1. Introduction
Laser welding has emerged as a promising technique for joining components due to its precision, speed, and ability to create strong and durable welds [
1]. The strength and quality of laser-welded joints can be enhanced by applying ultrasonic energy to the molten pool. The impact of vibrations on the solidification process of molten metal in casting or fusion welding has been extensively studied and researched throughout the twentieth century [
2,
3,
4].
The effect of ultrasonic vibration on the solidification phase significantly impacts on the final structure, mechanical properties, and electrical characteristics of the material [
5]. This is particularly critical when dealing with metal alloys or combinations of dissimilar materials, as observed in lap joining for battery cell connectors in the production of electric vehicle battery packs [
6,
7]. The coexistence of liquid and solid phases, owing to the varying melting points of different metals, leads to the agglomeration of similar particles during solidification, which ideally should be uniformly dispersed throughout the liquid phase [
8]. However, commonly observed phenomena such as voids, gas presence, and variable grain sizes contribute to the degradation of the final material's properties. This degradation gives rise to issues like hot cracking, resulting in fragile battery connections, and high electric impedance, causing energy loss and temperature elevation in battery packs [
9,
10,
11]. The occurrence of acoustic cavitation in the molten pool aids in the fragmentation and shaping of intermetallic compounds, which are the primary culprits behind property degradation. Previous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of ultrasonic waves in this regard [
12].
Khavari et al. [
13] showed the mechanism behind cavitation driven shock waves, vital for optimizing the effectiveness of ultrasound in diverse applications such as sonochemistry and material processing. Subroto et al. [
14] explored the impacts of ultrasonic cavitation melt treatment (UST) on the temperature distribution, sump profile, and resulting microstructure during the direct-chill (DC) casting of an AA6008 aluminium alloy. Utilising experimental setups with and without UST, alongside numerical modelling, the research demonstrates that UST alters the temperature gradients and sump profile, leading to a refined grain structure within the billets.
Liu et al. [
15] presented a comprehensive investigation into enhancing the efficiency of ultrasonic vibration-assisted laser welding through the optimisation of an ultrasonic oscillator's design and eigenfrequency tuning. The optimisation aims at mitigating the effects of high-temperature-induced eigenfrequency drift in ultrasonic systems, a common challenge during ultrasonic-assisted laser welding due to the heat transfer from the welding process. The study establishes a dynamic frequency model for the ultrasonic oscillator, integrating a finite element genetic algorithm and temperature field coupling to predict and adjust for eigenfrequency shifts effectively.
Theoretical aspects of using remote ultrasound vibration to initiate cavitation in the molten pool area during welding is studied by Teyeb et al. [
16]. Through computational simulations, the study identifies optimal positions and frequencies for ultrasound vibration to achieve maximum pressure in the fusion zone, thereby enhancing the welding process. The research demonstrates that side excitation of the plate generates significantly higher vibration displacement amplitudes compared to corner excitation, leading to more effective cavitation and improved welding quality. Their results present a comprehensive theoretical framework for understanding the interaction between ultrasound vibration and cavitation dynamics in welding, offering valuable insights for developing more efficient and high-quality welding techniques.
