1. Introduction
With the profound adjustment of economic globalization, the main driving forces of globalization are diverging and changing. In order to cope with the risk of power transfer [
1], traditional developed countries rely on hegemony to push their interests to the extreme of protectionism [
2], and advanced science and technology are the key engines for economic growth of various countries. It has become an important area for some developed countries to try to restrain the development of emerging countries, making science and technology shift from human shared globalism to technological nationalism [
3]. Indeed, the global flow of technological elements has narrowed the gap between China and the world's advanced scientific and technological level, which has helped the rapid development of China's economy, but it has also made some manufacturing enterprises in China fall into the dilemma of technological innovation when technological nationalism is rampant [
4]. The existing researches have widely discussed the factors that affect the innovation performance of enterprises from the production factors at the micro level to the external environment at the macro level. At the micro level, the main focus is on exploring internal factors within the enterprise, including the characteristics and environment of the firm, the education level of the workers [
5], the financial capital, technology information of the firm [
6], and the executive characteristics of the firm [
7], etc. In addition, some scholars have found that there is a difference in the impact of female-owned companies and male-owned companies on corporate innovation from a gender perspective [
8]. The factors on macro level involves legal environment, government effectiveness [
9], the diversity of supplier and customer, regional innovation environment [
10], and business environment of the society [
11], etc. At present, the research on the influencing factors of enterprise innovation performance has been relatively detailed, but there is still no further discussion on the innovation situation faced by enterprises and how the innovation dilemma will affect the operation efficiency of enterprises.
The report of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China first proposed ”high-quality development” in 2017, China’s economy from the high-speed growth stage to the stage of high-quality development, the development of China’s manufacturing industry needs to change the previous extensive and intensive production mode, and then to improve the technical level and product quality as the development goal. As a pillar industry of a country’s real economy, the high-quality development and upgrading of manufacturing industry is an important driving force for national economic growth. In addition, manufacturing enterprises are also an important subject of technological innovation and a link in the transformation of results. Therefore, the operational efficiency of manufacturing enterprises has always been the focus of scholars around the world. In terms of operation efficiency, a large number of scholars have conducted evaluation and research on the operation efficiency of various manufacturing industries, including listed companies in the transportation industry [
