1. Introduction
Intramedullary nailing (IMN) remains the gold standard for the treatment of tibial shaft fractures (TSF) allowing early weight-bearing and fast rehabilitation [
1,
2]. Malrotation and shortening can be avoided in TSF by using screws that interlock. Proximal interlocking screw placement is typically performed using an aiming jig that is secured to the nail [
3]. Because distal locking can take a long time and expose the patient, the surgery staff, and the surgeon to a significant quantity of radiation during the fluoroscopy, it continues to be a difficult and occasionally irritating aspect of IMN. The amount of radiation time required for distal locking can sometimes be close to half that required for IMN [
4]. Despite its limitations, most surgeons still prefer the freehand technique. However, there is a clear need for alternative techniques with limited or no radiation exposure [
5]. A new system has been developed that uses an electromagnetic (EM) field generator, a probe inserted into the nail, and computerized tracking technology [
6,
7]. The SURESHOTTM Distal Targeting System (Smith & Nephew, Inc., Memphis, TN, USA) offers real-time, three-dimensional input regarding the drill’s orientation and position in relation to the nail interlocking hole without requiring radiation exposure [
5].
Here, our aim is to compare the freehand technique and the electromagnetic guidance in terms of reductions in overall radiation exposure, dose area product, and surgery duration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Demographic Data
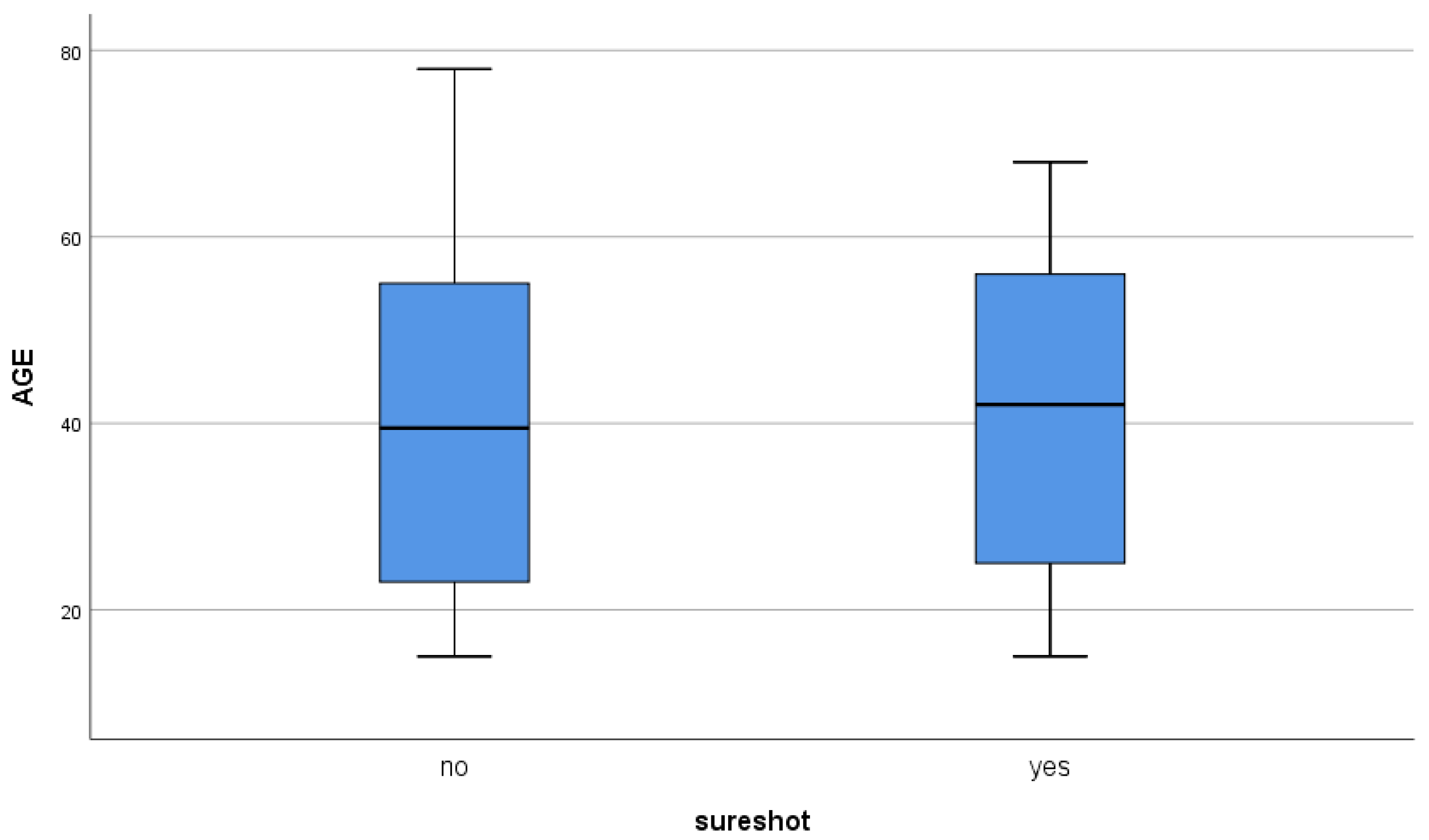
From January 2018 to May 2022, 63 patients with TSF who underwent intramedullary nailing were enrolled at our institute. Our patient cohort consisted of 40 men (63.5%) and 23 women (36.5%) with a mean age of 41.4±18.38 years (range 15-78) (
Figure 1).
The study enrolled patients with acute traumatic tibial shaft fractures (extra-articular) that were either single-bone or associated with fibular shaft fractures, and were treated conservatively. Patients with concomitant multiple fractures, Gustilo-Anderson fractures (type IIIB, IIIC), young patients treated with elastic nailing, and patients with multiple traumas requiring complex surgery were excluded.
The patients were divided into two groups: Group FH had 30 patients who underwent intramedullary nailing with two distal locking screws inserted using the standard freehand method under fluoroscopy control. Group SS comprised 33 patients who underwent treatment using an electromagnetic navigation system (SURESHOT, Smith & Nephew, Inc., Memphis, TN).
Of the patients recruited, 37 (58.7%) had a mono-osseous tibial fracture and 26 (41.6%) had both tibial and fibular shaft fractures. The mechanisms of injury were recorded: 57.30% traffic accidents (36/63), 22.22% traumatic injuries (14/63), 9.52% falls from height (6/63), and 11.11% other accidents (7/63). According AO classification, fractures were divided into three types: A, B, and C. Type A was the most common (
Table 1).
2.2. Details of Surgery
Three types of nails were used: 37 were Smith & Nephew TRIGEN META-NAILTM (58.8%), 21 were T2 Stryker Nailing System (33.3%), two were CITIEFFE tibial nail (3.2%), and three were Synthes Expert Tibial Nail PROtect (4.8%). Patients in group SS were treated exclusively with TRIGEN nails with distal locking performed using an EM device. On the other hand, patients in the FH group had all of the aforementioned nail treatments, including a few instances of TRIGEN nailing where distal locking was done at EM but under fluoroscopic guidance. A spinal anesthetic was used during the procedure. Surgeons with at least three years of experience conducted all operations. The dose area product, radiation exposure time, and the overall length of the surgery were the three primary characteristics taken into account for analysis. The following headings contained the data for the study, which were taken from the operating room’s surgical and radiation registries: date, age, gender, dosage (cGy/cm2), fluoroscopy time (s), surgery start/end time, and distal locking method (fluoroscopy or IMN).
