1. Introduction
Since 1960s, goat milk products have received widespread attention. Among all kinds of products, goat milk powder is the largest share of the market for goat milk products in China. They are favored by consumers due to the high nutritive value (Shu et al., 2008) and low allergenicity they have (Ballabio et al., 2011). In recent years, the market size of the goat milk products has been expending. However, due to the scarcity of goat milk resources and high production costs, adulteration often exists in goat milk and its dairy products (Di Pinto et al., 2017; Seckin et al., 2017). The most common way of adulteration is through the use of inexpensive and readily available cattle milk (Zhang et al., 2019). Besides, soybean milk is another common adulterant. Such adulteration not only harms consumers’ rights and interests, but also causes a series of problems such as food allergies. The proliferation of adulteration has attracted people’s attention (Gimonkar et al., 2021). Therefore, a number of detection methods for goat milk products have been developed to supervise the adulteration.
Analytical techniques such as electrophoresis (Jamnik et al., 2019), spectral analysis (Mueller-Maatsch et al., 2021), mass spectrometry (Piras et al., 2021), and fingerprinting techniques (He et al., 2023) have been used to analyze the composition of goat milk products. These techniques require a large number of expensive equipments and complicated operation. Immunochromatographic test strips have become a commonly used method for goat milk adulteration detection in market supervision nowadays due to the advantages of easy portability, simple operation, and fast response. However, due to the easy denaturation or cleavage of proteins during the processing of dairy products, the performance of protein-based detection methods is unstablethe protein level detection method is often only applicable to raw goat milk or lightly processed dairy products, and cannot be adapted to the detection needs of a large number of dairy products on the market, such as milk powder.
Nucleic acid detection assays have become the mainstream methods of species identification nowadays because of their advantages of high sensitivity and specificity (Baptista et al., 2021; Chen, 2022). Existing DNA-based methods for the detection of adulteration in goat milk, such as traditional PCR (Mustafa, 2019), DNA-based fluorometric microspheres method (Kounelli & Kalogianni, 2017), high-resolution melting (HRM) (He et al., 2021), and real-time PCR (Deng et al., 2020; Klancnik et al., 2016). Such methods require precision instruments and specialized technicians. The rapid and convenient characteristics of the isothermal detection methods such as Loopmediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) enable them to simplify the detection process while maintaining high sensitivity, realizing rapid on-site detection of goat milk adulteration (Kim & Kim, 2018; Yu et al., 2021), but LAMP containing multiple pairs of primers, making the system more unstable.
CRISPR/Cas, a revolutionary tool for gene editing, was later developed as a rising diagnostic tool (Li et al., 2019). Compared with the existing nucleic acid detection techniques, this method has great potential in developing rapid and accurate on-site detection techniques due to its simplicity of operation, high sensitivity and specificity, and lack of dependence on precision instruments (Li & Li, 2020). Currently, CRISPR/Cas detection technology has achieved better application in the field of medical diagnosis, and has also been gradually applied to the rapid detection of food safety, including genetically modified crops (Liu et al., 2021), meat adulteration (Zhao et al., 2022), the detection of foodborne pathogens (Liu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2020), and so on. Previously, we have established the detection method for adulteration of cattle-derived components in goat milk powder based on CRISPR/Cas12a (Huang et al., 2023). However, a detailed analysis of the products available on the market revealed that soybean-derived components are also common adulterants in goat milk powder. Cattle-derived components and soybean-derived components belong to two different sources, animal and plant respectively, making simultaneous nucleic acid co-extraction challenging, which leads to difficulties in rapid simultaneous detection. At present, there’s few research about dual detection of milk products. Since milk powder contains very little nucleic acid and a large amount of protein, polysaccharide and other impurities, the difficulty of simultaneous detection further increases.
In this study, in order to meet the demand for simultaneously detecting cattle-derived components and soybean-derived components in goat milk powder, a dual detection method was established using CRISPR/Cas12a coupled with recombinant enzyme polymerase amplification (RPA) technology. The specificity, sensitivity and validity of the method were fully evaluated, and the feasibility of the method was demonstrated by blind examination of commercial samples. The establishment of the dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method realizes the simultaneous extraction, amplification and detection of animal and plant DNA, which enables high-throughput and high-efficiency screening of goat milk powder adulterants, and provides a technical reference for food adulteration detection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All primers, ssDNA, and crRNA were synthesized by Genewiz Biotechnology (Suzhou, China). RPA assay kit was bought from TwistDW (Cambridge, UK). DNA isothermal rapid amplification kit was bought from Amp-Future Biotech (Changzhou, China). The Cas12a enzyme was provided by Editgene (Guangzhou, China). RNase inhibitor was obtained from Hai Gene (Harbin, China). NEBuffer 2.1 was acquired from New England Biolabs Inc. (Ipswich, UK). DreamTaq DNA Polymerase was bought from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). The qPCR Probe Master Mix was bought from Vazyme Biotech (Nanjing, China). The cattle milk powder was acquired from Yili company (Hohhot, China). The standard goat milk powder was acquired from Hongxing Meiing Dairy (Weinan, China). The soybean milk powder was acquired from Wuzhou Bingquan Industry. (Wuzhou, China). A total of 55 whole goat milk powder products were collected from Chinese online shopping platforms including Taobao, Pinduoduo, and Tik Tok.
2.2. DNA Extraction
Usually, it is difficult to co-extract nucleic acids from both animal and plant sources. In this study, cattle milk powder and soybean milk powder were respectively mixed into goat milk powder at different mass ratios, and the genomic DNA were extracted by the same method developed from an alkaline decomposition method (Wang et al., 2020), realizing the simultaneous extraction of animal- and plant-derived nucleic acids. The milk powder weighing 4 g was dissolved in 40 ml of saturated NaCl solution and centrifuged at 4500 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was discarded and the precipitate was re-suspended by 1 mL of ddH2O and 200ul of alkaline lysis solution (0.5 mol/L NaOH, 0.1 mol/L Na2EDTA). The solution was placed in a boiling water bath for 5 min and then centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was transferred to a new tube and 2.5 times the volume of anhydrous ethanol was added and shaken for 1 minute. The tubes were placed at 4°C for 30 minutes. The solution was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the supernatant was discarded. The precipitate was re-suspended in 1 ml of 70% ethanol and transferred to a new 1.5 mL tube. The solution was centrifuged at 4°C and 12,000 rpm for 5 min and the supernatant was again discarded. The precipitate was allowed to dry at room temperature for 5 minutes and re-suspended with 50 µL of sterilized ultrapure water. Purified DNA was measured for concentration using a NanoDrop 2000c and stored at -20°C for later use.
