Submitted:
16 April 2024
Posted:
17 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Atrial Fibrillation: The Size of the Problem
- -
- Irregular R-R intervals (when atrioventricular conduction is not impaired)
- -
- Absence of distinct repeating P waves
- -
- Irregular atrial activations. [1]
3. Pathophysiological Pathway of Atrial Fibrillation
4. Association between AF, Stroke/TIA and Dementia - The Emerging Concept of Atrial Myopathy
5. Evaluation of Atrial Cardiomyopathy
6. Potential Applications of AM Study in Clinical Practice
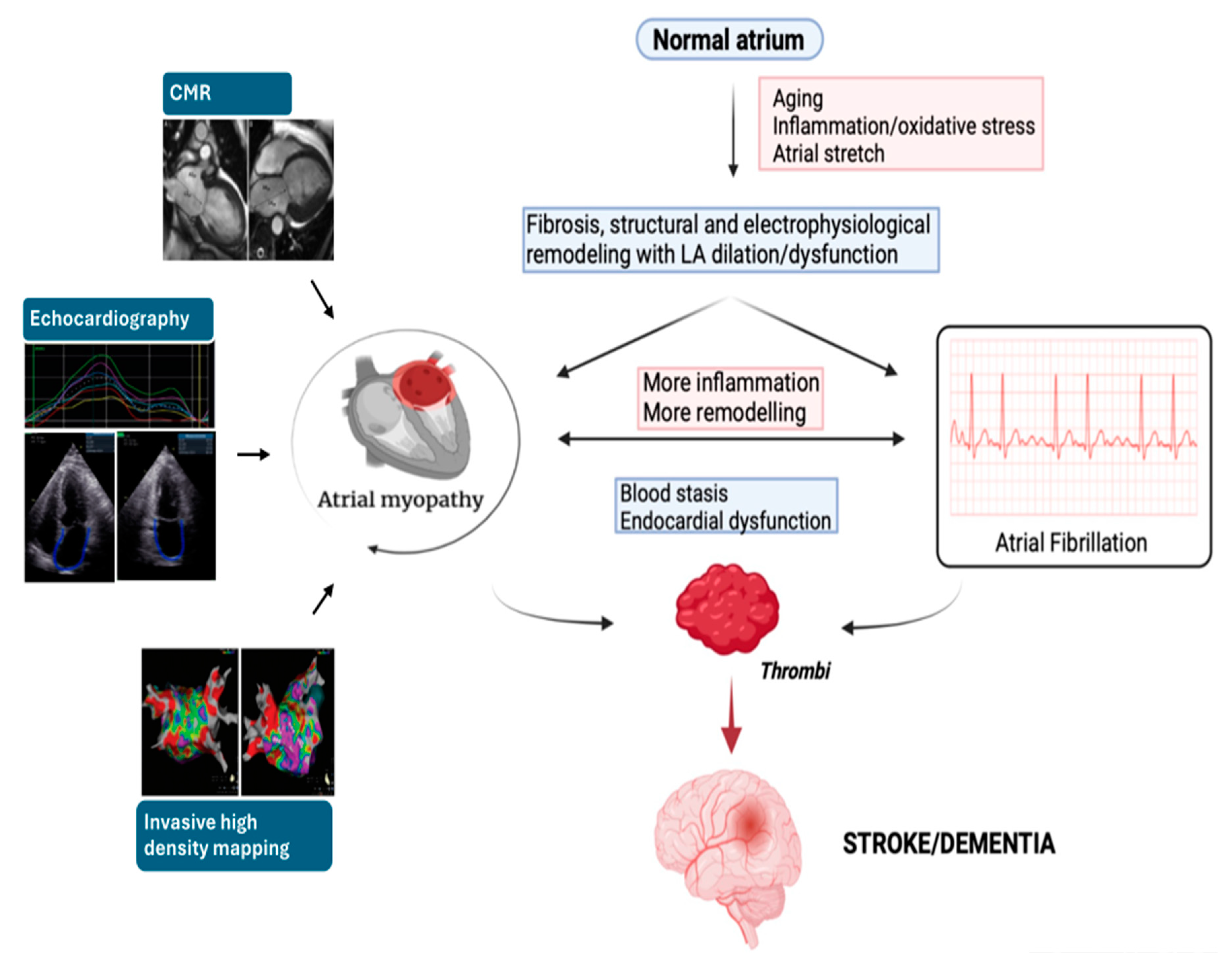
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC [published correction appears in Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):507] [published correction appears in Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):546-547] [published correction appears in Eur Heart J. 2021 Oct 21;42(40):4194]. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(5):373-498. [CrossRef]
- Colilla S, Crow A, Petkun W, Singer DE, Simon T, Liu X. Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(8):1142-1147. [CrossRef]
- Freedman JE, Gersh BJ. Atrial fibrillation and stroke prevention in aging patients: what's good can be even better. Circulation. 2014;130(2):129-131. [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan R, Kirkwood G, Visweswariah R, Fox DJ. How does Chronic Atrial Fibrillation Influence Mortality in the Modern Treatment Era?. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2015;11(3):190-198. [CrossRef]
- Thrall G, Lane D, Carroll D, Lip GY. Quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation: a systematic review. Am J Med. 2006;119(5):. [CrossRef]
- January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society [published correction appears in J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jul 30;74(4):599]. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(1):104-132. [CrossRef]
- Schotten U, Verheule S, Kirchhof P, Goette A. Pathophysiological mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: a translational appraisal [published correction appears in Physiol Rev. 2011 Oct;91(4):1533]. Physiol Rev. 2011;91(1):265-325. [CrossRef]
- Boriani G, Savelieva I, Dan GA, et al. Chronic kidney disease in patients with cardiac rhythm disturbances or implantable electrical devices: clinical significance and implications for decision making-a position paper of the European Heart Rhythm Association endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society and the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society. Europace. 2015;17(8):1169-1196. [CrossRef]
- Aune D, Feng T, Schlesinger S, Janszky I, Norat T, Riboli E. Diabetes mellitus, blood glucose and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. J Diabetes Complications. 2018;32(5):501-511. [CrossRef]
- Cadby G, McArdle N, Briffa T, et al. Severity of OSA is an independent predictor of incident atrial fibrillation hospitalization in a large sleep-clinic cohort. Chest. 2015;148(4):945-952. [CrossRef]
- Hobbelt AH, Siland JE, Geelhoed B, et al. Clinical, biomarker, and genetic predictors of specific types of atrial fibrillation in a community-based cohort: data of the PREVEND study. Europace. 2017;19(2):226-232. [CrossRef]
- Nalliah CJ, Sanders P, Kalman JM. The Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on Atrial Fibrillation. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018;20(12):137. Published 2018 Oct 12. [CrossRef]
- Lip GYH, Coca A, Kahan T, et al. Hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias: a consensus document from the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and ESC Council on Hypertension, endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS) and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulación Cardíaca y Electrofisiología (SOLEACE). Europace. 2017;19(6):891-911. [CrossRef]
- Gallagher C, Hendriks JML, Elliott AD, et al. Alcohol and incident atrial fibrillation - A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;246:46-52. [CrossRef]
- Ricci C, Gervasi F, Gaeta M, Smuts CM, Schutte AE, Leitzmann MF. Physical activity volume in relation to risk of atrial fibrillation. A non-linear meta-regression analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2018;25(8):857-866. [CrossRef]
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association [published correction appears in Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141(2):e33]. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56-e528. [CrossRef]
