1. Introduction
Peptide pools are mixtures of short peptides that are mainly used in experimental immunology. Important applications include monitoring cellular immune responses, such as those following infection or vaccination. It is also used for in-vitro T-cell activation and expansion in adoptive cancer immunotherapies, as well as for epitope discovery in vaccine development. It is extremely important that the composition of the peptide pools corresponds exactly to the design and purpose of the peptide pool. For example, a peptide pool for personalized cancer immunotherapy must safely contain all peptide neoantigens. In addition, no other peptides should be present in the pool. These can otherwise lead to incorrect results [
1]. Some manufacturers address this problem by double-checking the composition of the pools. One employee adds the peptide and a second employee checks that it is the correct peptide. Despite careful production methods, it is desirable to have an independent method for the correct composition of the peptide pool. In addition, some peptides in a peptide pool can also change over time. The quality of peptide pools may be compromised by synthesis errors, degradation, adsorptive losses, dimerization, and other unwanted chemical modifications. Consequently, these issues can lead to misleading experimental results and poor experiment reproducibility [
2]. Therefore, the development of improved methods for quality control (QC) of peptide pools is highly desirable. However, in many cases, routinely performed quality control protocols rely mainly on pre-characterizing individual peptides. Peptide quantification is commonly performed using HPLC-UV or the use of stable isotopically labeled (SIL) internal standards in HPLC-MS. However, this approach is not easily applicable to complex peptide pools. Quantification using HPLC-UV is difficult in complex samples, such as mixed peptide pools, due to a frequent lack of baseline separation. This issue is aggravated by the potential presence of an unknown number of synthesis byproducts and degradation products. A common analytical method to resolve complex samples is chromatography combined with mass-spectrometry and in particular HPLC-MS/MS. The use of tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), usually as a triple quadrupole (QqQ) system with standard resolution, achieves high selectivity by using specific mass transitions. This approach leads to excellent selectivity and can be considered the gold standard for quantification. However, these methods usually require isotopically labelled peptides for each of the peptides in the pool. This is a huge cost factor for QC considering the many different peptide pools on the market. During the last years, high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) has become more and more popular, due to its excellent mass precision and accuracy. It achieves high selectivity by utilizing a narrow mass extraction window (MEW). Also very attractive is the ability to computationally derive the elemental composition of ions, which leads to a strong support of the analyte’s identity and structure without the need of independent standard compounds or isotopically labelled compounds. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, but they both face common challenges in mass spectrometric quantification: Compound-dependent ionization efficiency and ion suppression in the ion source due to co-eluting substances, which may lead to strong matrix effects [
3].
For the latter problem, various solutions exist, which can be categorized as either reduction or compensation strategies. Reduction of matrix effects can be achieved through sample clean-up (e.g., extraction) [
4], separation (chromatography) [
5], or sample dilution (
dilute and shoot) [
6]. Compensation for matrix effects can be achieved through matrix-matched calibration [
7], standard addition [
8], the echo peak technique [
9], and internal standardization [
10]. When ion suppression is caused by co-eluting analytes, neither sample clean-up nor dilution may be effective. Chromatographic separation of such complex mixtures may be limited, even when UHPLC is applied. In addition, some peptides are poorly ionized in MS, and hence a quantitation is not possible without a standard compound or other independent determination of the response factors of each peptide. Some peptides are fully absent in MS for various reasons. A complete mass spectrometric coverage of a protein digest was therefore deemed unrealistic [
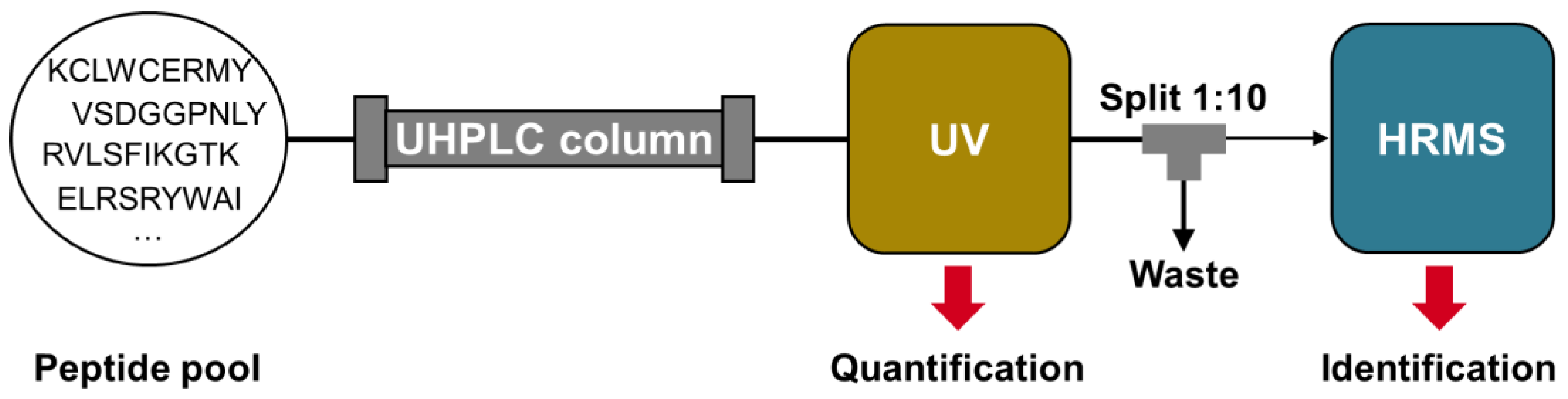
11]. In the context of a peptide pool, this would mean that some peptides would be missing and therefore could not be qualified at all. Among the mentioned compensation methods, matrix-matched calibration and standard addition are considered impractical due to calibration effort. The echo peak technique is quite difficult for multi-analyte analysis. Finally, internal standardization remains, which is a highly effective compensation method when using stable isotope-labeled analogues of the analyte. However, these are often either not commercially available or prohibitively expensive, so that they are usually not economically viable in the case of multi-analyte methods. Consequently, this study aims to explore cost- and time-efficient options for quality control of synthetic peptide pools. The hyphenated technique UHPLC-UV-HRMS, as shown in
Figure 1, was used for this purpose. However, unlike conventional approaches, quantification and identification were performed separately using two different detectors.
