1. Introduction
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) pose a significant challenge in the management of diabetes and represent a serious complication that requires careful attention. Every 1.2 seconds, someone develops a DFU and every 20 seconds, someone with DFU undergoes an amputation [
1]. One of the key treatment approaches for DFUs involves the use of offloading devices, which aim to distribute force and reduce pressure on the wound, thereby facilitating the healing process [
2]. While adhering to the appropriate use of these devices is recognized as a crucial strategy to promote DFU healing, some individuals who adhere to offloading device protocols still struggle to achieve healing. This suggests the existence of other contributing factors that need to be considered, including wound and diabetes characteristics, motor function, and patient-reported outcomes [3-5].
To distinguish between patients who experience successful healing and those who do not, it is crucial to evaluate and analyze various factors beyond device adherence. Understanding the underlying mechanisms associated with healing outcomes can enable healthcare professionals to provide personalized care, leading to more efficient and effective wound treatment. Thus, the objective of this study was to develop a comprehensive visualization tool capable of measuring digital biomarkers closely associated with unsuccessful healing and subsequent visualization.
By designing such a holistic visualization tool, our research team hypothesized that clinicians would gain valuable insights into how multiple factors contribute to DFU healing. This tool has the potential to empower healthcare professionals to become more aware of interacting factors that affect clinical outcomes, as they will be able to identify and monitor specific digital biomarkers associated with improved healing outcomes. Ultimately, the implementation of this tool could lead to more efficient wound treatment and enhanced patient outcomes in DFU management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining Digital Biomarkers Associated with Wound Healing
This manuscript presents preliminary findings from an ongoing parallel randomized controlled trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04460573) conducted at the Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California. The overarching goal of the parent study was to investigate how interactive offloading devices, called smart offloading, can improve adherence, and enhance wound healing outcomes in individuals with diabetes. The validity and acceptability of the smart boot for the real-time estimation of adherence to offloading and step count have been presented in prior studies [6, 7]. However, this study focused on designing and evaluating a holistic remote patient-monitoring system. This system aims to simplify the visualization of the key risk factors associated with unfavorable wound healing outcomes, aiding clinicians in personalizing wound care. It includes tailored patient education that may optimize healing outcomes while guiding patients in maintaining healthy mobility and mitigating secondary consequences such as frailty, poor balance, and gait. Participants meeting specific inclusion criteria, such as having diabetes and a diabetic foot wound, were enrolled in the study, whereas those with high A1c levels (>12), lack of mobility, multiple wounds, or poor adherence to offloading devices were excluded. The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of the University of Southern California.
