1. Introduction
The Brazilian Cerrado is widely recognized as one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots, being the second-largest biome in Brazil and South America. This biome is home to a wide range of native and endemic plant species, which have pharmacological, nutraceutical, and food potentials of great relevance. Among the plant species, Acrocomia aculeata and Campomanesia adamantium stand out, which are fruit species of high economic value.
Acrocomia aculeata (Arecaceae), known as bocaiuva or macaúba, is a palm tree found abundantly in tropical and subtropical regions of South and Central America. The bocaiuva fruit has a sweet edible pulp with a mucilaginous texture that is rich in fiber, carbohydrates, and minerals [
1], besides significant levels of vitamins, carotenoids, and flavonoids [
2,
3] being, therefore, able to contribute to human nutrition. Fiber is so important in a healthy diet that sometimes hydrocolloids are used to increase the fiber content of food products [
4]. The fiber content of green (maturation stage) bocaiuva pulp is approximately 65%, of which 20% corresponds to soluble fiber [
5] in the form of mucilage, a valuable nutritional component that is also used in the food industry as a thickening agent.
Campomanesia adamantium (Myrtaceae), whose fruits are popularly known as guavira or guabiroba, is recognized as a symbol of the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Recent studies have reported the antimicrobial activity of the leaves [
6], the anti-depressant action of the fruit peel [
7], and the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive action of the microencapsulated pulp [
8]. The fruit pulp can be potentially used in the food industry as a source of minerals, fiber, ascorbic acid, and phenolic compounds [
9]. However, these fruits are highly perishable and seasonal, hindering their conservation and consumption.
Dehydration remains the most widely used process for food preservation. Among the dehydration techniques, atomization or spray drying provides powdered products that still retain some of the nutrients even after high-temperature exposition for a short time. Additionally, atomization favors the formation of microcapsules depending on the encapsulating agents used. Therefore, atomization is the most commonly used microencapsulation technique because it is simple, fast, easily reproduced on an industrial scale, and low cost [
10].
Microencapsulation enables coating solid, gaseous, or liquid substances with a matrix capable of forming a shell that stabilizes sensitive substances protecting them from environmental conditions and eliminating incompatibilities. Microencapsulation has various applications, not only in the food industry but also in pharmaceuticals [
11], cosmetics [
12], textiles [
13], and agriculture as well as in the development of new pesticides [
14], among others.
Spray-drying microencapsulation is widely used to protect substances with nutraceutical properties, for example, phenolic compounds and anthocyanins [
15], proteins and ascorbic acid [
16], gallic acid and essential oil [
10], carotenoids [
17], among others. Encapsulants must be food-grade, biodegradable, and capable of forming a barrier between the internal and external phases. Carbohydrates (starch, dextrin, maltodextrin, cyclodextrin, modified starch, chitosan), cellulose, proteins, and gums are commonly used for this purpose [
18]. Although spray dehydration is relatively simple, material characteristics, encapsulating agents, nozzle diameter, feed rate, hot airflow, and temperature are important variables that directly affect the final product’s quality.
Given this, the response surface methodology (RSM) is an important process optimization tool that assists in choosing the process parameters to obtain the best conditions to meet the requirements of a given system, be it component preservation or yield [
19,
20]. The Simplex Centroid model is a useful RSM for optimizing formulations and processes with a limited number of experiments [
21,
22].
Therefore, this study evaluates the effect of added encapsulating materials (dehydrated bocaiuva pulp plus maltodextrin, gum arabic, or chitosan) and different nozzle diameters (1.0, 1.2, and 1.5 mm) on the properties of guavira pulp microencapsulated by spray drying.
2. Materials and Methods
3.2. Materials
Ripe guavira (Campomanesia adamantium) fruits were purchased in Ponta Porã, MS, Brazil, whereas green bocaiuva (Acrocomia aculeata) fruits were collected in Itaporã, MS, Brazil. After being botanically identified, an exsiccata of each species, A. aculeata under No. 4783 and C. adamantium No. 3755, was deposited in the Herbarium of the Grande Dourados Federal University, in Dourados, MS. Both species were registered in the national management system of the genetic heritage and associated traditional knowledge (SisGen) under access registration Nº A37EC3E.
