Submitted:
18 April 2024
Posted:
19 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
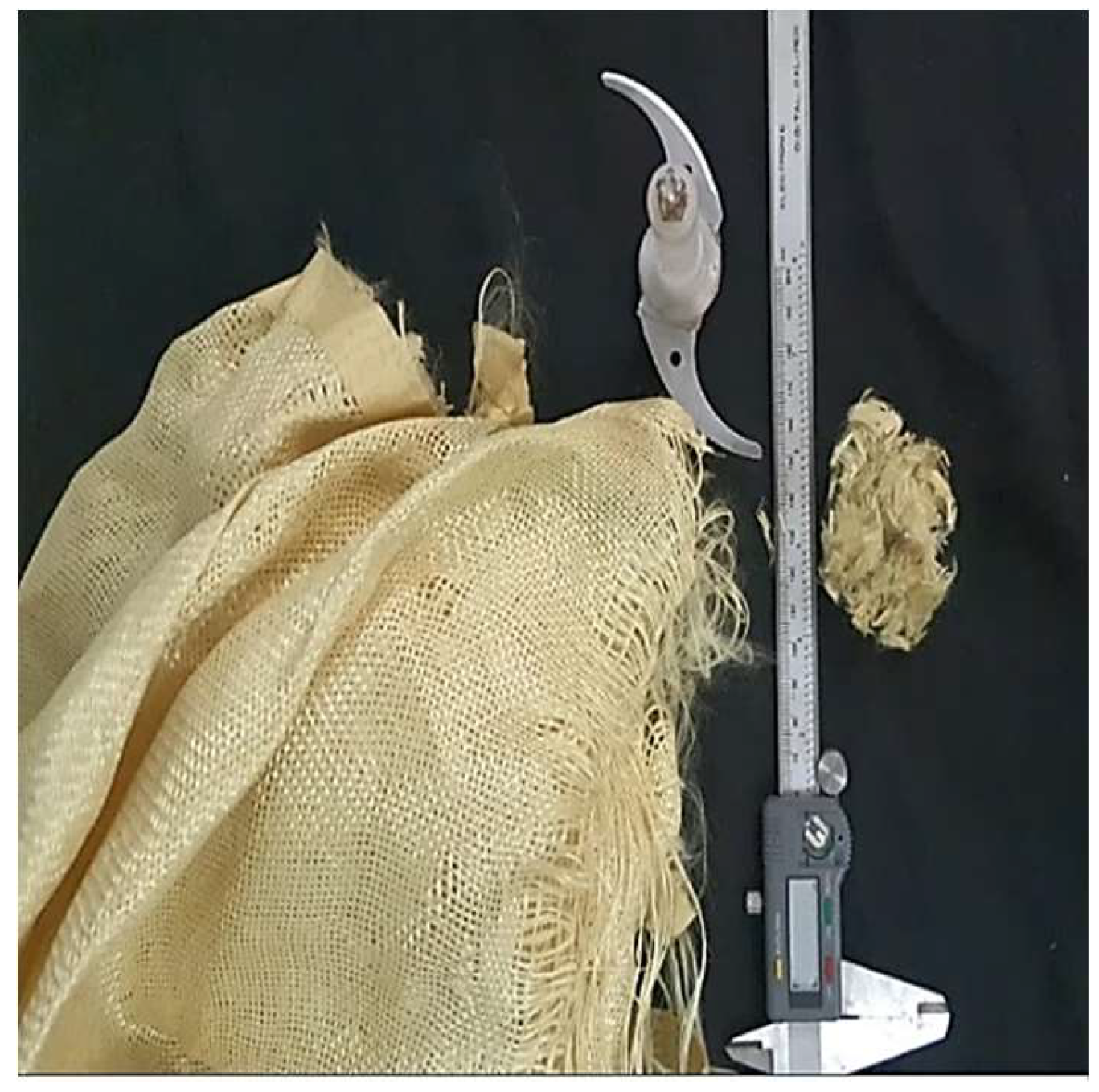
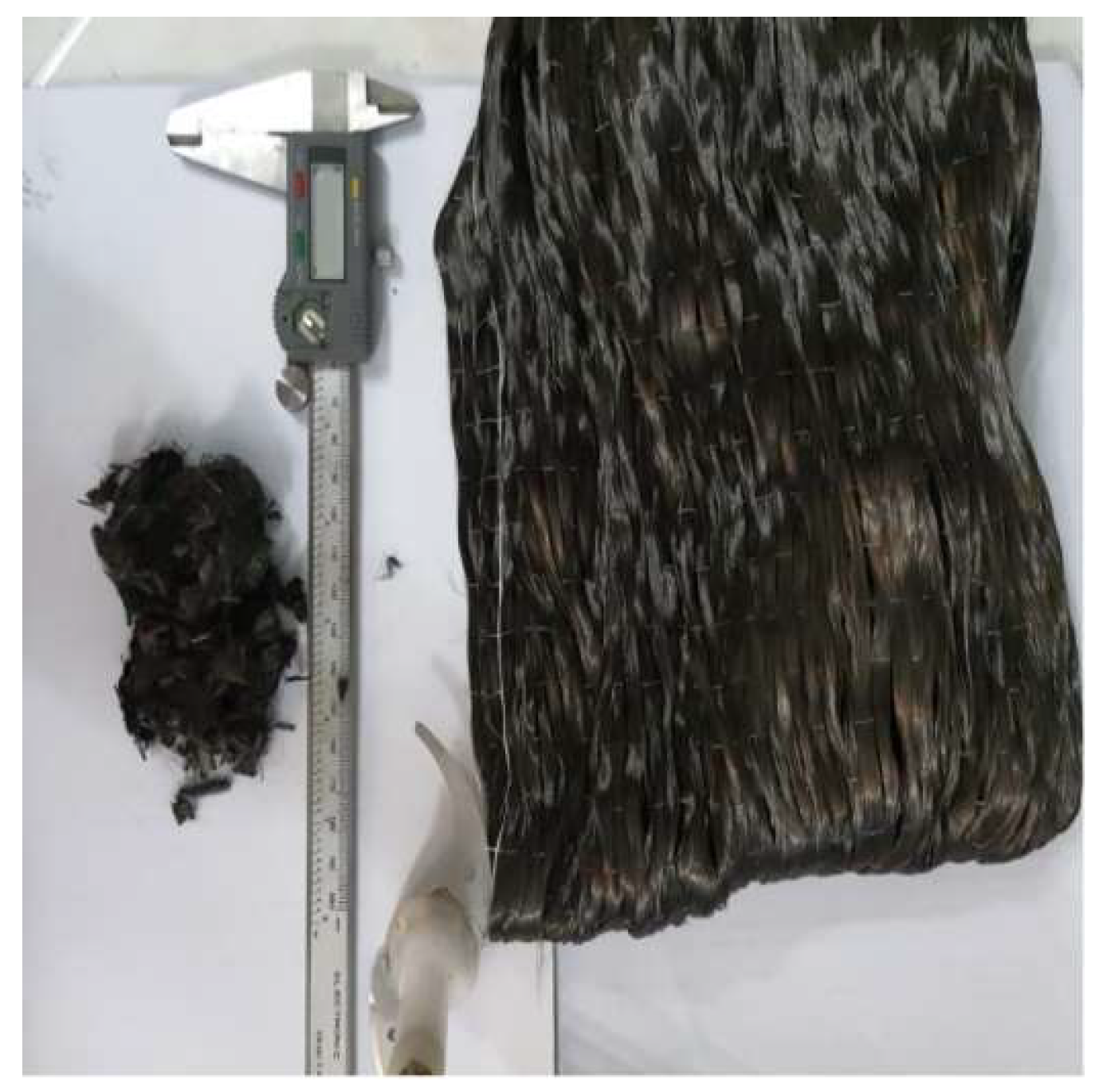


2.2. Preparation of Composite
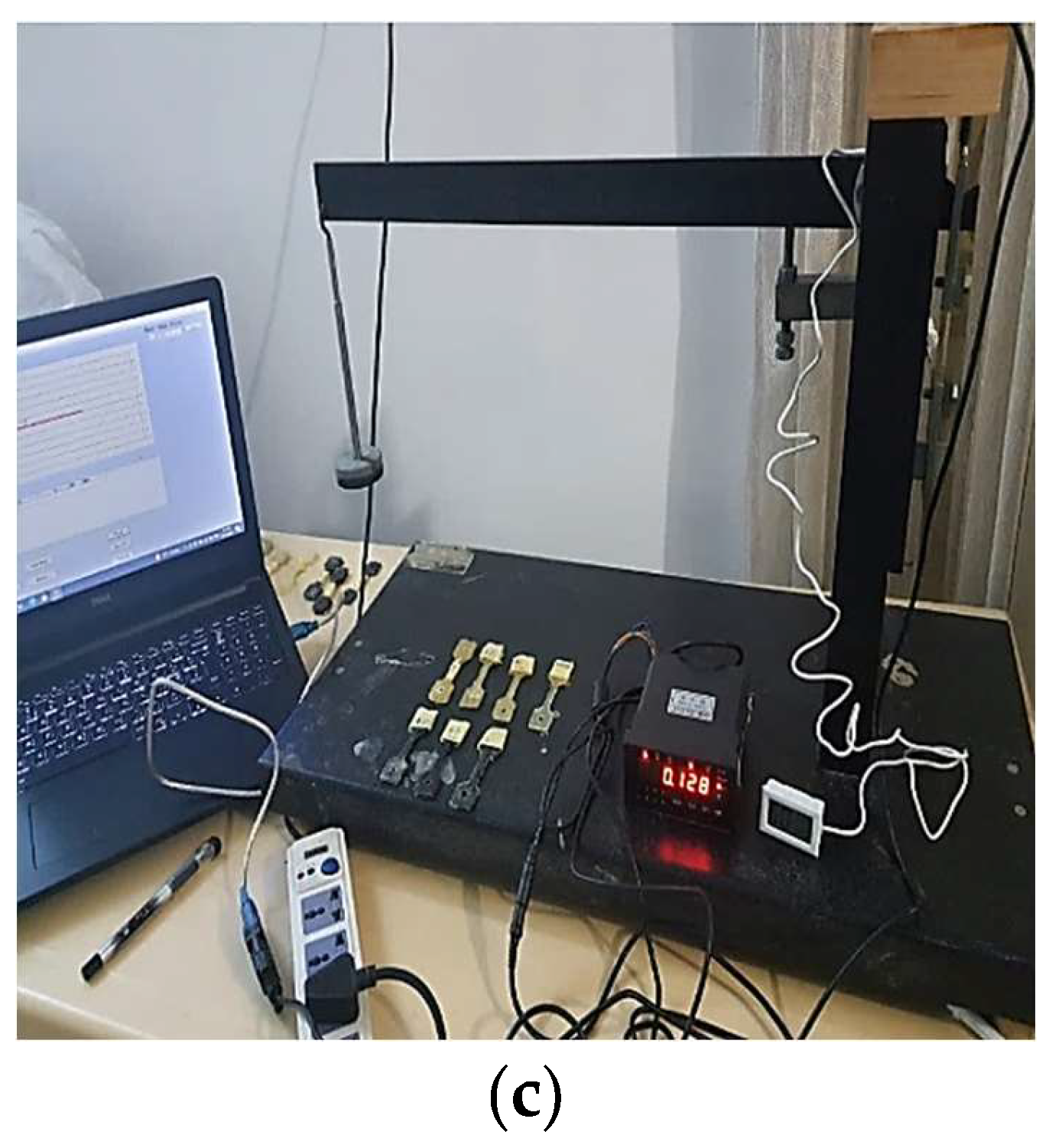
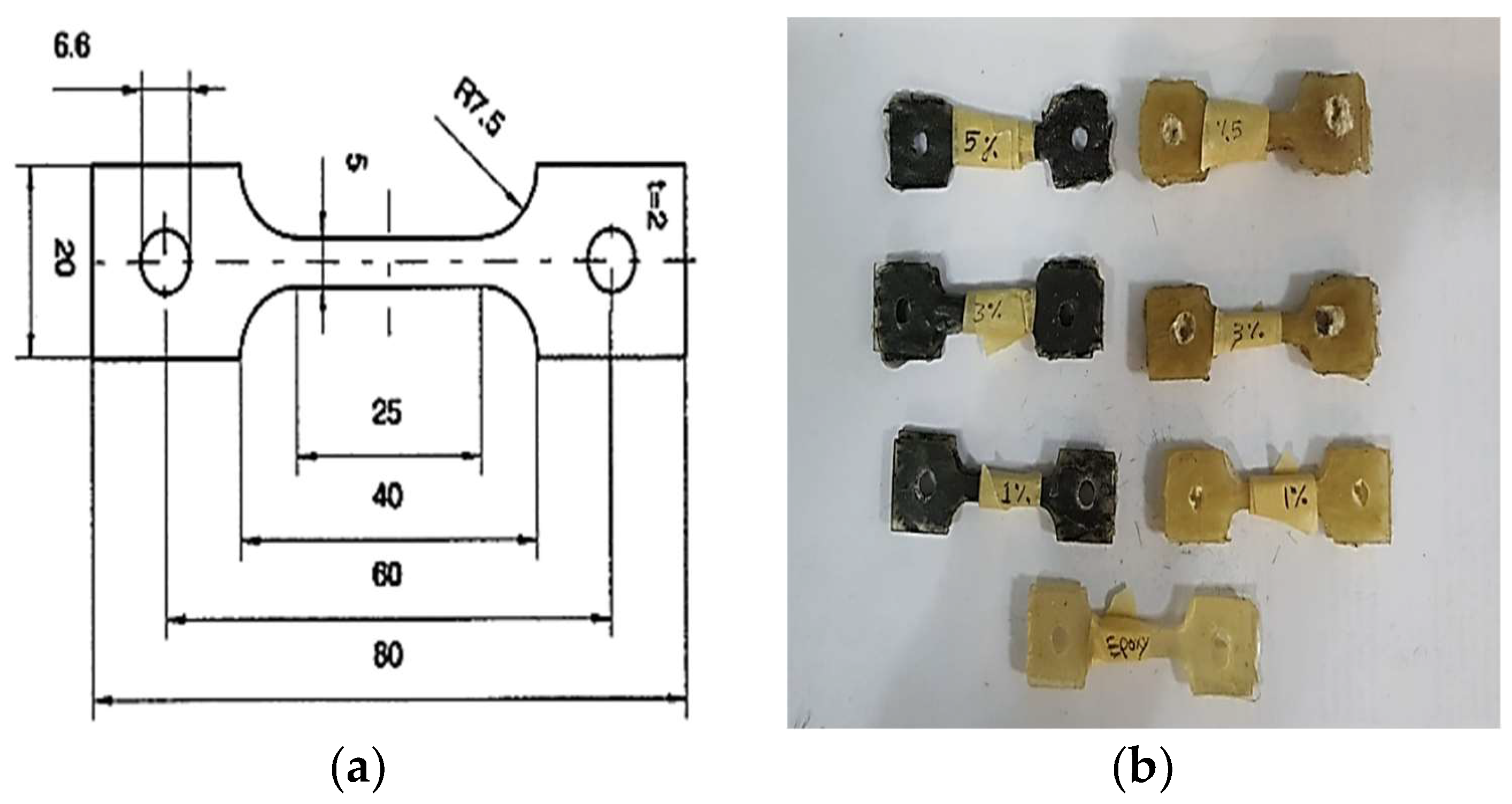
2.3. Mechanical Testing
2.3.1. Tensile Test
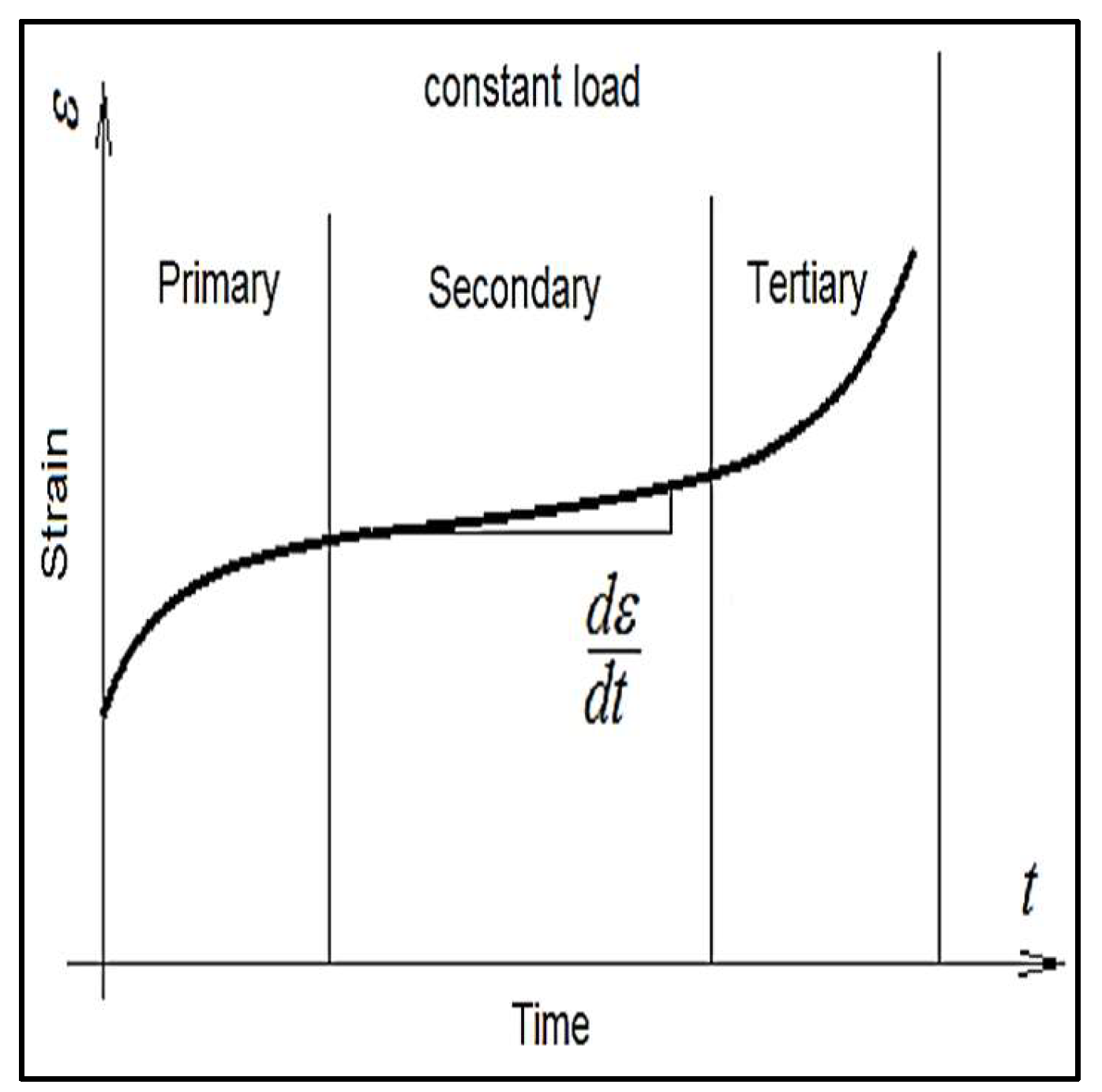
2.3.2. Creep Test
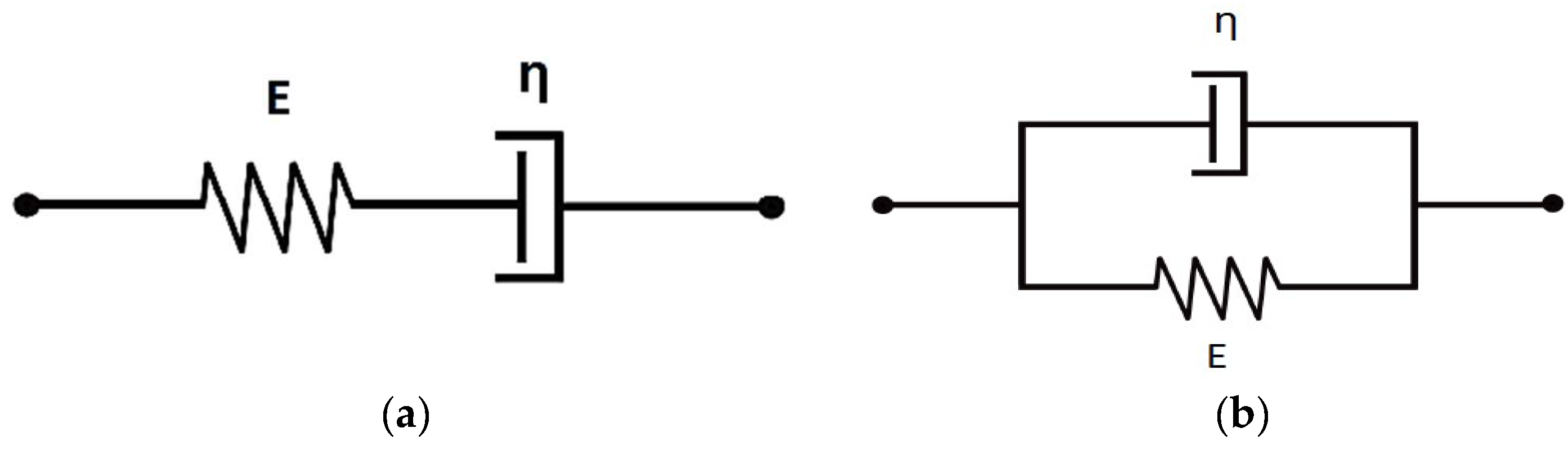