2.3. Primer Screening
With reference to the standard method “Technical Regulations for Authenticity Identification of Goat Milk” (NY/T 3050–2016), the endogenous gene of soybean lectin (NM_001354824.1) and cattle mitochondrial DNA (NC_006853.1) were selected as the detection targets. RPA primers were designed using Primer Premier 5.0 software following the instructions of TwistDx® and were initially screened by "Primer-BLAST" tool on NCBI website. Eight pairs of primers for cattle and soybean were designed respectively. The cattle primer pairs and soybean primer pairs were mixed in a 1:1 ratio and the genomic DNA extracted from pure cattle milk powder and soybean milk powder were used as templates for primer screening, according to the RPA reaction system recommended in the instruction manual of the commercial amplification kit. The RPA amplification products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis to screen out the primer pairs with clear and specific amplification bands. Then the primers screened out were tested for their interspecies specificity by using the DNA of cattle, goat, and soybean, respectively.
At the same time, the primers were also examined by a primary CRISPR/Cas12a system, following the instruction manual of Cas12a enzyme. Cattle crRNA and soybean crRNA were mixed by the ratio of 1:1. The RPA products were added into dual CRISPR/Cas12a system and incubated for 30 min. The primer combinations with good specificity and bright fluorescence that observed by the naked eye were finally selected.
2.4. RPA Optimization
In order to improve the reaction efficiency and excite fluorescence signals with the same intensity by the cattle and soybean genomic DNA, the RPA system was optimized. The optimization parameters include primer concentrations of each pair (300 nM, 400 nM, 500 nM, 600 nM), primer ratios (4:3, 3:2, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 2:3, 3:4), dNTPs concentrations (0.8 mM, 1.2 mM, 1.6 mM, 1.8 mM, 2 mM, 2.4 mM), MgOAc concentrations (7 mM, 10.5 mM, 14 mM, 17.5 mM, 21 mM) and amplification time (5 min, 10 min, 15 min, 20 min, 25 min, 30 min). The reaction products were analyzed according to the fluorescence intensity provided by the initial dual CRISPR/Cas12a system.
2.5. Establishment of Dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a Assay
In this study, we used for crRNA corresponding to cattle-derived and soybean-derived targets were designed the online tool Cas-Designer (
http://www.rgenome.net/cas-designer/), and preliminarily screened for their specificity by the "BLAST" tool on the NCBI website. The settled sequences were 5’-UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAUCACAAUCCAGAACUGACAC-3’ for cattle crRNA, and 5’- UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAUCCCAAAUGUGGAUGGGGGGGU-3’ for soybean crRNA. Then the reaction conditions of the CRISPR system were also optimized to achieve equivalent detection efficiency for cattle-derived and soybean-derived ingredients. First, the ratio of cattle crRNA, soybean crRNA was set at 1:1, and a range of Cas12a enzyme concentrations of 50 nM, 75 nM, 100 nM, 125 nM, and 150 nM were tested. Based on the optimal Cas12a enzyme concentration, different ratios of total crRNA to Cas12a enzyme, including 0.5:1, 1:1, 1.5:1, 2:1 and 2.5:1 were optimized. Then the optimal cattle and soybean crRNA ratio in total crRNA was investigated for, 2:1, 3:2, 8:7, 1:1, 7: 8, 2:3 and 1:2.
To carry out the experimental operation, the reaction components of the RPA amplification system were mixed in the tube, and the MgOAc was added to the cap of the tube. The reaction was started by mixing the MgOAC into RPA tube after a slight centrifugation and incubated at 37°C for 20 min. After the RPA reaction was completed, 4 µL of RPA products were added to the CRISPR system, mixed evenly, and placed at 37°C to start the reaction. When the cattle-derived or soybean-derived components present in the samples, the CRIPSR system can produce green fluorescence that visible to the naked eye under a mini BluView Transilluminator (Eastwin Life Sciences, Inc., Beijing, China) at the wavelength of 470 nm. The fluorescence intensity was also immediately captured using QuantStudio 3 Real-Time PCR (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The no-treatment control (NTC) was set by using ddH2O as template, instead of DNA template.
2.6. Specificity and Detectability of Dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a
The DNA from cattle, goat and soybean were used as templates to validate the specificity of the established dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method for the detection of cattle and soybean-derived components. The absolute detectability of the method was tested on diluted cattle and soybean genomic DNA with a concentration gradient from 10 - 6 ng/µL to 100 ng/µL. Meanwhile, a series of goat milk powder models adulterated with different proportions of cattle milk powder or soybean milk power respectively, set at 50%, 20%, 10%, 5%, 1%, and 0.1% (w/w), were used to evaluate the detection limit of the dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method.
2.7. Real Sample Testing and Statistical Analysis
To validate the utility of the established dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method, 55 different goat milk powder products collected from online shopping platforms were analyzed by the dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method. Each assay repeated three times. When the green fluorescence was observed, it indicated the presence of cattle or sobean-derived components in the sample, which will be judged as positive. In contrast, no green fluorescence indicated negative result.
Meanwhile, the fluorescence intensity was read by Real-Time PCR and analyzed by SPSS 21.0 multivariate analysis software (IBM, USA). Unpaired two-tailed t-test was used to compare the experimental group with the control group, and the significance of differences was expressed as p-value. A statistically significant difference at p < 0.05 (*) was considered a valid experiment.
