Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Measurement Methods and Indicator System Construction
2.1. Entropy Method
2.2. The Construction of Evaluation Index System
2.3. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
3. Measurement and Analysis of High-Quality Economic Development
3.1. Analysis of the Overall Index and Sub-Dimension Index
- 1)
- Analysis of the overall index of high-quality economic development
- 2)
- Analysis of the Subdimensional
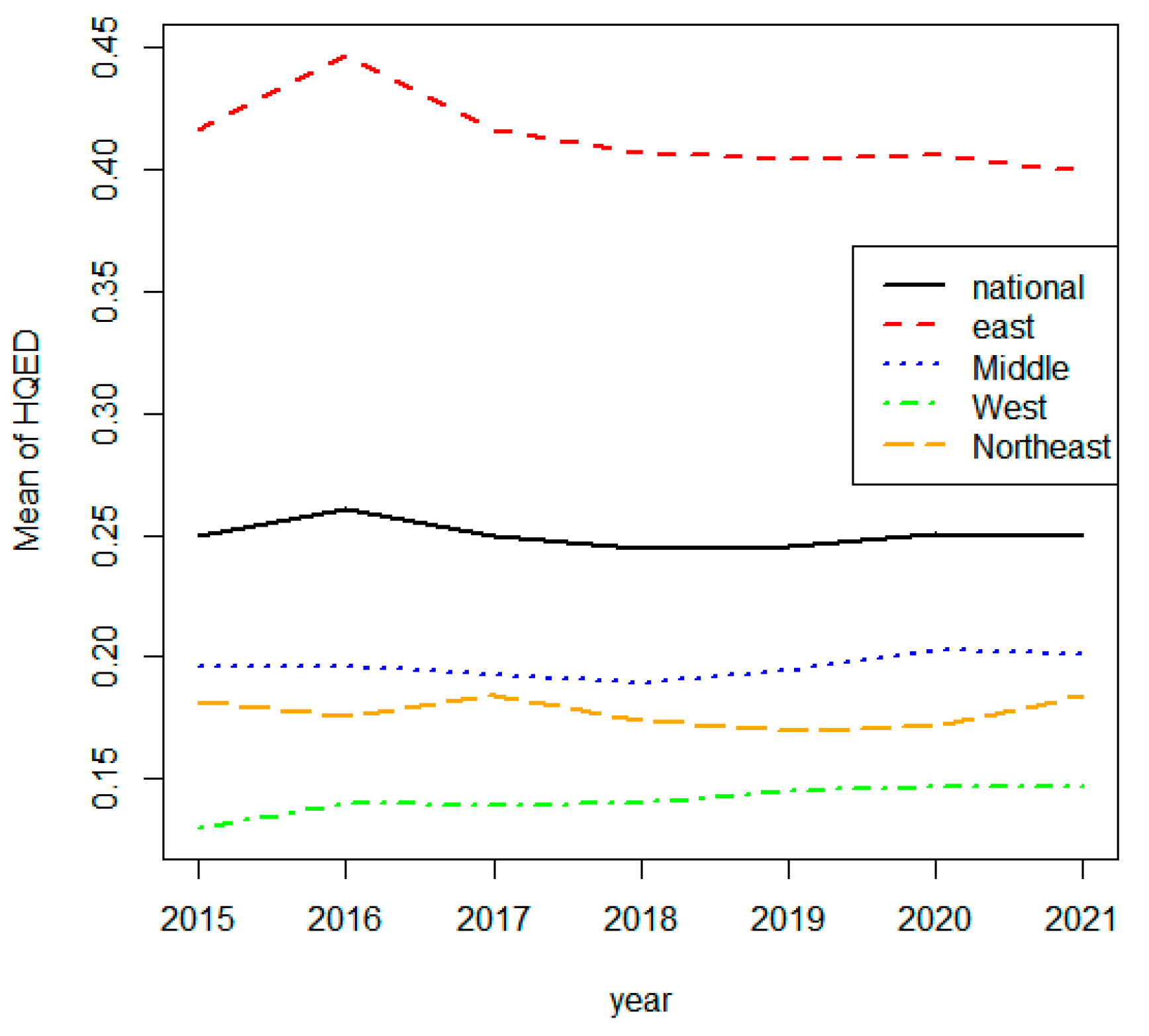
3.2. Temporal Evolution of High-Quality Economic Development
3.3. Spatial Analysis of High-Quality Economic Development
| Index | Innovation | Coordination | Greenness | Openness | Sharing | High-Quality Development |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | ||||||
| High level | Jiangsu Guangdong |
Heilongjiang | Beijing | Guangdong | Beijing | Guangdong Jiangsu |
| Middle high level | Zhejiang Shandong |
Shanxi, Liaoning Jilin, Anhui Guangxi, Qinghai Chongqing |
Jiangsu, Zhejiang Fujian, Shandong Hunan, Hainan |
Shanghai, Hainan | Tianjin, Shanghai Jiangsu, Zhejiang Guangdong |
Beijing, Shanghai Zhejiang, Shandong |
| Middle level | Beijing, Hebei Shanghai, Anhui Fujian, Henan Hubei, Hunan Sichuan, Shaanxi |
Beijing, Jiangsu Zhejiang, Guangdong Fujian, Guizhou Yunnan, Gansu |
Tianjin, Hebei Shanxi, Liaoning Jilin, Heilongjiang Anhui, Henan Hubei, Guangdong Chongqing, Yunnan Shanxi |
Beijing, Tianjin Jiangsu, Zhejiang Fujian, Shandong |
Inner Mongolia Fujian, Shandong Hubei, Hunan Chongqing, Sichuan Shaanxi, Xinjiang |
Tianjin, Hebei Liaoning, Anhui Fujian, Henan Hubei, Hunan Chongqing, Sichuan Hainan, Shaanxi |
| Low level | Tianjin, Liaoning, Shanxi, Jilin Inner Mongolia Heilongjiang, Jiangxi, Guangxi Hainan, Guizhou Yunnan, Gansu Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang, Chongqing |
Tianjin, Hebei, Inner Mongolia Shanghai, Hunan Sichuan, Jiangxi Shandong, Henan Hubei, HainanShaanxi, Ningxia, Xinjiang |
Inner Mongolia, Shanghai Sichuan, Guizhou Gansu, Jiangxi Guangxi, Qinghai Ningxia, Xinjiang |
Hunan, Sichuan Shaanxi, Hebei Shanxi, Inner Mongolia Liaoning, Jilin Heilongjiang, Anhui Jiangxi Henan, Hubei Guangxi, Guizhou Chongqing, Yunnan Gansu, Qinghai Ningxia, Xinjiang |
Hebei, Henan Hainan, Liaoning Jilin,Heilongjiang Anhui, Jiangxi Guizhou, Yunnan Shanxi, Gansu Qinghai, Ningxia |
Shanxi, Inner Mongolia Jilin, HeilongjiangJiangxi, Gu Guangxi, Yunnan Gansu, Qinghai Ningxia, Xinjiang |
4. Analysis of the Dynamic Evolution Distribution of High-Quality Economic Development
4.1. Principle of Kernel Density Estimation

4.2. Analysis of the Distribution and Dynamic Evolution Characteristics of High-Quality Economic Development in China