Zhou et al. [
17] innovatively introduces a follow-up ultrasonic vibration assisted welding process to address common defects in laser welding of dissimilar metals, specifically between Hastelloy C-276 and stainless steel 304, critical for nuclear reactor pump can end sealing. The process demonstrates significant improvement in the microstructure and mechanical properties of the weld joint, attributing to the optimised application of ultrasonic vibration.
Lei et al. [
18] addresses the challenges of welding porosity and poor weld formability in laser welding processes of magnesium alloys, specifically the AZ31B magnesium alloy. By employing an experimental approach to ultrasonic assisted laser welding, the research delineates significant enhancements in welding characteristics, including weld defect reduction and microstructure improvements. The introduction of ultrasonic vibration to the weld pool results in a notable decline in weld porosity from 4.3% to 0.9%, alongside a reduction in the average size of porosities.
In this paper, an investigation is carried out on the use of contactless ultrasonic vibration assistance to improve welding quality. This type of remote vibration is sometimes required when contact vibration is not feasible. For instance, in the case discussed here, such as in the welding of a car battery, it is crucial to avoid subjecting the battery to high-power ultrasound vibrations that may cause damage to its internal components. The investigation begins with the description of the current battery holder for laser welding in
Section 2. A simplified holder and plates are utilised in
Section 3 for the purpose of ultrasonic welding, followed by the analysis of data regarding pull test results and extension values. In
Section 4, the same experimental study is replicated, and microscopy tests are conducted. In
Section 6, numerical simulations using COMSOL Multiphysics are performed to elucidate some of the experimental findings. Finally, conclusions are drawn in
Section 7.
2. Experimental Configuration
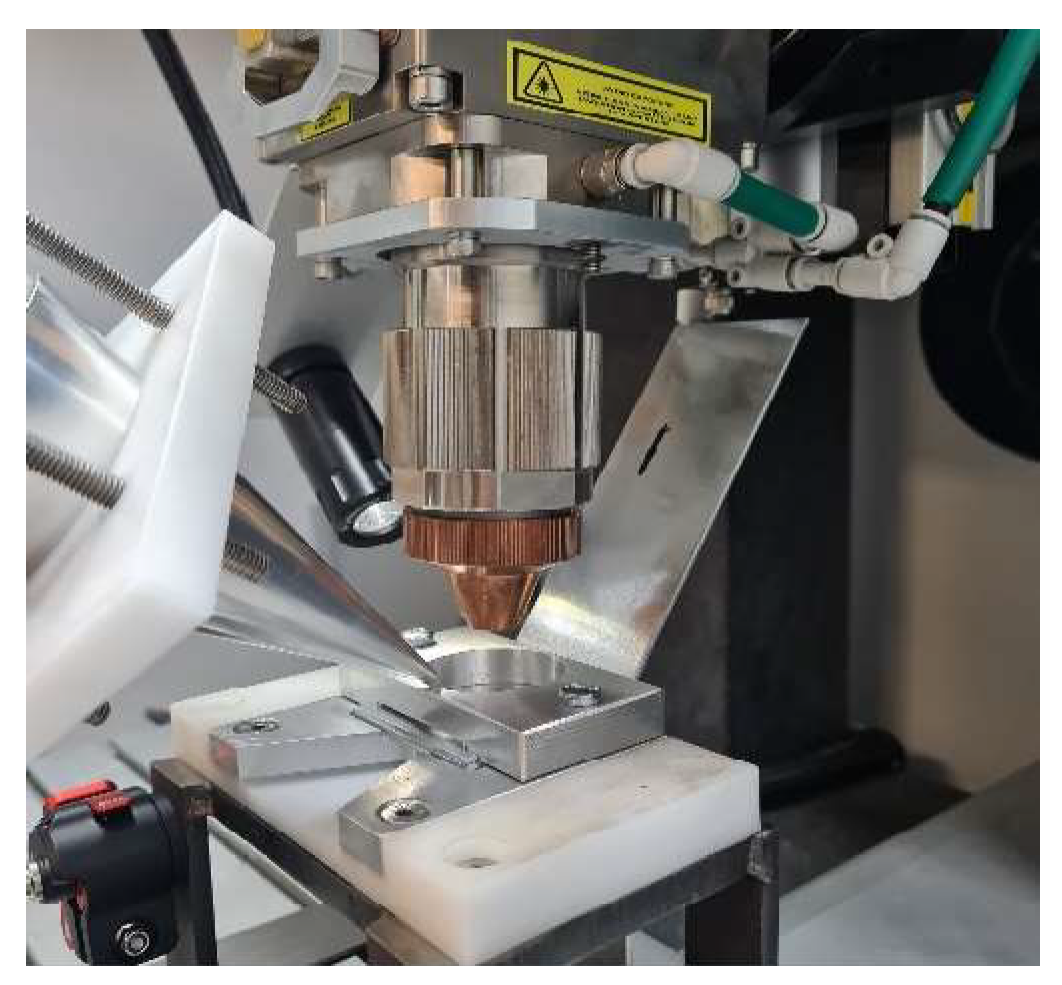
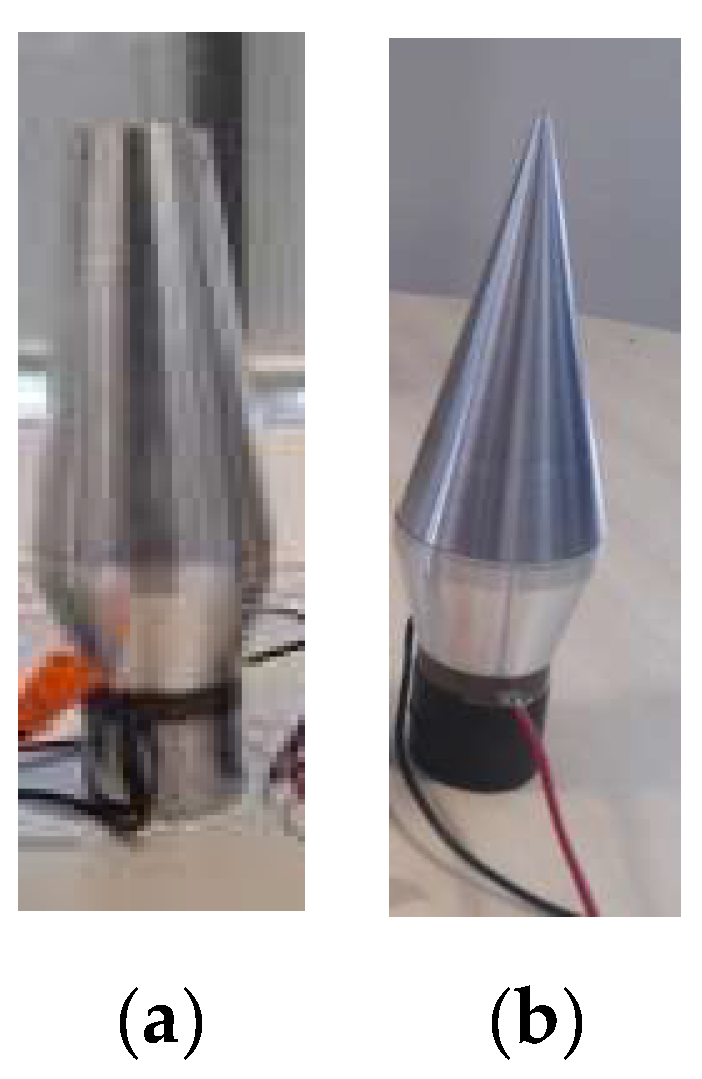
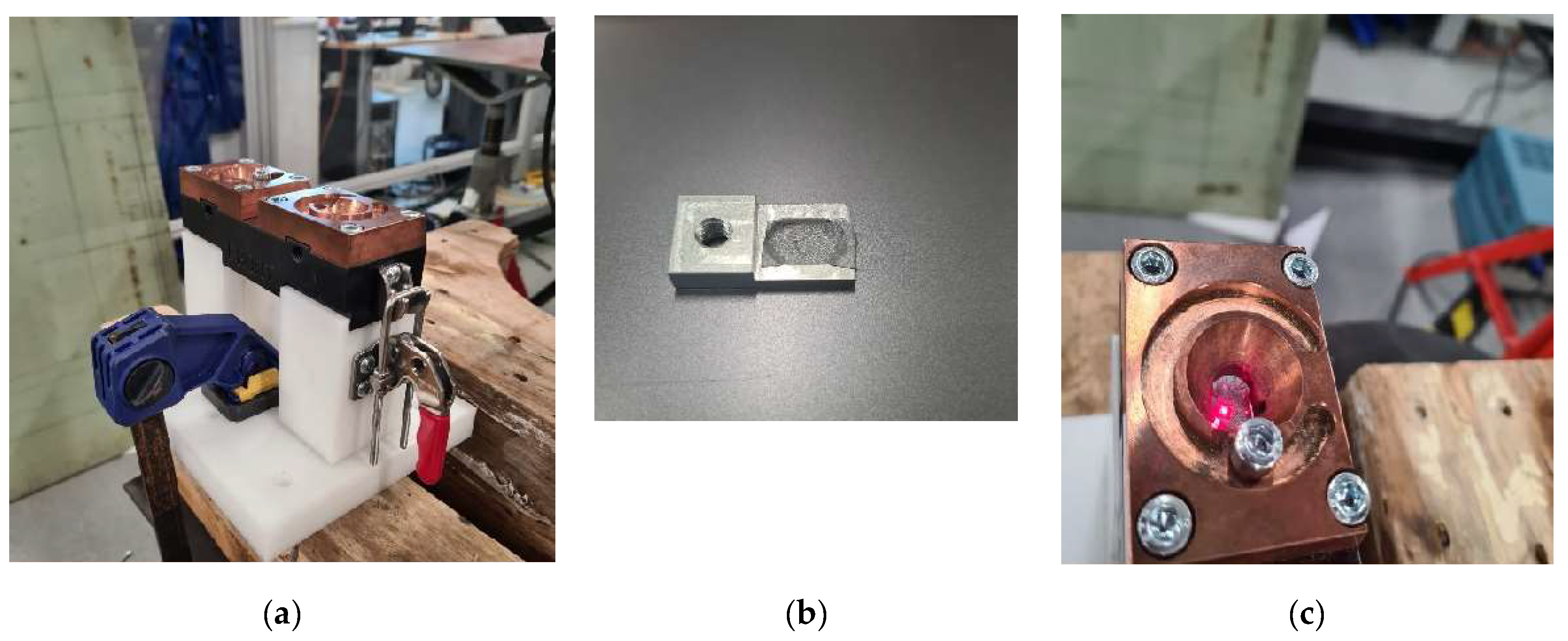
In the welding process, a battery is enclosed within a white plastic cover, as depicted in Error! Reference source not found.(a). The top plate, as shown in Error! Reference source not found.(b), is then welded to one of the battery terminals, which is composed of an aluminium alloy. Error! Reference source not found.(c) shows the location of welding, where the ultrasound vibration assistance is required during the welding.
Figure 1.
The battery plate holder (a) used for connecting the plate to the battery head (b) the plate inside the battery head connector that will be welded to the battery head, (c) the top view from the battery head connector.
Figure 1.
The battery plate holder (a) used for connecting the plate to the battery head (b) the plate inside the battery head connector that will be welded to the battery head, (c) the top view from the battery head connector.
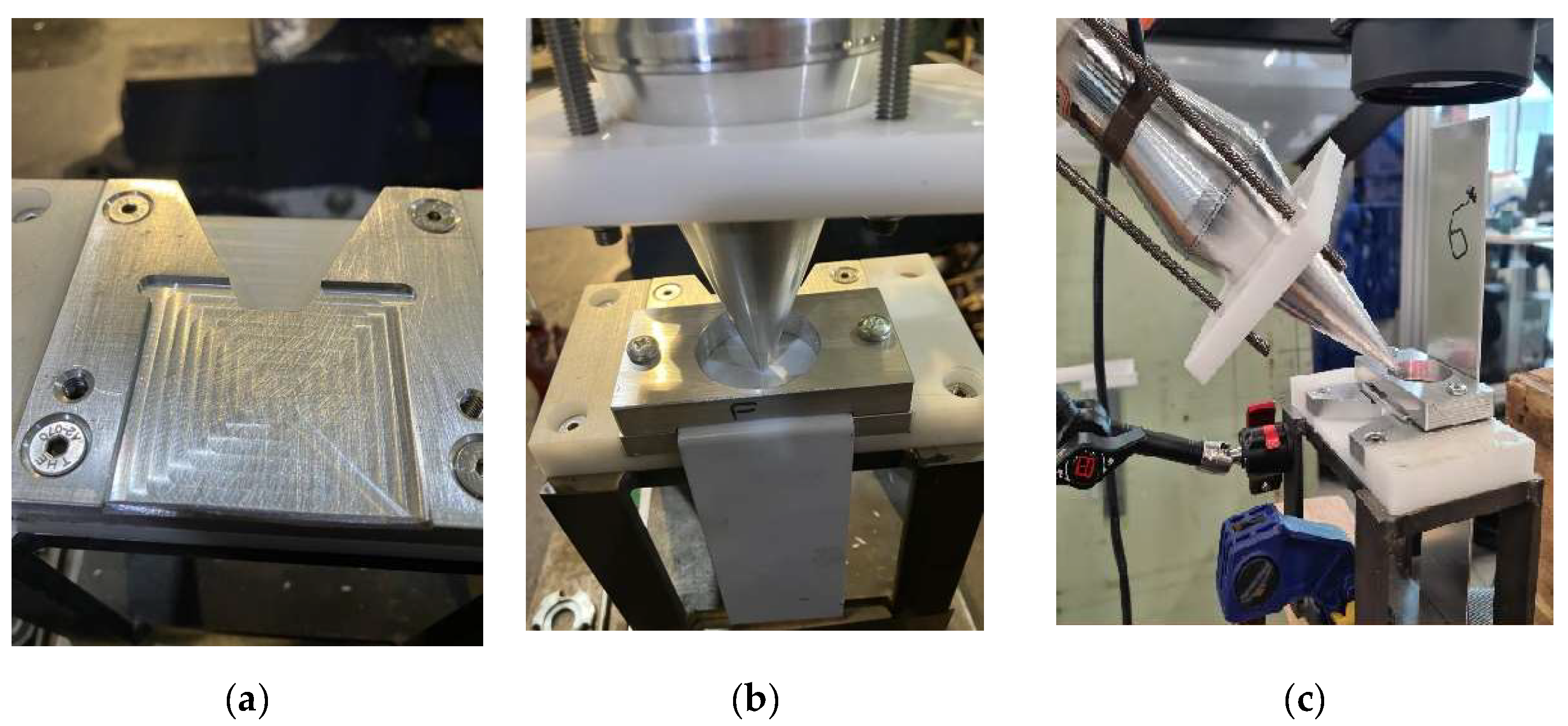
The current battery holder has a limited spaces to record the vibration transmission to the little plate terminal even using laser vibrometery the data was erratic. Furthermore, by welding the plate to the battery head it is difficult to analyse the welding in terms of pull test and microscopy. Therefore, a simplified holder was considered as illustrated in Error! Reference source not found..
