Submitted:
18 April 2024
Posted:
19 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
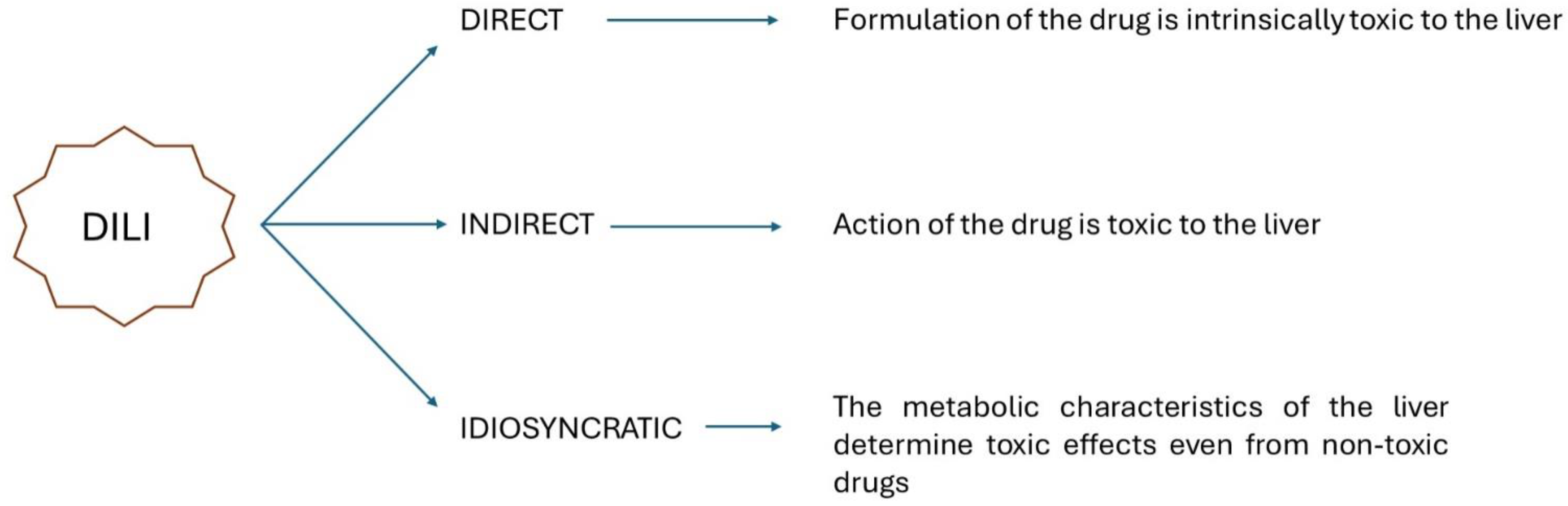
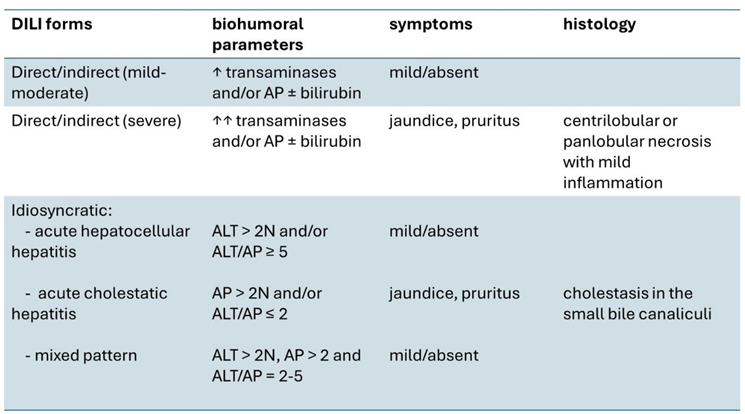
1. Introduction
2. Compounds of 5-aminosalicylic Acid
3. Immunosuppressants
4. Biologic Therapies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a comprehensive review. Front. Med. (Lausanne). 2021, 20, 8:765474. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Abbas, A.M.; Whang, N.; Balart, L.A.; Bazzano, L.A.; Kelly, T.N. Incidence of liver toxicity in inflammatory bowel disease patients treated with methotrexate: a meta-analysis of clinical trials. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2012, 18, 359–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, F.P.; Quera, R.; Bay, C.; Castro, F.; Mezzano, G. Drug-Induced Liver Injury used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns. Colitis. 2022, 16, 1168–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of acute (fulminant) liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1047-81.