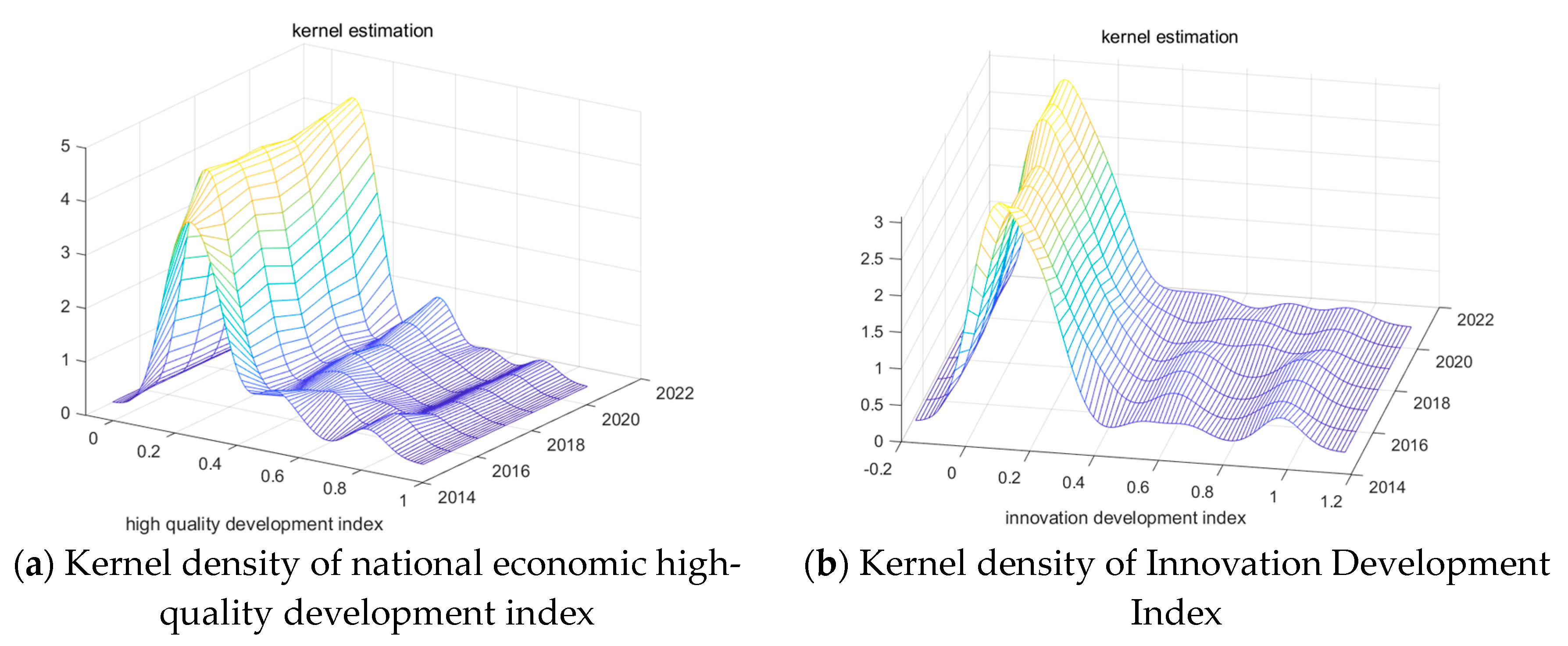

| Categories | Distribution Location | Main Peak Distribution Pattern | Distribution Extensibility | Polarization Phenomenon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-quality development index | right-shift | Peak rise, The width narrows |
Right trailing, Extension widen | Polarization, with three peaks observed in most years |
| Innovation | right-shift | The peak value first decreases, then increases and then decreases, The width narrows |
Right trailing, Extension narrows | Polarization, with three peaks observed in most years |
| Coordination | right-shift | The peak value first rises, then falls, then rises and then falls again, The width narrows |
Right trailing, Extension widen | No polarization phenomenon |
| Greenness | right-shift | The peak value first decreases then rises, then decreases, and then rises again, The width narrows |
Right trailing, Extension widen | Polarization phenomenon weakened |
| Openness | right-shift | The peak value first rises, then decreases, and then rises again, The width narrows |
Right trailing, Extension widen | Polarization, with three peaks observed in most years |
| Sharing | right-shift | The peak first value rises, then decreases, and then rises again, The width narrows |
Right trailing, Extension narrows | Polarization, with three peaks observed in most years |
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qashou, Y.; Samour, A.; Abumunshar, M. Does the Real Estate Market and Renewable Energy Induce Carbon Dioxide Missions? Novel Evidence from Turkey. Energies 2022, 15, 763. [Google Scholar]
- Samour, A.; Pata, U.K. The impact of the US interest rate and oil prices on renewable energy in Turkey: a bootstrap ARDL approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50352–50361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Zhang, Y. Measurement and Evaluation of the Coupling Coordination of Environmental Regulation and High-quality Economic Development. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X. National Capacity and Economic Development—Rethinking Based on the Goal of High-quality EconomicDevelopment. Economist. 2021, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.; Wang, J.; Hua, X.; Liu, Z. Entrepreneurship and high-quality economic development: based on the triple bottom line of sustainable development. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2020, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Chen, Z. The Convergence Analysis of Regional Growth Differences in China: The Perspective of the Quality of Economic Growth*. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. 