2.8. Method Validation
To validate the accuracy of the established dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a assay, 55 goat milk powder product samples were analyzed by Real-Time PCR at the same time. The accuracy of cattle-derived ingredient detection was validated according to a Chinese Group Standard “Qualitative detection method of cattle (domestic cattle, yak and buffalo) and sheep (goat and sheep) derived components in milk and dairy products (T/CNHFA 002-2022, China)”. When the CT value ≤30, the samples were judged to be positive. When the CT value ≥ 35, the samples were judged to be negative. When 30 < CT value < 35, the experiment was repeated, and the samples were judged positive if the CT value < 35. The accuracy of soybean-derived ingredient was validated following a Chinese National Standard "PCR method for the characterization of standard genes within soybean for the detection of the composition of genetically modified plants and their products". When the Ct value ≤ 36, the sample was judged as positive. When 36 < Ct value < 40, the experiment was repeated. If the result of repeated experiments is still 36 ≤ Ct value ≤ 40, it will be judged as positive. Pure cattle DNA and soybean DNA were used as positive controls. Pure goat DNA and ddH2O were used as negative control and blank control respectively. The experiment was valid when both the internal reference gene test and positive control were positive, and the negative control and blank control were negative. The experimental results were analyzed, plotted and discriminated using QuantStudioTM Design & Analysis software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DNA Extraction
The nucleic acid extraction method for milk powder samples still suffers from the issues of cumbersome operation and the inability to simultaneously extract DNA from both animals and plants. First, the consistency of nucleic acid levels for both species cannot be guaranteed, which may adversely affect subsequent detection. Second, different from simple tissue from animals or plants, the dairy products usually have low nucleic acid content and high levels of impurities that increased the difficulty of extraction. Therefore, in this study, we have improved the extraction method based on the common alkaline lysis method. During the sample pretreatment, milk powder was dissolved using a saturated NaCl