1. Introduction
The nest is an indispensable prerequisite for avian reproduction, and its characteristics to some extent reflect the parental investment in energy and provisioning during the breeding process [
1]. As a specialized site for avian reproductive activities, a high-quality nest in an appropriate location not only provides birds with suitable habitat, abundant food resources, water sources, and favorable climatic conditions throughout the breeding season [
2,
3], but also effectively mitigates adverse weather conditions, reduces predation rates, and minimizes human disturbances [
4,
5], thereby ensuring optimal growth and development of eggs and chicks while enhancing reproductive success rate [
6].
Research on avian nest site selection involves analyzing the ecological factors both within the nest itself and its surrounding environment, to uncover the reasons behind birds' choice of nesting sites [
7]. Nest site selection is critical for bird survival and reproduction as it directly affects breeding success rate in a given year [
8,
9] and indirectly influences population size and growth rate [
10]. Parent birds have two ways of selecting nest sites: through joint decision-making or individual choices made by male or female. This process is influenced by various factors including vegetation type, availability of food and water resources, predator abundance, as well as levels of human disturbance. Nest site selection not only requires suitable microclimatic conditions for embryo development and chick rearing (such as temperature, light exposure) but also aims to minimize predation risk [
11]. For instance, studies conducted by Zhao Shanshan et al. revealed that vegetation status, food resources, and human disturbance emerged as crucial factors constraining the selection of nesting sites by Grey Heron [
12,
13]. In contrast, Daurian Redstart in Northeast China exhibited a preference for constructing nests near villages,with frequent human activities to mitigate predation risk through increased canopy cover above their nests and reduced entrance size [
14]. Understanding the patterns of nest site selection among protected bird species can provide valuable insights into the ecological factors, which influencing their reproductive processes and specific requirements. This knowledge holds significant implications for effective conservation efforts targeting avian resources and habitat management practices [
15].
The Giant Babax (
Pterorhinus waddelli) is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Garrulacinae family in Passeriformes. It has an average length of 31-34cm and is endemic to China. Classified as a Near Threatened (NT) species by the IUCN [
16], it was listed in the “Catalogue of Terrestrial Wildlife Species with National Protection, Beneficial or Important Economic, and Scientific Research Value" in 2000y [
17]. In 2021y, it received second-level protection status from the Chinese government [
18]. This species primarily inhabits low shrubs at high altitudes from 2800-4600 m throughout the year in southern and southeastern regions of Tibet [
19,
20]. The species demonstrates remarkable adaptation to arid and frigid alpine climates, making it a prominent example of cooperative breeding birds on Tibetan Plateau [
21,
22,
23]. Its breeding season spans from May to July, during which it primarily relies on insects(Lepidoptera and Diptera) and plant berries as its main food sources. In winter, its diet predominantly consists of crop seeds, berries, and plant rhizomes [
24]. Presently, research on Giant Babax primarily focuses on reproduction, reproductive behavior, and conservation aspects. The studies on nest site selection provide only fundamental explanations, lacking systematic research of their capacity for adapting to human activities and breeding successful reproduction within the change of ecological environment and intensified human activities.
This study was conducted from March to October in 2023y around Lhasa,selecting four sample sites to investigate the nest characteristics and nest site selection of Giant Babax. Five nest characteristics and thirteen environment factors were collected, aiming to elucidate their influence on nest site selection and reproductive success rate of the Giant Babax. This research provides valuable reference materials for population conservation and ecological environment improvement efforts targeting the Giant Babax.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Study Area
Lhasa is situated in the central-southern part of the Tibet, on the northern bank of the Lhasa River, which is a tributary of the Yarlungzangbu River. Its precise geographical coordinates are 89°45′11"-92°37′22"E and 29°14′26"-31°03′47"N. With an average elevation of 3650 meters, Belongs to the animal boreal region. It exhibits a typical inland plateau temperate semi-arid monsoon climate characterized by abundant sunshine hours and aridity. The mean annual temperature stands at 9.45 ℃, with a maximum temperature reaching 25.9 ℃ and a minimum temperature dropping to -7.9 ℃, leading to significant diurnal temperature fluctuations. Precipitation is limited but concentrated, with an average annual rainfall measuring 539.8 mm and an average annual evaporation amounting to 866 mm. During the breeding season in this region, common bird species include Lanius tephronotus,Garrulax henrici,Streptopelia orientalis, Parus major,Turdus maximus, Upupa epops, Passer montanus and Alauda gulgula et al. For this study, four sampling sites were selected around Lhasa: 1) Sangpu Village at an average altitude of 3960 meters, with a habitat consisting of villages and secondary forests, is characterized by dominant vegetation such as Salix longistamina, Buddleja wardii,Rosa sericea Lindl.,Juglans, and Rhododendron primuliflorum Bur,et al. 2) Nima Tang at an average altitude of 3850 meters, mainly consists of Sea buckthorn forest mixed with shrubs including Hippophae gyantsensis ,Buddleja wardii ,Rosa sericea Lindl., Berberis hemsleyana Ahrendt and Cotoneaster microphyllus Lindl et al. 3) Qinu at an altitude of 3600 meters, features secondary forests adjacent to farmland where Salix longistamina, Betula platyphylla Suk., Populus szechuanica Schneid., Hippophae gyantsensis et al. can be found.4) Xiongse Village, at an average altitude of 4200 meters,the habitat is alpine scrub with main vegetation including Rosa sericea, Berberis lasiophylla, Salix sclerophylla Anderss., and Cotoneaster microphyllus. The four sampling sites are located within a range of 20-55 kilometers from each other.