The separation of quantification and identification between the UV detector and mass spectrometer provides several benefits. Firstly, it eliminates the need for stable isotope-labeled internal standards. MS-based identification eliminates the need for additional HPLC identification runs to determine the retention time (t
R) of each peptide, which might require all peptides in pure form, and enables non-target analysis of any other compounds, such as synthesis byproducts or degradation products, if necessary. The method was developed using a common peptide pool of 32 peptides (CEF peptide pool [
12,
13]). The optimal chromatographic results were obtained using a shallow gradient, elevated temperature, moderate flow rate, and the ion-pairing reagent TFA at low concentrations of 0.05% and 0.04% to flatten the baseline and to reduce ion suppression by TFA. Relative quantification could be achieved from the 214 nm UV signal, using the integration by the perpendicular drop method combined with the formation of a limited number of peak groups, or alternatively by using peak fitting algorithms. High-resolution mass-spectrometry (
Orbitrap) delivered a peak and compound assignment by comparison with the expected peptide mass (to charge ratio). As a bonus of the HRMS method, a total of at least 45 unexpected compounds could be tentatively identified.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
CEF advanced peptide pool (purity >90%), containing 32 peptides selected from specific HLA class I-restricted T-cell epitopes of cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and influenza virus, was obtained from peptides & elephants GmbH (Hennigsdorf, Germany). LC-MS grade trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) >99.5% (85183) was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Life Technologies GmbH (Darmstadt, Germany). LC-MS grade acetonitrile (ACN) was obtained from Th. Geyer GmbH & Co. KG (Renningen, Germany). Helium 6.0 (10100530) was purchased from Linde AG (Berlin, Germany). LC-MS grade LTQ ESI positive ion calibration solution >99.5% (88322) was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific GmbH (Dreieich, Germany). Water was purified by an Ultra-Pure Water System from Millipore Co., (Burlington, MA, USA), with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ·cm.
2.2. Sample Preparation
The lyophilized CEF advanced peptide pool sample (0.8 mg) was stored at -20°C and equilibrated at room temperature (RT) for 30 minutes before use. Afterwards, the sample was dissolved in 50 µL of ACN/TFA 0.05% (v/v) and then in 50 µL of water/TFA 0.05% (v/v) to obtain a stock solution of 8 µg/µL (approximately 0.25 µg/µL per peptide). Before use, both solvents were degassed by sonication (45 kHz, 15 min, RT). After 15 minutes of equilibration, the stock solution was divided into 20 µL aliquots and stored in 0.5 mL polypropylene micro tubes at -20°C. Before each LC-MS analysis, the 20 µL aliquots were thawed at room temperature and diluted with 180 µL of water/TFA 0.05% (v/v) to a final concentration of 0.8 µg/µL (approximately 0.025 µg/µL per peptide). After centrifugation (6000 rpm, 5 min, RT), 180 µL of the supernatant was transferred to an amber HPLC glass vial with a 200 µL glass insert.
The solvents used to dissolve the peptide pool were also utilized to prepare blank samples. After diluting 100 µL of a 1:1 mixture of water/TFA 0.05% (v/v) and ACN/TFA 0.05% (v/v) with 900 µl of water/TFA 0.05% (v/v), a blank solution with an ACN concentration of 5% was obtained. After centrifugation (6000 rpm, 5 min, RT), 800 µL of the supernatant was transferred to an amber HPLC glass vial and stored at -20°C.
2.3. UHPLC-HRMS Analysis
Peptide pool samples were analyzed on a Thermo Scientific UltiMate 3000 RSLCnano UHPLC System hyphenated to a Thermo Fisher Scientific Exactive Orbitrap High-Resolution Mass Spectrometer. The autosampler temperature was set to 4°C. Chromatographic separation was conducted using an Acclaim PepMap RSLC C18 column (100 Å, 2 µm, 0.3 mm x 150 mm) with an Acclaim PepMap RSLC C18 trap column (100 Å, 5 µm, 0.3 mm x 5 mm), both from Thermo Scientific. The mobile phases for chromatography consisted of 0.05% (v/v) TFA in water (A) and 0.04% (v/v) TFA in acetonitrile (B). The mobile phases were degassed by purging with helium for 5 minutes. The peptides were eluted using the following gradient: 4% B isocratic for 4 min (6 µL/min), linear increase to 44% B over 100 min (6 µL/min), linear increase to 95% B over 0.1 min (6 µL/min), held at 95% B for 6 min (10 µL/min), returned to initial conditions within 0.1 min (10 µL/min), and maintained at a flow rate of 10 µL/min for 11 min and 6 µL/min for 1 min. The column oven temperature was set at 55°C. The injection volume was 1 µL, conducted in full loop mode, with a flush volume of 5 µL, a flush volume 2 of 3 µL, and a loop overfill of 2 µL. UV detection was performed at 214 nm. Before analyzing the peptides in the mass spectrometer, the eluate was split in a 1:10 ratio using a T-piece. Subsequent electrospray ionization was conducted in positive mode (ESI+). The mass spectrometer settings were adjusted as follows: spray voltage at 4.5 kV, capillary voltage at 30 V, capillary temperature at 320°C, tube lens voltage at 80 V, skimmer voltage at 24 V, and the scan range from 200 to 1800 m/z. The MS scans were acquired with ultra-high resolution (100,000 at 200 m/z) at a scan rate of 1 Hz, balanced automatic gain control (AGC) target (1 x 106), and a maximum injection time (IT) of 500 ms. External mass calibration using LTQ ESI positive ion calibration solution provided a mass accuracy of <5 ppm. Data acquisition was performed using Xcalibur 2.2 with Dionex Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Link (DCMSLink).
2.4. Data Processing
Analysis of mass spectrometry data was conducted using Xcalibur 2.2. Theoretical exact masses and m/z values of the peptides were calculated using the ChemCal [
14]. Experimental m/z values were confirmed with a maximum mass tolerance of 5 ppm.
UV spectrometry data was analyzed either using Chromeleon 7.2.10 or PeakFit 4.12. In Chromeleon, baseline correction was performed by subtracting a blank run injection. A baseline with a defined start and end point was added. For peak detection and integration, a minimum area was defined. Peak areas were measured by the perpendicular drop method. In PeakFit, prior to peak fitting, a baseline is obtained using PeakFit's automated baseline fitting option (2nd Deriv Zero algorithm, BEST, tolerance 10%). The active baseline points were selected manually. To identify and fit peaks, the AutoFit Peaks I Residuals option was selected. The data for peak detection was smoothed using the Savitzky-Golay algorithm, and the optimal smoothing level was automatically determined by the AI Expert option (0.05%). Peaks were fitted using the EMG+GMG peak function. The amplitude rejection threshold was set at 2.5%, and residuals were added. Graphical adjustments were made alongside automatic peak placement. Peak fit preferences were adjusted with the following settings: Maximum iterations = 10,000, convergence to significant digits in Chi-Square = 6, built-in peak functions constraints at a0 = 99, a1 = 100, a3 = 140, a4 = 140, fit extent = 1/1. As a minimization procedure, the least-squares method was chosen. For constructing the curvature matrix, a sparse root-finding procedure was selected. The fits were rerun until the coefficient of determination (r²) did not change in the second decimal place.
