Submitted:
18 April 2024
Posted:
19 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Market Orientation and Agricultural Enterprises’ Willingness to Adopt Green Technologies
2.2. Organizational Learning Capability and Agricultural Enterprises’ Willingness to Adopt Green Technologies
2.3. Policy Effectiveness and Agricultural Enterprises’ Willingness to Adopt Green Technologies
2.4. The Chain-Mediating Role of Organizational Learning Capability and Policy Effectivenes
3. Research Design
3.1. Sample Selection and Data Sources
3.2. Variable Measurement
- (1)
- (2)
- The measurement indicators for the organizational learning ability (LEA) variable were based on the green organizational learning measurement scale developed by Atuahene et al. (2007) [46], and combined with the research findings of Dai Wanliang and Lu Wenling (2020) [47] and Zhang Xiue (2023) [5]. It included a total of 7 items, measuring both exploratory and exploitative learning.
- (3)
- The measurement indicators for the policy effectiveness (POL) variable were based on the research findings of Chen Qijie et al. (2010) [42] and Chen Zhuanqing (2021) [25]. It consisted of 4 items, focusing on the behavioral principles adopted by enterprises in response to green development-related policies.
- (4)
- The measurement indicators for the willingness to adopt green technologies (ADO) were based on the research findings of Wu Chunyou and Wu Di (2009) [12]. After consulting with agricultural enterprise management experts, a total of 3 items were developed for measurement, mainly focusing on pre-production green technologies purchasing behavior, in-production green technologies production behavior, and post-production green technologies sales behavior.
3.3. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis of Variables
3.4. Reliability and Validity Tests
3.5. Common Method Bias
4. Results Analysis
4.1. Path Analysis
4.2. Testing of Mediating Effects
4.2.1. Testing of Mediating Effects of Learning Capability and Policy Effectiveness
4.2.2. Testing of the Chain Mediating Effect of Learning Capability and Policy Effectiveness
4.2.3. Analysis of Differences
4.3. Robustness Test of the Mediation Effec
| Path | Estimate | Bias-corrected | Bias-corrected 95% CI |
Mean | P | Test results | |
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| MAR→LEA→ADO (ind1) | 0.183 | 0.085 | 0.078 | 0.426 | 0.062 | 0.004 | H2b is established. |
| MAR→POL→ADO (ind2) | 0.260 | 0.095 | 0.097 | 0.469 | 0.091 | 0.010 | H23 is established. |
| MAR→LEA→POL→ADO (ind3) | 0.032 | 0.064 | 0.005 | 0.261 | 0.036 | 0.043 | H4d is established. |
| Total Mediating Effect | 0.877 | 0.062 | 0.691 | 0.936 | 0.058 | 0.000 | |
| Total effect MAR→ADO |
0.961 | 0.029 | 0.915 | 0.995 | - | 0.000 | |
| Total indirect effect MAR→ADO |
0.713 | 0.123 | 0.225 | 0.713 | - | 0.002 | |
| diff1 | 0.116 | 0.139 | -0.303 | 0.155 | 0.116 | 0.516 | |
| diff2 | 0.069 | 0.107 | -0.027 | 0.302 | 0.069 | 0.261 | |
| diff3 | 0.100 | 0.133 | -0.075 | 0.476 | 0.100 | 0.223 | |
5. Research Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Research Conclusions
5.2. Policy Suggestions
References
- Guo Yan, Wang Xingdong, Nie Zhiping.(2024). Can Participating in Cooperatives Enhance Farmers’ Green Production Behaviors? Analysis Based on the Mediating Role of Technical Services and the Regulatory Effect of Social Norms [J]. Ecological Economy, 40(02): 133-141.
- Wang Jianhua, Zhou Jin, Ren Minhui.(2024). The Income Effect of Agricultural Producers’ Investment in Green Production Factors [J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Social Sciences Edition), 24(01): 110-123.
