Introduction
Streptococcus pneumoniae, commonly referred to as pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive bacterium known for causing a range of diseases, primarily affecting the respiratory tract (Xie et al. 2023). This pathogen is a significant cause of pneumonia, particularly in vulnerable populations such as infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals, often leading to severe complications such as bacteremia and meningitis (Gil et al. 2023). Understanding the bacterium's virulence mechanisms sheds light on its ability to cause disease. One such mechanism is biofilm formation, where pneumococcal cells adhere to surfaces and create complex structures that enhance their resistance to host immune defenses and antibiotics (Hameed et al. 2021).
Biofilms are immobile clusters of microorganisms that reside and multiply on the surfaces of medical equipment, such as catheters, by producing extracellular polymeric materials. These compounds have the capacity to cause infection. Biofilms consist of densely populated bacterial communities that are bound together by an extracellular matrix (Yahya et 2017; Yahya et al. 2018; Yaacob et al. in 2021). The matrix comprises many chemicals discharged by the bacteria, such as exopolysaccharides (EPS), extracellular DNA (eDNA), proteins, and amyloidogenic proteins (Sharma et al., 2019; Kamaruzzaman et al., 2022). Furthermore, they produce a diverse range of functional proteins that assist in their metabolic processes while they are dormant (Othman and Yahya 2019; Isa et al. 2022). Only a small proportion of bacteria in the natural environment survive by floating, while the bulk of bacteria flourish by creating biofilms to adapt to the difficult conditions. Once the biofilm is formed, its vulnerability to harm from various chemicals and medicines is significantly reduced (Zakaria et al. 2023). Therefore, it is difficult to completely eradicate it. Consequently, the presence of large amounts of antibiotics is not successful in eradicating harmful biofilms because the bacteria are well shielded within the biofilm's structure. Zhao et. al. (2017) found that biofilms demonstrate higher levels of resistance to antimicrobials in comparison to planktonic cells. Consequently, there is currently an active inquiry into the identification of new antimicrobial substances obtained from natural sources (Zawawi et al., 2020; Johari et al., 2020; Man et al., 2022).
Nicotinic acid, also known as niacin or vitamin B3, is essential for various physiological processes, including metabolism, DNA repair, and cell signaling (Faris et al. 2022). This water-soluble vitamin is vital for energy production and maintaining healthy skin, nerves, and digestion (Ringseis et al 2021). Nicotinic acid deficiency can lead to pellagra, a condition characterized by dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia, and potentially fatal complications if left untreated. Dietary sources rich in nicotinic acid include meat, fish, nuts, and whole grains. Antibacterial activity of nicotinic acid has been reported (Bartzatt et al. 2007; Asif 2014; Osigbemhe et al. 2022). However, the efficacy of nicotinic acid on S. pneumoniae biofilm remains not well investigated. Thus, the objective of the present study was to determine the effects of nicotinic acid on biomass and biochemical composition of S. pneumoniae biofilm.
Methodology
Preparation of Test Microorganism
The Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619 culture was transferred onto a Nutrient Agar (NA) plate using a sterile inoculating loop and then incubated at a temperature of 37 ºC for a duration of 24 hours. The colonies that are likely to be present and their physical characteristics that develop on the NA plate were observed and documented. Following the incubation time, the uncontaminated colony was subjected to Gram staining and examined using a microscope.
Pellicle Assay
The pellicle assay was conducted using the following steps: (i) the medium in the test tube was drained and dried for 10 minutes, (ii) the inner surface of the test tube was rinsed with distilled water, (iii) the test tube was then stained with 0.5% (w/v) crystal violet, (iv) the stain was washed off with distilled water and allowed to dry, (v) the pellicle biofilm was observed by examining the stained surface and looking for ring formation in the test tube.