Sample peak capacities were calculated using the equation PCS (sample peak capacity) = tf (retention time of the last peak) - ti (retention time of the first peak)/FWHM (peak width at 50% height). Peak widths were calculated for well-resolved peptides: peptide 3 for gradient optimization, peptide 31 for TFA concentration optimization, and peptide 1 for temperature optimization.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimized UHPLC Parameters
For the quantification of the peak areas obtained by a UV detector, baseline separation of all individual components would be desirable. For a fast check, the peak capacity of a separation can be calculated [
15,
16]. Peak capacity is considered the preferential measure of the performance of a gradient separation [
17]. As the most general definition, the peak capacity is the number of peaks that can be separated within a retention window. In practical terms, the peak capacity is the gradient run time divided by the average peak width. In a sample with a given number of components, the larger the peak capacity, the more likely it is for all components to be separated without critical overlap [
18]. Accordingly, in optimizing the general UHPLC method, the goal was to achieve a high peak capacity. Since changes in separation conditions affect both peak width and the retention window [
19], it is preferable to use the sample peak capacity (PC
S) related to the retention window as defined by Dolan et al. [
20] rather than the peak capacity related to gradient time. The concept of peak capacity is based on the idealized assumption that all peaks occur at regular intervals. However, usually peaks are more or less randomly distributed. Consequently, the highest peak capacity does not necessarily result in the best separation of a specific sample.
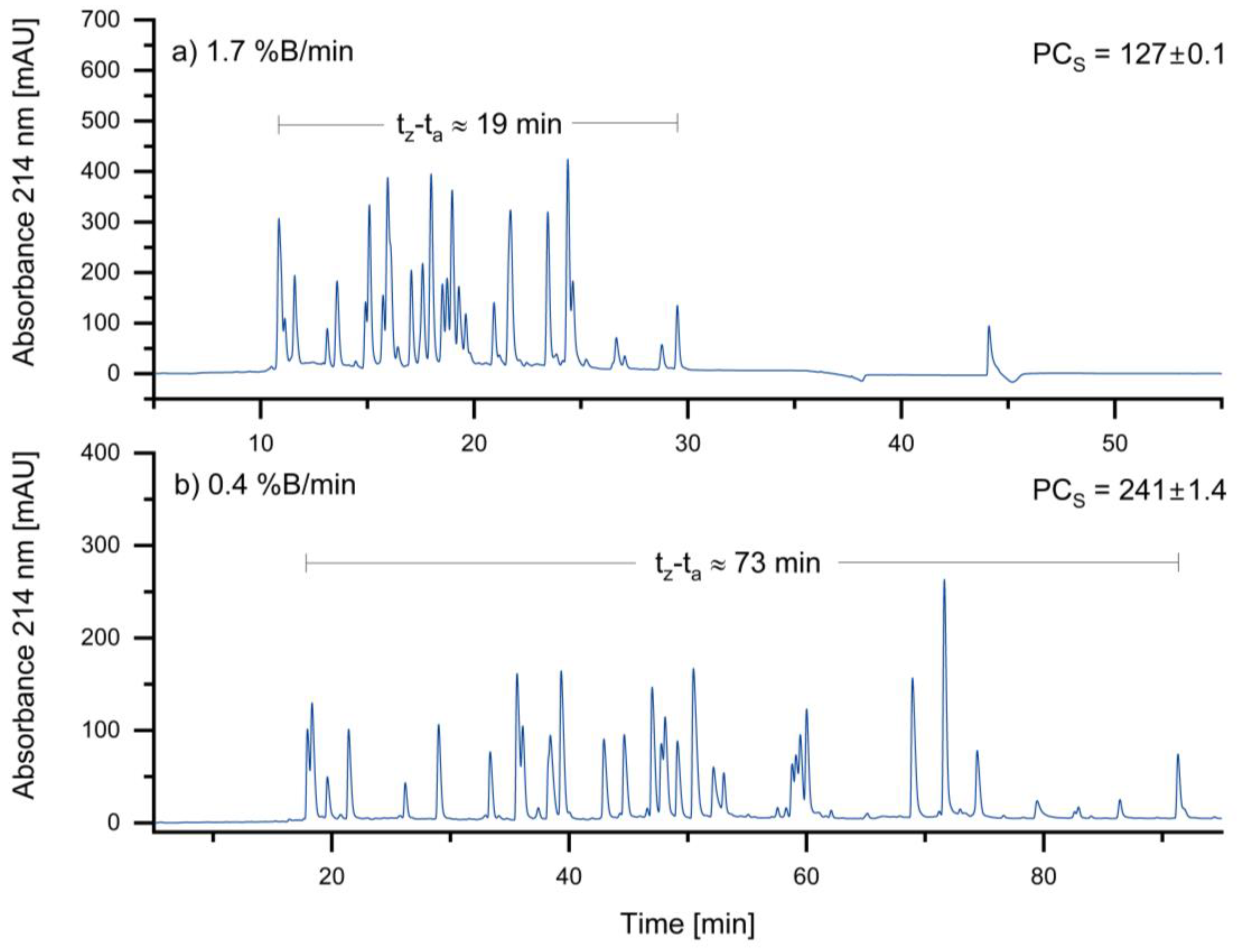
3.1.1. Optimizing Gradient Slope
In general, a lower gradient slope is expected to result in higher gradient retention factors, leading to increased resolution and peak capacity. Therefore, the initial gradient slope of 1.7 %B/min was reduced to 0.4 %B/min. The results of the different gradient slopes are shown in
Figure 2:
As expected, the sample peak capacity increases as the slope of the gradient decreases. Based on these results, a gradient of 0.4 %B/min was selected for the standard method. An even lower gradient was not considered due to the associated long run times.