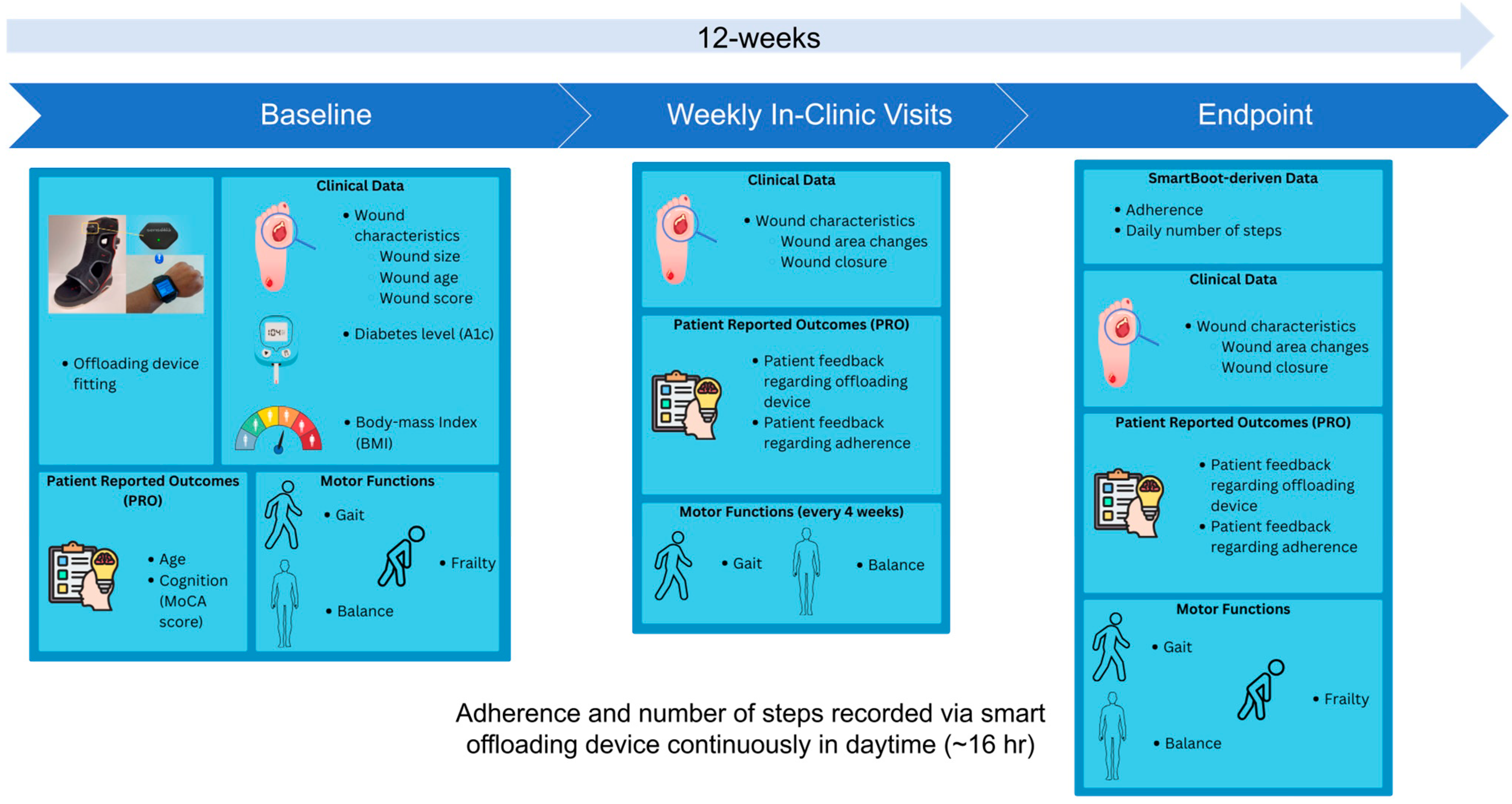
Figure 1 illustrates the overall study design.
Over a period of 12 weeks, participants attended weekly in-person visits, during which their ulcer photographs were taken with a wound monitoring device (eKare, eKare Inc., Fairfax, VA, USA) to measure wound dimensions, and their feedback regarding the offloading device and its usage was recorded. On the baseline visit data on wound complexity and A1c levels were collected from the participants' medical charts. Additionally, participants underwent a 20-second repetitive elbow flexion-extension test while sitting to assess upper-extremity frailty [8-12]. However, instead of using a wrist sensor to assess frailty, we used an alternative solution to extract elbow motion kinematics and then estimated the frailty index and frailty phenotypes such as exhaustion, weakness, and slowness using video analysis [13, 14]. In addition, to determine their cognitive level, a 12-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) questionnaire was administered by the study coordinator, and a score of 10 points was used as the threshold to determine whether a participant had cognitive impairment [
15].
At four-week intervals, wearable inertial measurement unit (IMU) sensors developed by BioSensics (LegSys + BalanSense, BioSensics, Newton, MA, USA) were used to measure the participants' mobility performance, including gait and balance assessments [16-25]. The gait assessment consisted of four walking tests: walking at normal speed, walking 15 feet unassisted at their normal walking speed, walking at fast speed, walking 15 feet unassisted at a safe rapid walking speed, walking at normal speed while counting backwards, and walking 15 feet unassisted at their normal walking speed while counting backwards out loud from the number given by the study coordinator; and Timed Up and Go (TUG), starting in a seated position, getting up, walking to the stop sign, turning around, walking back to the chair, and sitting down. The balance assessment consisted of four balance tests: single stance eyes open, single stance eyes closed, double stance eyes open, and double stance eyes closed. For the single-stance eyes open assessment, the patients stood on one leg unassisted and placed their arms on their hips. For a single stance eye closed assessment, they performed the same position with their eyes closed. During the double-stance eye open assessment, the participants stood facing the wall with their feet as close together as possible without touching and with their arms folded across their chest. For the double-stance eyes closed assessment, the participants stood in the same position, but their eyes were closed. The assessments each took 30 seconds.
