Submitted:
15 April 2024
Posted:
16 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
3.1. History of Lyme Disease and Brazilian Borreliosis
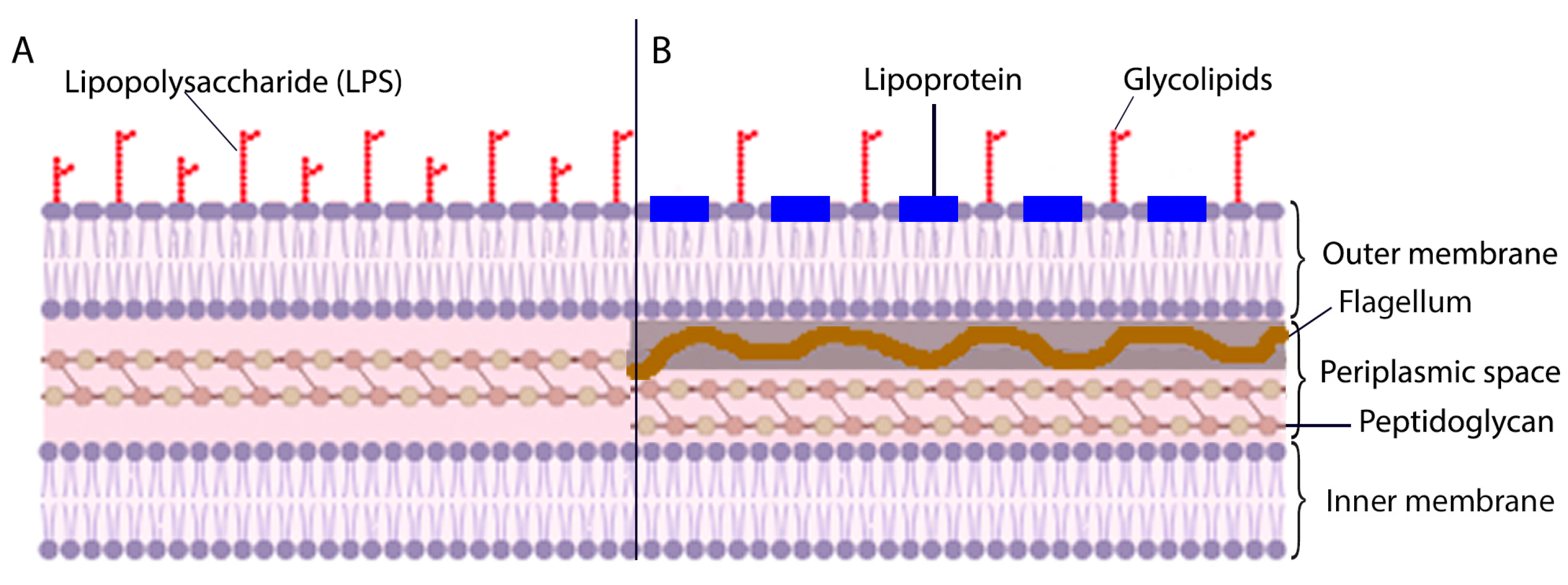
3.2. Morphological Features of Borrelia
3.3. Pathogenesis
3.4. Current Situation of Lyme Disease in Brazil
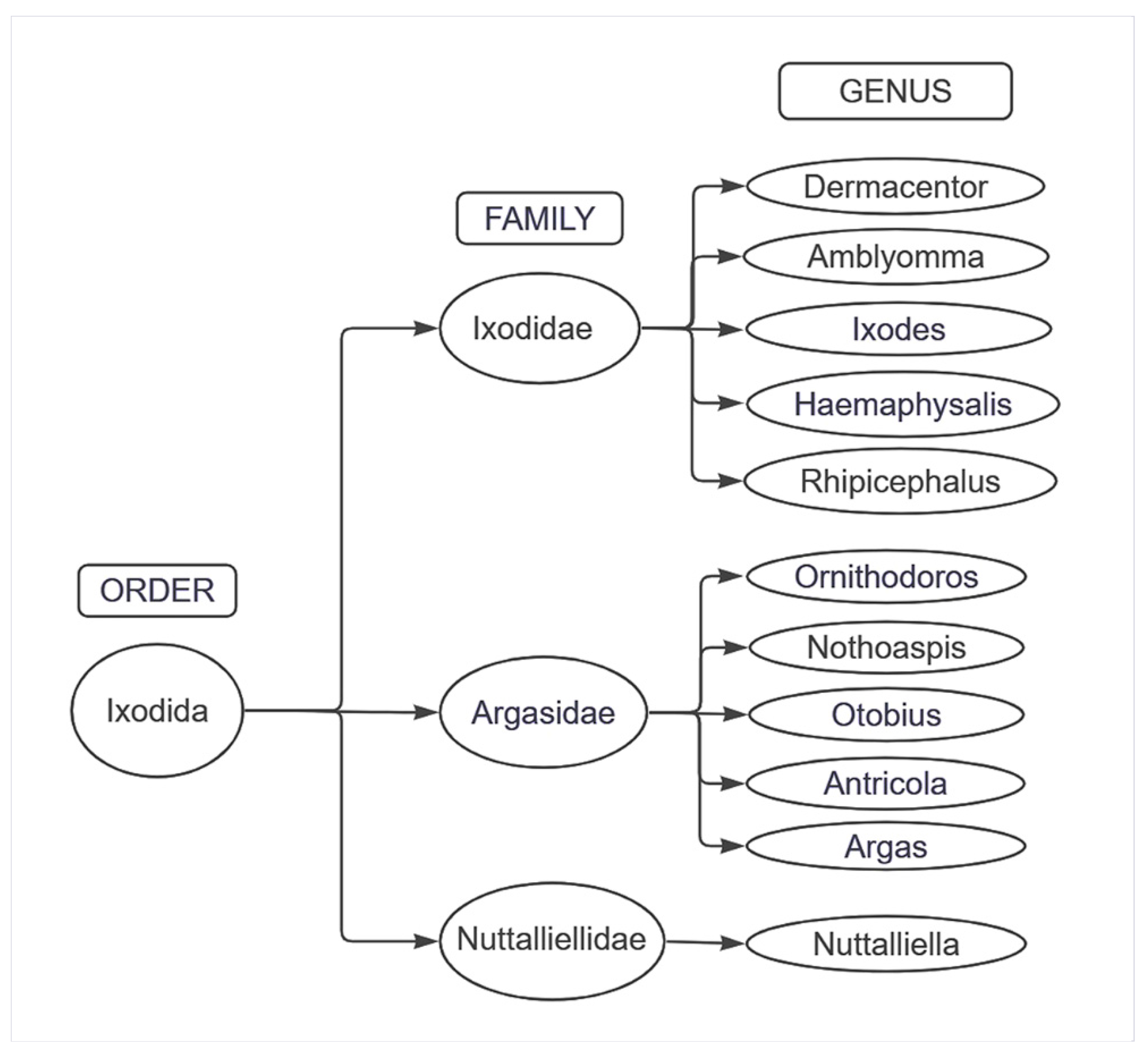
3.4.1. Tick Biological Cycle and Its Relationship with the Spread of the Disease
3.4.2. Clinical Picture of DLSB/Lyme
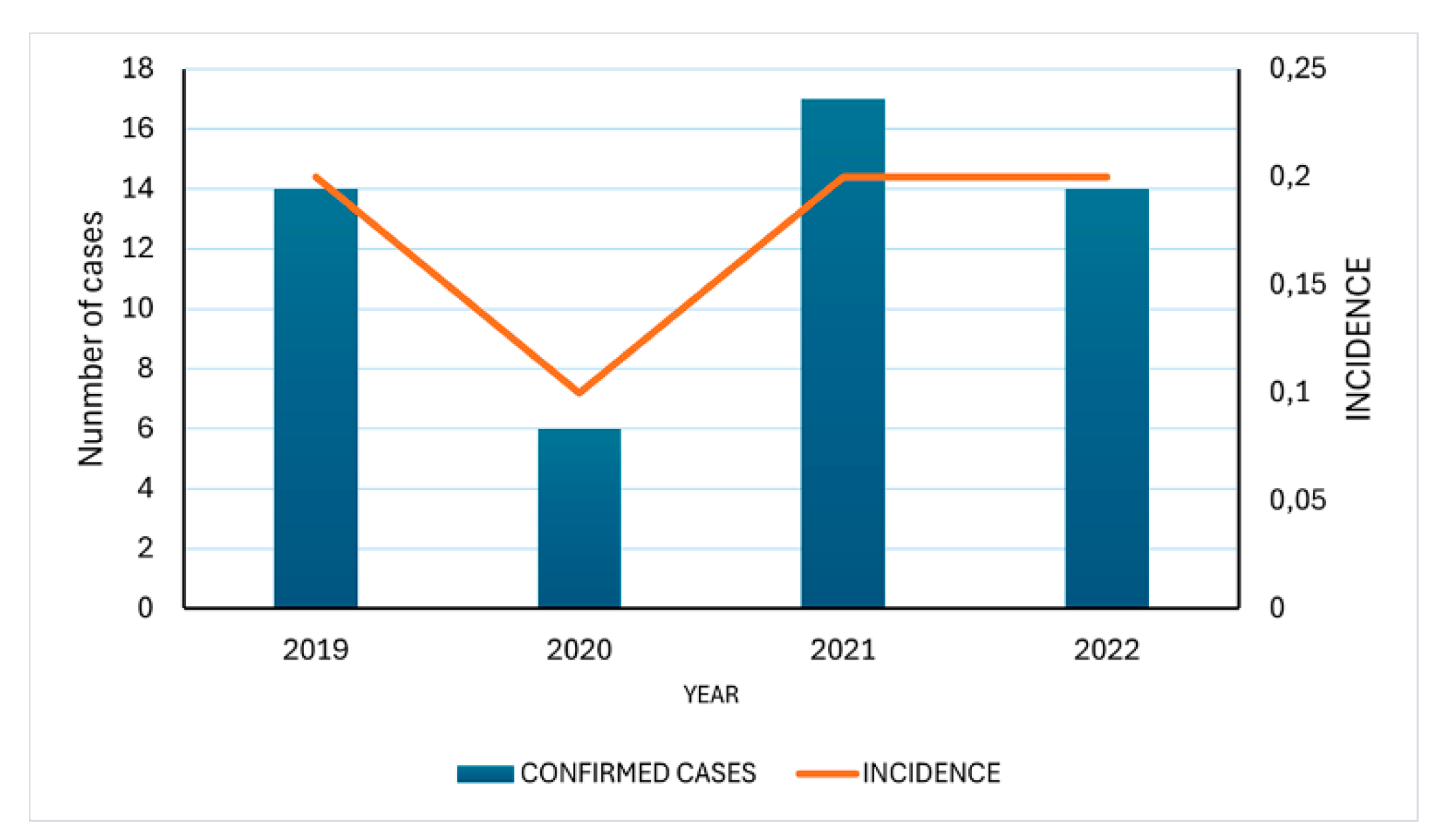
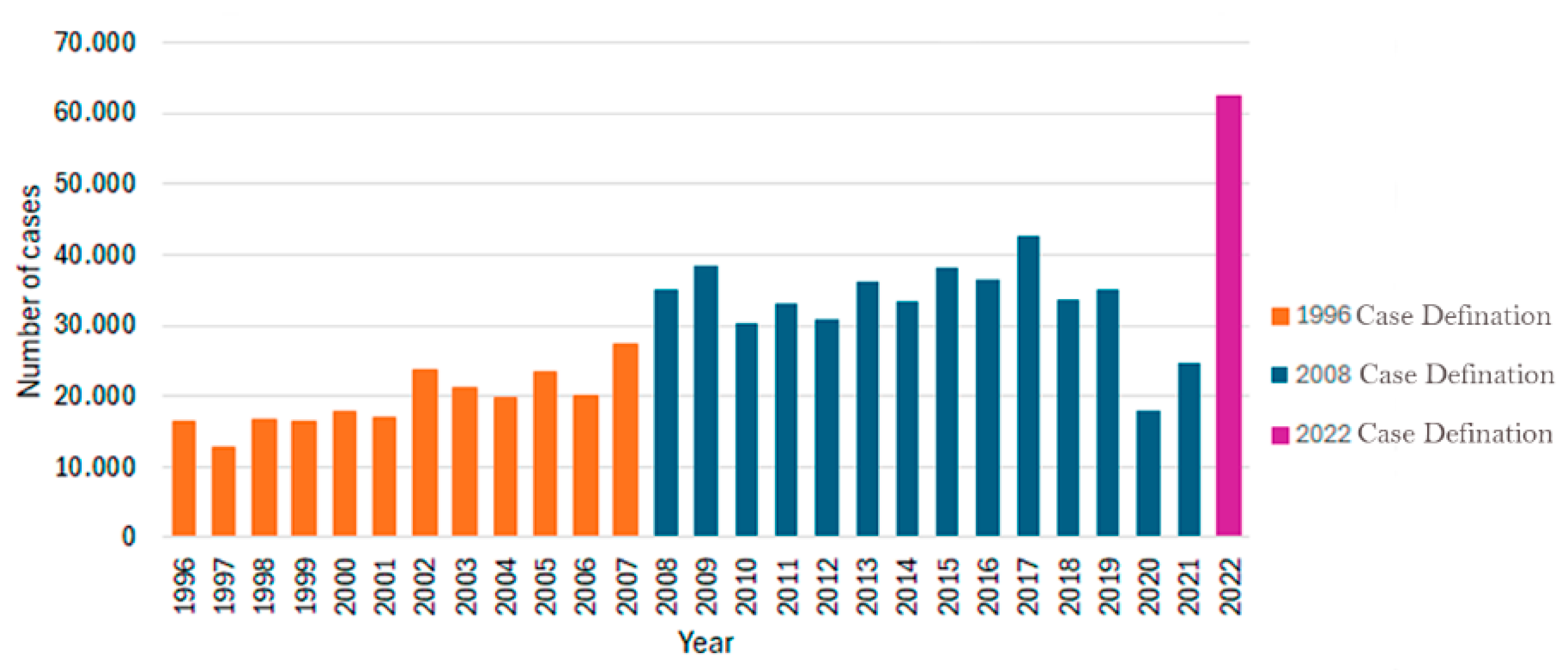
3.4.3. Epidemiological Trends of Brazilian Borreliosis Disease
3.5. Challenges in Brazilian Lyme-like Disease Diagnosis
Availability of Tests and Their Limitations in the Brazilian Context
3.6. Characteristics of the Antibody Response to B. burgdorferi
3.7. Recent Advances in DL
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radolf, J.D.; Strle, K.; Lemieux, J.E.; Strle, F. Lyme disease in humans. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2021, 42, 333–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantos, P.M.; Rumbaugh, J.; Bockenstedt, L.K.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Auwaerter, P.G.; Baldwin, K.; Bannuru, R.R.; Belani, K.K.; Bowie, W.R.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and American College of Rheumatology (ACR): 2020 Guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of Lyme disease. Clin Infect Dis 2021, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Alshehabat, M.A.; Hayajneh, W.A.; Roess, A.A. Seroprevalence, spatial distribution and risk factors of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Jordan. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2020, 73, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinari, N.H.; Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Bonin, S.; Falkingham, E.; Trevisan, G. The Current state of knowledge on Baggio-Yoshinori syndrome (Brazilian Lyme Disease-like Illness): Chronological presentation of historical and scientific events observed over the last 30 years. Pathogens 2022, 11, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, F.A.; Rezende, J.; Silva, D.; Alves, F.C.G.; Oliveira, C.E.; Costa, I.P.D. Molecular evidence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in patients in the Brazilian central-western region. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed 2017, 57, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vien, V.P.; Bassi, R.; Maxim, T.; Bogoch, I.I. Lyme disease vs. Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome in a returned traveler from Brazil. J Travel Med 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.V.d.; Oliveira, K.H.C.d.; Santos, J.P.D.; Gazeta, G.S. Geographical distribution of Lyme-like borreliosis in Brazil: Hot spots for research and surveillance. J Parasitic Dis: DiagTher 2017, 2. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, V.S.; Santana, M.M.d.; Gomes, D.d.L.X.; Medeiros, É.P.d.; Cordeiro, M.F.; Takenami, I. Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome: A literature review. Rev Med 2020, 99, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Wormser, G.P.; McKenna, D.; Karmen, C.L.; Shaffer, K.D.; Silverman, J.H.; Nowakowski, J.; Scavarda, C.; Shapiro, E.D.; Visintainer, P. Prospective evaluation of the frequency and severity of symptoms in Lyme disease patients with Erythema migrans compared with matched controls at baseline, six months, and 12 months. Clin Infect Dis 2020, 71, 3118–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geebelen, L.; Lernout, T.