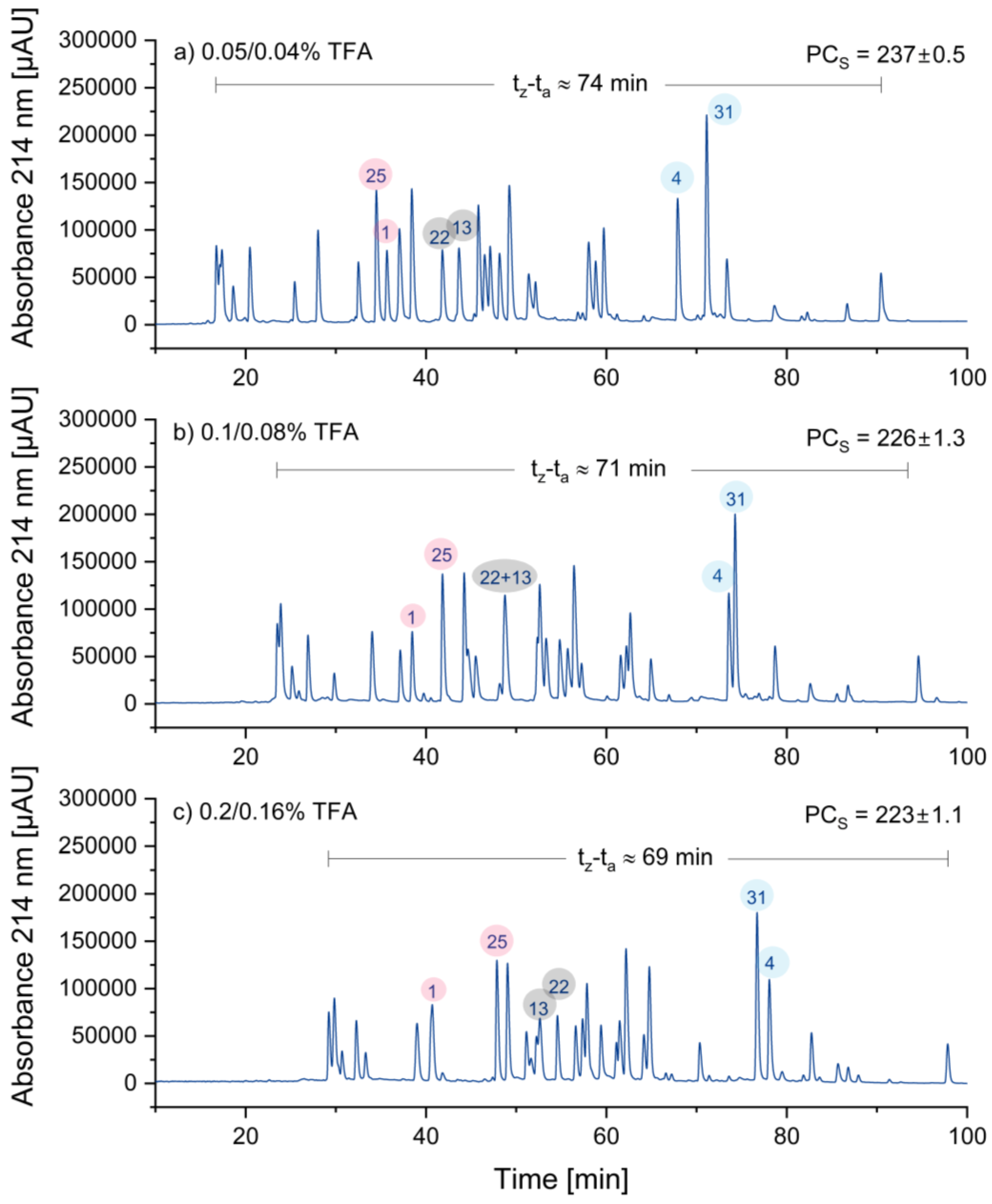
3.1.4. Optimizing Concentration of the Ion-Pairing Reagent TFA
In these experiments, the concentration of TFA was varied. Typically, TFA is used for peptide separations at concentrations ranging from 0.05% to 0.1% (v/v). However, Chen et al. [
21] argued that this concentration range is not ideal for most peptide applications. Hence, TFA concentrations of 0.05%, 0.1%, and 0.2% were tested in eluent A. In order to counteract baseline drift, the TFA concentration in eluent B was reduced by 20%. The results are displayed in
Figure 3:
The retention times in
Figure 3 increased as the TFA concentration increased. Since, the increase in retention times was more significant in the front region of the chromatograms compared to the rear region the retention window became smaller, which is a disadvantage. Consequently, the sample peak capacity decreased somehow with increasing TFA concentration. Most interestingly, three peptide peak pairs (25/1 in red, 22/13 in grey, and 4/31 in blue) are highlighted, showing significant changes in selectivity, resulting in a reversal in elution order. Due to potentially lower ion suppression and the wider retention window, the decision was made to choose the lowest concentration of TFA, which is 0.05/0.04%.
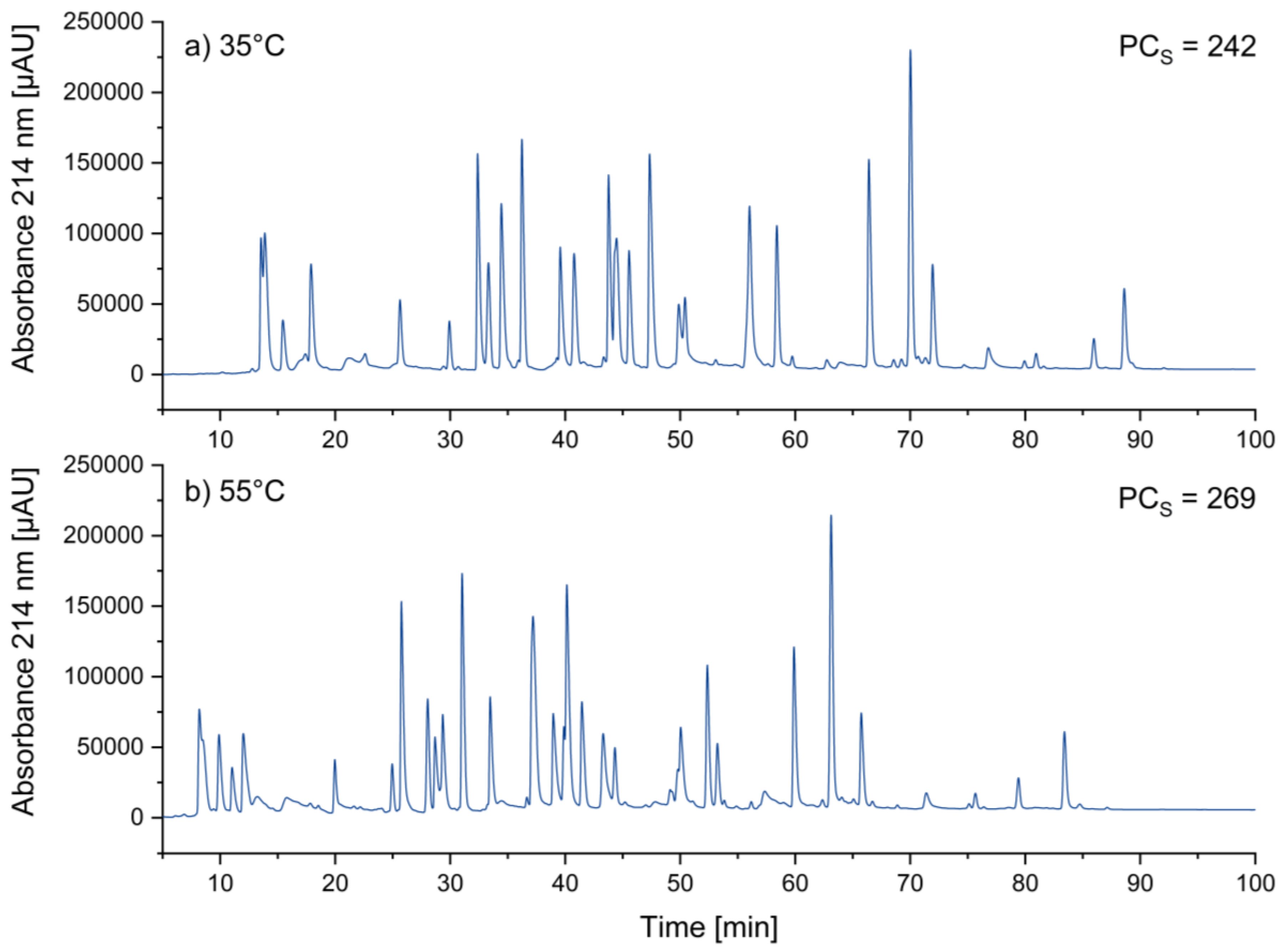
3.1.5. Optimizing Temperature
A change in temperature influences chromatographic separations in different ways. As the temperature increases, the viscosity of the liquid mobile phase decreases, which leads to higher diffusion coefficients and thus to somewhat narrower peaks. This is expected to increase peak capacity, and hence it is suggested to choose the highest temperature, which is feasible in a specific system [
19]. 60°C represented the maximum temperature specified by the UHPLC column manufacturer. As a compromise between separation power and column stability, we have finally chosen 55°C.