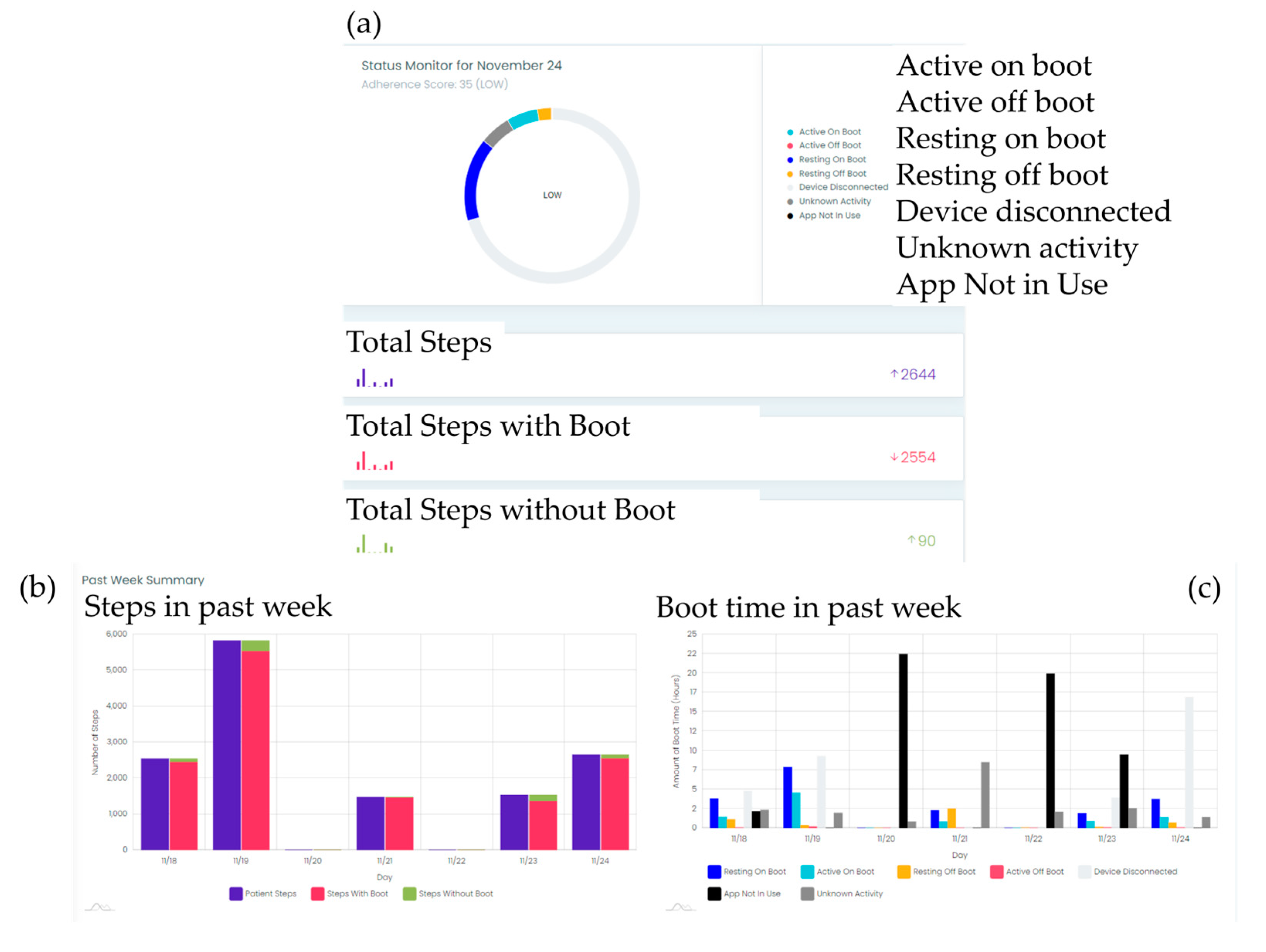
To monitor adherence to offloading device usage and collect step count data, a smart offloading boot system was employed. This system consisted of a removable offloading boot (Foot Defender, Defender Ops., South Miami, FL.), a Sensoria Core microelectronics device, and an Android 4G/LTE smartwatch custom app developed by Sensoria Health Inc. [6, 7]. The Sensoria Core utilized a 6 degrees-of-freedom IMU to capture boot movements and a Bluetooth low-energy (BLE) module to communicate with the smartwatch. The Sensoria Core transmits the collected data to the smartwatch, which processes and displays real-time information, including the boot condition (worn or not worn), activity status (active or resting), step count, and notifications. These data were also sent to the Sensoria cloud system. This enables clinical providers to evaluate patient adherence to offloading and visualize step counts with and without offloading, as shown in
Figure 2. Adherence to the offloading boot was calculated using embedded algorithms on the cloud and presented as graphics to the clinician team. Additionally, the website allowed recording of notifications and alerted the clinician team if the participants removed their boots.
2.2. Holistic Visualization to Empower Physicians and Patients
To effectively visualize the healing trajectory of the patients, we selected various parameters believed to affect wound healing outcomes. These parameters include demographics and digital metrics including wound characteristics, frailty phenotypes such as exhaustion and slowness, gait (cadence), balance, and Smart Boot derived digital metrics such as steps and adherence. For frailty phenotypes, we used metrics extracted from video-based 20-second repetitive elbow flexion extension test and selected phenotypes that were previously shown to be associated with wound healing including exhaustion and slowness [26, 27]. The details of these parameters, their definitions, and measurement methods are shown in
Table 1.