2016, 09, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Shang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shahzad, U. Green economic growth and its inherent driving factors in Chinese cities: Based on the Metafrontier-global-SBM super-efficiency DEA model. Gondwana Res. 2022, 106, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Lv, H.; Jin, X. Research on High-Quality Development Efficiency and Total Factor Productivity of Regional Economies in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, D. Smog pollution, government governance and high-quality economic development. Econ. Res. 2018, 53, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, H.; Wu, F. Digital economy empowers high-quality economic development: Theoretical mechanisms and empirical evidence. Nanjing Soc. Sci. 2021, 1, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, G. Can FDI and ODI two-way flows improve the quality of economic growth? Empirical Evidence from China. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 5028–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, H. Environmental management and labor productivity: The moderating role of quality management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 255, 109795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Lv, H.; Jin, X. Research on High-Quality Development Efficiency and Total Factor Productivity of Regional Economies in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhong, R.; Wang, Z.; Yu, M.; Wu, Y.; Irfan, M.; Hao, Y. Would the inequality of environmental quality affect labor productivity and the income gap? Evidence from China. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022, 67, 25–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W. Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Development in China. Scientific and Social Research. 2021, 5, 105–112http://journalsinnosciencepresscom/indexphp/ssr. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liang, J.; Tian, L.; Wang, S. Measurement and Coupling Coordination of High-Quality Development in Guangdong Province of China: A Spatiotemporal Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2023, 20, 4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, J. Impact of Environmental Regulation on High-Quality Economic Development. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cai, B.; Li, Y. Evaluation Index System and Measurement of High-quality Development in China. Rev. de Cercet. si Interv. Sociala 2020, 68, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, S. The Construction and Measurement of Evaluation System of China’s Economic Growth Quality under the New Normal. Economist 2018, 4, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C. Measurement of High Quality Development