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Björnsson, E.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury - Types and Phenotypes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 264–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.J.; Senior, J.R. Drug-related hepatotoxicity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 731–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, B.; Zaldana, F.; Liu, C. The pathology of acute liver failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 257–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, F.; López-Sanromán, A.; Algaba, A.; Van-Domselaar, M.; Gisbert, J.P.; García-Garzón, S.; Garrido, E.; Piqueras, B.; De La Poza, G.; Guerra, I. Mercaptopurine rescue after azathioprine-induced liver injury in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 120–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Fontana, R.; Lee, W.; Stolz, A.; Talwalkar, J.K.; Reddy, R.; Watkins, P.B.; Navarro, V.; Barnhart, H.; et al. Features and outcomes of 889 patients with drug-induced liver injury: the DILIN Prospective Study. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1340–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Chalasani, N.P.; Lee, W.M.; Fontana, R.J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Watkins, P.B.; Hayashi, P.H.; Davern, T.J.; Navarro, V.; Reddy, R.; et al. Hepatic histological findings in suspected drug-induced liver injury: systematic evaluation and clinical associations. Hepatology 2014, 59, 661–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.A.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Fontana, R.J.; Stolz, A.; Kleiner, D.E.; Hayashi, P.H.; Gu, J.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Chalasani, N. Clinical and histologic features of azithromycin-induced liver injury. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 369–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarey, D.; Verma, S. Drug-induced liver injury. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, s104–s109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Bonkovsky, H.L. Fontana, R.; Lee, W.; Stolz, A.; Talwalkar, J.; Reddy, K.R.; Watkins, P.B.; Navarro, V.; Barnhartet, H.; al. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: the DILIN prospective study. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1340–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuto, M.; Catanzaro, R. Composition of gut microbiota and its correlations with neurological, intestinal, cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2023, 70, 259–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.K.; Ai, Y.; Cheng, Z.L.; Yang, L.; Hou, X.H. Contribution of gut microbiota to drug-induced liver injury. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2023, 22, 458–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Lv, L.; Shi, D.; Ye, J.; Fang, D.; Guo, F.; Yating, Li.; He, X.; Li, L. Protective effect of Akkermansia muciniphila against immune-mediated liver injury in a mouse model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8:1804. [CrossRef]
- Heidari, R.; Rasti, M.; Shirazi Yeganeh, B.; Niknahad, H.; Saeedi, A.; Najibi, A. Sulfasalazine-induced renal and hepatic injury in rats and the protective role of taurine. Bioimpacts 2016, 6, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, F.P.; Castro, F.; Mezzano, G.; Quera, R.; Diaz, D.; Castro, L. Hepatobiliary manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease: a practical approach. World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 319–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Aboubakr, A.; Narula, N. Systematic review: safety of mesalazine in ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Haens, G.; Safroneeva, E.; Thorne, H.; Laoun, R. Assessing the clinical and endoscopic efficacy of extended treatment duration with different doses of mesalazine for mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis beyond 8 weeks of induction. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2023, 8, 51–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Shi, Y.; Ge, Z.; Qian, J. Effects of mesalamine combined with live combined Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and Enterococcus capsules on intestinal mucosa barrier function and intestinal microbiota in mildly active Crohn's disease patients. J. Invest. Surg. 2024, 37, 2297565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhill, M.S.; Steinberg, J.M.; Jennings, J.J.; Lewis, J.H. Hepatotoxicty of agents used in the management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: a 2020 update. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 22, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Aboubakr, A.; Narula, N. Systematic review: safety of mesalazine in ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Nishida, T.; Osugi, N.; Kitanaka, T.; Minoura, Y.; Okabe, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Fujii, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Nakamatsu, D.; et al. 5-Aminosalicylic acid-induced liver injury in a patient with ulcerative colitis: a case report. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2024, 18, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Horst, P.; Smolders, E.J.; den Besten, D. Mercaptopurine and metabolites in breast milk. Breastfeed Med. 2020, 15, 277–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.R.; Coenen, M.J.H.; Derijks, L.J.J.; Vermeulen, S.H.; van Marrewijk, C.J.; Klungel, O.H.; Scheffer, H.; Franke, B.; Guchelaar, H.J.; de Jong, D.J.; et al. Early prediction of thiopurine-induced hepatotoxicity in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, G.; Martelossi, S.; Barabino, A.; Decorti, G., Bartoli, F.; Montico, M.; Gotti, A.; Ventura, A. Glutathione-S-transferase genotypes and the adverse effects of azathioprine in young patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2007, 13, 57–64. [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, O.S.; Lewis, J.H. Hepatotoxicity of agents used in the management of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 508–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.; Ordas, I.; Cabre, E.; Garcia-Sanchez, V.; Bastida, G.; Peñalva, M.; Gomollón, F.; García-Planella, E.; Merino, O.; Gutiérrez, A.; et al. Safety of thiopurine therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: long-term follow-up study of 3931 patients. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2013, 19, 1404–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekman, M.; Coenen, M.; Marrewijk, C.; Wanten, G.J.A; Wong, D.R. , Verbeek, A.L.M.; Klungel, O.H.; Hooymans, P.M.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Scheffer, H.; et al. More dose-dependent side effects with mercaptopurine over azathioprine in IBD treatment due to relatively higher dosing. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2017, 23, 1873–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsson, E.; Gu, J.; Kleiner, D.; Chalasani, N.; Hayashi, P.H; Hoofnagle, J.H.; DILIN Investigators. Azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine induced liver injury: clinical features and outcomes. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 63–9.
- Schwartz, B.; Al-Sabti, R.; Reau, N. Late-onset acute liver injury from Azathioprine. ACG Case Rep. J. 2022, 9, e00847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, K.; Sasaki, E.; Higuchi, S.; Takai, S.; Tsuneyama, K.; Fukami, T.; Nakajima, M.; Yokoi, T. Involvement of oxidative stress and immune- and inflammation-related factors in azathioprine-induced liver injury. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 224, 215–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munnig-Schmidt, E.; Zhang, M.; Mulder, C.J.; Barclay, M.L. Late-onset rise of 6-MMP metabolites in IBD patients on azathioprine or mercaptopurine. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 892–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierik, M.; Rutgeerts, P.; Vlietinck, R.; Vermeire, S. Pharmacogenetics in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 3657–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Patients with IBD receiving Methotrexate are at higher risk of liver injury compared with patients with non-IBD diseases: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Front. Med. (Lausanne). 2021, 8, 774824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feagan, B.G.; McDonald, J.W.; Panaccione, R.; Enns, R.A.; Bernstein, C.N.; Ponich, T.P., Bourdages, R.; Macintosh, D.G., Dallaire, C.; Cohenet, A.; al.. Methotrexate in combination with infliximab is no more effective than infliximab alone in patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2014, 146, 681–8.
- Fournier, M.R.; Klein, J.; Minuk, G.Y.; Bernstein, C.N. Changes in liver biochemistry during methotrexate use for inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105:1620–6. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Lama, Y.; Taxonera, C.; Lopez-Sanroman, A.; Perez-Calle, J.L.; Bermejo, F.; Pajares, R.; McNicholl, A.G.; Opio, V.; Mendoza, J.L.; López, P.; et al.. Methotrexate in inflammatory bowel disease: a multicenter retrospective study focused on long-term efficacy and safety. The Madrid experience. Euro. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 1086–91.