Biofilm Biomass Assay
The susceptibility of S. typhimurium biofilm was evaluated at five distinct concentrations, ranging from 3.125 µg/mL to 100 µg/mL, using a sterile 96-well microplate. The test groups were administered with 100 μL of benzoic acid solution and 100 μL of bacterial inoculum. The negative control wells were filled with 100 μL of fresh medium and 100 μL of bacterial inoculum. Following a 6-hour incubation at a temperature of 37 ºC, the liquid containing freely floating cells was removed from the 96-well microplate and washed with a PBS solution two times. The biofilm wells, which were attached, were subjected to heat fixation at a temperature of 60 ºC for a duration of 30 minutes. This was followed by staining with crystal violet solution at a concentration of 0.5% (w/v) for a period of 5 minutes at room temperature. The soiled well was meticulously disposed of and cleansed with a PBS solution. Stained-biofilm wells were filled with a solution of absolute ethanol. The quantification of biofilm biomass was conducted using a BioTek Synergy H1 Hybrid microplate reader (Yahya et al., 2018) at a wavelength of 600nm, with slight modifications. The experiment was repeated for an incubation period of 12 and 18 hours.
FTIR Spectroscopy
Each well of a 6-well microplate was filled with 3 mL of a microbe culture that had been incubated overnight. Subsequently, 1 mL of nutrient broth pre-warmed to 37 °C and 1 mL of NIC were introduced into the well solution. Next, aseptic cover slips were placed into each well. The wells containing 3 mL of test microorganism and 2 mL of nutritional broth were utilised