Submitted:
13 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
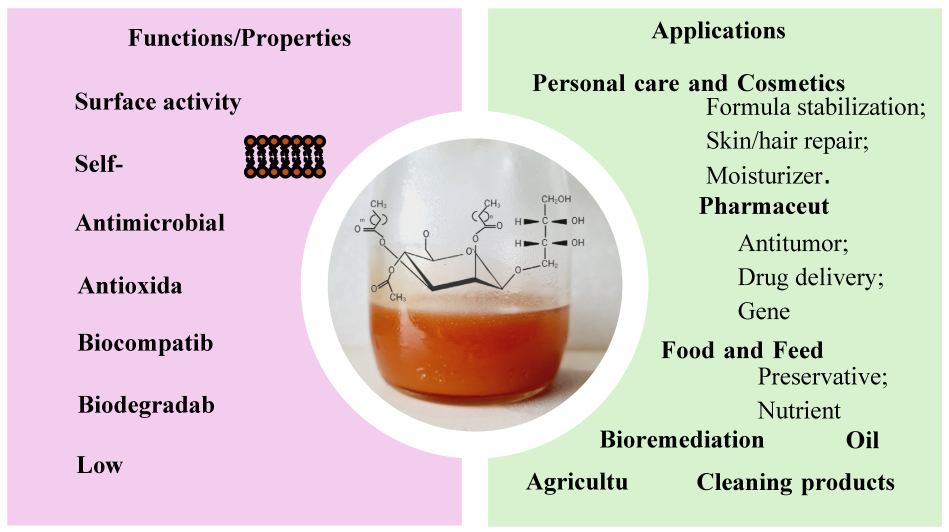
3. Mannosylerythritol Lipids Structure, Properties, and Production
4. Mannosylerythritol Applications Described in the Literature
4.1. Biomedical/Pharmaceutical Industry
4.2. Personal Care and Cosmetics
4.3. Agriculture
4.4. Food and Feed Industry
4.5. Environmental Responses
4.6. Others
5. Current and Future Perspectives About MELs in the Market
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh S, Ray A, Pramanik N. Self-assembly of surfactants: An overview on general aspects of amphiphiles. Biophys Chem. 2020;265:106429. [CrossRef]
- Johnson P, Trybala A, Starov V, Pinfield VJ. Effect of synthetic surfactants on the environment and the potential for substitution by biosurfactants. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;288:102340. [CrossRef]
- Banat IM, Thavasi R, eds. Microbial Biosurfactants and Their Environmental and Industrial Applications. CRC Press; 2019. [CrossRef]
- Precedence Research. Surfactants Market (By Type: Anionic Surfactants, Non-ionic Surfactants, Cationic Surfactants, Amphoteric Surfactants, Others; By Origin: Synthetic Surfactants, Bio-based Surfactants; By Application: Home Care, Personal Care, Oilfield Chemicals, Food & Beverage, Agrochemicals, Textiles, Plastics, Industrial & Institutional Cleaning) - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, Regional Outlook, and Forecast 2023 – 2032. Accessed February 28, 2024.
- Pradhan A, Bhattacharyya A. Quest for an eco-friendly alternative surfactant: Surface and foam characteristics of natural surfactants. J Clean Prod. 2017;150:127-134. [CrossRef]
- Madsen T, Boyd HB, Nylén D, Pendersen R, Petersen G, Simonsen F. Environmental and Health Assessment of Substances in Household Detergents and Cosmetic Detergent Products; 2000.