3.3. Obtaining the Pulps
After manual washing and peeling, the guavira fruits were sanitized with a 0.66% (w/v) Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate Dihydrate (Sumaveg®—Diversey Lever) solution. The obtained pulp was sieved to separate the seeds and stored at -20 °C until use.
The green bocaiuva fruits were peeled and the pulp was removed manually. The sliced pulp was dried in a dryer at 50 °C for 24 h. After drying, the pulp was ground and sieved through a 28-mesh screen.
3.4. Suspension Preparation and Atomization
The suspensions were prepared with 60% guavira pulp, 24% wall material, and approximately 16% water to correct soluble solids (30° Brix). The wall material consisted of 6% dehydrated green bocaiuva pulp plus 18% of either maltodextrin, gum Arabic, or chitosan, following the Simplex Centroid experimental design with seven formulations (
Table 1).
The mixture was homogenized at 18,000 rpm in Ultra-Turrax until complete dissolution of the carrier agents (5 min). At the end of the preparation, the suspensions had 30% soluble solids determined by a bench refractometer (RMT, Tecnal, Brazil). The amount of bocaiuva pulp added was previously determined in preliminary tests where the increasing viscosity of the mixture limited the amount to be used in the study to 6%.
Atomization was performed in a spray dryer (MSD 1.0, LabMaq, Brazil), with 180 °C inlet temperature, 0.5 L/h feed rate, 35 L/min drying air flow rate, and 120 °C outlet temperature as described by [
23]. The obtained powder of pulp guavira was collected in a glass bottle and then packed in low-density polyethylene containers, sealed, and protected from light until further analysis. The suspensions were atomized using spray nozzles with the following diameters 1.0 mm (B1), 1.2 mm (B2), and 1.5 mm (B3).
3.5. Powder Physicochemical Analysis
3.5.1. Yield
The yield of the pulp guavira powder was calculated by equation (1) [
24]:
where P is the obtained powder amount (g) and TS is, the total solid contents (g) used to prepare the suspension.
3.5.2. Solubility
The solubility of the microencapsulated guavira pulp was determined following the method described by [
25] with a few modifications. An aliquot of powdered guavira pulp (1g) was mixed in 100 mL distilled water and homogenized in Ultra-Turrax at 18,000 rpm until complete dissolution. The obtained solution was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 5 min. A 25 mL aliquot of the supernatant was transferred to previously tared Petri dishes and dried in a forced air circulation oven at 105 °C for 24 h. The mass difference was used to calculate solubility (%).
3.5.3. Hygroscopicity
Hygroscopicity was assessed based on the method described by [
26] with modifications. Approximately 1g of microencapsulated guavira pulp was placed in a hermetically sealed container at 25 °C containing a saturated NaCl solution to establish a microenvironment with 75.3% relative humidity inside the container. After seven days, the samples were removed and weighed. The hygroscopicity was calculated by dividing the absorbed moisture (g) by the sample’s initial mass (g). Hygroscopicity was expressed in g of moisture absorbed per 100 g of powder.
3.5.4. Vitamin C
Ascorbic acid content was quantified by Tillman’s method [
27], based on the reduction of the 2,6-dichlorophenol-indophenol (DCFI) sodium salt dye using the oxalic acid solution as a solvent in place of metaphosphoric acid. Results were expressed as mg vitamin C per 100 grams of the microencapsulated guavira pulp.