of Regional Economy in China. Mod. Bus 2021, 20, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. What Is the Mechanism of Resource Dependence and High-Quality Economic Development? An Empirical Test from China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Guo, T. Construction and Application of the High-quality Development Index—Also on the High-quality Development of Northeast China’s Economy. J. Northeast. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2020, 22, 31 (In Chinese). (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Deng, F.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, X. Digital Paradox: Platform Economy and High-Quality Economic Development—New Evidence from Provincial Panel Data in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cai, B.; Li, Y. Evaluation Index System and Measurement of High-quality Development in China. Rev. de Cercet. si Interv. Sociala 2020, 68, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md. Nazmul Islam, Kusay Faisal Al-tabatabaie, Md. Ahasan Habib, Sheikh Sharif Iqbal, Khurram Karim Qureshi and Eid M. Al-Mutairi, Design of a Hollow-Core Photonic Crystal Fiber Based Edible Oil Sensor, Crystals 2022, 7, 101. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, W. Evaluation of ecological city and analysis of obstacle factors under the background of high-quality development: Taking cities in the Yellow River Basin as examples. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitong, X.; Saiya, N.; Aoyang, L.; Bo, T. A Study on Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Optimization of High-Quality Development in the Pearl River-West River Economic Belt. Acad. J. Bus. Manag. 2023, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Huang, R. Whether Foreign Direct Investment can Promote High-quality Economic Development under Environmental Regulation: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21674–21683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Guo, J.; Zhu, C. Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Coupling and Coordination of High-Quality Development in Eastern Coastal Areas of China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, C.; Su, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Spatial-temporal differentiation pattern and influencing factors of high-quality development in counties: A case of Sichuan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Q.; Liu, Z.; Song, Z.; Wang, J. A study on dynamic evolution, regional differences and convergence of high-quality economic development in urban agglomerations: A case study of three major urban agglomerations in the Yangtze river economic belt. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, F. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of High-Quality Development and the Impact of Carbon Emissions Trading Schemes. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Geng, Y.; Liu, Z. The Spatial Correlation Network of China’s High-Quality Development and Its Driving Factors. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ding, R.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, T. Study on the Coupling Coordination and Spatial Correlation Effect of Green Finance and High-Quality Economic Development—Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. A Study on the Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Problem Area Identification of High-Quality Urban Development in the Central Region. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongsheng, C.; Deyuan, Z. Spatial and Temporal Differentiation Trends and Attributions of High-quality Development in the Huaihe Eco-Economic Belt. J. Resour. Ecol. 2023, 14, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Xu, L. Dynamic Development Characteristics and Driving Factors of High Quality Development Level in China’s Five Major Urban Agglomerations. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of coupling coordination between urban resilience and high-quality development in Yangtze River Delta Area, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, B. Valuation and Obstacle Factors of High-quality Development in Coastal Cities along the Yangtze River. Ocean & Coastal Management 2023, 244, 106818. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Han, R.; Zhao, M. Evaluation and Impact Mechanism of High-Quality Development in China’s Coastal Provinces. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2023, 20, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, R.; Zhao, M. Evaluation and Impact Mechanism of High-Quality Development in China’s Coastal Provinces. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2023, 20, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, C.; Jiang, T.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Song, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Measurement of Coupling Coordination Degree and Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the Social Economy and Ecological Environment in the Chengdu–Chongqing Urban Agglomeration under High-Quality Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao-Sheng, L.; Yu-Ling, L.; Rafique, M.Z.; Asl, M.G. The effect of fiscal decentralization, environmental regulation, and economic development on haze pollution: empirical evidence for 270 Chinese cities during 2007–2016. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 20318–20332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primary Indicators |