solution and centrifuged to remove a large amount of impurities. The high salt condition made plenty of milk proteins out of the solution, leaving only a small amount of insoluble protein impurities with high density. After alkaline lysis process, the DNA was further purified by 70% ethanol conditions, forming flocculent precipitates. This method selectively removed most impurities from the milk powder through a simple one-step operation, thereby simplified the cumbersome sample pretreatment steps and reduced the loss of DNA. The resulting DNA levels after simultaneous extraction were similar, with a final concentration of 96 ng/µL for cattle DNA and 115 ng/µL for soybean DNA.
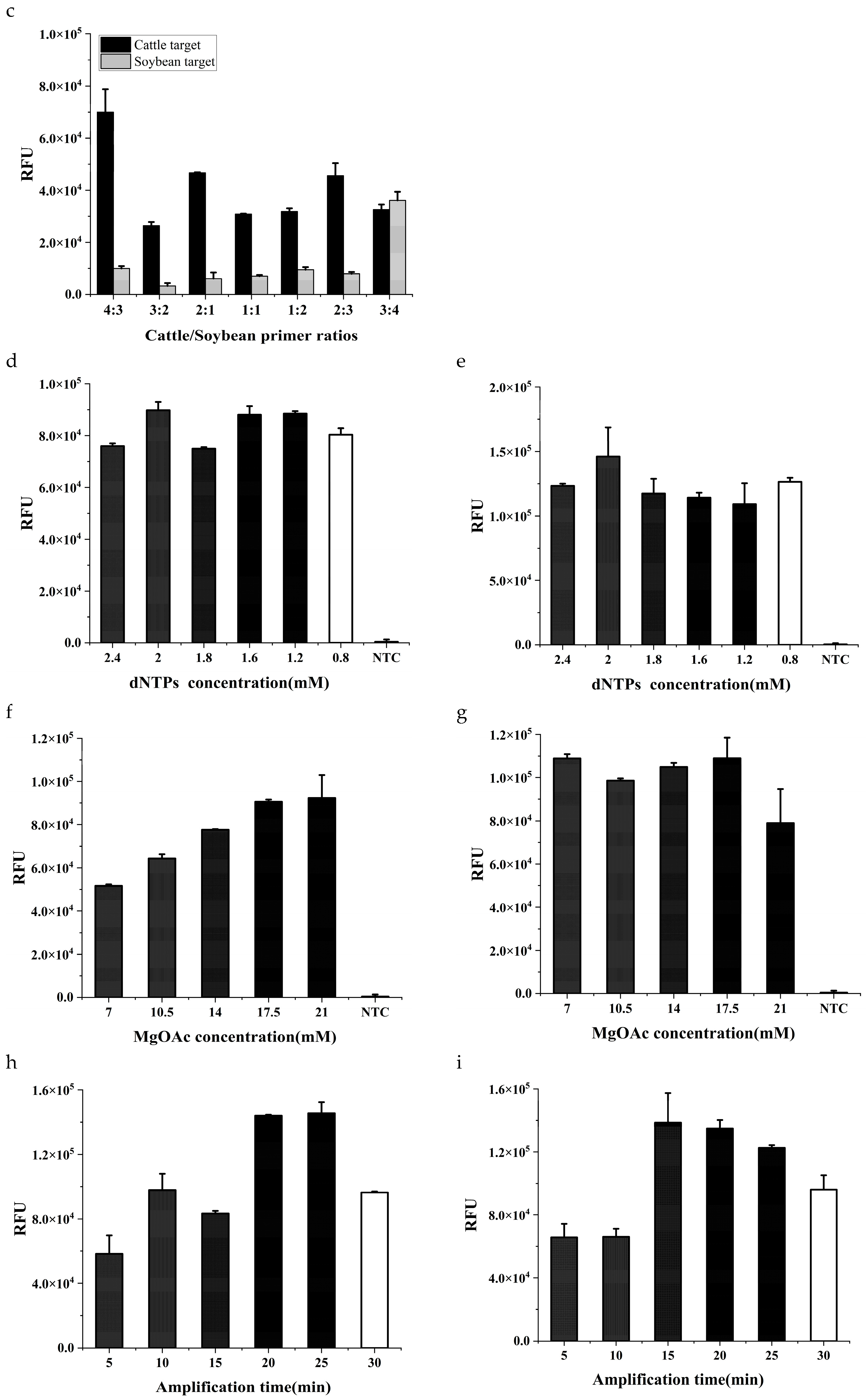
3.2. Primer Screening and RPA Optimization
RPA amplification primer combinations were screened from four cattle primer pairs and three soybean primer pairs. One combination containing two pairs of primers could meet the need for efficient amplification of cattle- and soybean-derived components at the same time (
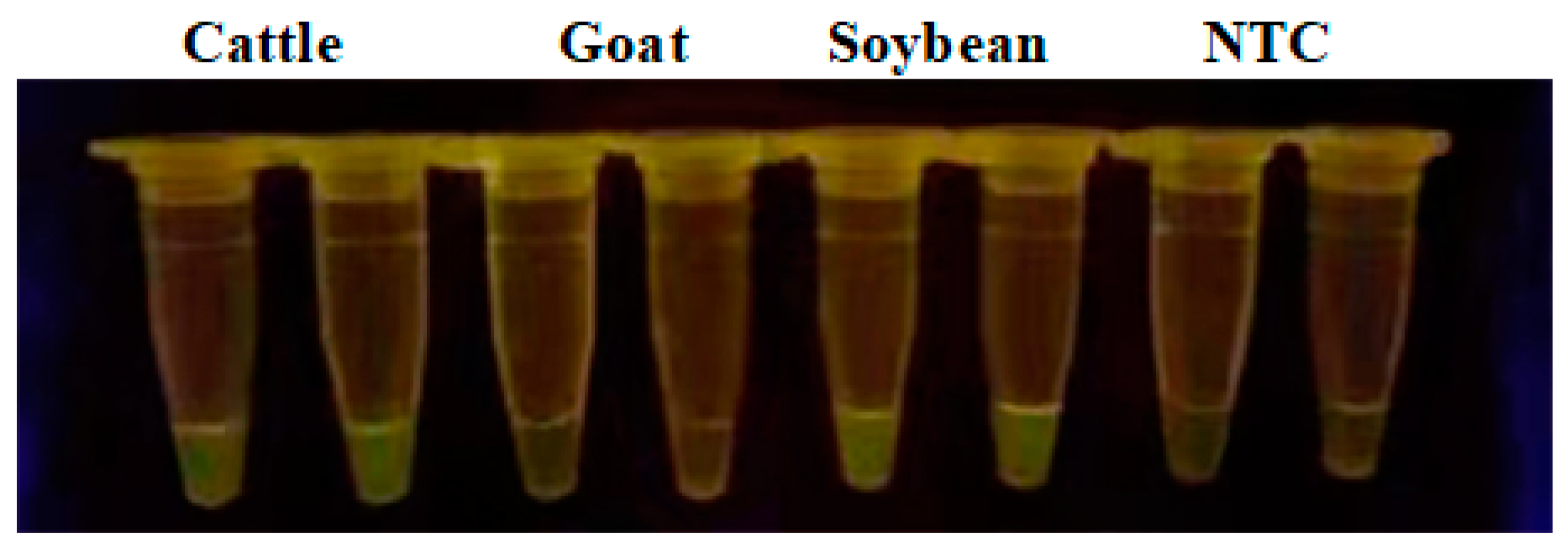
Figure S1). The specificity of primer combinations was examined among cattle, goat and soybean and the results showed good specificity (
Figure 1). It showed that both cattle and soybean were able to emit green fluorescence, while no fluorescence was produced in goat. The final cattle forward primer is 5’-GGGTTACGAGAGGGAGACCTAAAATTACAG-3’ and the reverse primer is 5’-GCTTGGGAATAGTACGATGCCGCAACTAGA-3’. The soybean forward primer is 5’-ACGCTATTGTGACCTCCTCGGGAAAGTTAC-3’ and the reverse primer is 5’-AGATAACCTGCATGTGTTTGTGGGCTTAGTG-3’.
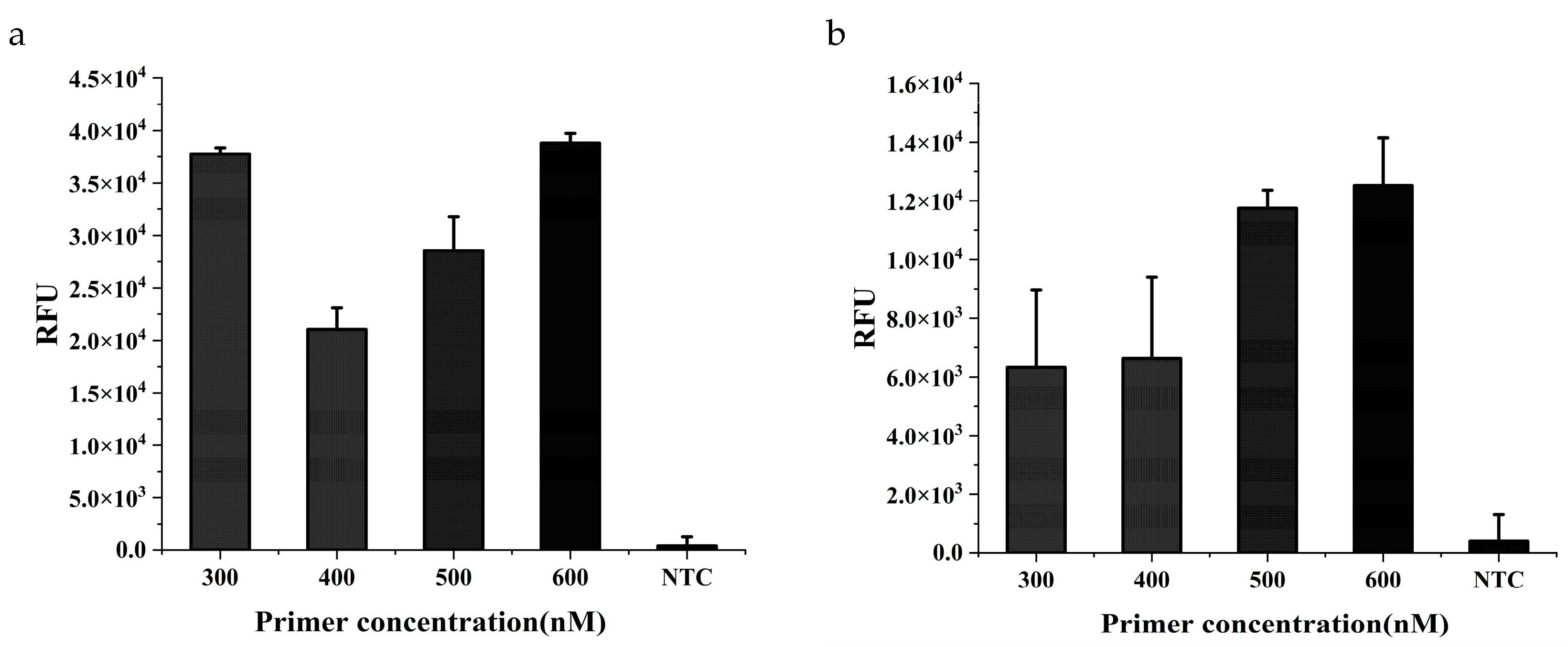
The appropriate concentration was first explored separately for cattle and soybean primers. The results showed that the amplification efficiency was highest for both target when the
respective primer concentration was 600 nM (
Figure 2a,b). In the dual RPA amplification, two primer pairs need to compete with each other for important components such as enzymes, dNTPs, MgOAc, and one often inhibits the other. In order to ensure that the amplification efficiency can be consistent for both components in the same system, the ratio between cattle and soybean primers were optimized subsequently. The amplification efficiency of the two targets was basically the same when the primer ratio between cattle and soybean was 3:4 (
Figure 2c).