- Allan V, Honarbakhsh S, Casas JP, et al. Are cardiovascular risk factors also associated with the incidence of atrial fibrillation? A systematic review and field synopsis of 23 factors in 32 population-based cohorts of 20 million participants. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(5):837-850. [CrossRef]
- Feghaly J, Zakka P, London B, MacRae CA, Refaat MM. Genetics of Atrial Fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(20):e009884. [CrossRef]
- Wijesurendra RS, Casadei B. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Heart. 2019;105(24):1860-1867. [CrossRef]
- Lubitz SA, Yin X, McManus DD, et al. Stroke as the Initial Manifestation of Atrial Fibrillation: The Framingham Heart Study. Stroke. 2017;48(2):490-492. [CrossRef]
- Bunch TJ. Atrial Fibrillation and Dementia. Circulation. 2020;142(7):618-620. [CrossRef]
- Friberg L, Rosenqvist M. Less dementia with oral anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(6):453-460. [CrossRef]
- Jacobs V, Woller SC, Stevens S, et al. Time outside of therapeutic range in atrial fibrillation patients is associated with long-term risk of dementia. Heart Rhythm. 2014;11(12):2206-2213. [CrossRef]
- Bunch TJ, Crandall BG, Weiss JP, et al. Patients treated with catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation have long-term rates of death, stroke, and dementia similar to patients without atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2011;22(8):839-845. [CrossRef]
- Jin MN, Kim TH, Kang KW, et al. Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation Improves 1-Year Follow-Up Cognitive Function, Especially in Patients With Impaired Cognitive Function. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019;12(7):e007197. [CrossRef]
- Ding WY, Gupta D, Lip GYH. Atrial fibrillation and the prothrombotic state: revisiting Virchow's triad in 2020. Heart. 2020;106(19):1463-1468. [CrossRef]
- Watson T, Shantsila E, Lip GY. Mechanisms of thrombogenesis in atrial fibrillation: Virchow's triad revisited. Lancet. 2009;373(9658):155-166. [CrossRef]
- Goette A, Kalman JM, Aguinaga L, et al. EHRA/HRS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus on atrial cardiomyopathies: Definition, characterization, and clinical implication. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14(1):e3-e40. [CrossRef]
- Kamel H, Bartz TM, Elkind MSV, et al. Atrial Cardiopathy and the Risk of Ischemic Stroke in the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study). Stroke. 2018;49(4):980-986. [CrossRef]
- Brambatti M, Connolly SJ, Gold MR, et al. Temporal relationship between subclinical atrial fibrillation and embolic events. Circulation. 2014;129(21):2094-2099. [CrossRef]
- Triposkiadis F, Pieske B, Butler J, et al. Global left atrial failure in heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;18(11):1307-1320. [CrossRef]
- Miller JD, Aronis KN, Chrispin J, et al. Obesity, Exercise, Obstructive Sleep Apnea, and Modifiable Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66(25):2899-2906. [CrossRef]
- Binici Z, Intzilakis T, Nielsen OW, Køber L, Sajadieh A. Excessive supraventricular ectopic activity and increased risk of atrial fibrillation and stroke. Circulation. 2010;121(17):1904-1911. [CrossRef]
- Larsen BS, Kumarathurai P, Falkenberg J, Nielsen OW, Sajadieh A. Excessive Atrial Ectopy and Short Atrial Runs Increase the Risk of Stroke Beyond Incident Atrial Fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66(3):232-241. [CrossRef]
- Kuppahally SS, Akoum N, Burgon NS, et al. Left atrial strain and strain rate in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation: relationship to left atrial structural remodeling detected by delayed-enhancement MRI. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;3(3):231-239. [CrossRef]
- Peigh G, Shah SJ, Patel RB. Left Atrial Myopathy in Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: Clinical Implications, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Targets. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2021;18(3):85-98. [CrossRef]
- Appleton CP, Galloway JM, Gonzalez MS, Gaballa M, Basnight MA. Estimation of left ventricular filling pressures using two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography in adult patients with cardiac disease. Additional value of analyzing left atrial size, left atrial ejection fraction and the difference in duration of pulmonary venous and mitral flow velocity at atrial contraction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22(7):1972-1982. [CrossRef]
