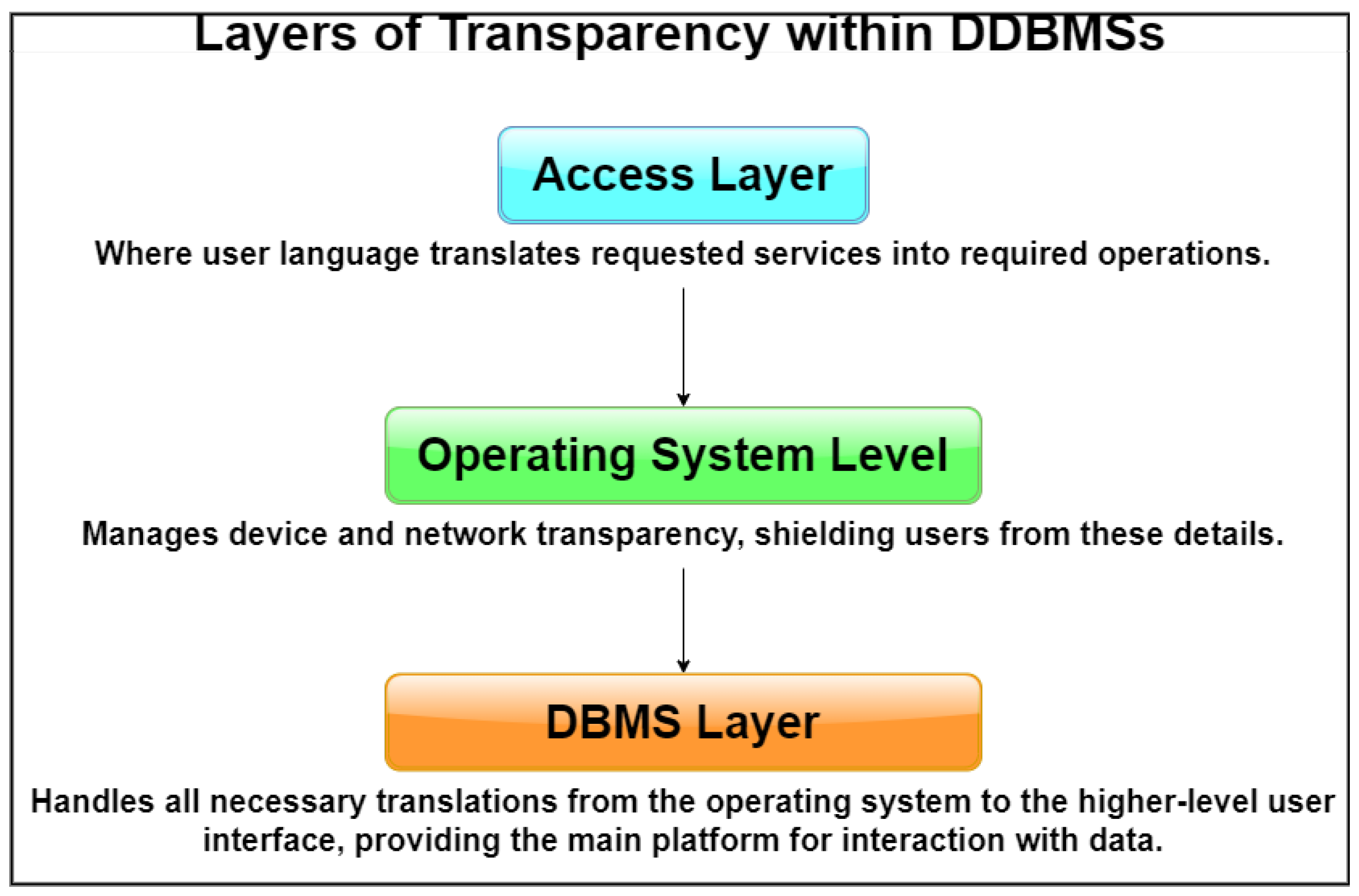
Who is Responsible for Providing Transparency?
To ensure an ideal user experience, it is critical to establish a database management system (DBMS) that provides access to all the previously mentioned service types in a seamless and intuitive manner. Nevertheless, it is critical to strike a balance between the expenses and difficulties associated with upholding elevated levels of transparency and the ease of use for users. Three distinct tiers exist within which transparency services may be provided. While it is common for individuals to perceive these as distinct methods of service provision, it is more precise to characterize them as interdependent.