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Kabamba-Mukadi, B.; Saegeman, V.; Belkhir, L.; De Munter, P.; Dubois, B.; Westhovens, R.; Van Oyen, H.; et al. Non-specific symptoms and posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome in patients with Lyme borreliosis: A prospective cohort study in Belgium (2016-2020). BMC Infect Dis 2022, 22, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donta, S.T. What We Know and Don't Know About Lyme Disease. Front Public Health 2021, 9, 819541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A. Persistent Symptoms After Treatment of Lyme Disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2022, 36, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.K.; Caboni, M.; Strandwitz, P.; D'Onofrio, A.; Lewis, K.; Patel, C.J. Systematic comparisons between Lyme disease and posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome in the U.S. with administrative claims data. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, L.M.; Vazquez-Pertejo, M.T. Tickborne illness-Lyme disease. Dis Mon 2018, 64, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanek, G.; Strle, F. Lyme disease: European perspective. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2008, 22, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steere, A.C.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P.; Hu, L.T.; Branda, J.A.; Hovius, J.W.; Li, X.; Mead, P.S. Lyme borreliosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016, 2, 16090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A. Willy Burgdorfer. Lancet 2015, 385, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, A.; Fong, J.; Cervantes, J. Borrelia Infection in Latin America. Rev Invest Clin 2018, 70, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, R.; Talhari, C.; Ferreira, L.C.L.; Zelger, B.; Talhari, S. Presence of Borrelia burgdorferi "Sensu Lato" in patients with morphea from the Amazonic region in Brazil. Int J Dermatol 2011, 50, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.H.d.; Salles, R.d.S.; Salles, S.d.A.N.; Madureira, R.C.; Yoshinari, N.H. Borreliose de Lyme simile: Uma doença emergente e relevante para a dermatologia no Brasil. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia 2005, 80, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.P.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Barros, P.J.; Bonoldi, V.L.; Leon, E.P.; Zeitune, A.D.; Cossermelli, W. [Lyme disease in Mato Grosso do Sul State, Brazil: Report of three clinical cases, including the first of Lyme meningitis in Brazil]. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo 1996, 51, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, E.; Costa, I.P.; Gauditano, G.; Bonoldi, V.L.; Higuchi, M.L.; Yoshinari, N.H. Description of Lyme disease-like syndrome in Brazil. Is it a new tickborne disease or Lyme disease variation? Braz J Med Biol Res 2007, 40, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margos, G.; Fingerle, V.; Cutler, S.; Gofton, A.; Stevenson, B.; Estrada-Peña, A. Controversies in bacterial taxonomy: The example of the genus Borrelia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2020, 11, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S. Spirochete Flagella and Motility. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charon, N.W.; Cockburn, A.