- Ma Junjie, Liu Qiang, Qin Wenshan. (2023). Green Certification and Improvement of Technical Efficiency - An Empirical Study Based on Agricultural Enterprises [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Social Sciences), 17(06): 54-62.
- Li Guolan, Zhou Yuxin, Chen Jing. (2024). The Impact of Two-way FDI on the Green Transformation of Enterprises: Promotion or Inhibition [J]. Journal of Finance and Accounting, 45(03): 33-40.
- Zhang Xiue. (2023). The Impact of Dual Green Strategy Orientation on Agricultural Enterprise Performance: A Moderated Mediation Model [J]. Science of Science and Management of S&T, 44(08): 148-163.
- Lv Fen. (2021).Research on the Impact of External Environment on the Adoption of Digital Technologies by Small and Medium-sized Enterprises [J]. Studies in Science of Science, 39(12): 2232-2240.
- SINKULA J M. (1994).Market information processing and organization learning [J]. Journal of Marketing, 58(1): 35-45. [CrossRef]
- Pei Xudong. (2020).Research on the Driving Mechanism of Enterprises’ Willingness to Continuously Adopt Breakthrough Technologies [J]. Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 22(11): 81-89.
- Zhang Yanlong, Wang Mingzhe, Qian Jingfei, et al. (2021).Development Characteristics, Issues, and Development Ideas of China’s Agricultural Industrialization Leading Enterprises [J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, (08): 135-144.
- BRAUM E, WIELD D. (1994).Regulation as a means for the social control of technology [J]. Technology Analysis and Strategic Management, 1994, 6(3): 259-272. [CrossRef]
- Klassen R.D., Mclaughlin C.P.. (1996).The Impact of Environmental Management on Firm Performance [J]. Management Science, 42(8): 1199-1214. [CrossRef]
- Wu Chunyou, Wu Di. (2009). Research on the Formation Path of Green Management Behavior of Enterprises under Market Orientation [J]. Nankai Business Review, 12(06): 111-120.
- Zhao Heping, Su Xianghui, Ma Ying, et al. (2022).Research on Farmers’ Willingness to Adopt Green and Ecological Agricultural Technologies under the Vision of Carbon Neutrality - A Comparative Analysis Based on Typical Agricultural and Pastoral Areas in Western China [J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Mechanization, 43(8): 216-223.
- Gao Xin. (2019). Empirical Research on Internal Influencing Factors of Farmers’ Green Production Behaviors under the Background of Rural Revitalization Strategy [J]. Journal of Economic Survey, (3): 41-48.
- Yu Lifan, Cao Dayu, Liao Bing. (2024). A Study on the Impact of Livelihood Capital and Ecological Cognition on Farmers’ Willingness to Adopt Green Production Technologies [J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, (02):1-15.
- Shi Zhiheng, Cui Min. (2020).Heterogeneous Impacts of Individual Differences on Farmers’ Different Green Production Behaviors: A Comparison of the Impacts of Age and Risk Preference on Labor-intensive and Capital-intensive Green Production Behav-iors [J]. Western Forum, 30(01): 111-119.
- Zhang Junbiao, Xie Tianren, Liang Zhihui. (2024).Ecological Cognition, Market Regulation, and Farmers’ Adoption Behaviors of Green Production Technologies: An Analysis Based on Survey Data from the Main Rice-producing Areas of Hubei Province [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 29(03): 204-216.
- González X., Pazó C. (2008).Do Public Subsidies Stimulate Private R&D Spending? [J]. Research Policy, 37(3): 371-389. [CrossRef]
- Kevin K.Y. Kuan, Patrick Y.K. Chau. (2001).A perception-based model for EDI adoption in small businesses using a technology organization environment framew-ork [J]. Information & Management, 38(8): 507-521. [CrossRef]
- Turner M, Kintchenham B, Brereton P, et al. (2010). Does the Technology Acceptance Model Predict Actual Use? A Systematic Literature Review [J]. Information and Software Technology, 52(5): 463-479. [CrossRef]
- Gao Tianzhi. (2023).A Study on Farmers’ Choice Behavior and Adoption Effects of Digital Agricultural Technology Promotion Services [D]. Northwest A&F University, 2023. DOI: 10.27409/d.cnki.gxbnu.2023.002387.