Secondary Indicators |
Tertiary Indicators | Unit | Indicator Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovation | Innovationinput | Number of R&D person A1 | person | + |
| R&D expenditure A2 | million yuan | + | ||
| Innovationoutput | The gross output value of large and medium-sized industrial enterprises A3 | billion yuan | + | |
| Number of patent applications received A4 | Individual | + | ||
| Coordination | Urban-rural coordination | The difference in per capita disposable income between urban and rural areas A5 | - | - |
| The difference between urban and rural per capita living consumption expenditure A6 | - | - | ||
| Economic and Social Coordination | The proportion of social security and employment expenditure to fiscal expenditure A7 | - | + | |
| Urban registered unemployment rate A8 | % | - | ||
| Greenness | Resource and energy consumption | Energy consumption per unit of GDP A19 | tons of standard coal per ten thousand Yuan | - |
| Electricity consumption per unit of GDP A10 | million hours/yuan | - | ||
| Ecological environment | Greening coverage rate of built-up area A11 | % | + | |
| Green Life | Public vehicles per 10,000 people A12 | Standard Vehicles per 10,000 individuals | + | |
| Urban sewage treatment rate A13 | % | + | ||
| Openness | Trade Openness | Total import/export/GDP A14 | - | + |
| Openness of Investment | Number of foreign-invested enterprises at the end of the year A15 | individual | + | |
| Foreign-invested enterprises’ total investment of A16 | million dollars | + | ||
| Sharing | Economic Achievement | GDP per capita A17 | % | + |
| General public service expenditure A18 | million yuan | + | ||
| Per capita education expenditure A19 | million yuan per individual | + | ||
| Social Achievements | Tertiary education per 100,000 individuals A20 | per 100,000 individuals | + | |
| Health technicians per 10,000 individuals A21 | per 10,000 individuals | + |
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cities | Score | Rank | Score | Rank | Score | Rank | Score | Rank | Score | Rank | Score | Rank | Score | Rank |
| Beijing | 0.405 | 6 | 0.5564 | 3 | 0.5152 | 3 | 0.4995 | 3 | 0.5075 | 3 | 0.4714 | 4 | 0.4537 | 3 |
| Tian jin | 0.3192 | 7 | 0.3401 | 7 | 0.2958 | 7 | 0.2717 | 7 | 0.2443 | 8 | 0.232 | 11 | 0.2638 | 8 |
| Hebei | 0.1974 | 17 | 0.1884 | 17 | 0.1888 | 17 | 0.1897 | 17 | 0.1869 | 17 | 0.2012 | 18 | 0.1942 | 18 |
| Shanxi | 0.1368 | 24 | 0.1271 | 25 | 0.1369 | 24 | 0.1366 | 24 | 0.1356 | 25 | 0.1455 | 24 | 0.1702 | 22 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.1517 | 20 | 0.1582 | 20 | 0.1497 | 21 | 0.138 | 23 | 0.1336 | 26 | 0.1379 | 25 | 0.1433 | 25 |