as control samples. The mixes in the microplates were subjected to incubation at 37 °C for three different time intervals: 6, 12, and 18 hours. Following the incubation period, the liquid containing free-floating cells was discarded. The residual biofilm attached to the cover slip was washed with distilled water and allowed to dry in the air. The presence of biofilm on each cover slip was assessed using a Thermo Scientific NICOLET 6700 ATR-FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA). The spectrometer analysed the biofilm attached to the cover slip with a resolution of 2 cm-1 across a range of 2000 to 600 cm-1. The Thermo Scientific OMNIC software (Yahya et al., 2017) was utilised for the collection and processing of all data.
Results and Discussion
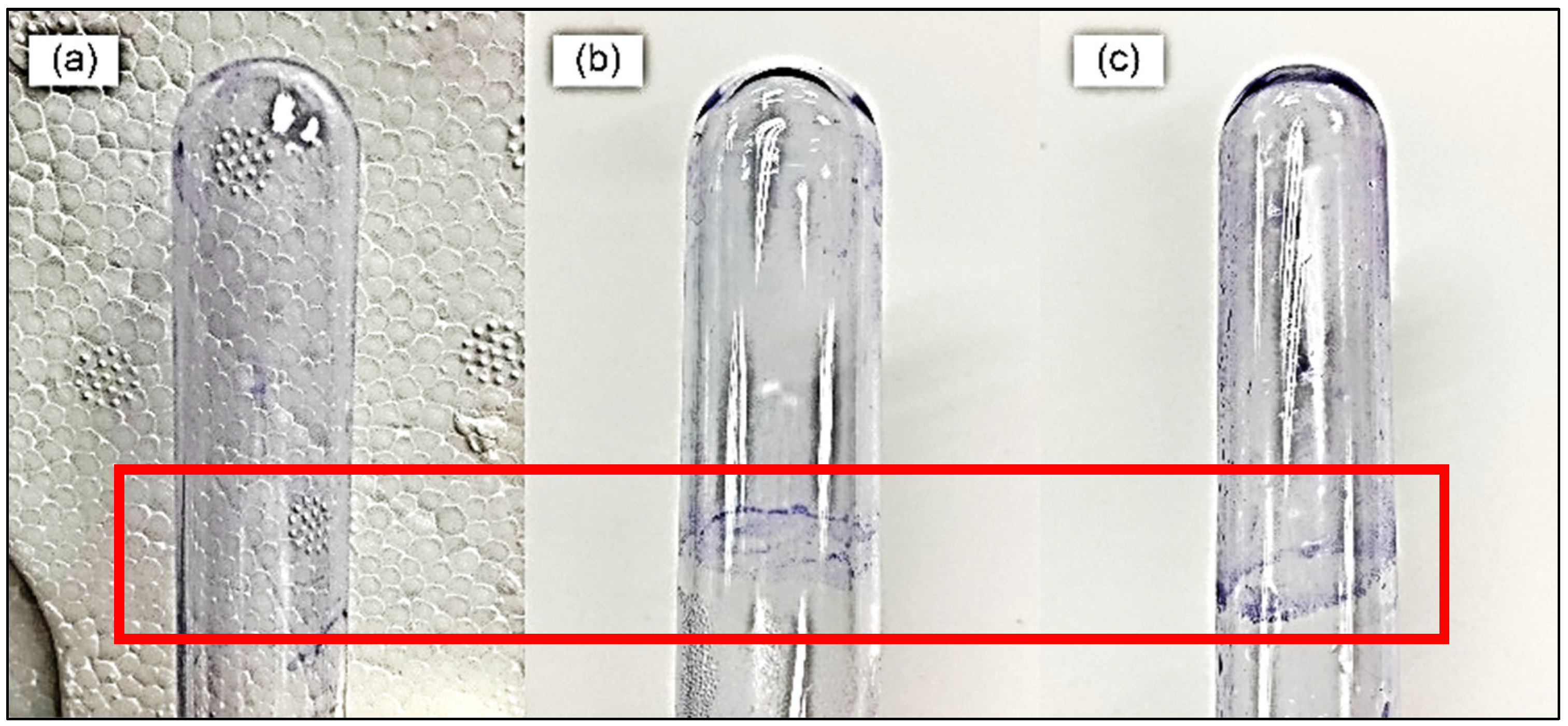
The pellicle assay demonstrated the formation of a ring at the air-liquid interface (
Figure 1). This confirms that
S. pneumoniae is capable of forming biofilms, particularly at the liquid-air interface.
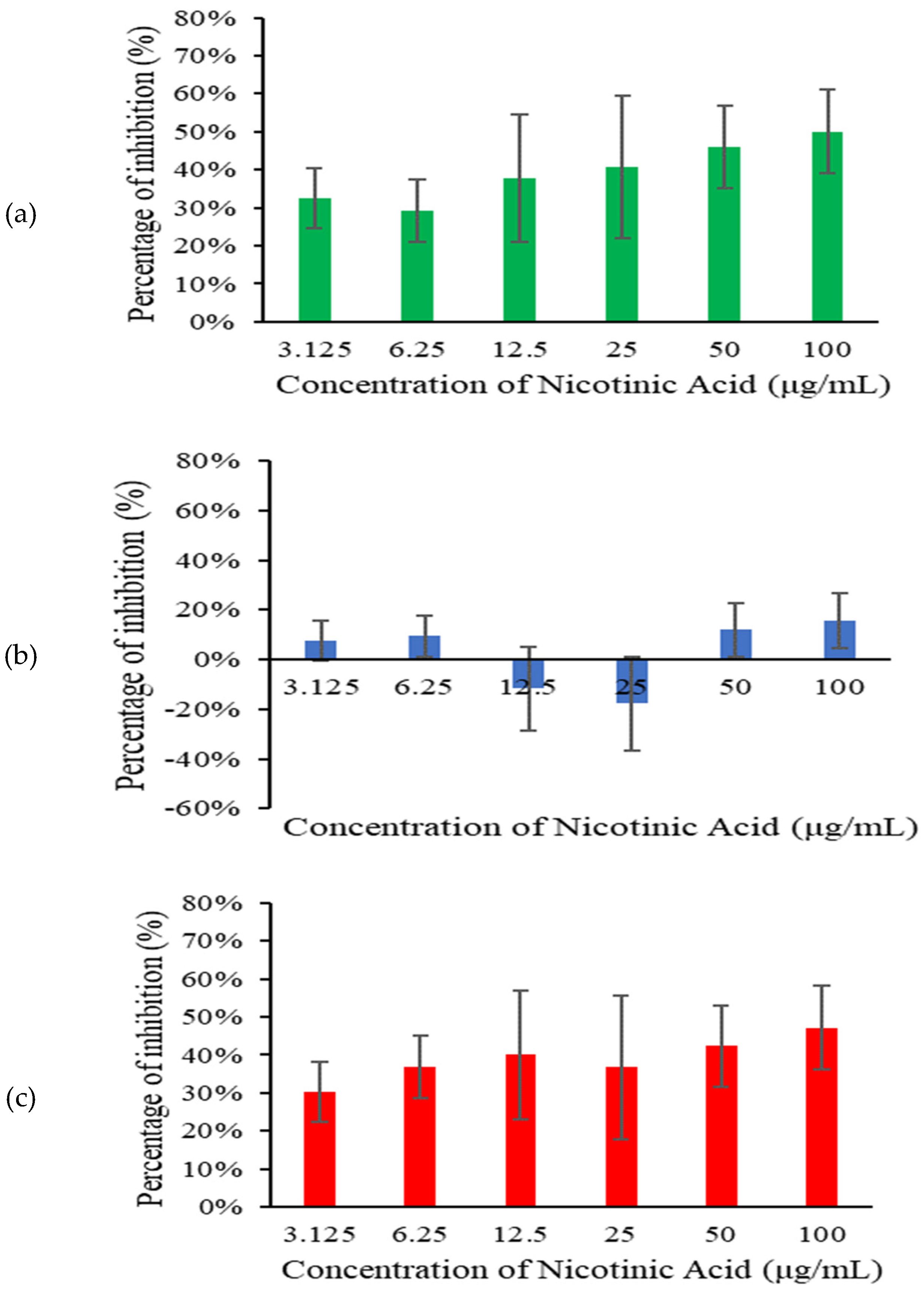
Across all tested concentrations, nicotinic acid significantly inhibited S. pneumoniae biofilm at 6 h and 18 h (
Figure 2). Higher concentrations of nicotinic acid resulted in lower biofilm biomass. This concentration-dependent response indicates that the effectiveness of nicotinic acid in inhibiting biofilm formation increases with higher concentrations. However, only minimal biofilm inhibition was observed at 12 h.
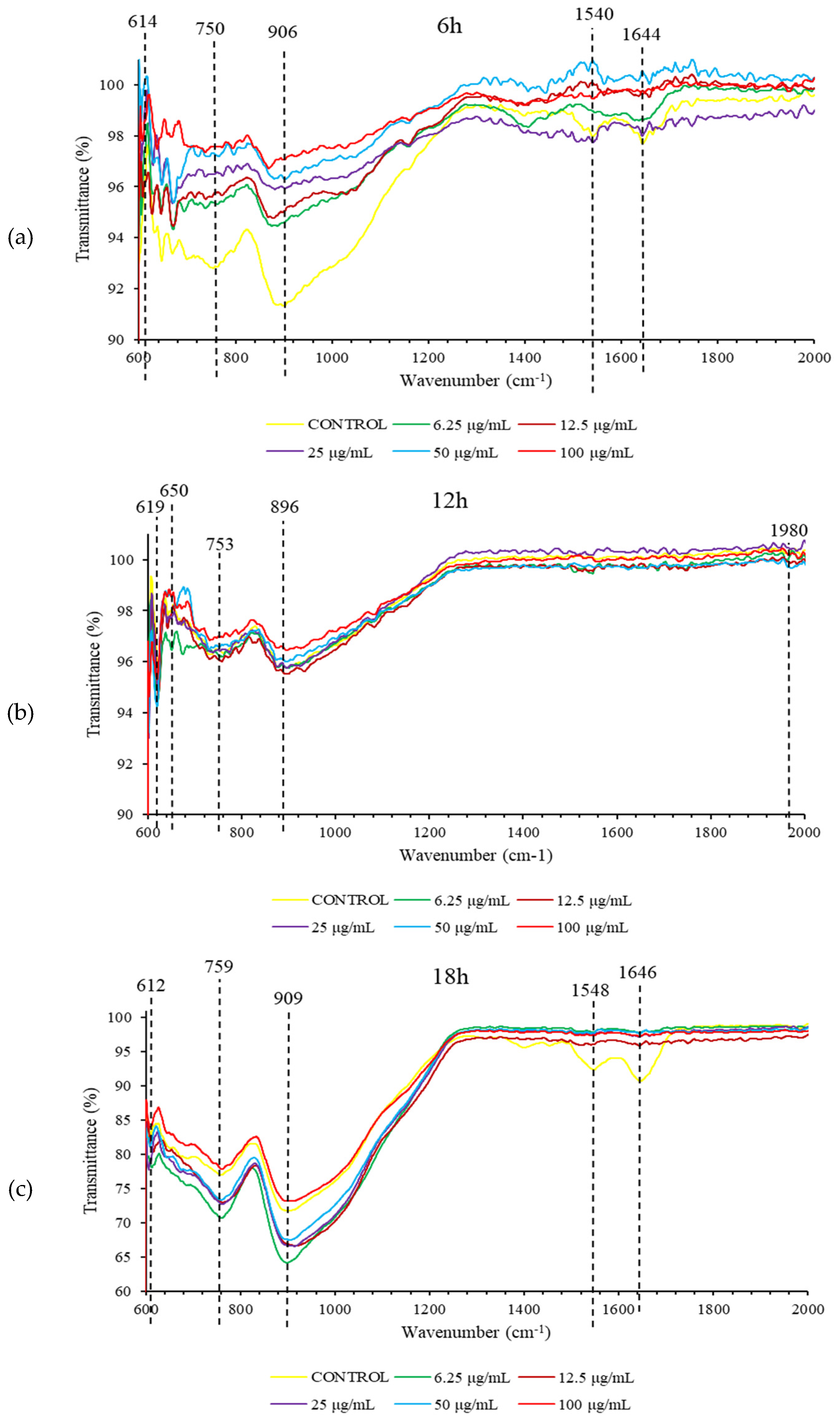
At 6 h, treatment with nicotinic acid resulted in FTIR spectral changes in S. pneumoniae biofilm (