To visualize the key digital metrics associated with poor wound healing on a single graph, we normalized various parameters believed to affect wound healing outcomes on a scale from 0 to 10, where higher values indicate increased risk. For normalization of these parameters, we categorized each metric to low risk (0), medium risk (5), and high risk (10) using standard benchmark reported in literature or if the standard benchmarks were unable, we used the cohort and percentile approach to determine low, medium, and high-risk groups. For example, Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels are known to correlate with healing outcomes, and higher values are associated with poor wound healing [
30]. Research [
31] shows that HbA1c levels above 8% indicate poor glycemic control, warranting the highest risk score of 10. Conversely, levels between 7-8% are regarded as fair glycemic control, and a medium risk score of 5 and below 7% is considered a low-risk score of 0. Using these thresholds, A1c levels were normalized on a scale from 0 to 10. For exhaustion and slowness, the decrease in elbow extension/flexion speed and average elbow flexion time were normalized between 0 and 1, respectively. The median value of the cohort was then determined. Values lower than the medium value were labelled as low risk (0), and those higher than the medium value were labelled as high risk (10). For metrics where higher values signify lower risk (e.g., the MoCA score), reverse scoring was applied to ensure uniform interpretation across all parameters.
Table 2 details the specific thresholds used for categorizing these metrics into low, medium, or high risk.
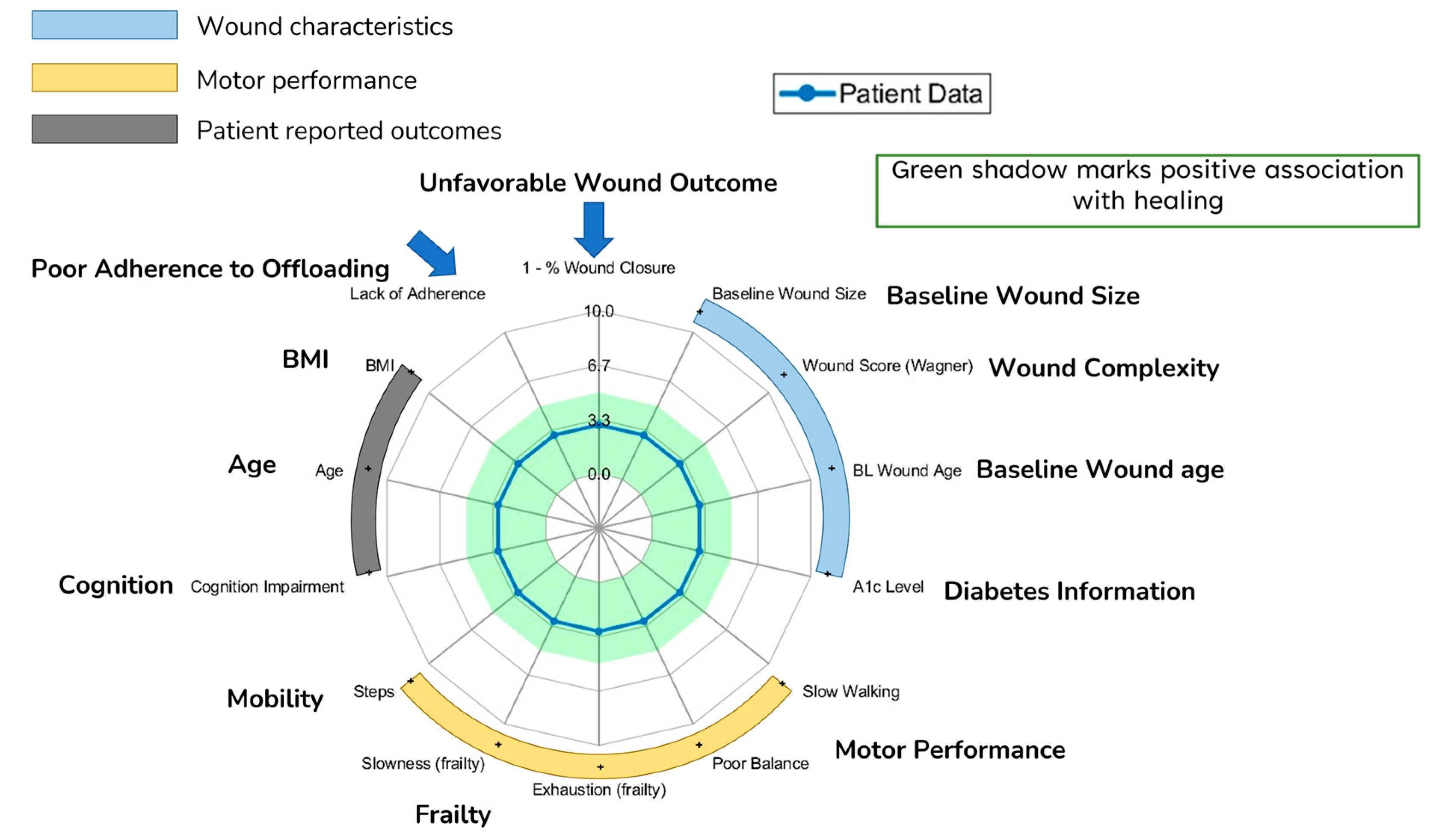
Radar charts based on these grades were created to provide a holistic visualization of the parameters as a group, subgroup and individual. The radar chart is shaded in green based on the low risk of unfavorable wound outcomes, where the grade was below the threshold.
