Submitted:
11 April 2024
Posted:
16 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
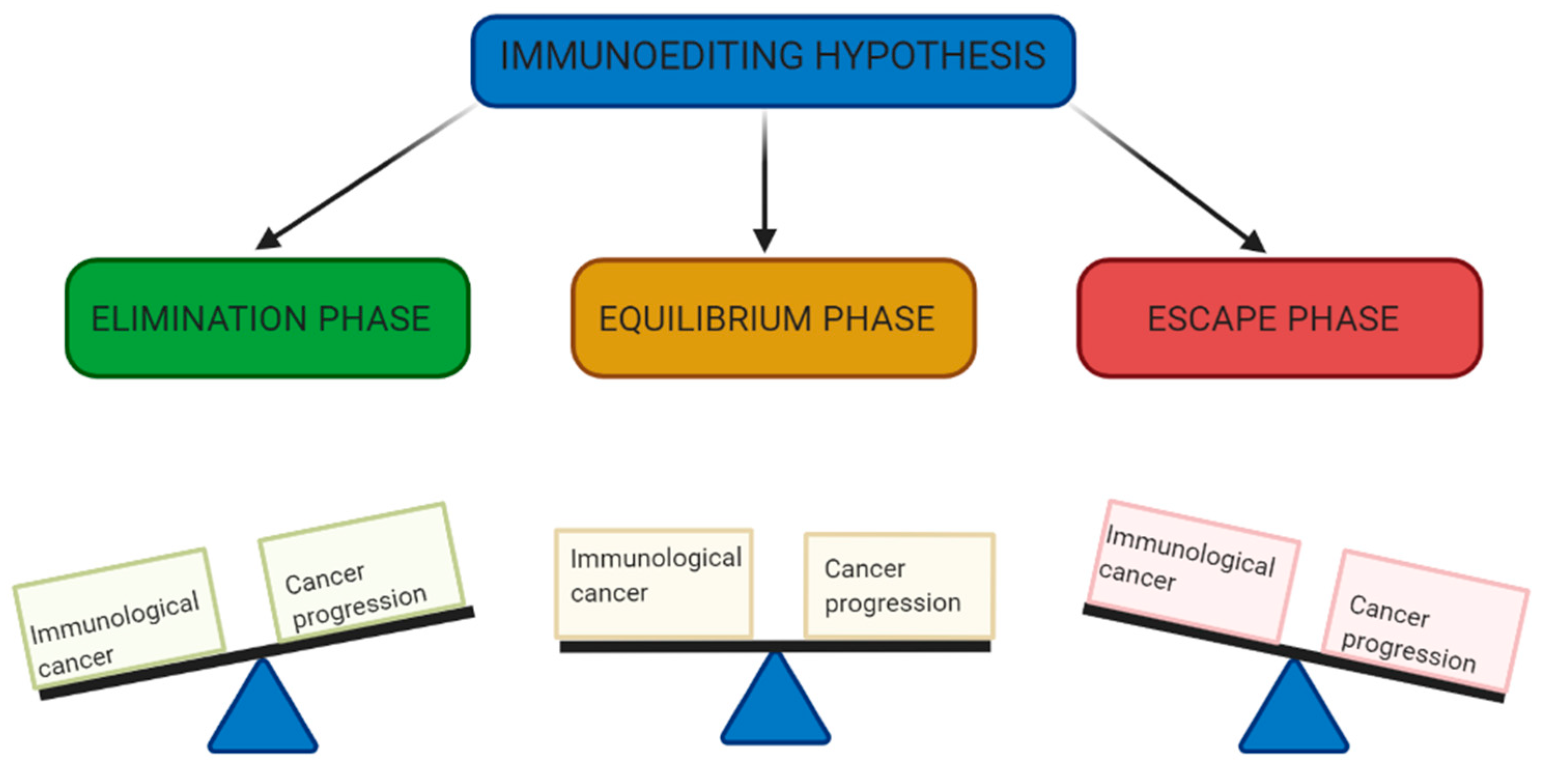
2. Immunoediting: Elimination, Equilibrium and Escape
3. The Anti-Tumour Immunity
3.1. Role of Innate Immune system
3.2. Role of Adaptive Immune system
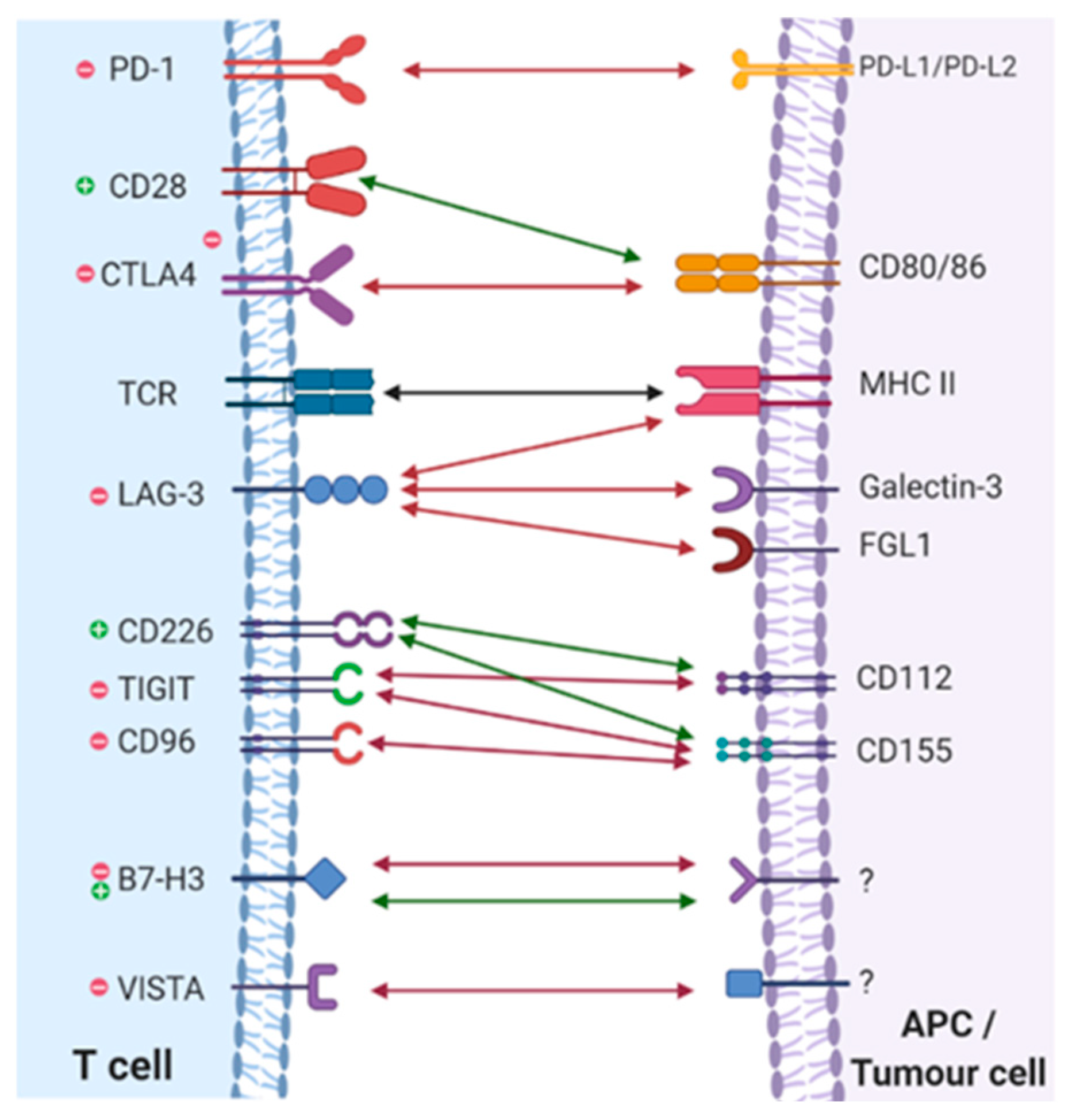
4. Immune Checkpoint Pathways
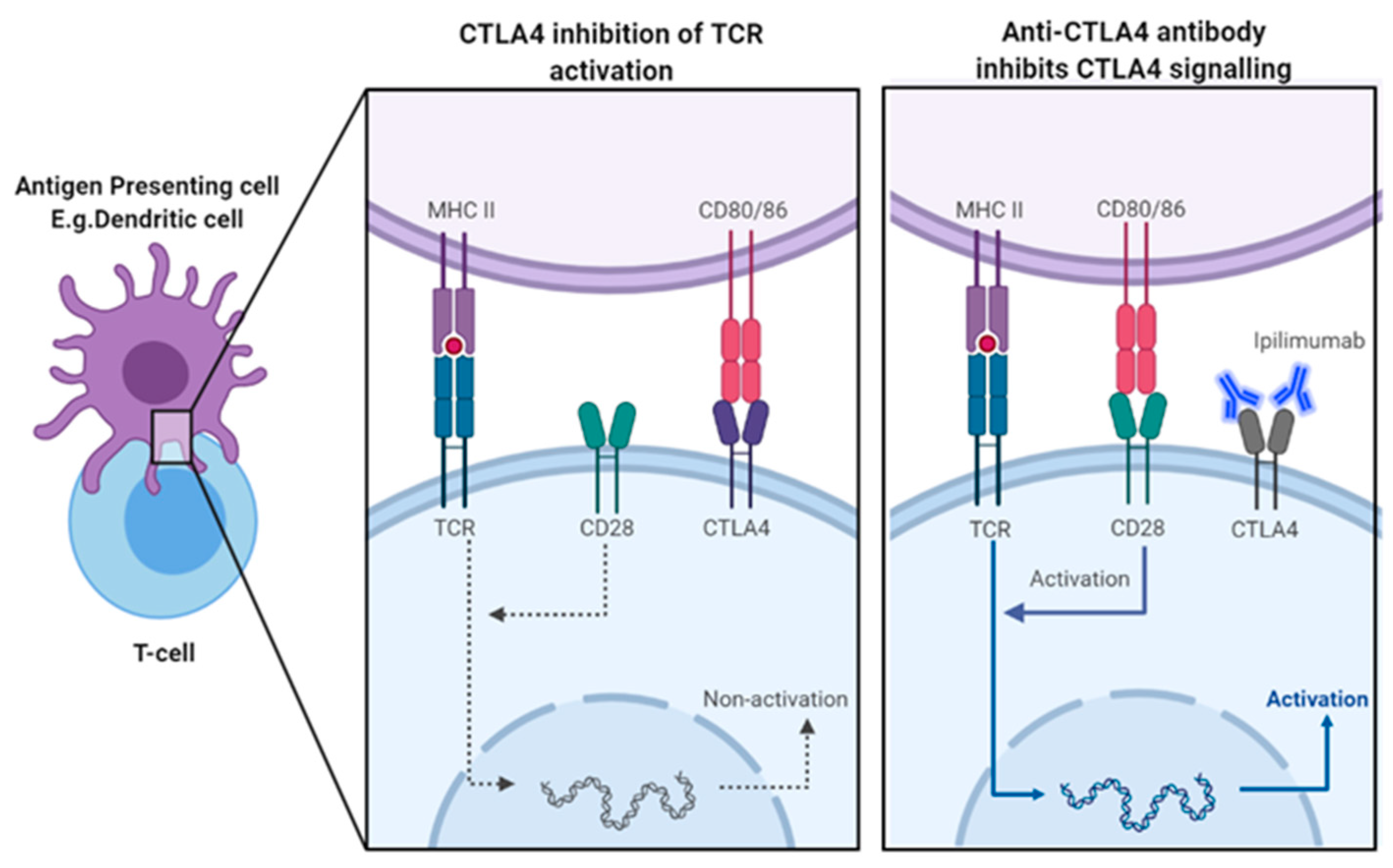
5. CTLA-4 Physiological Role
5.1. Mechanism of CTLA-4 Blockade Induced Tumour Rejection
5.2. Efficacy Of Iplilmumab In Treatment Of Advanced Melanoma
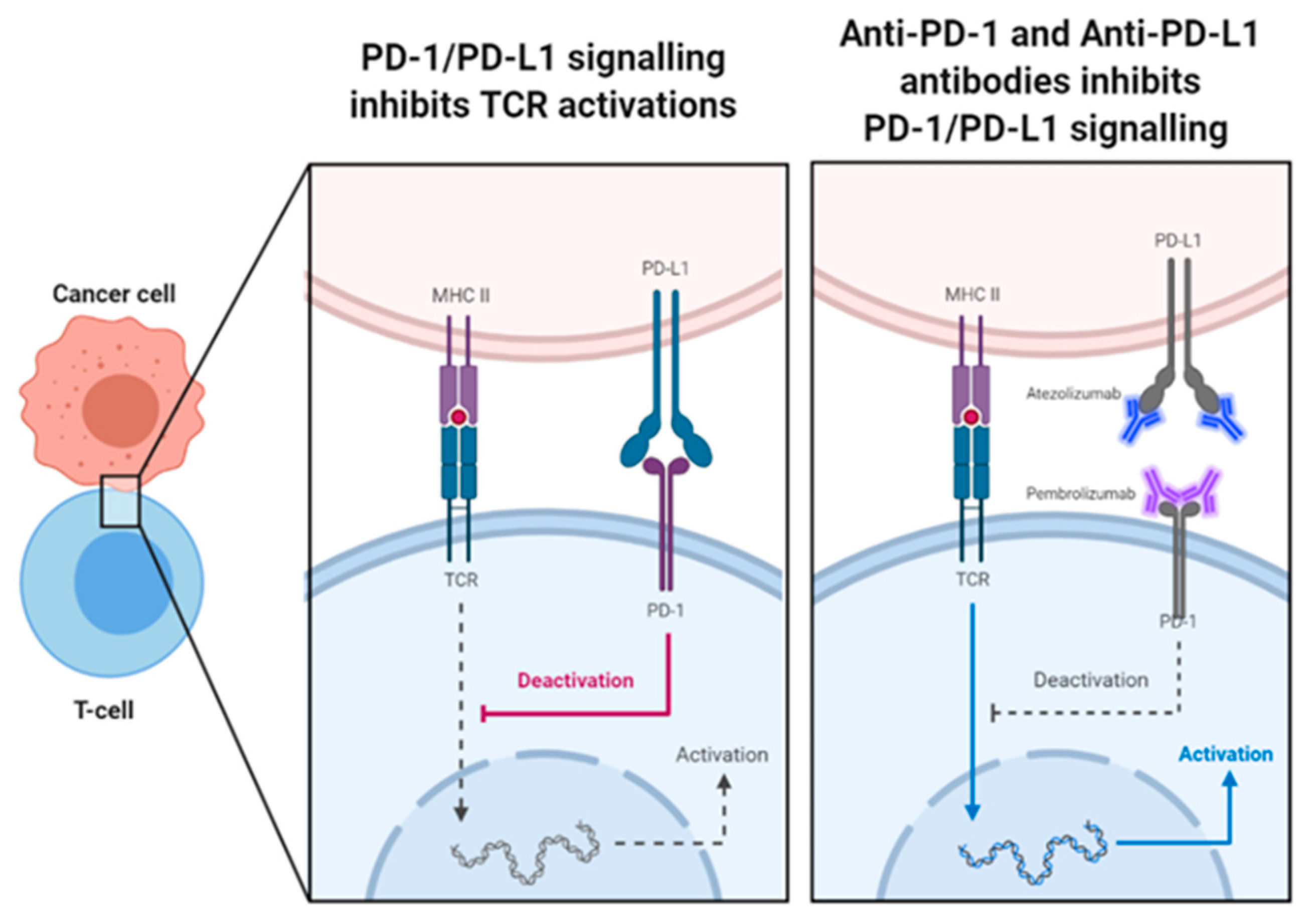
6. PD-1/PD-L1 Physiological Role
6.1. Mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Induced Tumour Rejection
6.2. Efficacy Of Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Agents
6.2.1. Pembrolizumab
6.2.2. Atezoluzumab
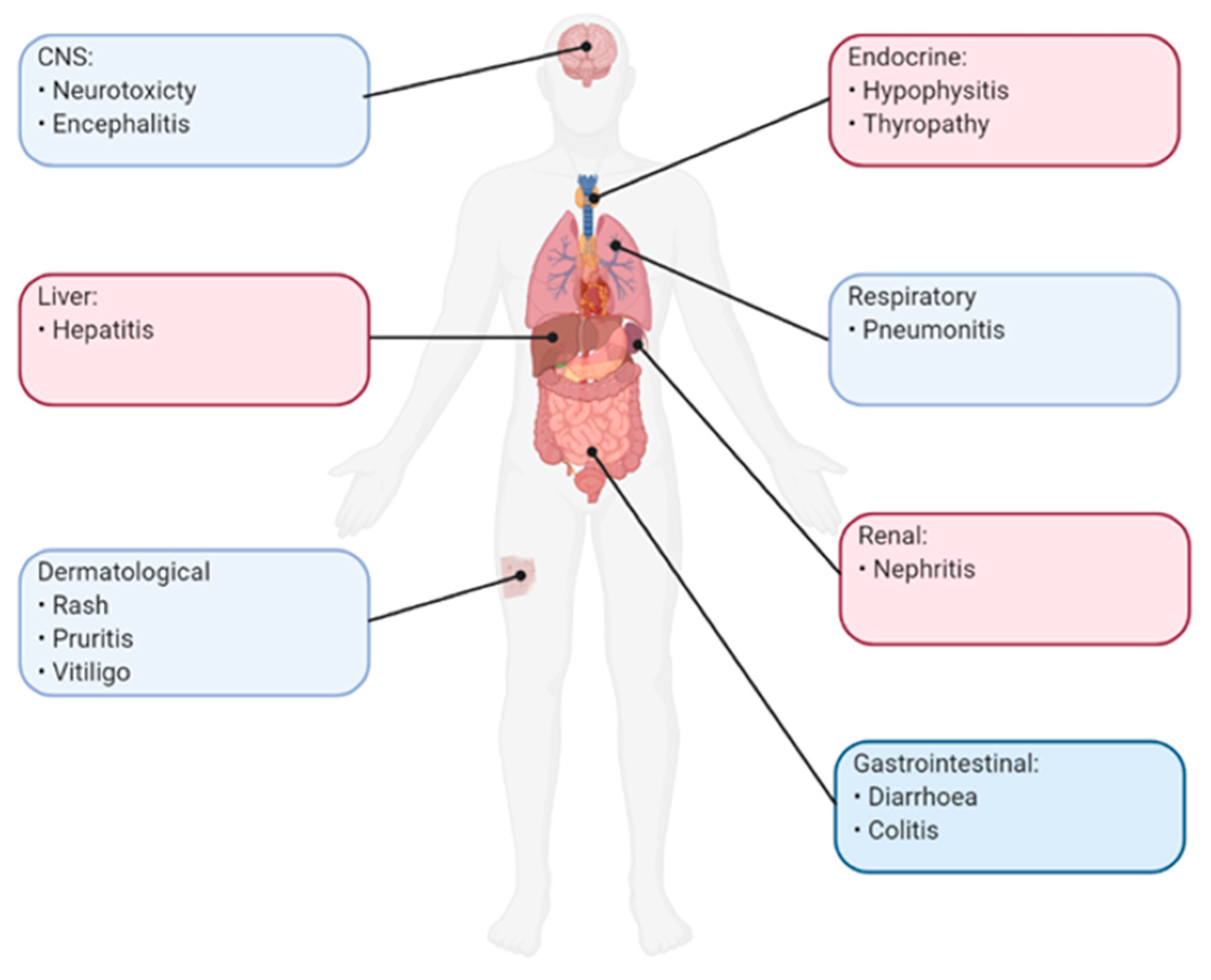