3.5.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
The microencapsulated guavira pulp with the highest vitamin C content was submitted to scanning electron microscopy (model TM-3000, HITACHI) in the Animal Science and Food Engineering School (FZEA) of the University of São Paulo. For the imaging, the samples were placed on a double-sided carbon tape and fixed on aluminum stubs at the following equipment settings, 3-5 mA current, 1 Volt, and 8-9.10–2 mbar. The mean particle diameter was determined from the individual measurement of 100 microparticles in the SEM micrographs using the image analysis software ImageJ (NIH, Bethesda, MD). The samples of microencapsulated guavira pulp were examined at magnifications of 200, 500, and 1500X.
3.6. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
The Simplex Centroid experimental design with seven mixtures (
Table 1) was applied to each spray nozzle diameter (1.0, 1.2, and 1.5 mm), where the carrier agents, maltodextrin (X1), gum arabic (X2), and chitosan (X3) were the independent variables and powder yield (%), solubility (%), hygroscopicity (g/100g) and vitamin C content (mg/100g) were the dependent variables.
Figure S1 shows that points 1, 2, and 3 (triangle vertices) correspond to the pure components, points 4, 5, and 6 refer to the binary mixtures of two wall materials while point 7 (center of the triangle) refers to the ternary mixture of the three wall materials.
Equations were obtained as coded variables, used to direct individual responses as a function of independent factors. Experimental data were submitted to analysis of variance (ANOVA) at 95% significance while model efficiency was analyzed by regression coefficient (R2) using the Statistica software, version 7.0 (StatSoft, Tulsa, EUA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Process yield
Yield is an important factor in atomization because it is related to process cost-effectiveness. The main causes of low yield are particle adhesion to the wall of the drying chamber and the low efficiency of the cyclone used to collect fine particles [
28]. In the case of cyclone absence, the product remains longer in the dryer thus affecting product quality caused by prolonged exposure to heat [