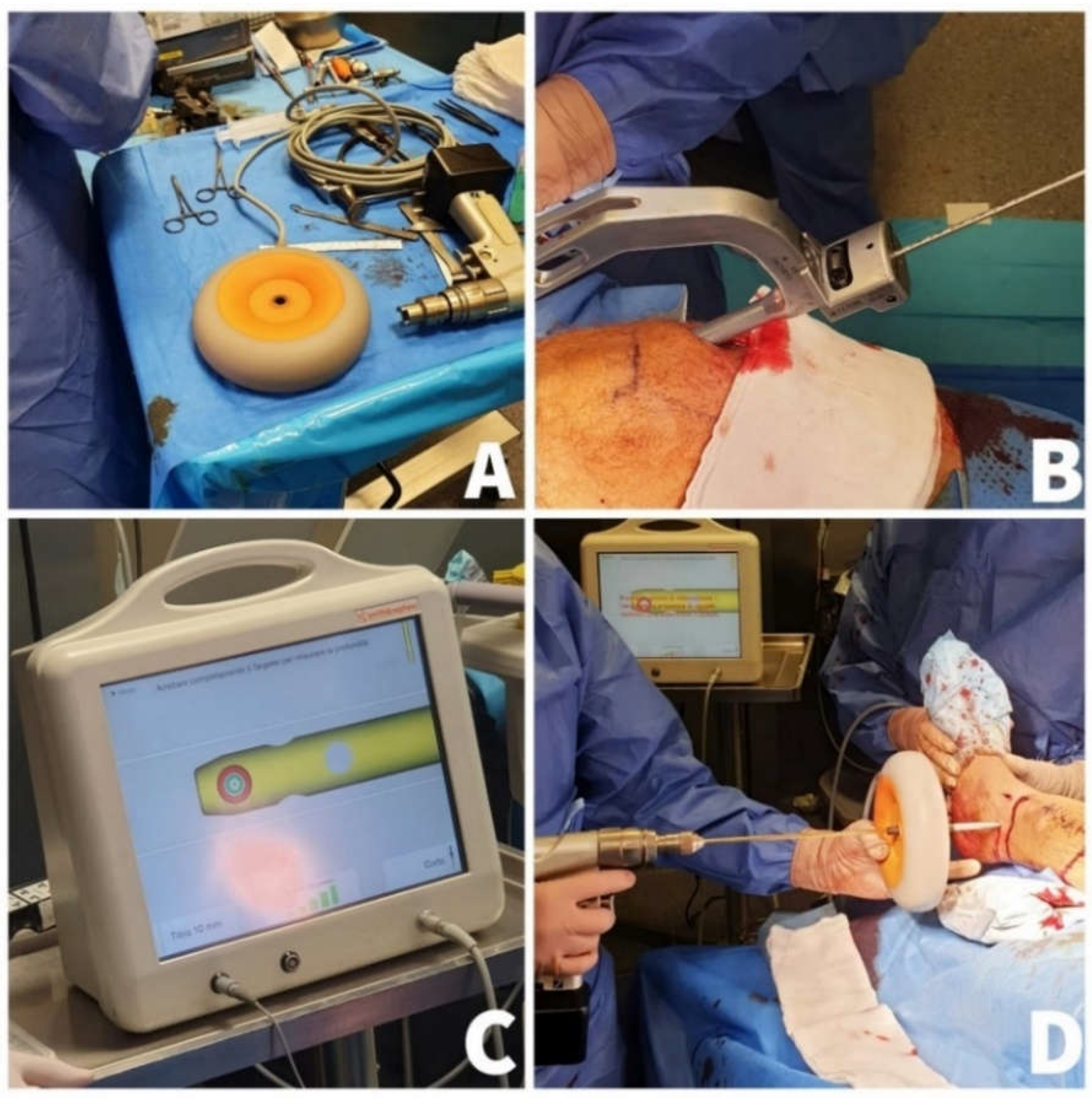
The Smith & Nephew TRIGEN SURESHOT Distal Targeting System was utilized for electromagnetic navigation (
Figure 2).
This is an orthopedic surgical computer tool that helps the surgeon place screws during intramedullary nail implantation (IM). By utilizing electromagnetic tracking data obtained intraoperatively, the surgeon is presented with a virtual image of the distal end of the nail on the screen, providing valuable information [
8]. The targeting system is comprised of three components. Firstly, a hand-held aiming device, shaped like a donut, creates a focused electromagnetic field. Secondly, a computerized control unit is housed within the display unit. Finally, a sensor probe is inserted into the nail to gather data and send it to the control unit. The entire procedure makes use of calibrated software and digital technology to track the electromagnetic field through a probe inserted into the middle