| Liaoning | 0.2501 | 9 | 0.2242 | 11 | 0.2435 | 9 | 0.2295 | 9 | 0.2152 | 14 | 0.2069 | 15 | 0.2157 | 13 |
| Jinlin | 0.1546 | 19 | 0.1572 | 21 | 0.1464 | 22 | 0.1434 | 21 | 0.1371 | 23 | 0.1482 | 23 | 0.158 | 23 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.1397 | 23 | 0.1452 | 23 | 0.1617 | 20 | 0.1482 | 20 | 0.1565 | 19 | 0.1585 | 20 | 0.1778 | 19 |
| Shanghai | 0.5102 | 3 | 0.5558 | 4 | 0.5095 | 4 | 0.4582 | 4 | 0.4433 | 5 | 0.4257 | 5 | 0.4103 | 5 |
| Jiangshu | 0.7074 | 2 | 0.7128 | 2 | 0.6312 | 2 | 0.5982 | 2 | 0.5868 | 2 | 0.5788 | 2 | 0.5713 | 2 |
| Zhejiang | 0.4287 | 5 | 0.4729 | 5 | 0.4423 | 5 | 0.4521 | 5 | 0.4676 | 4 | 0.484 | 3 | 0.4503 | 4 |
| Anhui | 0.23 | 12 | 0.2177 | 12 | 0.215 | 12 | 0.2179 | 12 | 0.2274 | 11 | 0.2472 | 8 | 0.2411 | 10 |
| Fujian | 0.2757 | 8 | 0.2813 | 8 | 0.2581 | 8 | 0.2693 | 8 | 0.2729 | 7 | 0.2737 | 7 | 0.2677 | 7 |
| Jiangxi | 0.16 | 18 | 0.1686 | 18 | 0.1666 | 18 | 0.1645 | 18 | 0.1733 | 18 | 0.1811 | 19 | 0.176 | 20 |
| Shandong | 0.451 | 4 | 0.4393 | 6 | 0.4044 | 6 | 0.3695 | 6 | 0.355 | 6 | 0.3995 | 6 | 0.4081 | 6 |
| Henan | 0.2418 | 10 | 0.24 | 10 | 0.2304 | 11 | 0.2181 | 11 | 0.2156 | 13 | 0.2262 | 13 | 0.2099 | 16 |
| Hubei | 0.2409 | 11 | 0.2543 | 9 | 0.2352 | 10 | 0.2273 | 10 | 0.229 | 10 | 0.2332 | 10 | 0.2371 | 11 |
| Hunan | 0.2069 | 15 | 0.1912 | 16 | 0.1989 | 16 | 0.2068 | 13 | 0.2321 | 9 | 0.2438 | 9 | 0.2289 | 12 |
| Guangdong | 0.7588 | 1 | 0.7595 | 1 | 0.7695 | 1 | 0.7927 | 1 | 0.7864 | 1 | 0.7661 | 1 | 0.7202 | 1 |
| Guangxi | 0.1398 | 22 | 0.1599 | 19 | 0.1617 | 19 | 0.1545 | 19 | 0.1447 | 20 | 0.1569 | 21 | 0.136 | 21 |
| Hainan | 0.143 | 21 | 0.1523 | 22 | 0.1387 | 23 | 0.1346 | 25 | 0.14 | 22 | 0.2301 | 12 | 0.1705 | 9 |
| Chongqing | 0.207 | 14 | 0.2066 | 14 | 0.2056 | 14 | 0.1997 | 16 | 0.2048 | 16 | 0.2016 | 17 | 0.2632 | 15 |
| Sichuan | 0.2085 | 13 | 0.1994 | 15 | 0.2052 | 15 | 0.2042 | 14 | 0.2234 | 12 | 0.2215 | 14 | 0.2128 | 14 |
| Guizhou | 0.1021 | 29 | 0.1154 | 27 | 0.1076 | 28 | 0.1156 | 27 | 0.1233 | 27 | 0.1255 | 27 | 0.2129 | 29 |
| Yunnan | 0.1102 | 25 | 0.1208 | 26 | 0.1282 | 26 | 0.1322 | 26 | 0.1419 | 21 | 0.1499 | 22 | 0.1077 | 24 |
| Shanxi | 0.2004 | 16 | 0.2129 | 13 | 0.2079 | 13 | 0.2022 | 15 | 0.2057 | 15 | 0.2064 | 16 | 0.1447 | 17 |
| Gansu | 0.1028 | 28 | 0.1113 | 28 | 0.0993 | 29 | 0.1004 | 30 | 0.1046 | 30 | 0.1042 | 30 | 0.2029 | 30 |
| Qinghai | 0.0843 | 30 | 0.1006 | 30 | 0.0974 | 30 | 0.1052 | 29 | 0.1179 | 28 | 0.1113 | 29 | 0.1057 | 27 |
| Ningxia | 0.1053 | 27 | 0.1072 | 29 | 0.1156 | 27 | 0.1085 | 28 | 0.1094 | 29 | 0.1118 | 28 | 0.1147 | 28 |
| Xinjiang | 0.1097 | 26 | 0.1392 | 24 | 0.1321 | 25 | 0.1411 | 22 | 0.1363 | 24 | 0.1365 | 26 | 0.1128 | 26 |
