1. Introduction - Context and Related Work
Landslides occur when a slope equilibrium is disturbed, causing downslope movement of soil, rock, and organic materials under the effects of gravity. They may be triggered by seismic activities, heavy rainfall, volcanic eruptions, or ground cover changes and can cause widespread damage to landscapes, infrastructure, and human lives and livelihoods [
1,
2]. It is therefore important to detect landslides accurately and quickly and we here propose a remote sensing (RS) approach to do this using landslide triggered by earthquakes as case studies.
1.1. Earthquakes
Earthquakes are ranked among the most devastating natural disasters [
3] and have caused about 750,000 deaths globally in the last 20 years [
4]. The magnitude, intensity, and duration of an earthquake play crucial roles in determining the level of destruction and harm they inflict. The damage is usually generated by earthquake-triggered disasters, including ground shaking, ground rupture, liquefaction, landslides, tsunamis, and floods [
5]. Additionally, the specific location and timing of these events also significantly influence their impacts. For instance, the ‘Tohoku Earthquake’ and subsequent earthquakes in Fukushima in 2011 led to 18,426 casualties (confirmed dead and missing), about one million destroyed buildings, and economic costs totaling USD 300 billion [
6].
Geospatial technologies provide crucial solutions for mitigating the damage earthquakes cause to human settlements [
7]. Developments in satellite RS and Geographic Information System (GIS) technologies have significantly improved our ability to handle various stages of earthquakes, including early warning [
8], occurrence prediction [
9], prevention assessments [
10], identification of vulnerabilities [
11], damage monitoring and assessment [
12,
13], risk modelling [
14,
15], and disaster preparedness [
9]. RS and GIS are part of operational workflows that aid earthquake preparedness, emergency management, and damage assessment [
7].
1.2. Coseismic Landslides
Landslide size or extent, and its impact, primarily depend on the type of landslide, the underlying topography (slope, aspect, elevation, surface curvature, and roughness), and its cause [
16]. In the event of an earthquake, coseismic ground deformation, and distance to the surface rupture zone are important influencing factors of landslide susceptibility [
17]. In addition, landslide susceptibility models often take into account landslide conditioning factors such as the amount of rainfall that triggered the landslide event, indices derived from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) including the Topographic wetness index (TWI) and the Sediment transport index (STI), as well as spectral vegetation indices such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) indicating vegetation density and health [
18,
19].
1.3. Satellite-Remote Sensing Based Landslide Detection
Detecting landslides using satellite-RS based solutions provides crucial information and evidence for landslide- and earthquake related research. Landslide detection time, location and spatial extent of identified landslides, together with information about changes in land surface materials, are not only important for landslide risk/susceptibility modelling, and for disaster impact assessment [
12], but also for early disaster response and monitoring. Captured satellite imagery available as near real-time (NRT) products with latency below three hours [
20,
21], together with effective cloud-based imagery processing and distribution of detected landslide locations to emergency response systems, are key to early response and can save lives and reduce damage.
Multiple relevant satellite imagery sensors for earthquake applications have been identified [
7]. RS-based landslide detection approaches utilize both, optical sensors (e.g., Landsat-8 (L8), Sentinel-2 (S2)), and radar sensors (e.g., Sentinel-1 (S1), PALSAR-2 (P2)), as well as elevation and slope raster datasets, usually derived from SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) acquisitions by Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) [
22]. Most SAR-based landslide detection methods utilize InSAR to quantify ground surface deformation through measured changes of radar phase between two (pre- and post-landslide event) acquisitions [
23,
24]. Alternatively, SAR radar backscatter intensity- and coherence can also be used to detect changes in ground surface properties (e.g., reflectance, roughness, dielectric properties). While optical sensors provide useful spectral information, SAR bands can inform about local surface deformation.
Processing and analysis of relevant satellite imagery for investigating earth surface properties is generally done by utilizing spectral indices or image classification [
25]. For change detection, a time series of imagery data, including pre- and post-landslide event, is required [
26]. When processing optical satellite imagery, cloud pixels can be avoided or reduced by mosaicking of quality-filtered multi-temporal images [
27].
Several reviews have discussed and compared satellite RS-based methods for landslide detection [
28,
29,
30,
31,
32]. In summary, most existing techniques apply a spectral index threshold (e.g., NDVI, rdNDVI (Relative Different NDVI), BSI (Bare Soil Index)), supervised image classification, or radar phase and backscatter change to an imagery obtained from a single satellite sensor. Most methods include pixel-based slope data in their algorithms and several approaches mask pixels below a defined slope threshold, excluding them from potential landslide pixels. In [
33] for instance, a slope threshold of 15 degrees was applied for masking.
Some methods also consider Principal component analysis (PCA) that transforms multiple spectral bands acquired at different times into distinct linear components which results in noise reduction and removal of redundant information in the data, ultimately enhancing the distinction between spectral bands [
34,
35]. An overview of existing studies is provided in
Table 1.
The Sudden Landslide Identification Product (SLIP) [
36] algorithm is widely used for landslide detection. It is an multi-sensor approach that explores changes using four thresholds: 1) Increases in red wavelength band to signify the exposure of bare earth; 2) Variations in the Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) bands to indicate changes in soil moisture; 3) Steep slopes, determined from DEM, to restrict the detection process to areas with pronounced topographic inclines; and 4) A land-cover mask to minimize errors of commission specifically within recognized agricultural regions. SLIP had been developed for MODIS and L8 imagery, adapted by integrating the inverse NDVI to assess the soil bareness (aSLIP) [
37] and improved to utilize S2 instead of L8 imagery (iSLIP) [
38]. In addition, Zhang, et al. [
39] discussed the potential presence of “old landslides” – areas of previously triggered landslides that did not (fully) recover at the time of the new incident. Such “old landslides” could be falsely detected as a new landslide but can be masked to avoid detecting them as False Positives (FP), if spatial data about the boundaries of such former landslides are available. Previous studies detecting landslides based on S2, L8, or similar multispectral optical sensors utilized in most cases Level-2A surface reflectance (SR) products, and in a few cases Level-1C Top of Atmosphere (TOA) products [
40,
41].
Validating the accuracy of landslide detection approaches is usually based on available ground truthing, in the form of either point samples of confirmed landslide locations or polygons representing their spatial boundaries. The latter is either captured in the field or created via digitization from Very High-Resolution (VHR) aerial or satellite RGB imagery on which the boundaries of landslides are clearly visible. Ground truthing-based accuracies assessment utilizes confusion matrix derived metrics including Overall Accuracy (OA), Balanced Accuracy (BA), Balanced Error (BE), Specificity (Spec), Recall, Precision (Prec), F1-Score (F1S), Negative Predictive Values (NPV), Positive Predictive Values (PPV), Omission Error (OE), Commission Error (CE), True negative rate (TNR), False positive rate (FPR), False negative rate (FNR), Quality percentage (QP), or Kappa Coefficient [
14,
42,
43].
The accuracies of published landslide detection methods (
Table 1) are challenging to compare because they strongly depend on detection and validation method, used imagery pixel resolution, reliability of ground truthing data, and on the study area size. For a reliable comparison, the methods would need to be implemented and applied to the same landslide events while using a comprehensive and accurate ground-truthing dataset for validation. With regard to reported accuracies, existing landslide detection methods (
Table 1) produced good, but not excellent, detection rates with most accuracies being between 55% and 75%. Combining different optical and SAR imagery while applying advanced Machine Learning-based models could further improve landslide detection accuracies [
32].
Table 1.
Comparison of existing literature addressing Satellite Imagery based landslide detection, including information about sensor source, detection method, and study location. ‘Change detection’ indicates whether images pre- and post- (‘yes’), or only post- (‘no’) landslide event were utilized. ‘GEE’ indicates whether a method was implemented using Google-Earth-Engine. ‘Coseismic’ indicates whether case studies used in each publications include coseismic landslides or not.
Table 1.
Comparison of existing literature addressing Satellite Imagery based landslide detection, including information about sensor source, detection method, and study location. ‘Change detection’ indicates whether images pre- and post- (‘yes’), or only post- (‘no’) landslide event were utilized. ‘GEE’ indicates whether a method was implemented using Google-Earth-Engine. ‘Coseismic’ indicates whether case studies used in each publications include coseismic landslides or not.
| No. |
Publication |
Satellite
Sensors |
Detection method |
Change detection |
GEE |
Study area |
Co
-seismic |
| M1 |
[44] |
L8, SRTM DEM |
∆NDVI, Supervised
classification |
yes |
yes |
Nepal |
yes |
| M2 |
[45] |
S2, SRTM DEM |
∆NDVI or rdNDVI |
yes |
yes |
Sulawesi |
yes |
| M3 |
[46] |
S2, L8 |
rdNDVI |
yes |
yes |
Papua New Guinea, Kenya |
yes1
|
| M4 |
[43] |
S2 |
∆BSI |
yes |
no |
Central America |
yes |
| M5 |
[33] |
S2, DTM (5m) |
∆NDVI, slope |
yes |
yes |
Italy |
no1
|
| M6 |
[35] |
S2,
ALOS GDEM |
Unsupervised classification (NDVIpost, slope, S2post bands) |
no |
no |
India, China, Taiwan |
yes1
|
| M7 |
[42] |
S2,
ALOS GDEM |
Supervised OBIA
(NDVIpost, slope) |
no |
no |
India, China, Taiwan |
no1
|
| M8 |
[47] |
L8 |
Supervised classification (NDWIpost, NDVIpost, DEM, slope) |
no |
yes |
India |
no1
|
| M9 |
[48] |
S1 or S2 |
∆NDVI, SAR backscatter (VV-VH) |
yes |
yes |
Norway |
no1
|
| M10 |
[23,49,50] |
S1 |
∆SAR backscatter (VH),
heatmap for visual
landslide interpretation |
yes |
yes |
Haiti; Vietnam;Japan: Hokkaido, Hiroshima; |
yes1
|
| M11 |
[51] |
S1 |
∆SAR backscatter (VV-VH) |
yes |
no |
Mexico |
yes |
| M12 |
[14,52] |
P2 |
∆SAR backscatter (HH) |
yes |
no |
Japan: Hokkaido |
yes |
| M13 |
[36] |
L8 |
SLIP (%RedChange, ∆mNDMI) |
yes |
no |
Nepal, Cameron |
yes1
|
| M14 |
[37] |
L8 |
aSLIP (mRedChange, ∆iNDVIn, ∆mNDMI) |
yes |
no |
Nepal, Cameron |
no1
|
| M15 |
[38] |
S2 |
iSLIP (mRedChange, ∆mNDMI) |
yes |
no |
Japan: Hokkaido |
yes |
| M16 |
[40] |
S1,
S2 |
∆SAR backscatter (VV) or
SLIP (%RedChange, ∆mNDMI) |
yes |
no |
India |
no |
| M17 |
[53,54] |
GE RGB
imagery |
ML: RetinaNet, YOLO v3,
Mask R-CNN, YOLOX |
no |
no |
China |
yes |
1.4. Cloud-Based Processing, Google Earth Engine and Machine Learning
Cloud-based satellite imagery processing offers numerous benefits. It enables seamless data integration and interoperability by easily combining satellite imagery with other data sources using standardized application programming interfaces. This allows for smooth integration into existing workflows and software applications. It ensures accessibility and scalability, as large volumes of satellite imagery can be processed and analyzed without the need for additional hardware or infrastructure. This eliminates the cost and maintenance associated with expensive equipment, making satellite image analysis more cost-effective and efficient. Moreover, cloud-based processing provides advanced capabilities for satellite imagery analysis, utilizing machine learning algorithms, computer vision techniques, and Artificial Intelligence tools [
55]. These enable researchers to extract valuable insights and patterns from imagery data, uncovering hidden relationships and trends for more accurate and sophisticated analysis.
Furthermore, cloud-based processing enables (near) real-time analysis, crucial for time-sensitive scientific investigations and monitoring applications. It allows researchers to leverage satellite imagery as soon as it becomes available, enhancing the timeliness of their research. Additionally, cloud-based platforms facilitate easy project collaboration, providing a centralized and accessible environment for researchers to collaborate, share data, and work collectively on projects. This promotes interdisciplinary research, knowledge exchange, and accelerates scientific progress. Lastly, cloud-based processing ensures data backup, guarantees data integrity, and reduces the risk of data loss [
56].
One prominent and freely available example of a cloud-based processing environment is Google Earth Engine (GEE), which allows users to visualize and process multi-petabyte archives of satellite imagery and geospatial datasets with planetary-scale analysis capabilities. GEE offers support tools to analyze and monitor environmental properties on a large scale [
57]. A rise in published journal articles related to GEE over the last three years highlights the increased popularity of GEE, with L8 and S2 being the most widely used earth observation satellite sensors, and articles based on Random Forest and Water Resources most often reported [
58]. Several existing landslide detection methods have been implemented in GEE [
14,
23,
33,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
59]. However, only Handwerger et al. [
49] provide a shared GEE script that allows replication and potential adjustment of the script to other landslide events. GEE offers not only the opportunity to implement and compare existing landslide detection methods, but also to apply and compare different ML classifiers for advanced landslide detection, an aspect that to our knowledge has not yet been addressed in the literature. Besides detection, a few other landslide-related studies implemented in GEE are worth noting, focusing on landslide deformation tracking [
60], recovery [
41], or susceptibility [
61,
62,
63,
64]. Khan, et al. [
65] provide a comprehensive comparison of all ML classifiers available in GEE (except Gradient Tree Boost (GTB)). The only published research using ML algorithms in GEE for landslide detection that we are aware of is based on RGB satellite imagery extracted from Google Earth Pro [
53,
54].
1.5. Research Gaps, Aim and Contributions of this Work
In summary, the following research gaps for RS-based landslide detection have been identified:
Existing methods built upon change detection of either spectral index or SAR backscatter, but the benefits of combining optical and SAR sensor bands have not yet been explored;
No study has applied and compared the performance of different ML classifiers available in GEE for landslide detection;
Existing studies using optical sensors (e.g., L8 or S2) have used SR products, but none have investigated the use of TOA vs SR products regarding resulting landslide detection performance;
No comparison of existing landslide detection methods has been applied to the same study dataset;
No study has investigated the benefits of Transfer Learning for landslide detection;
No ready-to-use ML-based solution to landslide detection is available in GEE.
The main aim of our work is to utilize ML algorithms and image fusion within GEE to improve RS-based landslide detection. Specifically, the following research questions will be addressed in this paper:
To what extent could ML-based landslide detection using stacked bands from multiple optical and radar sensors improve landslide detection compared to existing approaches?
How do ML classifiers, available in GEE and applied to landslide detection, compare in terms of performance and processing speed?
What are the possibilities in GEE for early landslide detection – how does the use of TOA radiance products compare to SR products?
How important are relevant spectral and derived topographic bands for landslide detection?
What other factors impact satellite imagery-based landslide detection accuracy?