of the nail, providing a distal locking system that works in real time without the need for fluoroscopy. The electromagnetic field generator’s central slot is first drilled through by the surgeon. The real-time information is then presented on a computer monitor together with the drill’s position and the locking holes. When the red and green target circles overlap on the computer monitor, the distal screws should be inserted. Finally, fluoroscopy confirms the correct positioning of the distal screw [
9,
10].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using a mean ± standard deviation to express continuous variables. The distribution non-normality was confirmed via the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, and the means were compared with the Mann-Whitney U test. The results are displayed in the following order: U (sample size), U test statistic, Z score (standardized test statistic), and p= probability (significance level). A p-value less than 0.05 on both sides was considered statistically significant. The 95% confidence interval for these findings is provided. The statistical software used for the analysis was version 25.0 of SPSS Statistics for Windows (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Results
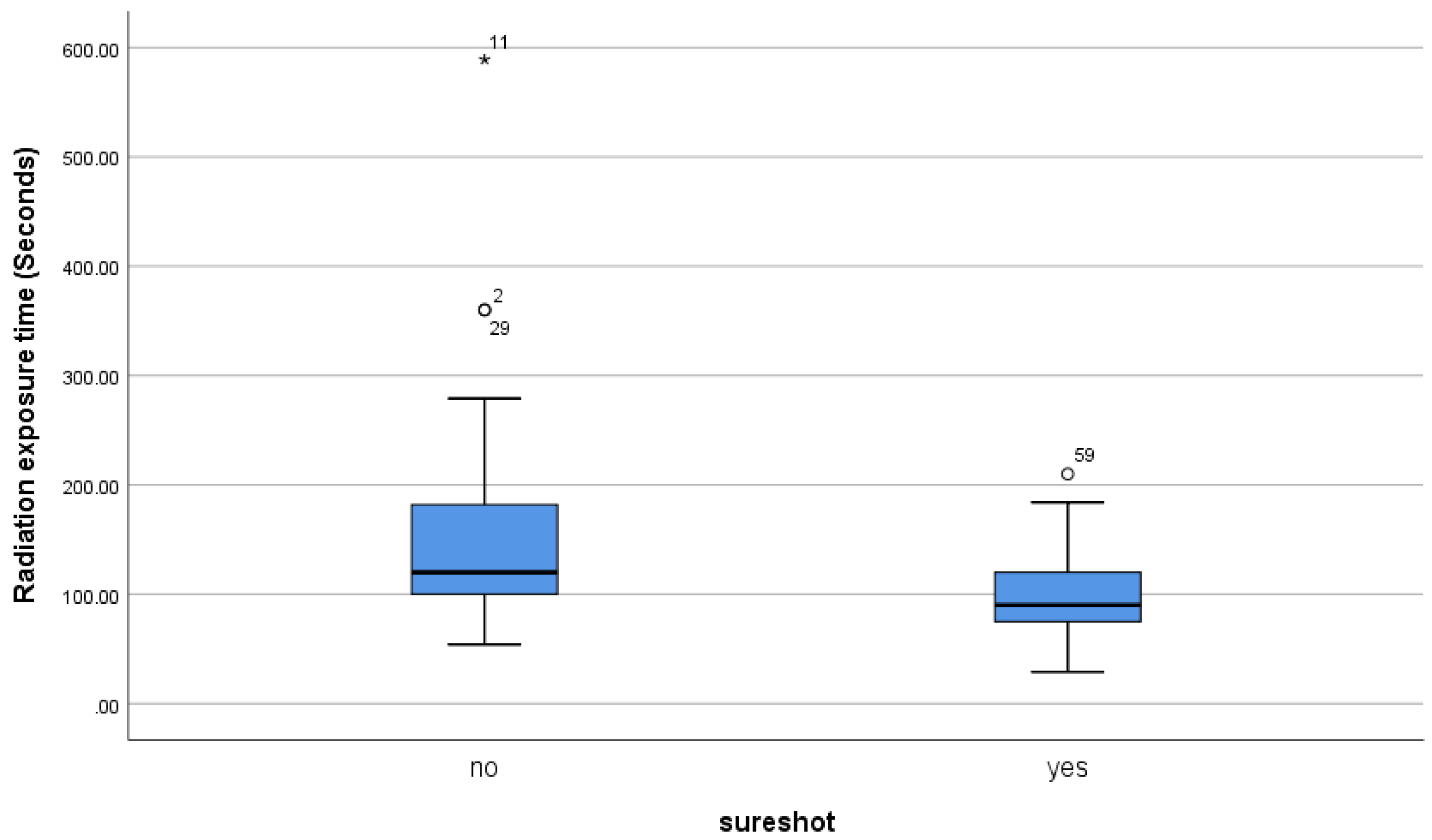
The mean duration of radiation exposure was 155.90±126.57 seconds (range 29-589) in group FH and 99.91±40.16 seconds (range 29-210) in group SS (
Table 2,
Figure 3).
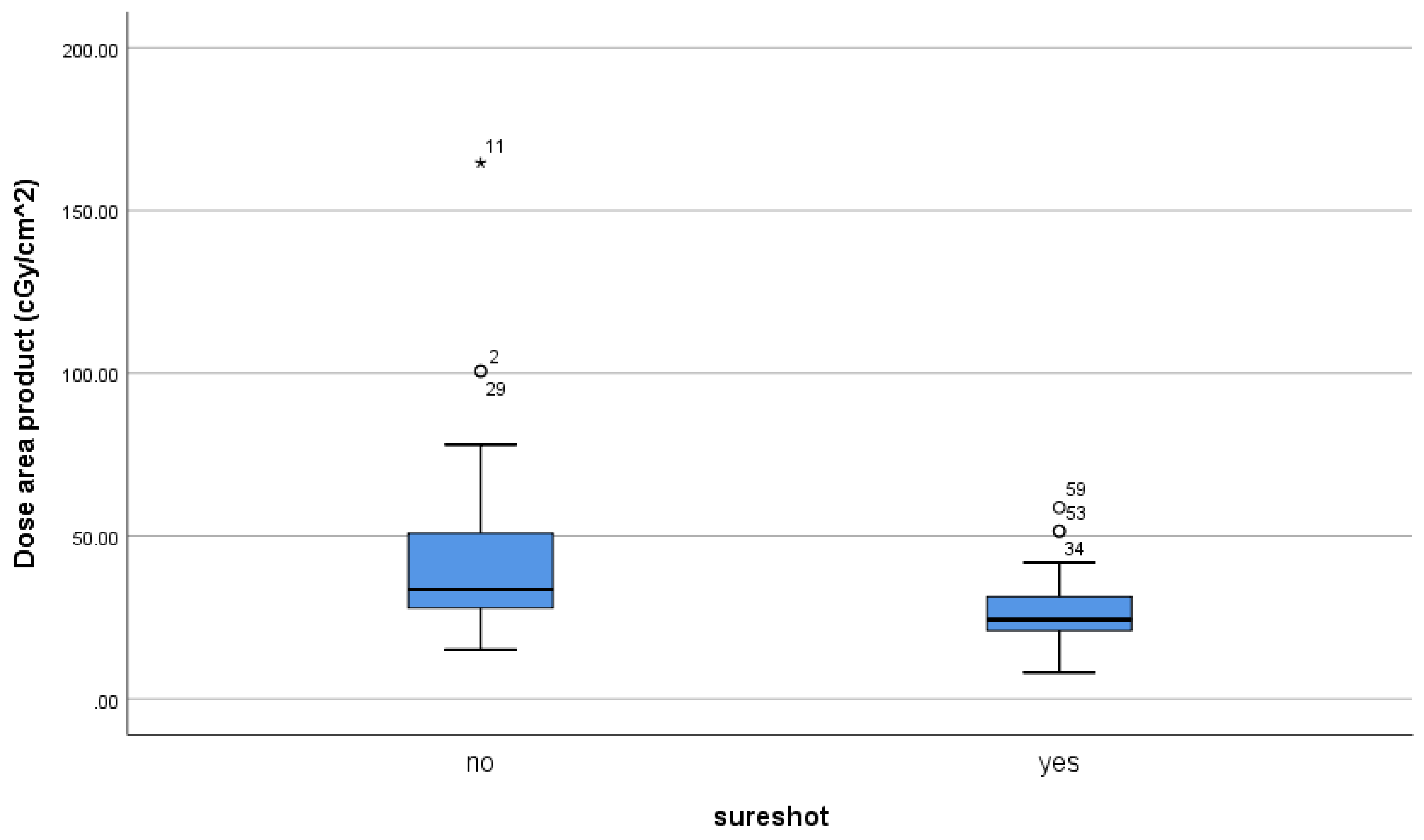
The mean dose area product was 43.57±31.57 cGy/cm
2 (range 15-164) in group FH and 27.62 ± 11.20 cGy/cm
2 (range 8.10-58.69) in group SS (
Table 3,
Figure 4)
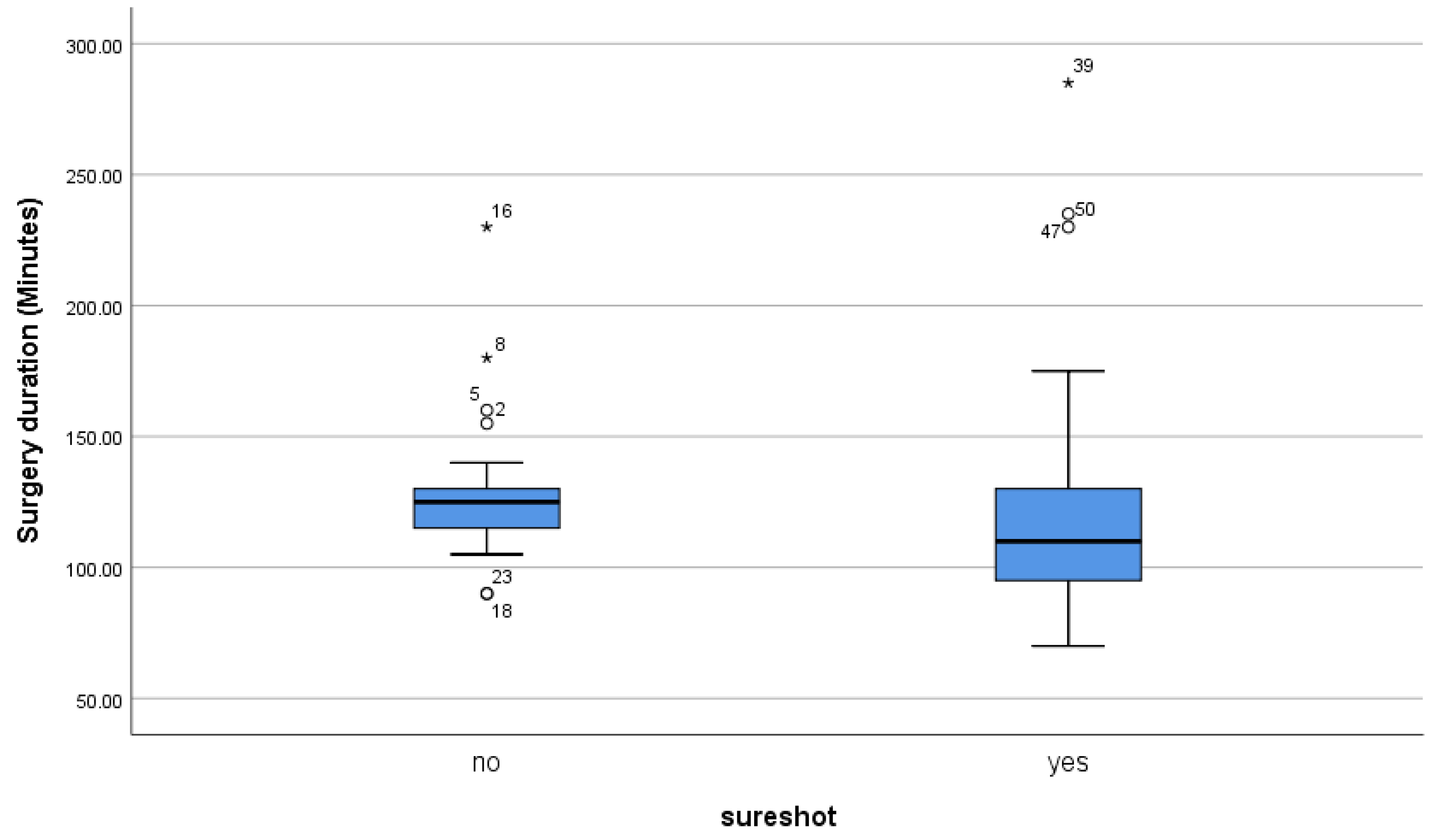
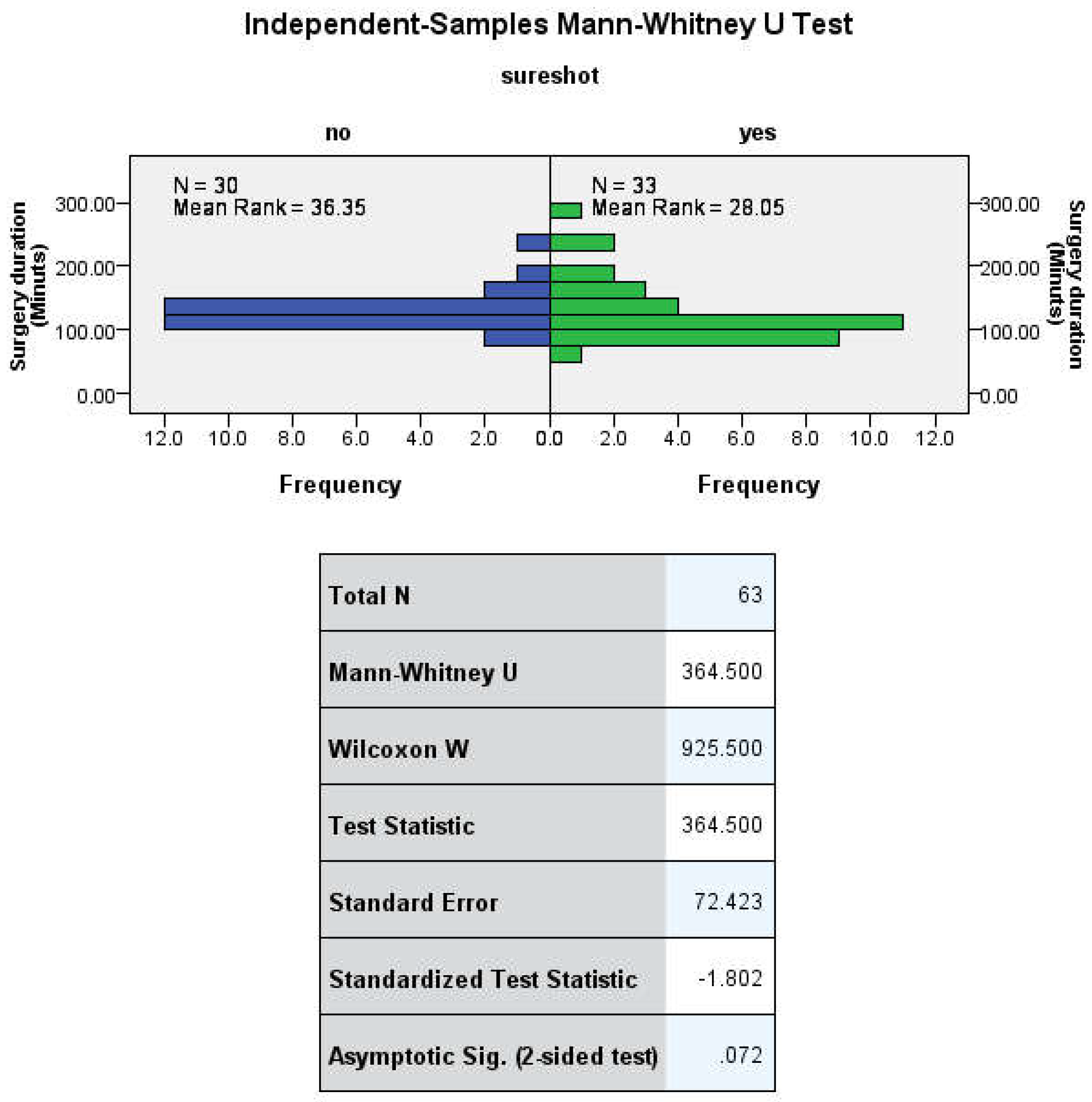
The mean duration of surgery was 128.83 ± 26.51 minutes (range 90-230) in group FH and 126.42 ± 48.31 minutes (range 70-285) in group SS (
Table 4;
Figure 5).