12], the LED lighting industry [
13] and high-end equipment manufacturing industry [
14], etc. Some scholars also discussed the factors affecting the operation efficiency of enterprises, including the Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) performance [
15], strategic flexibility [
16], internal audit function (IAF) quality [
17], and cash flow [
18], etc. However, the discussion on the enterprise operation efficiency has formed a system, but the innovation situation of the enterprise has not been taken into account.
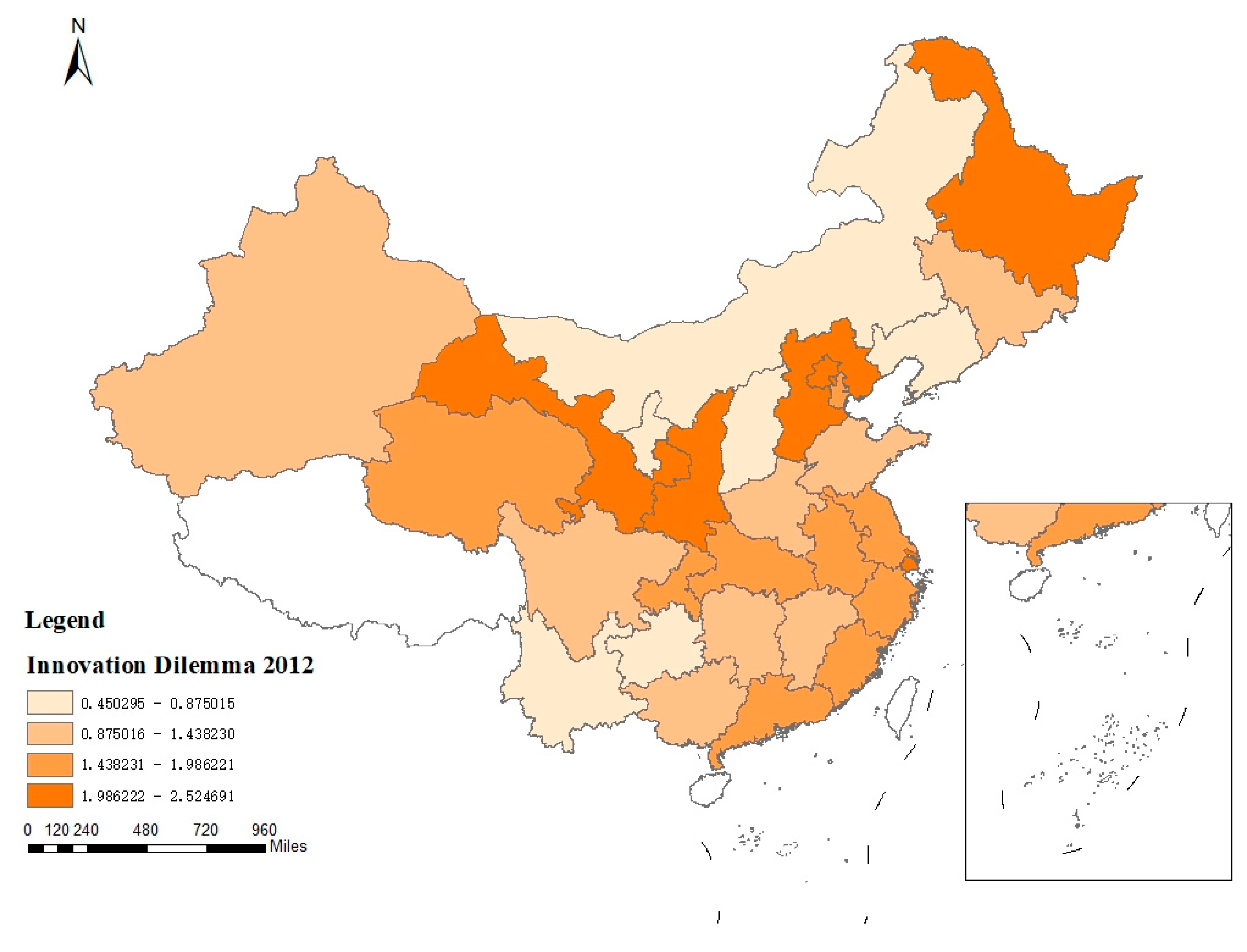
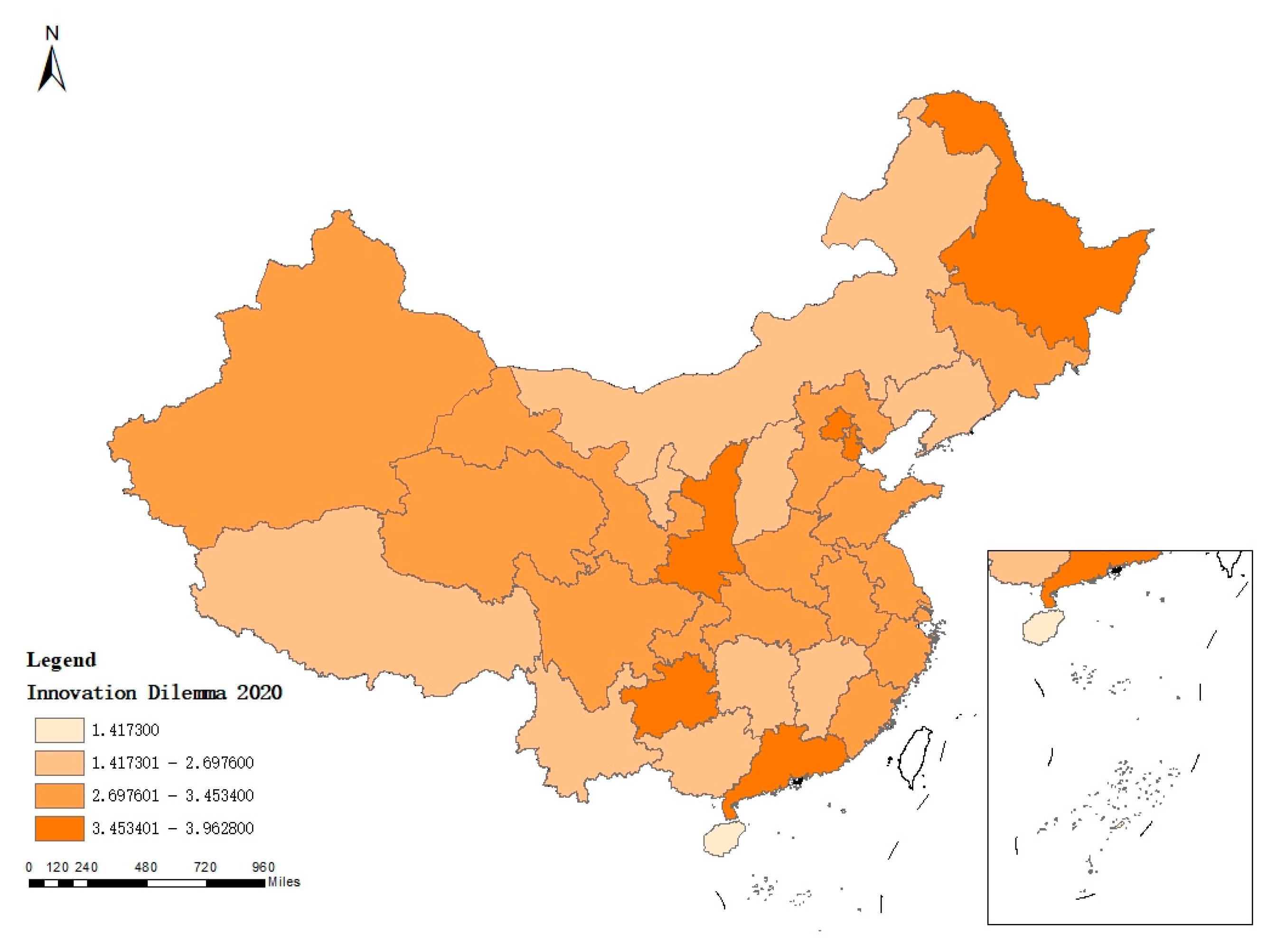
Before exploring how the innovation dilemma affects the operation efficiency, this paper briefly expounds and analyzes the current distribution status of the enterprise innovation dilemma in China. By classifying the sample data according to the provincial administrative region to which the enterprises belong, the distribution of innovation dilemmas of listed Chinese A-share manufacturing enterprises in each provincial administrative region can be obtained. This paper selects the data of innovation dilemmas of manufacturing enterprises in 2012 and 2020 after considering regional data integrity, and draws the regional distribution maps of innovation dilemmas faced by manufacturing enterprises. The changes of the distribution of innovation dilemma of manufacturing enterprises in different regions from 2012 to 2020 are compared and analyzed. As a note, the measurement of innovation dilemma level is referred to Lian, Y.L. et al [