To what extent can a ML-based landslide detection in GEE be fully automized to allow easy operational adjustment to any spatio-temporal scenario?
With the purpose of addressing these research questions and research gaps, our work will provide the following contributions:
Detailed comparison of the performance (accuracy assessment) of existing RS-based landslide detection methods using Ground-Truthing dataset from four different case sites;
-
Novel RS-based landslide detection solution that:
- ◦
utilizes stacked multi-band optical and SAR imagery at 10-m spatial resolution including S1, S2, P2, and elevation-derived topographic bands;
- ◦
applies landslide specific training and validation sampling strategy based on a novel slope masking approach;
- ◦
applies ML classifier with optimized parameters to boost performance and processing speed;
- ◦
utilizes new additional pseudobands as part of the ML classifier: Slope curvature, aspect, P2 SAR bands, S1 SAR band: combined VH-VV;
- ◦
is implemented in GEE with an accessible source code, including landslide inventory data for all four study sites and a guideline to adjust the GEE code to any study area;
Investigation of importance of each landslide conditioning band within the ML model;
Thorough investigation and comparison of ML classifiers in GEE for coseismic landslide detection;
Comprehensive across-geography applied transfer learning-based landslide detection and validation
Transfer Learning space transferability
Hence, our novel approach provides a significant contribution to RS-based landslide detection, which we illustrate using four different case studies on co-seismic landslides caused by 6.6 – 7.5 magnitude earthquakes that occurred across the globe between 2016 and 2021. The remaining content of this manuscript is structured as follows:
Section 2 introduces the study area, provides details on the satellite imagery datasets used, and explains in detail the workflow of our proposed approach that includes multi-sensor imagery fusion, ML-based landslide detection, experimental settings, and used evaluation metrics.
Section 3 will present the results and
Section 4 will discuss the results and provide insights into detection accuracies of existing solutions compared to our solution; discuss performance of different ML classifiers; explain importance of each sensor band; compare TOA vs SR as part of the detection solution; discuss space transferability; present the conclusion and explore future possibilities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Studies
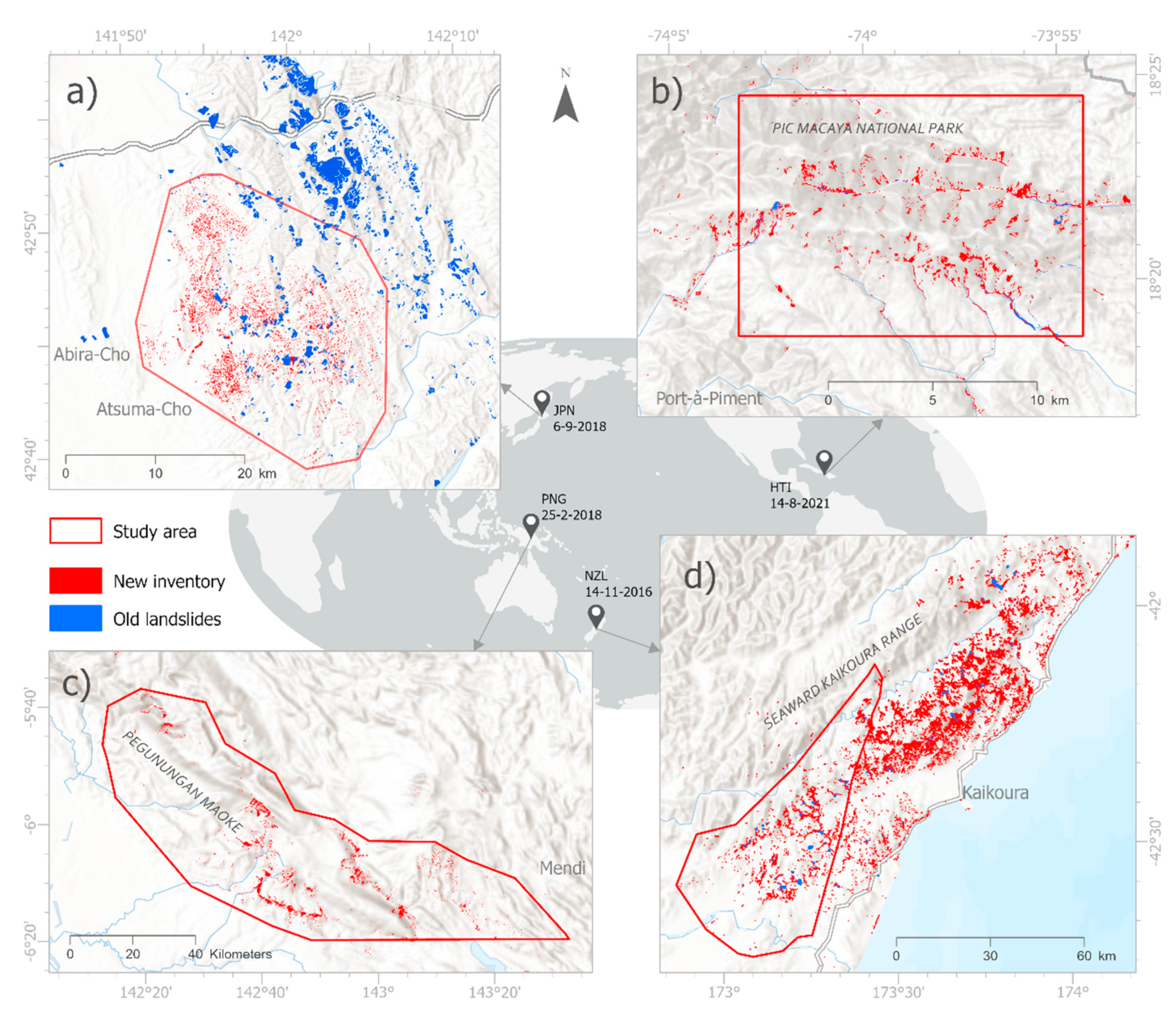
Below, four co-seismic earthquake case studies used in this paper are described.
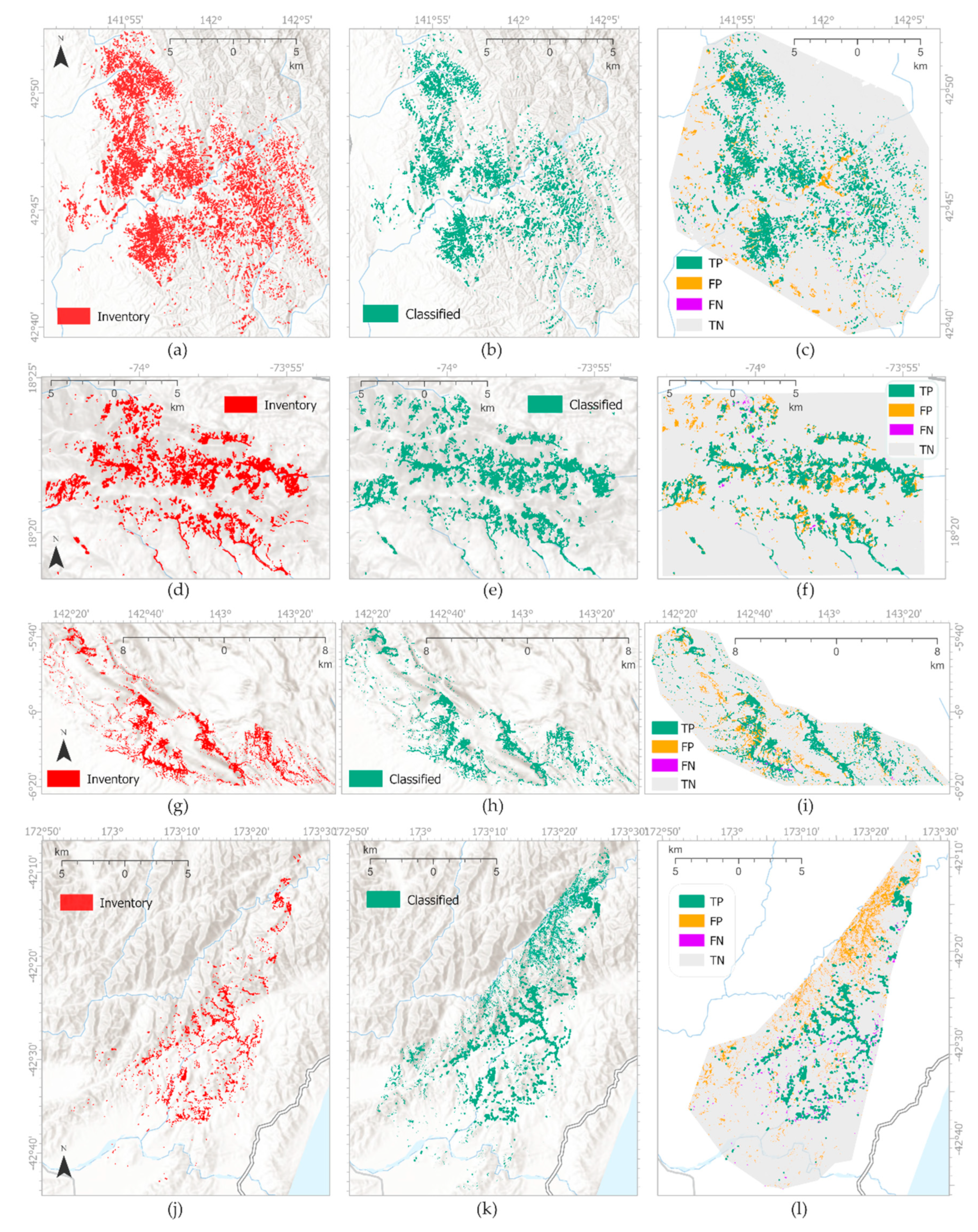
Table 2 provides an overview of each event, including details of the sourced landslide inventory data. In addition,
Figure 1 maps these inventory data as well as the used study area boundaries.
2.1.1. Japan, 2018 Mw 6.6 Hokkaido Earthquake
On September 6, 2018, a moment magnitude 6.6 earthquake struck the Iburi Subprefecture in southern Hokkaido, Japan, following Typhoon Jebi’s passage. The 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi earthquake is hereafter referred to as “JPN case study”. Aftershocks indicated compression along the ENE-SWS direction in the northern, southern, and Shallow Iburi faults [
66]. The earthquake caused extensive damage, triggering thousands of landslides. A comprehensive inventory map identified nearly 6,000 coseismic landslides, mostly small to medium translational ones with high mobility and long run-out distances ranging from 25 m
2 to up to 57,000 m
2. This dataset, representing ground-truth polygons of all landslides triggered during the 2018 Hokkaido earthquake, is hereafter referred to as “landslide inventory”. The spatial extent of the study area was defined by applying a convex hull around the landslide inventory polygons, resulting in an extend of 22 km (East-West) by 24 km (North-South) geodetic distance, while the convex hull-shaped study area spans a geodetic area of 359 km
2. Note that for computational reasons a few distant/isolated landslide inventory polygons had been excluded to reduce the total study area. Despite the area’s low population density (less than 10 persons per km
2), the landslides resulted in 41 fatalities and 691 people injured. The landslide concentration formed an elliptical area parallel to the region’s (active) faults, with the most affected aspect being southerly, perpendicular to the NNW/SSE striking faults. These coseismic landslides occurred in regions with a seismic intensity ranging from 7.0 to 8.0 on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale and peak ground acceleration between 0.4 and 0.7 g. They were densely distributed in hilly regions at elevations between 100 and 250 m, with slope angles ranging from 15° to 35°. Most of the landslides were shallow, several meters deep, and categorized as planar and spoon types [
67]. The area predominantly consists of Neogene sedimentary rocks overlaid by pumice layers from Tarumai volcano to the east. Surface soil layers in the low to middle mountain ranges contain interbedded pumice and ash, with a thickness of approximately 4-5 m [
14]. The landslide-prone area primarily consists of Miocene sedimentary rock. Slope failures occurred in stratified pyroclastic fall deposits due to a combination of strong seismic ground motion and intense antecedent precipitation [
39].
2.1.2. Haiti, 2021 Tiburon Peninsula Mw 7.2 Earthquake
On August 14, 2021, a seismic event of moment magnitude 7.2 struck the region of Nippes, Haiti, specifically on the Tiburon Peninsula, marking a significant geological event. This seismic disturbance was attributed to activity along the Enriquillo–Plantain Garden Fault, a seismogenic fault renowned for its tectonic significance in the area. The aftermath of this earthquake revealed a notable impact on the landscape, triggering over 8,444 landslides across an expanse of approximately 2,700 km
2. Among these, an area totaling 45.6 km
2 experienced direct landslide activity, with particular concentration observed in the western region of the Tiburon Peninsula. Notably, the Pic Macaya National Park emerged as a focal point, with approximately 6,100 landslides occurring within or near its confines, constituting 72.2% of the total landslide occurrences, hereafter referred to as “HTI case study”. Further analysis revealed that 89.4% of the landslides were predominantly situated in the hanging wall area and regions characterized by high relief, featuring slopes ranging between 35° and 55° [
68]. The consequences of these landslides were multifaceted, directly resulting in fatalities and extensive damage to infrastructure. Moreover, the obstruction of roads and other vital pathways hindered response efforts, exacerbating the challenges faced in the wake of this seismic event [
69].
The spatial extent of the study area was defined by applying an envelope around the landslide inventory polygons, resulting in an extend of 16 km (East-West) by 11 km (North-South) geodetic distance, while the convex hull-shaped study area spans a geodetic area of 170 km2. Note that for computational reasons a few distant/isolated landslide inventory polygons had been excluded to reduce the total study area.
2.1.3. Papua New Guinea, 2018 Mw 7.5 Earthquake
In the Highlands of central Papua New Guinea (PNG), close to Komo in the Hela Province, a seismic event of moment magnitude 7.5 took place on February 25, 2018. This event, hereafter referred to as “PNG case study”, stands as the most remarkable earthquake documented within this geographical expanse over the preceding century. Subsequently, the affected area experienced four substantial aftershocks (each with a moment magnitude equal to or exceeding 6.0) within a span of 9 days following the mainshock. The affected area is highly susceptible to landslide due to its climatic, geologic, and tectonic influences. Furthermore, local environmental conditions serve to amplify the seismic shaking, exacerbating the propensity for landslides. The aftermath of the seismic event was characterized by the huge amount of landslides throughout the region [
70].
The initial earthquake and its ensuing aftershocks triggered widespread landslides, with an estimated total exceeding 11,600, of which > 10,000 were triggered by the principal earthquake. These landslides collectively generated a cumulative planimetric failure area encompassing approximately 145 km
2. Steep hillslopes caused the activation of large landslides reaching dimensions of up to approximately 5 km
2 for single landslides. Analysis of the seismic event delineated a predominant reverse fault motion, with discernible displacement reaching up to approximately 0.7 meters along faults extending to depths surpassing 25 km [
71].