2.2. Parameter Selection and Measurement Method of Nest Site
In the period from March to October 2023y, a systematic search and tracking methodology was employed to locate Giant Babax nests within designated study sites. Once a nest was discovered, its precise coordinates were recorded using GPS, and appropriate markings and numbering were applied after assessing the condition of nest. Furthermore, infrared cameras were strategically installed within a 1-meter radius of each nest for continuous monitoring purposes. Nest site factors were determined by establishing 10x10 square meter plots centered around each nest for comprehensive data collection and measurements. These factors encompassed: 1. GPS positioning information including longitude, latitude, and altitude. 2. Nesting tree species. 3. Height of nesting trees(m),using a laser rangefinder (XR151098) to calculate distances between observers and both the nesting tree and the top of nesting tree, a2 = c2 - b2. 4. Distance to ground level(m), assessed with precision using a measuring tape. 5. Distance to road(m), accurately determined employing a laser rangefinder.6. Distance to house was measured using a laser rangefinder(m). 7. Distance to water sources was also measured with a laser rangefinder (m). 8. Nest position was categorized as follows: 1=on the main trunk section (cut surface due to sawing off the main trunk); 2=on side branches; 3=at junctions where the main trunk meets side branches. 9. Diameter at breast height of nesting trees was measured using a measuring tape at approximately 1.3 m above ground level [
25]. 10. Canopy closure index of nesting trees was estimated based on the shadow area cast on the ground by these trees. 11. Number of helpers present during breeding activities observed at each nest site. 12. Identification if it is an old or reused nest structure. 13. Parasite presence. The control group data were randomly obtained from 50-100 m in any direction of the nest site. The characteristic information of nests, including inner diameter (cm), outer diameter (cm), nest height (cm), and nest depth (cm), were measured using vernier calipers (15 cm,0.01 mm) and a straight ruler. To minimize disturbance to breeding activities of Giant Babax, only measured the dry weight of six nests for analysis.
2.3. Data Analysis Method
Before conducting data analysis, all continuous variables were standardized using Z-scores to assess normal distribution. T-tests were employed for normally distributed data, while U-tests were utilized for non-normally distributed data. Nest distances were calculated based on nest location information using ArcGIS (10.8.1). Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on the selected factors related to nest sites using R4.3.3.lnk in order to derive principal components and identify major influencing factors. Binomial Logistic Regression Analysis was applied to the nest site data, preceded by outlier tests for variance inflation factor (VIF) to ensure absence of severe collinearity or significant outliers among independent variables; VIF values below 10 and maximum Cook's distance value below 0.5 indicated no serious collinearity or significant outliers respectively. Correlation significance levels of P<0.05, P<0.01, and P<0.001 denoted associations, significant associations, and highly significant associations respectively between variables; breeding success rate was defined as successful nests/total nests where successful nests referred to those that produced at least one fledgling bird while total nests encompassed those that successfully hatched at least one egg [
26]. Descriptive statistics were presented as mean ± standard deviation.