7. Adverse Effects Of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
8. Predictive Biomarkers
9. Future Directions
10. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borghaei, H.; Smith, M.R.; Campbell, K.S. Immunotherapy of cancer. Vol. 625, European Journal of Pharmacology. 2009, 41–54.
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Current status and future directions of cancer immunotherapy. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellman, I.; Coukos, G.; Dranoff, G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature 2011, 480, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voena, C.; Chiarle, R. Advances in cancer immunology and cancer immunotherapy. Discov Med. 2016, 21, 125–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darvin, P.; Toor, S.M.; Sasidharan Nair, V.; Elkord, E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: recent progress and potential biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kates, M.; Sopko, N.A.; Matsui, H.; Drake, C.G.; Hahn, N.M.; Bivalacqua, T.J. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: a new frontier in bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2015, 34, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.H. CTLA-4 blockade with ipilimumab: Biology, safety, efficacy, and future considerations. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 661–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbee, M.S.; Ogunniyi, A.; Horvat, T.Z.; Dang, T.-O. Current Status and Future Directions of the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Ipilimumab, Pembrolizumab, and Nivolumab in Oncology. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 907–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Powles, T.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Balar, A.V.; Necchi, A.; Dawson, N.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Balmanoukian, A.; Loriot, Y.; et al. Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Aren Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenstein, T.; Coulie, P.G.; Gilboa, E.; Jaffee, E.M. The determinants of tumour immunogenicity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancello, L.; Gandini, S.; Pelicci, P.G.; Mazzarella, L. Tumor mutational burden quantification from targeted gene panels: major advancements and challenges. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourie, H.R.; Klastersky, J. Immune checkpoint inhibitors side effects and management. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthay, A. Does the immune system naturally protect against cancer? Vol. 5, Frontiers in Immunology. Frontiers Research Foundation; 2014.