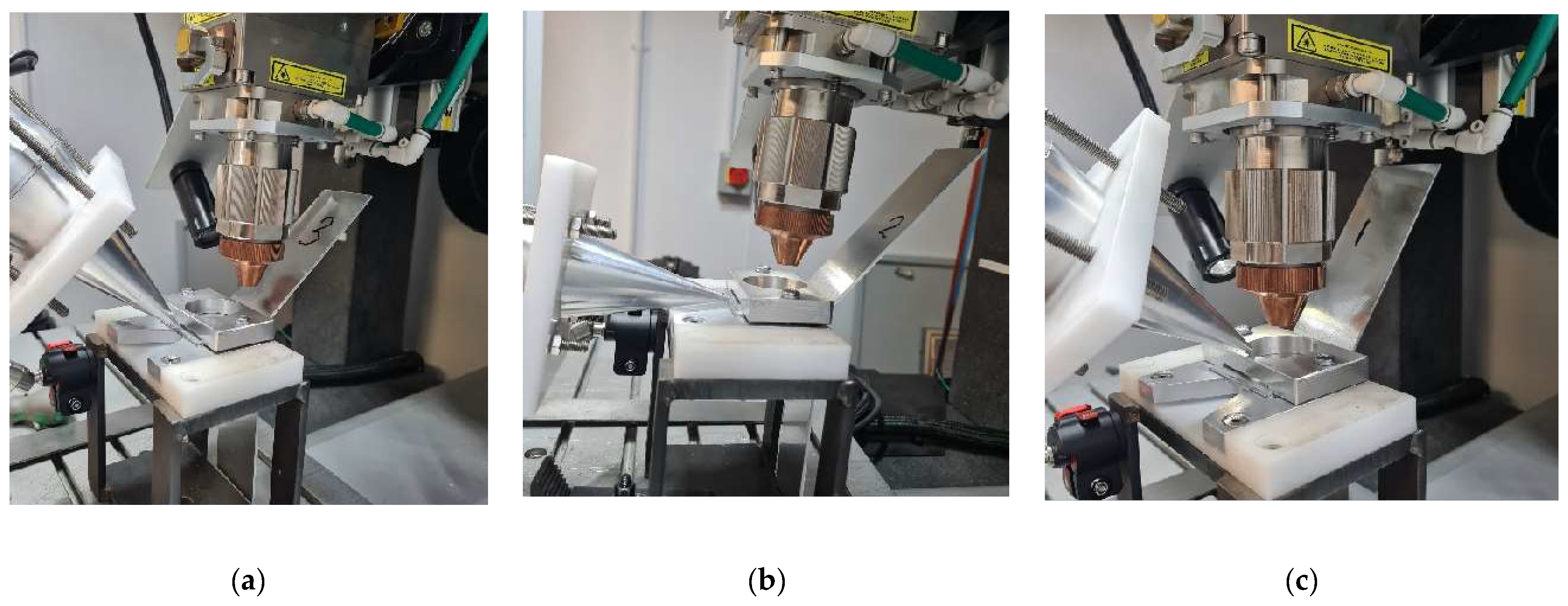
Figure 2.
The welding configuration includes the utilisation of an ultrasound transducer during laser welding. (a) the bottom holder, (b) fastened top holder to the bottom one (c) a picture showing the location of excitation from the transducer.
Figure 2.
The welding configuration includes the utilisation of an ultrasound transducer during laser welding. (a) the bottom holder, (b) fastened top holder to the bottom one (c) a picture showing the location of excitation from the transducer.
As illustrated in Error! Reference source not found., (b) and (c) a holder fastens two L-shaped plates, one at the top and another at the bottom. This simplification allows for the recording of the transmitted vibration in the area where welding will take place.
3. Laser Welding Multimode Laser
This section investigates the use of contact and contactless vibration methods to enhance laser welding quality by employing focused conical horns. To make the vibration level at its optimum value, the horn length should be proportional to half of the wavelength associated with the transducer. The utilisation of contactless vibration could present a viable solution for ultrasound-assisted laser welding, particularly when encountering restricted space, as illustrated in Error! Reference source not found..
Figure 3.
The welding configuration includes the utilisation of an ultrasound transducer during laser welding.
Figure 3.
The welding configuration includes the utilisation of an ultrasound transducer during laser welding.
For comparative purposes, several tests were carried out without ultrasonic assistance. In a related study, Salimi et al. [
19] characterised an industrial High Power Ultrasound Transducer (HPUT) to determine optimal distance and angle for contactless excitation.
3.1. Vibration Measurements
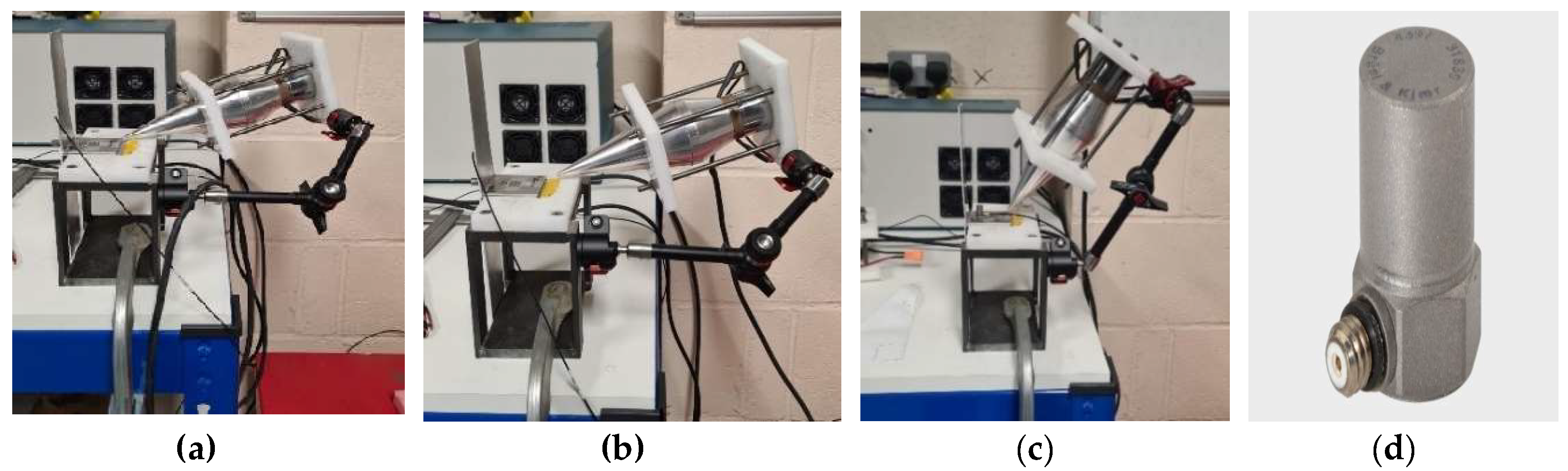
The experimental vibration consists of a transducer with a focused horn as illustrated in Error! Reference source not found.(a-c). In this measurement, a focused horn transducer with 20 kHz natural frequency is used.