Some other factors including dNTPs, MgOAc and amplification time were also investigated. The amplification efficiency fluctuated slightly with the change of dNTPs concentration (
Figure 2d,e), and the optimal concentration was 2 mM for both components. MgOAc provides energy to initiate the reaction process in RPA amplification. The reaction efficiency increased gradually with the increase of MgOAc concentration for cattle components (
Figure 2f), while varied indeterminately for soybean components (
Figure 2g). When the MgOAc concentration was 17.5 mM, the amplification efficiency for both targets was at a high level. As the RPA amplification proceeded, the amplification products continued to accumulate. However, the fluorescence intensity gradually decreases with time in the later stages, which may be due to the quenching of the probe caused by the long reaction time (
Figure 2h,i). When the RPA amplification time was 20 min, the dual system had reached a high level of RPA amplification for both targets. The final reaction mixture contained 1200 nM primers in total (cattle: soybean = 3:4), 2 mM dNTPs, 17.5 mM MgOAc, 2 µL DNA template, 10 µL 2×Reaction Buffer, 2 µL 10×Basic E-mix, 1 µL 20×Core reaction Mix. The reaction was carried out at a constant temperature of 37°C for 20 min.
3.3. Establishment of Dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a Method
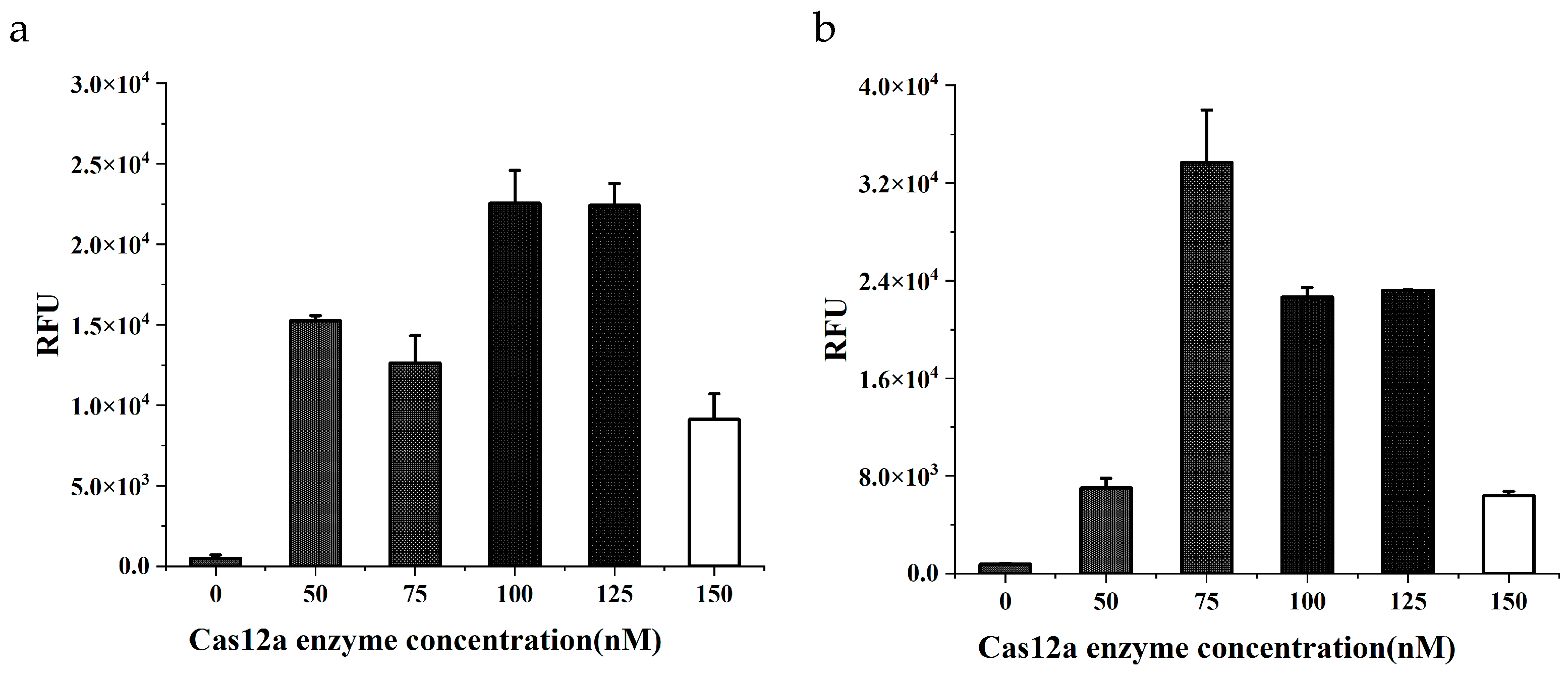
In the CRISPR/Cas12a system, Cas12a, crRNA, and target DNA form a ternary complex to activate the reaction. The concentration of Cas12a directly affects the reaction rate. As the Cas12a enzyme concentration increased, the fluorescence intensity first increased and then decreased. Maximum intensity was achieved at 100 nM and 75 nM Cas12a concentration for cattle-derived and soybean-derived components, respectively (
Figure 3a,b). After a comprehensive comparison of the fluorescence intensity, the final Cas12a concentration of 100 nM was selected.