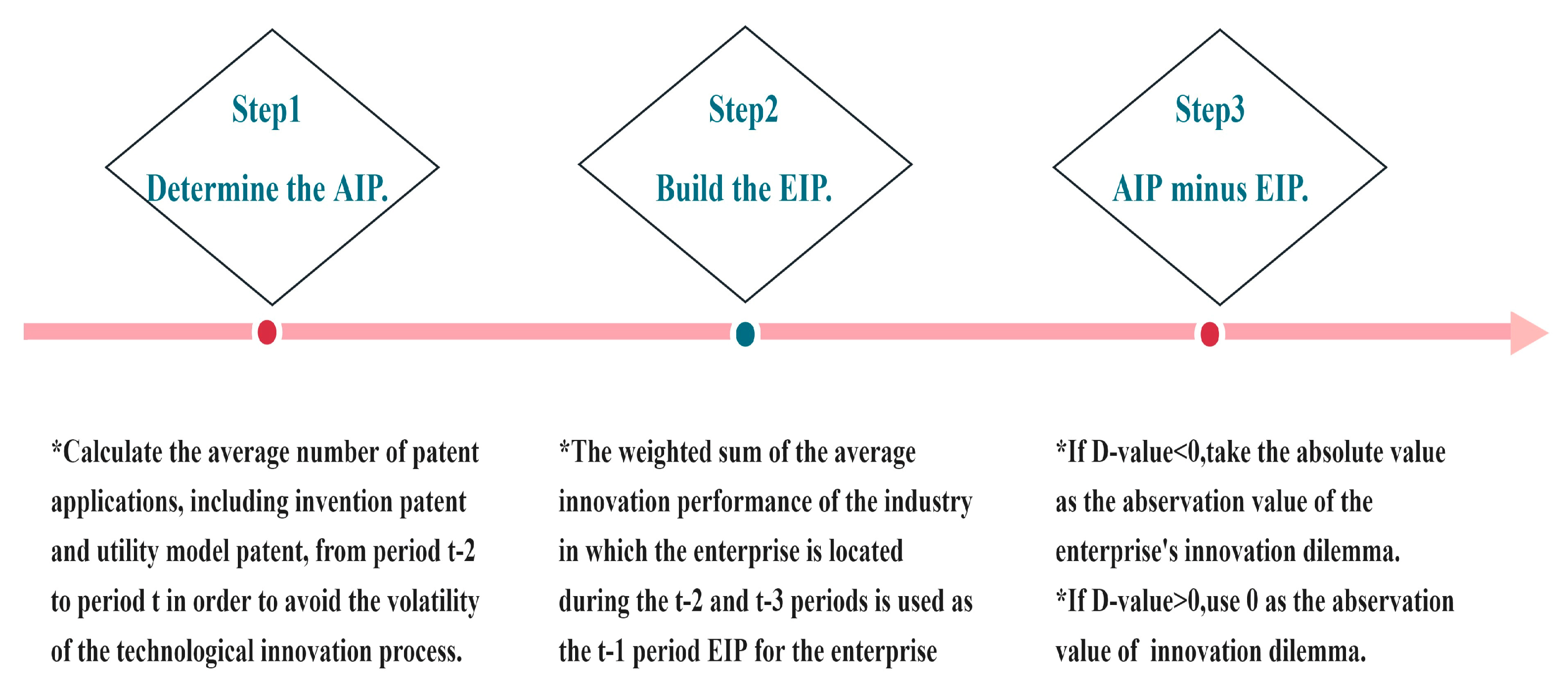
19], which will be explained in detail in the third section.
According to
Figure 1 and
Figure 2, in general, there are differences in the distribution of enterprise innovation dilemma between 2012 and 2020, and the group distance of the horizontal group of innovation dilemma between regions in 2020 becomes wider, indicating that the regional difference of enterprise innovation dilemma in 2020 is more obvious than that in 2012. In addition, the value range of the difference between the actual innovation performance and the expected innovation performance of enterprises in 2020 expands, indicating that the overall level of innovation dilemma of enterprises in 2020 is higher than that in 2012. By analyzing the reasons for the rising level of innovation dilemma, it can be seen that under the background of the increasing instability of the international technological innovation environment, independent research and development has gradually become the main way of technological innovation for Chinese manufacturing enterprises in order to break the technological monopoly. However, with the continuous progress of technological level, the demand for advanced and sophisticated technological breakthroughs has increased, and the difficulty of technological innovation has been increasing day by day. The diminishing marginal innovation of manufacturing enterprises has become the only way before making major technological breakthroughs. Admittedly, the deterioration of innovation situation at this time cannot be equated with the decline of technological innovation level.