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- European Comission. REACH Regulation. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/chemicals/reach-regulation_en (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Eras-Muñoz E, Farré A, Sánchez A, Font X, Gea T. Microbial biosurfactants: A review of recent environmental applications. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):12365-12391. [CrossRef]
- Krauter, J. Evonik and Unilever team up for large-scale production of world’s first “green” biosurfactant. Evonik. Published December 2019. Available online: https://household-care.evonik.com/en/news/press-releases/evonik-and-unilever-team-up-for-large-scale-production-of-worlds-first-green-biosurfactant-121470.html (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Wesche, B. BASF strengthens its position in bio-surfactants for Personal Care, Home Care and Industrial Formulators with two distinct partnerships. BASF. Published March 2021. Available online: https://www.basf.com/vn/en/media/news-releases/global/2021/03/p-21-148.html (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Stepan. Stepan Company Completes Acquisition of NatSurFact® Business from Logos Technologies. Published , 2020. Available online: https://www.stepan.com/content/stepan-dot-com/en/news-events/news---events/stepan-company-completes-acquisition-of-natsurfact.html (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Arutchelvi JI, Bhaduri S, Uppara PV, Doble M. Mannosylerythritol lipids: A review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;35(12):1559-1570. [CrossRef]
- Kim HS, Jeon JW, Kim SB, Oh HM, Kwon TJ, Yoon BD. Surface and physico-chemical properties of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, from Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett. 2002;24(19):1637-1641. [CrossRef]
- Imura T, Ohta N, Inoue K, et al. Naturally engineered glycolipid biosurfactants leading to distinctive self-assembled structures. Chemistry - A European Journal. 2006;12(9):2434-2440. [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka T, Yanagihara T, Imura T, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of a novel glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid-D and its aqueous phase behavior. Carbohydr Res. 2011;346(2):266-271. [CrossRef]
- Morita T, Konishi M, Fukuoka T, et al. Identification of Pseudozyma graminicola CBS 10092 as a Producer of Glycolipid Biosurfactants, Mannosylerythritol Lipids. J Oleo Sci. 2008;57(2):123-131. [CrossRef]
- Ceresa C, Hutton S, Lajarin-Cuesta M, et al. Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids (MELs) to be Used as Antimicrobial Agents Against S. aureus ATCC 6538. Curr Microbiol. 2020;77(8):1373-1380. [CrossRef]
- Jing C, Guo J, Li Z, et al. Screening and Research on Skin Barrier Damage Protective Efficacy of Different Mannosylerythritol Lipids. Molecules. 2022;27(14). [CrossRef]
- Feuser PE, Coelho ALS, de Melo ME, et al. Apoptosis Induction in Murine Melanoma (B16F10) Cells by Mannosylerythritol Lipids-B; a Glycolipid Biosurfactant with Antitumoral Activities. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021;193(11):3855-3866. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi M, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D. Glycolipid Biosurfactants, Mannosylerythritol Lipids, Show Antioxidant and Protective Effects against H 2 O 2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Cultured Human Skin Fibroblasts. Vol 61.; 2012. http://mc.manusriptcentral.
- Bae I, Lee ES, Yoo JW, et al. Mannosylerythritol lipids inhibit melanogenesis via suppressing ERK-CREB-MiTF-tyrosinase signalling in normal human melanocytes and a three-dimensional human skin equivalent. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28(6):738-741. [CrossRef]
- Bae IH, Lee SH, Oh S, et al. Mannosylerythritol lipids ameliorate ultraviolet A-induced aquaporin-3 downregulation by suppressing c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation in cultured human keratinocytes. The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology. 2019;23(2):113. [CrossRef]
- Keković P, Borges M, Faria NT, Ferreira FC. Towards Mannosylerythritol Lipids (MELs) for Bioremediation: Effects of NaCl on M. antarcticus Physiology and Biosurfactant and Lipid Production; Ecotoxicity of MELs. J Mar Sci Eng. 2022;10(11):1773. [CrossRef]
- Rau U, Nguyen LA, Roeper H, Koch H, Lang S. Fed-batch bioreactor production of mannosylerythritol lipids secreted by Pseudozyma aphidis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;68(5):607-613. [CrossRef]
- Faria NT, Nascimento MF, Ferreira FA, Esteves T, Santos MV, Ferreira FC. Substrates of Opposite Polarities and Downstream Processing for Efficient Production of the Biosurfactant Mannosylerythritol Lipids from Moesziomyces spp. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. Published online February 22, 202. [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto D, Yanagishita H, Shinbo T, Nakane T, Kamisawa C, Nakahara T. Surface active properties and antimicrobial activities of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants produced by Candida antarctica. J Biotechnol. 1993;29(1-2):91-96. [CrossRef]
- Shu Q, Niu Y, Zhao W, Chen Q. Antibacterial activity and mannosylerythritol lipids against vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus cereus. Food Control. 2019;106. [CrossRef]
- Shu Q, Wei T, Lu H, Niu Y, Chen Q. Mannosylerythritol lipids: Dual inhibitory modes against Staphylococcus aureus through membrane-mediated apoptosis and biofilm disruption. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;104(11):5053-5064. [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi S, Furukawa M, Kawahara A, et al. Roles of mannosylerythritol lipid-B components in antimicrobial activity against bovine mastitis-causing Staphylococcus aureus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;38(3). [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Zhang L, Pang X, et al. Synergistic antibacterial effect and mechanism of high hydrostatic pressure and mannosylerythritol Lipid-A on Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control. 2022;135. [CrossRef]
- Dempster C, Marchant R, Banat IM. Antimicrobial Potential of Biosurfactants as a Novel Combination Therapy Against Bacteria that Cause Skin Infections. In: ; 2019.
- Isoda H, Shinmoto H, Kitamoto D, Matsumura M, Nakahara T. Differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL60 by microbial extracellular glycolipids. Lipids. 1997;32(3):263-271. [CrossRef]
- Isoda H, Kitamoto D, Shinmoto H, Matsumura M, Nakahara T. Microbial Extracellular Glycolipid Induction of Differentiation and Inhibition of the Protein Kinase C Activity of Human Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Line HL60. Vol 61.; 1997.