The spatial extent of the study area was defined by applying an envelope around the landslide inventory polygons, resulting in an extend of 148 km (East-West) by 84 km (North-South) geodetic distance, while the convex hull-shaped study area spans a geodetic area of 5163 km2. Note that for computational reasons a few distant/isolated landslide inventory polygons were excluded to reduce the total study area.
2.1.4. New Zealand, 2016 Mw 6.7 Kaikōura Earthquake
On November 14, 2016, the northeastern South Island of New Zealand experienced a seismic event of Mw 7.8 known as the Kaikōura earthquake. This earthquake, hereafter referred to as “NZL case study”, exhibited a remarkably intricate rupturing mechanism, unprecedented in complexity within recorded seismic activity. The seismic instrumentation in place within the region provided comprehensive data on the event. A total of 14,233 landslides were documented, covering an extensive area of approximately 14,000 km2. The earthquake’s rupture sequence impacted a series of active faults, extending offshore and significantly affecting coastal and inland areas across the northeastern part of the South Island.
Analysis of global moment tensor solutions revealed the intricate nature of this multi-fault rupture earthquake. The rupture process was observed to propagate from south to north, establishing connections between the Hikurangi subduction system of the North Island and the oblique collisional regime of the South Island, notably the Alpine Fault. The impacts of the Kaikōura earthquake on both infrastructure and the environment were severe and widespread. Reconstruction efforts were estimated to cost between 3 and 8 billion NZD, underscoring the scale of the challenges posed by the event’s aftermath [
72].
The spatial extent of the study area was defined by applying an envelope around the landslide inventory polygons, resulting in an extend of 48 km (East-West) by 69 km (North-South) geodetic distance, while the convex hull-shaped study area spans a geodetic area of 1370 km2. Note that for computational reasons a few distant/isolated landslide inventory polygons had been excluded to reduce the total study area.
Table 2.
Inventory data of coseismic landslides case studies used in this paper.
Table 2.
Inventory data of coseismic landslides case studies used in this paper.
| Earthquake date |
Epicentre
location |
Epicentre Lat/Lon |
Focal
depth(km) |
Mw, death, injured |
Inventory method |
Ref. |
No.
inventory landslides |
Used landslides |
Study area
(km2) |
| 2018 Sept 6 |
Japan,
Hokkaido, Iburi |
42.662°N 142.011°E |
37 |
6.6,
41,
691 |
VHR UAV
imagery,
PlanetScope |
[73] |
5,625 |
5,208 (93%) |
359 |
| 2021 Aug 14 |
Haiti, Tiburon Peninsula, Pic Macaya NP |
18.434°N 73.482°W |
10 |
7.2,
2,200,
12,200 |
GE imagery,
PlanetScope |
[68] |
6,100 |
approx. 80% |
170 |
| 2018 Feb 25 |
PNG, Hela Province, Komo |
6.070°S 142.754°E |
15-30 |
7.5,
160,
500 |
GE imagery,
PlanetScope, Rapid Eye |
[71] |
11,607 |
8,912 (77%) |
5,163 |
| 2016 Nov 14 |
New Zealand, South Island, Kaikōura |
42.737°S 173.054°E |
15 |
6.7,
2,
618 |
GE imagery,
S2 |
[72] |
14,233 |
2,521 (18%) |
1,370 |
2.2. Methodology
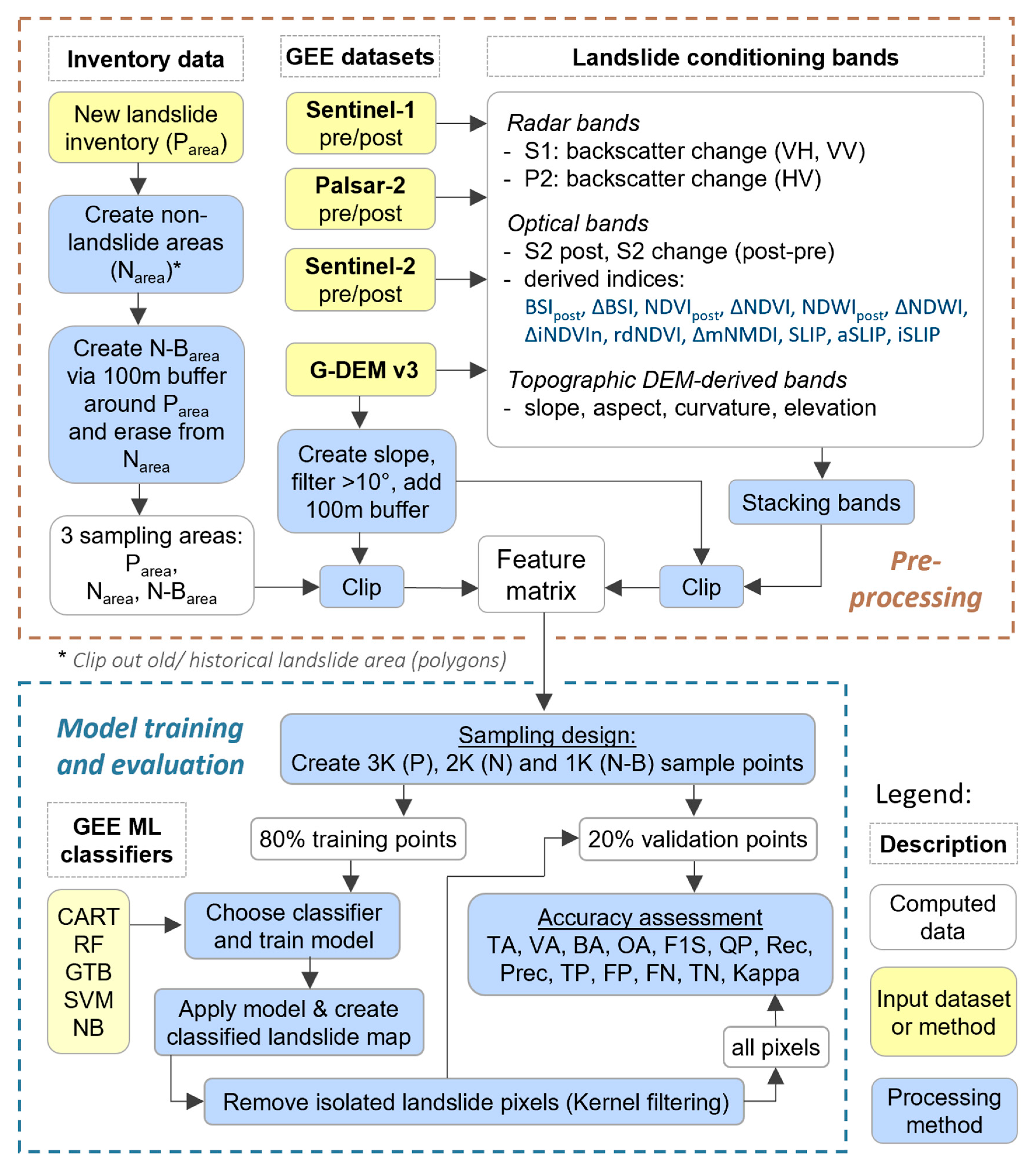
Our ML-LaDeCORsat approach involves two principal steps: a) preprocessing and b) training and evaluation of a ML algorithm used to classify a combined S2 optical S1 SAR imagery dataset into landslide and non-landslide pixels.
2.2.1. Data Preparation
Considering previous approaches (see
Table 1), several satellite sensors and imagery bands that are available in GEE are relevant for landslide detection as proposed in this work (
Table 3).
To prepare multispectral S2 data for landslide detection for each case study, two cloud-free sets of imagery covering the entire Area of interest (AOI) are necessary, representing the situations before and after the landslide events.
As indicated in
Table 2 and in
Figure 1, the inventories of landslides used in this work do not include the entire available inventory source dataset. For GEE performance reasons, a convex hull was applied covering the majority of all inventory data while excluding a small amount of rather isolated inventory landslides. In addition, for the NZL case study, available Sentinel-1 post event imagery only covered the South-East part of the available inventory data.
Except for the NZL case study, a single S2 imagery scene available in GEE did cover the respective AOI. In case of NZL, three adjacent cloud-free S2 imagery had to be joined using the GEE ImageCollection.mosaic() function.
Due to the likeliness of cloud coverage, it is suggested to compute multi-temporal image composites (“mosaics”) [
48]. In this work, S2 multi-temporal image mosaics were created for the pre- and post-earthquake scenario over the PNG case study due to significant cloud coverage in all S2 imagery in 2017 and 2018. In total 88 selected S2 imagery during 2017 were used to create a cloud-free S2 pre-earthquake mosaic and 67 selected S2 imagery between March and July 2018 to create a cloud-free S2 post-earthquake mosaic. Due to PNG’s geographic location being close to the equator causing its hot, humid climate with all months above 18°C, seasonal reflectance dynamics have only marginally impact on these mosaics if at all. For the other three case studies, nearly or completely cloud-free S2 imagery were available within a few months after each earthquake event. A cloud-free pre-earthquake S2 imagery was then extracted approximately one year earlier to avoid seasonal reflectance dynamics.
Since a S2-L1C (TOA) image product can be available (on GEE) up to a few hours earlier than S2-L2A (SR), it was decided to use the S2-L1C product, and to apply, dependent on its impact to landslide detection accuracies, the Sensor Invariant Atmospheric Correction (SIAC) method [
74] to convert TOA radiance into estimated SR values in GEE. Masking was applied to the few cloudy pixels in the pre-earthquake S2 image using the S2 QA60 (cloud mask) band.
Sentinel-1 imagery data accessible via GEE consists of radiometric calibrated, ortho-rectified SAR C-band backscatter images available in four polarization modes: 1) Single co-polarization: vertical transmitting, vertical receiving (VV), 2) Single co-polarization: horizontal transmitting, horizontal receiving (HH), 3) dual-band cross-polarization: vertical transmitting, vertical and horizontal receiving (VV and VH), and 4) dual-band cross-polarization: horizontal transmitting, horizontal and vertical receiving (HH and HV). As argued by [
23], HH and HV polarizations are less useful for landslide detection, thus only VV and VH polarization were considered due to their sensitivity to forest biomass structure [
75].
Due to the longer wavelength, the emitted L-band radar of ALOS-2/P2 can better penetrate through denser vegetation compared to S1’s C-band. The GEE-provided ortho-rectified and radiometrically calibrated and terrain-corrected normalized backscatter data of P2 used in this work, are available as HH and HV polarization bands.
The available S1 SAR imagery data included in this study comprised the period four months before and after the earthquake in order to identify sufficient ascending and descending pre-earthquake respectively post-earthquake imagery. Following the approach of [
23], the temporal median of the pre-event and post-event SAR data was computed, and ascending and descending data were combined by calculating their mean values.
Due to the differences between S1 and P2 in terms of sensor characteristics, polarimetry, orbit parameters, imaging strategies, and data availabilities in GEE, a much larger time window for P2 had to be selected. Even including all available P2 imagery since 2014 and until present, sufficient ascending and descending pre- and post-event P2 imagery were only available for the JPN case study.
Besides using elevation data sourced from ASTER GDEM to extract landslide conditioning factors, slope values derived from the GDEM were used to mask out irrelevant pixels below a certain slope threshold (e.g., 10 degrees).
Another potentially relevant conditioning factor is pixel-based solar radiation. However, the only globally available raster dataset in GEE is the Global Solar Atlas, generated using Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) derived elevation data combined with MTSAT and Himawari-8 reflectance data as reported in [
76]. Due to its coarse spatial resolution of 250 m, the solar atlas was not incorporated into this work.
2.2.2. Landslide Conditioning Factors
As shown in
Figure 2, several bands and derived bands (“pseudobands”) were identified from literature as relevant landslide conditioning factors – and used in the ML-LaDeCORsat approach. For S2, these include the following bands: a) all spectral bands of the prepared S2 post-earthquake image except B1 (aerosol), B9 (water vapor), and B10 (cirrus), b) the differences of each spectral band by subtracting pre-earthquake reflectance values from post-earthquake ones, and c) the below-listed computed spectral indices
1:
Soil index: BSIpost, ∆BSI [
43]
Vegetation index: NDVIpost, ∆NDVI, rdNDVI, ∆iNDVIn [
35,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48]
Water index: NDWIpost, ∆NDWI [
47]
Drought index: ∆mNMDI [
36,
38]
Sudden Landslide Identification Product/index: SLIP [
36], aSLIP [
37], iSLIP [
38]
Figure 2.
Conceptual overview of the ML-LaDeCORsat approach, involving Pre-processing (top box) and Model training and evaluation (bottom box).
Figure 2.
Conceptual overview of the ML-LaDeCORsat approach, involving Pre-processing (top box) and Model training and evaluation (bottom box).
Specific index formulas and thresholds can be found in the cited references. All these indices had been used in previous landslide detection methods, except BSIpost which was added to explore its importance for detection performance.
Utilizing S1 polarization bands, the same methodology as suggested in [
23] was followed to determine log ratio (and percentiles of it) for pre- and post-event S1 SAR intensity using different polarizations. It was then decided to include the following three bands which had been identified via empirical investigation as the best performing bands for landslide detection:
S1_log_VH: log ratio for pre- and post-event S1 SAR (VH) intensity
S1_90p_VH: 90th percentile of S1 log ratio (VH)
S1_90p_VH_VV: 90th percentile of S1 log ratio (VH and VV)
Utilizing P2 polarization bands, the same process as for S1 was applied and the following band was identified to be included in the ML classifier used in this study: P2_log_HV, the log ratio for pre- and post-event P2 SAR (HV) backscatter.
Derived from GDEM, the following topographic factors were included: slope, aspect, curvature, and elevation [
33,
35,
42]. These topographic data are derived from imagery taken prior to the earthquake event. Post-earthquake elevation data were not available in this work, but data including detailed changes in elevation might further improve detection results.
Further relevant topographic indices are TWI and STI, computed using slope and flow accumulation as inputs. While slope can be easily created in GEE from a given DEM, GEE does not provide a function to compute flow accumulation out of the box due to a significant amount of required iterative operations. TWI and STI could be, however, computed from a DEM using GIS software and uploaded into GEE. In GEE, available rainfall datasets do not provide the required spatial resolution to be considered for this work. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) dataset [
77], for instance, supplies global precipitation estimates updated every 30 minutes, but only at a spatial resolution of 0.1 degrees (approximately 11 km). As the focus in this work is to produce a replicable and ready to use GEE landslide detection product, the use of TWI and STI was not further investigated.
In summary, these identified indices, allow the proposed ML-LaDeCORsat detection method to address changes in surface vegetation, vegetation moisture, bare soil, soil moisture, and bare-earth exposures derived from S2 imagery; to consider alterations in ground surface properties (e.g., roughness, dielectric properties) through S1 and P2 SAR intensity and coherence changes; and to incorporate topography features of the study area (e.g., slope, aspect) using the GDEM.