Figure 3 shows the radar chart and the green-shaded area. All analyses were performed using MATLAB (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) and SPSS 29.0 (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA). 0.05 was set as the level of statistical significance.
3. Results
Of the 124 participants who met the inclusion criteria, 119 initially completed the study. However, 50 participants discontinued the study because of early dropouts for various reasons. These included an inability to attend weekly clinic visits and poor acceptability of offloading (21, 18%). Other reasons for discontinuation were adverse events, such as unplanned hospitalization, death, or limb amputation (4, 3%). In addition, 7 of the remaining participants discontinued the study due to loss of eligibility, such as lack of insurance or developing another disease. Consequently, data from the remaining 62 participants were deemed reliable and were utilized to develop and assess the remote visualization framework. This framework was designed to identify and display the digital biomarkers associated with poor wound healing. Participant demographics, foot ulcer conditions at baseline, and unfavorable outcomes are shown in
Table 3.
Among the 119 participants, 42% achieved successful healing, defined as ≥ 80% wound closure at 12 weeks. Meanwhile, 39% of the participants exhibited unfavorable outcomes, including less than 40% wound closure at 12 weeks or study-related discontinuation of the study.
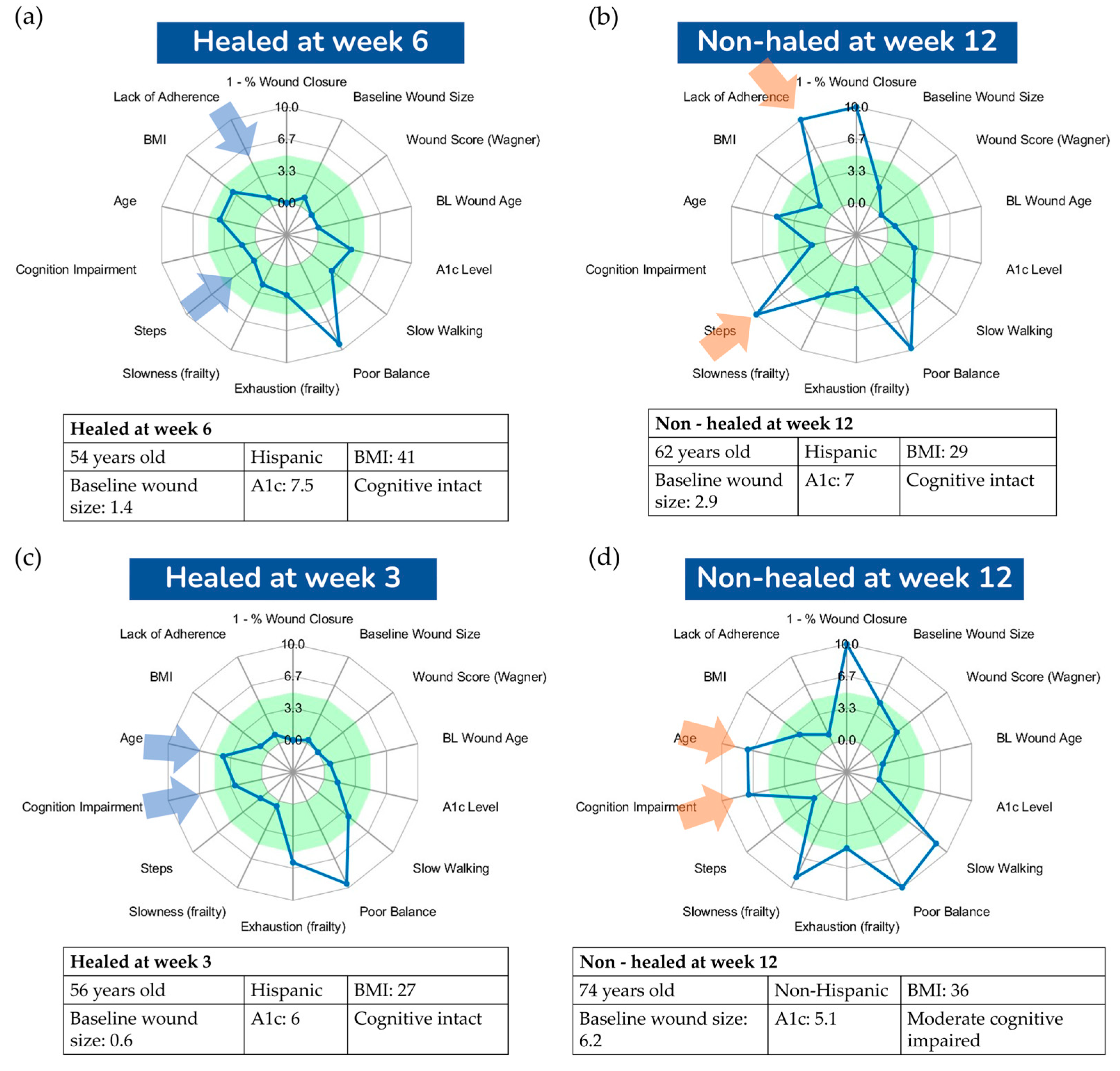
Figure 4 presents a visualization comparing four DFU cases, all with well-controlled glycemia (A1C less than 7.5%), yet two did not heal by 12 weeks while the other two healed before the 12-week mark. This visualization aims to offer deeper insights into the major risk factors influencing successful wound healing or contributing to failure. Both cases in
Figure 4a,c healed before the 12-week threshold, sharing characteristics such as high adherence to offloading and a relatively low amount of weight-bearing activities, as indicated by a small number of daily steps. In contrast, the case in
Figure 4b did not heal by the 12-week mark, likely due to poor offloading adherence and a high number of daily steps, presumably unprotected. This suggests that the combination of poor adherence and a high number of daily steps are key factors in suboptimal wound healing outcomes. Interestingly, the case in
Figure 4d demonstrates that good compliance with offloading and a low number of daily steps are not always sufficient for favorable wound healing outcomes. We hypothesize that in scenarios where adherence is high and daily steps are low, other factors, such as cognitive function and frailty, could become significant risk factors for poor healing. This particular case had mild cognitive impairment and exhibited signs of frailty, such as slowness, exhaustion, and low walking speed, potentially impacting the healing process. This aligns with other studies suggesting frailty as a determinant of wound healing outcomes [27, 40].
4. Discussion