- Geske JB, Sorajja P, Nishimura RA, Ommen SR. The relationship of left atrial volume and left atrial pressure in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an echocardiographic and cardiac catheterization study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009;22(8):961-966. [CrossRef]
- Guron CW, Hartford M, Rosengren A, Thelle D, Wallentin I, Caidahl K. Usefulness of atrial size inequality as an indicator of abnormal left ventricular filling. Am J Cardiol. 2005;95(12):1448-1452. [CrossRef]
- Simek CL, Feldman MD, Haber HL, Wu CC, Jayaweera AR, Kaul S. Relationship between left ventricular wall thickness and left atrial size: comparison with other measures of diastolic function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1995;8(1):37-47. [CrossRef]
- Ersbøll M, Andersen MJ, Valeur N, et al. The prognostic value of left atrial peak reservoir strain in acute myocardial infarction is dependent on left ventricular longitudinal function and left atrial size. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6(1):26-33. [CrossRef]
- Lønborg JT, Engstrøm T, Møller JE, et al. Left atrial volume and function in patients following ST elevation myocardial infarction and the association with clinical outcome: a cardiovascular magnetic resonance study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;14(2):118-127. [CrossRef]
- Barnes ME, Miyasaka Y, Seward JB, et al. Left atrial volume in the prediction of first ischemic stroke in an elderly cohort without atrial fibrillation. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004;79(8):1008-1014. [CrossRef]
- Benjamin EJ, D'Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Wolf PA, Levy D. Left atrial size and the risk of stroke and death. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1995;92(4):835-841. [CrossRef]
- Bolca O, Akdemir O, Eren M, Dagdeviren B, Yildirim A, Tezel T. Left atrial maximum volume is a recurrence predictor in lone atrial fibrillation: an acoustic quantification study. Jpn Heart J. 2002;43(3):241-248. [CrossRef]
- Di Tullio MR, Sacco RL, Sciacca RR, Homma S. Left atrial size and the risk of ischemic stroke in an ethnically mixed population. Stroke. 1999;30(10):2019-2024. [CrossRef]
- Flaker GC, Fletcher KA, Rothbart RM, Halperin JL, Hart RG. Clinical and echocardiographic features of intermittent atrial fibrillation that predict recurrent atrial fibrillation. Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation (SPAF) Investigators. Am J Cardiol. 1995;76(5):355-358. [CrossRef]
- Kottkamp H. Fibrotic atrial cardiomyopathy: a specific disease/syndrome supplying substrates for atrial fibrillation, atrial tachycardia, sinus node disease, AV node disease, and thromboembolic complications. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012;23(7):797-799. [CrossRef]
- Tsang TS, Barnes ME, Bailey KR, et al. Left atrial volume: important risk marker of incident atrial fibrillation in 1655 older men and women. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001;76(5):467-475. [CrossRef]
- Vaziri SM, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. Echocardiographic predictors of nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1994;89(2):724-730. [CrossRef]
- Tsang TS, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Bailey KR, Seward JB. Risks for atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure in patients >/=65 years of age with abnormal left ventricular diastolic relaxation. Am J Cardiol. 2004;93(1):54-58. [CrossRef]
- Tsang TS, Gersh BJ, Appleton CP, et al. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction as a predictor of the first diagnosed nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in 840 elderly men and women. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40(9):1636-1644. [CrossRef]
- Beinart R, Boyko V, Schwammenthal E, et al. Long-term prognostic significance of left atrial volume in acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(2):327-334. [CrossRef]
- Moller JE, Hillis GS, Oh JK, et al. Left atrial volume: a powerful predictor of survival after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2003;107(17):2207-2212. [CrossRef]
- Dini FL, Cortigiani L, Baldini U, et al. Prognostic value of left atrial enlargement in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89(5):518-523. [CrossRef]
- Kim H, Cho YK, Jun DH, et al. Prognostic implications of the NT-ProBNP level and left atrial size in non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2008;72(10):1658-1665. [CrossRef]