- Isoda H, Nakahara T. Mannosylerythritol lipid induces granulocytic differentiation and inhibits the tyrosine phosphorylation of human myelogenous leukemia cell line K562. Cytotechnology. 1997;25(1/3):191-195. [CrossRef]
- Feuser PE, Coelho ALS, de Melo ME, et al. Apoptosis Induction in Murine Melanoma (B16F10) Cells by Mannosylerythritol Lipids-B; a Glycolipid Biosurfactant with Antitumoral Activities. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021;193(11):3855-3866. [CrossRef]
- Zhao X, Wakamatsu Y, Shibahara M, et al. Mannosylerythritol lipid is a potent inducer of apoptosis and differentiation of mouse melanoma cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1999;59(2):482-486.
- Morita Y, Tadokoro S, Sasai M, Kitamoto D, Hirashima N. Biosurfactant mannosyl-erythritol lipid inhibits secretion of inflammatory mediators from RBL-2H3 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2011;1810(12):1302-1308. [CrossRef]
- Isoda H, Shinmoto H, Matsumura M, Nakahara T. The Neurite-Initiating Effect of Microbial Extracellular Glycolipids in PC12 Cells. Vol 31.; 1999.
- Shibahara M, Zhao X, Wakamatsu Y, et al. Mannosylerythritol Lipid Increases Levels of Galactoceramide in and Neurite Outgrowth from PC12 Pheochromocytoma Cells. Vol 33.; 2000.
- Igarashi S, Hattori Y, Maitani Y. Biosurfactant MEL-A enhances cellular association and gene transfection by cationic liposome. Journal of Controlled Release. 2006;112(3):362-368. [CrossRef]
- Ueno Y, Hirashima N, Inoh Y, Furuno T, Nakanishi M. Characterization of Biosurfactant-Containing Liposomes and Their Efficiency for Gene Transfection. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30(1):169-172. [CrossRef]
- Inoh Y, Kitamoto D, Hirashima N, Nakanishi M. Biosurfactants of MEL-A increase gene transfection mediated by cationic liposomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289(1):57-61. [CrossRef]
- Inoh Y, Furuno T, Hirashima N, Kitamoto D, Nakanishi M. Rapid delivery of small interfering RNA by biosurfactant MEL-A-containing liposomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414(3):635-640. [CrossRef]
- Bakur A, Elshaarani T, Niu Y, Chen Q. Comparative study of antidiabetic, bactericidal, and antitumor activities of MEL@AgNPs, MEL@ZnONPs, and Ag-ZnO/MEL/GA nanocomposites prepared by using MEL and gum arabic. RSC Adv. 2019;9(17):9745-9754. [CrossRef]
- Bakur A, Niu Y, Kuang H, Chen Q. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles derived from mannosylerythritol lipid and evaluation of their bioactivities. AMB Express. 2019;9(1):62. [CrossRef]
- Bakur A, Hongyun L, Elshaarani T, Albashir D, Mohammed A, Chen Q. Antioxidant and Anticancer Properties of Biosynthesized GA/Ag-Fe3O4@ Nanocomposites. J Clust Sci. 2022;33(3):903-911. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Geng J, Cheng X, et al. Cosmetic-Derived Mannosylerythritol Lipid-B-Phospholipid Nanoliposome: An Acid-Stabilized Carrier for Efficient Gastromucosal Delivery of Amoxicillin for In Vivo Treatment of Helicobacter pylori. ACS Omega. 2022;7(33):29086-29099. [CrossRef]
- Cheng X, Geng J, Wang L, et al. Berberine-loaded mannosylerythritol lipid-B nanomicelles as drug delivery carriers for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori biofilms in vivo. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2023;193:105-118. [CrossRef]
- Yu G, Wang X, Zhang C, Chi Z, Chi Z, Liu G. Efficient production of mannosylerythritol lipids by a marine yeast Moesziomyces aphidis XM01 and their application as self-assembly nanomicelles. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2022;4(3):373-383. [CrossRef]
- Yu G, Wang X, Zhang C, Chi Z, Chi Z, Liu G. Efficient production of mannosylerythritol lipids by a marine yeast Moesziomyces aphidis XM01 and their application as self-assembly nanomicelles. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2022;4(3):373-383. [CrossRef]
- Ito S, Imura T, Fukuoka T, et al. Kinetic studies on the interactions between glycolipid biosurfactant assembled monolayers and various classes of immunoglobulins using surface plasmon resonance. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2007;58(2):165-171. [CrossRef]
- Kim MK, Jeong ES, Kim KN, Park SH, Kim JW. Nanoemulsification of pseudo-ceramide by molecular association with mannosylerythritol lipid. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;116:597-602. [CrossRef]
- Zanotto AW, Kanemaru MYS, de Souza FG, Duarte MCT, de Andrade CJ, Pastore GM. Enhanced antimicrobial and antioxidant capacity of Thymus vulgaris, Lippia sidoides, and Cymbopogon citratus emulsions when combined with mannosylerythritol a lipid biosurfactant. Food Research International. 2023;163:112213. [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa M, Nishimoto K, Tanaka T. Cosmetic pigments, their production method, and cosmetics containing the cosmetic pigments. Published online 2015.