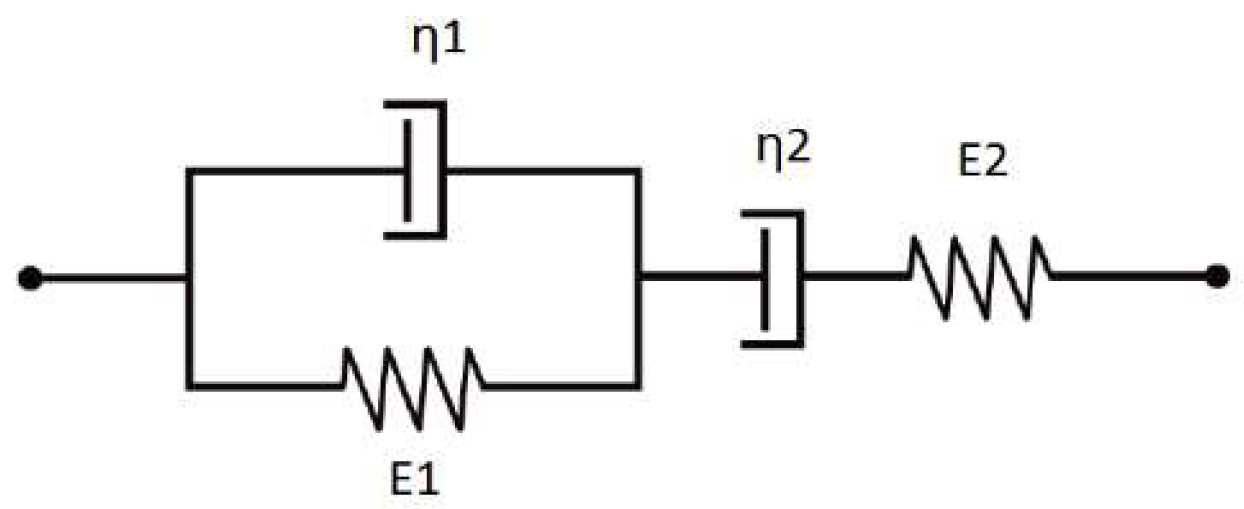
3. Constitutive Creep Equations
| Constant values of Burgers model for epoxy reinforced Kevlar | |||||||
|
Additives % |
P 1 min |
P 2 Min2 |
q 1 Mpa. min |
q 2 Mpa.min2 |
A Min2 |
r1 |
r2 |
| 0 | 330.3054 | 271.4549 | 36630.0366 | 36683.1002 | 328.6577 | 0.0030 | 1.2137 |
| 1 | 803.0154 | 1016.5172 | 105263.157 | 206609.1898 | 800.4796 | 0.0012 | 0.7887 |