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Miller, K.A.; Miller, M.R.; Motaleb, M.A.; Wolgemuth, C.W. The unique paradigm of spirochete motility and chemotaxis. Annu Rev Microbiol 2012, 66, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, N.W.; Eckert, J.; Stübs, G.; Schumann, R.R. Immune responses induced by spirochetal outer membrane lipoproteins and glycolipids. Immunobiology 2008, 213, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strnad, M.; Rudenko, N.; Rego, R.O.M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Borrelia burgdorferi. Virulence 2023, 14, 2265015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, E.; Marangoni, R.G.; Gauditano, G.; Bonoldi, V.L.; Yoshinari, N.H. Amplification of the flgE gene provides evidence for the existence of a Brazilian borreliosis. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2012, 54, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.F.; Pal, U.; Alani, S.M.; Fikrig, E.; Norgard, M.V. Essential role for OspA/B in the life cycle of the Lyme disease spirochete. J Exp Med 2004, 199, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, U.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Bockenstedt, L.K.; Anderson, J.F.; Flavell, R.A.; Norgard, M.V.; Fikrig, E. OspC facilitates Borrelia burgdorferi invasion of Ixodes scapularis salivary glands. J Clin Invest 2004, 113, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belperron, A.A.; Liu, N.; Booth, C.J.; Bockenstedt, L.K. Dual role for Fcγ receptors in host defense and disease in Borrelia burgdorferi-infected mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzer, H.; Glaesner, J.; Baerenwaldt, A.; Reitinger, C.; Lux, A.; Heger, L.; Dudziak, D.; Harrer, T.; Gessner, A.; Nimmerjahn, F. Human Fcγ-receptor IIb modulates pathogen-specific versus self-reactive antibody responses in Lyme arthritis. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutras, B.L.; Lochhead, R.B.; Kloos, Z.A.; Biboy, J.; Strle, K.; Booth, C.J.; Govers, S.K.; Gray, J.; Schumann, P.; Vollmer, W.; et al. Borrelia burgdorferi peptidoglycan is a persistent antigen in patients with Lyme arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2019, 116, 13498–13507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.; Brissette, C.A. The brilliance of Borrelia: Mechanisms of host immune evasion by Lyme disease-causing spirochetes. Pathogens 2021, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petnicki-Ocwieja, T.; Kern, A. Mechanisms of Borrelia burgdorferi internalization and intracellular innate immune signaling. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014, 4, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Aniz, P.A.E.A.; Pereira, R.M.R. Innate and Th1/Th17 adaptive immunity in acute and convalescent Brazilian borreliosis disease. Braz J Infect Dis 2021, 25, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, M.; Cincotta, A. Effects of Borrelia on host immune system: Possible consequences for diagnostics. Adv Integ Med 2015, 2, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, B.C.F.; Campos, A.K.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Pinter, A.; Martins, T.F. Soft and hard ticks (Parasitiformes: Ixodida) on humans: A review of Brazilian biomes and the impact of environmental change. Acta Trop 2022, 234, 106598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, C.B.; Eisen, L.; Eisen, R.J. The Rise of Ticks and Tickborne Diseases in the United States-introduction. J Med Entomol 2021, 58, 1487–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, I.S.; Marzagão, G.