Specifically, the provincial administrative regions with the highest level of innovation distress in 2012 and 2020 mainly involve the regions with leading economic development and the regions where old industrial cities are located. In 2012, the provincial-level administrative regions with the highest level of innovation distress included Beijing and Shanghai, as well as Gansu, Shaanxi and Heilongjiang provinces. The provincial-level administrative regions with the highest level of innovation dilemma in 2020 involve Beijing, Tianjin, Guangdong Province, and Shaanxi and Heilongjiang provinces. It is true that enterprises in old industrial areas have long faced innovation difficulties due to the great pressure of industrial structure transformation and technological upgrading. Then, how to understand the distribution map of innovation dilemma shows that enterprises in regions with higher economic development level are faced with more serious innovation dilemma? Explore the general reasons behind this law from a macro perspective: According to the theory of new economic geography, in the development of high-tech industry, the flow of various input factors will promote the geographical agglomeration of economic activities of enterprises and related organizations in the industry. The correlation effect between different enterprises in the industrial chain will also promote the preference of enterprises to choose to carry out their production activities in regions with larger market size [
20], the actual situation is consistent with the theory that the spatial distribution of China's high-tech industry is concentrated in the eastern coastal areas with high economic development level, such as the Bohai Rim area with Beijing as the center, the Yangtze River Delta area with Shanghai as the head and the Pearl River Delta area with Shenzhen and Guangzhou as the center [
21]. The high-tech industry has relatively high technical difficulty and innovation requirements, which makes it easier to face innovation bottlenecks. Therefore, economically developed areas with concentrated high-tech industries inevitably face more severe innovation problems. In addition, compared to underdeveloped regions, regions with higher levels of economic development have more manufacturing enterprises, greater competitive pressure, and higher levels of technological innovation. Therefore, before achieving major technological breakthroughs, more developed regions may have a situation of diminishing marginal innovation. Based on the above reasons, the regional distribution of innovation difficulties in manufacturing enterprises presents a situation where more developed regions are facing more serious innovation difficulties.
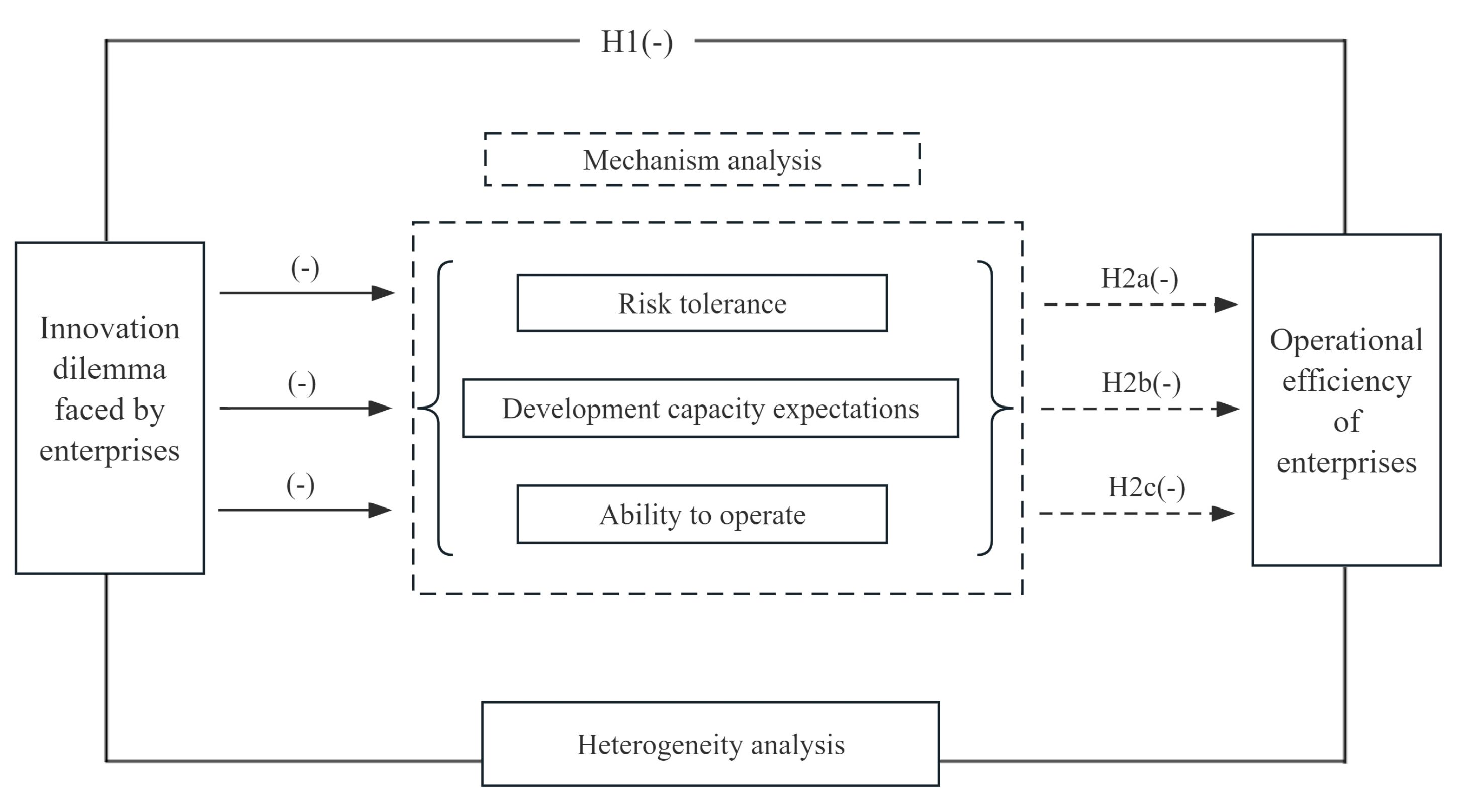
This paper takes unbalanced panel data of China’s A-share manufacturing listed companies from 2011 to 2020 as research samples to empirically test the impact of innovation dilemma on operational efficiency. It is found that the innovation dilemma has a significant inhibitory effect on the operation efficiency of enterprises. After that, this paper conducts a series of robustness tests. In order to solve the endogenous problems caused by sample selection and measurement errors, the instrumental variable method, propensity score matching method and DID model are used. The robustness of the conclusion is enhanced by replacing the dependent variable and changing the parameters of the dependent variable for calculation. As shown in