3. Results
3.1. Nest Characteristics and Nest Spacing
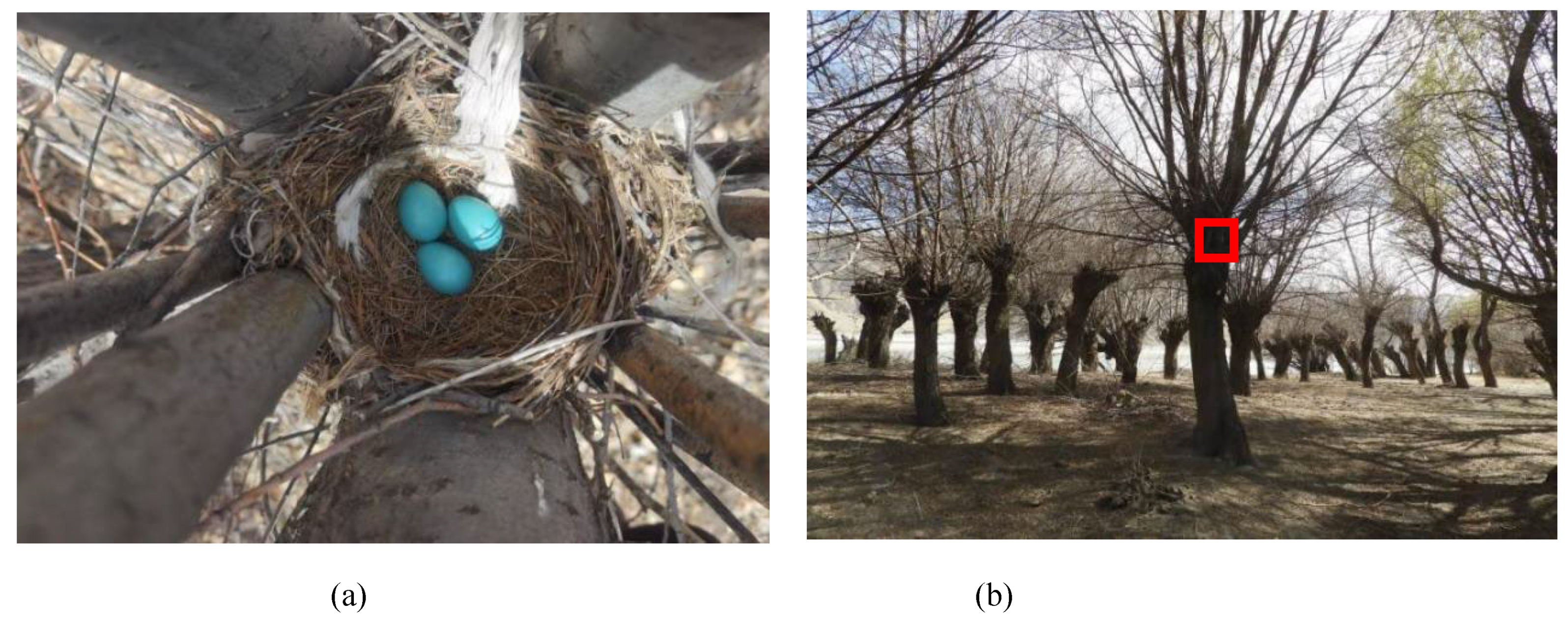
We have collected a total of 34 nest Character data, with an average depth of 7.70±1.47 cm (n=27), a height of 19.58±2.97 cm (n=27), an inner diameter of 10.64±1.73 cm (n=27), and an outer diameter of 24.65±4.8 cm (n=27). The average weight of the nest is 162.3±13.5 g (n=6). The nest of Giant Babax is bowl-shaped, structure comprises two layers, with the intricately woven inner layer predominantly composed of filamentous materials such as aerial roots from herbaceous plants, thin branches from willow trees, and a small amount of animal hair, accounting for approximately 30%. The outer layer exhibits a rougher texture primarily consisting tree branches, leaves, bark, and sturdy grass roots that form the foundational framework for the entire structure's stability and integrity . Occasionally , artificial waste materials like fragments cloth or plastic bags , disposable chopstick packaging , wool or toilet paper are incorporated into its design to embellish the external surface appearance(
Figure 1).
The average nest spacing in the sampled area was 396.93 m, ranging from a minimum distance of 9.73 m to a maximum distance of 1268.94 m. When comparing nest characteristics across the four sampled areas, it was observed that Nima Tang exhibited the largest nests and highest breeding success rate (92.86%, n=14), while Qinu had comparatively smaller nests and lower breeding success rate (64.54%, n=13),
Table 1.
