Submitted:
18 April 2024
Posted:
18 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Enumeration of Salmonella and Campylobacter
2.3. Minimum inhibitory concentration for Campylobacter and Salmonella
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
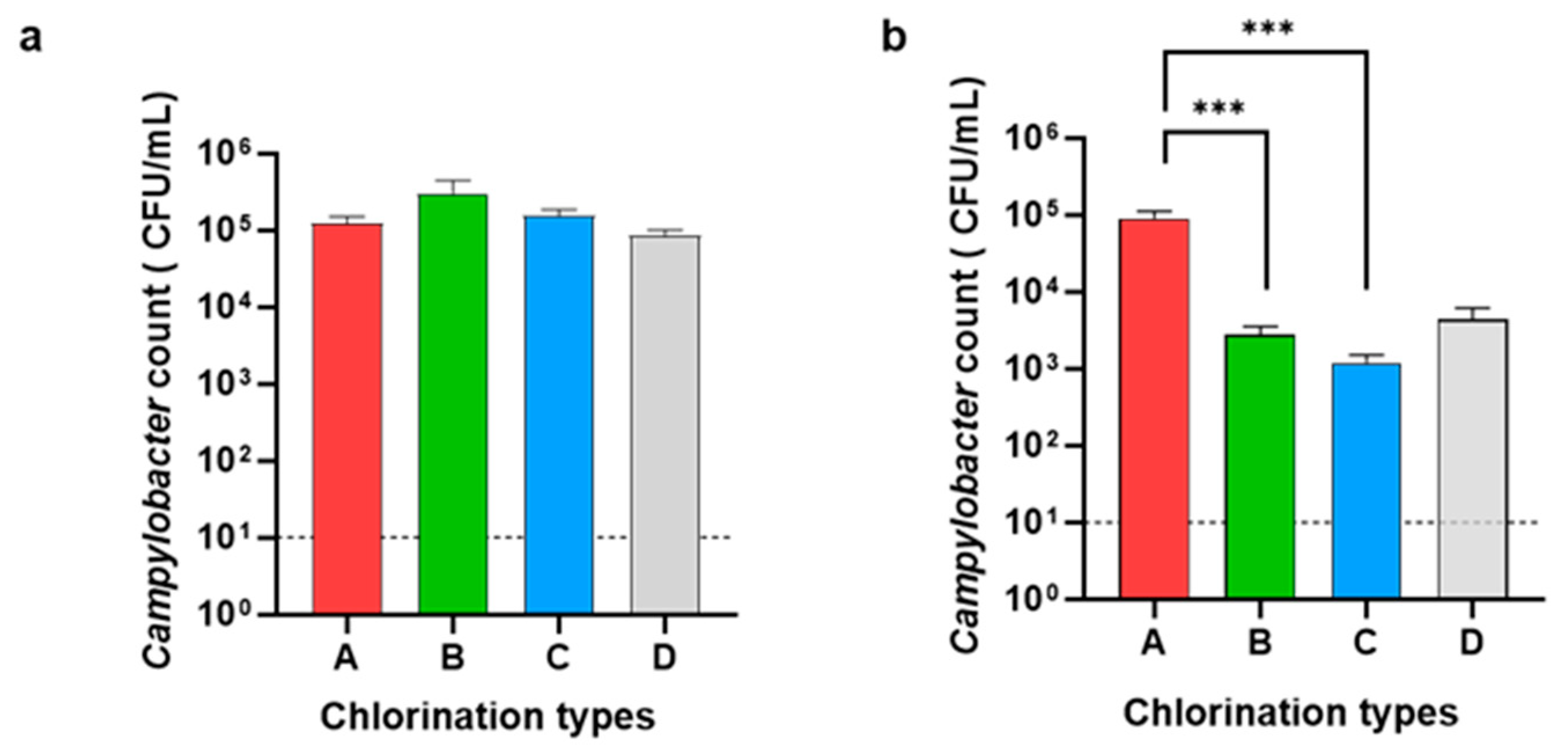
3.1. Enumeration of Campylobacter and Salmonella
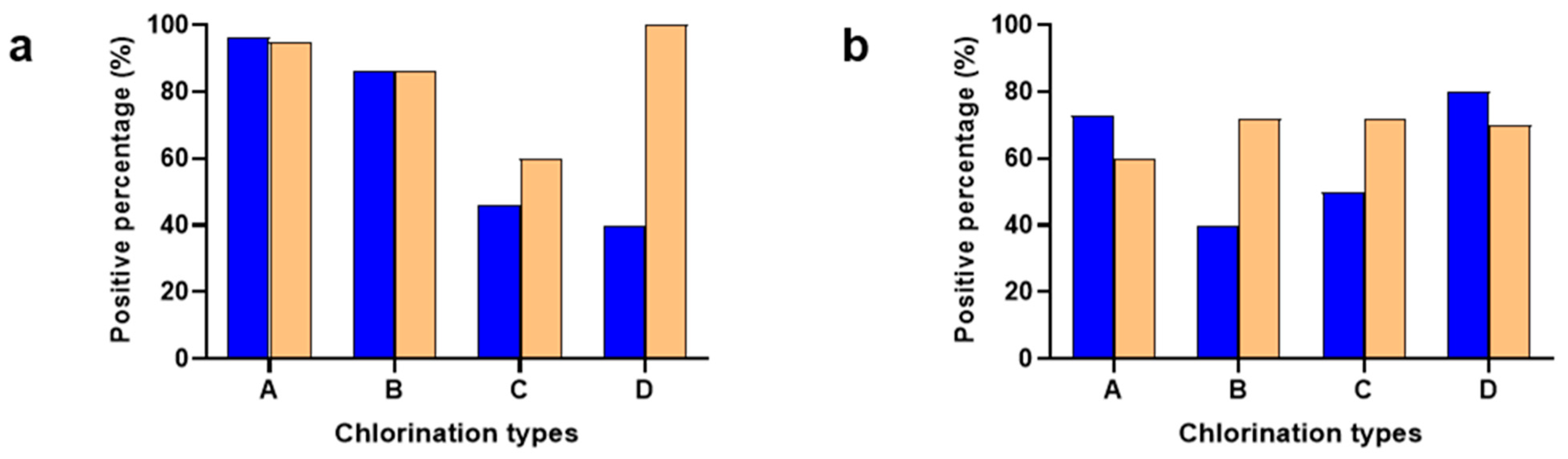