- Morita T, Kitagawa M, Yamamoto S, et al. Activation of Fibroblast and Papilla Cells by Glycolipid Biosurfactants, Mannosylerythritol Lipids. J Oleo Sci. 2010;59(8):451-455. [CrossRef]
- Morita T, Kitagawa M, Yamamoto S, et al. Glycolipid Biosurfactants, Mannosylerythritol Lipids, Repair the Damaged Hair. J Oleo Sci. 2010;59(5):267-272. [CrossRef]
- Morita T, Kitagawa M, Suzuki M, et al. A Yeast Glycolipid Biosurfactant, Mannosylerythritol Lipid, Shows Potential Moisturizing Activity toward Cultured Human Skin Cells: The Recovery Effect of MEL-A on the SDS-damaged Human Skin Cells. J Oleo Sci. 2009;58(12):639-642.
- Yamamoto S, Morita T, Fukuoka T, et al. The Moisturizing Effects of Glycolipid Biosurfactants, Mannosylerythritol Lipids, on Human Skin. J Oleo Sci. 2012;61(7):407-412. [CrossRef]
- Kondo T, Yasui C, Banno T, et al. Self-Assembling Properties and Recovery Effects on Damaged Skin Cells of Chemically Synthesized Mannosylerythritol Lipids. ChemBioChem. 2022;23(2). [CrossRef]
- Tokudome Y, Tsukiji H. Mannosylerythritol Lipid B Enhances the Skin Permeability of the Water-Soluble Compound Calcein via OH Stretching Vibration Changes. Colloids and Interfaces. 2020;4(1):10. [CrossRef]
- Mawani JS, Mali SN, Pratap AP. Formulation and evaluation of antidandruff shampoo using mannosylerythritol lipid (MEL) as a bio-surfactant. Tenside Surfactants Detergents. 2023;60(1):44-53. [CrossRef]
- Hua Z, Chen Y, Du G, Chen J. Effects of biosurfactants produced by Candida antarctica on the biodegradation of petroleum compounds. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;20:25-29.
- Kitamoto D, Ikegami T, Suzuki GT, et al. Microbial conversion of n-alkanes into glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, by Pseudozyma (Candida antarctica). Biotechnol Lett. 2001;23(20):1709-1714. [CrossRef]
- Farooq U, Szczybelski A, Ferreira FC, Faria NT, Netzer R. A Novel Biosurfactant-Based Oil Spill Response Dispersant for Efficient Application under Temperate and Arctic Conditions. ACS Omega. Published online 2023. [CrossRef]
- Barreau S, Packet D, Couleon P, Fouquet M. Petroleum Demulsifier. Published online January 12, 2021.
- 范琳琳, 王英, 刘小莉, 周剑忠, 李亚辉. Anthocyanin nutrition carrier and preparation method thereof. Published online March 31, 2020.
- Shu Q, Wei T, Liu X, Liu S, Chen Q. The dough-strengthening and spore-sterilizing effects of mannosylerythritol lipid-A in frozen dough and its application in bread making. Food Chem. 2022;369. [CrossRef]
- Liu S, Gu S, Shi Y, Chen Q. Alleviative effects of mannosylerythritol lipid-A on the deterioration of internal structure and quality in frozen dough and corresponding steamed bread. Food Chem. 2024;431. [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka T, Yoshida S, Nakamura J, et al. Application of Yeast Glycolipid Biosurfactant, Mannosylerythritol Lipid, as Agrospreaders. J Oleo Sci. 2015;64(6):689-695. [CrossRef]
- Ga’al H, Yang G, Fouad H, Guo M, Mo J. Mannosylerythritol Lipids Mediated Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: An Eco-friendly and Operative Approach Against Chikungunya Vector Aedes albopictus. J Clust Sci. 2021;32(1):17-25. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida S, Koitabashi M, Nakamura J, et al. Effects of biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, on the hydrophobicity of solid surfaces and infection behaviours of plant pathogenic fungi. J Appl Microbiol. 2015;119(1):215-224. [CrossRef]
- Farmer S, Zorner P, Alibek K, et al. Materials and Methods for the control of Nematodes. Published online November 28, 2019.