3.2. Nesting Tree Selsection
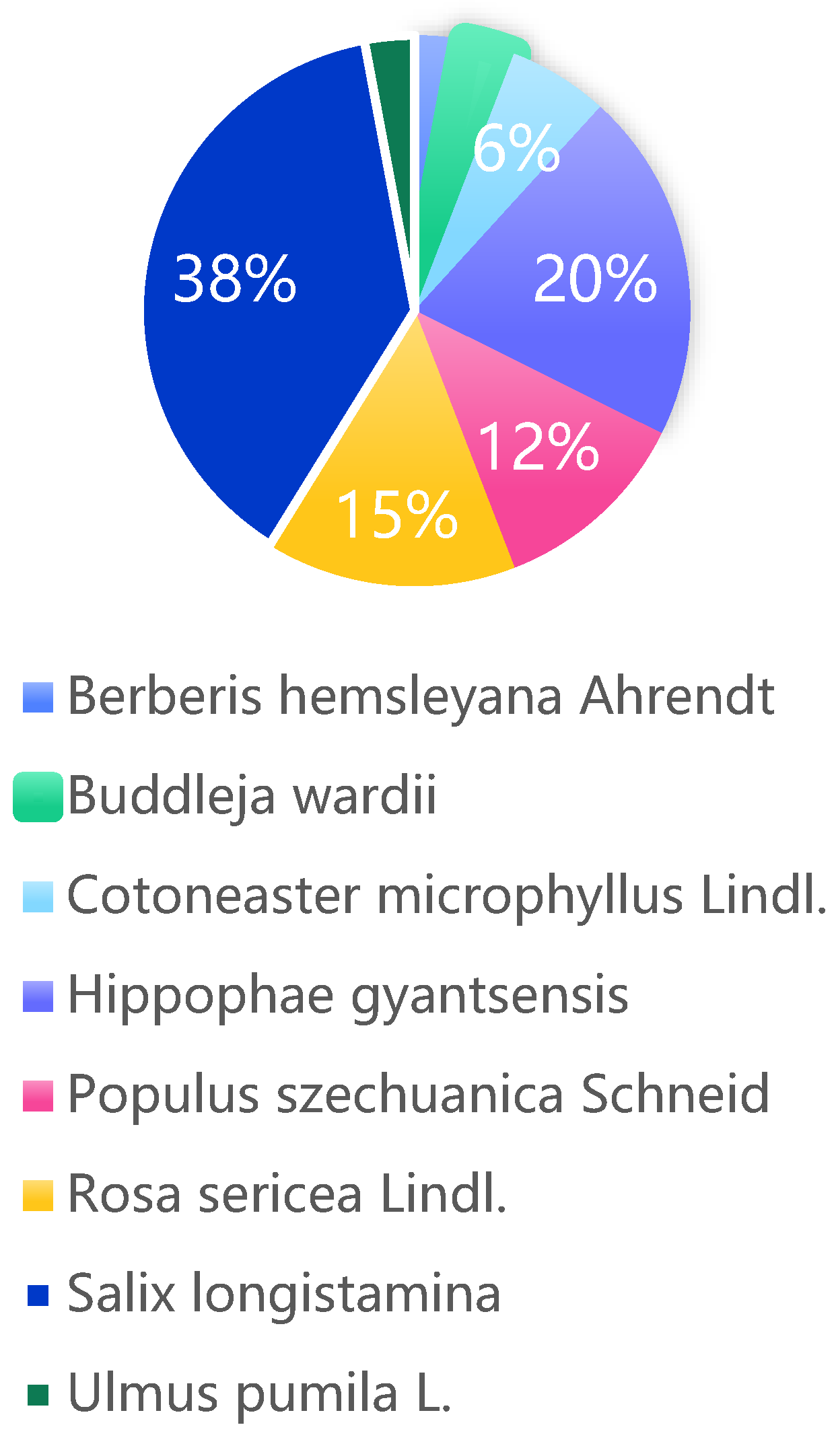
We collected a total of 34 nest site records for Giant Babax, utilizing a diverse range of 8 tree species.Among them, Salix longistamina accounted for 38.24%, Hippophae gyantsensis accounted for 20.59%, Rosa sericeaLindl accounted for 14.71%, Populus szechuanica Schneid. accounted for 11.76%, and Cotoneaster microphyllus Lindl accounted for 5.88%. Buddleja wardii, Berberis hemsleyana Ahrendt, and Elm each represented 2.94% of the utilized tree species (
Figure 2).