- Smyth, M.J.; Dunn, G.P.; Schreiber, R.D. Cancer Immunosurveillance and Immunoediting: The Roles of Immunity in Suppressing Tumor Development and Shaping Tumor Immunogenicity. Vol. 90, Advances in Immunology. 2006, 1–50.
- Burnet, F.M. The concept of immunological surveillance. Vol. 13, Progress in experimental tumor research. Fortschritte der experimentellen Tumorforschung. Progres de la recherche experimentale des tumeurs. 1970, 1–27.
- Thomas, L. On Immunosurveillance in Human Cancer. Vol. 55, THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE. 1982.
- Vesely, M.D.; Kershaw, M.H.; Schreiber, R.D.; Smyth, M.J. Natural Innate and Adaptive Immunity to Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.P.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. The Three Es of Cancer Immunoediting. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.P.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. The Immunobiology of Cancer Immunosurveillance and Immunoediting. Immunity 2004, 21, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, D.; Gubin, M.M.; Schreiber, R.D.; Smyth, M.J. New insights into cancer immunoediting and its three component phases-elimination, equilibrium and escape. Vol. 27, Current Opinion in Immunology. 2014, 16–25.
- Efremova, M.; Rieder, D.; Klepsch, V.; Charoentong, P.; Finotello, F.; Hackl, H.; Hermann-Kleiter, N.; Löwer, M.; Baier, G.; Krogsdam, A.; et al. Targeting immune checkpoints potentiates immunoediting and changes the dynamics of tumor evolution. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, G.L.; Gladney, W.L. Immune Escape Mechanisms as a Guide for Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, S.W.; Cepero, E.; Evan, G. Intrinsic tumour suppression. Nature 2004, 432, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narendra, B.L.; Reddy, K.E.; Shantikumar, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Immune system: a double-edged sword in cancer. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Innate Immunity. 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Flajnik, M.F.; Kasahara, M. Origin and evolution of the adaptive immune system: genetic events and selective pressures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 11, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, D.D. Overview of the immune response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S3–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, K.T. Innate and adaptive immune responses to cancer. In: Fundamentals of Cancer Prevention. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2005, 79–108.
- Collin, M.; Bigley, V. Human dendritic cell subsets: an update. Immunology 2018, 154, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.-B.; Lü, M.-H.; Fan, Y.-H.; Cao, Y.-L.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Yang, S.-M. Macrophages in Tumor Microenvironments and the Progression of Tumors. J. Immunol. Res. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, J.K.; Knowles, H.J.; Harris, A.L. Macrophages and the hypoxic tumour microenvironment. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 4298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Helming, L.; Gordon, S. Alternative Activation of Macrophages: An Immunologic Functional Perspective. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Hashemi Goradel, N.; Farhood, B.; Salehi, E.; Nashtaei, M.S.; Khanlarkhani, N.; et al. Macrophage polarity in cancer: A review [Internet]. Vol. 120, Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. Wiley-Liss Inc.; 2019, 2756–65. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30270458.
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Hughes, R.; Lewis, C.E. Tumor-associated macrophages: Effectors of angiogenesis and tumor progression [Internet]. Vol. 1796, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Reviews on Cancer. 2009, 11–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19269310.
- Laoui, D.; Movahedi, K.; Van Overmeire, E.; Van den Bossche, J.; Schouppe, E.; Mommer, C.; Nikolaou, A.; Morias, Y.; De Baetselier, P.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. Tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer: distinct subsets, distinct functions. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Bevan, M.J. CD8+ T Cells: Foot Soldiers of the Immune System. Immunity 2011, 35, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheipers, P.; Reiser, H. Role of the CTLA-4 receptor in t cell activation and immunity. Immunol. Res. 1998, 18, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chong, M.M.W.; Littman, D.R. Plasticity of CD4+ T Cell Lineage Differentiation [Internet]. Vol. 30, Immunity. 2009 [cited 2020 Feb 10], 646–55. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19464987.
- Schwartz, R.H. T C ELL A NERGY. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003, 21, 305–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, M.; Fanelli, G.; Albany, C.J.; Giganti, G.; Lombardi, G. Past, Present, and Future of Regulatory T Cell Therapy in Transplantation and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W. Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy [Internet]. Vol. 6, Nature Reviews Immunology. 2006, 295–307. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16557261.