Figure 4 shows the transition from 35°C to 55°C. This change led at least to a small improvement of the peak width (FWHM) from 0.31 min to 0.28 min.
3.1.6. Final UHPLC Method
The optimization of gradient slope, concentration of ion-pairing reagent TFA, and temperature led to the UHPLC method outlined in
Table 1:
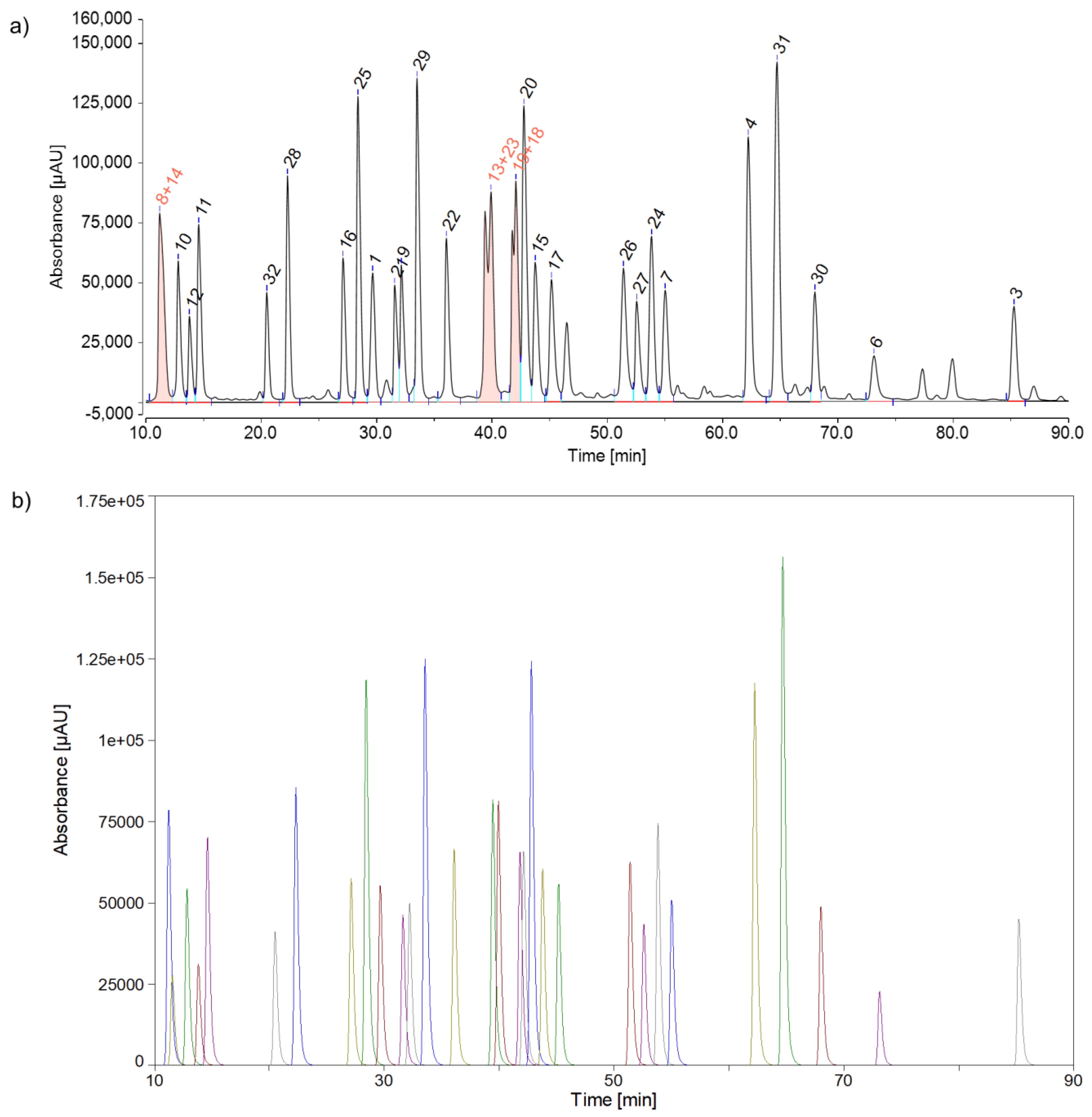
Altogether, the optimized parameters in
Table 1 led to the separation of 30 of the 32 peptides in the CEF advanced peptide pool. Two out of the 32 peptides exhibited poor peak shapes and were excluded from quantification. Both affected peptides possess a N-terminal cysteine. This might have led to undesired interactions between the N-terminus and active sites in the chromatographic system, resulting in significant peak broadening and potential analyte loss. Six out of the 32 peptides highly overlapped (peak to valley ratio of less than 2), which had to be considered in the integration step.
3.2. Relative UV Quantification
The primary use of the developed method was for relative quantification. This enables a cost-efficient evaluation of whether a sample has degraded during storage or transportation. Additionally, it can be utilized to compare samples from various batches or manufacturers for any discrepancies. Relative quantification does not necessarily require calibration, eliminating the need for highly characterized standard peptides and the labor-intensive determination of calibration functions. Only the peak areas of peptides from the compared samples are required. When comparing two sets of measurements, a relative deviation in percent from the reference mean is calculated for each peptide. This mean deviation ± confidence interval can be compared to the method's precision (relative standard deviation, RSD) for the respective peptide. If the mean deviation of a peptide exceeds the method precision in a relevant way, it indicates a potential change in composition of the peptide pool. If the mean deviations ± confidence interval are all less than or equal to the corresponding method precision, the peptide pool can be considered unchanged based on the result of this method.
However, it is important to note that a significant deviation does not necessarily mean that the product is out of specification. Independent criteria must be used to define what deviation from the previous composition can be tolerated from a practical point of view. This is especially true for peptide pools, as it has been shown that in respect of T cell activation, some peptides are present in a large excess, while others are present in a more limited concentration [
13], which can make any losses more critical. This assessment can also depend heavily on the application, which can vary greatly from customer to customer.