This study aimed to design a holistic visualization tool to determine and visualize possible multiple digital biomarkers associated with poor diabetic wound healing. Our major findings suggest that employing a holistic visualization system could help identify digital biomarkers associated with unsuccessful healing of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) within a 12-week timeframe. By analyzing the radar plot for each patient, we were able to discern combination of various parameters contributing to healing outcomes. This approach allows for a comprehensive evaluation of multiple digital biomarkers, thereby enhancing our understanding of the factors that influence healing.
The utilization of a visualization system in this context has significant practical implications. Traditional methods for treating DFUs often rely on subjective assessments and limited data points, which can lead to suboptimal outcomes. However, our approach enables a more nuanced and personalized understanding of the healing process, thereby facilitating the development of more effective remote treatment plans. By considering a range of digital biomarkers, beyond adherence to offloading devices, we gained insight into the complex interplay of factors influencing DFU healing. The implementation of our visualization system has the potential to revolutionize the management of DFUs. By providing clinicians with a clear and intuitive representation of digital biomarkers associated with healed and non-healed groups, the system enables informed decision-making. Clinicians can use this information to adjust treatment strategies, provide targeted interventions, and closely monitor patient progress. However, considering only the group effects can mask the individual parameters, which can be important for creating personalized treatment plans. For instance, within our sample group, the baseline wound size exhibited the most substantial effect size when distinguishing between the healed and non-healed groups. It is crucial to highlight that this parameter falls within the range indicative of a positive association with the healing process in our specific case studies. Conversely, other parameters such as age, cognition, and steps contribute to unsuccessful healing. Therefore, a thorough assessment of each case is imperative. This comprehensive evaluation enables clinicians to identify and address the specific barriers to healing that may be present in individual patients. Consequently, personalized treatment plans can be tailored to meet specific needs, thereby enhancing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Moreover, the use of remote treatment plans supported by visualization systems offers several advantages. This reduces the need for frequent in-person visits by providing convenient and efficient care planning. Patients can receive ongoing support and guidance, ensure adherence to treatment protocols, and facilitate early intervention in cases of poor adherence or other complications. This remote approach has the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes, particularly in individuals who may face challenges in accessing healthcare facilities or adhering to traditional treatment regimens for personal or work-related reasons.