- Modena MG, Muia N, Sgura FA, Molinari R, Castella A, Rossi R. Left atrial size is the major predictor of cardiac death and overall clinical outcome in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: a long-term follow-up study. Clin Cardiol. 1997;20(6):553-560. [CrossRef]
- Sabharwal N, Cemin R, Rajan K, Hickman M, Lahiri A, Senior R. Usefulness of left atrial volume as a predictor of mortality in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 2004;94(6):760-763. [CrossRef]
- Maddukuri PV, Vieira ML, DeCastro S, et al. What is the best approach for the assessment of left atrial size? Comparison of various unidimensional and two-dimensional parameters with three-dimensional echocardiographically determined left atrial volume. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2006;19(8):1026-1032. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Gutman JM, Heilbron D, Wahr D, Schiller NB. Atrial volume in a normal adult population by two-dimensional echocardiography. Chest. 1984;86(4):595-601. [CrossRef]
- Whitlock M, Garg A, Gelow J, Jacobson T, Broberg C. Comparison of left and right atrial volume by echocardiography versus cardiac magnetic resonance imaging using the area-length method. Am J Cardiol. 2010;106(9):1345-1350. [CrossRef]
- Aune E, Baekkevar M, Roislien J, Rodevand O, Otterstad JE. Normal reference ranges for left and right atrial volume indexes and ejection fractions obtained with real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2009;10(6):738-744. [CrossRef]
- Peluso D, Badano LP, Muraru D, et al. Right atrial size and function assessed with three-dimensional and speckle-tracking echocardiography in 200 healthy volunteers. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;14(11):1106-1114. [CrossRef]
- Poulsen MK, Dahl JS, Henriksen JE, et al. Left atrial volume index: relation to long-term clinical outcome in type 2 diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25):2416-2421. [CrossRef]
- Kojima T, Kawasaki M, Tanaka R, et al. Left atrial global and regional function in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation has already been impaired before enlargement of left atrium: velocity vector imaging echocardiography study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;13(3):227-234. [CrossRef]
- Gupta DK, Shah AM, Giugliano RP, et al. Left atrial structure and function in atrial fibrillation: ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(22):1457-1465. [CrossRef]
- Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28(1):1-39.e14. [CrossRef]
- Olshansky B, Heller EN, Mitchell LB, et al. Are transthoracic echocardiographic parameters associated with atrial fibrillation recurrence or stroke? Results from the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45(12):2026-2033. [CrossRef]
- Rusinaru D, Tribouilloy C, Grigioni F, et al. Left atrial size is a potent predictor of mortality in mitral regurgitation due to flail leaflets: results from a large international multicenter study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;4(5):473-481. [CrossRef]
- Wade MR, Chandraratna PA, Reid CL, Lin SL, Rahimtoola SH. Accuracy of nondirected and directed M-mode echocardiography as an estimate of left atrial size. Am J Cardiol. 1987;60(14):1208-1211. [CrossRef]
- Lester SJ, Ryan EW, Schiller NB, Foster E. Best method in clinical practice and in research studies to determine left atrial size. Am J Cardiol. 1999;84(7):829-832. [CrossRef]
- Loperfido F, Pennestri F, Digaetano A, et al. Assessment of left atrial dimensions by cross sectional echocardiography in patients with mitral valve disease. Br Heart J. 1983;50(6):570-578. [CrossRef]
- Vyas H, Jackson K, Chenzbraun A. Switching to volumetric left atrial measurements: impact on routine echocardiographic practice. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2011;12(2):107-111. [CrossRef]
- Gottdiener JS, Kitzman DW, Aurigemma GP, Arnold AM, Manolio TA. Left atrial volume, geometry, and function in systolic and diastolic heart failure of persons > or =65 years of age (the cardiovascular health study). Am J Cardiol. 2006;97(1):83-89. [CrossRef]
- Rossi A, Cicoira M, Zanolla L, et al. Determinants and prognostic value of left atrial volume in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40(8):1425. [CrossRef]
- Takemoto Y, Barnes ME, Seward JB, et al. Usefulness of left atrial volume in predicting first congestive heart failure in patients > or = 65 years of age with well-preserved left ventricular systolic function. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(6):832-836. [CrossRef]