Due to the limited spaces contact and contactless ultrasound vibration is used for the ultrasonic assisted welding. The contact and contactless vibration output from the focused transducer were measured on the plates, made of aluminium alloy 1050, as shown in Error! Reference source not found.(a-c). To find the vibration level associated with each measurement, the high-frequency accelerometer type 4397 is used, see Error! Reference source not found.(d), to evaluate plate response. The accelerometer is operating on a single axis, hence, to record the plate vibration for the in-plane and out-of-plane excitation, the accelerometer should be oriented in the desired direction. It is expected that the vibration at a zero-degree angle generates an in-plane motion to the plate in the contact and the contactless excitation mode. From the previous assessments made on this particular transducer, it was found that the transducer produces the highest vibration at a 45-degree angle in contact mode. For the contactless excitation, it was found that the maximum vibration is associated with the case where the transducer is positioned at 60 degrees with 20 mm distance from the end tip of the horn and the plate.
Figure 4.
The experimental configuration generates (a) contact, (b) contactless vibration at approximately 0 degrees and (c) contactless vibration at 45-degree angle; (d) the high-frequency accelerometer type 4397.
Figure 4.
The experimental configuration generates (a) contact, (b) contactless vibration at approximately 0 degrees and (c) contactless vibration at 45-degree angle; (d) the high-frequency accelerometer type 4397.
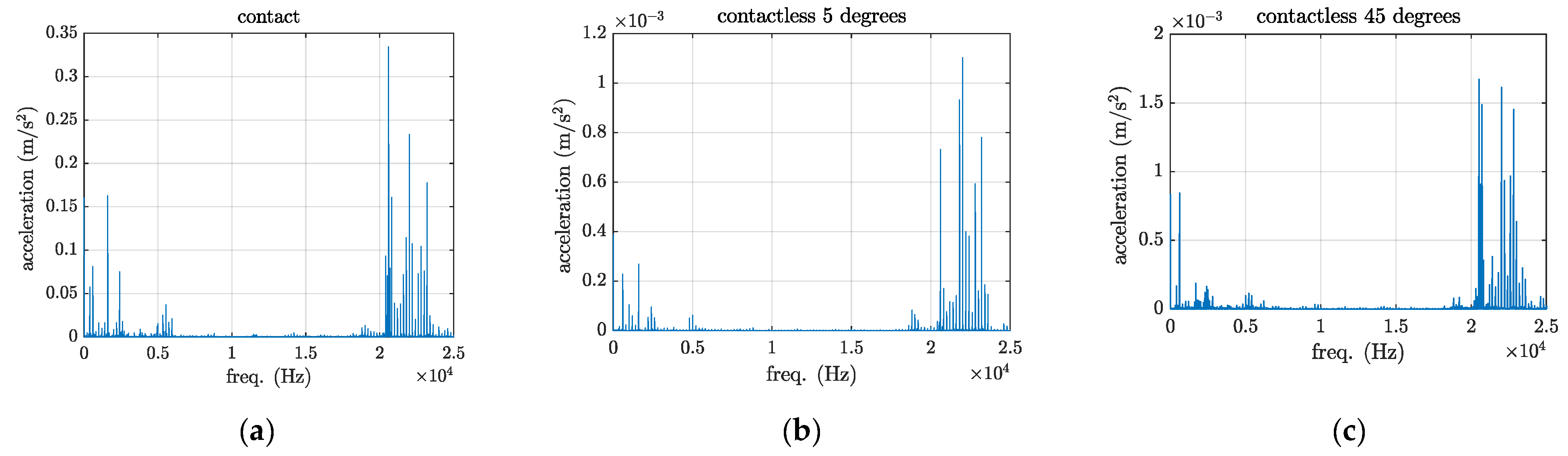
As illustrated in
Error! Reference source not found. the vibration level from the contact excitation is approximately 50 times higher in amplitude compared with the contactless one. Low-intensity ultrasound does not generate any cavitation or shock waves in the molten pool area [
13].
Figure 5.
The vibration output from the (a) contact, (b) contactless excitation, and (c) contactless excitation at a 45-degree angle.
Figure 5.
The vibration output from the (a) contact, (b) contactless excitation, and (c) contactless excitation at a 45-degree angle.
The transducer with 45-degree angle generates shear and compressional waves with approximately the same amplitude. In contrast, the transducer with the 0-degree angle is expected to produce the in-plane or compressional waves.
3.2. 20 kHz Transducer
For this frequency, a focused ultrasound horn operating at 20 kHz and an industrial horn are used. The focus of this study is to generate ultrasonic vibrations at a specific location. Therefore, contact vibration is employed to primarily transmit compressional waves into the fluid-filled area. The produced vibration for the contactless excitation was performed at 60 degrees with a 20 mm distance from the molten pool area, on the aluminium alloy 1050 plates. Error! Reference source not found. shows the different HPUT positions for producing shear, compressional and contactless vibration at the welding molten pool area during the laser operation.
Figure 6.
Ultrasound vibration-assisted welding using (a) shear, (b) compressional and (c) contactless vibration.
Figure 6.
Ultrasound vibration-assisted welding using (a) shear, (b) compressional and (c) contactless vibration.
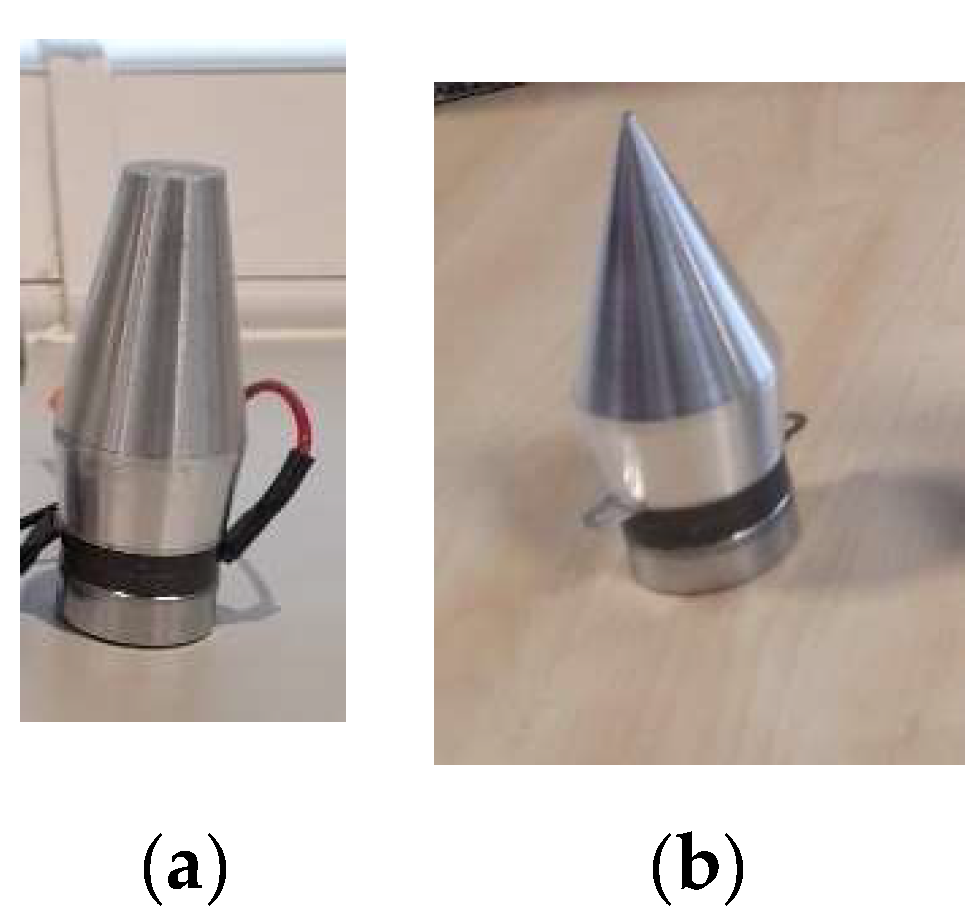
The 20 kHz transducer utilized in this study is depicted in Error! Reference source not found.. The transducer, featuring a larger horn tip as shown in Error! Reference source not found. (a), transmits greater overall pressure waves to the molten pool area. Conversely, the focused ultrasound, illustrated in Error! Reference source not found. (b), offers enhanced usability in constrained spaces typically encountered during welding.