Figure 3). The shape of spectral peaks at 750 cm
-1, 906 cm
-1, 1540 cm
-1, and 1644 cm
-1 were found to change substantially. These spectral peaks represent protein biomolecules in S. pneumoniae biofilm (
Table 1). Meanwhile, treatment with nicotinic acid also caused FTIR spectral changes in 18 h S. pneumoniae biofilm at 1548 cm
-1 and 1646 cm
-1 representing protein biomolecules. However, no FTIR spectral changes were observed in 12 h S. pneumoniae biofilm following exposure to nicotinic acid.
The antibiofilm activity of nicotinic acid reported herein is in line with Gömeç et al. (2024) demonstrating the antibiofilm efficacy of nicotinamide against Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213), Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (ATCC 43300), Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC
29212), Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 700603), and Candida albicans (ATCC10231). Meanwhile, Fayyad et al. (2019) demonstrated the synergistic effects of imipenem antibiotic combined with nicotinic acid against P. aeuruginosa biofilm. In the present study, the FTIR spectral changes in S. pneumoniae biofilm due to treatment with nicotinic acid probably explain the structural damage of biofilm (Yahya et al. 2018; Kamaruzzaman et al. 2022; Johari et al. 2023).
Conclusion
Nicotinic acid exhibited substantial suppression of S. pneumoniae biofilm development at both 6 hours and 18 hours. Moreover, greater doses of nicotinic acid resulted in reduced biofilm biomass, indicating a response that is dependent on the concentration. Nevertheless, there was only a small amount of