In preparation for the image classification, pre-processed SAR and topographic bands were spatially reprojected and resampled to match pixel dimension (10 m) and position of S2 pixels. Next, all 40 landslide conditioning bands were combined into a single image using the addBands GEE function. This multi-band stacked image was then fed into the ML feature matrix.
Investigations into PCA bands derived from S2 post and S2 change bands did not lead to improved landslide detection accuracies, for none of the four case studies, hence PCA bands were not included in this work.
2.2.3. ML Sampling Strategy
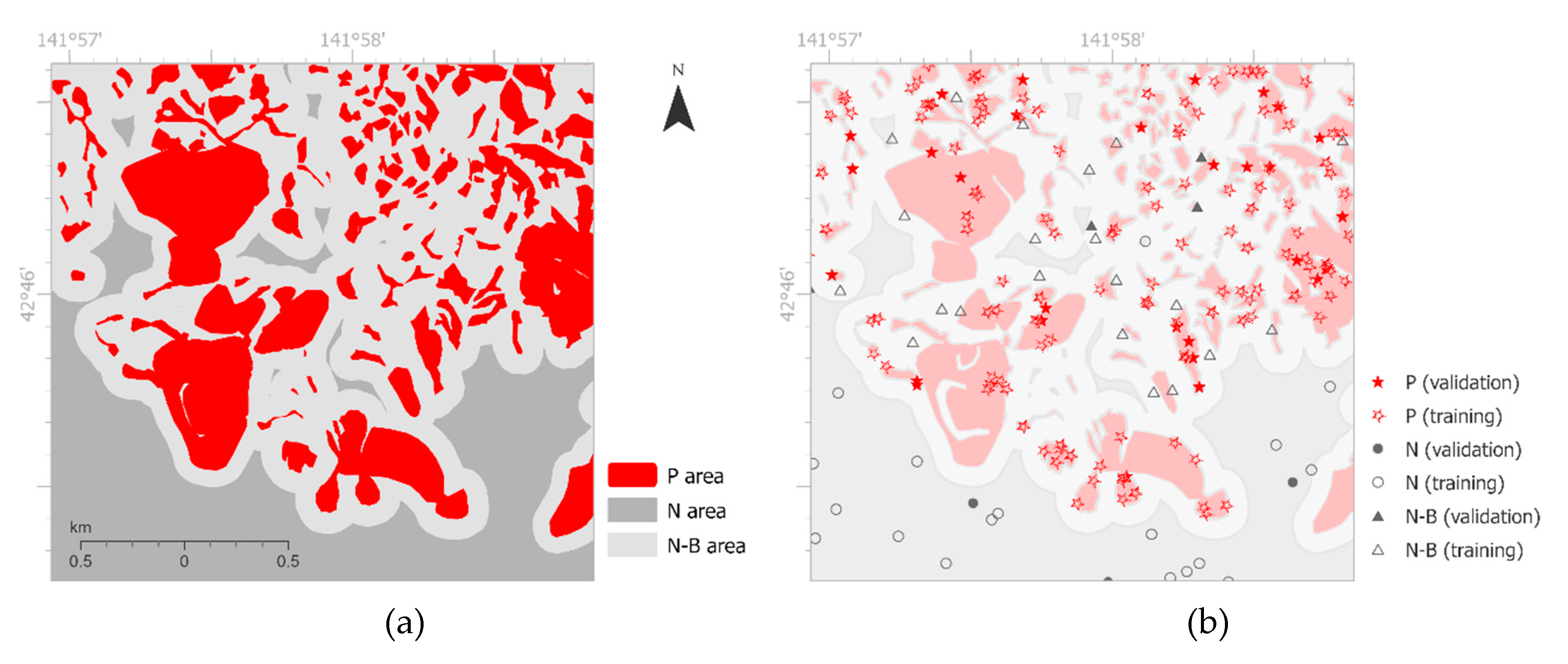
A sampling strategy specifically designed for ML-based classification of landslides was developed: This strategy consists of several geoprocessing steps, illustrated in the preprocessing part of the provided flowchart in
Figure 2. First, three sampling areas were defined. Utilizing the above-mentioned landslide inventories to define a ”Positive” sampling area (P
area), the GIS Erase tool was applied to generate an initial non-landslide “Negative” sampling area (N
area). To allow a stratified random sampling method to create sufficient sampling points near inventoried landslide polygons, a 100 m ring-buffer was created around the P
area, forming a second “Negative” sampling area: the N-B
area. This ring-buffer area was also erased from the initial N
area. Sampling points inside N-B
area allow the model to put emphasize on “border“ areas around landslides.
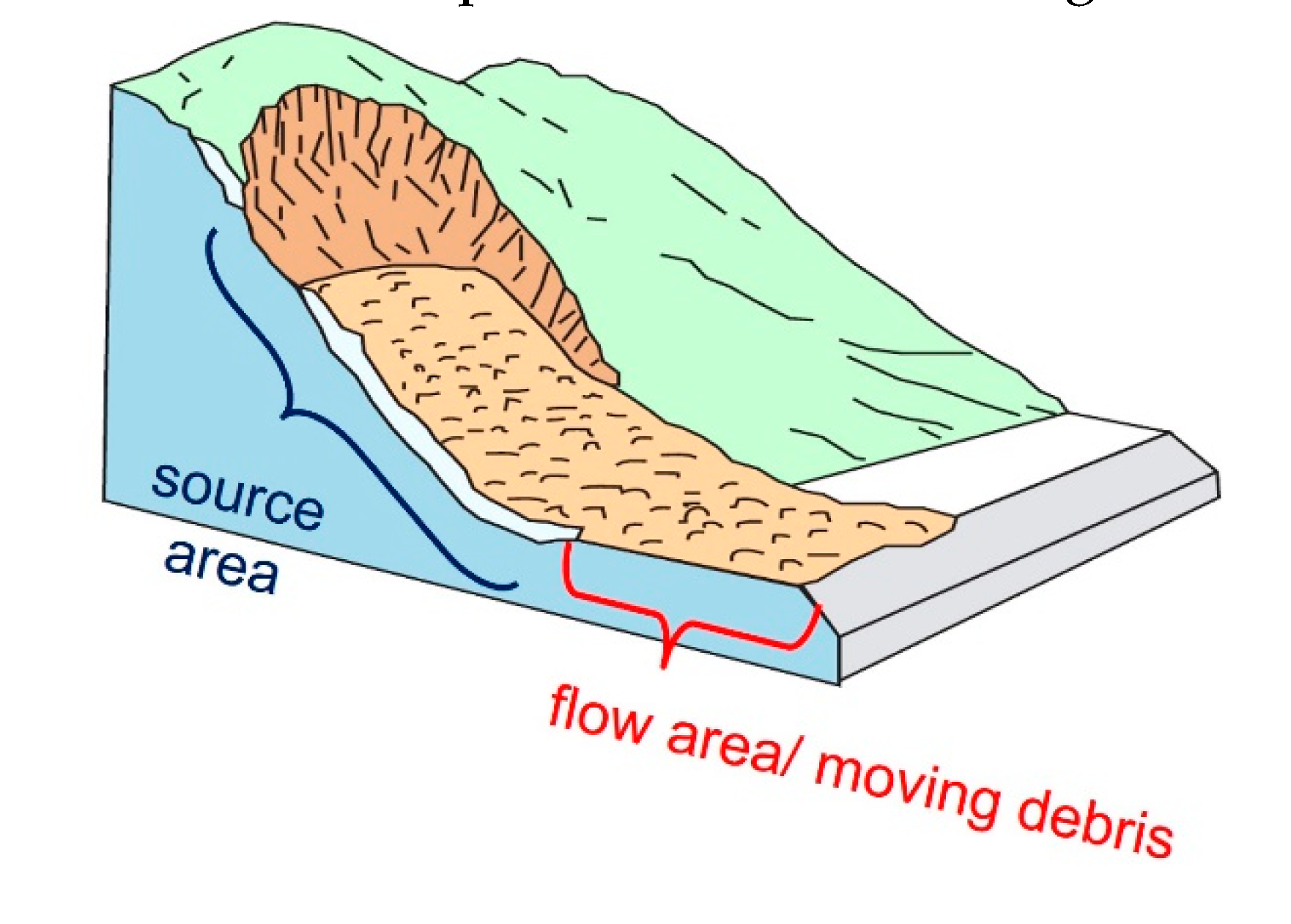
Next, the spatial extent of sampling areas and the multi-band stacked input image were reduced removing pixels within areas of low slopes, less than 10 degrees. Such slope-filtering is being applied in many of the existing RS-based landslide detection approaches, including [
33,
36,
37,
38]. This, however, can cause False Positives (FP) for scenarios in which the landslide is triggered at steeper slopes but its flow area reaches into areas of lower slopes, as illustrated in
Figure 3.
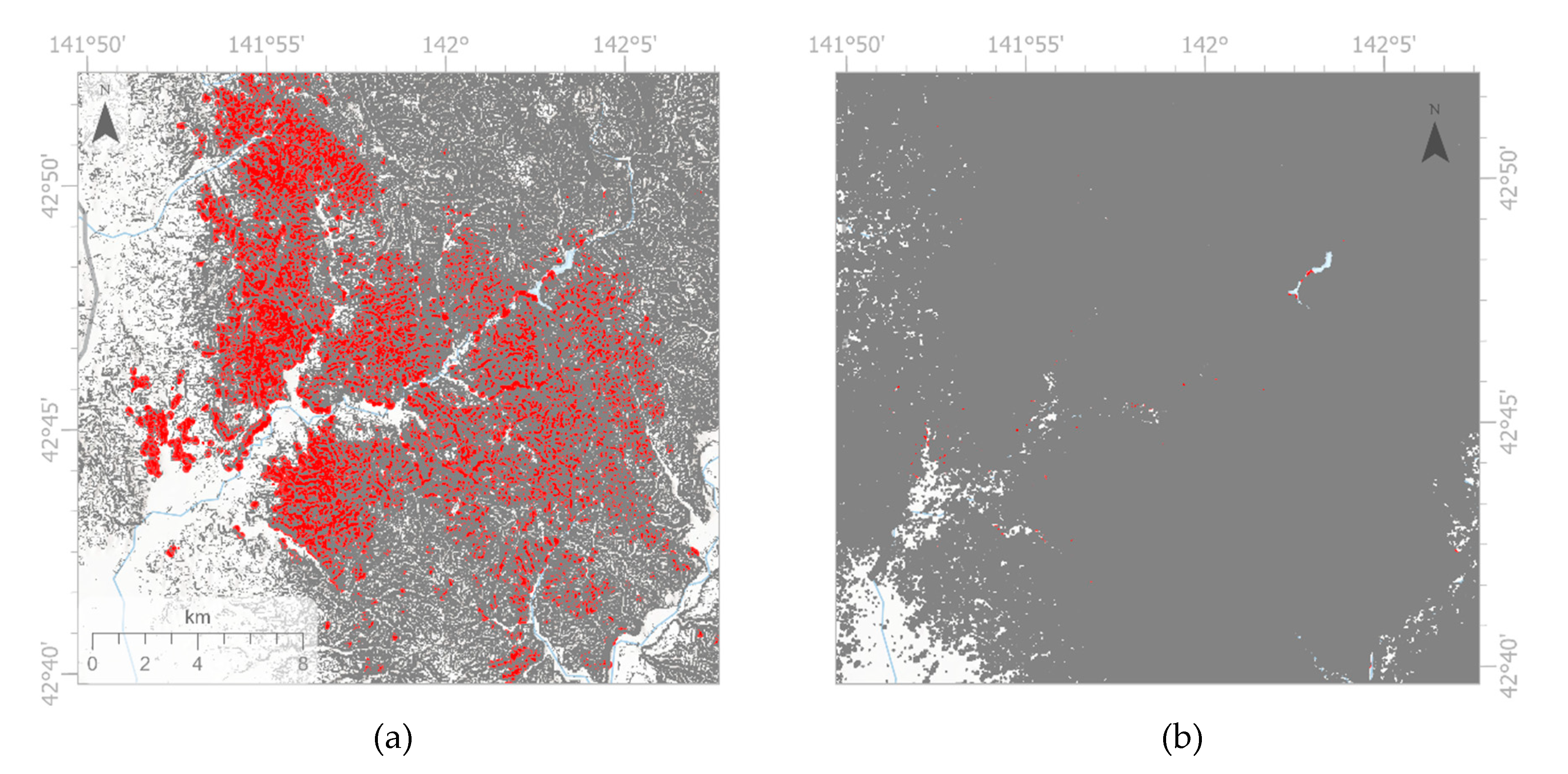
To address this issue, a 100 m buffer was added to the slope filtering (using >10 degrees) before clipping the ML-input image with the final sampling areas. The buffer size of 100 m was determined empirically. Not applying such buffer has a strong impact on causing FP as can be seen in
Figure 4: Pixels with slopes >20 degrees are mapped in grey on top of red-color coded landslide inventory areas. The slope threshold of >10 degrees applied to the JPN case study did only overlap 24% of the landslide inventory polygons (P
area). Only when adding the 100 m buffer, more than 99% of the inventory data were covered, as shown in
Figure 4b.
Table 4 lists landslide inventory areas not covered by a >10 degree slope threshold for all four case studies.
2.2.4. ML Classifier
For ML model training and evaluation, a randomly stratified point sampling approach was implemented using in total 6,000 sampling points that consists of 3,000 “landslide” points inside P
area, 2,000 “non-landslide” points inside N
area, and another 1,000 “non-landslide” points inside N-B
area.
Figure 5 Each of these three parts were then split into 80% training points and 20% validation points as exemplarily shown in
Figure 5.
Next, all available ML classifiers in GEE were implemented, including Classification and Regression Trees (CART), Naive Bayes (NB), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Gradient Tree Boost (GTB). For a consistent comparison, a fixed randomization seed with a value of ‘0’ was applied to ensure using the exact same set of randomly distributed sampling points for ML model training and validation. Aiming to compare the performance of all ML classifiers for landslide detection, the optimal settings for the classifiers’ parameter were empirically investigated and finally defined as listed in
Table 5. Details about GEE classifier and their parameters are described in [
78,
79]. To further improve detection accuracy, a Gaussian kernel filter (radius: 60 m, sigma: 30) was applied as suggested in [
80] to the classified image to remove wrongly detected isolated single landslide pixels. Older landslides triggered by previous events were excluded from training and predication. If not considered the prediction will likely suffer from high number of FP.