- Cao, X.; Cai, S.F.; Fehniger, T.A.; Song, J.; Collins, L.I.; Piwnica-Worms, D.R.; Ley, T.J. Granzyme B and Perforin Are Important for Regulatory T Cell-Mediated Suppression of Tumor Clearance. Immunity 2007, 27, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curiel, T.J.; Coukos, G.; Zou, L.; Alvarez, X.; Cheng, P.; Mottram, P.; Evdemon-Hogan, M.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Burow, M.; et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Qiu, S.-J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.-Y.; Xiao, Y.-S.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.-W.; Tang, Z.-Y. Intratumoral Balance of Regulatory and Cytotoxic T Cells Is Associated With Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, D.M.; Droeser, R.A.; Viehl, C.T.; Zlobec, I.; Lugli, A.; Zingg, U.; Oertli, D.; Kettelhack, C.; Terracciano, L.; Tornillo, L. High frequency of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ regulatory T cells predicts improved survival in mismatch repair-proficient colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéry, L.; Hugues, S. Th17 Cell Plasticity and Functions in Cancer Immunity. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immune Checkpoint Signaling Pathway - Creative Diagnostics [Internet]. [cited 2020 Mar 21]. Available from: https://www.creative-diagnostics.com/immune-checkpoint-signaling-pathway.htm.
- Nirschl, C.J.; Drake, C.G. Molecular Pathways: Coexpression of Immune Checkpoint Molecules: Signaling Pathways and Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4917–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Duffy, C.R.; Allison, J.P. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juneja, V.R.; McGuire, K.A.; Manguso, R.T.; LaFleur, M.W.; Collins, N.; Haining, W.N.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-L1 on tumor cells is sufficient for immune evasion in immunogenic tumors and inhibits CD8 T cell cytotoxicity. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Xu, L.; Yi, M.; Yu, S.; Wu, K.; Luo, S. Novel immune checkpoint targets: moving beyond PD-1 and CTLA-4. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways similarities, differences, and implications of their inhibition. Vol. 39, American Journal of Clinical Oncology: Cancer Clinical Trials. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2016, 98–106.
- Sansom, D.M. CD28, CTLA-4 and their ligands: Who does what and to whom? Vol. 101, Immunology. Wiley-Blackwell; 2000, 169–77.
- Qureshi, O.S.; Zheng, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Attridge, K.; Manzotti, C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Baker, J.; Jeffery, L.E.; Kaur, S.; Briggs, Z.; et al. Trans-Endocytosis of CD80 and CD86: A Molecular Basis for the Cell-Extrinsic Function of CTLA-4. Science 2011, 332, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallarino, F.; Fields, P.E.; Gajewski, T.F. B7-1 Engagement of Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen 4 Inhibits T Cell Activation in the Absence of CD28. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, P.; Penninger, J.M.; Timms, E.; Wakeham, A.; Shahinian, A.; Lee, K.P.; Thompson, C.B.; Griesser, H.; Mak, T.W. Lymphoproliferative Disorders with Early Lethality in Mice Deficient in Ctla-4. Science 1995, 270, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.R.; Krummel, M.F.; Allison, J.P. Enhancement of Antitumor Immunity by CTLA-4 Blockade. Science 1996, 271, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.H.; Antonia, S.; Sosman, J.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Gajewski, T.F.; Redman, B.; Pavlov, D.; Bulanhagui, C.; Bozon, V.A.; Gomez-Navarro, J.; et al. Phase I/II Trial of Tremelimumab in Patients With Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Kefford, R.; Marshall, M.A.; Punt, C.J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Marmol, M.; et al. Phase III randomized clinical trial comparing tremelimumab with standard-of-care chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol [Internet]. 2013, 31, 616–22. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23295794.
- Rotte, A. Combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockers for treatment of cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Levine, J.H.; Cogdill, A.P.; Zhao, Y.; Anang, N.-A.A.S.; Andrews, M.C.; Sharma, P.; Wang, J.; Wargo, J.A.; Pe’Er, D.; et al. Distinct Cellular Mechanisms Underlie Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade. Cell 2017, 170, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J. T cell exhaustion. Vol. 12, Nature Immunology. 2011, 492–9.
- Simpson, T.R.; Li, F.; Montalvo-Ortiz, W.; Sepulveda, M.A.; Bergerhoff, K.; Arce, F.; Roddie, C.; Henry, J.Y.; Yagita, H.; Wolchok, J.D.; et al. Fc-dependent depletion of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells co-defines the efficacy of anti–CTLA-4 therapy against melanoma. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1695–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selby, M.J.; Engelhardt, J.J.; Quigley, M.; Henning, K.A.; Chen, T.; Srinivasan, M.; Korman, A.J. Anti-CTLA-4 Antibodies of IgG2a Isotype Enhance Antitumor Activity through Reduction of Intratumoral Regulatory T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulliard, Y.; Jolicoeur, R.; Windman, M.; Rue, S.M.; Ettenberg, S.; Knee, D.A.; Wilson, N.S.; Dranoff, G.; Brogdon, J.L. Activating Fc γ receptors contribute to the antitumor activities of immunoregulatory receptor-targeting antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Tang, F.; Liu, M.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Devenport, M.; A Lazarski, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; et al. A reappraisal of CTLA-4 checkpoint blockade in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peggs, K.S.; Quezada, S.A.; Chambers, C.A.; Korman, A.J.; Allison, J.P. Blockade of CTLA-4 on both effector and regulatory T cell compartments contributes to the antitumor activity of anti–CTLA-4 antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramagopal, U.A.; Liu, W.; Garrett-Thomson, S.C.; Bonanno, J.B.; Yan, Q.; Srinivasan, M.; Wong, S.C.; Bell, A.; Mankikar, S.; Rangan, V.S.; et al. Structural basis for cancer immunotherapy by the first-in-class checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, E4223–E4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altekruse S, Kosary C, Krapcho M, gov/csr NN cancer., 2010 undefined. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2007, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, based on November 2009 SEER data submission, posted to the.