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Schumaker, T.T. Borrelia-like spirochetes recovered from ticks and small mammals collected in the Atlantic Forest Reserve, Cotia county, State of São Paulo, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2000, 95, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall'Agnol, B.; Michel, T.; Weck, B.; Souza, U.A.; Webster, A.; Leal, B.F.; Klafke, G.M.; Martins, J.R.; Ott, R.; Venzal, J.M.; et al. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Ixodes longiscutatus ticks from Brazilian Pampa. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2017, 8, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montandon, C.E.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Milagres, B.S.; Mazioli, R.; Gomes, G.G.; Moreira, H.N.; Padilha Ade, F.; Wanderley, G.G.; Mantovani, E.; Galvão, M.A.; et al. Evidence of Borrelia in wild and domestic mammals from Minas Gerais, Brazil. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 2014, 23, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.C.; Velásquez, C.V.; Aquib, A.; Al-Nazal, A.; Parveen, N. Transmission Cycle of Tickborne infections and co-infections, animal models and diseases. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrink, A.; Brugger, K.; Margos, G.; Kraiczy, P.; Klimpel, S. The evolving story of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato transmission in Europe. Parasitol Res 2022, 121, 781–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, R.C.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Mantovani, E.; Bonoldi, V.N.; Macoris, D.D.; Queiroz-Neto, A. Brazilian borreliosis with special emphasis on humans and horses. Braz J Microbiol 2017, 48, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg Infect Dis 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, N.; Bachiega, T.M.; Vetorasso, G.H.; Duarte, T.F.; Capalbo, R.V. Manifestações neuroftalmológicas associadas a doença de Lyme. Revista Brasileira de Oftalmologia 2019, 78, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, J.L. Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Lyme Disease. Clin Lab Med 2015, 35, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, J.A.; Attah, R.; Khianey, R.; Capitle, E.; Schutzer, S.E. Arthritis and Diagnostics in Lyme Disease. Trop Med Infect Dis 2021, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Monco, J.C.; Benach, J.L. Lyme Neuroborreliosis: Clinical Outcomes, Controversy, Pathogenesis, and Polymicrobial Infections. Ann Neurol 2019, 85, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa Neto, N.S.; Gauditano, G.; Yoshinari, N.H. Chronic lymphomonocytic meningoencephalitis, oligoarthritis, and erythema nodosum: Report of Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome of long and relapsing evolution. Rev Bras Reumatol 2014, 54, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross Russell, A.L.; Dryden, M.S.; Pinto, A.A.; Lovett, J.K. Lyme disease: Diagnosis and management. Pract Neurol 2018, 18, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, E.A.; Alves, M.F.; Mantovani, E.; Oyafuso, L.K.; Bonoldi, V.L.; Yoshinari, N.H. Profile of patients with Baggio-Yoshinari Syndrome admitted at "Instituto de Infectologia Emilio Ribas. " Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2010, 52, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, N.H. A long journey to understand Borrelia burgdorferi in Brazil. Rev Bras Reumatol 2009, 49, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, E.N.; Costa, I.P.d.; Soares, C.O.; Yoshinari, N.H. Síndrome de Lyme-símile ou complexo infecto-reacional do carrapato: Uma causa de artrite reacional. In Anais do Congresso. Belo Horizonte: Fac Med. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari, N.H.; Mantovani, E.; Bonoldi, V.L.; Marangoni, R.G.; Gauditano, G. Brazilian lyme-like disease or Baggio-Yoshinari syndrome: Exotic and emerging Brazilian tickborne zoonosis. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) 2010, 56, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugeler, K.J.; Schwartz, A.M.; Delorey, M.J.; Mead, P.S.; Hinckley, A.F. Estimating the frequency of Lyme disease diagnoses, United States, 2010-2018. Emerg Infect Dis 2021, 27, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.A.; Vieira, R.F.; Vieira, T.S.; Toledo, R.D.; Tamekuni, K.; Santos, N.J.; Gonçalves, D.D.; Vieira, M.L.; Biondo, A.W.; Vidotto, O. Serosurvey of Borrelia in dogs, horses, and humans exposed to ticks in a rural settlement of southern Brazil. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 2016, 25, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Dwyer, L.H.; Soares, C.O.; Massard, C.L.; Souza, J.C.P.d.; Flausino, W.; Fonseca, A.H.d. Soroprevalência de Borrelia burgdorferi latu sensu associada à presença de carrapatos em cães de áreas rurais do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Ciência Rural 2004, 34, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.S.; Cordeiro, M.D.; Dos Santos, L.M.R.; Araújo, I.M.; da Fonseca, A.H.; Labruna, M.B.; Guedes, E. Research of Rickettsia spp. and Borrelia spp. in dogs in Southeast Brazil. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Rep 2022, 30, 100706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joppert, A.M.; Hagiwara, M.K.; Yoshinari, N.H. Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies in dogs from Cotia county, São Paulo State, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2001, 43, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galo, K.R.; Fonseca, A.H.; Madureira, R.C.; Barbosa Neto, J.D. Freqüência de anticorpos homólogos anti-Borrelia burgdorferi em eqüinos na mesorregião metropolitana de Belém, Estado do Pará. Pesq Vet Brasileira 2009, 29, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, R.F.S.; Campos, C.H.C.; Cordeiro, M.D.; Pires, M.S.; Mafra, C.; Cepeda, M.B.; Massard, C.L.; Fonseca, A.H. Seroprevalence of homologous anti Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies in horses of military use in Brazil. Rev Bras Ciência Veterinária 2017, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.; Souza, A.M.; Bueno, M.G.; Catao-Dias, J.L.; Toma, H.K.; Pissinati, A.; Molina, C.V.; Kierulff, M.C.M.; Silva, D.G.F.; Almosny, N.R.P. Molecular detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in free-living golden headed lion tamarins (Leontopithecus chrysomelas) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2018, 60, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, I.P.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Barros, P.J.L.; Bonoldi, V.L.N.; Leon, E.P.; Zeitune, A.D.; Cossermelli, W. Doenca de lyme em mato grosso do sul: Relato de tres casos clinicos, incluindo o primeiro caso de meningite de lyme no brasil. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Univ Sao Paulo 1996, 51, 253–257. [Google Scholar]