Based on the optimal concentration of Cas12a, the crRNA/Cas12a ratio was investigated. The effects of crRNA/Cas12a ratios were different for cattle and soybean targets (
Figure 3c,d). It may be related to crRNA design. Different crRNA have different efficiency and specificity to bind Cas12a, as well as paring with target DNA. For the consideration of balancing the reaction efficiency, the final crRNA/Cas12a ratio of 1.5:1 was chosen. Since there are two crRNAs in the dual system, changing the ratio between the two crRNAs will also change the ratio of a single crRNA to the Cas12a enzyme, which will simultaneously affect the efficiency of the CRISPR reaction and the consistency of the detection results of cattle- and soybean-derived components. In this study, when the assay was performed on cattle-derived components, the reaction efficiency declined generally as the cattle crRNA percentage decreased. However, when the soybean-derived components were detected, the relationship between reaction efficiency and soybean crRNA percentage showed a weak correlation. In the end, the ratio of cattle crRNA to soybean crRNA was selected as 7:8 to keep good consistency in the detection (
Figure 3e). The optimal Cas12a enzyme reaction system is consisted of 100 nM Cas12a, 70 nM cattle crRNA, 80 nM soybean crRNA, 500 nM reporter gene ssDNA, 0.8 U RNase inhibitor, 2.5 µL of 10 × NEBuffer 2.1, 4 µL of DNA template, and was supplemented with sterile water to a total volume of 20 µL. The optimal dual CRISPR/Cas12a system can produce enough visible green fluorescence under the blue light within 20 min. Thus the whole dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a detection can be completed in 40 min under a constant temperature of 37°C.
3.4. The Specificity and Sensitivity of Dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a Method
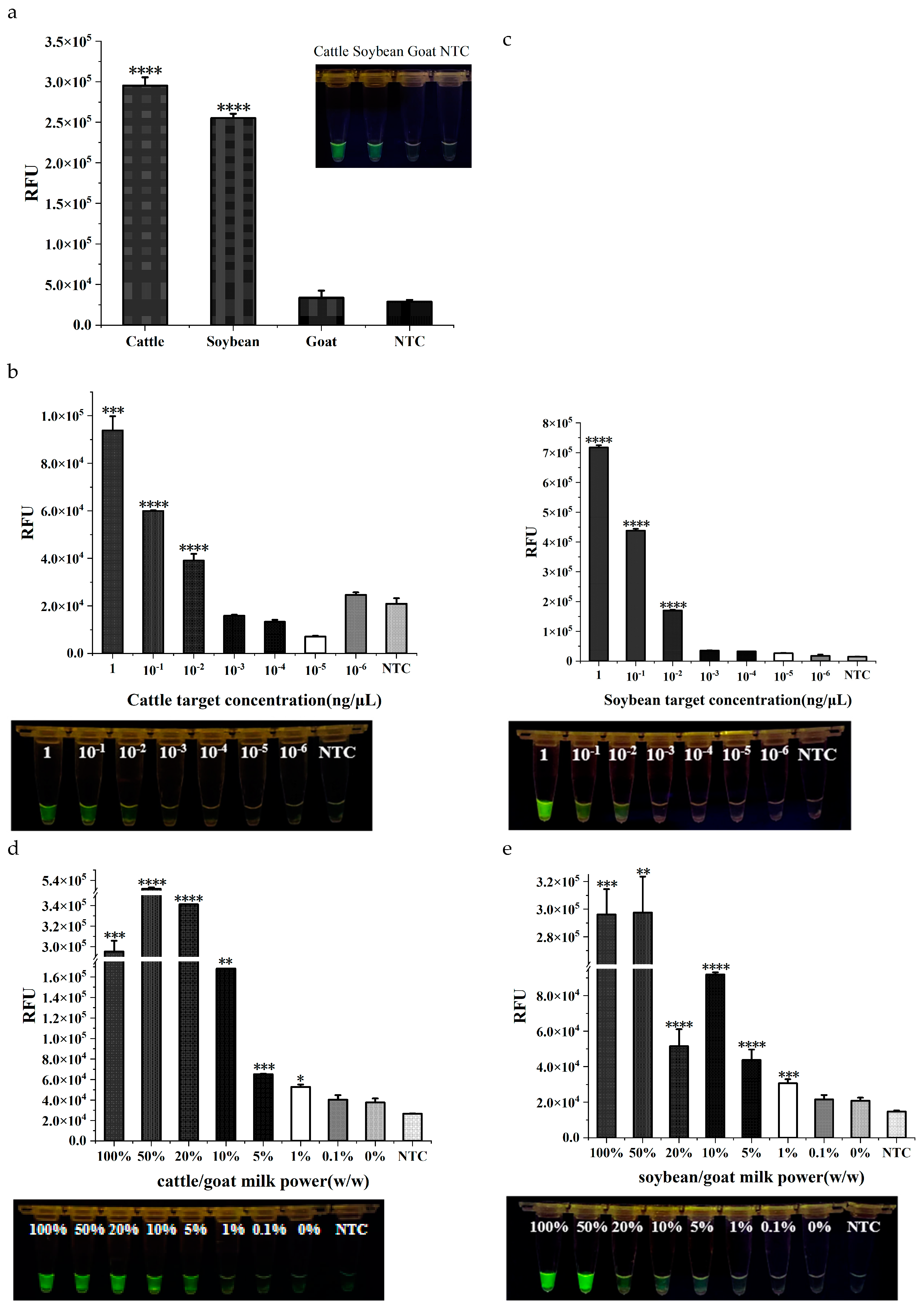
DNA from cattle, goat, and soybean were selected as templates to verify the specificity of the dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method. The experimental results showed that cattle or soybean DNA was able to activate Cas12a enzyme and emit visible fluorescence (
Figure 4a), whereas there was no significant difference between goat and the blank control. It proved that the dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method established in this study could differentiate cattle-derived and soybean-derived components from goat.
The detectability of the dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a method was identified from two levels. On one hand, absolute sensitivity was tested at genomic DNA level. When the concentration of both cattle and soybean genomic DNA was ≥10
-2 ng/μL, green fluorescence could be observed by the naked eye, which was consistent with the results of statistical analysis (P < 0.001 for cattle DNA and P < 0.0001 for soybean). When the DNA concentration was <10
-2 ng/μL, the fluorescence produced was not significantly different from the blank group. The dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a rapid assay had the same level of sensitivity for the detection of cattle- and soybean-derived components (
Figure 4b,c). On the other hand, different proportions of cattle milk or soybean milk powder were mixed with goat milk powder to determine the detection limit of adulteration level. From the fluorescence value analysis, the detection limits of both cattle and soybean were at 1%. To the naked eye, significant fluoresce produced by cattle and soybean ingredients can be observed at 5% adulteration ratio. In general, real adulteration is not too low for the pursuit of economic gain. Therefore, naked-eye observation will be enough for the practical detection (
Figure 4d,e).