16].
The yields of the microencapsulated guavira pulp for the studied nozzle diameters are shown in
Table 2. The yield was significantly higher (p <0.05) in tests 1 (M), 4 (M + G), 5 (M + Q), 6 (G + Q), and 7 (M + G + Q) for the 1.5 mm spray nozzle. Also, higher yields were observed in tests 2 (G) and 3 (Q) for the 1.0 and 1.2 mm nozzles, respectively. Possibly, the larger diameter of the spray nozzle promotes the formation of larger suspension droplets during the atomization process so that, during drying, larger powder particles are formed, reducing the adhesion inside the drying chamber and, thus, increasing the yield.
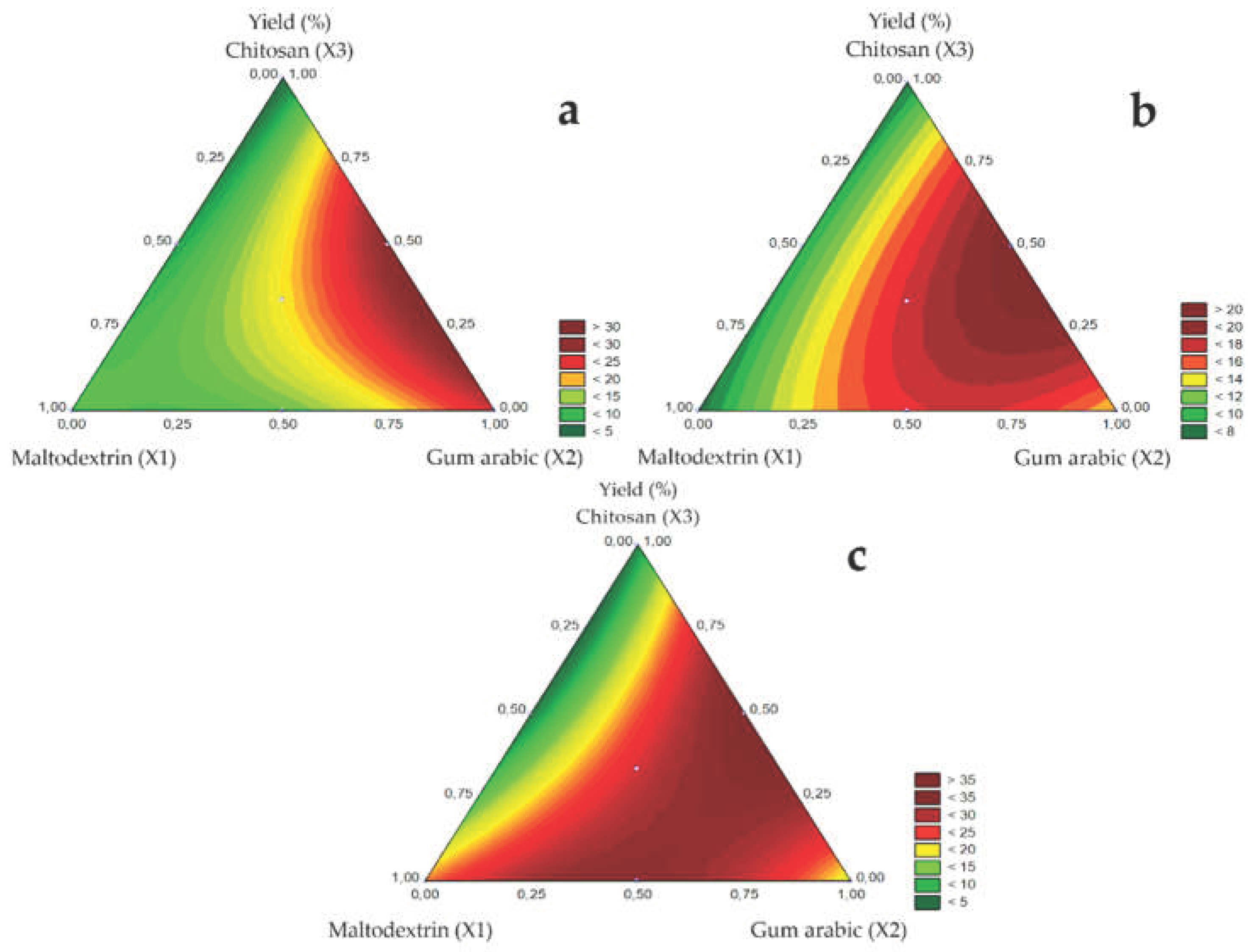
Regarding the influence of carrier agents on yield, the contour diagrams of
Figure 2 A (1.0 mm), B (1.2 mm), and C (1.5 mm) show that yield increased linearly with added gum arabic (X2), followed by maltodextrin (X1) and chitosan (X3). In the binary mixture, the yield increased for the gum arabic and chitosan mixture, followed by the maltodextrin and gum arabic mixture. Low yields were observed for the maltodextrin and chitosan mixture. The highest yields may be attributed to the gum Arabic properties, such as high solubility and the ability to form stable low-viscosity emulsions [
29]. Additionally, the chitosan-containing suspensions had high viscosity, possibly caused by the interaction between chitosan and bocaiuva green pulp, probably affecting yield.
Figure 2.
Response surfaces for Yield (%) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters:1.0 mm (a), 1.2 mm (b), and 1.5 mm (c).
Figure 2.
Response surfaces for Yield (%) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters:1.0 mm (a), 1.2 mm (b), and 1.5 mm (c).
Retention of the product to the chamber wall during drying is undesirable since it requires frequent cleaning stops. Also, as the deposits get burned on the wall, when unglued and mixed again, they contaminate the final product deteriorating product quality, in addition, these deposits influence drying volume and heat transfer processes between chamber walls and moving fluids [
30].