3.3. Principal Component Analysis of Nest Site Selection
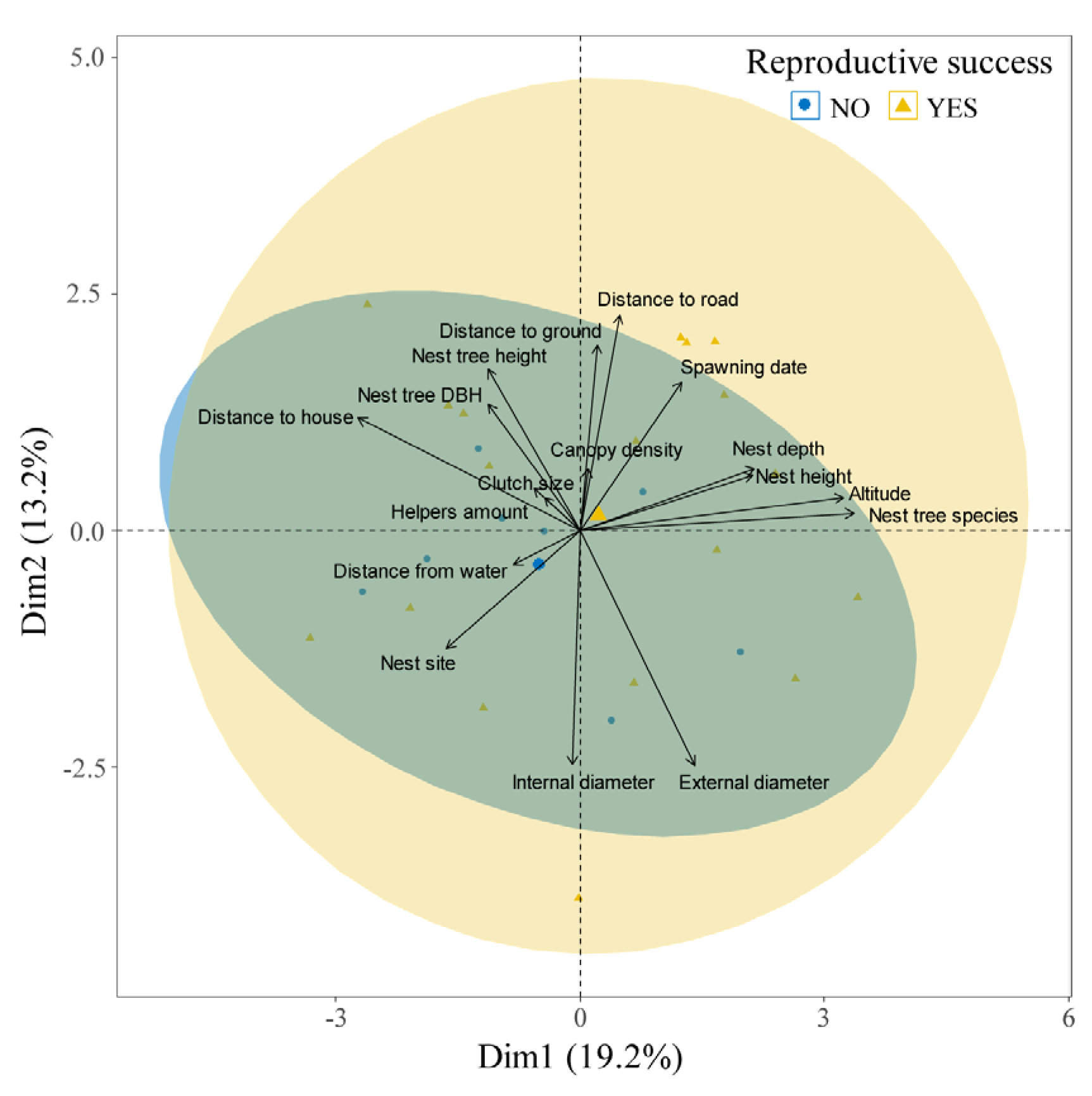
A principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted on a total of 34 nests, considering ten nest site factors including canopy closure, nesting tree DBH, altitude, and distance to houses et al. Four principal components with eigenvalues greater than 1 were identified, accounting for a cumulative contribution rate of 75.52% (
Table 2). These four components encompassed all the information from all nest site factors and were further examined for their correlations with relevant nest site variables. The first principal component exhibited a contribution rate of 27.12% and displayed strong associations with canopy closure, nesting tree height, and number of helpers. The second principal component had a contribution rate of 19.54%, and demonstrated significant relationships with nesting tree species,altitude, and distance to houses. The third principal component had a contribution rate of 14.95%, showing high correlation solely with distance to road. Lastly, the fourth principal component had a contribution rate of 13.91% and revealed stronger correlation with distance to water (
Table 3).