biofilm inhibition seen after 12 hours. The application of nicotinic acid resulted in modifications to the FTIR spectra of protein biomolecules in the biofilm of S. pneumoniae at 6 hours and 18 hours. These changes were observed by shifts in the spectral peaks at 750 cm-1, 906 cm-1, 1540 cm-1, 1548 cm-1, and 1644 cm-1. No significant changes in the FTIR spectra were seen in the 12-hour Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilm after being exposed to nicotinic acid. The findings indicate that nicotinic acid hinders the growth of S. penumoniae biofilm in a manner that depends on both time and concentration. This effect is likely achieved by modifying the structure of protein biomolecules present in the biofilm.
References
- Asif, M. (2014). Antimicrobial potential of nicotinic acid derivatives against various pathogenic microbes. European Reviews of Chemical Research, 1(1), 10-21.
- Bartzatt, R., Cirillo, S. L., & Cirillo, J. D. (2007). Antibacterial activity of dipeptide constructs of acetylsalicylic acid and nicotinic acid. Drug delivery, 14(2), 105-109.
- Faris, P., Casali, C., Negri, S., Iengo, L., Biggiogera, M., Maione, A. S., & Moccia, F. (2022). Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate induces intracellular Ca2+ signalling and stimulates proliferation in human cardiac mesenchymal stromal cells. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 10, 874043.
- Fayyad, S. A., Majeed, M. R., & Mahmoud, S. S. (2019). Evaluation of synergistic effect of nicotinic acid with imipenem as antibiofilm for clinical Pseudomonas Aeruginosa isolates. Iraqi Journal of Science, 50-56.