3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration for Campylobacter and Salmonella
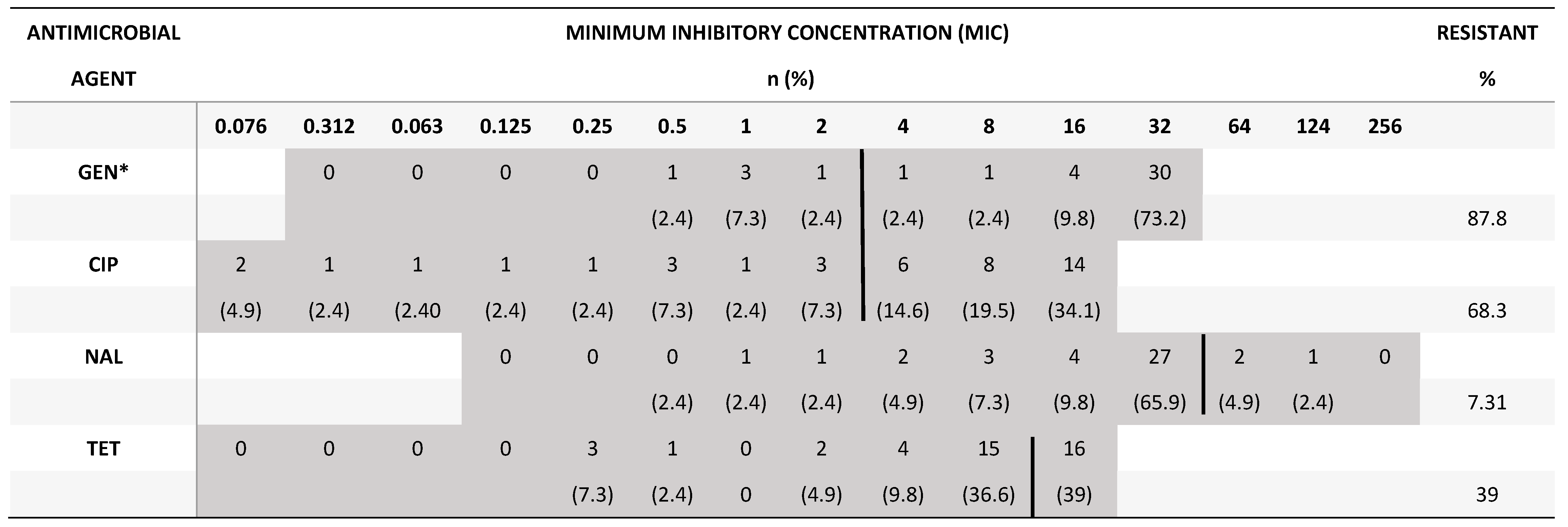
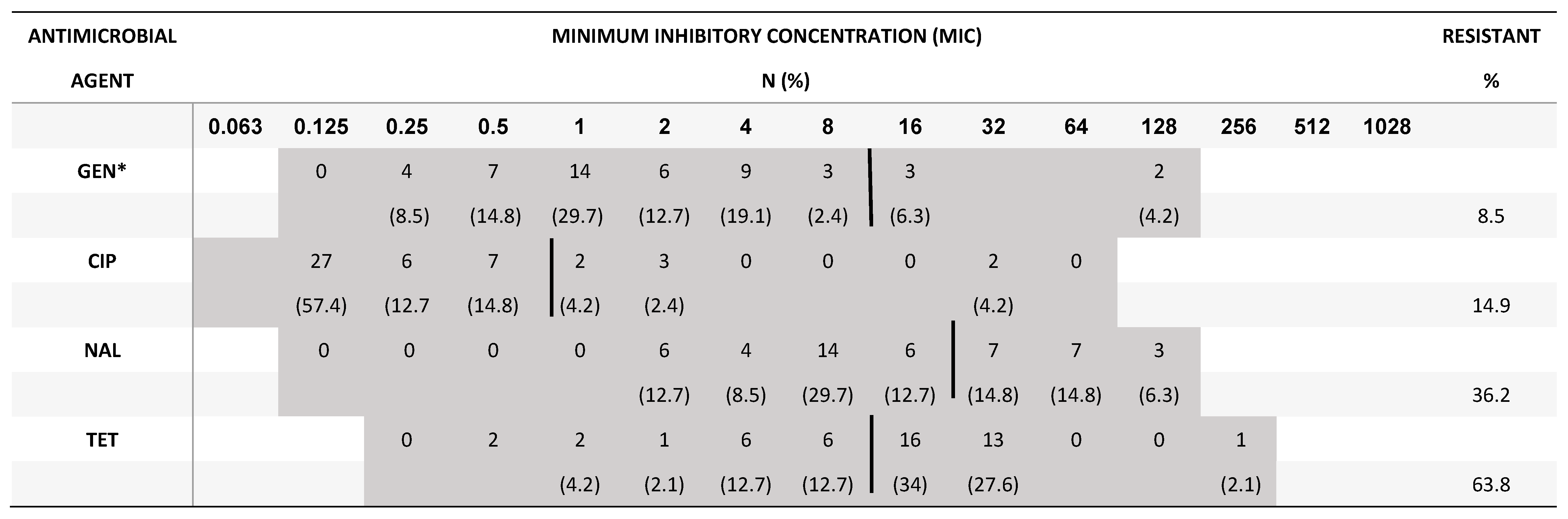
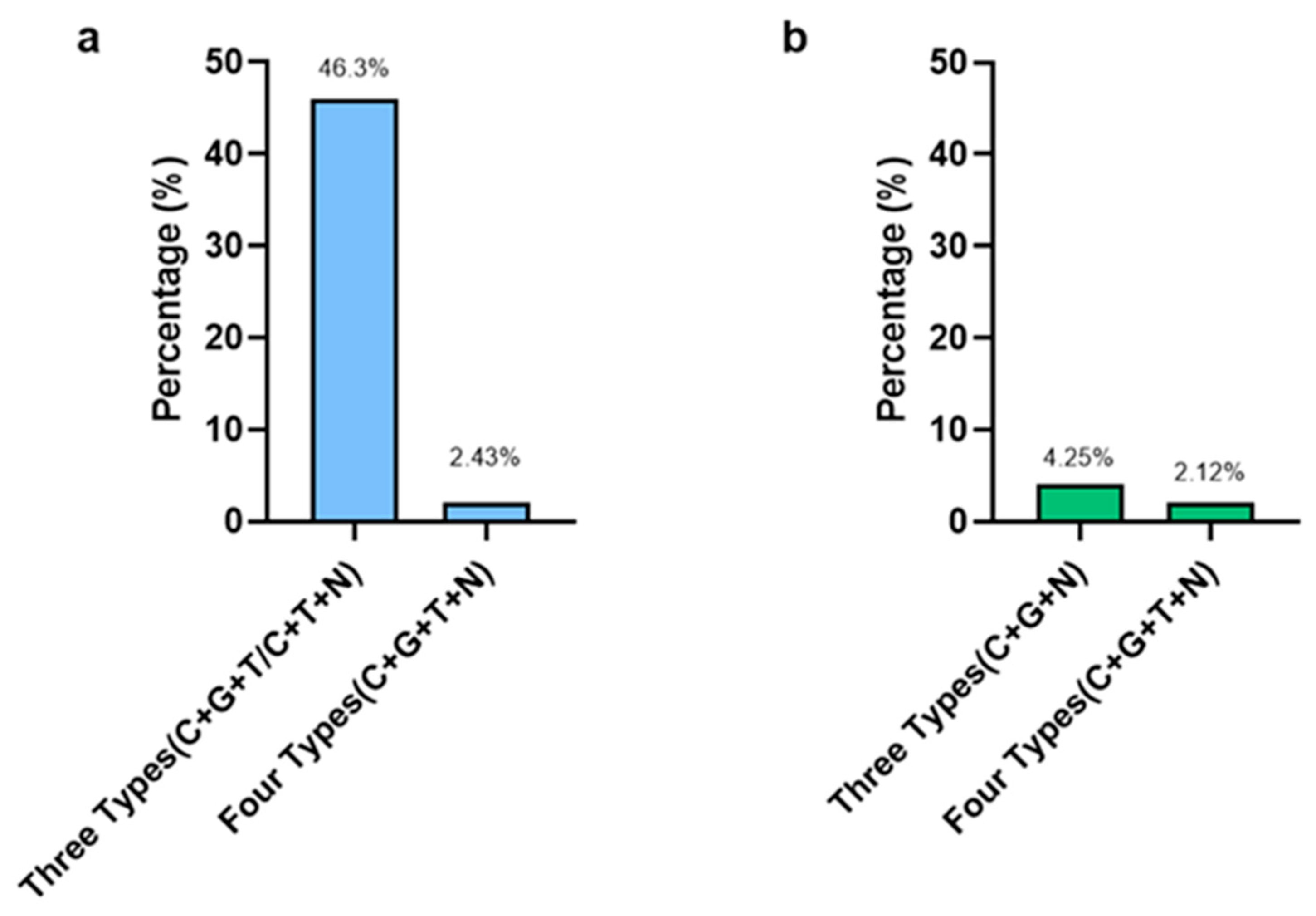
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO (2013). "The global view of campylobacteriosis: report of an expert consultation, Utrecht,Netherlands ,July 2012." 9-11. 20 July.