3.5. Real Sample Testing
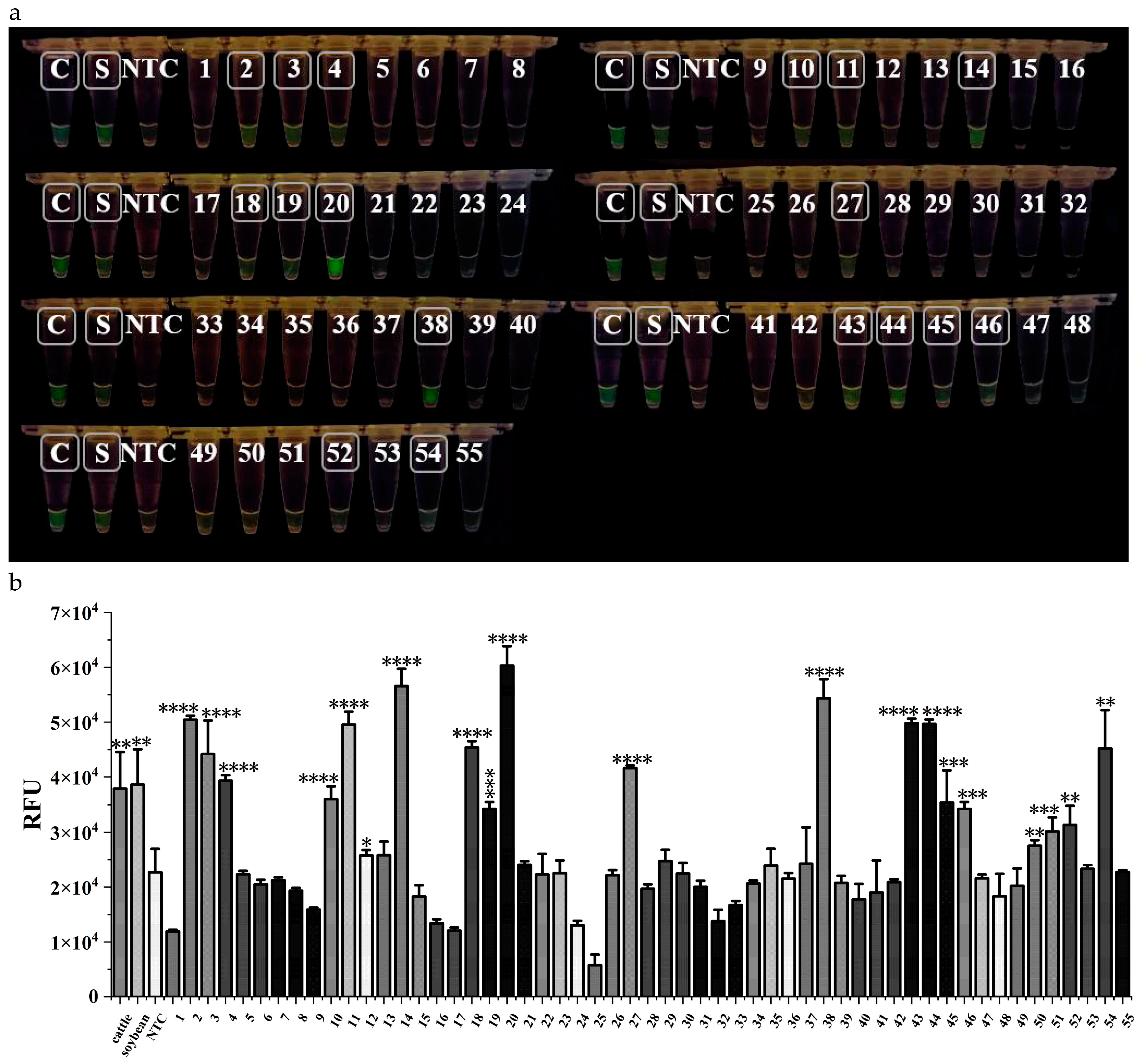
Fifty-five commercially available goat milk powder products were purchased to validate the feasibility of the established dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a rapid assay. The results showed that 17 samples produced green fluorescence visible to the naked eye (
Figure 5a), consistent with the statistical analysis of the data (
Figure 5b). Besides, samples No. 12, No. 50, and No. 51 were also judged positive from the fluorescence values. The test results showed that among 55 goat milk powder products on the market, a total of 20 samples were adulterated, accounting for 36.36% of the total samples. In other reports in China, 2-3 out of 10 goat milk powder samples were found to contain cattle-derived ingredients (Ma, 2019; Tan, 2020), while our results also include soybean-derived ingredients. Thus, our finding indicates that adulterations in the current goat milk powder market still happened frequently, which should be noticed by the regulators.
3.6. Method Validation
The method validation for adulteration of cattle-derived components in goat milk powder was carried out based on the qPCR method in the Group Standard (T/CNHFA 002-2022) (Huang et al., 2023). A Chinese National Standard "PCR method for the characterization of standard genes within soybean for the detection of the composition of genetically modified plants and their products" was used to validate the detection results of soybean-derived components. The results showed that 20 out of 55 samples of goat milk powder were adulterated. Compared with the dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a detection method established in this study, the results were consistent. Among the positive samples, 13 samples were adulterated using only cattle-derived ingredients (Huang et al., 2023), 5 samples were adulterated using only soy-derived ingredients, and 2 samples were adulterated using both cattle- and soybean-derived ingredients. No. 12, No. 50, and No. 51 samples, which showed very weak fluorescence in dual RPA-CRISPR/Cas assay, were all adulterated with soybean-derived ingredients. Since the detection limit of the standard method was 0.5 g/kg (equal 0.5‰), which is higher than this dual detection method (1%), it might be due to the low content of soybean-derived ingredients present in the samples, which made the fluorescence indistinguishable. In conclusion, the dual detection method has good accuracy in detecting goat milk powder adulterants.