- Matosinhos RD, Cesca K, Carciofi BAM, de Oliveira D, de Andrade CJ. The Biosurfactants Mannosylerythritol Lipids (MELs) as Stimulant on the Germination of Lactuca sativa L. Agriculture. 2023;13(9):1646. [CrossRef]
- Madihalli C, Sudhakar H, Doble M. Mannosylerythritol Lipid-A as a Pour Point Depressant for Enhancing the Low-Temperature Fluidity of Biodiesel and Hydrocarbon Fuels. Energy & Fuels. 2016;30(5):4118-4125. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira F, Faria N, Fonseca C. Production of fuels from microbial glycolipids with lipid chains comprising 6 to 14 carbons. Published online November 19, 2015.
- José de Andrade C, Maria Pastore G. Comparative study on microbial enhanced oil recovery using mannosylerithritol lipids and surfactin. International Journal of Scientific World. 2016;4(2):69. [CrossRef]
- Sajna KV, Sukumaran RK, Jayamurthy H, et al. Studies on biosurfactants from Pseudozyma sp. NII 08165 and their potential application as laundry detergent additives. Biochem Eng J. 2013;78:85-92. [CrossRef]
- Hellmuth H, Bode N, Dreja M, Buhl A. Detergent with mannosylerythritol lipid. Published online April 28, 2016. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/DE102014221889A1/en (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Kitamoto D, Yanagishita H, Endo A, Nakaiwa M, Nakane T, Akiya T. Remarkable antiagglomeration effect of a yeast biosurfactant, diacylmannosylerythritol, on ice-water slurry for cold thermal storage. Biotechnol Prog. 2001;17(2):362-365. [CrossRef]
- Coderch L, López O, de la Maza A, Parra JL. Ceramides and Skin Function. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(2):107-129. [CrossRef]
- Yoo JW, Hwang YK, BIN SA, Kim YJ, Lee JH. Skin whitening composition containing mannosylerythritol lipid. Published online February 17, 2021.
- Ito S, Suzuki M, Suzuki K, Kobayashi Y. Feed additive and feed. Published online September 30, 2010.
- Sajna KV, Sukumaran RK, Gottumukkala LD, Pandey A. Crude oil biodegradation aided by biosurfactants from Pseudozyma sp. NII 08165 or its culture broth. Bioresour Technol. 2015;191:133-139. [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante Fai AE, Resende Simiqueli AP, de Andrade CJ, Ghiselli G, Pastore GM. Optimized production of biosurfactant from Pseudozyma tsukubaensis using cassava wastewater and consecutive production of galactooligosaccharides: An integrated process. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2015;4(4):535-542. [CrossRef]
- Madihalli C, Sudhakar H, Doble M. Mannosylerythritol Lipid-A as a Pour Point Depressant for Enhancing the Low-Temperature Fluidity of Biodiesel and Hydrocarbon Fuels. Energy and Fuels. 2016;30(5):4118-4125. [CrossRef]
- Mannosylerythritol Lipids Market, By End-use Industries (Household Detergent (Laundry, Dish Wash, Personal Care & Cosmetics (Skincare, Hair Care), Pharmaceuticals, Food, Others)), and By Region (North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa) - Size, Share, Outlook, and Opportunity Analysis, 2023 – 2030. Coherent Market Insights. Published June 2023. Available online: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/market-insight/mannosylerythritol-lipids-market-3692 (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Kitamoto D, Fuzishiro T, Yanagishita H, Nakane T, Nakahara T. Production of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants by resting cells ofCandida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett. 1992;14(4):305-310. [CrossRef]
- Jarvis FG, Johnson MJ. A Glyco-lipide Produced by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J Am Chem Soc. 1949;71(12):4124-4126. [CrossRef]
- Gorin PAJ, Spencer JFT, Tulloch AP. Hydroxy Fatty Acid Glycosided of Sophorose from Torulopsis Magnoliae. Can J Chem. 1961;39(4):846-855. [CrossRef]
- Miao Y, To MH, Siddiqui MA, et al. Sustainable biosurfactant production from secondary feedstock—recent advances, process optimization and perspectives. Front Chem. 2024;12. [CrossRef]
- Ashby RD, McAloon AJ, Solaiman DKY, Yee WC, Reed M. A process model for approximating the production costs of the fermentative synthesis of sophorolipids. J Surfactants Deterg. 2013;16(5):683-691. [CrossRef]
- Lang S, Wullbrandt D. Rhamnose lipids - biosynthesis, microbial production and application potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999;51:22-32.