Figure 7.
20 kHz Ultrasound transducer used during the laser welding. Transducer with (a) large horn tip, (b) small horn tip.
Figure 7.
20 kHz Ultrasound transducer used during the laser welding. Transducer with (a) large horn tip, (b) small horn tip.
The results of these experiments are summarized in Error! Reference source not found.. During the experiments, the laser speed was set at 2750 mm/min, and the laser power was set at 200 W. The ultrasonic power compatible with the Brunel amplifier was 70, while the industrial transducer had a power output of 20%. It is not recommended to increase the power amplification of the industrial horn as it tends to overheat and produce low amplitude noise instead of the desired signal. A noticeable improvement in the contactless mode could be attributed to the resonance frequency matching between the molten pool area and the applied vibration in the contactless mode.
Table 1.
Pull test results associated with the 20 kHz tapered and focused transducer, repeated three times.
Table 1.
Pull test results associated with the 20 kHz tapered and focused transducer, repeated three times.
| Transducer Type |
Placement/Angle |
Average Load, N |
Average Final Extension (mm) |
| Small-Tip |
Contactless on the Spot/45Deg
|
195.82 |
13.96 |
| Large-Tip |
Contact Compressional |
113.01 |
3.22 |
| Large-Tip |
Contactless on the Spot/45Deg |
173.88 |
12.16 |
3.3. 40 kHz Transducers
The welding process was carried out using the 40 kHz power ultrasonic. The transducer, characterised by a larger end tip and a smaller horn tip, is illustrated in Error! Reference source not found..
Figure 8.
40 kHz Ultrasound transducer used during the laser welding. Transducer with (a) large horn tip, (b) small horn tip.
Figure 8.
40 kHz Ultrasound transducer used during the laser welding. Transducer with (a) large horn tip, (b) small horn tip.
The outcomes corresponding to this specific frequency are depicted in Error! Reference source not found..
Better results in terms of welding strength and average final extension were obtained compared to the results obtained with the 28 kHz transducer. However, using the transducer with the larger tip produced better welding strength compared to using the 20 kHz transducer.
Table 2.
Pull test results associated with the 40 kHz tapered and focused transducer, repeated three times.
Table 2.
Pull test results associated with the 40 kHz tapered and focused transducer, repeated three times.
| Transducer Type |
Placement/Angle |
Average Load, N |
Average Final Extension (mm) |
| Small-Tip |
Contactless on the Spot/45Deg |
173.29 |
12.91 |
| Large-Tip |
Contact Compressional |
125.7393 |
7.31 |
| Large-Tip |
Contactless on the Spot/45Deg |
164.97 |
11.75 |
4. Ultrasonic Assisted Welding Using Single Mode Laser
This section explores the application of Power Ultrasonic Vibration Treatment (PUVT) in the laser welding of Copper and Aluminium connections. This approach addresses the challenge of forming brittle intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in such dissimilar material welds. PUVT has been observed to modify the grain structure, hinder the epitaxial growth of dendrites, and alter the morphology of IMCs, potentially enhancing the ductility and strength of Copper-Aluminium joints.
4.1. 20 kHz Transducer
In this section, ultrasonic vibration is utilised in both the contacted and contactless modes, and the average load connected to the weld is documented. In the contacted mode, the ultrasound transducer is positioned parallel to the plate, and the transmitted vibration to the molten pool plate primarily consists of compressional waves.
4.2. Experimental Set Up
In a recent experiment, two transducers were chosen based on the best results obtained from a Peel Test. These transducers included a 40 kHz focused horn transducer operating at 70% power and a 20kHz industrial needle transducer operating at 20% power. Both transducers were contactless and positioned towards the weld, as shown in Error! Reference source not found..
Throughout the trials, certain parameters were kept constant. This included the thickness of the plates being welded, which were 0.9mm for copper and 2mm for aluminium. The shape of the weld was consistently oval, and the laser power used was 2000W. The speed of the laser-head was set at 2750 mm/min, and the wobble had a width of 0.7mm and a frequency of 250Hz. The specific laser used in the experiment was the Laser IPG, which can be further referenced in the Istanbul paper. The experiment consisted of two baseline trials, one using the 40kHz focused transducer and another using the 20kHz needle transducer.
4.3. Sample Preparation
Once the welding process was completed, samples were taken for further analysis. To expose the internal structure of the weld, the samples were cut in a transverse manner through the centre. This was achieved using a metallurgical abrasive cutting machine known as the MetCut 300.
To prepare the samples for examination, they were then mounted using a mounting press and a Carbon Conductive Black Resin called CitoPress-15. This ensured that the samples were securely held in place and allowed for accurate observation. To achieve a smooth and polished surface, a manual polishing system called the OmegaPol Twin 200 mm was utilised. The samples underwent a polishing process using sandpaper with grit sizes of 240 and 1200, with the polishing machine set at a speed of 300rpm. To further refine the surface, Colloidal Silica was applied, followed by a 3 µm Diamond Suspension on a polishing cloth, with the machine running at 150rpm. For a comprehensive analysis, the samples were then subjected to a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) procedure, along with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The detailed findings and observations from this procedure can be found in the report provided by the laboratory.
5. Microscopy Results
The welding of Copper to Aluminium connections is highly sought-after due to the increase in demand of efficient power transfer between battery and vehicle. However, the joining of dissimilar materials like Copper to Aluminium you are faced the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds (IMC’s). The use of Power Ultrasonic Vibration Treatment (PUVT) when laser welding has proven to refine the grain structure, disrupt the epitaxial growth of dendrites and transform the shapes of IMC’s. Using the PUVT technology this paper aims to achieve similar results in an attempt to improve the ductility and strength of Copper to Aluminium joints.