4. Conclusions
Cattle-derived and soybean-derived ingredients are common adulterants in goat milk powder. However, due to the immaturity of universal DNA extraction methods for animals and plants in dairy products, current research on dual detection methods still extracted DNA separately and relyed on large precision instruments in the laboratory (Fan et al., 2016). This study combines improved sample pretreatment and alkaline lysis method to extract DNA from cattle-derived and soybean-derived ingredients simultaneously, thus realize dual extraction, dual amplification and dual detection of cattle- and soybean-derived components in goat milk powder for the first time, which is very promising for rapid on-site screening.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Yuanjun Wen: conceptualization, methodology, Sofware, validation, writing—original draft preparation. Shuqin Huang: conceptualization, methodology, Sofware, validation. Hongtao Lei: supervision, funding acquisition. Xiangmei Li: formal analysis, visualization. Xing Shen: conceptualization, methodology, validation, visualization, resources, project administration, funding acquisition.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Scientific Foundation of China (32361133553) and the National Key Research and Development Program of the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan (2023YFF1104701).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that they have no conflicts of interest with respect to the work described in this manuscript.
References
- Ballabio, C.; Chessa, S.; Rignanese, D.; Gigliotti, C.; Pagnacco, G.; Terracciano, L.; Fiocchi, A.; Restani, P.; Caroli, A.M. Goat milk allergenicity as a function of αs1-casein genetic polymorphism. Journal of Dairy Science 2011, 94, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, M.; Cunha, J.T.; Domingues, L. Dna-based approaches for dairy products authentication: a review and perspectives. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 109, 386–397. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A. Research Progress on Qualitative Discrimination Technology of Food Authenticity Based on Amplification Detection of Species-Specific Single DNA Marker. Agricultural Products Quality and Safety 2022, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Li, A.; Gao, Y.; Shen, T.; Yue, H.; Miao, J.; Li, R.; Yang, J. Detection of the cattle milk adulterated in camel, horse, and goat milk using duplex pcr. Food Analytical Methods 2020, 13, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pinto, A.; Terio, V.; Marchetti, P.; Bottaro, M.; Mottola, A.; Bozzo, G.; Bonerba, E.; Ceci, E.; Tantillo, G. Dna-based approach for species identification of goat-milk products. Food Chemistry 2017, 229, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Bian, R.; Huo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Bu, X. Establishment of a Multiple Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Method for Detecting Cattle Milk and Soybean Components in Goat Milk. Shandong Agricultural Sciences 2016, 48, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gimonkar, S.; Van Fleet, E.E.; Boys, K.A. 2021. Dairy product fraud: Elsevier. p 249-279.
- He, X.; Ma, X.; Xu, Q. PCR High-Resolution Melting Detection Method for Differentiating Cattle and Sheep Milk. Food and Fermentation Industries 2021, 47, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wan, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. Rapid detection of adulteration of goat milk and goat infant formulas using near-infrared spectroscopy fingerprints. International Dairy Journal 2023, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gai, Z.; Lei, H.; Shen, X. A rapid rpa-crispr/cas12a detection method for adulteration of goat milk powder. Foods 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnik, P.; Volk, H.; Ogrinc, N.; Jersek, B. Potential of cattle kappa - casein as biomarker for detection of adulteration of goat’s milk with cattle’s milk. Mljekarstvo 2019, 69, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, H. Direct duplex real-time loop mediated isothermal amplification assay for the simultaneous detection of cattle and goat species origin of milk and yogurt products for field use. Food Chemistry 2018, 246, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klancnik, A.; Toplak, N.; Kovac, M.; Ogrinc, N.; Jersek, B. Robust pcr-based method for quantification of cattle milk in cheeses made from caprine and ovine milk. International Journal of Dairy Technology 2016, 69, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounelli, M.L.; Kalogianni, D.P. A sensitive dna-based fluorometric method for milk authenticity of dairy products based on spectrally distinct microspheres. European Food Research and Technology 2017, 243, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W. Research Progress on CRISPR-Cas Biosensors. Biotechnology Advances 2019, 9, 579–591. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, J. Crispr bioanalytical chemistry technology. Progress in Chemistry 2020, 32, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Tang, X. Rpa-cas12a-fs: a frontline nucleic acid rapid detection system for food safety based on crispr-cas12a combined with recombinase polymerase amplification. Food Chemistry 2021, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H.; Shen, X. Development of rapid and easy detection of salmonella in food matrics using rpa-crispr/cas12a method. Lwt-Food Science and Technology 2022, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma X. (2019). Study on PCR High-Resolution Melting Detection Method for cattle and Ovine-Derived
Components in Milk and Dairy Products [Shaanxi University of Science and Technology].
- Mueller-Maatsch, J.; Alewijn, M.; Wijtten, M.; Weesepoel, Y. Detecting fraudulent additions in skimmed milk powder using a portable, hyphenated, optical multi-sensor approach in combination with one-class classification. Food Control 2021, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, J.Y. Using species-specific polymerase chain reaction technique for detection of cattles, buffallos, seeps and goats milk and cheeses in basra city. Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development 2019, 10, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Parkash, S.; Jenness, R. 1968. The composition and characteristics of goats’ milk: a review.
- Piras, C.; Hale, O.J.; Reynolds, C.K.; Jones, A.K.; Taylor, N.; Morris, M.; Cramer, R. Speciation and milk adulteration analysis by rapid ambient liquid maldi mass spectrometry profiling using machine learning. Scientific Reports 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckin, A.K.; Yilmaz, B.; Tosun, H. Real-time pcr is a potential tool to determine the origin of milk used in cheese production. Lwt-Food Science and Technology 2017, 77, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Chen, H.; Lv, J.; Zhang, L. Comparison of Physicochemical Properties of Sheep Milk and Goat Milk. Food Industry Science and Technology 2008, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, T. 2020. Study on On-Site LAMP Detection Method for cattle and Ovine-Derived Components in Milk and Dairy Products [Shaanxi University of Science and Technology].
- Wang, Y.; Ke, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Ding, X. A one-pot toolbox based on cas12a/crrna enables rapid foodborne pathogen detection at attomolar level. Acs Sensors 2020, 5, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Yu, W.; Chen, A. A Study on a Rapid Genomic DNA Extraction Method Suitable for Dairy Products. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection 2020, 11, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, L.; Xie, R.; Zhang, J.; Bian, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A. Multiple authentications of high-value milk by centrifugal microfluidic chip-based real-time fluorescent lamp. Food Chemistry 2021, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, L.; Dang, G.; Liu, Y. Research Progress on Adulteration Detection Technology of Sheep Milk Products. China Dairy Industry 2019, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, C.; Xie, P.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Xian, Y.; Lei, H.; Shen, X. Alkaline lysis-recombinase polymerase amplification combined with crispr/cas12a assay for the ultrafast visual identification of pork in meat products. Food Chemistry 2022, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).