- Tani T, Tanabe K, Ono M, et al. Left atrial volume and the risk of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2004;17(6):644-648. [CrossRef]
- Tsang TS, Abhayaratna WP, Barnes ME, et al. Prediction of cardiovascular outcomes with left atrial size: is volume superior to area or diameter?. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(5):1018-1023. [CrossRef]
- Pritchett AM, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, Rodeheffer RJ, Bailey KR, Redfield MM. Left atrial volume as an index of left atrial size: a population-based study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(6):1036-1043. [CrossRef]
- Jenkins C, Bricknell K, Marwick TH. Use of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography to measure left atrial volume: comparison with other echocardiographic techniques. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18(9):991-997. [CrossRef]
- Thomas L, Levett K, Boyd A, Leung DY, Schiller NB, Ross DL. Compensatory changes in atrial volumes with normal aging: is atrial enlargement inevitable?. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40(9):1630-1635. [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi K, Tanabe K, Tani T, et al. Left atrial volume in normal Japanese adults. Circ J. 2006;70(3):285-288. [CrossRef]
- Maceira AM, Cosín-Sales J, Roughton M, Prasad SK, Pennell DJ. Reference left atrial dimensions and volumes by steady state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2010;12(1):65. Published 2010 Nov 11. [CrossRef]
- Rodevan O, Bjornerheim R, Ljosland M, Maehle J, Smith HJ, Ihlen H. Left atrial volumes assessed by three- and two-dimensional echocardiography compared to MRI estimates. Int J Card Imaging. 1999;15(5):397-410. [CrossRef]
- Stojanovska J, Cronin P, Patel S, et al. Reference normal absolute and indexed values from ECG-gated MDCT: left atrial volume, function, and diameter. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(3):631-637. [CrossRef]
- Ujino K, Barnes ME, Cha SS, et al. Two-dimensional echocardiographic methods for assessment of left atrial volume. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98(9):1185-1188. [CrossRef]
- Aurigemma GP, Gottdiener JS, Arnold AM, Chinali M, Hill JC, Kitzman D. Left atrial volume and geometry in healthy aging: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009;2(4):282-289. [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka Y, Tsujimoto S, Maeba H, et al. Left atrial volume by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography: validation by 64-slice multidetector computed tomography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011;24(6):680-686. [CrossRef]
- Rohner A, Brinkert M, Kawel N, et al. Functional assessment of the left atrium by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography using a novel dedicated analysis tool: initial validation studies in comparison with computed tomography. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2011;12(7):497-505. [CrossRef]
- Artang R, Migrino RQ, Harmann L, Bowers M, Woods TD. Left atrial volume measurement with automated border detection by 3-dimensional echocardiography: comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2009;7:16. Published 2009 Mar 31. [CrossRef]
- Mor-Avi V, Yodwut C, Jenkins C, et al. Real-time 3D echocardiographic quantification of left atrial volume: multicenter study for validation with CMR. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;5(8):769-777. [CrossRef]
- Caselli S, Canali E, Foschi ML, et al. Long-term prognostic significance of three-dimensional echocardiographic parameters of the left ventricle and left atrium. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(3):250-256. [CrossRef]
- Suh IW, Song JM, Lee EY, et al. Left atrial volume measured by real-time 3-dimensional echocardiography predicts clinical outcomes in patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction and in sinus rhythm. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21(5):439-445. [CrossRef]
- Chen L.Y., Ribeiro A.L.P., Platonov P.G., Cygankiewicz I., Soliman E.Z., Gorenek B., Ikeda T., Vassilikos V.P., Steinberg J.S., Varma N., et al. P Wave Parameters and Indices: A Critical Appraisal of Clinical Utility, Challenges, and Future Research-A Consensus Document Endorsed by the International Society of Electrocardiology and the International Society for Holter and Noninvasive Electrocardiology. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2022;15:e010435.