- Liu Di, Sun Jian, Huang Mengsi, et al. (2019).Analysis of the Synergistic Effect of Markets and Governments on Farmers’ Adoption of Green Prevention and Control Technologies [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28(5): 1154-1163.
- Liu Jie, Li Cong, Wang Gangyi. (2022). Does Farmers’ Organization Promote the Adoption of Green Technologies? [J]. Rural Economy, (1): 69-78.
- Li Fenni, Zhang Junbiao, He Ke. (2019).The Impact of Informal Institutions and Environmental Regulations on Farmers’ Green Production Behaviors: Based on Survey Data from 1105 Farmers in Hubei Province [J]. Resources Science, 41(07): 1227-1239.
- Chen Zhuanqing. (2021).The Impact of Policy Orientation and Market Orientation on Farmers’ Green Production: An Empirical Analysis Based on 865 Farmers in Henan Province [J]. Journal of Management Science, 34(05): 109-125.
- Luo L, et al. (2022). Training of Farmers’ Cooperatives, Value Perception and Members’ Willingness of Green Production [J]. Agriculture, 12(8): 1145. [CrossRef]
- Gao Jing, Zhou Ji. (2023)The Mechanism and Effectiveness of Cooperatives’ HighQuality Development in Promoting the Improvement of Agricultural Green Productivity [J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning: (09):1-12.
- Schultz, T. (1964)Transforming Traditional Agriculture [M]. New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Narver J. C., Slater S. F. (1990).The Effect of a Market Orientation on Business Profitability [J]. Journal of Marketing, 54(4): 20-35. [CrossRef]
- Sher A, Mazhar S, Zulfiqar F, et al. (2019).Green Entrepreneurial Farming: A Dream or Reality [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 220(20): 1131-1142. [CrossRef]
- Hu Jing, Wen Ya, Chen Kai. (2020).Research on the Impact of Market Orientation and Policy Orientation on the Performance of Biomass Energy Enterprises: Based on the Mediating Effect of Organizational Learning [J]. Forestry Economics, 40(01): 72-79.
- Liu Wei, Nong Fengpian, Wei Jingnan, et al. (2024).Research on the Performance Differences of Green Production Behaviors Among Different Types of Chinese Herbal Medicine Farmers: An Empirical Analysis Based on Survey Data from Herbal Medicine Farmers in Chifeng City [J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture (Chinese and English): (02)1-13.
- Wang Yong’an. (2019).A Study on the Impact of Organizational Learning Capability on Product Upgrading in OEM Enterprises [D].Donghua University.
- Crossan, M. Chris Argyris and Donald Schon’s,(2003). "Organizational Learning": There is no Silver Bullet [J]. Academy of Management Executive, (2): 37-39.
- Zeng Ping. (2011).Learning, Innovation, and Dynamic Capabilities: An Empirical Study of Enterprises in South China [J]. Management Review, 23(1): 85-95.
- Yang Zhiqing. (2019).How Does Education Affect Agricultural Green Productivity? An Empirical Analysis Based on Different Forms of Rural Education in China [J]. China Soft Science, (08): 52-65.
- Ying Ruiyao, Zhu Yong. (2015).The Impact of Agricultural Technical Training Methods on Farmers’ Use of Agricultural Chemical Inputs: Evidence from Experimental Economics [J]. China Rural Survey, (01): 50-58+83+95.
- Zhang Minglin, Wen Lijian.(2016). Empirical Analysis of the Impact of Support Policies on the Relative Performance of Leading Green Food Agricultural Enterprises: Based on DEA-Tobit Analysis Method [J]. Journal of Agro-Forestry Economics and Management, (5): 524-531.