- Brazil. Boletim epidemiológico. Tocantins, TO: Setor de vigilância em saúde e segurança do paciente. HDT-UFT/EBSERH. 2018. Available online: https://www.gov.br/ebserh/pt-br/hospitais-universitarios/regiao-norte/hdt-uft/saude/boletim-epidemiologico-do-hdt-uft/BoletimEpidemiolgico2018.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Brazil. Boletim epidemiológico do HDT-UFT. Tocantins, TO. 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.br/ebserh/pt-br/hospitais-universitarios/regiao-norte/hdt-uft/saude/boletim-epidemiologico-do-hdt-uft/copy_of_BoletimEpidemiolgicodoHDTUFT2019.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Brazil. Secretaria Municipal de Saúde de Vila Velha. Boletim Epidemiológico. 1º Semestre 2021. Available online: https://www.vilavelha.es.gov.br/midia/paginas/BE%2001-2021%20REVISADO.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Brazil. Secretaria Municipal de Saúde de Vila Velha. Boletim Epidemiológico. 1º Semestre 2020. Available online: https://www.vilavelha.es.gov.br/midia/paginas/BE%2001-2021%20REVISADO.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Brazil. Relatório da diretoria de vigilância epidemiológica (2019–2022). Santa Catarina: Secreta ria de Estado da Saúde. Available online: https://dive.sc.gov.br/index.php/a-dive (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Kobayashi, T.; Auwaerter, P.G. Diagnostic testing for Lyme disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2022, 36, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, L.A.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Harding, S.; Lindsay, R.; Ogden, N. The Accuracy of Diagnostic Tests for Lyme Disease in Humans, A systematic review and meta-analysis of North American research. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theel, E.S. The Past, Present, and (possible) future of serologic testing for Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol 2016, 54, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alby, K.; Capraro, G.A. Alternatives to serologic testing for the diagnosis of Lyme disease. Clin Lab Med 2015, 35, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; McHugh, G.A.; Damle, N.; Sikand, V.K.; Glickstein, L.; Steere, A.C. Burden and viability of Borrelia burgdorferi in skin and joints of patients with erythema migrans or lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2011, 63, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllegger, R.R.; Glatz, M. Skin manifestations of lyme borreliosis: Diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol 2008, 9, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, M.G.; Alcorta, D.A.; Padilla, A.E.; Nollner, D.W.; Hasenkampf, N.R.; Lambert, H.S.; Embers, M.E.; Spector, N.L. Visualizing Borrelia burgdorferi infection using a small-molecule imaging probe. J Clin Microbiol 2021, 59, e0231320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisendle, K.; Grabner, T.; Zelger, B. Focus floating microscopy: "gold standard" for cutaneous borreliosis? Am J Clin Pathol 2007, 127, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, P.; Petersen, J.; Hinckley, A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019, 68, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabin, A.P.; Scholze, B.P.; Lovrich, S.D.; Callister, S.M. Clinical evaluation of a Borrelia modified two-tiered testing (MTTT) shows increased early sensitivity for Borrelia burgdorferi but not other endemic Borrelia species in a high incidence region for Lyme disease in Wisconsin. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2023, 105, 115837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegalajar-Jurado, A.; Schriefer, M.E.; Welch, R.J.; Couturier, M.R.; MacKenzie, T.; Clark, R.J.; Ashton, L.V.; Delorey, M.J.; Molins, C.R. Evaluation of modified two-tiered testing algorithms for Lyme disease laboratory diagnosis using well-characterized serum samples. J Clin Microbiol 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, S.M.; Chan, S.L. A focused review on Lyme disease diagnostic testing: An update on serology algorithms, current ordering practices, and practical considerations for laboratory implementation of a new testing algorithm. Clin Biochem 2023, 117, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, I.S.d.; Gadelha, A.d.R.; Ferreira, L.C.d.L. Estudo histopatológico de casos de eritema crônico migratório diagnosticados em Manaus. Anais Brasil Dermatol 2003, 78, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.D.; Meireles, V.M.d.B.; Braz, M.N. Borreliose de lyme símile: Relato de caso. Revista Paraense de Medicina 2007, 21, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhari, S.; de Souza Santos, M.N.; Talhari, C.; de Lima Ferreira, L.C.; Silva, R.M.; Zelger, B.; Massone, C.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, R. Borrelia burgdorferi "sensu lato" in Brazil: Occurrence confirmed by immunohistochemistry and focus floating microscopy. Acta Trop 2010, 115, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahdenne, P.; Panelius, J.; Saxen, H.; Heikkilä, T.; Sillanpää, H.; Peltomaa, M.; Arnez, M.; Huppertz, H.I.; Seppälä, I.J.T. Improved serodiagnosis of erythema migrans using novel recombinant borrelial BBK32 antigens. J Med Microbiol. 2003, 52 Pt 7, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dattwyler, R.J.; Volkman, D.J.; Luft, B.J. Immunologic aspects of Lyme borreliosis. Rev Infect Dis 1989, 11 (Suppl. S6), S1494–S1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, R.A.; McHugh, G.; Granquist, J.; Shea, B.; Ruthazer, R.; Steere, A.C. Persistence of immunoglobulin M or immunoglobulin G antibody responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10-20 years after active Lyme disease. Clin Infect Dis 2001, 33, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannian, P.; McHugh, G.; Johnson, B.J.; Bacon, R.M.; Glickstein, L.J.; Steere, A.C. Antibody responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with antibiotic-refractory, antibiotic-responsive, or non-antibiotic-treated Lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2007, 56, 4216–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, G.S.; Alugupalli, K.R. Deciphering the role of Toll-like receptors in humoral responses to Borreliae. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2012, 4, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Wang, G.; Schwartz, I.; Wormser, G.P. Diagnosis of lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 2005, 18, 484–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowicz, M.; Reiter, M.; Gamper, J.; Stanek, G.; Stockinger, H. Persistent anti-Borrelia IgM antibodies without Lyme borreliosis in the clinical and immunological Context. Microbiol Spectr 2021, 9, e0102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grąźlewska, W.; Holec-Gąsior, L. Antibody cross-reactivity in serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. Antibodies 2023, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiernstedt, G.; Eriksson, G.; Enfors, W.; Jörbeck, H.; Svenungsson, B.; Sköldenberg, B.; Granström, M. Erythema chronicum migrans in Sweden: Clinical manifestations and antibodies to Ixodes ricinus spirochete measured by indirect immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Scand J Infect Dis 1986, 18, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Arco, C.