To determine peak areas, a classical perpendicular drop method [
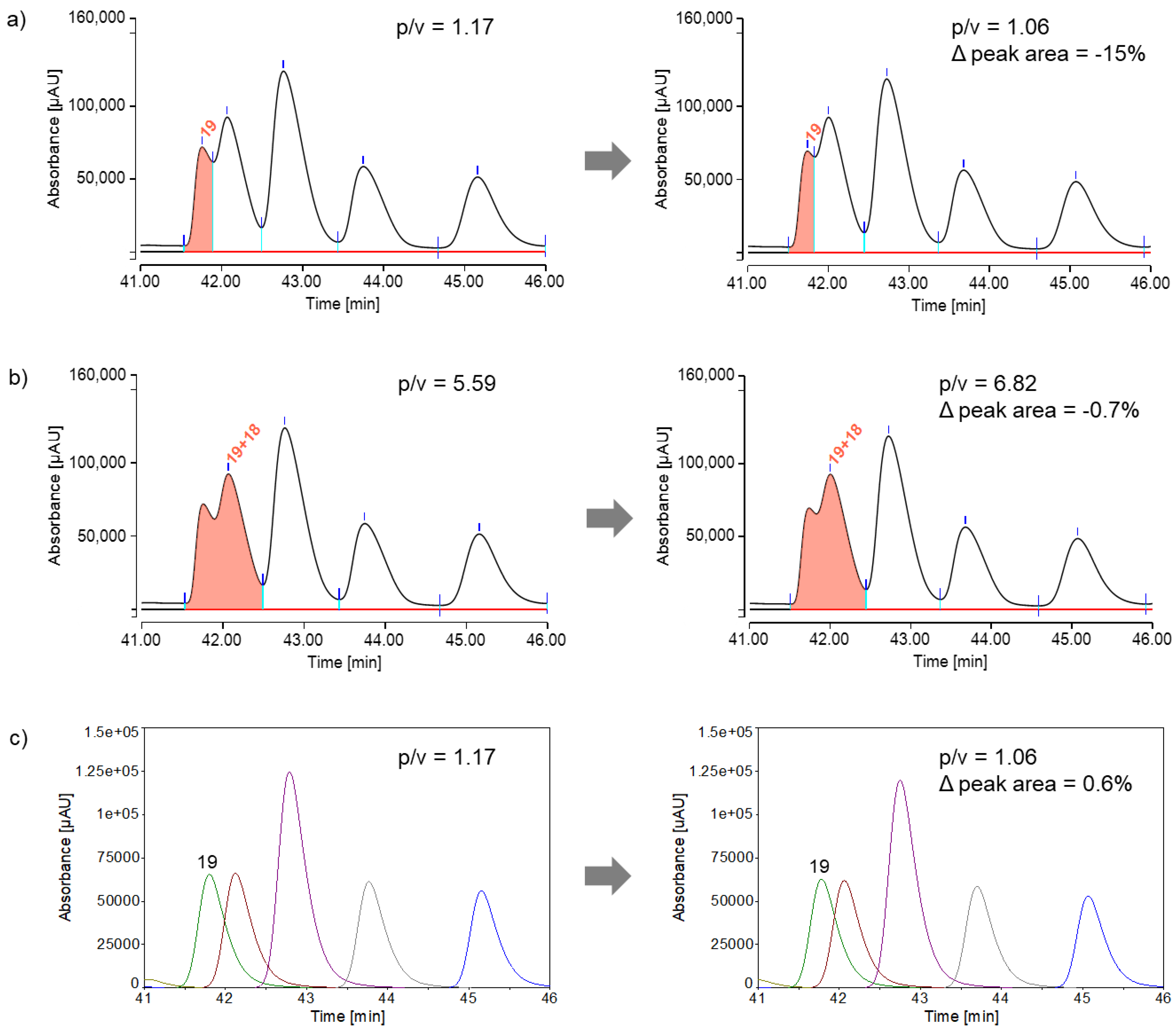
22] was used as the default. However, due to the considerable overlap of some peptide peaks, some peak areas could not be reliably determined. When slight variations in analysis conditions cause minor changes in the separation of closely overlapping peaks, using perpendicular drop integration can lead to significant variations in peak areas and, consequently, inaccurate results. This problem is illustrated by peptide 19 in
Figure 5a, showing two injections from different series (injection #10 on the left and injection #20 on the right) of peptide pool measurements. There was a 42-hour interruption between these series. As a result, the separation (peak-to-valley ratio) between peptide 19 and the subsequent peptide 18 was altered, perhaps due to a slight change of the mobile phase.
One potential solution was to group peaks as shown in
Figure 5b. Grouping peaks lead to significantly reduced integration errors. When peptide 19 was evaluated as part of a peak group using the perpendicular drop method, the peak area deviation decreased from -15% to less than -1%. Another potential solution was peak fitting as depicted in
Figure 5c, which was considered more robust against changes in the overlap of poorly resolved peaks. Even for the strongly overlapping peptide 19, the fitted peaks (green) showed only minimal differences in peak area. The reproducibility (relative standard deviation, RSD) of peak areas for all peptides in the CEF advanced peptide pools from seven consecutive measurements is shown in
Table 2, comparing the perpendicular drop method (perp. drop) with the peak fitting method.
When using the perpendicular drop method, it is evident that the peak area of peptide 19 fluctuates significantly more, with a relative standard deviation of 2.0%, compared to the other peaks. Therefore, peptide 19 was grouped with the highly overlapping peptide 18, significantly improving peak area reproducibility (peptides 19+18: 0.1%) compared to individual peaks. When using the peak fitting method, even this highly overlapping peptide exhibited low relative standard deviation in peak area (peptide 19: 0.3%), eliminating the need for a peak group. Peptides 13 and 23 also showed low peak-to-valley ratios (p/v<2). Therefore, when using the perpendicular drop method, it is recommended to group these peaks, which is unnecessary for the peak fitting method. Peptides 8 and 14 were unresolved in some replicates using the perpendicular drop method, requiring them to be assessed as a peak group from the beginning. When applying peak fitting to peptides 8 and 14, two distinct peaks were identified, with a relative standard deviation in peak area below 1%, indicating acceptable results. Peptides 2 and 5 could neither be analyzed with the perpendicular drop method nor with the peak fitting method, as they exhibited poor peak shapes. As already mentioned, one possible reason for this could be undesirable interactions between the analyte and the non-inert surfaces of the chromatographic system.
Figure 6 provides an overview of the two integration options.