3.2. Solubility
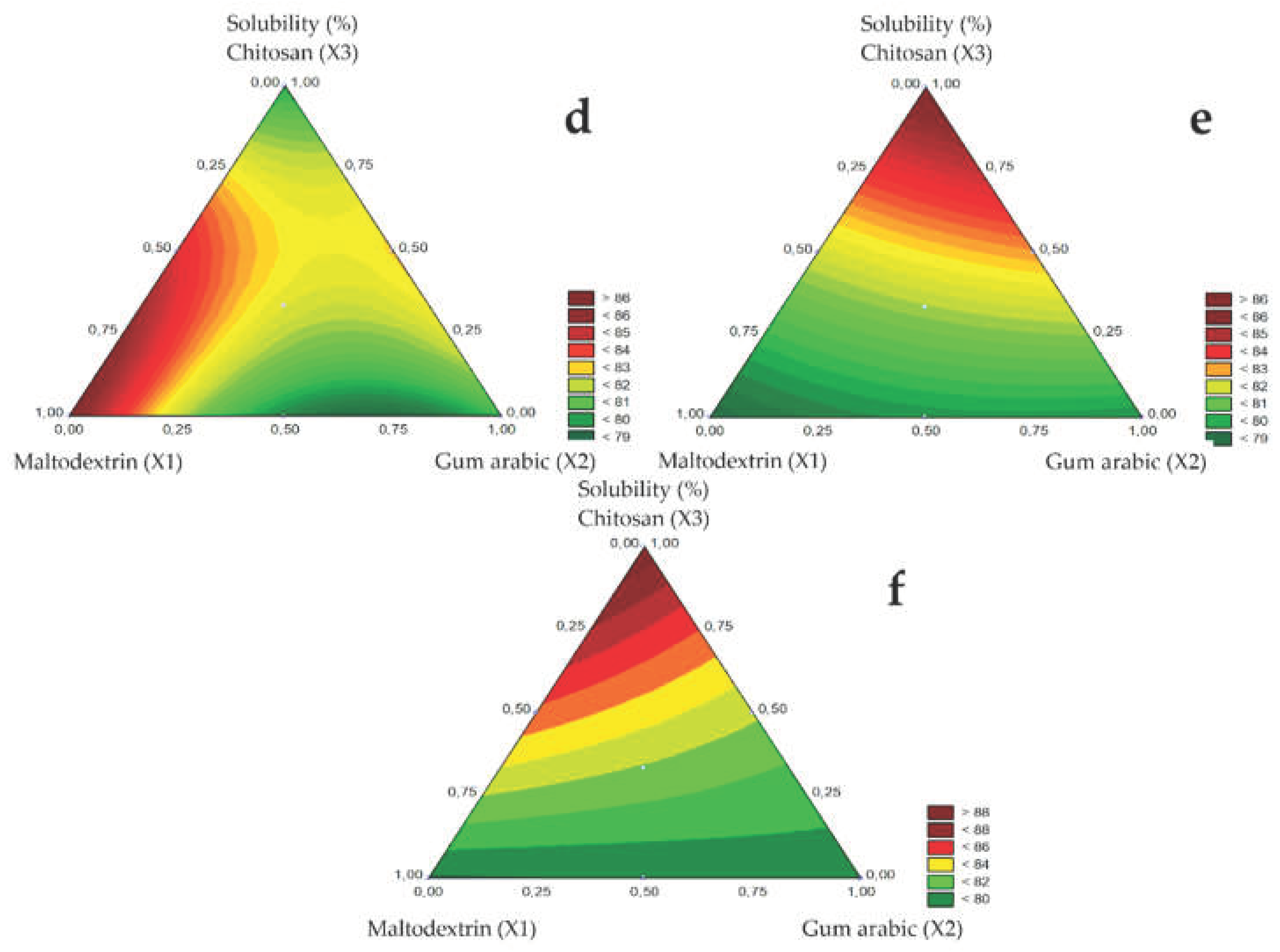
The solubility of microencapsulated guavira pulp ranged from 78% to 89% with changing spray nozzle diameter as shown in
Table 3. The highest solubility (88.78%) of the microencapsulated guavira pulp was obtained using the 1.5 mm nozzle diameter in test 3 (Q), in the presence of chitosan and dehydrated green bocaiuva pulp as carrier agents.