3.1. Statistical Findings
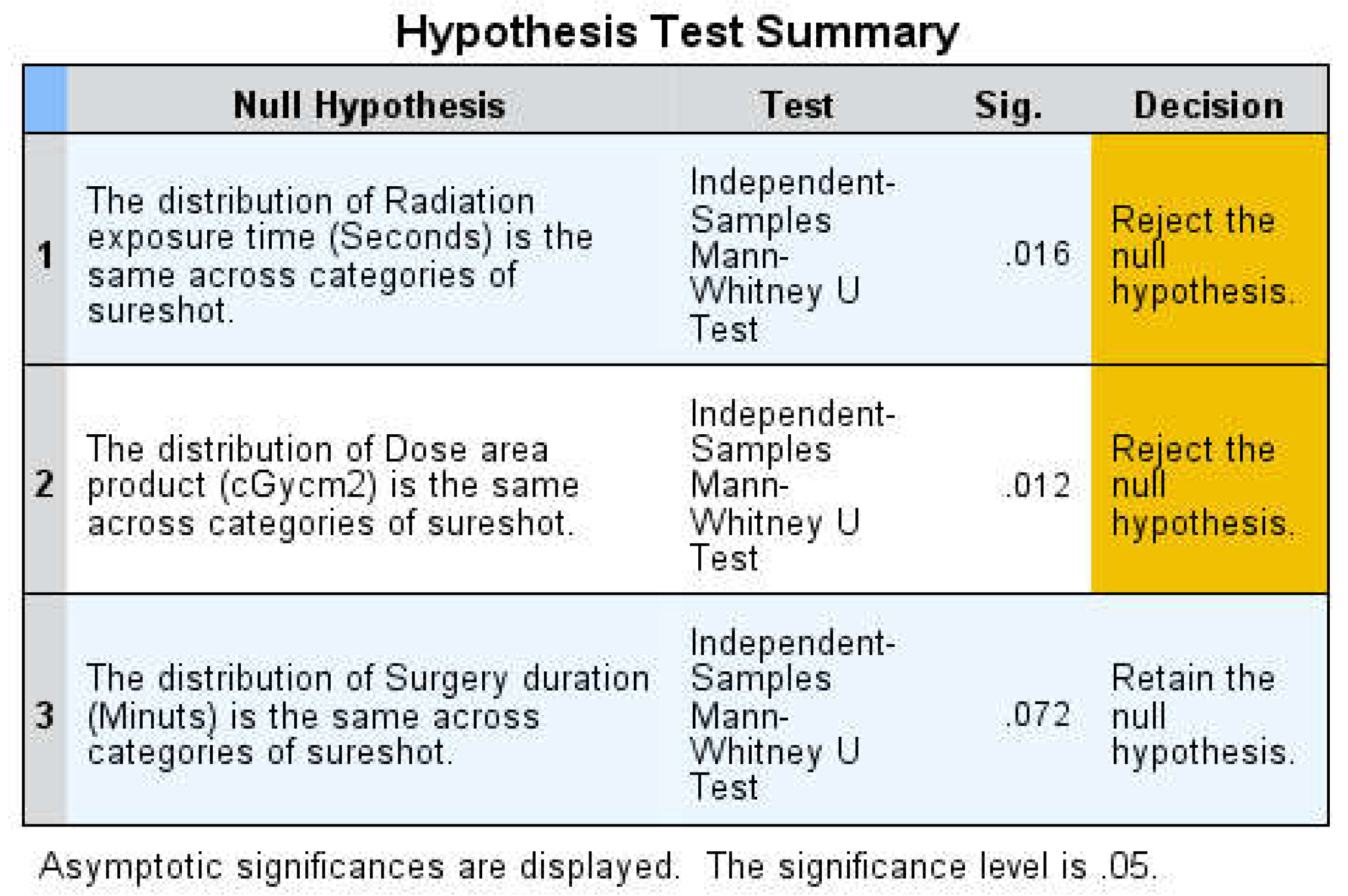
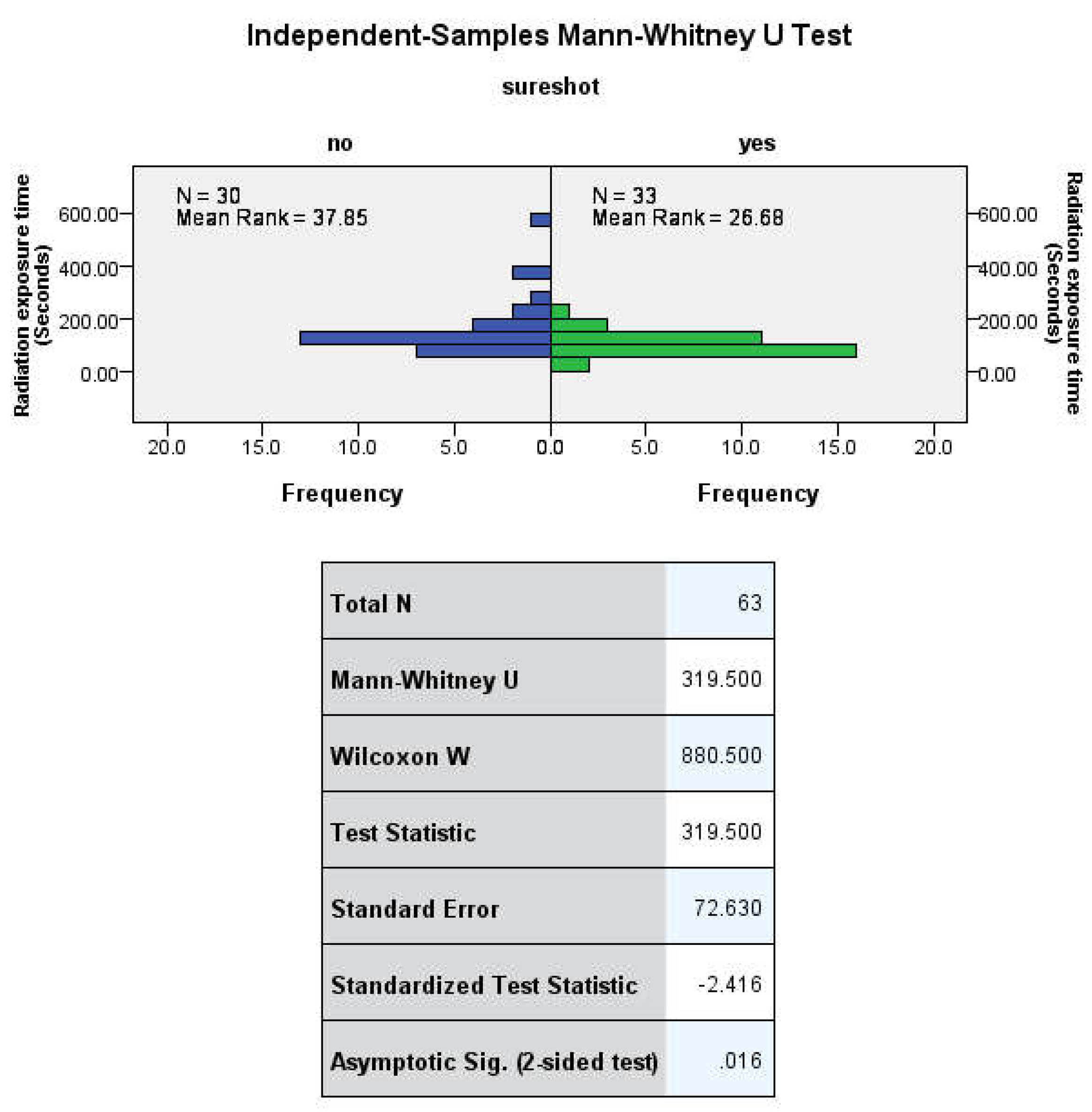
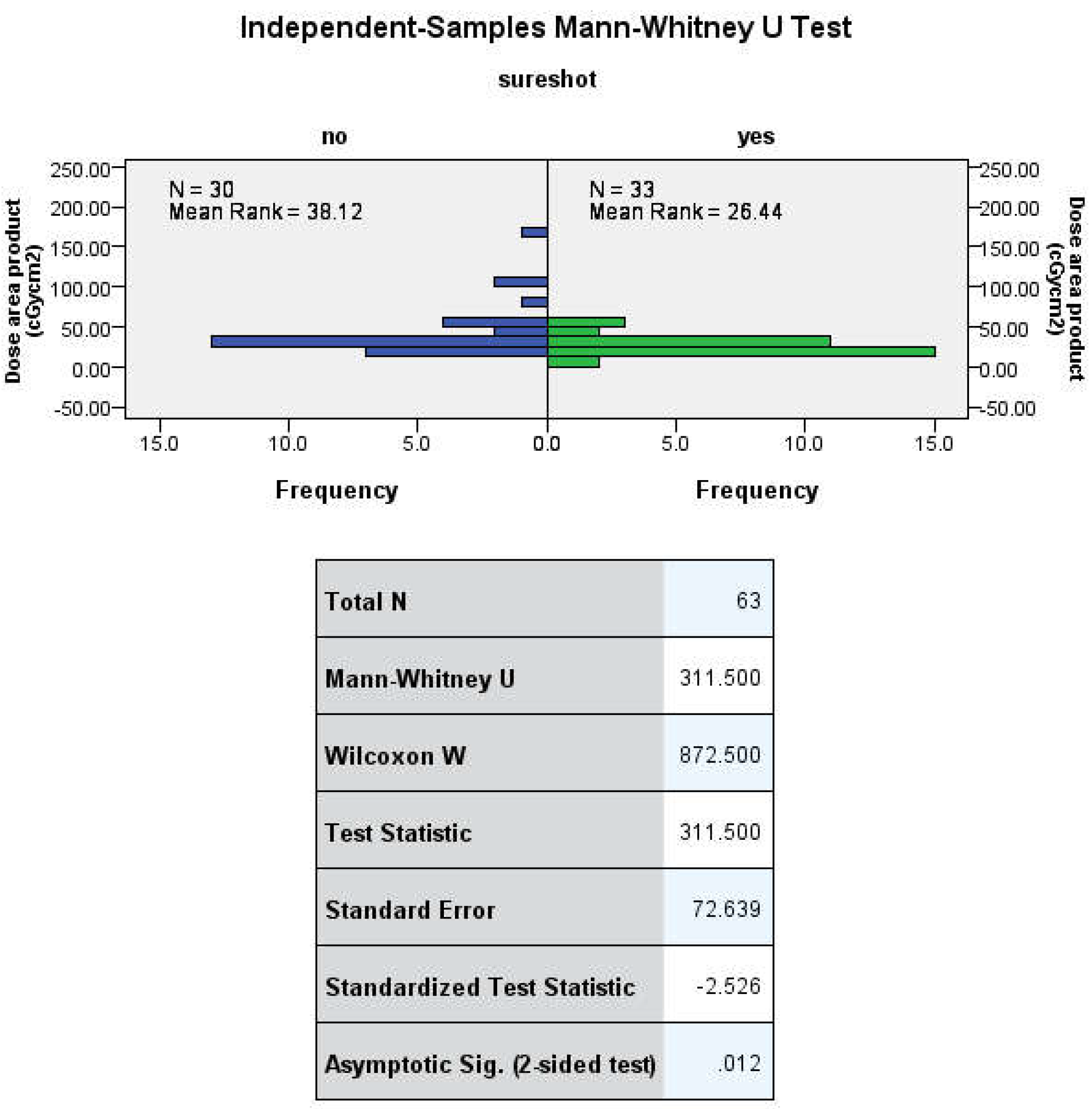
The nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare group means due to non-normal distribution. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk tests confirmed significant deviation from normality in all analyzed fields (irradiation time, absorbed radiation dose, duration of surgery). The Mann-Whitney U test showed statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of irradiation time U (30no, 33yes) = 319.500, Z= -2.416 p= 0.016 and dose area product U (30no, 33yes) = 311.500, Z= -2.526 p= 0.012.
A two-sided p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. However, no significant difference was found in the duration of surgery U (30no, 33yes) = 364.500 Z= -1.802 p= 0.072 (
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9)
4. Discussion
Although the freehand approach is crucial for inserting distal locking screws, medical professionals’ exposure to ionizing radiation is a significant concern for their safety, especially for orthopedic surgeons. Recent studies indicate that their risk of cancer is higher due to occupational exposure to radiation. Mehlman and Di Pasquale [
11] discovered that surgeons who operate within 24 inches of the fluoroscopic beam expose their hands, thyroid gland, and unprotected eyes to a considerable amount of radiation. The surgeon’s hand, eyes, and thyroid gland are always this far away from the primary beam during fluoroscopy-guided distal locking. The intramedullary nailing (IMN) of long bones is thought to be the most significant source of radiation exposure in orthopedic procedures conducted under fluoroscopic supervision [
12], with distal locking accounting for up to 50% of the total radiation time in IMN operations [
13]. Few studies have evaluated patient radiation exposure. According to Madan et al. [
14], radiation exposure to patients’ gonads during intramedullary tibial nailing was within the suggested limits. As a result, reducing the possibility of radiation exposure during the aforementioned treatment is crucial.
Both fluoroscopic and EM guidance were found to be equally effective in terms of clinical efficacy, as all nails were placed correctly. The primary difference between the two groups was the duration of radiation exposure and the absorbed radiation dose. However, even with the use of EM field-generating equipment, complete elimination of radiation exposure was not possible. In fact, fluoroscopy was still required to confirm the placement of the nails.