- Lie, E.; van der Heijde, D.; Uhlig, T.; Heiberg, M.S.; Koldingsnes, W.; Rodevand, E.; Kaufmann, C.; Mikkelsen, K.; Kvienet, T.K. Effectiveness and retention rates of methotrexate in psoriatic arthritis in comparison with methotrexate-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheumatic. Dis. 2010, 69, 671–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askari, B.S.; Krajinovic, M. Dihydrofolate reductase gene variations in susceptibility to disease and treatment outcomes. Curr. Genomics. 2010, 11, 578–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejnovic, D.; Milic, V.; Popovic, B.; Damnjanovic, T.; Maksimovic, N.; Bunjevacki, V.; Krajinović, M.; Novaković, I.; Damjanov, N.; Jekić, B. Association of C35T polymorphism in dihydrofolate reductase gene with toxicity of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Expert Opin. Drug. Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 253–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.P.; Santos, F.P.; Branco, J.C. Methotrexate: Implications of pharmacogenetics in the treatment of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. ARP Rheumatol. 2022, 1, 225–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rundquist, S.; Sachs, M.C.; Eriksson, C.; Olén, O.; Montgomery, S.; Halfvarson, J.; SWIBREG Study Group. Drug survival of anti-TNF agents compared with vedolizumab as a second-line biological treatment in inflammatory bowel disease: results from nationwide Swedish registers. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 53, 471-83. [CrossRef]
- Ghabril, M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Kum, C.; Davern, T.; Hayashi, P.H.; Kleiner, D.E.; Serrano, J.; Rochon, J.; Fontana, R.J.; Bonacini, M.; US Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network. Liver injury from tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists: analysis of thirty-four cases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 558-64. [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, H.K.; Gudbjornsson, B.; Björnsson, E.S. Infliximab-induced liver injury: clinical phenotypes, autoimmunity and the role of corticosteroid treatment. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, R.; Kaur, N. Liver injury secondary to anti-TNF-alpha therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: a case series and review of the literature. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2014, 956463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aby, E.S.; Lake, J.R.; Vaughn, B.P. The impact of biologics for the management of inflammatory bowel disease on liver enzymes. Clin. Liver Dis. (Hoboken). 2020, 16, 212–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, M.M.; Mansoor, E.; Satyavada, S.; Greer, K.; Xin, W.; Cohen, S.; Cooper, G.; Katz, J. Infliximab-induced acute liver failure in a patient with Crohn’s disease requiring orthotopic liver transplantation. ACG Case Rep. J. 2021, 8, e00586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, I.; O’Beirne, J.; Rossi, R.; Tsochatzis, E.; Manousou, P.; Theocharidou, E.; Hamilton, M.; Murray, C.; Epstein, O.; Burroughs, A.K. Elevated liver enzymes in inflammatory bowel disease: the role and safety on infliximab. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 786–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worland, T.; Chin, K.L.; van Langenberg, D.; Garg, M.; Nicoll, A. Retrospective study of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury from infliximab in an inflammatory bowel disease cohort: the IDLE study. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2020, 33, 162–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, E.S.; Gunnarsson, B.I.; Gröndal, G.; Jonasson, J.G.; Einarsdottir, R.; Ludviksson, B.R.; Gudbjörnsson, B.; Olafsson, S. Risk of drug-induced liver injury from tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 602–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachou, M.; Pikramenos, K.; Panoutsakou, M.; Lalla, E.; Androutsakos, T. Infliximab (IFX)-Biosimilar induced Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI): a case report. Cureus 2022, 14, e32525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, S.; Sawada, K.; Moriichi, K.; Fujiya, M. A case report of drug-induced liver injury due to the infliximab biosimilar CT-P13 on switching from original infliximab in a patient with Crohn's disease. Ther. Adv. Drug. Saf. 2022, 13, 20420986221100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, T.; Galambosova, M.; Filakovska, S.; Kubincova, M.; Hlavaty, T.; Toth, J.; Krajcovicova, A.; Payer, J. Drug-induced liver injury in inflammatory bowel disease: 1-year prospective observational study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4102–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L.; Asmussen, D.; Benson, J. Drug induced-hepatotoxicity with concurrent use of adalimumab and mesalamine for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2015, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Jeen, Y.T. Anti-integrin therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1868–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarenhas Saraiva, M.; Ribeiro, T.; Dias, E.; Lopes, J.; Cardoso, H.; Macedo, G. Vedolizumab-induced liver injury. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 28, 410–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, I.; O’Beirne, J.; Rossi, R.E.; Tsochatzis, E.; Manousou, P.; Theocharidou, E.; Hamilton, M.; Murray, C.; Epstein, O.; Burroughs, A.K. Elevated liver enzymes in inflammatory bowel disease: the role and safety of infliximab. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 786–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombel, J.F.; Sands, B.E.; Rutgeerts, P.; Sandborn, W.; Danese, S.; D'Haens, G.; Panaccione, R.; Loftus Jr, E.V.; Sankoh, S.; Fox, I. The safety of vedolizumab for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2017, 66, 839–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