Although these preliminary findings are promising, our sample was both small and homogenous. This homogeneity might account for the lack of significant differences in demographics and comorbidities between the healed and non-healed groups. Furthermore, most of the participants were male. Given these factors, there is a pressing need to validate our findings using a larger and more diverse sample that truly represents the demographic spread of individuals with DFU. In addition, future studies could explore the long-term impact of the visualization system on healing outcomes and investigate additional digital biomarkers that may further enhance our understanding of DFU healing. Additionally, assessing the cost-effectiveness and scalability of implementing such a system in a clinical setting would be valuable.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study suggests a holistic visualization system for identifying multiple digital biomarkers associated with successful DFU healing. By leveraging this approach, clinicians can gain valuable insights into the complex dynamics of healing, leading to personalized and effective treatment plans. Ultimately, the integration of such a system into routine clinical practice has the potential to significantly improve the management and outcomes of patients with DFUs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, DGA and BN; Data Curation, GC, JG; Formal Analysis, GC; Funding Acquisition, DGA and BN; Methodology, GC and MGF; Project Administration, DGA and BN; Resources, DGA and BN; Software, BN; Supervision, DGA, BN and JMG; Visualization, GC; Writing (Original Draft), GC; Writing (Review & Editing), All authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (1R01124789-01A1). Additionally, in-kind support was provided by Sensoria Health Inc., based in Redmond, WA, the manufacturer of Sensoria Core used in this study and Defender Operations LLC, based in South Miami, FL, the manufacturer of Foot Defender (Smart Boot) used in this study. The content is solely the responsibility of authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsor(s).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the University of Southern California (protocol code HS-20-00526 initially approved August 11th, 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request by contacting the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Maria Noun for communication with IRB, Dr. Jason Hanft (Defender Operations LLC, South Miami, FL), Davide Vigano, and Maurizio Macagno (Sensoria Health Inc., Redmond, WA) for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
B.N., Co-Author, is a consultant for BioSensics LLC (MA, USA), the manufacturer of the IMUs (LegSys and BalanSense) used in this study, on projects not related to this study's scope. He was also not involved in data analysis from this study. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
References
- Armstrong, D.G., et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 62–75. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, K.A., et al. Current Status and Principles for the Treatment and Prevention of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in the Cardiovascular Patient Population: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 149, e232–e253. [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Crocker, R.M.; Palmer, K.N.B.; Gomez, C.; Armstrong, D.G.; Marrero, D.G. A qualitative study of barriers to care-seeking for diabetic foot ulceration across multiple levels of the healthcare system. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2022, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Penfield, N.W., et al., Evaluation and Management of Diabetes-related Foot Infections. Clin Infect Dis 2023, 77, e1–e13. [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.A.; Armstrong, D.G.; Goodney, P.P.; Hamburg, N.M.; Kirksey, L.; Lancaster, K.J.; Mena-Hurtado, C.I.; Misra, S.; Treat-Jacobson, D.J.; Solaru, K.T.W.; et al. Health Disparities in Peripheral Artery Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catherine, P., et al., Smart Offloading Boot System for Remote Patient Monitoring: Toward Adherence Reinforcement and Proper Physical Activity Prescription for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Patients. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology 2022.
- Finco, M.G.; Cay, G.; Lee, M.; Garcia, J.; Salazar, E.; Tan, T.-W.; Armstrong, D.G.; Najafi, B. Taking a Load Off: User Perceptions of Smart Offloading Walkers for Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using the Technology Acceptance Model. Sensors 2023, 23, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, B.; Toosizadeh, N.; Jokar, T.O.; Heusser, M.R.; Mohler, J.; Najafi, B. Upper-Extremity Function Predicts Adverse Health Outcomes among Older Adults Hospitalized for Ground-Level Falls. Gerontology 2016, 63, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toosizadeh, N.; Berry, C.; Bime, C.; Najafi, B.; Kraft, M.; Mohler, J. Assessing upper-extremity motion: An innovative method to quantify functional capacity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toosizadeh, N.; Mohler, J.; Najafi, B. Assessing Upper Extremity Motion: An Innovative Method to Identify Frailty. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toosizadeh, N.; Najafi, B.; Reiman, E.M.; Mager, R.M.; Veldhuizen, J.K.; O’connor, K.; Zamrini, E.; Mohler, J. Upper-Extremity Dual-Task Function: An Innovative Method to Assess Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Joseph, B.; Enriquez, A.; Najafi, B. Toward Using a Smartwatch to Monitor Frailty in a Hospital Setting: Using a Single Wrist-Wearable Sensor to Assess Frailty in Bedbound Inpatients. Gerontology 2017, 64, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zahiri, M.; Vaziri, A.; Najafi, B. Dual-Task Upper Extremity Motor Performance Measured by Video Processing as Cognitive-Motor Markers for Older Adults. Gerontology 2023, 69, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahiri, M.; Wang, C.; Gardea, M.; Nguyen, H.; Shahbazi, M.; Sharafkhaneh, A.; Ruiz, I.T.; Nguyen, C.K.; Bryant, M.S.; Najafi, B. Remote Physical Frailty Monitoring—The Application of Deep Learning-Based Image Processing in Tele-Health. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 219391–219399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, D.; Kumar, G.; Singh, A.K. Quick screening of cognitive function in Indian multiple sclerosis patients using Montreal cognitive assessment test-short version. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2013, 16, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B.; Khan, T.; Wrobel, J. Laboratory in a box: Wearable sensors and its advantages for gait analysis. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA; 2011; pp. 6507–6510. [Google Scholar]