The responsibility of guaranteeing transparent access to data resources could be delegated to the access layer. The integration of transparency features into the user language enables the translation of requested services into essential operations in a seamless manner. In essence, the compiler or interpreter performs the operation without providing the implementer with any transparent services.
Operating system-level transparency can be implemented as well, thereby incorporating an additional stratum into the system. Contemporary operating systems provide consumers with a certain level of transparency. From the perspective of an IT project manager, it is evident that the complex operations of the operating system are managed by the device drivers, which ensure that every peripheral device executes the intended functions. In most cases, application programmers and common computer users do not need to be concerned with developing device drivers in order for peripheral devices to function. This procedure is executed in the background, allowing users to concentrate on their assignments without any inconvenience. It is feasible to provide operating system-level transparent access to resources within a distributed environment. If a distributed database management system is implemented, network resource management is in this instance managed by the middleware or distributed operating system. There are several concerns that require attention regarding this methodology. It is noteworthy that not all distributed operating systems that are commercially available provide an adequate degree of transparency with regard to network management. An additional concern emerges when specific applications desire access to the complexities of distribution in order to fine-tune performance without being shielded from them.
At the third layer, the DBMS can provide support for transparency. In general, the transparency and support provided by the underlying operating system for database functions are considerably restricted. Typically, it exclusively addresses fundamental operations that are essential for particular duties. The DBMS is tasked with the responsibility of managing all necessary translations that occur between the operating system and the elevated user interface. This method of operation is prevalent across numerous industries. However, there are a number of concerns that emerge when the DBMS is entrusted with the responsibility of guaranteeing absolute transparency. Extensive coverage of these subjects in this book pertains to the interaction between the distributed DBMS and the operating system. The arrangement of the transparencies is illustrated in a hierarchical fashion in
Figure 6.
4. Summary
This in-depth investigation has explored the complexities of Distributed Database Management Systems (DDBMS), explaining their structural foundations, operational dynamics, and the crucial importance of transparency in their efficient management. With a focus on technological advancements as well as changing data management paradigms, the discussion highlights the evolution of DDBMS from foundational definitions to advanced operational frameworks.
In the earlier parts of the article, important terms were defined and the complex nature of DDBMS was examined. The concept of "distributed" was explained in the context of computer networks, where data processing and storage are not limited to one location but are instead managed across multiple nodes. With this setup, data accessibility and system reliability are greatly improved, making it ideal for complex applications that need strong data interaction across different geographical locations.
The discussion primarily revolved around the importance of transparency in DDBMS. This is crucial as it helps to hide the intricacies of distributed systems from the end-user, making interactions simpler and improving system usability. Different forms of transparency were examined, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of DDBMS. These include data, replication, performance, scaling, and network transparency. The importance of data independence, a type of transparency, was highlighted due to its ability to facilitate system expansion and reconfiguration without affecting user applications.
The advantages of adopting DDBMS were clearly explained, highlighting the improved reliability, responsiveness, and cost-efficiency as the main benefits. These systems offer a strong foundation that guarantees uninterrupted data access, even when individual components encounter issues. This ensures that business operations can continue smoothly, regardless of any technical obstacles.
In
Section 5, the article discussed future trends and potential research directions that could have an impact on the development of DDBMS in the coming years. It accurately anticipated the integration of DDBMS with advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and blockchain. These technologies are poised to bring about substantial improvements in data processing, security, and system sustainability. These advancements indicate a future where DDBMS will be even more autonomous and secure, while also being better equipped to handle the growing complexities of global data management requirements.
Figure 7, which showcases the various transparencies available in DDBMSs and provides a comprehensive summary of all transparency types in DDBMS.
5. Future Advice
Technological advancements and evolving data administration requirements are substantial factors influencing the development of Distributed Database administration Systems (DDBMS). The aforementioned forecasts underscore prospective developments and their potential ramifications for DDBMS technologies.
The data trends highlighted in
Table 1 indicate a move towards more autonomous, secure, and effective data management solutions that are in harmony with recent technological progress and societal needs. Given the evolving nature of DDBMS, several research areas are crucial for the advancement of the field. Addressing these issues presents a significant opportunity to improve the functionality, efficiency, and application of DDBMS across different industries.
DDBMS that adjusts itself: In order to handle shifting workloads and urgent data needs, researchers have concentrated on developing database management systems (DBMS) that dynamically adapt their performance and resource allocation.
Distributed Environment Security: DDBMS security measures have been reinforced, particularly to fend off the recent wave of cyberattacks and adhere to stringent data protection regulations.