- Vasan RS, Larson MG, Levy D, et al. Doppler transmitral flow indexes and risk of atrial fibrillation (the Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 2003;91(9):1079-1083. [CrossRef]
- Mattioli AV, Tarabini Castellani E, Vivoli D, Molinari R, Mattioli G. Restoration of atrial function after atrial fibrillation of different etiological origins. Cardiology. 1996;87(3):205-211. [CrossRef]
- Yuda S, Nakatani S, Isobe F, Kosakai Y, Miyatake K. Comparative efficacy of the maze procedure for restoration of atrial contraction in patients with and without giant left atrium associated with mitral valve disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31(5):1097-1102. [CrossRef]
- Shizukuda Y, Bolan CD, Tripodi DJ, et al. Significance of left atrial contractile function in asymptomatic subjects with hereditary hemochromatosis. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98(7):954-959. [CrossRef]
- Manning WJ, Leeman DE, Gotch PJ, Come PC. Pulsed Doppler evaluation of atrial mechanical function after electrical cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989;13(3):617-623. [CrossRef]
- Oki T, Fukuda N, Iuchi A, et al. Left Atrial Systolic Performance in the Presence of Elevated Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure: Evaluation by Transesophageal Pulsed Doppler Echocardiography of Left Ventricular Inflow and Pulmonary Venous Flow Velocities. Echocardiography. 1997;14(1):23-32. [CrossRef]
- Oki T, Iuchi A, Tabata T, et al. Transesophageal pulsed Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of left atrial systolic performance in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: combined analysis of transmitral and pulmonary venous flow velocities. Clin Cardiol. 1997;20(1):47-54. [CrossRef]
- Sakai H, Kunichika H, Murata K, et al. Improvement of afterload mismatch of left atrial booster pump function with positive inotropic agent. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37(1):270-277. [CrossRef]
- Iuchi A, Oki T, Tabata T, et al. J Cardiol. 1995;25(6):317-324.
- Ari H, Ari S, Akkaya M, et al. Predictive value of atrial electromechanical delay for atrial fibrillation recurrence. Cardiol J. 2013;20(6):639-647. [CrossRef]
- Hoshi Y, Nozawa Y, Ogasawara M, et al. Atrial electromechanical interval may predict cardioembolic stroke in apparently low risk elderly patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography. 2014;31(2):140-148. [CrossRef]
- Acar G, Akcay A, Sokmen A, et al. Assessment of atrial electromechanical delay, diastolic functions, and left atrial mechanical functions in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009;22(6):732-738. [CrossRef]
- Nar G, Ergul B, Aksan G, Inci S. Assessment of Atrial Electromechanical Delay and Left Atrial Mechanical Functions in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Echocardiography. 2016;33(7):970-976. [CrossRef]
- Aksan G, Nar G, Soylu K, et al. Assessment of atrial electromechanical delay and left atrial mechanical functions in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Echocardiography. 2015;32(4):615-622. [CrossRef]
- Ilter A, Kırış A, Kaplan Ş, et al. Atrial conduction times and left atrium mechanical functions in patients with active acromegaly. Endocrine. 2015;48(2):653-660. [CrossRef]
- Akıl MA, Akıl E, Bilik MZ, et al. The relationship between atrial electromechanical delay and left atrial mechanical function in stroke patients. Anatol J Cardiol. 2015;15(7):565-570. [CrossRef]
- Pozios I, Vouliotis AI, Dilaveris P, Tsioufis C. Electro-Mechanical Alterations in Atrial Fibrillation: Structural, Electrical, and Functional Correlates. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023;10(4):149. Published 2023 Mar 31. [CrossRef]
- Müller P, Weijs B, Bemelmans NMAA, et al. Echocardiography-derived total atrial conduction time (PA-TDI duration): risk stratification and guidance in atrial fibrillation management. Clin Res Cardiol. 2021;110(11):1734-1742. [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu K, Ito T, Miyamura M, Kanzaki Y, Sohmiya K, Hoshiga M. Usefulness of tissue Doppler-derived atrial electromechanical delay for identifying patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2020;18(1):22. Published 2020 Jun 22. [CrossRef]
- Müller P, Hars C, Schiedat F, et al. Correlation between total atrial conduction time estimated via tissue Doppler imaging (PA-TDI Interval), structural atrial remodeling and new-onset of atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24(6):626-631. [CrossRef]
- Erdem FH, Erdem A, Özlü F, et al. Electrophysiological validation of total atrial conduction time measurement by tissue doppler echocardiography according to age and sex in healthy adults. J Arrhythm. 2016;32(2):127-132. [CrossRef]
- Abou R, Leung M, Tonsbeek AM, et al. Effect of Aging on Left Atrial Compliance and Electromechanical Properties in Subjects Without Structural Heart Disease. Am J Cardiol. 2017;120(1):140-147. [CrossRef]