2.2.5. Evaluation Metrics
A range of different evaluation metrics were implemented to allow comparison of landslide detection accuracy achieved in this work with existing methods (listed in
Table 1). Evaluation metrics used in this study included Kappa, OA, BA, BE, Spec, Recall, Prec, F1S, NPV, PPV, OE, CE, TNR, FPR, and FNR. Furthermore, pixel counts of TP, FP, FN, TN were computed and added to the results to allow others to determine any further evaluation metrics, such as omission or commission error. For comparing different classification settings within this work (classifier parameters, sampling input, selected bands, and pseudobands), it was decided to use the BA as one of the main comparative validation metric due to its advantages for measuring the prediction quality of all target classes as described by [
81], along with OA, Recall, Prec, F1S, and Kappa. Moreover, Training Accuracy (TA) and Validation Accuracy (VA) were computed to investigate and address potential model overfit (in case of larger differences between TA and VA). A detailed description of each metric can be found in [
81]. For each case study, the evaluation metrics were computed using approximately 2,000 randomly distributed validation points, containing at least 600 points inside landslide inventory polygons. Computing the same evaluation metrics was then repeated considering all pixels of the entire study area. Although a heavier computational task in GEE, the ‘all-pixel’ evaluation approach provides the best possible evaluation.
2.2.6. Band Importance Investigations
When using a set of potentially relevant features or variables (in this case spectral bands or derived indices) for a ML algorithm, it is crucial to investigate the importance of each band to achieve a better insight into what feature contributes towards performance improvement and to decide which features to exclude in order to reduce the classification computation time and memory. To investigate the importance of each band, we utilized the GEE inbuilt function: classifier.explain() which returns a dictionary that describes the results of a trained classifier and includes band importance factors.
2.2.7. Transfer Learning Investigations
Transfer learning or domain adaptation has been widely used in image classification and other fields [
82,
83]. It is crucial to note that models predicting landslides may be applied in geographical areas distinct from those where the model’s training data was gathered.
To verify the performance of ML-LaDeCORsat applied to landslide events, we designed and conducted across domain transfer learning for each case study with training the ML-LaDeCORsat model using different subsets of target site samples together with the complete sampling point dataset from other case studies. The model was trained on data from one up to three sites and with or without a portion of training data from site four and is applied to the test data of site four for evaluation. Comparing and validation of across domain trained ML-LaDeCORsat outputs followed the same approach as described earlier.
3. Results
3.1. Landslide Detection Accuracies
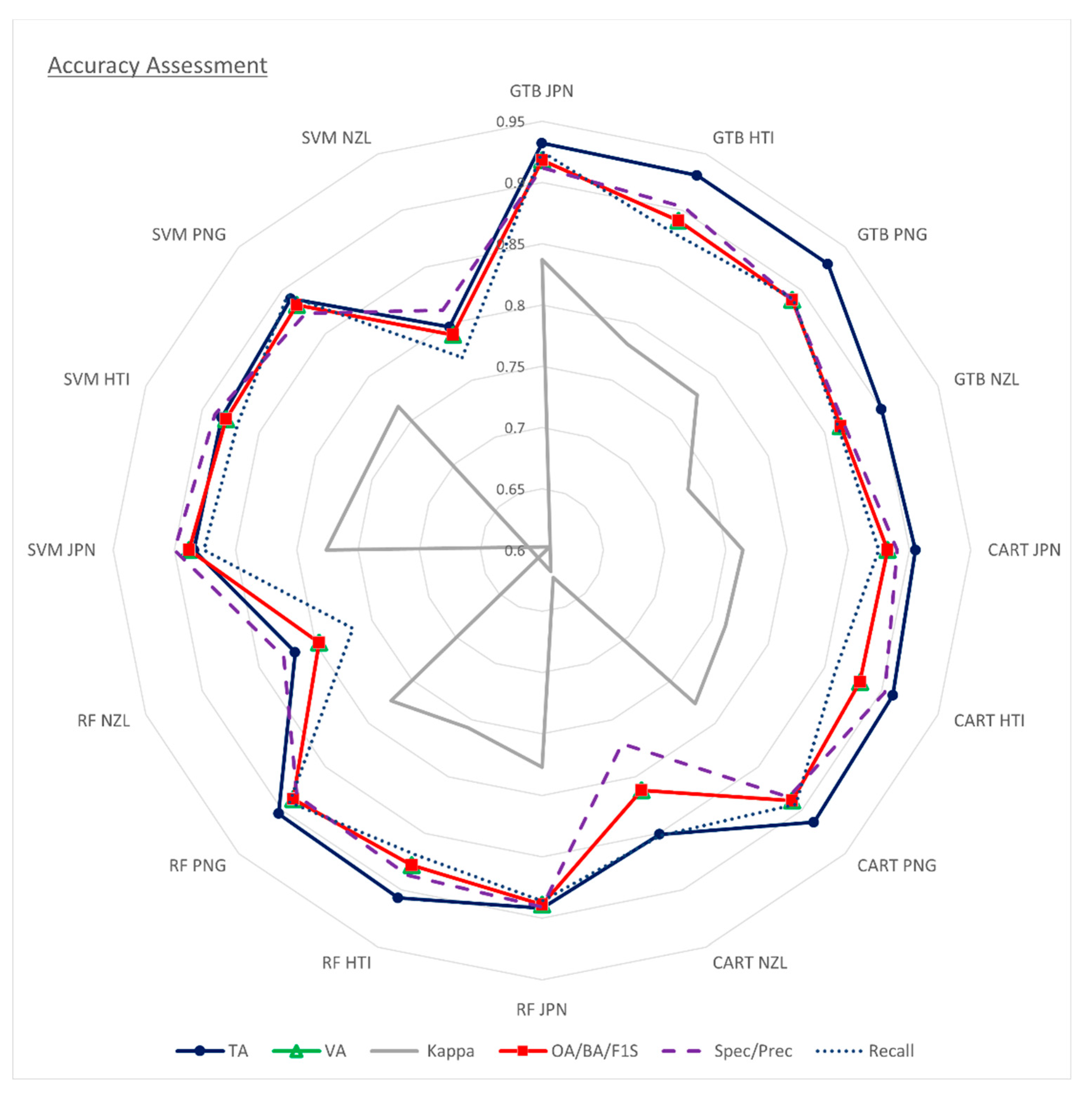
Figure 6 presents ML-LaDeCORsat performance results for validation sampling points at each case study site using CART, RF, GTB, or SVM classifier. In each case, S2-L1C (TOA) bands have been used as they resulted in slightly better detection accuracies compared to using SIAC-derived S2-L2A (SR) bands. Nevertheless, the shared ML-LaDeCORsat GEE scripts do include both options. The classification performance measures include TA, VA, Kappa, Spec, and Recall. BA and F1S outputs were almost identical to OA, so was Prec to Spec.
Supplementary Table S1 and
Table S2 list the specific performance measures for these and all other validation metrics, as described in section 2.2.5., for validation samples and for ‘all pixels’ applying each of all available classifiers included NB.
Results clearly revealed that the GTB-classifier achieved the best landslide detection accuracy with OA of 92% of all validation pixels correctly classified for JPN, 89% for HTI and PNG, and 86% for NZL. CART, RF, and SVM classifier performed less accurate resulted in OA of 80-88%. Using NB did result in the least accurate prediction of only 49-57%. Comparing different classifiers based on the amount of overfitting (differences between training and validation accuracy), all classifiers indicate very small differences of less than 4%, indicating that the model is not overfitted.
To compare the best detection accuracy achieved using ML-LaDeCORsat with GTB, landslides of all four case studies were predicted in GEE using one or more bands that represent existing methods or additional landslide condition bands as previously presented in
Table 1. Resulting ‘all pixel’-based BA and Kappa validation values are listed in
Table 6. In each case ML-LaDeCORsat outperformed all existing methods. The work of [
47] utilizing a supervised classification applied to four conditioning factors (NDWIpost, NDVIpost, DEM, and slope) was identified as the best performing existing method, but it achieved, taking the JPN case study as an example, 5% lower BA and 10% lower Kappa than ML-LaDeCORsat. Detailed accuracy assessment can be found in supplementary
Table S3 until
Table S6. Running ML-LaDeCORsat with the best performing classifier, GTB, a binary classified landslide map was created and as well as an error map (
Figure 7) providing visual insights into distribution and spatial density of TN and FN within the study area.
3.2. Importance Factors of Landslide Conditioning Bands
For investigating the importance of each landslide conditioning band for ML-LaDeCORsat accuracy, we used band importance values provided as an output of GEE
classifier.explain() function, which is available for CART, RF, and GTB.
Figure 8 displays normalized GEE band importance values for each of these three classifiers, sorted by their sum over all case studies. High values indicate high importance factors. For all three classifiers the following bands showed the highest importance factors: NDVI
post, BSI
post, dem, S1_log_VH, ΔB4, ΔB5, ΔNDWI. Surprisingly, S2 NIR and SWIR bands were less important. Further experiments investigating the detection performance with or without S1 bands confirmed for each case study that including S1 derived bands always improved the landslide detection accuracy. It should be noted that P2_log_HV band is not included in
Figure 8 since it was only used for the JPN case study. It had average importance for GTB (normalized importance of 0.2) and for CART (0.12), and no importance for RF classifier (0.05).
Using the JPN case study,
Table 7 lists OA and BA as well as Earth Engine Compute Unit (EECU) in minutes, representing the amount of instantaneous processing power, peak memory (MB), and the count of operations – for running the entire GEE script including image compilation, filtering, calculation of pseudobands, image band stacking, training the ML classifier etc. OA, BA and the three computational measures are provided for running the script with all 40 bands for all classifiers and with using only the best 20, 15, 10, or 5 bands for the three best performing classifiers, GTB, RF, and CART. These results clearly indicate the benefit of using a selected number of identified important bands in a ML classifier for the used processing power in GEE. Using a significantly reduced number of bands, identified as most important, still allows to detect landslides with OA of 89%, and it did also significantly reduce computation efforts in GEE. Computational savings revealing time savings of up to 87%, peak memory reduction of up to 72%, and a decrease of used operations of up to 23%. Detailed accuracy assessment for running ML-LaDeCORsat with selected important bands can be found in supplementary
Table S7,
Table S8, and
Table S9.
3.3. Transfer Learning
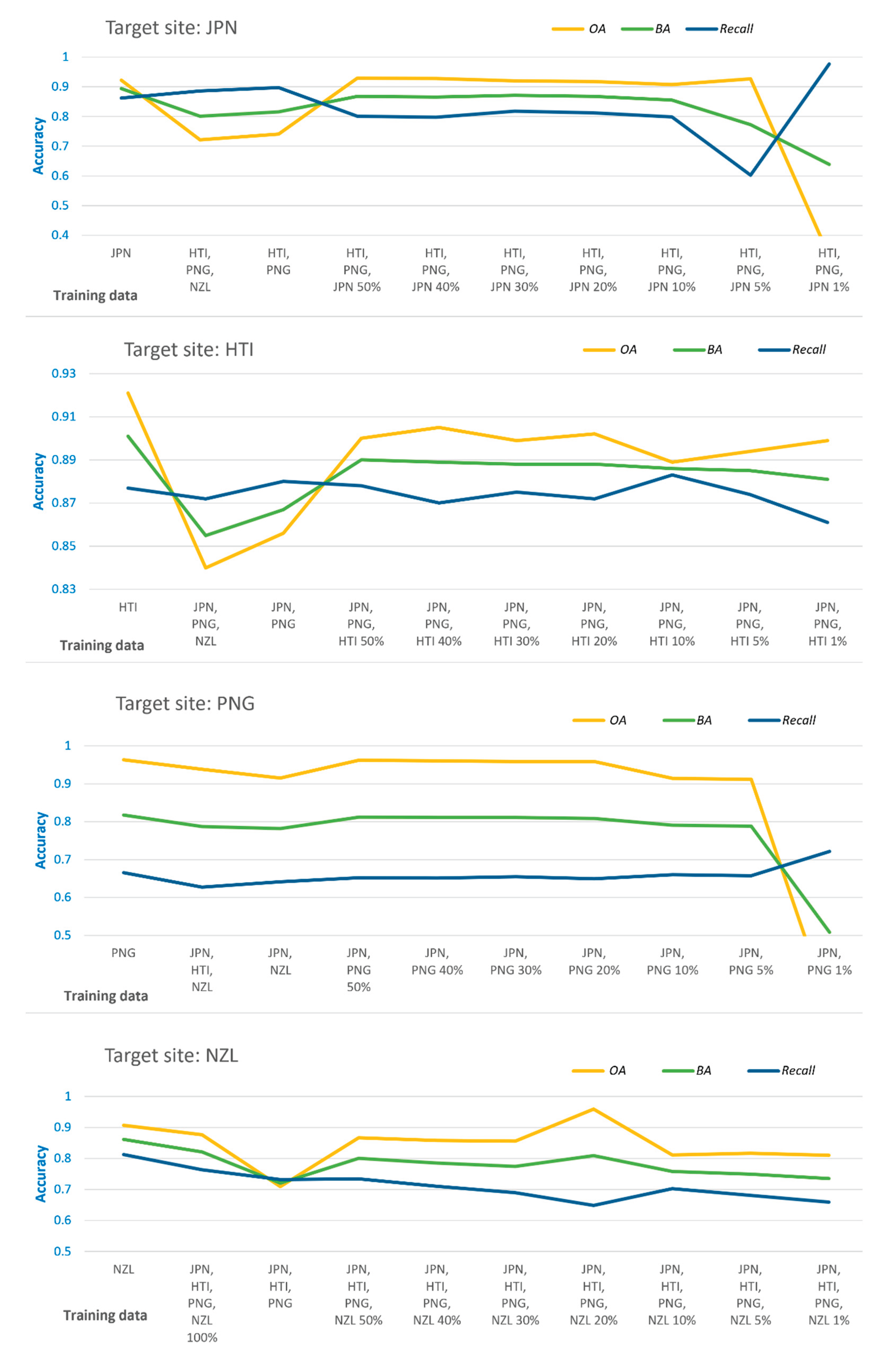
Results for across domain transfer learning investigations using the best performing classifier (GTB) for ML-LaDeCORsat are presented in
Figure 9. For each case study site, OA, BA, and Recall metrics are plotted against different training options: using all training samples from 1) target site, 2) all other sites, 3) the ‘best performing’ other sites, 4-10) the ‘best performing’ other sites plus a subset (50/40/30/20/10/5/1%) of the target site. The ‘best performing’ other sites have been identified by comparing detection accuracies for a target site using all possible combinations of across domain training sites (e.g., training option for JPN target site: HTI only; PNG only; NZL only; HTI and PNG; PNG and NZL; HTI and NZL; all three). Consequently, HTI and PNG combined resulted as best performing training sites for target JPN. JPN and PNG combined resulted as best performing training sites for target HTI. Best results for PNG delivered the GTB classifier trained by only JPN. For NZL, all other three sites combined resulted as the best option. Detailed accuracy assessment for across sites transfer learning can be found in Supplementary
Tables S10–S13.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
We propose a novel machine learning-based approach for Coseismic Landslide Detection using Combined Optical and Radar Satellite Imagery (ML-LaDeCORsat), to identify the locations of landslides using freely available imagery in GEE. Furthermore, we demonstrate the improved reliability and accuracy of the approach by comparing its performance with other methods using a landslide event triggered by four different earthquake case studies. ML-LaDeCORsat hence has great potential to enable more effective responses to landslides globally.