3.4. Nest Site Factors Affecting Reproductive Success of Giant Babax
A breeding success rate of 76.5% was achieved. Utilizing binomial logistic regression analysis, we investigated the nest site factors influencing Giant Babax nest site selection and breeding success rate. The findings revealed a significant positive correlation between canopy density (P=0.00138 **) and nest site selection (
Table 4). Notably, key factors impacting their breeding success rate were identified as canopy density (P=0.0173 *) and helpers amount (P=0.0109 *), as presented in
Table 5. Principal component analysis was conducted on 17 nest site factors, highlighting that major contributors to Giant Babax's breeding success rate included nesting tree species, altitude, distance to houses, nest height, and nest depth (
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Nesting Tree Species
According to research findings, the Giant Babax predominantly utilizes eight types of nesting trees, including Salix longistamina, Salix longistamina,Rosa sericea Lindl., Populus szechuanica Schneid, and Cotoneaster microphyllus Lindl..Approximately 52.94% of nests are constructed on secondary vegetation such as Salix longistamina Populus szechuanica Schneid, and elm. Based on literature records [
22], it is observed that 91.3% of their nests build in natural alpine vegetation like Rosaceae, Berberidaceae, Cotoneaster Medik.,and Salix sclerophylla Andersson in Xiongshui Valley; only a minority select human-planted forests along rivers as their nest sites. These findings indicate a gradual inclination of Giant Babax towards utilizing human-planted secondary forests as part of its adaptive strategy to answer environmental changes and anthropogenic activities.
4.2. The Main Nest Site Factors of Nesting Site Selection of Giant Babax
The findings of this study demonstrate that the primary factors influencing nest site selection include canopy density, nesting tree height, helpers amount, nesting tree species, altitude, distance to houses, distance to roads, and distance to water. Notably, among these factors, the canopy density exerts a particularly significant influence on nest site selection. Further comparison between experimental data and control data, reveals a preference for building nests in habitats characterized by dense and lush trees,distance from human settlements and roadways but in close proximity to water sources. Consequently, we can categorize the main factors influencing into three distinct categories: 1) concealment , Giant Babax exhibit a preference for large trees with abundant foliage that provide effective concealment as nesting sites. This ensures their spatial requirements for nesting while enhancing their ability to evade predators and mitigate environmental pressures such as climate conditions. As a result of these preferences, breeding success rates are improved along with population numbers [
27]. 2.Food and water resources: During the breeding season , abundant caterpillars can be found on the nesting trees such as Salix longistamina and Populus szechuanica Schneid, providing a plentiful source of high-protein food for breeding adults. Additionally, the berries of Hippophae gyantsensism ,Rosa sericea Lindl., and Cotoneaster microphyllus Lindl. serve as significant food resources . Their selection of nesting areas in close proximity to water effectively reduces its foraging and drinking time, allowing parents to invest more time in raising chicks and thereby enhancing reproductive efficiency [
28]. 3.Human disturbance: Human activities play a pivotal role in influencing nest site selection among bird species. Some birds exhibit a preference for constructing nests within human habitats by utilizing man-made structures as nesting sites. For instance, Tree Sparrows [
29], Barn Swallows, and Northern Redstarts [
14] often choose crevices in human buildings as suitable locations for their nests while relying on leftover human food as sustenance. This represents a specific adaptation to human activities. Meadow Buntings have gradually begun building nests in secondary forests established by humans, demonstrating certain adaptability towards anthropogenic influences. However, they still tend to avoid selecting nest sites near roads or houses when choosing locations for their nests; indicating that Giant Babax continue to exhibit avoidance behavior towards human activities.
4.3. Nest Site Factors Affecting Reproductive Success of Giant Babax
Through BLRA and PCA analysis, we identified nesting tree canopy cover and the number of helpers as the primary factors influencing the breeding success rate . Other factors related to nest sites include nesting tree species, altitude, distance to houses, nest height, and nest depth. nesting tree canopy cover directly impacts predator detection likelihood in nesting sites, while a higher number of helpers enhances overall defense capability within the breeding group and reduces predation risk [
30]. The Giant Babax is a typical cooperative breeder found on high plateaus where breeding pairs and helpers maintain a purely cooperative relationship. Breeding responsibilities such as nest building and incubation are shared by both breeders, while helpers assist with chick rearing and defense tasks [
22]. Despite some deceptive behaviors exhibited by helpers during the chick-rearing period, their role in chick rearing and nest defense remains crucial for the entire breeding group [
24,
31].