| 3 | 354.0365 | 598.5443 | 79051.3833 | 184735.9090 | 350.6389 | 0.0028 | 0.5886 |
| 5 | 203.7521 | 258.5752 | 104112.441 | 184696.5895 | 201.1980 | 0.0049 | 0.7830 |
| Constant values of Burgers model for epoxy reinforced Carbon | |||||||
| 1 | 625.456 | 422.264 | 7502.944 | 6246.478 | 420.260 | 0.2429 | 1.2382 |
| 3 | 1898.479 | 1192.898 | 58993.569 | 38480.515 | 1190.896 | 0.2965 | 1.2949 |
| 5 | 921.341 | 1029.704 | 45997.102 | 64356.514 | 1027.702 | 0.0516 | 0.9464 |
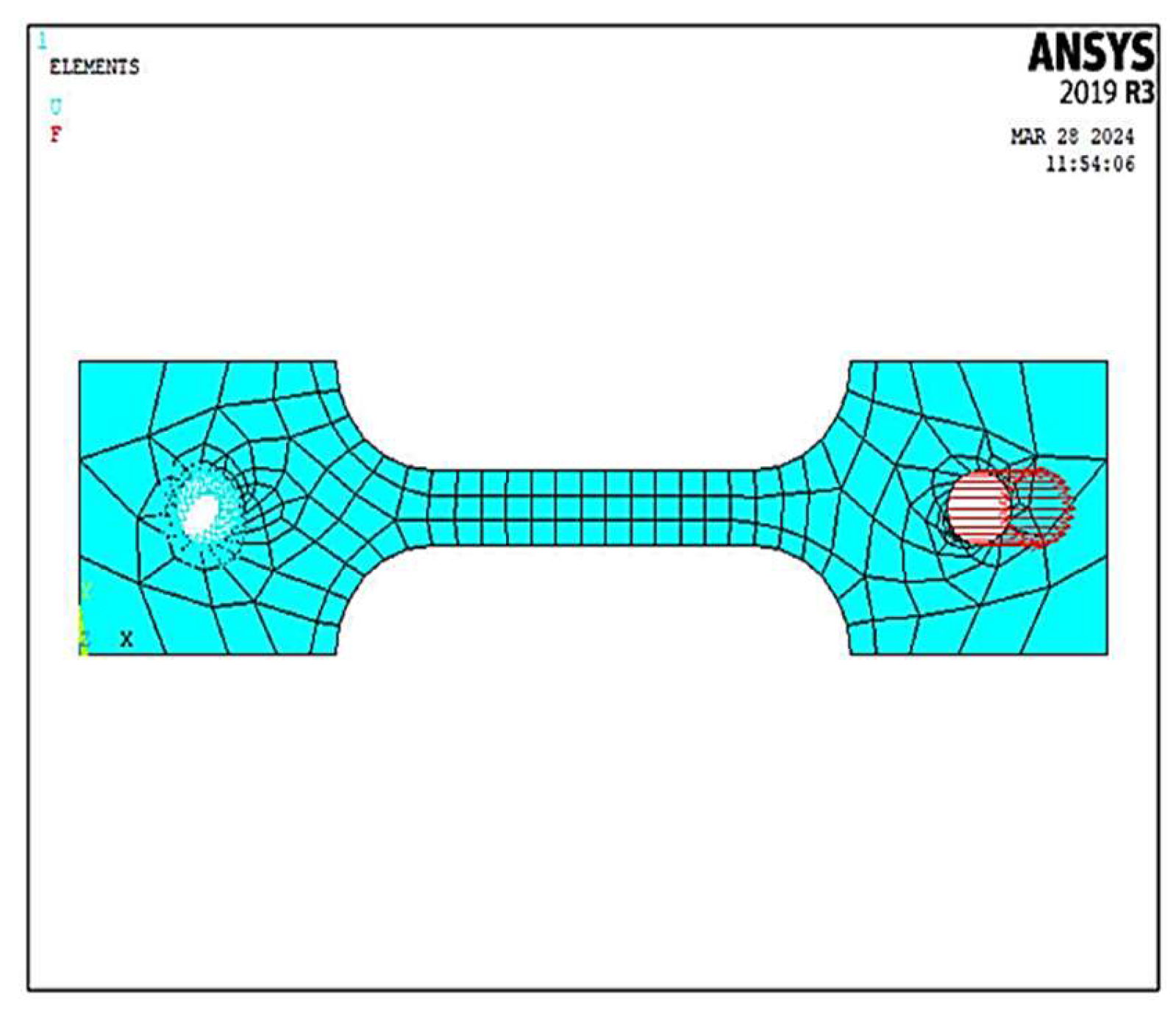
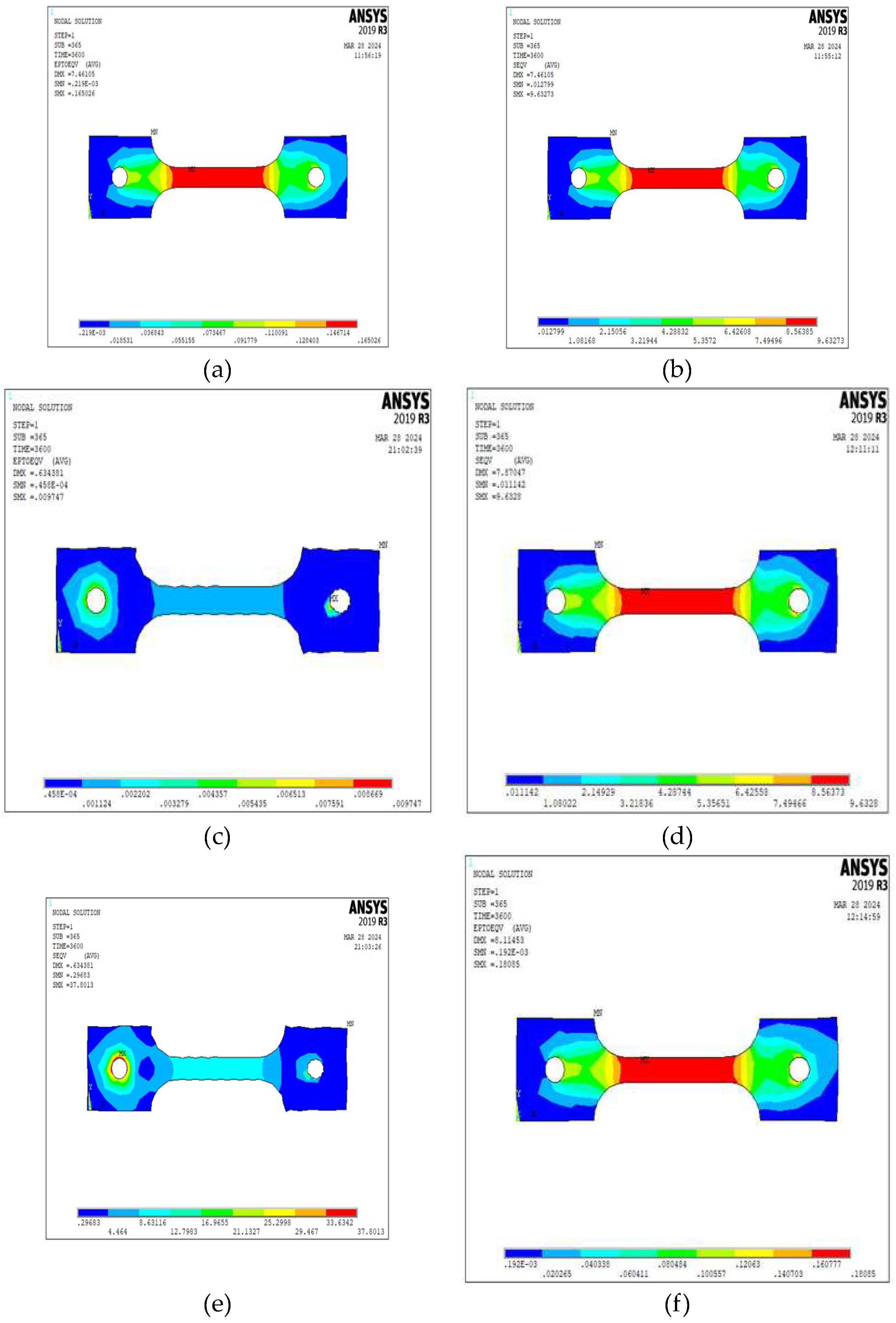
4. Finite Element Modeling
5. Results and Discussion
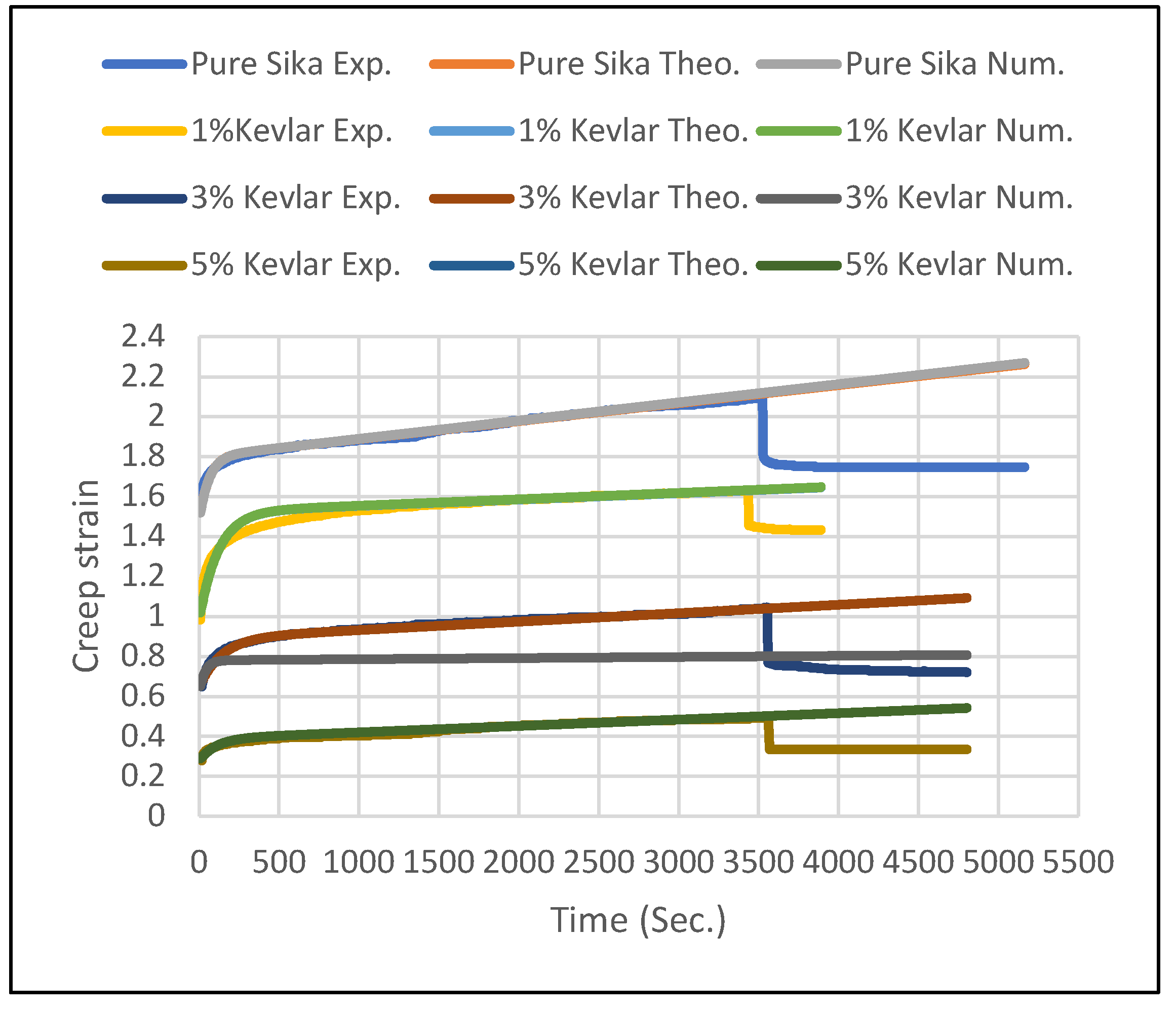
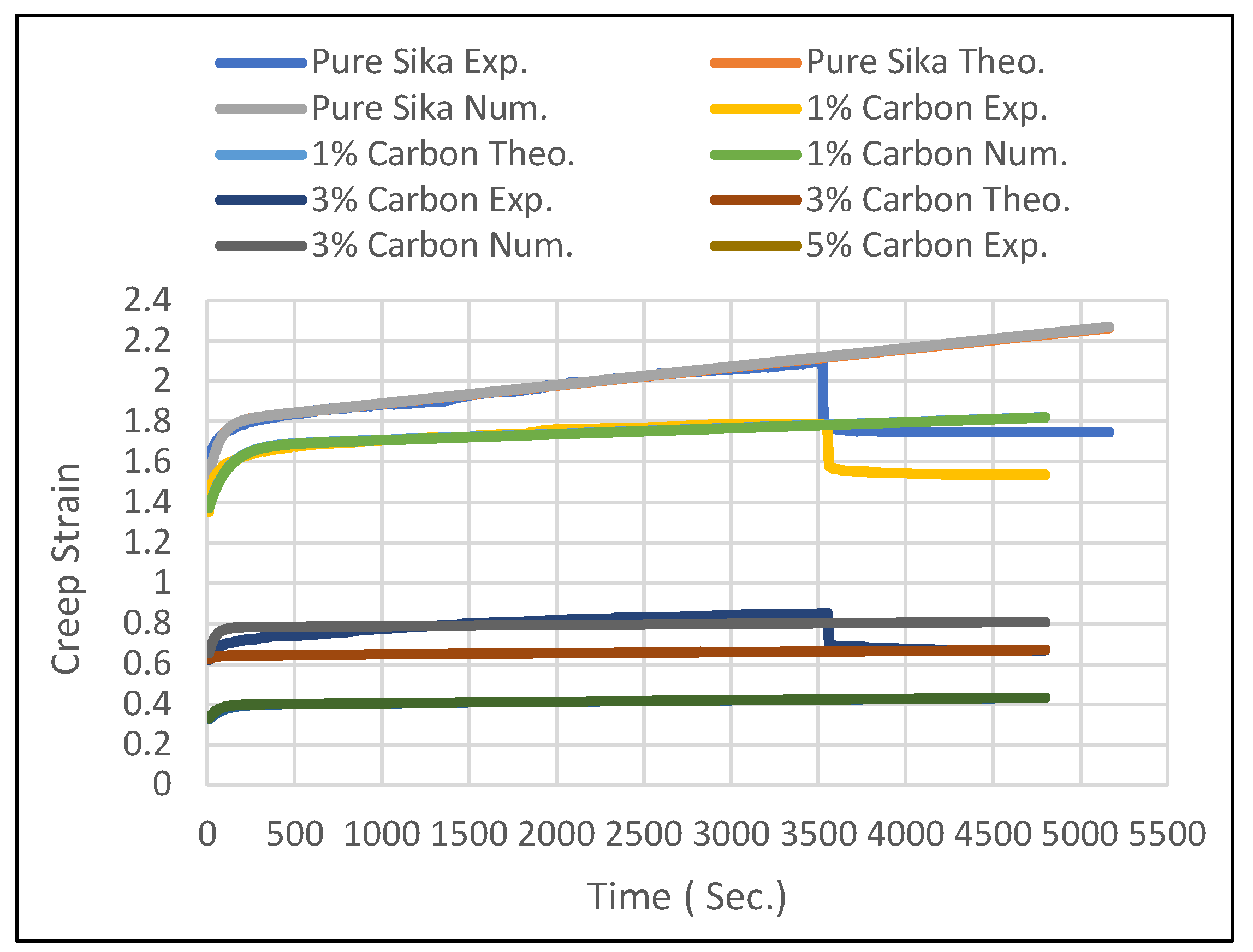
5.1. Creep Strain
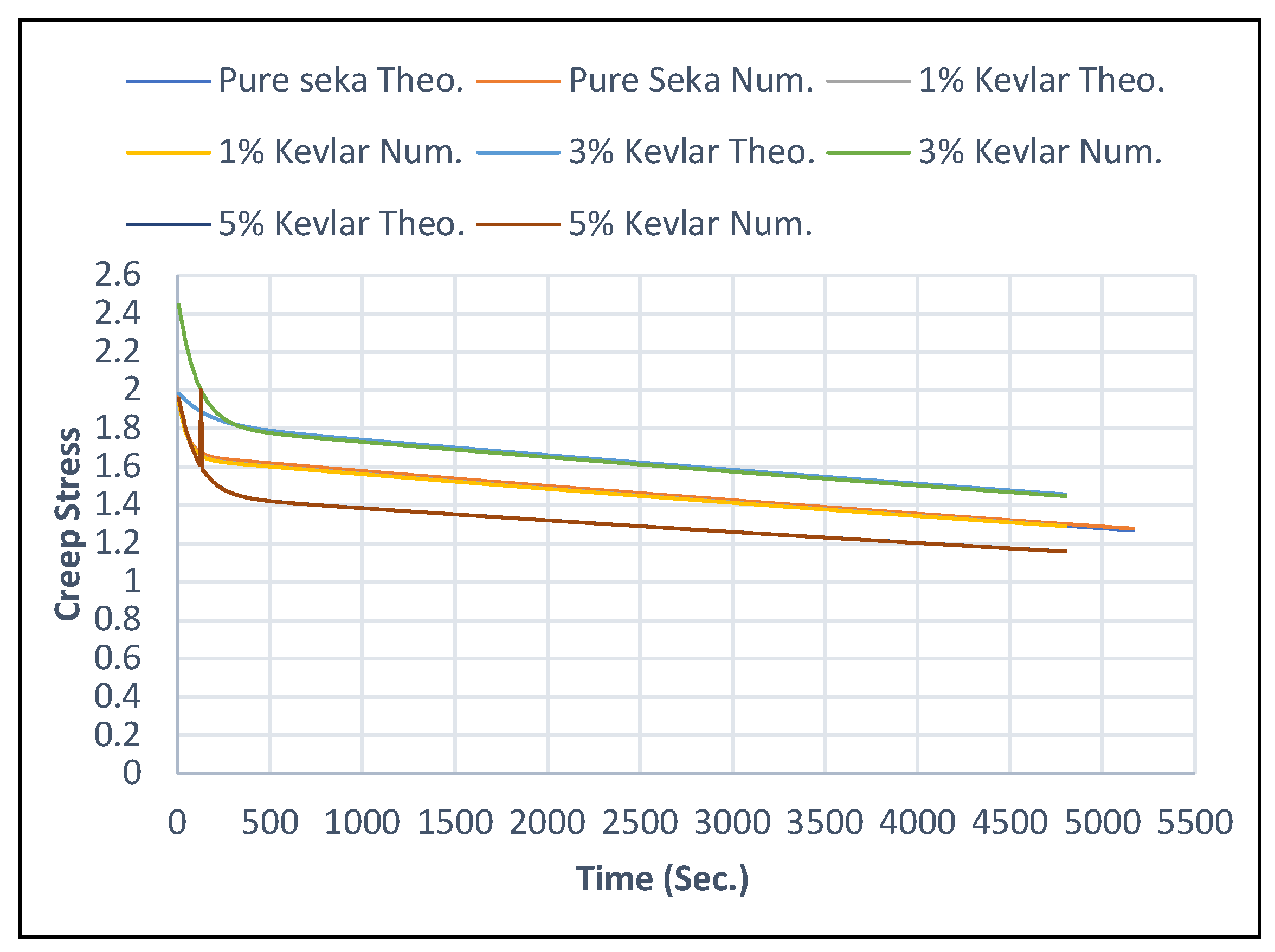
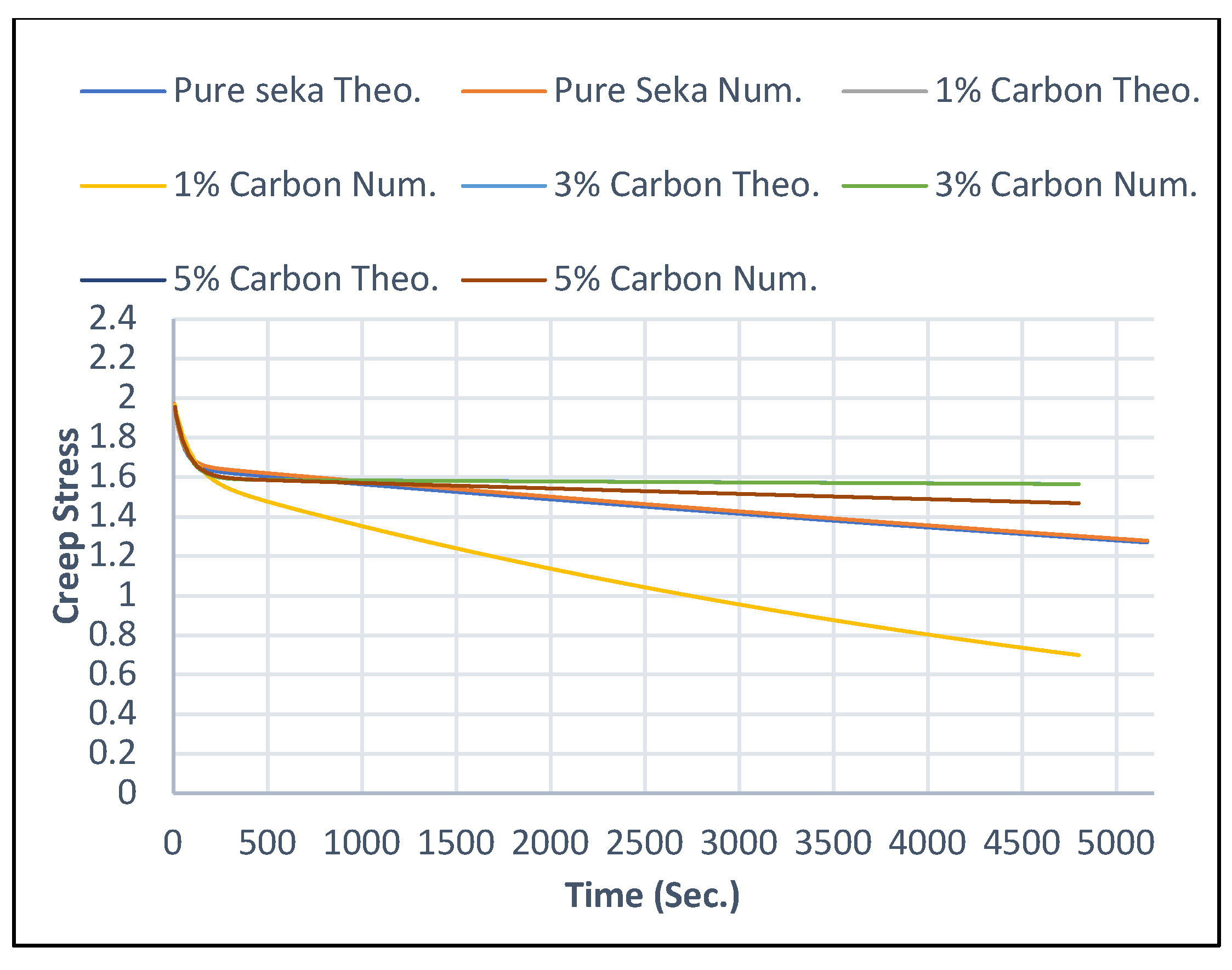
5.2. Creep Stress
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nabeel, M., et al., Numerical and experimental evaluation of the mechanical behavior of Kevlar/glass fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2020. 34: p. 4613-4619. [CrossRef]
- Agwa, M., et al., Integrated vacuum assisted resin infusion and resin transfer molding technique for manufacturing of nano-filled glass fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Journal of Industrial Textiles, 2022. 51(3_suppl): p. 5113S-5144S. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, Z., Epoxy in nanotechnology: A short review. Progress in organic coatings, 2019. 132: p. 445-448. [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, V., et al., Characterization on thermal properties of glass fiber and kevlar fiber with modified epoxy hybrid composites. Journal of materials research and technology, 2020. 9(3): p. 3158-3167. [CrossRef]
- Ghouti, H.A., et al., Multifunctional hybrid composites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties based on polybenzoxazine and chopped kevlar/carbon hybrid fibers. Polymers, 2018. 10(12): p. 1308. [CrossRef]
- Hallad, S.A., et al. Kevlar reinforced polymer matrix composite for structural application. in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2018. IOP Publishing.