- WHO (2015). WHO estimates of the global burden of foodborne diseases: foodborne disease burden epidemiology reference group 2007-2015, World Health Organization.
- Heredia, N.; García, S. Animals as sources of food-borne pathogens: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FoodNet 2014. FoodNet Annual Surveillance Report 2014. Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodnet/pdfs/2014-foodnet-surveillance-report.pdf.
- Akil, L.; Ahmad, H.A. Quantitative Risk Assessment Model of Human Salmonellosis Resulting from Consumption of Broiler Chicken. Diseases 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, O.B.; Clarke, J.; Mattos, F.; Wang, B. A quantitative microbial risk assessment model of Campylobacter in broiler chickens: Evaluating processing interventions. Food Control. 2019, 100, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA -FSIS. The U.S. Department of Agriculture's (USDA) Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS).USDA finalizes new food safety measures reduce Salmonella and Campylobacter in Poultry, Washington, Feb. 4, 2016. www.usda.gov/media/press- releases/2016/02/04/usda-finalizes-new-food-safety-measures-reduce-salmonella-and Campylobacter in poultry 2016.
- Ta, Y.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; To, P.B.; Pham, D.X.; Le HT, H.; Thi, G.N.; Alali, W.Q.; Walls, I.; Doyle, M.P. Quantification, serovars, and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella isolated from retail raw in Vietnam. Journal of food protection 2014, 77, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Khoo, W.J.; Zheng, Q.; Chung, H.-J.; Yuk, H.-G. Counts, serotypes, and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolates on retail raw poultry in the People’s Republic of China. Journal of food protection 2014, 77, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAPH. Annual Report of the Department of Animal Production and Health; DAPH: Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DAPH. Annual Report of the Department of Animal Production and Health; DAPH: Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- DAPH. Annual Report of the Department of Animal Production and Health; DAPH: Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kottawatta KS, A.; Van Bergen MA, P.; Abeynayake, P.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Veldman, K.T.; Kalupahana, R.S. Campylobacter in broiler chicken and broiler meat in Sri Lanka: Influence of semi-automated vs. wet market processing on Campylobacter contamination of broiler neck skin samples. Foods 2017, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keener, K.; Bashor, M.; Curtis, P.; Sheldon, B.; Kathariou, S. Comprehensive Review of Campylobacter and Poultry Processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2004, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasooriya, G.D.B.N.; Amarasiri, M.K.U.T.; Abeykoon, A.M.H.; Kalupahana, R.S. Salmonella, Campylobacter and Escherichia coli in raw chicken meat, chicken products and cooked chicken in retail markets in Kandy, Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka Veter- J. 2019, 66, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Foodborne burden. 2011. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden/2011-foodborne-estimates.html.
- Engberg, J.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Taylor, D.E.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Nachamkin, I. Quinolone and macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli: resistance mechanisms and trends in human isolates. Emerging infectious diseases 2001, 7, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanska, B.; Andrzejewska, M.; Spica, D.; Klawe, J.J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from children and environmental sources in urban and suburban areas. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, A.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X. Molecular Identification of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobacter Species From Diarrheal Patients and Poultry Meat in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, M.P. Multidrug-resistant Campylobacter jejuni outbreak linked to puppy exposure—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2018, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousalkar, K.; Sims, S.; McWhorter, A.; Khan, S.; Sexton, M. The Effect of Sanitizers on Microbial Levels of Chicken Meat Collected from Commercial Processing Plants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2019, 16, 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017. Microbiology of the food chain — Horizontal method for the detection, enumeration and serotyping of Salmonella — Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp.2017,P.1-50. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:6579:-1:ed-1:v1:en.