The nests in Nima Tang exhibited the largest size and highest breeding success rate, while those in Qinu were characterized by smaller size, a higher number of helpers, but the lowest breeding success rate. Based on these findings, it appears that smaller nests and an increased number of helpers have a negative impact on nest breeding success. However, infrared camera monitoring unveiled that nesting failures in Qinu site primarily resulted from predation by grey-backed shrikes,Chinese Grey Shrike, stray cats, and Mountain Weasel. In Sangpu sample site, Oriental Magpie and stray cats were identified as predators , but only twice during monitoring. In Nima Tang sample site, only stray cats were observed as predators; however, due to their feeding habits near temples, there was no evidence suggesting their predation on eggs or chicks of Giant Babax. Therefore, it can be concluded that the main reason for the low breeding success rate in Qinu site is predator abundance rather than nest size or number of helpers. Smaller nests and large number of helpers are strategies employed by Giant Babax to cope with high predation. Smaller nests enhance concealment while a greater number of helpers strengthens their collective ability to defend against enemies as a reproductive team overall thus improving overall breeding success.
4.4. The Threat to the Population Development of Giant Babax
Based on five surveys conducted, only one breeding group and three active groups (with no nests be found) were discovered in the Xiongse Valley. Despite the presence of human observation differences, the result continues to be a cause for concern.it is difficult to dismiss doubts regarding the population of Giant Babax in Xiongse Valley were reductived. As early as 2004y, Lu Xin et al. proposed that the distribution area of Giant Babax primarily concentrated in the Yarlungzangbu River Basin, which also happens to be a region characterized by dense population and rapid economic development in Tibet. The local deforestation activities carried out by residents have resulted in vegetation degradation within shrub forests, posing a significant threat to the growth of Giant Babax populations. The current research results provide preliminary confirmation for this viewpoint. Unfortunately, similar threats are also present in Qinu site where villagers have initiated tree cutting practices targeting species such as Salix longistamina and Populus szechuanica Schneid that exhibit high nest-building rates favored by Giant Babax . Undoubtedly, this poses a substantial hidden risk for ensuring sustained development of Giant Babax populations.
5. Conclusions
After conducting research, it has been determined that the application of artificial secondary forests established by large grasshopper birds exhibits a gradual enhancement in adaptability to human activities. When selecting nesting sites, safety is the foremost consideration. By opting for densely vegetated trees with high canopy cover as nesting trees, the concealment of nests can be heightened, thereby reducing predation rates. Additionally, food and water resources are pivotal factors in nest site selection as they directly impact reproductive efficiency. Lastly, human disturbance remains a significant threat to the growth of large grasshopper bird populations, particularly habitat fragmentation caused by tree felling. Therefore, habitat conservation plays a crucial role in safeguarding large grasshopper birds and necessitates collaborative efforts from government departments, forestry agencies, and scientific research institutions to formulate unified plans that effectively promote sustainable population growth for this species.
In response to various threats encountered, birds exhibit continuous adaptive behaviors. For instance, large grasshopper birds counteract higher predation rates by decreasing nest size and increasing helper numbers. During nest construction measures are implemented to minimize disturbances from human interference by maintaining distance from roads and buildings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Le Yang and Shengling Zhou; methodology, Shengling Zhou and Rui Wang; software, Hui Han and Shengling Zhou; investigation, Zhaoxiang Wang and Huaiming Jin; writing—original draft preparation, Shengling Zhou.; writing—review and editing, Le Yang; visualization, Shengling Zhou;project administration, Shengling Zhou; funding acquisition, Shengling Zhou & Le Yang. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This Research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2022YFC2602500 and Key science and technology R&D projects of Tibet Autonomous Region, grant number XZ202201ZR0021G and XZ202201ZY0005G.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article (and Supplementary Materials).
References
- Neve, L.D.; Soler, J.J. Nest-building activity and laying date influence female reproductive investment In magpies:an experimental study. Animal Behaviour 2002, 63, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.M.; Nol, E. Influence of food abundance, nest-site habitat, and forest fragmentation on breeding ovenbirds. The Auk: Ornithological Advances 1998, 115, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler, D.C.; Haig, S.M. Microclimate and nest-site selection in Micronesian Kingfishers. Pacific Science 2005, 59, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, T.B.; Schmutz, J.A. Lindberg, M.S., et al. Risk of predation and weather events affect nest site selection by sympatric pacific (Gaviapacifica) and Yellow-billed (Gaviaadamsii)loons inarctic habitats. Waterbirds.