Given that the main purpose of rapidly identifying landslides is to improve disaster management responses, accuracy is a key criterion for any approach. The prediction accuracy is impacted by several aspects, including ML sampling design (number of sampling points, distribution and density, topographic and other factors to be considered into a stratified sampling approach), spatial accuracy and precision of geo-referenced landslide inventory polygons, used satellite imagery and derived pseudobands, image processing steps, the used ML classifier, its parameters, and the chosen evaluation metrics. In this study, all these aspects were carefully investigated and addressed to achieve the best possible landslide detection accuracy in GEE while using ready-made datasets in GEE. Comparisons with existing approaches [
14,
23,
33,
35,
36,
37,
38,
42,
43,
44,
45,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52] demonstrated superior performance of ML-LaDeCORsat of at least 10% higher detection accuracy.
Compared to previous RS-based landslide detection research, this study has, to our knowledge for the first time in literature, combined various relevant landslide conditioning bands utilizing S2 spectral reflectance bands and indices with radar-derived backscatter change information into a single feature matrix used to train a ML model. Furthermore, the performance of the ML-LaDeCORsat model has been tested applying different available GEE ML classifiers and compared to existing solutions incorporating all validation sampling points, but then also using all pixels to have a best possible accuracy assessment. The GTB ML classifier revealed the best prediction results, for all study sites with OA of 92% compared to CART with 88%, RF with 89%, SVM with 89%, and NB with 66% validation pixels correctly classified, taking the JPN case study as an example.
A landslide specific sampling design combined with a novel slope- and slope-buffer based masking approach demonstrated to be highly effective in reducing FP, in particular in scenarios where a landslide flow area reached pixels with slopes below the slope-threshold. In addition, applying a Gaussian kernel filter to the predicted landslide map helped to remove isolated single FP pixels. In summary, the introduced novel ML-LaDeCORsat approach significantly improves landslide detection through image combining optical and radar imagery and ML and is easily adaptable to other landslide scenarios with the GEE script being available.
Pixel size, source data accuracy, and imagery availability on GEE pose limitations on ML-LaDeCORsat that could be partially addressed in future studies. In case a sampling pixel is located at the edge of a landslide, it is either defined as landslide pixel or as a non-landslide one, depending on whether the respective part of a landslide inventory polygon is covering more (or less) than 50% of an image pixel. Smaller imagery pixel-size and more accurate landslide inventory boundaries will lower the potential occurrences of such false sampling cases and, consequently, improve detection accuracies. Sampling pixels located on landslide inventory edges could also be removed or avoided. In regard to the quality of the landslide inventory dataset used, it was discovered that at a few locations, in particular at the edge of some landslide polygons, the inventory did not always match with the visual landslide information available from a very high (sub-meter) resolution true-color satellite composite (accessed through Google Earth Pro). A manual correction of these mismatches could potentially further improve prediction accuracies. A few of the randomly distributed training and validation samples had been positioned over pixels located near the edge of a landslide inventory polygon, causing the use of a potential false sample. Although an undertaken verification of sampling points did not reveal any false samples, it was not possible to manually inspect all of them due to the large amount of sampling points (60,000 for each study site). Detection results could be further improved by incorporating each of the following additional bands – if made available in GEE at a reasonably high spatial resolution (e.g., of 20 m or better): TWI, STI, and a raster image with annual rainfall data. This study also lacked post-earthquake elevation data, but if available, the inclusion of data containing precise elevation changes could potentially further enhance the accuracy of the detection results. Lastly, the availability of post-earthquake S1 imagery and near cloud-free S2 imagery does impact timely landslide detection when using our approach.
There are plans to extend this work. Firstly, we hope to further improve detection results by considering the pixel neighborhoods within the ML classification – similar to [
42] and by including additionally imagery that are not available in GEE, that is PlanetScope (Dove/SuperDove) or VHR historical RGB Satellite Imagery extracted from GE [
84]. Secondly, we plan to convert our GEE JavaScript solution into a GEE Python Notebook to access TensorFlow libraries for further advancing the ML model. Thirdly, our approach could be tested with different landslide types, such as avalanche or mudslide where optical and radar input imagery likely comprises different spectral characteristics. It may be particularly important to apply the approach to landslide events triggered by extreme weather events, such as heavy rainfall, which are forecast to become more frequent or more intense under anthropogenic climate change [
85]. For example, the rainfall associated with tropical cyclones (also known as hurricanes or typhoons) is known to trigger landslide events and are forecast to increase in intensity [
86,
87,
88]. Lastly, the suggested ML-LaDeCORsat approach could be adapted to improve existing work on landslide susceptibility [
17,
18,
19]. Accurate and rapid identification of landslides will likely become more important because extreme weather events are forecast to become more frequent, implying an increased likelihood of earthquakes following heavy precipitation events, which would increase the number of associated landslides.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1. Accuracy assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat applied to JPN and HTI study sites. Table S2. Accuracy assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat applied to PNG and NZL study sites. Table S3. Accuracy Assessment of existing landslide detection methods for JPN case study. Table S4. Accuracy Assessment of existing landslide detection methods for HTI case study. Table S5. Accuracy Assessment of existing landslide detection methods for PNG case study. Table S6. Accuracy Assessment of existing landslide detection methods for NZL case study. Table S7. Normalized sorted band importance outputs for ML-LaDeCORsat for each study site using GTB, CART, or RF ML classifier, sorted by their overall sum. Table S8. Accuracy Assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using selected bands – case study JPN. Table S9. Accuracy Assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using selected bands – case study HTI. Table S10. Accuracy Assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using Transfer Learning for JPN. Table S11. Accuracy Assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using Transfer Learning for HTI. Table S12. Accuracy Assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using Transfer Learning for PNG. Table S13. Accuracy Assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using Transfer Learning for NZL.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P., P.X. and J.L.; Methodology, S.P., G.K. and A.W.; Software, S.P.; Validation, S.P., J.L. and Z.Z.; Formal Analysis, S.P.; Investigation, S.P.; Resources, S.P.; Data Curation, S.P.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, S.P.; Writing – Review & Editing, J.L., G.K., A.W. and P.X.; Visualization, S.P.; Project Administration, S.P.; Funding Acquisition, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The University of South Australia, Unit of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) supported this project financially through the Professional Experience Program 2023 granted to the first author.
Data Availability
Publicly available Google Earth Engine (GEE) scripts and datasets develop and used in this study can be found in the following GEE repository:
The GEE repository includes scripts with our implemented ML_LaDeCORsat landslide detection method, and scripts of previously existing landslide detection methods (for comparison) implemented and validated in GEE using inventory dataset for four case studies.
The GEE repository includes the following scripts:
LaDeCORsat_JPN: Japan, Hokkaido, Iburi 2018 case study
LaDeCORsat_HTI: Haiti, Tiburon Peninsula, Pic Macaya NP 2021 case study
LaDeCORsat_PNG: Papua New Guinea, Hela Province, Komo, 2018 case study
LaDeCORsat_NZL: New Zealand, Kaikōura 2016 case study
LaDeCORsat_Transfer_Learning: across study sites training and classification
Other_landslides_detection_methods: implemented landslide detection methods as listed in
Table 6.
These GEE scripts include shared GEE assets. For each case study shared assets include a study area polygon (“AOI”), landslide ground truthing polygons (“GT”), a pre-processed multi-band stacked input image (“img_for_ML”) and training and validation point samples.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the ESA Copernicus program, NASA, and GEE for providing freely available satellite imagery data and cloud-based processing tools. We also acknowledge Zhang, Li, Wang and Iio [
39] for providing the Hokkaido landslide inventory. Part of this research was carried out at Kyoto University, Disaster Prevention Research Institute (DPRI), which we thank for cooperation in form of hosting the first author as a Visiting Research Fellow.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this paper:
AOI Area of interest
BA Balanced Accuracy
BSI Bare Soil Index
CART Classification and Regression Trees
CE Commission Error
CNN Convolutional Neural Network
DL Deep Learning
EECU Earth Engine Compute Unit
ESA European Space Agency
FN False Negative
FP False Positive
gDEM Global Digital Elevation Model
GE Google Earth
GEE Google Earth Engine
GTB Gradient Tree Boost
IR Infra-Red
iSLIP Improved Sudden Landslide Identification Product
L8 Landsat-8
LULC Land Use Land Cover
ML Machine Learning
MODIS Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer
Narea Area for negative training samples
N-Barea Area for negative training samples inside ring-buffers
NASA National Aeronautics and Space Administration
NB Naive Bayes
NDVI Normalized Difference Vegetation Index
NIR Near-Infra-Red
NRT Near real-time
OA Overall Accuracy
OE Omission Error
PCA Principal component analysis
P2 Palsar-2
QP Quality percentage
RF Random Forest
RS Remote Sensing
S1 Sentinel-1
S2 Sentinel-2
SIAC Sensor Invariant Atmospheric Correction
SLIP Sudden Landslide Identification Product
SR Surface reflectance
STI Sediment Transport Index
SVM Scalable Vector Machine
SWIR Short-Wave Infra-Red
TA Training Accuracy
TN True Negative
TOA Top-Of-Atmosphere (reflectance)
TOA2SR Top of Atmosphere reflectance corrected to Surface Reflectance
Parea Area for positive training samples (Ground-truth)
TP True Positive
TWI Topographic Wetness Index
VA Validation Accuracy
VHR Very High-Resolution
Notes
| 1 |
Prefixes in front of spectral index abbreviation: ‘∆‘ refers to change (post minus pre), ‘i' refers to inverse, ‘m’ refers to modified, ‘n’ refers to normalized, and ‘rd’ refers to relative difference. |
References
- Highland, Lynn, and Peter T Bobrowsky. The Landslide Handbook: A Guide to Understanding Landslides: US Geological Survey Reston, VA, USA, 2008.
- Keefer, David K. "Landslides Caused by Earthquakes." Geological Society of America Bulletin 95, no. 4 (1984): 406-21.
- Ritchie, Hannah, and Max Roser. "Natural Disasters." https://ourworldindata.org/natural-disasters (accessed July 9th).
- Wallemacq, Pascaline, Regina Below, and Denis McClean. Economic Losses, Poverty & Disasters: 1998-2017: United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction, 2018.
- Quigley, Mark, and Brendan Duffy. "Effects of Earthquakes on Flood Hazards: A Case Study from Christchurch, New Zealand." Geosciences 10, no. 3 (2020): 114.
- Noy, Ilan, Toshihiro Okubo, Eric Strobl, and Thomas Tveit. "The Fiscal Costs of Earthquakes in Japan." International Tax and Public Finance (2022): 1-26.
- Shafapourtehrany, Mahyat, Maryna Batur, Farzin Shabani, Biswajeet Pradhan, Bahareh Kalantar, and Haluk Özener. "A Comprehensive Review of Geospatial Technology Applications in Earthquake Preparedness, Emergency Management, and Damage Assessment." Remote Sensing 15, no. 7 (2023): 1939.
- Akhoondzadeh, Mehdi. "Advances in Seismo-Lai Anomalies Detection within Google Earth Engine (Gee) Cloud Platform." Advances in Space Research 69, no. 12 (2022): 4351-57.
- Singh, Deepak, DN Pandey, and Usha Mina. "Earthquake—a Natural Disaster, Prediction, Mitigation, Laws and Government Policies, Impact on Biogeochemistry of Earth Crust, Role of Remote Sensing and Gis in Management in India—an Overview." J. Geosci 7, no. 2 (2019): 88-96.
- Elliott, JR. "Earth Observation for the Assessment of Earthquake Hazard, Risk and Disaster Management." Surveys in geophysics 41, no. 6 (2020): 1323-54.
- Yariyan, Peyman, Mohammadtaghi Avand, Fariba Soltani, Omid Ghorbanzadeh, and Thomas Blaschke. "Earthquake Vulnerability Mapping Using Different Hybrid Models." Symmetry 12, no. 3 (2020): 405.
- Dell’Acqua, Fabio, and Paolo Gamba. "Remote Sensing and Earthquake Damage Assessment: Experiences, Limits, and Perspectives." Proceedings of the IEEE 100, no. 10 (2012): 2876-90.
- Rojas, Carolina, Vivanco Mauricio, Opazo Sergio, Stefan Peters, and Villaroel Constanza. "Pre and Post Earthquake Land Use and Land Cover Identification in Concepción." Earth Observation of Global Changes (EOGC) (2013): 223-31.
- Aimaiti, Yusupujiang, Wen Liu, Fumio Yamazaki, and Yoshihisa Maruyama. "Earthquake-Induced Landslide Mapping for the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake Using Palsar-2 Data." Remote Sensing 11, no. 20 (2019): 2351.
- Lam, CY, K Tai, and AM Cruz. "Topological Network and Gis Approach to Modeling Earthquake Risk of Infrastructure Systems: A Case Study in Japan." Applied geography 127 (2021): 102392.
- Cruden, David Milne. "Cruden, Dm, Varnes, Dj, 1996, Landslide Types and Processes, Transportation Research Board, Us National Academy of Sciences, Special Report, 247: 36-75." Landslides Eng. Pract 24 (1993): 20-47.
- Zhao, Yu, Zeng Huang, Zhenlei Wei, Jun Zheng, and Kazuo Konagai. "Assessment of Earthquake-Triggered Landslide Susceptibility Considering Coseismic Ground Deformation." Frontiers in Earth Science 10 (2023): 993975.
- Ali, Sk Ajim, Farhana Parvin, Jana Vojteková, Romulus Costache, Nguyen Thi Thuy Linh, Quoc Bao Pham, Matej Vojtek, Ljubomir Gigović, Ateeque Ahmad, and Mohammad Ali Ghorbani. "Gis-Based Landslide Susceptibility Modeling: A Comparison between Fuzzy Multi-Criteria and Machine Learning Algorithms." Geoscience Frontiers 12, no. 2 (2021): 857-76.
- Fan, Xinyue, Bin Liu, Jie Luo, Ke Pan, Suyue Han, and Zhongli Zhou. "Comparison of Earthquake-Induced Shallow Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Based on Two-Category Lr and Kde-Mlr." Scientific Reports 13, no. 1 (2023): 833.
- Yao, Tian, David Green, Karen Michael, and Diane Davies. "Using Nasa Lance near Real-Time Products for Disaster Risk Reduction." Paper presented at the FOSS4G 2021 (Free and Open Source Software for Geospatial) 2021.
- NASA. "Near Real Time (Nrt) Data from Esa Sentinel Satellites." (2021), https://appliedsciences.nasa.gov/join-mission/publications-resources/near-real-time-nrt-data-esa-sentinel-satellites.