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Arnaboldi, P.M. Borrelia burgdorferi-specific IgA in Lyme Disease. EBioMedicine 2017, 19, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukic, M.; Schmidt-Samoa, C.; Lange, P.; Spreer, A.; Neubieser, K.; Eiffert, H.; Nau, R.; Schmidt, H. Cerebrospinal fluid findings in adults with acute Lyme neuroborreliosis. J Neurol 2012, 259, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluth, M.H.; Robin, J.; Ruditsky, M.; Norowitz, K.B.; Chice, S.; Pytlak, E.; Nowakowski, M.; Durkin, H.G.; Smith-Norowitz, T.A. IgE anti-Borrelia burgdorferi components (p18, p31, p34, p41, p45, p60) and increased blood CD8+CD60+ T cells in children with Lyme disease. Scand J Immunol 2007, 65, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, P.L.; Sauzade, M.; Brouzes, E. dPCR: A Technology Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leth, T.A.; Joensen, S.M.; Bek-Thomsen, M.; Møller, J.K. Establishment of a digital PCR method for detection of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex DNA in cerebrospinal fluid. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 19991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucott, J.N. Posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2015, 29, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGroat, W.; Abdelhalim, H.; Patel, K.; Mendhe, D.; Zeeshan, S.; Ahmed, Z. Discovering biomarkers associated and predicting cardiovascular disease with high accuracy using a novel nexus of machine learning techniques for precision medicine. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boligarla, S.; Laison, E.K.E.; Li, J.; Mahadevan, R.; Ng, A.; Lin, Y.; Thioub, M.Y.; Huang, B.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Nasri, B. Leveraging machine learning approaches for predicting potential Lyme disease cases and incidence rates in the United States using Twitter. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2023, 23, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucott, J.N.; Soloski, M.J.; Rebman, A.W.; Crowder, L.A.; Lahey, L.J.; Wagner, C.A.; Robinson, W.H.; Bechtold, K.T. CCL19 as a Chemokine risk factor for posttreatment Lyme disease syndrome: A prospective clinical cohort study. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2016, 23, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, J.T.; Drouin, E.E.; Pianta, A.; Strle, K.; Wang, Q.; Costello, C.E.; Steere, A.C. A Highly Expressed human protein, apolipoprotein b-100, serves as an autoantigen in a subgroup of patients with Lyme disease. J Infect Dis 2015, 212, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzke, M.M.; Volyanskyy, K.; Mao, Y.; Arevalo, B.; Zohn, R.; Quituisaca, J.; Wormser, G.P.; Dimitrova, N.; Schwartz, I. Global transcriptome analysis identifies a diagnostic signature for early disseminated Lyme disease and its resolution. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslund-Gourley, B.S.; Hou, J.; Woloszczuk, K.; Horn, E.J.; Dempsey, G.; Haddad, E.K.; Wigdahl, B.; Comunale, M.A. Host glycosylation of immunoglobulins impairs the immune response to acute Lyme disease. eBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
| Stage of the disease | USA | Brazil | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute infection | ME, fever, headache, arthralgia, myalgia. | Cutaneous manifestation, fever, general malaise, myalgias | [4,8,46,47] |
| Disseminated Disease | Migratory arthralgias, Lyme carditis, meningitis, facial paralysis | ||
| Chronic infection | Encephalopathy, monoarthritis, peripheral neuropathy | Neurological changes, ocular symptoms, psychiatric and psychosocial disorders, oligoarthritis, autoimmune symptoms, and chronic fatigue syndrome |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