5.1. Baseline 1
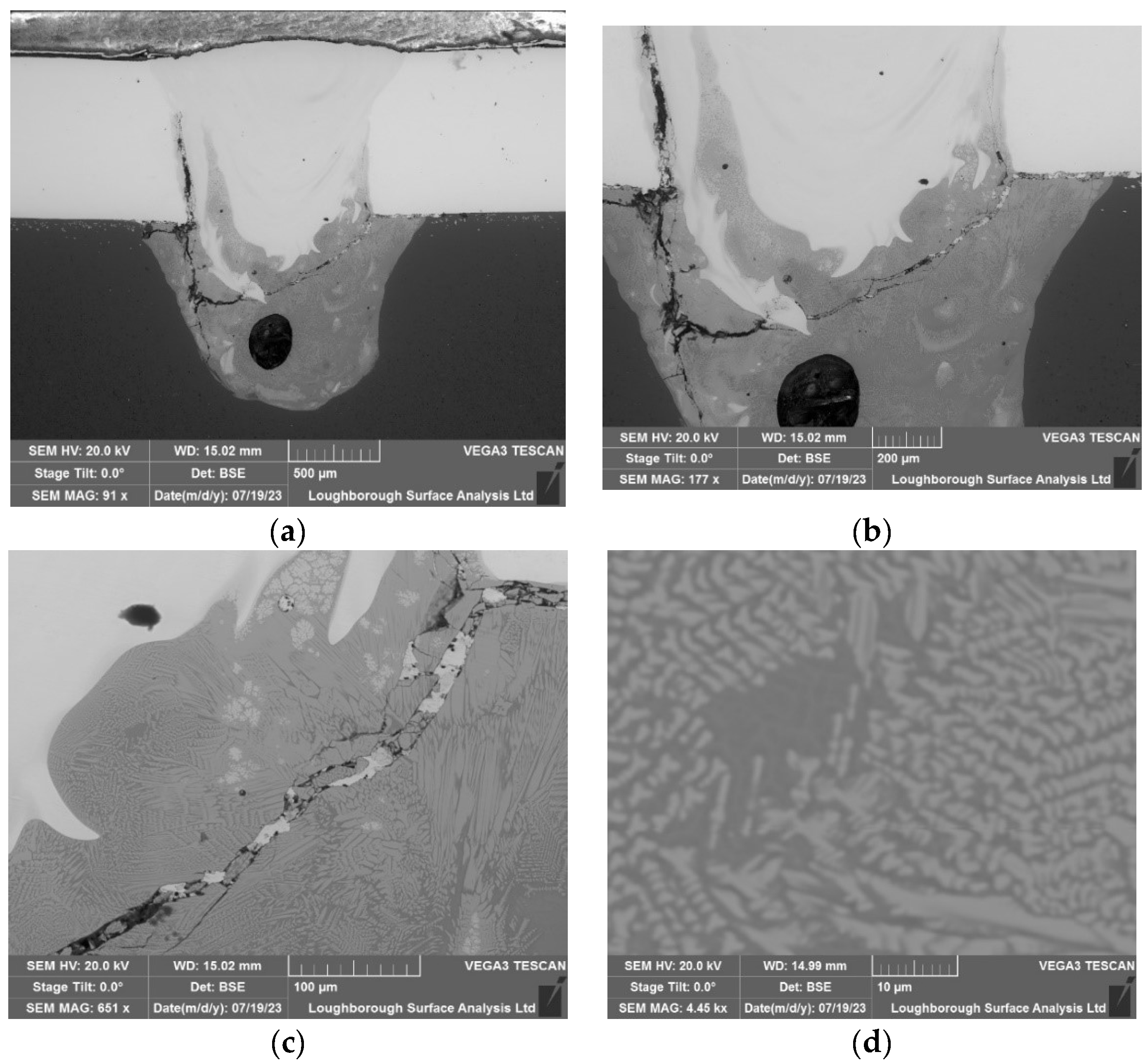
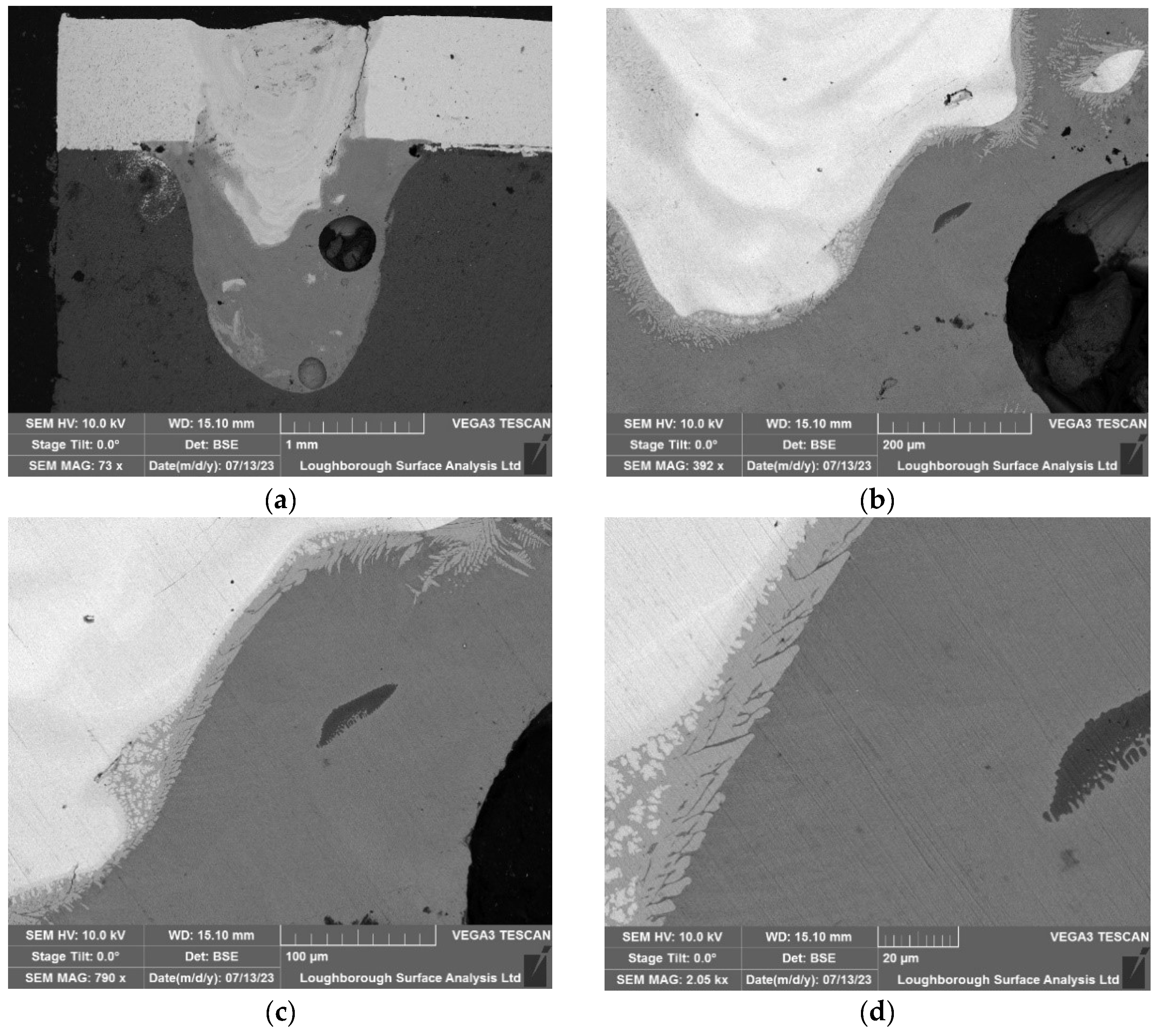
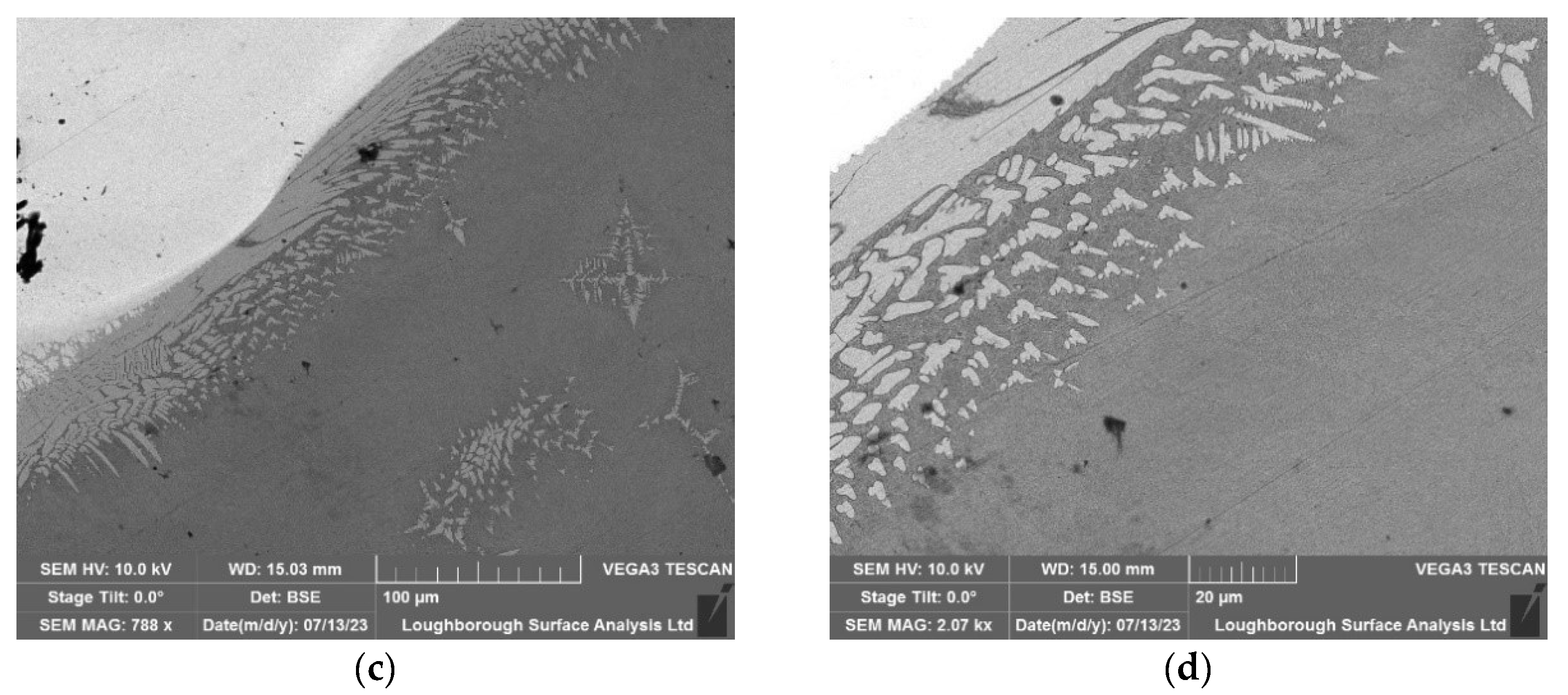
In this section, ultrasonic technology was not employed during the welding process. Upon examining the microscopy results, it is evident that there is a significant scattering of copper particles onto the aluminium surface, resulting in a homogenized distribution. The expected effect of ultrasound would have been to promote the grouping of materials, thereby preventing this favourable homogenization phenomenon from occurring.