- Hao Aimin, Liu Yuting, Xie Menghan. (2024).The Impact of Digital and Intelligent Productive Services on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity: With a Discussion on the Regulatory Role of Government Environmental Regulations [J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 44(02): 163-171.
- Yang Jiudong. (2018).Green Development Is a Major Mission for Modern Agricultural Construction [N]. Guangming Daily, 07-11.
- Trujillo B A, Pennings J M E, Hofenk D.(2016). Understanding Producers’ Motives for Adopting Sustainable Practices: The Role of Expected Rewards, Risk Perception and Risk Tolerance [J]. European Review of Agricultural Economics, 43(3): 359-382. [CrossRef]
- Chen Qijie, Jiang Ruochen, Cao Guangming.(2024). Research on the Impact Mechanism of the "Market-Policy" Dual Orientation on the Performance of Agricultural Enterprises: Taking the Agricultural Leading Enterprises in the Pan-Yangtze River Delta Region as an Example [J]. Nankai Business Review, 44(02): 163-171.
- M. Alavi and D.E. Leidner,(2001). “Review: Knowledge Management and Knowledge Management Systems: Conceptual Foundations and Research Issues,” [J]. MIS Quarterly, 25(1): 107-136. [CrossRef]
- Yang Hongshan, Li Wu. (2023).Organizational Learning in Policy Experiments: A Process Framework [J]. Xuehai, (05): 25-32+50.
- Fatoki O. (2019).Green Marketing Orientation and Environmental and Social Performance of Hospitality Firms in South Africa [J]. Foundations of Management, 11(1): 277-290. [CrossRef]
- Atuahene-Gima, K., and Janet Murray.(2007). “Exploratory and Exploitative Learning in New Product Development: A Social Capital Perspective in New Technology Ventures in China”, [J]. Journal of International Marketing, 15(2): 1-29. [CrossRef]
- Dai Wanliang, Lu Wenling. (2020).The Impact of Environmental Protection Public Opinion Pressure on the Green Innovation Capability of Manufacturing Enterprises: The Chain Mediating Effect of Leadership’s Environmental Awareness and Organizational Green Learning [J]. Science & Technology Progress and Policy,37(09): 131-137.
- Zhang Lixia, Lyu Guoqing, Jia Lei. (2018).Technology Introduction, Technology Absorptive Capacity, and Innovation Performance - An Empirical Analysis Based on Shanghai Agricultural Enterprises [J]. Journal of Agricultural Technological Economics, (09): 80-87.