The contour plots of the microencapsulated guavira pulp solubility for the different spray nozzle diameters are shown in
Figure 3D (1.0 mm), E (1.2 mm), and F (1.5 mm). Additionally, solubility varied significantly with spray nozzle diameter and carrier agents. In the atomization step, the highest powder solubility was obtained for maltodextrin (X1) using the 1.0 mm spray nozzle, whereas, solubility increased in the presence of chitosan (X3), for the larger diameters (1.2 and 1.5 mm). Similarly, Sablania and Don Bosco [
19] reported higher solubility using maltodextrin as a carrier agent and a 0.5 mm spray nozzle diameter.
In the contour curves, the vertices correspond to pure components, the sides to the binary mixtures, and the inner points represent the ternary mixtures. Solubility was higher for pure components since the triangle vertices tend to the maximum values for maltodextrin using the B1 nozzle and chitosan using the B2 and B3 nozzles. In the binary mixture, the highest solubility was obtained for the maltodextrin and chitosan mixture. Furthermore, solubility was not affected by the ternary mixture for any of the spray nozzle diameters studied
Figure 3.
Response surfaces for the Solubility (%) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters: 1.0 mm (d), 1.2 mm (e), and 1.5 mm (f).
Figure 3.
Response surfaces for the Solubility (%) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters: 1.0 mm (d), 1.2 mm (e), and 1.5 mm (f).
3.3. Hygroscopicity
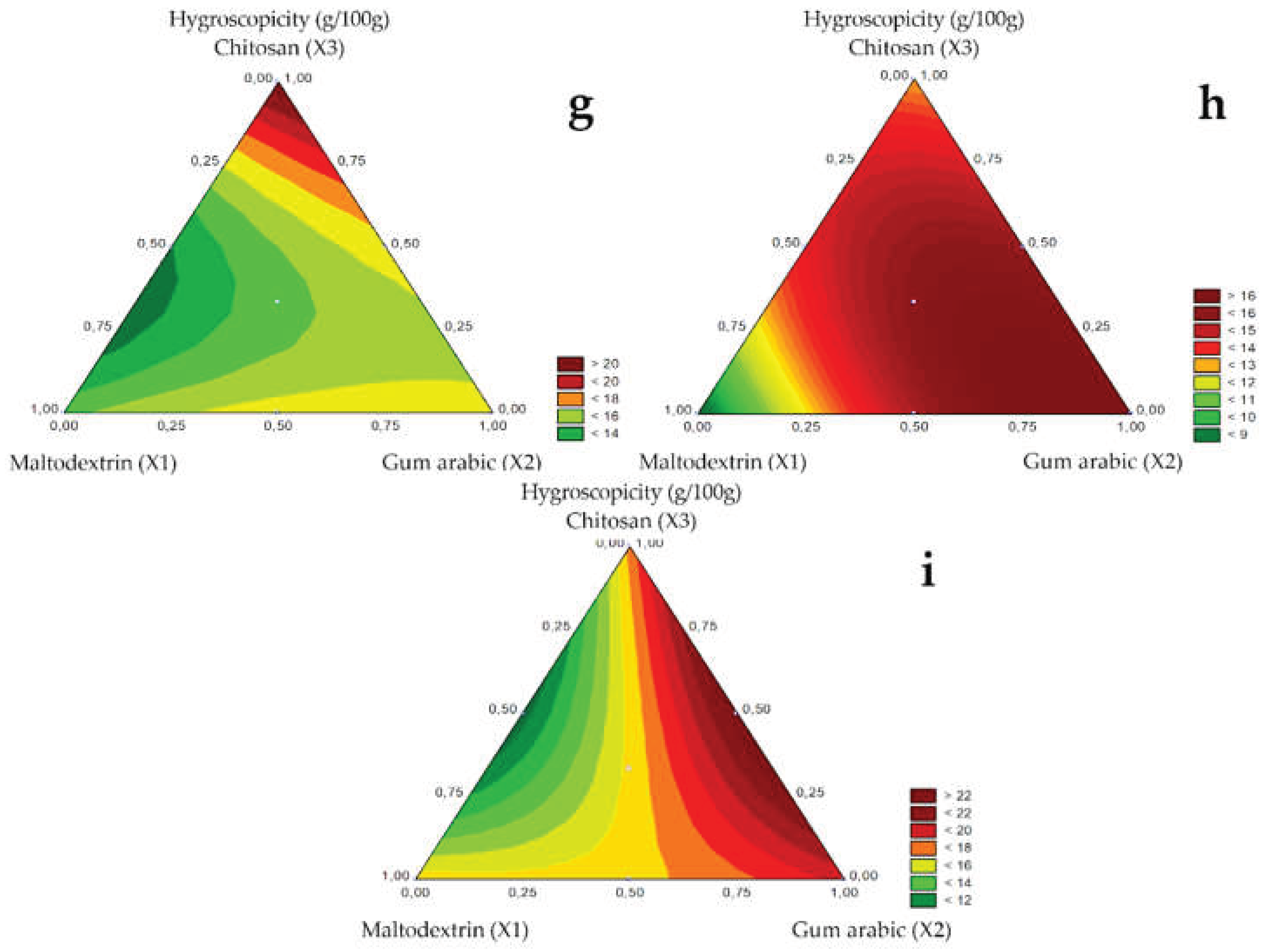
Hygroscopicity is the capacity of absorbing moisture from the environment, being, therefore, an important parameter in food processing because it influences food stability. The hygroscopicity of the microencapsulated guavira pulp for the 1.0, 1.2, and 1.5 mm diameter spray nozzles is presented in
Table 4, and the respective response surfaces in
Figure 4G (1.0 mm), H (1.2 mm), and I (1.5 mm). The absorbed humidity ranged from 8.24 to 24.10 g/100g.
Figure 4.
Response surfaces for the Hygroscopicity (g/100g) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters: 1.0 mm (g), 1.2 mm (h), and 1.5 mm (i).
Figure 4.
Response surfaces for the Hygroscopicity (g/100g) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters: 1.0 mm (g), 1.2 mm (h), and 1.5 mm (i).
For the pure components, hygroscopicity was lower in test 1 with maltodextrin and dehydrated green bocaiuva pulp, regardless of nozzle diameter. Likewise, Zotarelli et al. [
17] also reported that adding maltodextrin reduced the hygroscopicity of mango powders obtained by spray drying. Alves et al. [