Hyper-Transactional/Analytical Processing (HTAP): There is continuous work to create adaptable systems that can handle transactional and analytical tasks with ease, guaranteeing efficacy and efficiency.
DDBMS Integration with IoT: The project has looked at several architectures and techniques for integrating DDBMS with the Internet of Things (IoT) in order to manage the massive volume of data coming in from many devices.
Localization and Data Sovereignty: The difficult legal and technological issues involved in managing data internationally and satisfying the data residency requirements of global DDBMS installations are addressed in this field of research.
Conclusion
The future of distributed database management systems (DDBMS) hinges on the intersection of innovation and the growing demand for data processing capabilities. By directing research efforts towards these areas, the field can advance towards creating resilient, intelligent, and efficient systems, ensuring that DDBMS remains a cornerstone for current data-driven applications.
This evaluation not only scrutinized the state of DDBMS but also laid out a roadmap for future advancements. It calls for exploration into developing intricate, secure, and user-friendly DDBMS that can address the challenges of an increasingly data-centric world. Incorporating emerging technologies into DDBMS frameworks has the potential to revolutionize data management practices, keeping these systems at the forefront of progress while offering support for a wide range of applications relying on extensive distributed data environments.
References
- Noah Webster. Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary: Eleventh Edition. Logos Bible Software. Merriam-Webster, Incorporated, 2004. ISBN 9780877798095. URL https://books.google.com.tr/books?id=TAnheeIPcAEC.
- S.K. Rahimi and F.S. Haug. Distributed Database Management Systems: A Practical Approach. Wiley, 2010. ISBN 978-0-470-60236-2. URL https://books.google.com.tr/books?id=0TqLzJBGImcC.
- A.S. Tanenbaum and M. van Steen. Distributed Systems. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2017. ISBN 978-1-5430-5738-6. URL https://books.google.com.tr/books?id=c77GAQAACAAJ.
- Okungbowa Aihanuwa Augusta Seji Happy Alfred and Lambo Kenibanemi Egi. Impact of distributed database management system to individuals, institutions and organizations all over the world. BW Academic Journal, 1(1):10, 2022. URL https://www.bwjournal.org/index.php/bsjournal/article/view/758.
- Ramez Elmasri and Sham Navathe. Fundamentals of database systems. Pearson, seventh edition edition, 2016. ISBN 0-13-397077-9 978-0-13-397077-7 978-1-292-09761-9 1-292-09761-2.
- Okardi Biobele and Asagba O. Prince. Overview of distributed database system. International Journal of Computer Techniques, 2021. ISSN 2394-2231. URL http://www.ijctjournal.org.
- Philip A. Bernstein and Eric Newcomer. Principles of Transaction Processing (Second Edition). The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Data Management Systems. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, second edition edition, 2009. ISBN 978-1-55860-623-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-55860-623-4.00013-5. URL https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781558606234000135.
- M. Tamer Özsu and Patrick Valduriez. Principles of Distributed Database Systems. Springer, 4th edition, 2020.
- Edgar F. Codd. A relational model of data for large shared data banks. Communications of the ACM, 13(6):377–387, 1970. [CrossRef]
- Stefano Ceri and Giuseppe Pelagatti. Distributed Databases: Principles and Systems. McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1984.
- Andrew S. Tanenbaum and Maarten Van Steen. Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms. Prentice Hall, 1994.
- Theo Härder, Erhard Rahm, and Harald Schöning. Data management in the cloud: Challenges and opportunities. it - Information Technology, 53(4):181–185, 2011.
- Alejandro Corbellini, Cristian Mateos, Alejandro Zunino, Daniela Godoy, and Silvia Schiaffino. Handling big data: Research challenges and future directions. Journal of Computer Science & Technology, 18(2):e33, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Ira J. Kalet. List of figures. In Principles of Biomedical Informatics (Second Edition). Academic Press, San Diego, second edition edition, 2014. ISBN 978-0-12-416019-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416019-4.00018-4. URL https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124160194000184.
- George Coulouris, Jean Dollimore, and Tim Kindberg. Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design. Addison-Wesley, 5th edition, 2011.
- Sudheer R Mantena. Transparency in distributed systems. The University of Texas at Arlington, 2019.
- Vera Goebel. Distributed database systems. Department Informatics, University of Oslo, Oslo, 2011.
- Ajay D. Kshemkalyani and Mukesh Singhal. Distributed Computing: Principles, Algorithms, and Systems. Cambridge University Press, 2011.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).