- Özlü MF, Erdem K, Kırış G, et al. Predictive value of total atrial conduction time measured with tissue Doppler imaging for postoperative atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2013;37(1):27-33. [CrossRef]
- Müller P, Schiedat F, Dietrich JW, et al. Reverse atrial remodeling in patients who maintain sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion: evidence derived from the measurement of total atrial conduction time assessed by PA-TDI interval. J Echocardiogr. 2014;12(4):142-150. [CrossRef]
- Den Uijl DW, Delgado V, Bertini M, et al. Impact of left atrial fibrosis and left atrial size on the outcome of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Heart. 2011;97(22):1847-1851. [CrossRef]
- Chao TF, Lin YJ, Tsao HM, et al. Prolonged atrium electromechanical interval is associated with stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24(4):375-380. [CrossRef]
- Inaba Y, Yuda S, Kobayashi N, et al. Strain rate imaging for noninvasive functional quantification of the left atrium: comparative studies in controls and patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18(7):729-736. [CrossRef]
- Vianna-Pinton R, Moreno CA, Baxter CM, Lee KS, Tsang TS, Appleton CP. Two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography of the left atrium: feasibility and regional contraction and relaxation differences in normal subjects. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009;22(3):299-305. [CrossRef]
- Kim DG, Lee KJ, Lee S, et al. Feasibility of two-dimensional global longitudinal strain and strain rate imaging for the assessment of left atrial function: a study in subjects with a low probability of cardiovascular disease and normal exercise capacity. Echocardiography. 2009;26(10):1179-1187. [CrossRef]
- Cameli M, Caputo M, Mondillo S, et al. Feasibility and reference values of left atrial longitudinal strain imaging by two-dimensional speckle tracking. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2009;7:6. Published 2009 Feb 8. [CrossRef]
- Cianciulli TF, Saccheri MC, Lax JA, Bermann AM, Ferreiro DE. Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography for the assessment of atrial function. World J Cardiol. 2010;2(7):163-170. [CrossRef]
- Cameli M, Lisi M, Focardi M, et al. Left atrial deformation analysis by speckle tracking echocardiography for prediction of cardiovascular outcomes. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(2):264-269. [CrossRef]
- Thomas L, McKay T, Byth K, Marwick TH. Abnormalities of left atrial function after cardioversion: an atrial strain rate study. Heart. 2007;93(1):89-95. [CrossRef]
- Wang T, Wang M, Fung JW, et al. Atrial strain rate echocardiography can predict success or failure of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation: a combined transthoracic tissue Doppler and transoesophageal imaging study. Int J Cardiol. 2007;114(2):202-209. [CrossRef]
- Schneider C, Malisius R, Krause K, et al. Strain rate imaging for functional quantification of the left atrium: atrial deformation predicts the maintenance of sinus rhythm after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(11):1397-1409. [CrossRef]
- Mirza M, Caracciolo G, Khan U, et al. Left atrial reservoir function predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: a two-dimensional speckle strain study. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2011;31(3):197-206. [CrossRef]
- O'Connor K, Magne J, Rosca M, Piérard LA, Lancellotti P. Left atrial function and remodelling in aortic stenosis. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2011;12(4):299-305. [CrossRef]
- O'Connor K, Magne J, Rosca M, Piérard LA, Lancellotti P. Impact of aortic valve stenosis on left atrial phasic function. Am J Cardiol. 2010;106(8):1157-1162. [CrossRef]
- Todaro MC, Choudhuri I, Belohlavek M, et al. New echocardiographic techniques for evaluation of left atrial mechanics. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;13(12):973-984. [CrossRef]
- Nikitin NP, Witte KK, Thackray SD, Goodge LJ, Clark AL, Cleland JG. Effect of age and sex on left atrial morphology and function. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2003;4(1):36-42. [CrossRef]
- Tsai WC, Lee CH, Lin CC, et al. Association of left atrial strain and strain rate assessed by speckle tracking echocardiography with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography. 2009;26(10):1188-1194. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Tan H, Zhong M, Jiang G, Zhang Y, Zhang W. Strain rate imaging for noninvasive functional quantification of the left atrium in hypertensive patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Cardiology. 2008;109(1):15-24. [CrossRef]
- Modesto KM, Dispenzieri A, Cauduro SA, et al. Left atrial myopathy in cardiac amyloidosis: implications of novel echocardiographic techniques. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(2):173-179. [CrossRef]