Figure 9.
The microscopy results associated with the non-ultrasonic welding; (a) 500 µm (b) 200 µm(c) 100 µm (d) 10 µm.
Figure 9.
The microscopy results associated with the non-ultrasonic welding; (a) 500 µm (b) 200 µm(c) 100 µm (d) 10 µm.
5.2. Ultrasonic-Assisted Welding at 20 kHz
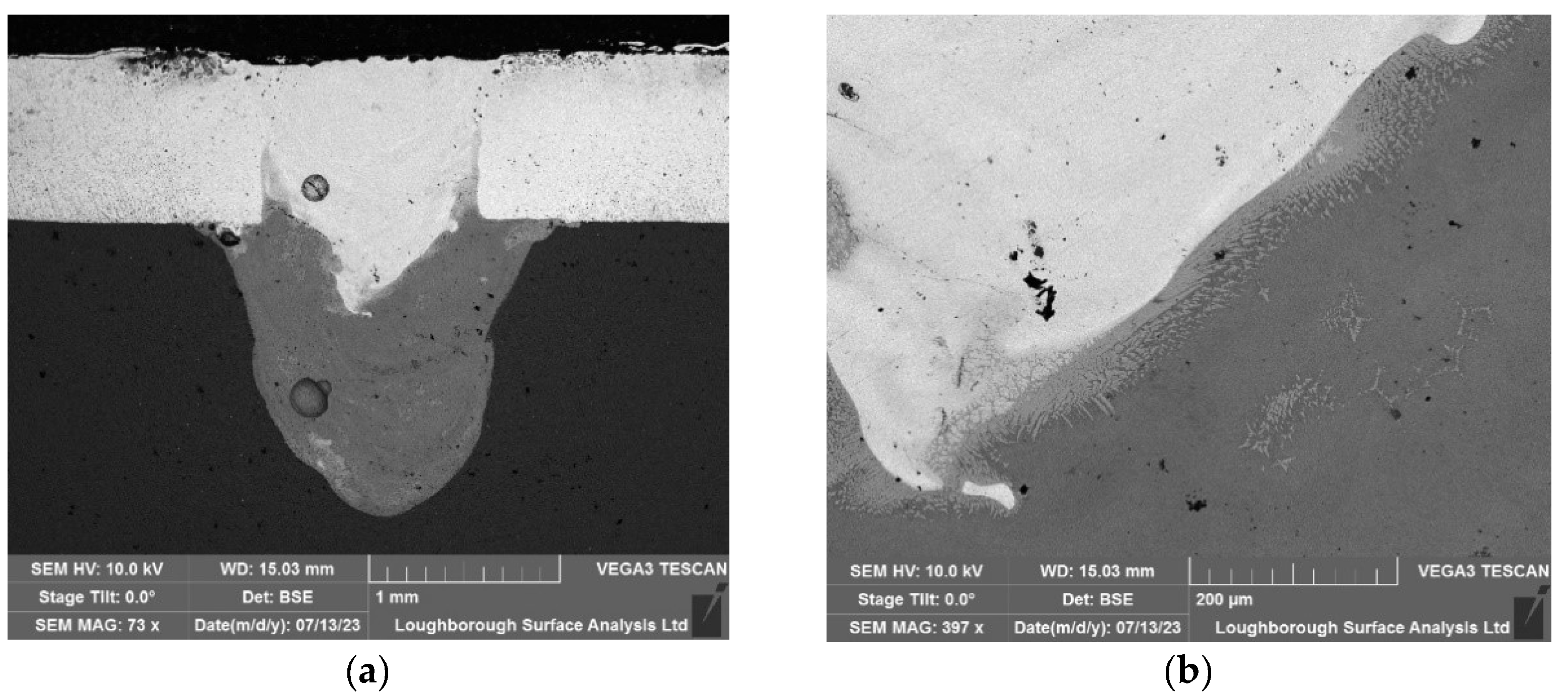
The same procedure was carried out on the welding, where the 20 kHz transducer in contactless mode were used. As it was expected the copper material is not homogenised into the aluminium and they are accumulated as a spot into the aluminium.
Figure 10.
Microscopy of the test associated with the 20 kHz transducer in the contactless mode; (a) 500 µm (b) 200 µm(c) 100 µm (d) 10 µm.
Figure 10.
Microscopy of the test associated with the 20 kHz transducer in the contactless mode; (a) 500 µm (b) 200 µm(c) 100 µm (d) 10 µm.
5.3. Ultrasonic-Assisted Welding at 40 kHz
In this section, the welding process involved the application of ultrasonic vibration. As a result, there was a noticeable reduction in the homogenisation of copper into the aluminium. This outcome aligns with the anticipated effect of ultrasound on the welding process.
Figure 11.
Microscopy of the test associated with the 40 kHz transducer in the contactless mode; (a) 500 µm (b) 200 µm(c) 100 µm (d) 10 µm.
Figure 11.
Microscopy of the test associated with the 40 kHz transducer in the contactless mode; (a) 500 µm (b) 200 µm(c) 100 µm (d) 10 µm.
6. Direct Vibration Transmission to the Molten Pool Area
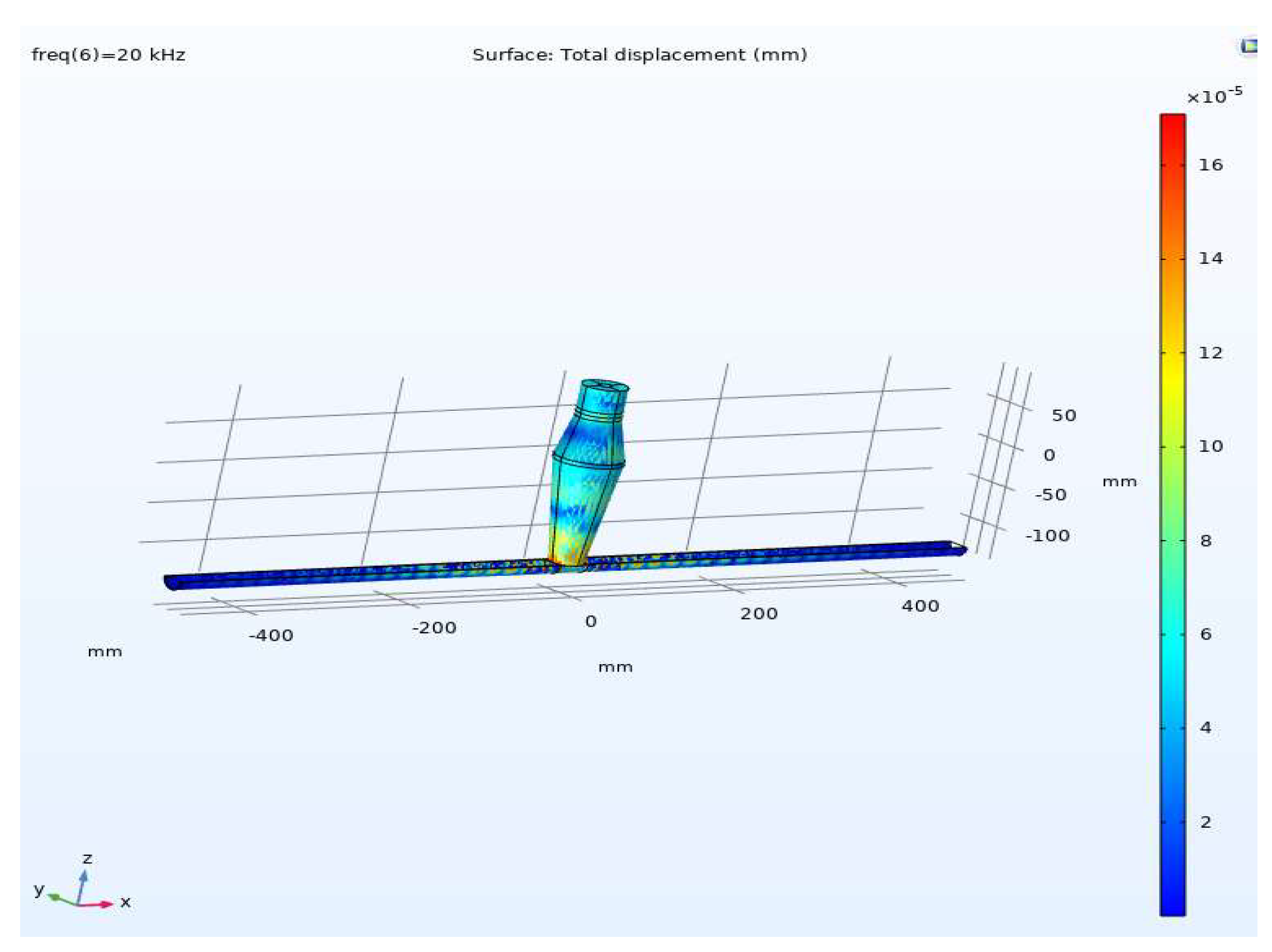
Considering the effect of direct vibration transmission to the molten pool area can be modelled by using an ultrasonic vibration on a sliced cylinder shape object as shown in this study, the piezoelectric materials modeled were glass and zirconate titanate (PZT-4). The material used for the ultrasonic horn was AISI 4340 steel. To accurately analyse the ultrasonic strengthening process, the acoustic field model was discretized using triangular and quadrilateral meshes, with the mesh size established at one-sixth of the wavelength.