- Yang Q, Shen L, Yu F, et al. Enhanced fermentation of biosurfactant mannosylerythritol lipids on the pilot scale under efficient foam control with addition of soybean oil. Food and Bioproducts Processing. 2023;138:60-69. [CrossRef]
- Morita T, Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D. Microbial conversion of glycerol into glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, by a basidiomycete yeast, Pseudozyma antarctica JCM 10317T. J Biosci Bioeng. 2007;104(1):78-81. [CrossRef]
- Faria NT, Santos M, Ferreira C, Marques S, Ferreira FC, Fonseca C. Conversion of cellulosic materials into glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, by Pseudozyma spp. under SHF and SSF processes. Microb Cell Fact. 2014;13(1):155. [CrossRef]
- Mawani J, Jadhav J, Pratap A. Fermentative Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids using Sweetwater as Waste Substrate by Pseudozyma antarctica (MTCC 2706). Tenside Surfactants Detergents. 2021;58(4):246-258. [CrossRef]
- Andrade CJ de, Andrade LM de, Rocco SA, Sforça ML, Pastore GM, Jauregi P. A novel approach for the production and purification of mannosylerythritol lipids (MEL) by Pseudozyma tsukubaensis using cassava wastewater as substrate. Sep Purif Technol. 2017;180:157-167. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento MF, Barreiros R, Oliveira AC, Ferreira FC, Faria NT. Moesziomyces spp. cultivation using cheese whey: New yeast extract-free media, β-galactosidase biosynthesis and mannosylerythritol lipids production. Biomass Convers Biorefin. Published online June 2, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Niu Y, Wu J, Wang W, Chen Q. Production and characterization of a new glycolipid, mannosylerythritol lipid, from waste cooking oil biotransformation by Pseudozyma aphidis ZJUDM34. Food Sci Nutr. 2019;7(3):937-948. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento MF, Coelho T, Reis A, Gouveia L, Faria NT, Ferreira FC. Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids Using Oils from Oleaginous Microalgae: Two Sequential Microorganism Culture Approach. Microorganisms. 2022;10(12):2390. [CrossRef]
- Beck A, Werner N, Zibek S. Mannosylerythritol Lipids: Biosynthesis, Genetics, and Production Strategies. In: Biobased Surfactants. Elsevier; 2019:121-167. [CrossRef]
- Roelants S, Solaiman DKY, Ashby RD, Lodens S, Van Renterghem L, Soetaert W. Production and Applications of Sophorolipids. In: Biobased Surfactants. Elsevier; 2019:65-119. [CrossRef]
- Saika A, Koike H, Fukuoka T, Morita T. Tailor-made mannosylerythritol lipids: Current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018;102(16):6877-6884. [CrossRef]
- Suh SJ, Invally K, Ju LK. Rhamnolipids: Pathways, Productivities, and Potential. In: Biobased Surfactants. Elsevier; 2019:169-203. [CrossRef]
- Shephard JJ, Callear SK, Imberti S, Evans JSO, Salzmann CG. Microstructures of negative and positive azeotropes. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2016;18(28):19227-19235. [CrossRef]
- Gunther, M. Mikrobielle Synthese, Aufarbeitung, Modifizierung Und Tensideigenschaften von Mannosylerythritollipinden Und Cellobioselipiden (Microbial Synthesis, Processing, Modification and Surfactant Properties of Mannosylerythritol Lipids and Cellobiose Lipids). Fraunhofer IGB; 2015.
- Smyth TJP, Perfumo A, Marchant R, Banat* IM. Isolation and Analysis of Low Molecular Weight Microbial Glycolipids. In: Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2010:3705-3723. [CrossRef]
- Rau U, Nguyen LA, Roeper H, Koch H, Lang S. Downstream processing of mannosylerythritol lipids produced by Pseudozyma aphidis. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology. 2005;107(6):373-380. [CrossRef]
- Goossens E, Wijnants M, Packet D, Lemière F. Enhanced separation and analysis procedure reveals production of tri-acylated mannosylerythritol lipids by Pseudozyma aphidis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;43(11):1537-1550. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento MF, Keković P, Ribeiro IAC, Faria NT, Ferreira FC. Novel Organic Solvent Nanofiltration Approaches for Microbial Biosurfactants Downstream Processing. Membranes (Basel). 2023;13(1):81. [CrossRef]
- Global Market Insights. Natural Cosmetics Market Size - By Product Type (Skin Care and Sun Care, Hair Care, Body Care, Men’s Grooming, Makeup, Fragrance), By Packaging Type, By Price Range, By Consumer Group, By Distribution Channel, & Global Forecast 2024 – 2032. Published December 2023. Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/natural-cosmetics-market (accessed on 12 March 2024).