- Di Salvo G, Caso P, Lo Piccolo R, et al. Atrial myocardial deformation properties predict maintenance of sinus rhythm after external cardioversion of recent-onset lone atrial fibrillation: a color Doppler myocardial imaging and transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic study. Circulation. 2005;112(3):387-395. [CrossRef]
- D'Andrea A, Caso P, Romano S, et al. Association between left atrial myocardial function and exercise capacity in patients with either idiopathic or ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy: a two-dimensional speckle strain study. Int J Cardiol. 2009;132(3):354-363. [CrossRef]
- D'Andrea A, Caso P, Romano S, et al. Different effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy on left atrial function in patients with either idiopathic or ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy: a two-dimensional speckle strain study. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(22):2738-2748. [CrossRef]
- Cameli M, Mandoli GE, Loiacono F, Sparla S, Iardino E, Mondillo S. Left atrial strain: A useful index in atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 2016;220:208-213. [CrossRef]
- Yoon YE, Kim HJ, Kim SA, et al. Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2012;20(3):140-145. [CrossRef]
- Laish-Farkash A, Perelshtein Brezinov O, Valdman A, et al. Evaluation of left atrial remodeling by 2D-speckle-tracking echocardiography versus by high-density voltage mapping in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2021;32(2):305-315. [CrossRef]
- Lisi M, Mandoli GE, Cameli M, et al. Left atrial strain by speckle tracking predicts atrial fibrosis in patients undergoing heart transplantation. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022;23(6):829-835. [CrossRef]
- Lisi M, Cameli M, Mandoli GE, et al. Detection of myocardial fibrosis by speckle-tracking echocardiography: from prediction to clinical applications. Heart Fail Rev. 2022;27(5):1857-1867. [CrossRef]
- Sade LE, Keskin S, Can U, et al. Left atrial mechanics for secondary prevention from embolic stroke of undetermined source. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022;23(3):381-391. [CrossRef]
- Alhakak AS, Biering-Sørensen SR, Møgelvang R, et al. Usefulness of left atrial strain for predicting incident atrial fibrillation and ischaemic stroke in the general population. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022;23(3):363-371. [CrossRef]
- Azemi T, Rabdiya VM, Ayirala SR, McCullough LD, Silverman DI. Left atrial strain is reduced in patients with atrial fibrillation, stroke or TIA, and low risk CHADS(2) scores. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2012;25(12):1327-1332. [CrossRef]
- Saha SK, Anderson PL, Caracciolo G, et al. Global left atrial strain correlates with CHADS2 risk score in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011;24(5):506-512. [CrossRef]
- Obokata M, Negishi K, Kurosawa K, et al. Left atrial strain provides incremental value for embolism risk stratification over CHA₂DS₂-VASc score and indicates prognostic impact in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014;27(7):709-716.e4. [CrossRef]
- Park JJ, Park JH, Hwang IC, Park JB, Cho GY, Marwick TH. Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Heart Failure. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;13(10):2071-2081. [CrossRef]
- Akintoye E, Majid M, Klein AL, Hanna M. Prognostic Utility of Left Atrial Strain to Predict Thrombotic Events and Mortality in Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023;16(11):1371-1383. [CrossRef]
- Cameli M, Lisi M, Reccia R, et al. Pre-operative left atrial strain predicts post-operative atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;30(2):279-286. [CrossRef]
- Pastore MC, Degiovanni A, Grisafi L, et al. Left Atrial Strain to Predict Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024;17(1):e015969. [CrossRef]
- Zhang MJ, Ji Y, Wang W, et al. Association of Atrial Fibrillation With Stroke and Dementia Accounting for Left Atrial Function and Size. JACC Adv. 2023;2(5):100408. [CrossRef]
- Smiseth OA, Morris DA, Cardim N, et al. Multimodality imaging in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: an expert consensus document of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022;23(2):e34-e61. [CrossRef]
| Atrial Myopathy: EHRAS classification | |
|---|---|
| EHRAS CLASS | HISTOLOGICAL FEATURES |
| I | Morphological/molecular changes affecting the cardiomyocytes (hypertrophy and myocytolysis). Absence of significant tissue fibrosis or interstitial changes |
| II | Predominance of fibrotic changes. Normal appearance of cardiomyocytes |
| III | Combination of changes in the cardiomyocyte and tissue fibrosis |
| IV a f i o |
Non-fibrotic alteration of interstitial matrix Amyloid accumulation Fatty infiltration Inflammatory cells Other interstitial alterations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