- Wysocki, D. Nest site selection in the urban population of blackbirds Turdus merula of Szczecin(NWP oland). Acta Ornithologica 2014, 40, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, Y.M.; Hu, J.C.; et al. Nest Site Selection and Materials of Pycnonotus sinensis in NanchongSichuan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology 2006, 25, 590–593. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Zhao, Q.S.; Liu, C.J.; et al. Giant babaxes mix brood reduction and brood survival strategies. Journal of Ornithology 2012, 153, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badyaev, A.V. Nesting habitat and nesting success of easternwild Turkeys in the Arkansas Ozark Highlands. Cooper Ornithological Society 1995, 97, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Rands, M.R.W. The Effect of Nest Site Selection on Nest Predation in Grey Partridge Perdix perdix andRed-Legged Partridge Alectorisrufa. Ornis Scandinavica 1988, 19, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.D.; Best, L.B. Nest-site selection and reproductive success of Common Yellow throats in managed Iowa grasslands. The Condor:Ornithological Applications 2014, 116, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.Q.; Zheng, G.M. The nest site selection of Tragopan caboti. Acta Zoologica Sinica 1997, 43, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.S.; Chu, Y.F.; Jiang, X.Y.; et al. Nests Characteristics and Nest-site Selection of Ardea cinerea in Xinxiang Yellow River Wetland Birds National Nature Reserve. Henan.Sichuan Journal of Zoology 2018, 37, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.G.; Zhang, L.; et al. The nest site selection of Grey Heron in Kubuqi Desert, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment 2015, 29, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, J.; et al. Nest site selection and breeding success of Daurian redstart Phoenicurus auroreus in northeast China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2020, 40, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.Y.; Guo, S.L.; Dou, Z.L.; et al. Nest-site selection of sand martins (Riparia riparia) in the suburbs of Zhengzhou, Henan Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2016, 36, 7006–7013. [Google Scholar]
- John, M.K. PASSERIFORMES. In Guide to the Birds of China; The Comcial Press: Bieiing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zheng, G.M. Birds. In China’s Red List of Biodiversity: Vertebrates; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021; Volume Ⅱ, p. 410. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese National Forestry and Grassland Administration; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. Chinese Journal of Wildlife 2021, 42, 623. [CrossRef]
- Stattersfield, A.J.; Crosby, M.J.; Long, A.J; et al. Endemic Bird Areas of the World: Priority for Biodiversity Conservation; Bird Life International: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.X.; Zheng, B.L.; Long, Z.Y. Fauna Sinica, Timaliinae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.Y.; Gao, L.F.; Wang, Q.; et al. Giant babax(Babaxwaddelli) helpers cheat at provisioning nestlings in poor conditions. Behavioral Ecologyand Sociobiology 2023, 77, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X. Concervation status and reproductive ecology of giant babax Babaxvaddelli (Aves, timaliinae)Endemic to the Tibet plateau. Oryx 2004, 38, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X. Leiothrichidae. The birds in Tibetan Plateau of China; Hunan Science Press: Changsha, China, 2018; pp. 603–604. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, H.B.; Lu, T.S.; et al. Study on the Characteristics of Temperature Changes in Lhasa City over the Past 49 Years. Earth and Environment 2021, 49, 492–503. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.X.; Sui, J.L.; Ma, Q. Influencing Factors Analysis of Nest Site Selection and Reproductive Efficiency of Chinese Sparrowhawk. Scientia Silvae sinicae 2020, 56, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, D.W. The Breeding of the blackbirds, song thrush and mistle thrush in Great Britain PartII. Clutch-Size. Bird Study 1955, 2, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Borgmann, K.L.; Conway, C.J. The nest-concealment hypothesis: New insights from a comparative analysis. The Wilson Journal of Ornithology 2015, 127, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Yu, L.; Bai, J.; et al. Nest Characteristics and Nest Site Selection of Tetraophasis obscurus in the Wanglang National Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.P.; Zheng, G.M.; Xu, J.L. Habitat use of urban tree sparrows in the process of urbanization: Beijing as a case study. Biodiversity Science 2006, 14, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ma, X.; Fan, L. Nesting and Cooperative Breeding Behaviours of High-Altitude Babbler, Tibetan Babax Babaxkoslowi. Acta Ornithologica 2007, 42, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.E.; Owens, I.P.F.; Goldizen, A.W. Division of labour within cooperatively breeding groups. Behaviour 2005, 142, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).