Figure 3, mechanism analysis shows that the innovation dilemma faced by enterprises will inhibit the operational efficiency of enterprises by reducing their risk tolerance, development ability expectation and profitability. Moreover, the impact of innovation dilemma on operational efficiency is heterogeneous and variable. From the perspective of the company, the innovation dilemma faced by enterprises more significantly affects the operating efficiency of private enterprises, small and medium-sized enterprises, enterprises in the stage of development and decline. From the perspective of industry and region, the innovation dilemma has a more obvious inhibitory effect on the operating efficiency of high-tech enterprises and enterprises in the eastern region.
Compared with the previous research, the marginal contribution of this paper is mainly reflected in the following three aspects. First, against the background of the uncertainty of technological innovation brought about by technological nationalism in the international environment, this paper expounds the current situation of the innovation dilemma of domestic manufacturing enterprises, empirically analyzes the impact of innovation dilemma on the operating efficiency of manufacturing enterprises, and enriches the research on the factors affecting the operating efficiency of manufacturing enterprises. The causal effect can be inferred more accurately by the quasi-natural experiment proposed by “high-quality development” , combined with the causal identification techniques such as randomized controlled trial and matching method. Secondly, in terms of the quality of the paper, this paper helps to understand the variables that affect the operational efficiency of manufacturing enterprises. From the existing research, scholars’ research on factors affecting the operating efficiency of manufacturing enterprises has established a system. At the micro level, they mainly focus on various production factors, but pay less attention to the innovation situation of enterprises, especially the impact of innovation dilemmas on the operating efficiency of enterprises. This paper makes up for this gap. Third, the study has practical implications for both manufacturing companies and policymakers. The research on innovation dilemmas faced by manufacturing enterprises can improve the enterprises’ attention to their own innovation situation, and pay attention to the impact of innovation dilemmas on the business efficiency of enterprises, so as to encourage enterprises to improve their innovation ability and avoid falling into the vicious circle of innovation dilemmas inhibiting business efficiency. In addition, the research results provide support and insights for policy makers to promote the high-quality development of manufacturing enterprises, help policy makers understand the innovation situation of manufacturing enterprises, use fiscal and monetary policies to reduce the burden of technological innovation of enterprises, promote manufacturing enterprises to improve product quality and technological innovation level, and accelerate the transformation and upgrading of manufacturing industry. We will promote the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry.
The basic structure of this paper is as follows. The second part is theoretical analysis and research hypothesis. The third part introduces the data source, model setting, related variables and their measurement. The fourth part shows the empirical results of innovation dilemma and operation efficiency of manufacturing enterprises and a series of robustness tests, and further carries out mechanism analysis and heterogeneity analysis. The fifth part emphasizes the conclusion of empirical analysis and provides further discussion.
Figure 3.
Diagram of Mechanism Analysis.
Figure 3.
Diagram of Mechanism Analysis.