When comparing two sets of measurements, it is crucial to consider that the resolution of individual peaks may vary significantly. This variation may result from differences in concentration or column separation efficiency. In this case, it might be necessary to modify the criteria for creating peak groups. One alternative approach could involve forming peak groups until a minimum resolution of 1.5 (almost baseline separation) is achieved (refer to Table S1 and Figure S1 in the Supplementary Materials). Although quality problems cannot be immediately traced back to a single peptide and some minor sensitivity issues may occur, defining peak groups seems to be a straightforward and efficient method for detecting degradation of poorly resolved peaks without excessive effort. It is also important to note that the used PeakFit software had some limitations when compared to commonly used chromatography data software (CDS). The raw data had to be initially reduced because it exceeded the maximum number of data points. Additionally, the software has an upper limit of 100 peaks to be fitted. Furthermore, the user has to select a peak fitting method, including the Residuals method, Second Derivative method, and Gaussian Deconvolution method. Also, a suitable peak function needs to be identified, which may be dependent on the sample and the experimental system. A good understanding of nonlinear curve fitting is necessary for these aspects. Hence, for routine analytical purposes, it is recommended to use a CDS, possibly in combination with peak grouping, due to its user-friendliness and simplicity, as long as automated peak fitting methods are not included in most standard chromatography software.
3.3. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
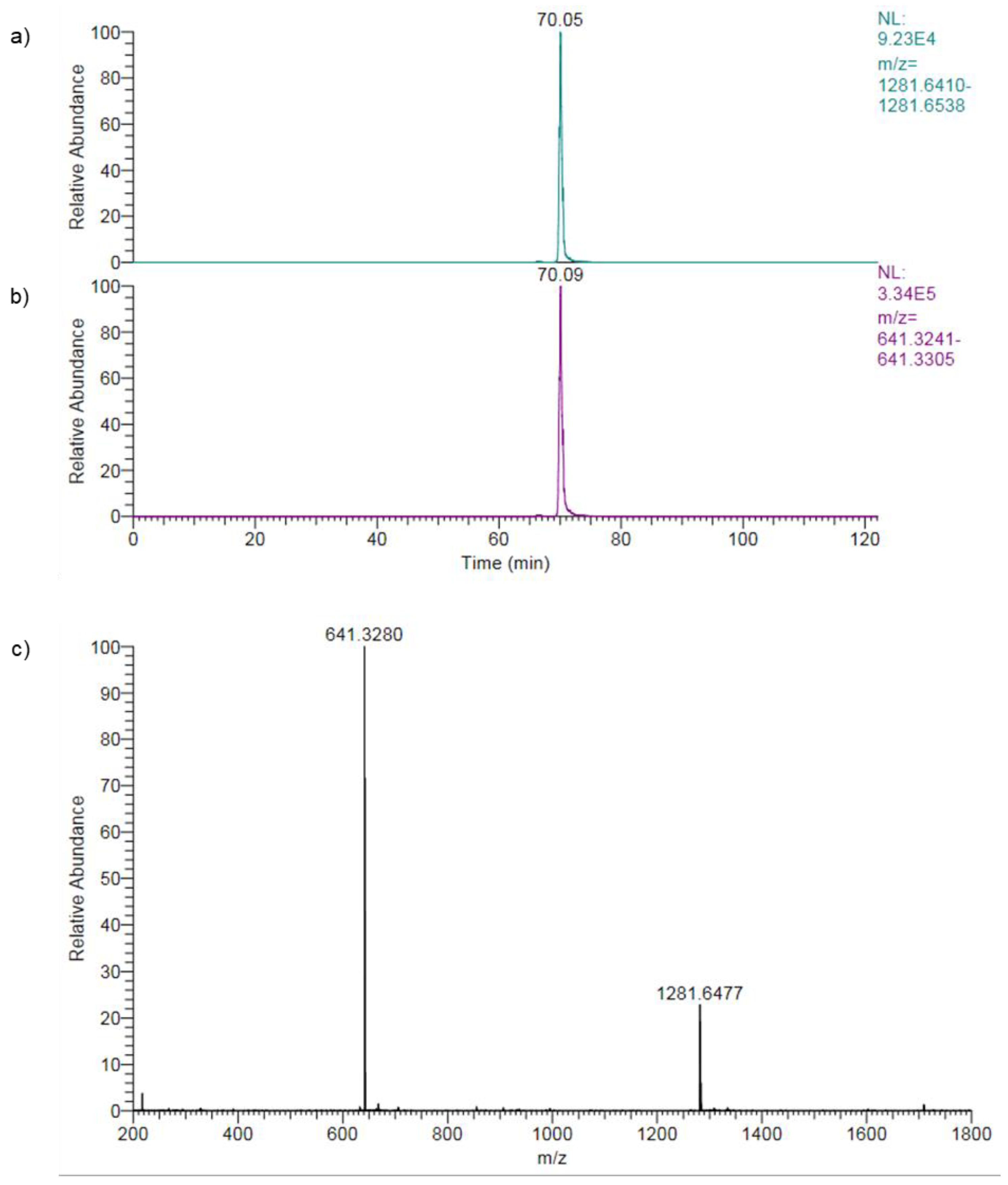
High-resolution mass spectrometry is a powerful technique for accurately identifying and quantifying compounds in complex samples by measuring molecule masses (or m/z) precisely. The high mass accuracy enables reliable identification of compounds. Using the high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometer in this study, narrow mass extraction windows (MEW) of 5 ppm were applied to confirm the peptide structure, as shown for peptide 30 in
Figure 7.
Retention times (UV), the most intense ion, and the deviation between experimental and calculated m/z values are listed for each peptide in the CEF advanced peptide pool in
Table 3.
The identity of all 32 expected peptides could be confirmed with very low deviation between the observed m/z value (experimental m/z) and the theoretical m/z value (calculated m/z). In most cases, the observed m/z value matched the calculated m/z value up to the third decimal place, with a maximum ppm value of 2.4. Two out of the 32 peptides exhibited poor peak shapes, hindering the identification of their retention times. As suspected earlier, this might have been caused by unwanted interactions between the analyte and non-inert surfaces in the chromatographic system.
Confirming peptide structures in complex mixtures does not necessarily require a high-resolution mass spectrometer [
23]. Common triple quadrupole mass spectrometers (QqQ-MS/MS) are known for their high selectivity using specific mass transitions (ion-fragment pairs). Additionally, the investment costs are usually lower than those of HRMS systems. However, HRMS provides some benefits, including high mass accuracy and the ability to provide isotopic patterns that assist in structural elucidation. Moreover, working in full scan mode (FS mode) is possible without a significant loss of sensitivity. Full scan mode enables non-targeted and retrospective data analysis. Hence, this feature allows users to examine degradation products at any time. Developing HRMS methods is quicker and simpler than the commonly used Multiple Reaction Monitoring mode (MRM mode) in tandem mass spectrometry. In MRM mode, detecting mass transitions involves identifying parent ions and fragment ions. In general, three mass transitions are identified, with the most intense transition serving as the quantifier and the other two as qualifiers. Collision energy is optimized for selected mass transitions. These steps must be carried out for each analyte, making MRM method development relatively time-consuming. Overall, both HRMS and MS/MS are valuable mass spectrometry tools, and the choice between the two techniques depends on the specific analytical requirements and experimental objectives.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the potential for a cost- and time-efficient UHPLC-HRMS quality control for synthetic peptide pools using the popular peptide pool CEF advanced. For the chromatographic separation of a complex peptide pool, a flat gradient, elevated temperature, and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) at a concentration of 0.05/0.04% were beneficial. The optimized separation protocol enabled the relative quantification of 30 out of the 32 peptides in the peptide pool. Two peptides were identified based on their masses, but quantification was not performed due to poor peak shape. Since both peptides contain an N-terminal cysteine, modifying the respective peptide pool(s) should be considered to avoid potential interactions between free thiol groups and the HPLC system. In addition, using inert HPLC systems might eliminate this problem. Determining UV peak areas was challenging due to significant overlap among some peaks. When using simple perpendicular drop integration, relative quantification was possible by grouping peaks for insufficiently resolved peaks. An alternative approach to dealing with the observed resolution changes and avoiding the need for peak grouping would be to use more computationally demanding peak fitting methods.