- Tarhini, A.; Lo, E.; Minor, D.R. Releasing the Brake on the Immune System: Ipilimumab in Melanoma and Other Tumors. Cancer Biotherapy Radiopharm. 2010, 25, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peggs, K.S.; A Quezada, S.; Korman, A.J.; Allison, J.P. Principles and use of anti-CTLA4 antibody in human cancer immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, E.M.; O’day, S.J.; Powderly, J.; Khan, K.D.; Pavlick, A.C.; Cranmer, L.D.; Samlowski, W.E.; Nichol, G.M.; Yellin, M.J.; Weber, J.S. A phase II multicenter study of ipilimumab with or without dacarbazine in chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced melanoma. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 29, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, E.; Weber, J.; Powderly, J.; Pavlik, A.; Nichol, G.; Yellin, M.; Cranmer, L.; Urba, W.; O'Day, S. Long-term survival of patients (pts) with advanced melanoma treated with ipilimumab with or without dacarbazine. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 9038–9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Neyns, B.; Linette, G.; Negrier, S.; Lutzky, J.; Thomas, L.; Waterfield, W.; Schadendorf, D.; Smylie, M.; Guthrie, T.; et al. Ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 2, dose-ranging study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Hodi, F.S.; Weber, J.S.; Allison, J.P.; Urba, W.J.; Robert, C.; O'Day, S.J.; Hoos, A.; Humphrey, R.; Berman, D.M.; et al. Development of ipilimumab: a novel immunotherapeutic approach for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2013, 1291, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadendorf, D.; Hodi, F.S.; Robert, C.; Weber, J.S.; Margolin, K.; Hamid, O.; Patt, D.; Chen, T.-T.; Berman, D.M.; Wolchok, J.D. Pooled Analysis of Long-Term Survival Data From Phase II and Phase III Trials of Ipilimumab in Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X. PD-1 and its ligands are important immune checkpoints in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and Its Ligands in Tolerance and Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokosuka, T.; Takamatsu, M.; Kobayashi-Imanishi, W.; Hashimoto-Tane, A.; Azuma, M.; Saito, T. Programmed cell death 1 forms negative costimulatory microclusters that directly inhibit T cell receptor signaling by recruiting phosphatase SHP2. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riella, L.V.; Paterson, A.M.; Sharpe, A.H.; Chandraker, A. Role of the PD-1 Pathway in the Immune Response. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 2575–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Nose, M.; Hiai, H.; Minato, N.; Honjo, T. Development of Lupus-like Autoimmune Diseases by Disruption of the PD-1 Gene Encoding an ITIM Motif-Carrying Immunoreceptor. Immunity 1999, 11, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Yu, P.-C.; Long, D.; Liao, X.-L.; Zhang, S.; You, X.-M.; Zhong, J.-H.; Li, L.-Q. Prognostic value of PD -L1 expression in patients with primary solid tumors. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 5058–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PD-1/PD-L1 Landscape Analysis - Cancer Research Institute (CRI) [Internet]. Available from: https://www.cancerresearch.org/scientists/immuno-oncology-landscape/pd-1-pd-l1-landscape.
- Loke, P.; Allison, J.P. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are differentially regulated by Th1 and Th2 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 5336–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butte, M.J.; Keir, M.E.; Phamduy, T.B.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, H. PD-L1 interacts specifically with B7-1 to inhibit T cell proliferation. Immunity [Internet]. 2009, 27, 111–22. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2707944%7B&%7Dtool=pmcentrez%7B&%7Drendertype=abstract.
- Khoja, L.; Butler, M.O.; Kang, S.P.; Ebbinghaus, S.; Joshua, A.M. Pembrolizumab. J. Immunother. Cancer 2015, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hodi, F.S.; Hamid, O.; Kefford, R.; Weber, J.S.; Joshua, A.M.; Hwu, W.-J.; Gangadhar, T.C.; et al. Anti-programmed-death-receptor-1 treatment with pembrolizumab in ipilimumab-refractory advanced melanoma: a randomised dose-comparison cohort of a phase 1 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Five-year survival outcomes for patients with advanced melanoma treated with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-001. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Ribas, A.; Schachter, J.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.-J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.M.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma (KEYNOTE-006): post-hoc 5-year results from an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garon, E.B.; Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Carcereny, E.; Leighl, N.B.; Ahn, M.-J.; Eder, J.P.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Aggarwal, C.; Horn, L.; et al. Five-Year Overall Survival for Patients With Advanced Non‒Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Pembrolizumab: Results From the Phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Garon, E.B.; Kim, D.-W.; Cho, B.C.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Arvis, C.D.; Majem, M.; Forster, M.D.; Monnet, I.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes and Retreatment Among Patients With Previously Treated, Programmed Death-Ligand 1‒Positive, Advanced Non‒Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the KEYNOTE-010 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atezolizumab for Urothelial Carcinoma | FDA [Internet]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/atezolizumab-urothelial-carcinoma.