- Gil, E., Wall, E., Noursadeghi, M., & Brown, J. S. (2023). Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis and the CNS barriers. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 12, 1106596.
- Gömeç, M., Nasif, V., Kafa, A. H. T., Sayin, K., Gezegen, H., & Ataseven, H. (2024). Designed, Synthesis, In Vitro and Computational Analyses of Anticancer Nicotinamide Derivatives. Indian Journal of Chemistry (IJC), 63(2), 145-158.
- Isa, S. F. M., Abdul Hamid, U. M., & Zaman Raja Yahya, M. F. (2022). Treatment with the combined antimicrobials triggers proteomic changes in P. aeruginosa-C. albicans polyspecies biofilms. ScienceAsia, 48(2).
- Johari, N. A., Amran, S. S. D., Kamaruzzaman, A. N. A., Man, C. A. I. C., and Yahya, M. F. Z. R. (2020). Anti-biofilm potential and mode of action of malaysian plant species: a review. Sci. Lett. 14, 34–46.
- Johari, N. A., Aazmi, M. S., & Yahya, M. F. Z. R. (2023). FTIR Spectroscopic Study of Inhibition of Chloroxylenol-Based Disinfectant Against Salmonella enterica serovar Thyphimurium Biofilm. Malaysian Applied Biology, 52(2), 97-107.
- Kamaruzzaman, A.N.A., Mulok, T.E.T.Z., Nor, N.H.M. & Yahya, M.F.Z.R. 2022a. FTIR spectral changes in Candida albicans biofilm following exposure to antifungals. Malaysian Applied Biology, 51(4): 57-66.
- Man, C. A. I. C., Razak, W. R. W. A., & Yahya, M. F. Z. R. (2022). Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of Swietenia macrophylla King ethanolic extract against foodborne pathogens. Malaysian Applied Biology, 51(4), 45-56.
- Osigbemhe, I. G., Louis, H., Khan, E. M., Etim, E. E., Oyo-Ita, E. E., Oviawe, A. P.,... & Obuye, F. (2022). Antibacterial potential of 2-(-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-methylidene)-amino) nicotinic acid: experimental, DFT studies, and molecular docking approach. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 194(12), 5680-5701.
- Othman, N.A. & Yahya, M.F.Z.R. 2019. In silico analysis of essential gene and non-homologous proteins in Salmonella typhimurium biofilm. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1349: 012133.
- Ringseis, R., Gessner, D. K., Beer, A. M., Albrecht, Y., Wen, G., Most, E.,... & Eder, K. (2020). Nicotinic acid improves endurance performance of mice subjected to treadmill exercise. Metabolites, 10(4), 138.
- Xie, M. Z., Dong, M., Du, J., Zhang, S. S., Huang, F., & Lu, Q. B. (2023). Epidemiological features of Streptococcus pneumoniae in patients with acute respiratory tract infection in Beijing, China during 2009–2020. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 16(5), 719-726.
- Yaacob, M. F., Murata, A., Nor, N. H. M., Jesse, F. F. A., & Yahya, M. F. Z. R. (2021). Biochemical composition, morphology and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis biofilm. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 33(1), 101225.
- Yahya, M. F., Alias, Z., & Karsani, S. A. (2017). Antibiofilm activity and mode of action of DMSO alone and its combination with afatinib against gram-negative pathogens. Folia Microbiologica, 63(1), 23–30. [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M. F., Alias, Z., & Karsani, S. A. (2017). Subtractive protein profiling of Salmonella typhimurium biofilm treated with DMSO. The Protein Journal, 36(4), 286–298. [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N.F.S., Yahya, M.F.Z.R., & Jamil, N.M. (2023). Multiple Bacterial Strategies to Survive Antibiotic Pressure: A Review. Preprints 2023, 2023040591.
- Zawawi, W.M.A.W.M., Ibrahim, M.S.A., Rahmad, N., Hamid, U.M.A. & Yahya, M.F.Z.R. (2020). Proteomic analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated with Chromolaena odorata extracts. Malaysian Journal of Microbiology, 16(2): 124-133.
- Zhao, X., Zhao, F., Wang, J., & Zhong, N. (2017). Biofilm Formation and control strategies of Foodborne Pathogens: Food Safety Perspectives. Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 7(58), 36670–36683. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).