Overall, this study shows that cost-efficient quality control of synthetic peptide pools is possible by relative quantification using UV detection and peptide confirmation by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Some limitations arise from the need to form peak groups as long as algorithms for peak fitting are not generally available in standard chromatography software. The method presented here represents a significant improvement for the quality control of peptide pools up to medium size. The applicability to much larger peptide pools has yet to be demonstrated. Further improvements to this method could include the use of the latest UHPLC systems with higher resolution and the use of longer columns and separation times to increase peak capacity. The evaluation of peak purity with a diode array detector or the parallel use of a second column with at least partially orthogonal separation properties could provide additional information. At present, the mass spectrometric evaluation was performed manually. Automated peak assignment and confirmation could be also added. It should be noted that high-resolution mass spectrometry, as used in this study, is not mandatory. In many cases, standard resolution MS, such as triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS systems), would be sufficient to confirm the presence of the respective peptide. However, HRMS can be very useful for non-target analysis to identify degradation products, synthesis by-products and other impurities. For new and larger peptide pools, the use of a chromatography optimization software and the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) for the optimization of the separation and integration methods, as well as the examination of complex mass spectra would be attractive objectives for future developments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.B.B., and M.G.W.; methodology, G.B.B., and M.G.W.; investigation, G.B.B., and S.E.; data curation, G.B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, G.B.B.; writing—review and editing, G.B.B., O.J.K. and M.G.W.; visualization, G.B.B.; supervision, M.G.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM), grant number Ideen_2016_15.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
Dr. Oliver J. Kreuzer is founder and director of peptides & elephants GmbH and a commercial provider of peptide pools. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- de Graaf, M.T.; de Beukelaar, J.W.; Burgers, P.C.; Luider, T.M.; Kraan, J.; Smitt, P.A.S.; Gratama, J.W. Contamination of Synthetic HuD Protein Spanning Peptide Pools with a CMV-Encoded Peptide. Cytom Part A 2008, 73a, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.G. The Protocol Gap. Method Protocol 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furey, A.; Moriarty, M.; Bane, V.; Kinsella, B.; Lehane, M. Ion suppression; A critical review on causes, evaluation, prevention and applications. Talanta 2013, 115, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Schäfer, P.; Störtzel, M.; Vogt, S.; Weinmann, W. Ion suppression effects in liquid chromatography-electrospray-ionisation transport-region collision induced dissociation mass spectrometry with different serum extraction methods for systematic toxicological analysis with mass spectra libraries. J Chromatogr B 2002, 773, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larger, P.J.; Breda, M.; Fraier, D.; Hughes, H.; James, C.A. Ion-suppression effects in liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry due to a formulation agent, a case study in drug discovery bioanalysis. J Pharmaceut Biomed 2005, 39, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, B.; Chevallier, O.; Quinn, B.; Botana, L.M.; Elliott, C.T. Redefining dilute and shoot: The evolution of the technique and its application in the analysis of foods and biological matrices by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 2021, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Development of a multi-residue analytical methodology based on liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for screening and trace level determination of pharmaceuticals in surface and wastewaters. Talanta 2006, 70, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Tsukada, K. Matrix effect and correction by standard addition in quantitative liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins. J Chromatogr A 2002, 943, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrostlíková, J.; Hajslová, J.; Poustka, J.; Begany, P. Alternative calibration approaches to compensate the effect of co-extracted matrix components in liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry analysis of pesticide residues in plant materials. J Chromatogr A 2002, 973, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.; Strand, D.H. 13C labelled internal standards - A solution to minimize ion suppression effects in liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analyses of drugs in biological samples? J Chromatogr A 2011, 1218, 9366–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.; Papasotiriou, D.G.; Karas, M. 100% protein sequence coverage: a modern form of surrealism in proteomics. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, I.; Targoni, O.; Zhang, W.J.; Sundararaman, S.; Lehmann, P.V. How frequently are predicted peptides actually recognized by CD8 cells? Cancer Immunol Immun 2016, 65, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Moldovan, I.; Targoni, O.S.; Subbramanian, R.A.; Lehmann, P.V. How much of Virus-Specific CD8 T Cell Reactivity is Detected with a Peptide Pool when Compared to Individual Peptides? Viruses-Basel 2012, 4, 2636–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiny, L.; Borel, A. ChemCalc: A Building Block for Tomorrow's Chemical Infrastructure. J Chem Inf Model 2013, 53, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, C.G.; Lipsky, S.R. Peak Capacity in Chromatography. Anal Chem 1967, 39, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, J.C. Maximum Number of Components Resolvable by Gel Filtration and Other Elution Chromatographic Methods. Anal Chem 1967, 39, 1027–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neue, U.D. Theory of peak capacity in gradient elution. J Chromatogr A 2005, 1079, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Giddings, J.C. Statistical-Theory of Component Overlap in Multicomponent Chromatograms. Anal Chem 1983, 55, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Stoll, D.R.; Schellinger, A.P.; Carr, P.W. Peak capacity optimization of peptide separations in reversed-phase gradient elution chromatography: Fixed column format. Anal Chem 2006, 78, 3406–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, J.W.; Snyder, L.R.; Djordjevic, N.M.; Hill, D.W.; Waeghe, T.J. Reversed-phase liquid chromatographic separation of complex samples by optimizing temperature and gradient time I. Peak capacity limitations. J Chromatogr A 1999, 857, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mehok, A.R.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Optimum concentration of trifluoroacetic acid for reversed-phase liquid chromatography of peptides revisited. J Chromatogr A 2004, 1043, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.; Petrovic, K.; Wicar, S. Efficacy of Corrections Applied in Resolution of Overlapping Chromatographic Peaks by Perpendicular Drop Method. J Chromatogr 1971, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.M.; Hoffmann, H.; Montes-Bayón, M.; Weller, M.G. Improved LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of hepcidin-25 in clinical samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 2018, 410, 3835–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).