- Liu, Xiaojie, Chaoying Zhao, Qin Zhang, Zhong Lu, Zhenhong Li, Chengsheng Yang, Wu Zhu, Jing Liu-Zeng, Liquan Chen, and Chuanjin Liu. "Integration of Sentinel-1 and Alos/Palsar-2 Sar Datasets for Mapping Active Landslides Along the Jinsha River Corridor, China." Engineering Geology 284 (2021): 106033.
- Handwerger, Alexander L, Shannan Y Jones, Pukar Amatya, Hannah R Kerner, Dalia B Kirschbaum, and Mong-Han Huang. "Strategies for Landslide Detection Using Open-Access Synthetic Aperture Radar Backscatter Change in Google Earth Engine." Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Discussions. pp (2021): 1-35.
- Wang, Wandi, Mahdi Motagh, Simon Plank, Aiym Orynbaikyzy, and Sigrid Roessner. "Application of Sar Time-Series and Deep Learning for Estimating Landslide Occurrence Time." The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 43 (2022): 1181-87.
- Jensen, John R. Remote Sensing of the Environment: An Earth Resource Perspective 2/E: Pearson Education India, 2009.
- Fitzgerald, Donna L, Stefan Peters, Gregory R Guerin, Andrew McGrath, and Gunnar Keppel. "Quantifying Dieback in a Vulnerable Population of Eucalyptus Macrorhyncha Using Remote Sensing." Land 12, no. 7 (2023): 1271.
- Schmitt, Michael, Lloyd H Hughes, Chunping Qiu, and Xiao Xiang Zhu. "Aggregating Cloud-Free Sentinel-2 Images with Google Earth Engine." ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 4 (2019): 145-52.
- Martinez, Sabrina N, Lauren N Schaefer, Kate E Allstadt, and Eric M Thompson. "Evaluation of Remote Mapping Techniques for Earthquake-Triggered Landslide Inventories in an Urban Subarctic Environment: A Case Study of the 2018 Anchorage, Alaska Earthquake." Frontiers in Earth Science 9 (2021): 673137.
- Ray, Ram L, Maurizio Lazzari, and Tolulope Olutimehin. "Remote Sensing Approaches and Related Techniques to Map and Study Landslides." Landslides-Investig. Monit 2 (2020): 1-25.
- Xu, Chong, Tolga Gorum, and Hakan Tanyas. "Application of Remote Sensing and Gis in Earthquake-Triggered Landslides." Frontiers in Earth Science 10 (2022): 964753.
- Byrraju, Sumanth Varma. Landslide Detection Using Remote Sensing Methods a Review of Current Techniques. University of South Carolina, 2019.
- Kader, Md Abdul, and Israt Jahan. "A Review of the Application of Remote Sensing Technologies in Earthquake Disaster Management: Potentialities and Challenges." Paper presented at the Proceedings of the International Conference on Disaster Risk Management, Dhaka, Bangladesh 2019.
- Notti, Davide, Martina Cignetti, Danilo Godone, and Daniele Giordan. "Semi-Automatic Mapping of Shallow Landslides Using Free Sentinel-2 and Google Earth Engine." Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Discussions (2022): 1-34.
- Lu, Ping, Yuanyuan Qin, Zhongbin Li, Alessandro C Mondini, and Nicola Casagli. "Landslide Mapping from Multi-Sensor Data through Improved Change Detection-Based Markov Random Field." Remote Sensing of Environment 231 (2019): 111235.
- Shahabi, Hejar, Maryam Rahimzad, Sepideh Tavakkoli Piralilou, Omid Ghorbanzadeh, Saied Homayouni, Thomas Blaschke, Samsung Lim, and Pedram Ghamisi. "Unsupervised Deep Learning for Landslide Detection from Multispectral Sentinel-2 Imagery." Remote Sensing 13, no. 22 (2021): 4698.
- Fayne, Jessica V, Aakash Ahamed, Justin Roberts-Pierel, Amanda C Rumsey, and Dalia Kirschbaum. "Automated Satellite-Based Landslide Identification Product for Nepal." Earth Interactions 23, no. 3 (2019): 1-21.
- Ngandam Mfondoum, Alfred Homère, Pauline Wokwenmendam Nguet, Jean Valery Mefire Mfondoum, Mesmin Tchindjang, Sofia Hakdaoui, Ryan Cooper, Paul Gérard Gbetkom, Joseph Penaye, Ateba Bekoa, and Cyriel Moudioh. "Adapting Sudden Landslide Identification Product (Slip) and Detecting Real-Time Increased Precipitation (Drip) Algorithms to Map Rainfall-Triggered Landslides in Western Cameroon Highlands (Central-Africa)." Geoenvironmental Disasters 8, no. 1 (2021): 1-26.
- Piralilou, Sepideh Tavakkoli, Hejar Shahabi, and Robert Pazur. "Automatic Landslide Detection Using Bi-Temporal Sentinel 2 Imagery." GI_Forum 9 (2021): 39-45.
- Zhang, Shuai, Ran Li, Fawu Wang, and Akinori Iio. "Characteristics of Landslides Triggered by the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake, Northern Japan." Landslides 16 (2019): 1691-708.
- Sivasankar, Thota, Swakangkha Ghosh, and Mayank Joshi. "Exploitation of Optical and Sar Amplitude Imagery for Landslide Identification: A Case Study from Sikkim, Northeast India." Environmental monitoring and assessment 193, no. 7 (2021): 386.
- Yang, Wentao, Wenwen Qi, and Jian Fang. "Using Google Earth Engine to Monitor Co-Seismic Landslide Recovery after the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake." Earth Surface Dynamics Discussions 2020 (2020): 1-14.
- Ghorbanzadeh, Omid, Hejar Shahabi, Alessandro Crivellari, Saeid Homayouni, Thomas Blaschke, and Pedram Ghamisi. "Landslide Detection Using Deep Learning and Object-Based Image Analysis." Landslides 19, no. 4 (2022): 929-39.
- Ariza, Alexander, Norma Angelica Davila, Hannah Kemper, and Gerhard Kemper. "Landslide Detection in Central America Using the Differential Bare Soil Index." The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 43 (2021): 679-84.
- Yu, Bo, Fang Chen, and Shakir Muhammad. "Analysis of Satellite-Derived Landslide at Central Nepal from 2011 to 2016." Environmental earth sciences 77 (2018): 1-12.
- Subiyantoro, A., C. J. Van Westen, B. V. Den Bout, R. A. Yuniawan, and A. R. Mulyana. "Semi-Automatic Landslide Detection Using Google Earth Engine, a Case Study in Poi Village, Central Sulawesi." Paper presented at the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Aerospace Electronics and Remote Sensing Technology (ICARES), 24-25 Nov. 2022 2022.
- Scheip, Corey M, and Karl W Wegmann. "Hazmapper: A Global Open-Source Natural Hazard Mapping Application in Google Earth Engine." Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 21, no. 5 (2021): 1495-511.
- Singh, Pawan, V Maurya, and Ramji Dwivedi. "Pixel Based Landslide Identification Using Landsat 8 and Gee." Paper presented at the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS 2021.
- Lindsay, Erin, Regula Frauenfelder, Denise Rüther, Lorenzo Nava, Lena Rubensdotter, James Strout, and Steinar Nordal. "Multi-Temporal Satellite Image Composites in Google Earth Engine for Improved Landslide Visibility: A Case Study of a Glacial Landscape." Remote Sensing 14, no. 10 (2022): 2301.
- Handwerger, Alexander L, Mong-Han Huang, Shannan Y Jones, Pukar Amatya, Hannah R Kerner, and Dalia B Kirschbaum. "Generating Landslide Density Heatmaps for Rapid Detection Using Open-Access Satellite Radar Data in Google Earth Engine." Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 22, no. 3 (2022): 753-73.
- Handwerger, Alexander L, Shannan Y Jones, Mong-Han Huang, Pukar Amatya, Hannah R Kerner, and Dalia B Kirschbaum. "Rapid Landslide Identification Using Synthetic Aperture Radar Amplitude Change Detection on the Google Earth Engine." Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Discussions 2020 (2020): 1-24.
- Hernandez, Norma Davila, Alexander Ariza Pastrana, Lizeth Caballero Garcia, Juan Carlos Villagran de Leon, Antulio Zaragoza Alvarez, Leobardo Dominguez Morales, Xanat Antonio Nemiga, and Gustavo Dominguez Posadas. "Co-Seismic Landslide Detection after M 7.4 Earthquake on June 23, 2020, in Oaxaca, Mexico, Based on Rapid Mapping Method Using High and Medium Resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (Sar) Images." Landslides 18, no. 12 (2021): 3833-44.
- Fujiwara, Satoshi, Takayuki Nakano, Yu Morishita, Tomokazu Kobayashi, Hiroshi Yarai, Hiroshi Une, and Kyonosuke Hayashi. "Detection and Interpretation of Local Surface Deformation from the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake Using Alos-2 Sar Data." Earth, Planets and Space 71, no. 1 (2019): 1-17.
- Ju, Yuanzhen, Qiang Xu, Shichao Jin, Weile Li, Yanjun Su, Xiujun Dong, and Qinghua Guo. "Loess Landslide Detection Using Object Detection Algorithms in Northwest China." Remote Sensing 14, no. 5 (2022): 1182.
- Yu, Zhengbo, Ruichun Chang, and Zhe Chen. "Automatic Detection Method for Loess Landslides Based on Gee and an Improved Yolox Algorithm." Remote Sensing 14, no. 18 (2022): 4599.
- Zhao, Liang, Jixue Liu, Stefan Peters, Jiuyong Li, Simon Oliver, and Norman Mueller. "Investigating the Impact of Using Ir Bands on Early Fire Smoke Detection from Landsat Imagery with a Lightweight Cnn Model." Remote Sensing 14, no. 13 (2022): 3047.
- Gomes, Vitor CF, Gilberto R Queiroz, and Karine R Ferreira. "An Overview of Platforms for Big Earth Observation Data Management and Analysis." Remote Sensing 12, no. 8 (2020): 1253.
- Mutanga, Onisimo, and Lalit Kumar. "Google Earth Engine Applications." 591: MDPI, 2019.
- Pérez-Cutillas, Pedro, Alberto Pérez-Navarro, Carmelo Conesa-García, Demetrio Antonio Zema, and Jesús Pilar Amado-Álvarez. "What Is Going on within Google Earth Engine? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis." Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 29 (2023): 100907.
- Smith, William D, Stuart A Dunning, Stephen Brough, Neil Ross, and Jon Telling. "Geraldine (Google Earth Engine Supraglacial Debris Input Detector): A New Tool for Identifying and Monitoring Supraglacial Landslide Inputs." Earth Surface Dynamics 8, no. 4 (2020): 1053-65.
- Van Natijne, AL, TA Bogaard, FJ van Leijen, RF Hanssen, and RC Lindenbergh. "World-Wide Insar Sensitivity Index for Landslide Deformation Tracking." International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 111 (2022): 102829.
- Wu, Wenhuan, Qiang Zhang, Vijay P Singh, Gang Wang, Jiaqi Zhao, Zexi Shen, and Shuai Sun. "A Data-Driven Model on Google Earth Engine for Landslide Susceptibility Assessment in the Hengduan Mountains, the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau." Remote Sensing 14, no. 18 (2022): 4662.
- Ilmy, Hafsah Fatihul, Mohammad Rohmaneo Darminto, and Amien Widodo. "Application of Machine Learning on Google Earth Engine to Produce Landslide Susceptibility Mapping (Case Study: Pacitan)." Paper presented at the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021.
- Ado, Moziihrii, Khwairakpam Amitab, Arnab Kumar Maji, Elżbieta Jasińska, Radomir Gono, Zbigniew Leonowicz, and Michał Jasiński. "Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Machine Learning: A Literature Survey." Remote Sensing 14, no. 13 (2022): 3029.
- Li, Bohao, Kai Liu, Ming Wang, Qian He, Ziyu Jiang, Weihua Zhu, and Ningning Qiao. "Global Dynamic Rainfall-Induced Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Machine Learning." Remote Sensing 14, no. 22 (2022): 5795.
- Khan, Muhammad Muzamil, Bushra Ghaffar, Rasim Shahzad, M Riaz Khan, Munawar Shah, Ali H Amin, Sayed M Eldin, Najam Abbas Naqvi, and Rashid Ali. "Atmospheric Anomalies Associated with the 2021 M W 7.2 Haiti Earthquake Using Machine Learning from Multiple Satellites." Sustainability 14, no. 22 (2022): 14782.
- Ohtani, Makiko, and Kazutoshi Imanishi. "Seismic Potential around the 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake Assessed Considering the Viscoelastic Relaxation." Earth, Planets and Space 71, no. 1 (2019): 1-15.
- Yamagishi, Hiromitsu, and Fumiaki Yamazaki. "Landslides by the 2018 Hokkaido Iburi-Tobu Earthquake on September 6." Landslides 15, no. 12 (2018): 2521-24.
- Zhao, Bo, Yunsheng Wang, Weile Li, Huiyan Lu, and Zhengyou Li. "Evaluation of Factors Controlling the Spatial and Size Distributions of Landslides, 2021 Nippes Earthquake, Haiti." Geomorphology 415 (2022): 108419.
- Martinez, Sabrina N, Kate E Allstadt, Stephen L Slaughter, Robert G Schmitt, Elaine Collins, Lauren N Schaefer, and Sonia Ellison. "Landslides Triggered by the August 14, 2021, Magnitude 7.2 Nippes, Haiti, Earthquake." US Geological Survey, 2021.
- Wang, Shuai, Caijun Xu, Zhenhong Li, Yangmao Wen, and Chuang Song. "The 2018 Mw 7.5 Papua New Guinea Earthquake: A Possible Complex Multiple Faults Failure Event with Deep-Seated Reverse Faulting." Earth and Space Science 7, no. 3 (2020): e2019EA000966.
- Tanyaş, Hakan, Kevin Hill, Luke Mahoney, Islam Fadel, and Luigi Lombardo. "The World’s Second-Largest, Recorded Landslide Event: Lessons Learnt from the Landslides Triggered During and after the 2018 Mw 7.5 Papua New Guinea Earthquake." Engineering Geology 297 (2022): 106504.
- Tanyaş, Hakan, Tolga Görüm, Islam Fadel, Cengiz Yıldırım, and Luigi Lombardo. "An Open Dataset for Landslides Triggered by the 2016 Mw 7.8 Kaikōura Earthquake, New Zealand." Landslides 19, no. 6 (2022): 1405-20.
- Wang, Fengrui, Xuanmei Fan, Ali P Yunus, Srikrishnan Siva Subramanian, Andres Alonso-Rodriguez, Lanxin Dai, Qiang Xu, and Runqiu Huang. "Coseismic Landslides Triggered by the 2018 Hokkaido, Japan (M W 6.6), Earthquake: Spatial Distribution, Controlling Factors, and Possible Failure Mechanism." Landslides 16 (2019): 1551-66.