Results indicate that, approximately 100 mm from the excitation source near the molten pool area—assumed to be a fluid-filled cylinder—the vibration effectively transmits to the vicinity of the welding area. Within the framework of ultrasound-assisted laser welding, a movable transducer in contact mode with the plate can generate vibrations near the laser welding head and move synchronously with it.
Figure 12.
Applying sonication directly to the molten pool area at 20 kHz.
Figure 12.
Applying sonication directly to the molten pool area at 20 kHz.
7. Conclusions
The study illustrates the effectiveness of integrating ultrasonic vibration in laser welding processes for EV battery connectors. By utilising different frequencies and modes of ultrasonic transducers, the welding quality in terms of strength and ductility was notably improved. This approach not only addresses the challenges in welding dissimilar materials like copper and aluminium but also paves the way for advancements in EV battery technology. The combination of experimental and numerical analyses offers a thorough understanding of the mechanisms behind ultrasonic vibration-assisted welding, contributing considerably to the manufacturing techniques in the EV industry. This research underscores the potential of ultrasonic technology in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of EV battery systems, thereby supporting the broader adoption of electric vehicles.
The effect of different wave types on laser welding improvement was investigated. While contact vibration leads to an acceleration amplitude approximately 50 times higher than contactless vibration, utilising compressional and shear waves to excite the plate results in improvements of 10% and 6% in the pull tests value compared with contactless assisted welding, respectively. Using the contactless ultrasound excitation improved 6 % of the welding quality in terms of the pull test values, compared with the non-ultrasonic sample. The highest pull test value was associated with ultrasonic-assisted welding with the compressional wave, as the pure fluid cannot support shear wave propagation.
References
- Sadeghian, A.; Iqbal, N. A Review on Dissimilar Laser Welding of Steel-Copper, Steel-Aluminium, Aluminum-Copper, and Steel-Nickel for Electric Vehicle Battery Manufacturing. Opt Laser Technol 2022, 146, 107595. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ma, G.; Dongjiang, W.; Chai, D.; Lei, M. Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Laser Welding of Nickel-Based Alloy and Austenite Stainless Steel. J Manuf Process 2018, 31, 759–767. [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Bi, J.; Li, P.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D. Melt Flow and Grain Refining in Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Laser Welding Process of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. Opt Laser Technol 2018, 108, 409–417. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.-D.; Du, B.; Zhang, S.-H.; Tao, W.-W.; Wang, Q.; Shen, H.-B. Effect and Action Mechanism of Ultrasonic Assistance on Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Laser Cladding 316L Stainless Steel Coating. Surf Coat Technol 2022, 433, 128122. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Wu, C.S.; Padhy, G.K.; Ding, W. Application of Ultrasonic Vibrations in Welding and Metal Processing: A Status Review. J Manuf Process 2017, 26, 295–322. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, Y. Ultrasonic Vibration Aided Laser Welding of Al Alloys: Improvement of Laser Welding-quality. J Laser Appl 1995, 7, 38–46. [CrossRef]
- Teyeb, A.; Silva, J.; Kanfoud, J.; Carr, P.; Gan, T.-H.; Balachandran, W. Improvements in the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Aluminium Alloys Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Laser Welding. Metals (Basel) 2022, 12, 1041. [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhou, S.; Wu, H.; Ma, X.; Liu, H.; Li, M. Dissimilar Joining of Low-Carbon Steel to Aluminum Alloy with TiC Particles Added in a Zero-Gap Lap Joint Configuration by Laser Welding. Mater Charact 2021, 182, 111574. [CrossRef]
- Cicală, E.; Duffet, G.; Andrzejewski, H.; Grevey, D.; Ignat, S. Hot Cracking in Al–Mg–Si Alloy Laser Welding–Operating Parameters and Their Effects. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2005, 395, 1–9.
- Zhang, P.; Jia, Z.; Yu, Z.; Shi, H.; Li, S.; Wu, D.; Yan, H.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, F. A Review on the Effect of Laser Pulse Shaping on the Microstructure and Hot Cracking Behavior in the Welding of Alloys. Opt Laser Technol 2021, 140, 107094. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Vollertsen, F. Influence of Grain Refinement on Hot Cracking in Laser Welding of Aluminum. Welding in the World 2014, 58, 355–366. [CrossRef]
- . Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z.; Cui, W.; Shi, Y. Effect of Ultrasonic Power on Porosity, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties of the Aluminum Alloy Joint by Ultrasonic Assisted Laser-MIG Hybrid Welding. Opt Laser Technol 2019, 119, 105619. [CrossRef]
- Khavari, M.; Priyadarshi, A.; Hurrell, A.; Pericleous, K.; Eskin, D.; Tzanakis, I. Characterization of Shock Waves in Power Ultrasound. J Fluid Mech 2021, 915. [CrossRef]
- Subroto, T.; Lebon, G.S.B.; Eskin, D.G.; Skalicky, I.; Roberts, D.; Tzanakis, I.; Pericleous, K. Numerical Modelling and Experimental Validation of the Effect of Ultrasonic Melt Treatment in a Direct-Chill Cast AA6008 Alloy Billet. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2021, 12, 1582–1596. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, X.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.; Li, J. Design Optimization and Eigenfrequency Tuning of Ultrasonic Oscillator of One-Dimensional Longitudinal Vibration at High Temperature for Laser Welding. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2022, 119, 4011–4029. [CrossRef]
- Teyeb, A.; Salimi, M.; El Masri, E.; Balachandran, W.; Gan, T.H. Analytical Simulation of the Microbubble Collapsing in a Welding Fusion Pool. Materials 2023, 16. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, B.; Wu, D.; Ma, G.; Yang, G.; Wei, W. Follow-up Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Laser Welding Dissimilar Metals for Nuclear Reactor Pump Can End Sealing. Nuclear Materials and Energy 2021, 27. [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Bi, J.; Li, P.; Guo, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D. Analysis on Welding Characteristics of Ultrasonic Assisted Laser Welding of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. Opt Laser Technol 2018, 105, 15–22. [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Teyeb, A.; Masri, E. El; Hoque, S.; Carr, P.; Balachandran, W.; Gan, T.-H. On the Use of Contactless Vibration to Improve the Welding Quality; ISBN 9789899121294.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).