| Application Area | Specification | Brief Description of the Results | MELs Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomedical/ Pharmaceutics | Anti microbial activity |
▪ Both MELs were strongly active against gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis, Micrococcus luteus, Mycobacterium rhodoochrous, Staphylococcus aureus). | MEL-A 99% and MEL-B 99% |
[27] |
| ▪ MELs had antimicrobial activity against S. aureus and biofilm disruption activity. | MELs mixture | [18] | ||
| ▪ MEL-A inhibited the germination of Bacillus cereus spores. | MEL-A 80% | [28] | ||
| ▪ MEL-A inhibited planktonic cells and biofilm of S. aureus. | MEL-A 80% | [29] | ||
| ▪ MEL-B inhibited the growth of bovine mastitis causative S. aureus. | MEL-B | [30] | ||
| ▪ The combination of MEL-A with high hydrostatic pressure led to a higher bactericidal effect against Listeria monocytogenes (than the hydrostatic pressure alone). | MEL-A 80% | [31] | ||
| ▪ MELs inhibited the growth of E. coli and P. aeruginosa. The combination of MELs and antibiotics potentiated antibiotics’ efficiency. | NA | [32] | ||
| Application area | Specification | Brief description of the results | MELs used | References |
|
Biomedical/ Pharmaceutics (continuation) |
Antitumor |
▪ MELs induced the differentiation of Human Promyelocytic Leukemia cells HL60 and inhibited Protein Kinase C activity. | MELs mixture |
[33,34] |
| ▪ MELs inhibited Tyrosine Kinase activity, inhibiting proliferation and inducing the differentiation of Human Myelogenous Leukemia cells K562. | MELs mixture |
[35] | ||
| ▪ MEL-B reduced cell viability and induced death by apoptosis of B16F10 Mouse Melanoma cells. | MEL-B 95% Toyobo | [36] | ||
| ▪ MELs stimulated Tyrosinase activity and melanin production, leading to apoptosis and cell-differentiation of B16 Mouse Melanoma cells. |
NA | [37] | ||
| Anti- inflammatory |
▪ MELs inhibit the secretion of inflammatory mediators by Rat Basophilic Leukemia RBL-2H3 cells (a mast cell line). |
MEL-A and MEL-B | [38] | |
| Neural repair | ▪ MELs induce the outgrowth of neurites from and enhance the activity of acetylcholinesterase in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. | MEL-A | [39,40] | |
| Genetic material transfection or drug- carrying |
▪ MEL-A increased the efficiency of gene transfection by cationic liposomes with a cholesterol derivative or DC-Chol. | MEL-A | [41,42,43] | |
| ▪ MEL-A-containing cationic liposome was able to deliver siRNA rapidly and directly. | MEL-A | [44] | ||
| ▪ MELs were used as stabilizing agents for silver and zinc oxide nanocomposites, gold nanoparticles and for silver and magnetic iron oxide nanocomposites synthesis, to be used in human liver cancer cells inhibition (HepG2). | NA | [45,46,47] | ||
| ▪ Nanoliposomes made of soybean lecithin and cholesterol, when incorporated with MEL-B, have enhanced stability to pH 3-7 and deliver amoxicillin for Helicobacter pylori infection treatment in vivo. | MEL-B, Toyobo | [48] | ||
| ▪ MEL-B nanomicelles successfully carried berberine for H. pylori biofilm disintegration and infection eradication. | MEL-B, Toyobo | [49] | ||
| Drug Delivery |
▪ Preparation of MELs nanomiceles for drug delivery (clarithromycin). It was shown that, by varying the pH, it is possible to control clarithromycin delivery (pH 1.2, in 2 h, 37.1% of drug was delivery, while, at pH 7.4, only 9.7% was released). | MELs mixture |
[50] | |
| Immunoglobulin purification |
▪ MEL-A shows high binding affinity towards HIgG, HIgA and HIgM. | MEL-A | [51,52] | |
| Application area | Specification | Brief description of the results | MELs used | References |
|
Cosmetics and personal care |
Formulation stabilization | ▪ Emulsification of pseudo-ceramide is stabilized by molecular association with MELs. | Damy chemicals | [53] |
| MELs stabilize the foaming, emulsification, and wetting properties of Sodium Lauryl Sulphate. | MELs mixture |
[54] | ||
| ▪ Coating cosmetics (lip primer, foundation and sunscreen) pigments with MELs, enhance their skin adhesion. | NA | [55] | ||
| Skin whitening |
▪ MELs inhibit melanogenesis via suppressing ERK-CREB-MiTF-tyrosinase signalling in human melanocytes and a three-dimensional human skin equivalent. | MELs from DKBIO, MEL-B 85% | [22] | |