- Hoffman-Censits, J.H.; Grivas, P.; Van Der Heijden, M.S.; Dreicer, R.; Loriot, Y.; Retz, M.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Rezazadeh, A.; Bracarda, S.; et al. IMvigor 210, a phase II trial of atezolizumab (MPDL3280A) in platinum-treated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 355–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balar, A.V.; Galsky, M.D.; Rosenberg, J.E.; Powles, T.; Petrylak, D.P.; Bellmunt, J.; Loriot, Y.; Necchi, A.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; et al. Atezolizumab as first-line treatment in cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atezolizumab (TECENTRIQ) | FDA [Internet]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/atezolizumab-tecentriq.
- Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D.; Artal-Cortes, A.; Lewanski, C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hematology/Oncology (Cancer) Approvals & Safety Notifications | FDA [Internet]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/hematologyoncology-cancer-approvals-safety-notifications.
- FDA approves atezolizumab for PD-L1 positive unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer | FDA [Internet]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-approves-atezolizumab-pd-l1-positive-unresectable-locally-advanced-or-metastatic-triple-negative.
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Hegg, R.; Im, S.-A.; Shaw Wright, G.; et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials Using Atezolizumab - National Cancer Institute [Internet]. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/clinical-trials/intervention/atezolizumab.
- Weinmann, S.C.; Pisetsky, D.S. Mechanisms of immune-related adverse events during the treatment of cancer with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Rheumatology 2019, 58 (Suppl. 7), vii59–vii67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Zang, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-C.; Huang, S.-S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, P. Diagnosis and Management of Immune Related Adverse Events (irAEs) in Cancer Immunotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Schachter, J.; Long, G.V.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Johnson, D.B. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, A. Treating with Checkpoint Inhibitors-Figure $1 Million per Patient. Am Heal drug benefits 2015, 8, 9–9. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, S.; Velichinskii, R.; Lesh, R.W.; Ali, U.; Kubiak, M.; Bansal, P.; Borghaei, H.; Edelman, M.J.; Boumber, Y. Existing and Emerging Biomarkers for Immune Checkpoint Immunotherapy in Solid Tumors. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 2638–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.A.; Patel, V.G. The role of PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker: an analysis of all US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, A.M.; Kato, S.; Bazhenova, L.; Patel, S.P.; Frampton, G.M.; Miller, V.; et al. Tumor mutational burden as an independent predictor of response to immunotherapy in diverse cancers. Mol Cancer Ther [Internet]. 2017, 16, 2598–608. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28835386.
- Schlötterer, C.; Harr, B.; Schlo, C. Microsatellite Instability Microsatellite Instability. 2017, 1–4.
- Drescher, K.M.; Sharma, P.; Watson, P.; Gatalica, Z.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Lynch, H.T. Lymphocyte recruitment into the tumor site is altered in patients with MSI-H colon cancer. Fam. Cancer 2009, 8, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duruisseaux, M.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Calleja-Cervantes, M.E.; Moran, S.; de Moura, M.C.; Davalos, V.; Piñeyro, D.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Girard, N.; Brevet, M.; et al. Epigenetic prediction of response to anti-PD-1 treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, J.J.; Chowell, D.; Chan, T.A. The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, G.T.; Weiner, L.M.; Atkins, M.B. Predictive biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e542–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maçon-Lemaître, L.; Triebel, F. The negative regulatory function of the lymphocyte-activation gene-3 co-receptor (CD223) on human T cells. Immunology [Internet]. 2005, 115, 170–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15885122.
- Andrews, L.P.; Marciscano, A.E.; Drake, C.G.; Vignali, D.A.A. LAG3 (CD223) as a cancer immunotherapy target. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignone, C.; Escudier, B.; Grygar, C.; Marcu, M.; Triebel, F. A phase I pharmacokinetic and biological correlative study of IMP321, a novel MHC class II agonist, in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res [Internet]. 2009, 15, 6225–31. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19755389.
- Brignone, C.; Gutierrez, M.; Mefti, F.; Brain, E.; Jarcau, R.; Cvitkovic, F.; Bousetta, N.; Medioni, J.; Gligorov, J.; Grygar, C.; et al. First-line chemoimmunotherapy in metastatic breast carcinoma: combination of paclitaxel and IMP321 (LAG-3Ig) enhances immune responses and antitumor activity. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 71–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-Y.; Francois, A.; McGray, A.R.; Miliotto, A.; Odunsi, K. Compensatory upregulation of PD-1, LAG-3, and CTLA-4 limits the efficacy of single-agent checkpoint blockade in metastatic ovarian cancer. OncoImmunology 2016, 6, e1249561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliger, B. Combinatorial Approaches With Checkpoint Inhibitors to Enhance Anti-tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.-J.; Rutkowski, P.; Lao, C.D.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Five-Year Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanpouille-Box, C.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Toward precision radiotherapy for use with immune checkpoint blockers [Internet]. Vol. 24, Clinical Cancer Research. American Association for Cancer Research Inc.; 2018, 259–65. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28751442.
- Rudqvist, N.P.; Pilones, K.A.; Lhuillier, C.; Wennerberg, E.; Sidhom, J.W.; Emerson, R.O.; et al. Radiotherapy and CTLA-4 blockade shape the tcr repertoire of tumor-infiltrating t cells. Cancer Immunol Res [Internet]. 2018, 6, 139–50. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29180535.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