- Yin, Feng, Philip E Lewis, and Jose L Gómez-Dans. "Bayesian Atmospheric Correction over Land: Sentinel-2/Msi and Landsat 8/Oli." Geoscientific Model Development 15, no. 21 (2022): 7933-76.
- Le Toan, T, A Beaudoin, J Riom, and D Guyon. "Relating Forest Parameters to Sar Data." Paper presented at the [Proceedings] IGARSS’91 Remote Sensing: Global Monitoring for Earth Management 1991.
- Suri, M. "Global Solar Atlas 2.0 Technical Report." Washington, DC: World Bank (2019).
- Google. "The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission (Gpm)." https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/NASA_GPM_L3_IMERG_V06 (accessed 02/09/2023).
- ———. "Supervised Classification - the Classifier Package Handles Supervised Classification by Traditional Ml Algorithms Running in Earth Engine." https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/guides/classification (accessed 15/02/2023).
- Aksoy, Samet, Aylin Yildirim, Taha Gorji, Nikou Hamzehpour, Aysegul Tanik, and Elif Sertel. "Assessing the Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms for Soil Salinity Mapping in Google Earth Engine Platform Using Sentinel-2a and Landsat-8 Oli Data." Advances in Space Research 69, no. 2 (2022): 1072-86.
- Al-Amri, Salem Saleh, Namdeo V Kalyankar, and Santosh D Khamitkar. "A Comparative Study of Removal Noise from Remote Sensing Image." arXiv preprint arXiv:1002.1148 (2010). arXiv:1002.1148 (2010).
- Velez, Digna R, Bill C White, Alison A Motsinger, William S Bush, Marylyn D Ritchie, Scott M Williams, and Jason H Moore. "A Balanced Accuracy Function for Epistasis Modeling in Imbalanced Datasets Using Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction." Genetic Epidemiology: the Official Publication of the International Genetic Epidemiology Society 31, no. 4 (2007): 306-15.
- He, Tao, Shibiao Mu, Houkui Zhou, and Junguo Hu. "Wood Species Identification Based on an Ensemble of Deep Convolution Neural Networks." Wood Res 66, no. 1 (2021): 1-14.
- Zhao, Liang, Jixue Liu, Stefan Peters, Jiuyong Li, Norman Mueller, and Simon Oliver. "Learning Class-Specific Spectral Patterns to Improve Deep Learning-Based Scene-Level Fire Smoke Detection from Multi-Spectral Satellite Imagery." Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment (2024): 101152.
- Luo, Lei, Xinyuan Wang, Huadong Guo, Rosa Lasaponara, Pilong Shi, Nabil Bachagha, Li Li, Ya Yao, Nicola Masini, and Fulong Chen. "Google Earth as a Powerful Tool for Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Applications: A Review." Remote Sensing 10, no. 10 (2018): 1558.
- Masson-Delmotte, VP, Panmao Zhai, SL Pirani, C Connors, S Péan, N Berger, Y Caud, L Chen, MI Goldfarb, and Pedro M Scheel Monteiro. "Ipcc, 2021: Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change." (2021).
- Altman, Jan, Olga N Ukhvatkina, Alexander M Omelko, Martin Macek, Tomas Plener, Vit Pejcha, Tomas Cerny, Petr Petrik, Miroslav Srutek, and Jong-Suk Song. "Poleward Migration of the Destructive Effects of Tropical Cyclones During the 20th Century." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115, no. 45 (2018): 11543-48.
- Bloemendaal, Nadia, Hans de Moel, Andrew B Martinez, Sanne Muis, Ivan D Haigh, Karin van der Wiel, Reindert J Haarsma, Philip J Ward, Malcolm J Roberts, and Job CM Dullaart. "A Globally Consistent Local-Scale Assessment of Future Tropical Cyclone Risk." Science advances 8, no. 17 (2022): eabm8438.
- Knutson, Thomas R, Maya V Chung, Gabriel Vecchi, Jingru Sun, Tsung-Lin Hsieh, and Adam JP Smith. "Climate Change Is Probably Increasing the Intensity of Tropical Cyclones." Critical Issues in Climate Change Science, Science Brief Review. https://doi. org/10.5281/zenodo 4570334, no. 4 (2021).
Figure 1.
Study area showing the boundaries of all case studies and the distribution of coseismic (old and new) landslides, based on available landslide inventory data.
Figure 1.
Study area showing the boundaries of all case studies and the distribution of coseismic (old and new) landslides, based on available landslide inventory data.
Figure 3.
Schematic landslide event illustrating source and flow area, adapted from [
1], figure 17.
Figure 3.
Schematic landslide event illustrating source and flow area, adapted from [
1], figure 17.
Figure 4.
Slope filtering (grey) mapped on top of landslide inventory (red) with (a): slope threshold >10 degrees and (b) slope threshold >10 degrees plus 100 m buffer, exemplary for JPN case study.
Figure 4.
Slope filtering (grey) mapped on top of landslide inventory (red) with (a): slope threshold >10 degrees and (b) slope threshold >10 degrees plus 100 m buffer, exemplary for JPN case study.
Figure 5.
exemplary zoom in for (a): showing sampling areas (Parea, Narea, and N-Barea) with 10 degrees slope and 100 m buffer filter applied; (b): randomly placed training and validation points within each sampling area.
Figure 5.
exemplary zoom in for (a): showing sampling areas (Parea, Narea, and N-Barea) with 10 degrees slope and 100 m buffer filter applied; (b): randomly placed training and validation points within each sampling area.
Figure 6.
Accuracy assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using GEE ML classifiers.
Figure 6.
Accuracy assessment for ML-LaDeCORsat using GEE ML classifiers.
Figure 7.
Landslide inventory polygons for (a) JPN, (d) HTI, (g) PNG, (j) NZL; predicted landslides with GTB for (b) JPN, (e) HTI, (h) PNG, (k) NZL; and error maps for (c) JPN, (f) HTI, (i) PNG, (l) NZL.
Figure 7.
Landslide inventory polygons for (a) JPN, (d) HTI, (g) PNG, (j) NZL; predicted landslides with GTB for (b) JPN, (e) HTI, (h) PNG, (k) NZL; and error maps for (c) JPN, (f) HTI, (i) PNG, (l) NZL.
Figure 8.
Normalized sorted band importance outputs for ML-LaDeCORsat applied to each study site using either a) GTB, b) CART, and c) RF – sorted by their sum.
Figure 8.
Normalized sorted band importance outputs for ML-LaDeCORsat applied to each study site using either a) GTB, b) CART, and c) RF – sorted by their sum.
Figure 9.
Across sites Transfer Learning and accuracies using ’all pixel’ validation.
Figure 9.
Across sites Transfer Learning and accuracies using ’all pixel’ validation.
Table 3.
Satellite imagery bands available in GEE that are relevant to landslide detection.
Table 3.
Satellite imagery bands available in GEE that are relevant to landslide detection.
Table 4.
Percentual coverage of inventory landslides by 10 degree (10°) slope area.
Table 4.
Percentual coverage of inventory landslides by 10 degree (10°) slope area.
| Site |
Slope max. |
Slope mean |
Inventory and slopes |
Area in sqm |
% |
| JPN |
61 |
19 |
Inventory area covered by 10°slope |
18,240,288 |
76% |
| |
|
|
Not covered |
5,752,553 |
24% |
| |
|
|
Total |
23,992,841 |
100% |
| HTI |
75 |
29 |
Inventory area covered by 10° slope |
10,556,567 |
95% |
| |
|
|
Not covered |
566,587 |
5% |
| |
|
|
Total |
11,123,154 |
100% |
| PNG |
85 |
22 |
Inventory area covered by 10° slope |
161,196,491 |
87% |
| |
|
|
Not covered |
23,864,695 |
13% |
| |
|
|
Total |
185,061,186 |
100% |
| NZL |
73 |
24 |
Inventory area covered by 10° slope |
13,144,818 |
88% |
| |
|
|
Not covered |
1,787,069 |
12% |
| |
|
|
Total |
14,931,887 |
100% |
Table 5.
Optimal GEE ML classifier parameters for ML-LaDeCORsat.
Table 5.
Optimal GEE ML classifier parameters for ML-LaDeCORsat.
| Classifier |
Training samples |
No. of trees |
MinLeafPop
1
|
Bag
Fraction |
Split |
Max
Nodes |
Shrinkage |
Sampling
Rate |
| CART |
4,800 |
N/A |
7 |
N/A |
N/A |
40 |
N/A |
N/A |
| RF |
4,800 |
500 |
7 |
0.5 |
10 |
20 |
N/A |
N/A |
| GTB |
4,800 |
650 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
20 |
0.00095 |
0.173 |
| NB |
4,800 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
| Classifier |
No. of samples |
Type |
KernelType |
Decision Procedure |
Shrinking |
Degree |
Gamma |
Coef0 |
| SVM |
4,800 |
C_SVC |
Poly |
Margin |
TRUE |
1 |
0.5 |
10 |
Table 6.
Kappa and BA of existing landslide detection methods or additional landslide condition bands applied to all 4 case studies and compared with Kappa and BA for ML-LaDeCORsat (GTB).
Table 6.
Kappa and BA of existing landslide detection methods or additional landslide condition bands applied to all 4 case studies and compared with Kappa and BA for ML-LaDeCORsat (GTB).
| Existing methods /bands |
References |
JPN |
HTI |
PNG |
NZL |
| Kappa |
BA |
Kappa |
BA |
Kappa |
BA |
Kappa |
BA |
| M1 |
∆NDVI: supervised
classification |
[44] |
0.70 |
0.85 |
0.70 |
0.85 |
0.38 |
0.69 |
0.68 |
0.84 |
| M2, M3 |
∆NDVI, rdNDVI, slope |
[45] |
0.47 |
0.73 |
0.58 |
0.79 |
0.23 |
0.62 |
0.42 |
0.71 |
| M4 |
∆BSI |
[43] |
-0.09 |
0.46 |
-0.59 |
0.20 |
-0.22 |
0.39 |
-0.07 |
0.47 |
| M5 |
∆NDVI, slope |
[33] |
0.40 |
0.70 |
0.53 |
0.77 |
0.17 |
0.58 |
0.35 |
0.68 |
| M6 |
NDVIpost, slope: unsupervised classification2
|
[35] |
0.05 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| M7 |
NDVIpost, slope:
supervised classification |
[42] |
0.34 |
0.67 |
0.52 |
0.76 |
0.25 |
0.63 |
0.40 |
0.70 |
| M8 |
NDWIpost, NDVIpost, DEM, slope: supervised
classification |
[47] |
0.74 |
0.87 |
0.74 |
0.87 |
0.64 |
0.82 |
0.70 |
0.86 |
| M10 |
S1_90p_VH |
[23,49,50] |
0.32 |
0.67 |
0.24 |
0.62 |
-0.02 |
0.49 |
0.20 |
0.60 |
| M10 |
S1_log_VH |
[23,49,50] |
0.33 |
0.67 |
0.25 |
0.62 |
0.00 |
0.50 |
0.19 |
0.60 |
| M11, M9 |
S1_90p_VH_VV |
[48,51] |
0.28 |
0.65 |
0.14 |
0.57 |
-0.02 |
0.49 |
0.04 |
0.52 |
| M12 |
P2_log_HV1
|
[14,52] |
0.09 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| M13, M16 |
SLIP |
[36] |
0.19 |
0.60 |
0.41 |
0.70 |
0.19 |
0.60 |
0.12 |
0.56 |
| M14 |
aSLIP |
[37] |
0.30 |
0.66 |
0.39 |
0.69 |
0.21 |
0.61 |
0.09 |
0.55 |
| M15 |
iSLIP |
[38] |
0.07 |
0.54 |
0.50 |
0.75 |
0.16 |
0.58 |
0.23 |
0.61 |
| new |
ML-LaDeCORsat (GTB) |
new |
0.84 |
0.92 |
0.78 |
0.89 |
0.78 |
0.89 |
0.73 |
0.87 |
Table 7.
Computational measures of ML classifiers in GEE using all 39 or 20/15/10/5 selected most important bands for JPN case study.
Table 7.
Computational measures of ML classifiers in GEE using all 39 or 20/15/10/5 selected most important bands for JPN case study.
| Used bands |
Classifier |
validation pixels |
all pixels |
EECU
minutes1
|
Peak Memory
(MB)1
|
Count of operations
1
|
| OA |
BA |
OA |
BA |
All
40
bands |
CART |
0.883 |
0.869 |
0.883 |
0.869 |
3.1 |
|
19515864 |
|
2490 |
|
| RF |
0.889 |
0.876 |
0.889 |
0.876 |
37.9 |
|
23429664 |
|
2490 |
|
| GTB |
0.919 |
0.894 |
0.919 |
0.894 |
47.1 |
|
26217076 |
|
2490 |
|
| SVM |
0.888 |
0.871 |
0.888 |
0.871 |
53.6 |
|
62084948 |
|
1834 |
|
| NB |
0.668 |
0.607 |
0.668 |
0.607 |
2.7 |
|
19359664 |
|
1830 |
|
20 most
important bands |
CART |
0.881 |
0.866 |
0.881 |
0.866 |
2.4 |
24% |
9168112 |
53% |
2068 |
17% |
| RF |
0.891 |
0.875 |
0.891 |
0.875 |
20.0 |
47% |
15366896 |
34% |
2068 |
17% |
| GTB |
0.917 |
0.894 |
0.917 |
0.894 |
17.6 |
63% |
17570796 |
33% |
2088 |
16% |
15 most
important bands |
CART |
0.881 |
0.872 |
0.881 |
0.872 |
2.2 |
29% |
7940596 |
59% |
2018 |
19% |
| RF |
0.891 |
0.875 |
0.891 |
0.875 |
12.8 |
66% |
14440848 |
38% |
2018 |
19% |
| GTB |
0.913 |
0.892 |
0.913 |
0.892 |
13.2 |
72% |
16044596 |
39% |
2018 |
19% |
10 most
important bands |
CART |
0.881 |
0.875 |
0.881 |
0.875 |
2.1 |
32% |
6713312 |
66% |
1968 |
21% |
| RF |
0.885 |
0.874 |
0.885 |
0.874 |
14.6 |
61% |
13510296 |
42% |
1968 |
21% |
| GTB |
0.910 |
0.890 |
0.910 |
0.89 |
9.5 |
80% |
15033080 |
43% |
1968 |
21% |
5 most
important bands2
|
CART |
0.868 |
0.865 |
0.868 |
0.865 |
2.0 |
36% |
5402080 |
72% |
1918 |
23% |
| GTB |
0.890 |
0.881 |
0.890 |
0.881 |
6.3 |
87% |
14090680 |
46% |
1918 |
23% |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).