- Deepak, M., K. Subbaya, and S. Thilak, IMPACT BEHAVIOR OF HYBRID NANO FILLED KEVLAR REINFORCED COMPOSITES. 2020.
- Vasudevan, A., et al., Layer-wise damage prediction in carbon/Kevlar/S-glass/E-glass fibre reinforced epoxy hybrid composites under low-velocity impact loading using advanced 3D computed tomography. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2019.
- Sahu, P., N. Sharma, and S.K. Panda, Numerical prediction and experimental validation of free vibration responses of hybrid composite (Glass/Carbon/Kevlar) curved panel structure. Composite Structures, 2020. 241: p. 112073. [CrossRef]
- Behera, A., et al., Tensile and failure behavior of kevlar fiber reinforced epoxy matrix composite exposed to different environmental conditions. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018. 5(9): p. 20250-20256. [CrossRef]
- Almeida Jr, J.H.S., et al., Creep and interfacial behavior of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy filament wound laminates. Polymer Composites, 2018. 39(S4): p. E2199-E2206. [CrossRef]
- Battawi, A. and B. Abed, Experimental, theoretical and numerical investigation of creep characteristics of fish scale powder-chicken feather filled polyester composites. Journal of Applied Engineering Science, 2022. 20(4): p. 1307-1316. [CrossRef]
- BATTAWI, A. and B.H. ABED, CREEP CHARACTERISTICS OF POLYESTER COMPOSITES WITH NATURAL FIBER REINFORCEMENT (HORSE HAIR/SHEEP WOOL).
- Abed, B.H. and A.A. Battawi, Effect of fish scales on fabrication of polyester composite material reinforcements. Open Engineering, 2021. 11(1): p. 915-921. [CrossRef]
- Abed, B.H., A.A. Battawi, and A.W.H. Khuder, Effect of Immersion Media for Polyester Composite Reinforced with Chicken Feathers on Creep Behavior. Strojniški vestnik-Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022. 68(6): p. 377-384. [CrossRef]
- Abed, B., K. Jadee, and A. Battawi, Experimental and numerical study on the effect of creep behavior on epoxy composites reinforced with yttrium oxide powder. International Journal of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020. 25(4): p. 203-213.
- Yang, Z., et al., Flexural creep tests and long-term mechanical behavior of fiber-reinforced polymeric composite tubes. Composite Structures, 2018. 193: p. 154-164. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, K., et al., The experimental analysis of creep and corrosion properties of polymeric tube reinforced by glass, carbon and Kevlar fibers. Materials Research Express, 2021. 8(6): p. 065307. [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, M., S. Claramunt, and S. Srinivasan, Modeling creep relaxation of polytetrafluorethylene gaskets for finite element analysis. International Journal of Materials, Mechanics and Manufacturing, 2017. 5(2): p. 123-126. [CrossRef]
- Katouzian, M., et al., Modeling Study of the Creep Behavior of Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review. Polymers, 2022. 15(1): p. 194. [CrossRef]
- Zehsaz, M., F. Vakili-Tahami, and M.-A. Saeimi-Sadigh, Modified creep constitutive equation for an epoxy-based adhesive with nonlinear viscoelastic behavior. The Journal of Strain Analysis for Engineering Design, 2015. 50(1): p. 4-14. [CrossRef]
- Ngudiyono, N., et al., Review of creep modelling for predicting of long-term behavior of glued-laminated bamboo structures. 2019.


| Constant values of PRONY SERIES for epoxy reinforced Kevlar | ||||||||
|
Additive % |
β 1/sec |
p1 sec2 |
Ʈ1 sec |
g1 N/mm | α 1/sec |
p2 sec2 |
Ʈ2 sec |
g2 N/mm |
| 0 | 5.1098E-05 | 19617.1253 | 19570.0164 | 1.801 | 0.0212 | 921922.4436 | 47.1089 | 8.888 |
| 1 | 2.0782E-05 | 48193.6442 | 48117.5351 | 2.710 | 0.0131 | 3662182.7608 | 76.1091 | 4.952 |
| 3 | 4.7303E-05 | 21242.1908 | 21140.2640 | 4.115 | 0.0098 | 2154759.642 | 101.926 | 11.028 |
| 5 | 8.2314E-05 | 12225.1288 | 12148.5045 | 9.523 | 0.0130 | 930870.8113 | 76.6243 | 24.691 |
| Constant values of PRONY SERIES for epoxy reinforced Carbon | ||||||||
| 1 | 1.7494E-05 | 57248.7134 | 57160.9726 | 1.975 | 0.0113 | 5015351.5541 | 87.7408 | 8.1300 |
| 3 | 3.1619E-06 | 316324.895 | 316256.9103 | 4.301 | 0.0147 | 21500570.718 | 67.9845 | 16.606 |
| 5 | 1.8059E-05 | 55439.2245 | 55371.803 | 8.333 | 0.0148 | 3733197.7323 | 67.4205 | 33.167 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