| 1 | The definition of green technology in this paper refers to Guo Kesha, Tian Xiaoxiao. Green technology and green transformation of industrial development mode [J]. Tianjin Social Sciences, 2024 (02) :99-107, including green manufacturing (production) technology and green service technology. |
| 2 | Some enterprises have multiple business portfolios, and the sum of the percentages may not equal 100%. |
| 3 | Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.6 or above is generally acceptable, Rong Taisheng. AMOS and Research Methods [M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2009. |
| Variable | Mean | S.d | MAR | LEA | POL | ADO |
| MAR | 2.531 | 1.038 | 0.813 | |||
| LEA | 2.957 | 1.286 | 0.241** | 0.870 | ||
| POL | 3.201 | 1.311 | 0.148** | 0.237** | 0.810 | |
| ADO | 2.977 | 1.302 | 0.136** | 0.141** | 0.260** | 0.860 |
| Variables | Items | factor loading | Cronbach’ s a | C.R | AVE |
| MAR | The green business objectives of our enterprise are mainly driven by consumer satisfaction. | 0.866 | 0.967 | 0.951 | 0.661 |
| Our enterprise continuously monitors its commitment level and direction in meeting consumers’ green needs. | 0.781 | ||||
| Our enterprise freely communicates with consumers and employees about its green products and services. | 0.830 | ||||
| Our enterprise’s competitive advantage strategy is based on understanding consumers’ green needs. | 0.845 | ||||
| We frequently measure consumer satisfaction with our enterprise’s green products and services. | 0.810 | ||||
| Our enterprise has routine consumer service initiatives. | 0.808 | ||||
| Our enterprise invests more in green products and services that meet consumer needs compared to competitors. | 0.780 | ||||
| Our enterprise believes that the main purpose of business is to serve consumers (including green consumers). | 0.839 | ||||
| Our enterprise surveys consumers at least once a year to assess the quality of our green products and services. | 0.770 | ||||
| Data on consumer satisfaction with our enterprise’s products and services (including green products) is regularly published at all levels of this business unit. | 0.793 | ||||
| LEA | One of our purposes in searching for information is to find more energy-efficient solutions to problems. | 0.874 | 0.936 | 0.956 | 0.758 |
| One of our purposes in searching for information is to ensure energy conservation and emission reduction, and reduce environmental pollution. | 0.819 | ||||
| We pay attention to more environmentally friendly production processes when developing new products. | 0.899 | ||||