| Innovation | Coordination | Greenness | Openness | Sharing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cities | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank | score | rank |
| Beijing | 0.322 | 5 | 0.2595 | 29 | 0.9167 | 1 | 0.2886 | 6 | 0.8409 | 1 |
| Tian jin | 0.0795 | 19 | 0.461 | 13 | 0.5872 | 9 | 0.2279 | 8 | 0.4229 | 6 |
| Hebei | 0.1366 | 13 | 0.453 | 15 | 0.5658 | 13 | 0.0663 | 17 | 0.2021 | 23 |
| Shanxi | 0.087 | 18 | 0.5505 | 7 | 0.5127 | 16 | 0.0317 | 24 | 0.204 | 22 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.0636 | 20 | 0.4278 | 18 | 0.3426 | 29 | 0.0203 | 26 | 0.2672 | 11 |
| Liaoning | 0.1105 | 17 | 0.6134 | 3 | 0.5877 | 8 | 0.1293 | 11 | 0.1805 | 27 |
| Jinlin | 0.0411 | 23 | 0.5564 | 6 | 0.4744 | 19 | 0.0406 | 23 | 0.2282 | 17 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.0327 | 25 | 0.8699 | 1 | 0.5775 | 11 | 0.051 | 21 | 0.1342 | 30 |
| Shanghai | 0.2278 | 8 | 0.4316 | 17 | 0.4384 | 21 | 0.5143 | 2 | 0.5714 | 2 |
| Jiangshu | 0.8069 | 2 | 0.3636 | 23 | 0.6808 | 3 | 0.3574 | 4 | 0.5062 | 3 |
| Zhejiang | 0.5847 | 3 | 0.2878 | 27 | 0.6765 | 4 | 0.2726 | 7 | 0.441 | 4 |
| Anhui | 0.2304 | 7 | 0.6037 | 4 | 0.5819 | 10 | 0.0754 | 14 | 0.1864 | 25 |
| Fujian | 0.2366 | 6 | 0.2862 | 28 | 0.6174 | 7 | 0.1757 | 9 | 0.2884 | 9 |
| Jiangxi | 0.1174 | 16 | 0.458 | 14 | 0.4161 | 23 | 0.0588 | 19 | 0.2271 | 18 |
| Shandong | 0.457 | 4 | 0.3796 | 22 | 0.7374 | 2 | 0.291 | 5 | 0.3459 | 7 |
| Henan | 0.2031 | 10 | 0.4029 | 20 | 0.5124 | 17 | 0.0565 | 20 | 0.2286 | 16 |
| Hubei | 0.224 | 9 | 0.4997 | 9 | 0.507 | 18 | 0.067 | 16 | 0.2808 | 10 |
| Hunan | 0.1927 | 11 | 0.4651 | 12 | 0.6297 | 6 | 0.0689 | 15 | 0.2435 | 15 |
| Guangdong | 1 | 1 | 0.3067 | 26 | 0.4607 | 20 | 0.7571 | 1 | 0.4387 | 5 |
| Guangxi | 0.0477 | 22 | 0.5306 | 8 | 0.4016 | 24 | 0.137 | 10 | 0.1746 | 28 |
| Hainan | 0.002 | 29 | 0.4129 | 19 | 0.6697 | 5 | 0.441 | 3 | 0.1904 | 24 |
| Chongqing | 0.1178 | 15 | 0.6034 | 5 | 0.5659 | 12 | 0.0809 | 13 | 0.2482 | 14 |
| Sichuan | 0.1855 | 12 | 0.4678 | 10 | 0.4177 | 22 | 0.0857 | 12 | 0.2511 | 13 |
| Guizhou | 0.041 | 24 | 0.224 | 30 | 0.3487 | 28 | 0.0184 | 27 | 0.2067 | 21 |
| Yunnan | 0.0505 | 21 | 0.3258 | 25 | 0.517 | 14 | 0.0471 | 22 | 0.2107 | 20 |
| Shanxi | 0.1355 | 14 | 0.3841 | 21 | 0.5128 | 15 | 0.0609 | 18 | 0.3247 | 8 |
| Gansu | 0.0187 | 27 | 0.3472 | 24 | 0.3854 | 25 | 0.0143 | 28 | 0.1676 | 29 |
| Qinghai | 0.0014 | 30 | 0.6231 | 2 | 0.2485 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 0.2189 | 19 |
| Ningxia | 0.0128 | 28 | 0.4658 | 11 | 0.3598 | 27 | 0.0096 | 29 | 0.1849 | 26 |
| Xinjiang | 0.0316 | 26 | 0.4513 | 16 | 0.3681 | 26 | 0.0248 | 25 | 0.2563 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