- Najafi, B.; Horn, D.; Marclay, S.; Crews, R.T.; Wu, S.; Wrobel, J.S. Assessing Postural Control and Postural Control Strategy in Diabetes Patients Using Innovative and Wearable Technology. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B.; Aminian, K.; Loew, F.; Blanc, Y.; Robert, P.A. Measurement of stand-sit and sit-stand transitions using a miniature gyroscope and its application in fall risk evaluation in the elderly. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminian, K.; Najafi, B.; Büla, C.; Leyvraz, P.-F.; Robert, P. Spatio-temporal parameters of gait measured by an ambulatory system using miniature gyroscopes. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, E.D., et al., Quantification of everyday motor function in a geriatric population. J Rehabil Res Dev 2007, 44, 417–428. [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, U.; Najafi, B.; Zijlstra, W.; Hauer, K.; Muche, R.; Becker, C.; Aminian, K. Distance to achieve steady state walking speed in frail elderly persons. Gait Posture 2008, 27, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B.; Aminian, K.; Paraschiv-Ionescu, A.; Loew, F.; Bula, C.; Robert, P. Ambulatory system for human motion analysis using a kinematic sensor: monitoring of daily physical activity in the elderly. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B., et al., Does walking strategy in older people change as a function of walking distance? Gait Posture 2009, 29, 261–266. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B.; Lee-Eng, J.; Wrobel, J.S.; Goebel, R. Estimation of Center of Mass Trajectory using Wearable Sensors during Golf Swing. J Sports Sci Med 2015, 14, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B.; Armstrong, D.G.; Mohler, J. Novel Wearable Technology for Assessing Spontaneous Daily Physical Activity and Risk of Falling in Older Adults with Diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.K.; Bara, R.O.; Zulbaran-Rojas, A.; Park, C.; Fernando, M.E.; Ross, J.; Lepow, B.; Najafi, B. The Application of Digital Frailty Screening to Triage Nonhealing and Complex Wounds. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2022, 18, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, M.E.; Blanchette, V.; Mishra, R.; Zulbaran-Rojas, A.; Rowe, V.; Mills, J.L.; Armstrong, D.G.; Najafi, B. Frailty in People with Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia and Diabetes-Related Foot Ulcers: A Systematic Review. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 89, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patry, J., et al., Outcomes and prognosis of diabetic foot ulcers treated by an interdisciplinary team in Canada. International Wound Journal 2021, 18, 134–146. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P., et al., Wagner's classification as a tool for treating diabetic foot ulcers: Our observations at a suburban teaching hospital. Cureus 2022, 14.
- Christman, A.L.; Selvin, E.; Margolis, D.J.; Lazarus, G.S.; Garza, L.A. Hemoglobin A1c Predicts Healing Rate in Diabetic Wounds. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, R.G.; Demesse, E.S.; Boko, W.D. Evaluation of glycemic control and related factors among outpatients with type 2 diabetes at Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, M. and B. Manna. Hyperbaric Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer. 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430783/.
- Dasari, N.; Jiang, A.; Skochdopole, A.; Chung, J.; Reece, E.M.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Winocour, S. Updates in Diabetic Wound Healing, Inflammation, and Scarring. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBrule, M., A Closer Look At Gait Analysis In Patients With Diabetes. Podiatry Today 2014, 27.
- Catrine, T.-L., et al., How fast is fast enough? Walking cadence (steps/min) as a practical estimate of intensity in adults: a narrative review. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2018, 52, 776. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B., et al., Can’t stand the pressure: the association between unprotected standing, walking, and wound healing in people with diabetes. Journal of diabetes science and technology 2017, 11, 657–667. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siru, R.; Burkhardt, M.S.; Davis, W.A.; Hiew, J.; Manning, L.; Ritter, J.C.; Norman, P.E.; Makepeace, A.; Fegan, P.G.; Bruce, D.G.; et al. Cognitive Impairment in People with Diabetes-Related Foot Ulceration. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, T. and M. Mutluoglu. Diabetic Foot Ulcer. 2023. Cited 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537328/.
- Manikanta, K. and G. Monisha, Comparative study of diabetic foot outcome between normal vs high BMI individuals-Is obesity paradox a fallacy in ulcer healing. Clin Surg 2019, 4, 1–6.
- Mishra, R.K.; Bara, R.O.; Zulbaran-Rojas, A.; Park, C.; Fernando, M.E.; Ross, J.; Lepow, B.; Najafi, B. The Application of Digital Frailty Screening to Triage Nonhealing and Complex Wounds. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2022, 18, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).