The position of the screw in the distal locking hole was confirmed using fluoroscopy. The nail holes were also checked to ensure correct drill passage. While efforts were made to reduce radiation exposure, the process was not completely free from radiation. According to the SURESHOT literature data, tibial locking can be achieved with 100% accuracy and an average reduction in radiation exposure time of 36±13 s [
15]. This is consistent with our findings. Grimwood et al. [
16] demonstrated a statistically significant (p = 0.038) 46% decrease in tibial IM nailing that resulted in a 49 s reduction. Our study produced similar outcomes, with a mean difference of 56 s (36%) (Z= -2.416 p= 0.016). Therefore, we can conclude that fluoroscopy time was significantly reduced when using EM in our research.
A study by Grimwood et al. [
16] demonstrated a mean reduction of 18.03 cGy/cm
2 (p = 0.046) during tibial IM nailing in terms of radiation dose. Our study also found a similar result, with a mean difference of 15.96 cGy/cm
2 (Z= -2.526 p= 0.012). This means that there was an overall 36% reduction in radiation absorption. There are no studies similar to Grimwood et al. 16 to corroborate these results. However, studies by Chan et al. [
17], Langfitt et al. [
18], Stathopoulos et al. [
6], and Moreschini et al. [
5] did not record radiation doses but only examined fluoroscopy and distal locking times.
Previous studies on the EMN device have shown that it can save up to 5 minutes of intraoperative time for distal locking [
5,
6,
15]. However, our study only showed a reduction of 3 minutes. This result was not statistically significant, possibly due to the lack of training and experience with the device. These findings are consistent with a study by Grimwood et al. [
16] which also did not find a significant reduction in overall operative time.
Our study aimed to evaluate the impact of using electromagnetic guidance systems for distal locking on total operative time, total exposure time, and total absorbed radiation dose. These parameters are highly dependent on the surgeon’s training and experience. Langfitt et al. [
18] found that fluoroscopy duration is often directly related to the surgeon’s level of experience. During the procedures, either a manufacturer’s representative or a consultant was present to provide guidance, which likely affected the overall duration. According to Smith & Nephew, the technology is easy to learn, allowing for rapid training of the surgeon [
8]. However, the surgeon must be familiar with the freehand technique in case the system malfunctions [
19]. Our findings suggest that this device is reliable and effective if used correctly.
Our results have shown that this method is reliable and legitimate when applied appropriately. However, there were two shortcomings in the study - the small sample size and the retrospective nature of data collection. The recruitment process was hindered due to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. In fact, as per the study conducted by Kale et al. [
20], orthopedic physicians in Louisiana and their practices were significantly impacted by the COVID-19 epidemic, leading to a decline in patient volume, surgical volume, and revenue. Although orthopedic and trauma surgery was not directly affected by the outbreak, several areas reported a significant decrease in the number of instances [
21].
It is possible that there could be considerable time saved if this operation is included in the regular surgical schedule and larger sample sizes are used. However, more research is needed to determine whether using this technology instead of the manual approach is also more cost-effective.
5. Conclusions
Our study aimed to compare the effectiveness of electromagnetic navigation and freehand approach for distal locking. Despite the small sample size, our findings indicate that both methods are feasible and effective. However, the electromagnetic navigation system seems to be a better option as it requires a lower radiation dose and shorter irradiation period. Larger sample size studies have shown that this approach leads to quicker surgical times. It was not feasible to randomize participants in the study due to the limited number of eligible patients. However, every eligible patient was included in the study, so it remained unbiased. It is important to consider that the patient’s body type, bone density, and the complexity of the fracture reduction can affect the duration of the operation and the amount of radiation exposure. Finally, productivity gains can be achieved with better resource management, which can help prevent surgical delays.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.T.; methodology, F.S.; software, M.S.; validation, G.T.; formal analysis, G.V.; investigation, L.C.; resources, G.V.; data curation, S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, G.V.; writing—review and editing, G.T.; visualization, G.T.; supervision, V.P.; project administration, V.P.; funding acquisition, V.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to its retrospective nature.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Research data are included in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kempf, I.; Grosse, A.; Beck, G. Closed locked intramedullary nailing. Its application to comminuted fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985, 67, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winquist, R.A.; Hansen, S.T., Jr. Clawson DK. Closed intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. A report of five hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984, 66, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelle, B.A.; Boni, G. Safe surgical technique: Intramedullary nail fixation of tibial shaft fractures. Patient Saf Surg. 2015, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whatling, G.M.; Nokes, L.D. Literature review of current techniques for the insertion of distal screws into intramedullary locking nails. Injury. 2006, 37, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreschini, O.; Petrucci, V.; Cannata, R. Insertion of distal locking screws of tibial intramedullary nails: A comparison between the free-hand technique and the SURESHOT™ Distal Targeting System. Injury. 2014, 45, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathopoulos, I.; Karampinas, P.; Evangelopoulos, D.S.; Lampropoulou-Adamidou, K.; Vlamis, J. Radiation-free distal locking of intramedullary nails: Evaluation of a new electromagnetic computer-assisted guidance system. Injury. 2013, 44, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Schröder, M.; Lehmann, W.; Kammal, M.; Rueger, J.M.; Herrman Ruecker, A. Next generation distal locking for intramedullary nails using an electromagnetic X-ray-radiation-free real-time navigation system. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 73, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 8. TRIGENTM SURESHOTTM Distal Targeting System V3.0. Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics GmbH.
- Han, B.; Shi, Z.; Fu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Jing, J.; Li, J. Comparison of free-hand fluoroscopic guidance and electromagnetic navigation in distal locking of femoral intramedullary nails. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017, 96, e7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, B.; Shi, Z.; Fu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Jing, J.; Li, J. Comparison of free-hand fluoroscopic guidance and electromagnetic navigation in distal locking of tibia intramedullary nails. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018, 97, e11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlman, C.T.; DiPasquale, T.G. Radiation exposure to the orthopaedic surgical team during fluoroscopy: “how far away is far enough? ”. J Orthop Trauma. 1997, 11, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalafoutas, I.A.; Tsapaki, V.; Kaliakmanis, A.; Pneumaticos, S.; Tsoronis, F.; Koulentianos, E.D.; Papachristou, G. Estimation of radiation doses to patients and surgeons from various fluoroscopically guided orthopaedic surgeries. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2008, 128, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, P.E.; Schoen, R.W. Jr.; Browner, B.D. Radiation exposure to the surgeon during closed interlocking intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987, 69, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, S.; Blakeway, C. Radiation exposure to surgeon and patient in intramedullary nailing of the lower limb. Injury. 2002, 33, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornetta, P.; Pattel, P.; Tseng, S.; Whitten, A.; Ricci, W. Distal locking using an electromagnetic field guided computer based real time system. Presented at Orthopaedic Trauma Association (OTA) Annual Meeting, 2009; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Grimwood, D.; Harvey-Lloyd, J. Reducing intraoperative duration and ionising radiation exposure during the insertion of distal locking screws of intramedullary nails: A small-scale study comparing the current fluoroscopic method against radiation-free, electromagnetic navigation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016, 26, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.S.; Burris, R.B.; Erdogan, M.; Sagi, H.C. The insertion of intramedullary nail locking screws without fluoroscopy: A faster and safer technique. J Orthop Trauma. 2013, 27, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfitt, M.K.; Halvorson, J.J.; Scott, A.T.; Smith, B.P.; Russell, G.B.; Jinnah, R.H.; Miller, A.N.; Carroll, E.A. Distal locking using an electromagnetic field-guided computer-based real-time system for orthopaedic trauma patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2013, 27, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, G.; Stuflesser, W.; Crippa, C.; Touloupakis, G. A distal-lock electromagnetic targeting device for intramedullary nailing: Suggestions and clinical experience. Chin J Traumatol. 2016, 19, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, N.N.; Patel, A.H.; Leddy, M.J.; Savoie, F.H.; Sherman, W.F. The Effect of COVID-19 on Orthopedic Practices and Surgeons in Louisiana. Orthopedics. 2020, 43, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, P.; Putzer, D.; Liebensteiner, M.C.; Dammerer, D. Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery—A Systematic Review of the Current Literature. In Vivo. 2021, 35, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Box plot of age.