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Discussion
In recent years, in the context of the continuous fierce competition in technological innovation, the complexity of the global technological innovation environment has been increasing and impacting on China’s manufacturing industry, and the innovation situation faced by Chinese manufacturing enterprises has gradually become the focus of attention. The innovation dilemma is a situation that manufacturing enterprises are unwilling to face, as it is an important factor that is not conducive to risk-taking, sustainable development, and sustainable operation. In this context, the efficiency of enterprise operation, as an important indicator to measure the operational status of enterprises, has attracted the attention of scholars and practitioners in its relationship with innovation dilemma.
This article puts the innovation status of enterprises in the context of the resurgence of international technology protectionism. This article uses data from Chinese A-share listed manufacturing companies from 2011 to 2020, and based on theoretical analysis, empirically verifies the relationship between innovation difficulties and operational efficiency of manufacturing companies.
The conclusions are as follows. Firstly, the innovation dilemma can have negative effects on the operational efficiency of enterprises. This article solves endogeneity problems through instrumental variable method and propensity score matching method. Robustness testing includes methods such as adding macro level control variables, changing the parameters of the measured dependent variable, and replacing sample time intervals. Secondly, the impact of innovation dilemma on business efficiency can be achieved through three paths, include reducing a company’s risk-taking ability, development ability expectations, and profitability. In addition, the inhibitory effect of innovation dilemma on operational efficiency of enterprises is more pronounced in private enterprises, small and medium-sized enterprises, ascend or decline period enterprises, high-tech enterprises and enterprises in the eastern region.
However, there are several limitations that need to be improved in this article. Firstly, due to data limitations, indicators for measuring the operational efficiency of manufacturing enterprises may need improvement. Currently, a large number of researchers use the DEA method and Tobit model to calculate and evaluate operational efficiency. Future research can improve operational efficiency indicators and use them to study the impact of technological innovation on manufacturing enterprises. There is also room for improvement in the indicators of innovation dilemma, and future research can be calculated from basic data other than innovation output. Secondly, based on this article’s analysis of provincial-level administrative regions in China in this article, the future innovation difficulties are still some topics worth paying close attention to. For example, the factors and paths that lead to enterprises falling into innovation difficulties, and the impact of innovation difficulties on other aspects of the enterprise. Thirdly, the differences in innovation dilemmas among enterprises in different regions are currently quite evident. Future research can conduct specific analysis based on regional differences, which can help regions to address innovation dilemmas in a targeted manner, narrow the gap in technological innovation development across regions, and provide theoretical and data support for the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry. Finally, future research can delve deeper into the unresolved issues mentioned above. We can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the relationship between technological innovation and enterprises, which can contribute to the improvement of technological innovation level and the high-quality development of manufacturing industry. Against the backdrop of the continuous improvement of global technological level, the importance of technological innovation for the development of enterprises is self-evident. The innovation status of enterprises still needs further research in the future, and the changes in the innovation situation and technological breakthroughs of manufacturing enterprises, regions, and even countries require long-term planning and sustained efforts.
5.2. Conclusion
Based on the research findings of this article, governments and businesses can refer to the following policy recommendations.
The innovation situation of manufacturing enterprises has a negative impact on their survival and development. In order to strengthen the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry, it is necessary to pay attention to the innovation situation of manufacturing enterprises. There is a significant gap in the level of innovation dilemma among different regions in China, and there is still room for improvement in the level of technological innovation in some regions. The government should relax the policy of talent introduction and provide good and fair employment opportunities for skilled and capable talents. In addition, providing monetary and fiscal policy support for enterprise technological innovation, especially for private enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises, helps these enterprises break through innovation bottlenecks, reduce innovation difficulties, and reduce the negative impact on the survival and development of enterprises by developing their risk tolerance, development ability, and profitability, thereby improving the survival rate of private enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises.
Based on heterogeneity analysis, targeted support plans should be developed and implemented for enterprises with different property rights, scales, and life-cycles, with a focus on high-tech enterprises and strengthening talent and funding investment in high-precision and cutting-edge fields. Accelerate the establishment of Innovation Industrial Cluster in the central and western regions, narrow the gap in technological innovation levels, and promote balanced and high-quality development of China's manufacturing industry.