| Hair growth promotion | ▪ MEL-A produced from soybean oil increases cultured Fibroblast cells and 3D Human Skin model cells viability and activates Human Papilla cells. | MEL-A 80.1% | [56] | |
| Damaged hair repair | ▪ MEL-A and MEL-B shown similar activity as ceramides for hair damage repair, and increase of hair flexibility. | MEL-A 99% MEL-B 90% | [57] | |
| Skin repair and moisturization |
▪ MELs ameliorate UVA-induced aquaporin-3 downregulation by suppressing c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation in cultured human keratinocytes. | MELs from DKBIO | [23] | |
| ▪ MEL-A had a recovery effect on SDS damaged skin cells | MEL-A | [58] | ||
| ▪ MEL-A and MEL-B produced with olive oil show activities similar to natural ceramides on the cell viability and SDS-induced damage repair of cultured human skin cells; MEL-B increased the water content in the stratum corneum and reduced water loss by perspiration. | MEL-A 100% MEL-B 100% |
[59] | ||
| ▪ MELs with carbon chains with 10 or more carbons exhibit better cell damage repair than a natural C18 ceramide, particularly MEL-D C10 (MELs purified by acetylation level and carbon chain size, see original paper) | MELs purified |
[60] | ||
| ▪ MEL-B protected both HaCaT and 3D skin cell models from UVB- and SDS-induced damage by up-regulating the expression of the skin barrier damage-associated key mRNA genes and proteins LOR, FLG, and TGM1 (MELs mixture 34.94% MEL-A, 28.46% MEL-B and 11.32% MEL-C). | MELs mixture. |
[19] | ||
| ▪ MEL-B liposomes increase skin permeability to water-soluble compounds (calcein) in mice. | MEL-B, Toyobo | [61] | ||
| Antioxidant | ▪ MEL-C has antioxidant activity through DPPH radical and superoxide anion scavenging and protection of cultured human fibroblast cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress | MEL-C 80.7-92.5% | [21] | |
| Anti microbial |
▪ MELs have antimicrobial activity against Malassezia furfur, the yeast that causes dandruff. A shampoo formulated with MELs and SLS had increased anti-dandruff activity | NA | [62] | |
| Application area | Specification | Brief description of the results | MELs used | References |
| Bioremediation | Oil spills | ▪ MELs increase the bioavailability and biodegradation rate of n-alkanes, diesel, kerosene and crude oil (MELs mixture: 68% MEL-A, 28% MEL-B and -C and 4% MEL-D). | NA MELs mixture |
[63,64,65] |
| ▪ Patent using MELs as petroleum demulsifier agents | NA | [66] | ||
| Food | Nutrient carriers |
▪ MELs were used in the formulation of a stable anthocyanin nutrient carrier | NA | [67] |
| Food preservation |
▪ MEL-A enhances the rheological properties and water holding capacity of frozen dough, minimizing the freezable water content, while killing B. cereus cells and spores | MEL-A | [28,68,69] | |
| ▪ Emulsification of essential oils with MEL-B (Thymus vulgaris, Lippia sidoides and Cymbopogon citratus), leads to an enhance of essential oils’ antioxidant activity and preservation of antimicrobial activity. | MEL-B | [54] | ||
| Agriculture | Agro-spreader | ▪ MEL used as agrochemical spreader for biopesticides for hydrophobic plant surfaces (MELs mixture: 58% MEL-A, 25% MEL-B and 10% MEL-D). | MEL mixture | [70] |
| Wetting agent | ▪ MEL solutions showed good wetting ability on poorly wettable Gramineae plant surfaces. | MEL-A, MEL-B, MEL-C | [70] | |
| Biocide | ▪ MEL-Ag nanoparticles; activity against mosquito larvae and pupae | MELs mixture |
[71] | |
| Powdery mildew was suppressed on MEL-treated leaves. | MEL-A | [72] | ||
| ▪ MELs, combined with other ingredients, are used for nematodes control. | NA | [73] | ||
| ▪ MEL-B, biostimulant and phytotoxic effect on lettuce plant germination and growth for given concentrations. | MEL-B 95% Toyobo | [74] | ||
| Fuels additive |
▪ MEL-A enhances the fluidity of fuels at low temperatures. | MEL-A | [75] | |
| Others | Jet biofuel | ▪ MELs are used as precursors for fuel with lipid chains comprising 6 to 14 carbons production. | NA | [76] |
| Enhanced oil recovery | ▪ MEL-B can create emulsions with heavy oils. | MEL-B | [77] | |
| Detergent | ▪ MELs had stability over wide pH and temperature ranges and improved detergent efficiency in removing stains from fabric in a proportion of 1:1 (w detergent/w MELs) | MELs mixture |
[78,79] | |
| Ice prevention | Suppression of agglomeration and growth of ice particles | MEL-A | [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