Figure 1.
Box plot of age.
Figure 2.
A. The electromagnetic field generator. B. Nail length adjusted probe inserted into the proximal end of the nail. C. The location of drill and locking holes visualized on the computer monitor. D. Distal screws inserted when the green and the red targeting circles are overlaps presented on the computer monitor.
Figure 2.
A. The electromagnetic field generator. B. Nail length adjusted probe inserted into the proximal end of the nail. C. The location of drill and locking holes visualized on the computer monitor. D. Distal screws inserted when the green and the red targeting circles are overlaps presented on the computer monitor.
Figure 3.
Radiation time exposure descriptive analysis steam and leaf plot.
Figure 3.
Radiation time exposure descriptive analysis steam and leaf plot.
Figure 4.
Radiation time exposure descriptive analysis steam and leaf plot.
Figure 4.
Radiation time exposure descriptive analysis steam and leaf plot.
Figure 5.
Surgery duration stem and leaf plot.
Figure 5.
Surgery duration stem and leaf plot.
Figure 6.
Mann-Whitney test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Figure 6.
Mann-Whitney test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Figure 7.
Radiation exposure time Mann-Whitney U test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Figure 7.
Radiation exposure time Mann-Whitney U test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Figure 8.
Radiation absorbed dose Mann-Whitney U test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Figure 8.
Radiation absorbed dose Mann-Whitney U test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Figure 9.
Duration of surgery Mann-Whitney U test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Figure 9.
Duration of surgery Mann-Whitney U test from SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0; (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
Table 1.
Distribution of AO-classification 42-(N).
Table 1.
Distribution of AO-classification 42-(N).
| TYPE |
A1 |
A2 |
A3 |
B1 |
B2 |
B3 |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
TOT |
| N |
22 |
11 |
8 |
9 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
63 |
| % |
34.9 |
17.4 |
12.6 |
14.2 |
9.5 |
4.7 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
3.1 |
100 |
Table 2.
Radiation exposure descriptive analysis.
Table 2.
Radiation exposure descriptive analysis.
| |
Technique groups |
Statistic |
Std. Error |
| Radiation exposure time (Seconds) |
FH |
Mean |
155.900 |
20.625 |
| 95% Confidence Interval for Mean |
Lower Bound |
113.716 |
|
| Upper Bound |
198.083 |
|
| 5% Trimmed Mean |
141.629 |
|
| Median |
120.000 |
|
| Variance |
12761.886 |
|
| Std. Deviation |
112.968 |
|
| Minimum |
54.00 |
|
| Maximum |
589.00 |
|
| Range |
535.00 |
|
| Interquartile Range |
89.00 |
|
| Skewness |
2.420 |
.427 |
| Kurtosis |
6.924 |
.833 |
| SS |
Mean |
99.909 |
6.990 |
| 95% Confidence Interval for Mean |
Lower Bound |
85.669 |
|
| Upper Bound |
114.149 |
|
| 5% Trimmed Mean |
97.973 |
|
| Median |
90.000 |
|
| Variance |
1612.77 |
|
| Std. Deviation |
40.1593 |
|
| Minimum |
29.00 |
|
| Maximum |
210.00 |
|
| Range |
181.00 |
|
| Interquartile Range |
47.50 |
|
| Skewness |
.992 |
.409 |
| Kurtosis |
1.109 |
.798 |
Table 3.
Absorbed adiation dose descriptive analysis.
Table 3.
Absorbed adiation dose descriptive analysis.
| |
Technique groups |
Statistic |
Std. Error |
| Dose area product (cGy/cm2) |
FH |
Mean |
43.571 |
5.765 |
| 95% Confidence Interval for Mean |
Lower Bound |
31.780 |
|
| Upper Bound |
55.362 |
|
| 5% Trimmed Mean |
39.582 |
|
| Median |
33.540 |
|
| Variance |
997.058 |
|
| Std. Deviation |
31.5762 |
|
| Minimum |
15.09 |
|
| Maximum |
164.63 |
|
| Range |
149.54 |
|
| Interquartile Range |
24.87 |
|
| Skewness |
2.420 |
.427 |
| Kurtosis |
6.925 |
.833 |
| SS |
Mean |
27.617 |
1.950 |
| 95% Confidence Interval for Mean |
Lower Bound |
23.645 |
|
| Upper Bound |
31.590 |
|
| 5% Trimmed Mean |
27.043 |
|
| Median |
24.310 |
|
| Variance |
125.531 |
|
| Std. Deviation |
11.204 |
|
| Minimum |
8.10 |
|
| Maximum |
58.69 |
|
| Range |
50.59 |
|
| Interquartile Range |
12.16 |
|
| Skewness |
1.078 |
.409 |
| Kurtosis |
1.268 |
.798 |
Table 4.
Duration of surgery descriptive analysis.
Table 4.
Duration of surgery descriptive analysis.
| |
Technique groups |
Statistic |
Std. Error |
| Surgery duration (Minutes) |
FH |
Mean |
128.833 |
4.840 |
| 95% Confidence Interval for Mean |
Lower Bound |
118.933 |
|
| Upper Bound |
138.733 |
|
| 5% Trimmed Mean |
126.296 |
|
| Median |
125.000 |
|
| Variance |
702.902 |
|
| Std. Deviation |
26.5123 |
|
| Minimum |
90.00 |
|
| Maximum |
230.00 |
|
| Range |
140.00 |
|
| Interquartile Range |
16.25 |
|
| Skewness |
2.097 |
.427 |
| Kurtosis |
6.838 |
.833 |
| SS |
Mean |
126.424 |
8.409 |
| 95% Confidence Interval for Mean |
Lower Bound |
109.293 |
|
| Upper Bound |
143.554 |
|
| 5% Trimmed Mean |
121.734 |
|
| Median |
110.000 |
|
| Variance |
2334.002 |
|
| Std. Deviation |
48.3115 |
|
| Minimum |
70.00 |
|
| Maximum |
285.00 |
|
| Range |
215.00 |
|
| Interquartile Range |
47.50 |
|
| Skewness |
1.759 |
.409 |
| Kurtosis |
3.151 |
.798 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).