| We tend to use environmental protection knowledge related to existing projects. | 0.892 | ||||
| One of our purposes in searching for information is to learn more about environmental protection knowledge. | 0.873 | ||||
| One of our purposes in searching for information is to develop new green projects and enter new markets (LEA3). | 0.894 | ||||
| We collect information that is more environmentally friendly and green than the technical experience in the existing market. | 0.842 | ||||
| POL | Every year, we spend time studying the impact of environmental policies on agricultural production. | 0.856 | 0.817 | 0.884 | 0.657 |
| We often conduct many market surveys on environmental policies. | 0.722 | ||||
| We collect environmental policy information through various informal channels. | 0.792 | ||||
| We regularly collect documents on environmental protection policies. | 0.865 | ||||
| ADO | We are willing to use green procurement behavior before production. | 0.855 | 0.788 | 0.895 | 0.741 |
| We are willing to use green production behavior during production. | 0.862 | ||||
| We are willing to use green sales behavior after production. | 0.864 |
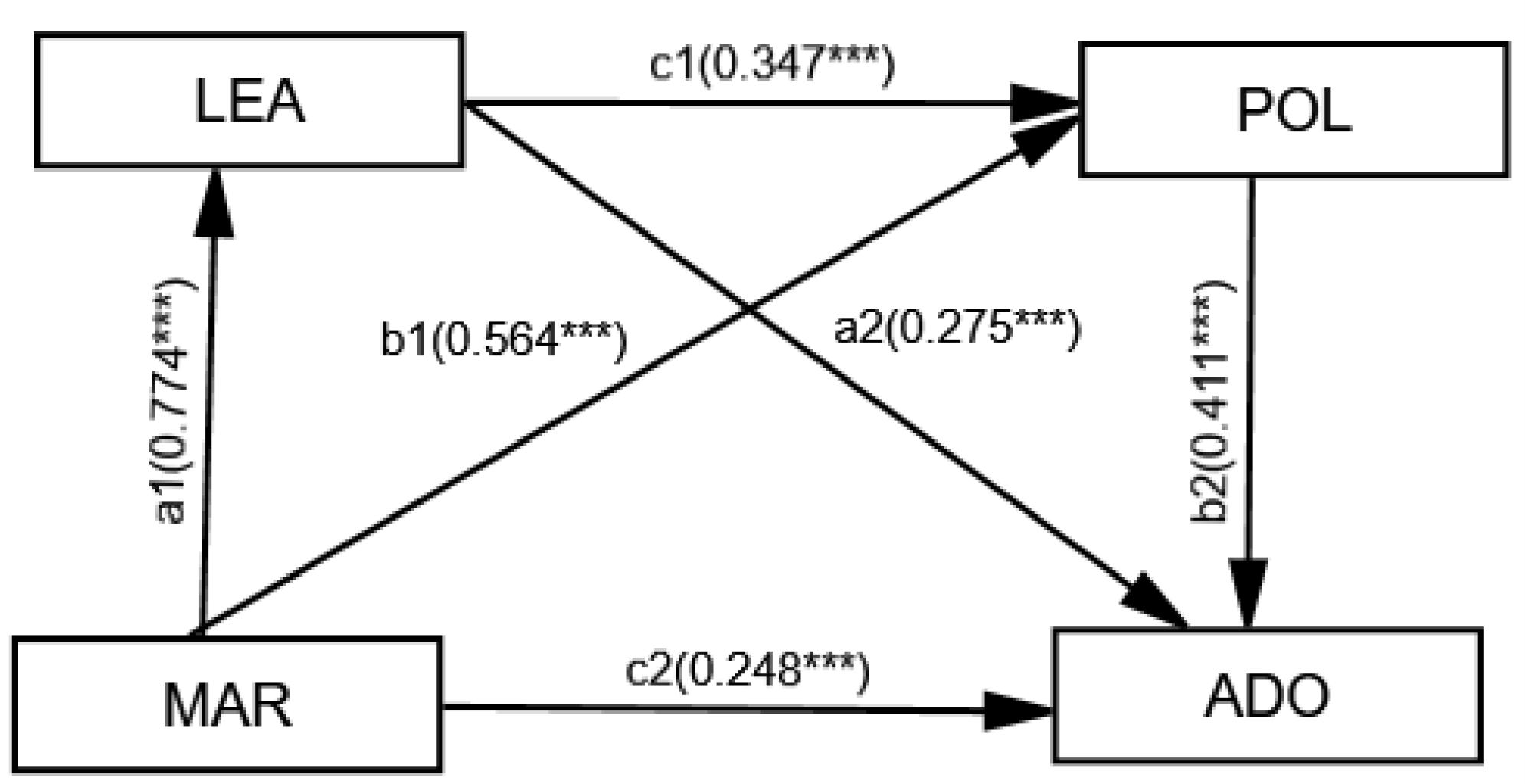
| Research hypothesis | Standardized Regression Weights | S.E. | C.R. | P | Test result | |||
| H1a | ADO | <--- | MAK | 0.288 | 0.076 | 3.276 | *** | T |
| H2a | ADO | <--- | LEA | 0.289 | 0.078 | 3.531 | *** | T |
| H3a | ADO | <--- | POL | 0.457 | 0.074 | 5.541 | *** | T |
| H4a | LEA | <--- | MAK | 0.856 | 0.061 | 12.629 | *** | T |
| H4b | POL | <--- | LEA | 0.328 | 0.107 | 3.240 | *** | T |
| H4c | POL | <--- | MAK | 0.590 | 0.096 | 5.873 | *** | T |
| Path | Estimate | Bias-corrected | Bias-corrected 95% CI |
Mean | P | Test results | |
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| MAR→LEA→ADO (ind1) | 0.213 | 0.085 | 0.078 | 0.426 | 0.206 | 0.005 | H2b is T |
| MAR→POL→ADO (ind2) | 0.232 | 0.095 | 0.097 | 0.469 | 0.241 | 0.003 | H23 is T. |
| MAR→LEA→POL→ADO (ind3) | 0.110 | 0.064 | 0.005 | 0.261 | 0.107 | 0.040 | H4d is T. |
| Total Mediating Effect | 0.804 | 0.062 | 0.691 | 0.936 | 0.807 | 0.000 | |
| Total effectMAR→ADO | 0.934 | 0.029 | 0.861 | 0.976 | - | 0.001 | |
| Total indirect effect MAR→ADO |
0.645 | 0.120 | 0.394 | 0.863 | - | 0.002 | |
| diff1 | -0.019 | 0.139 | -0.271 | 0.277 | -0.035 | 0.987 | |
| diff2 | 0.103 | 0.107 | -0.112 | 0.315 | 0.099 | 0.297 | |
| diff3 | 0.122 | 0.133 | -0.105 | 0.422 | 0.134 | 0.277 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