- CLSI M100. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 34th Edition. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/.
- EUCAST antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast_of_bacteria.
- EUCAST antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints.
- Johnson, R. US-EU poultry dispute on the use of pathogen reduction treatments (PRTs); Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Scientific Assessment of the Public Health and Safety of Poultry Meat in Australia; Food Standards Australia New Zealand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kalupahana, R.S.; Kottawatta, K.S.A.; Kanankege, K.S.T.; van Bergen, M.A.P.; Abeynayake, P.; Wagenaar, J.A. Colonization of Campylobacter spp. in Broiler Chickens and Laying Hens Reared in Tropical Climates with Low-Biosecurity Housing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, S.; Nadal, L.; Álvarez, I.; Mañas, P.; Cebrián, G. Impact of the Resistance Responses to Stress Conditions Encountered in Food and Food Processing Environments on the Virulence and Growth Fitness of Non-Typhoidal Salmonellae. Foods 2021, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasooriya, G.; Khan, S.; Chousalkar, K.K.; McWhorter, A.R. Invasive potential of sub-lethally injured Campylobacter jejuni and Salmonella Typhimurium during storage in chicken meat juice. Food Control. 2022, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Harrison, M.A.; Berrang, M.E. Postchill Antimicrobial Treatments To Control Salmonella, Listeria, and Campylobacter Contamination on Chicken Skin Used in Ground Chicken. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidaullah, H.; Abirami, N.; Shamila-Syuhada, A.K.; Chuah, L.-O.; Nurul, H.; Tan, T.P.; Abidin, F.W.Z.; Rusul, G. Prevalence of Salmonella in poultry processing environments in wet markets in Penang and Perlis, Malaysia. Veter- World 2017, 10, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, P.; Madhavarao, T.; Rao, L. Study on the incidence of Salmonella enteritidis in Poultry and meat Samples by Cultural and PCR Methods. Veter- World 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Alali, W.; Harrison, M.; Hofacre, C. Prevalence of Salmonella in Neck Skin and Bone of Chickens. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs-Reitsma, W. Campylobacter in the food supply. Campylobacter, 2nd ed.; Nachamkin, I., Blaser, M., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pavic, A.; Cox, J.M.; Chenu, J.W. Effect of extending processing plant operating time on the microbiological quality and safety of broiler carcasses. Food Control. 2015, 56, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashor, M.P.; Curtis, P.A.; Keener, K.M.; Sheldon, B.W.; Kathariou, S.; Osborne, J.A. Effects of Carcass Washers on Campylobacter Contamination in Large Broiler Processing Plants. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenault, J.; Letellier, A.; Quessy, S.; Boulianne, M.; Arsenault, A.L.J.; Giombelli, A.; Gloria, M.B.A.; Carrillo, C.D.; Plante, D.; Iugovaz, I.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Salmonella and Campylobacter spp. Carcass Contamination in Broiler Chickens Slaughtered in Quebec, Canada. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, D.; Van Deun, K.; Messens, W.; Martel, A.; Van Immerseel, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Rasschaert, G.; Heyndrickx, M.; Pasmans, F. Campylobacter control in poultry by current intervention measures ineffective: Urgent need for intensified fundamental research. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I.; Mahmood, M.S.; Akhtar, M.; Khan, A. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in meat, milk and other food commodities in Pakistan. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillard, H. Factors affecting the persistence of Salmonella during the processing of poultry. J. Food Prot. 1989, 52, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuzihara, T.O.; Fernandes, S.A.; Franco, B.D.G.M. Prevalence and Dissemination of Salmonella Serotypes along the Slaughtering Process in Brazilian Small Poultry Slaughterhouses. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenquist, H.; Nielsen, N.L.; Sommer, H.M.; Nørrung, B.; Christensen, B.B. Quantitative risk assessment of human campylobacteriosis associated with thermophilic Campylobacter species in chickens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 83, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virto, R.; Manas, P.; Alvarez, I.; Condon, S.; Raso, J. Membrane Damage and Microbial Inactivation by Chlorine in the Absence and Presence of a Chlorine-Demanding Substrate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5022–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, G.; Bauermeister, L.; Bratcher, C.; Singh, M.; McKee, S. Salmonella and Campylobacter reduction and quality characteristics of poultry carcasses treated with various antimicrobials in a post-chill immersion tank. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 165, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, V.; Coton, E.; Rigalma, K.; Dantigny, P. Effects of disinfectants on inactivation of mold spores relevant to the food industry: a review. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2021, 38, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanadhas, D.P.; Marathe, S.A.; Chakravortty, D. Biocides – resistance, cross-resistance mechanisms and assessment. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 22, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasooriya, G.; McWhorter, A.R.; Khan, S.; Chousalkar, K.K. Transcriptomic response of Campylobacter jejuni following exposure to acidified sodium chlorite. npj Sci. Food 2021, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhandiramlage, G.K.; McWhorter, A.R.; Chousalkar, K.K. Chlorine Induces Physiological and Morphological Changes on Chicken Meat Campylobacter Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Mangen, M.-J.J.; de Koeijer, A.A.; Bogaardt, M.-J.; Evers, E.G.; Jacobs-Reitsma, W.F.; van Pelt, W.; Wagenaar, J.A.; de Wit, G.A.; van der Zee, H.; et al. Effectiveness and Efficiency of Controlling Campylobacter on Broiler Chicken Meat. Risk Anal. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasao, B.d.S.; Medeiros, V.; Barbosa, A.V.; de Aguiar, W.S.; dos Santos, F.F.; Abreu, D.L.d.C.; Clementino, M.M.; de Aquino, M.H.C. Detection of fluoroquinolone resistance by mutation in gyrA gene of Campylobacter spp. isolates from broiler and laying (Gallus gallus domesticus) hens,from Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. 2015, 45, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravisi, M.; Laviniki, V.; Bassani, J.; Filho, H.K.; Carvalho, D.; Wilsmann, D.; Borges, K.; Furian, T.; Salle, C.; Moraes, H.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni Isolated from Brazilian Poultry Slaughterhouses. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.; Martiny, D.; Van Waterschoot, N.; Hallin, M.; Maniewski, U.; Bottieau, E.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Vlieghe, E.; Ombelet, S.; Vandenberg, O.; et al. Antibiotic susceptibility profiles among Campylobacter isolates obtained from international travelers between 2007 and 2014. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgaciu, A.; Tabaran, A.; Colobatiu, L.; Mihaiu, R.; Dan, S.D.; Mihaiu, M. Concerning Increase in Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Pathogenic Strains of Salmonella Isolated in Poultry Meat Products. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramianfard, H.; Derakhshandeh, A.; Naziri, Z.; Farahani, R.K. Prevalence, virulence factor and antimicrobial resistance analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis from poultry and egg samples in Iran. BMC Veter- Res. 2021, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavri, A.; Možina, S.S. Development of antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli adapted to biocides. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 160, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasooriya, G.; Khan, S.; Chousalkar, K.K.; McWhorter, A.R. Invasive potential of sub-lethally injured Campylobacter jejuni and Salmonella Typhimurium during storage in chicken meat juice. Food Control. 2022, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample type | Sample number |
Salmonella Positive Percentage (%) |
Campylobacter positive Percentage (%) |
| Carcass wash | 150 | 80.66 (121/150) | 68.66 (103/150) |
| Neck Skin | 100 | 73 (73/100) | 57 (57/100) |
| Caeca | 100 | 79 (79/100) | 63 (63/100) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