31] stated that powders with maltodextrin absorbed less moisture than those with gum arabic, attributing this result to the number of branches containing hydrophilic groups. Thus, dehydrated products with this wall material are typically less hygroscopic. Among binary mixtures, hygroscopicity was low in test 5 with maltodextrin and chitosan.
3.4. Vitamin C
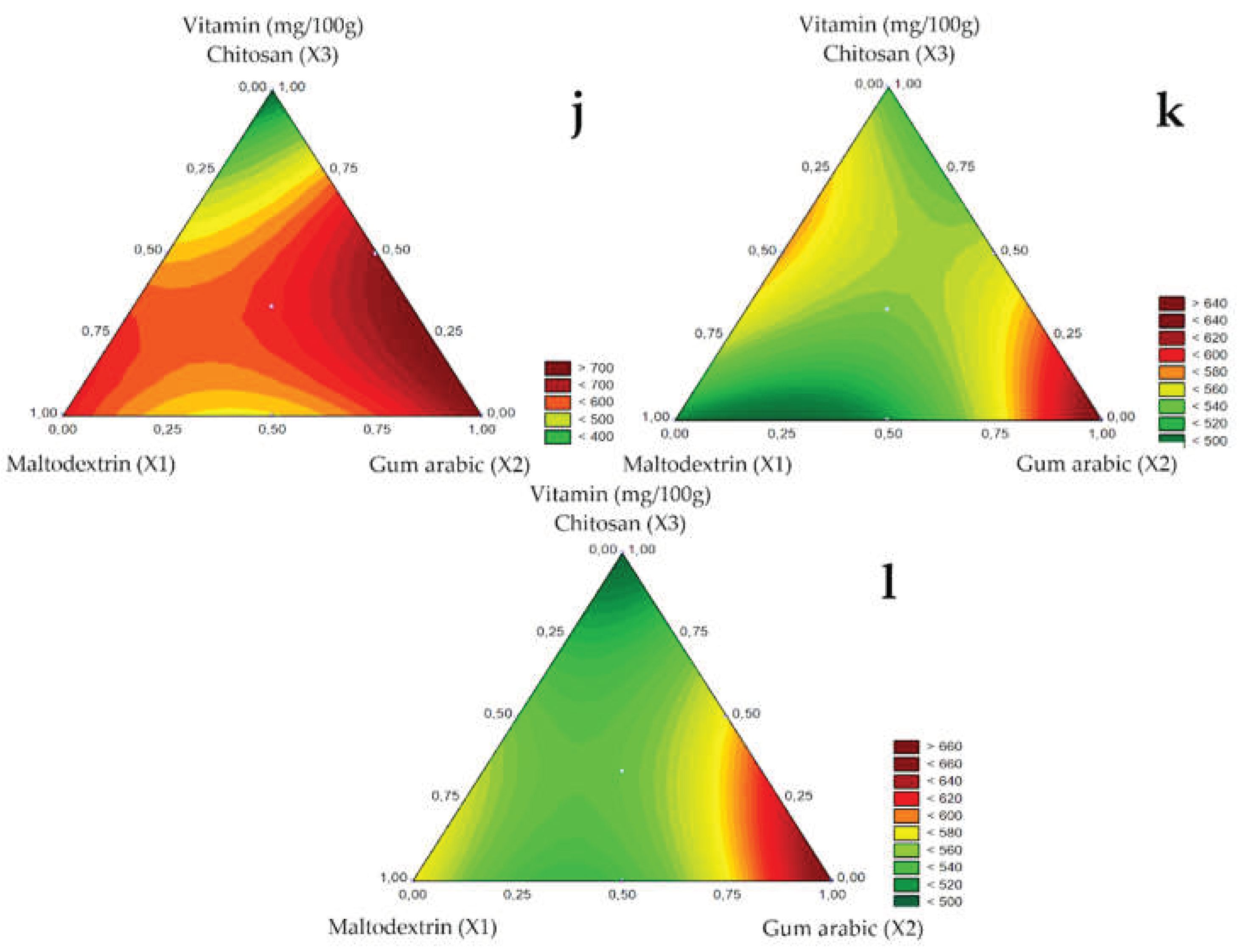
The ascorbic acid content of microencapsulated guavira pulp for the 1.0, 1.2, and 1.5 mm spray nozzle diameters is shown in
Table 5. The highest vitamin C contents ranged between 630.71 and 737.97 mg/100g sample for suspensions with pure maltodextrin and gum arabic (tests 1 and 2) and mixtures of gum arabic and chitosan (test 6) and maltodextrin, gum arabic and chitosan (test 7) using the 1.0 mm diameter spray nozzle.
Oliveira, Argandoña, and Oshiro [
23] reported 48% vitamin C retention in microencapsulated guavira pulp with the mixture of maltodextrin, gum Arabic, and chitosan encapsulating agents using the 1.2 mm spray nozzle, whereas in this study, under the same conditions, retention was 75%, as suspensions averaged 780 mg vitamin C/100g sample. However, the highest ascorbic acid retention (94%) was obtained using the 1.0 mm spray nozzle with bocaiuva pulp and gum arabic as encapsulating agents in test 2 (780 mg vitamin C/100g sample).
The addition of gum arabic as a carrier agent (test 2) favored vitamin C retention regardless of nozzle diameter, as shown in the contour diagrams of
Figure 5J (1.0 mm), K (1.2 mm), and L (1.5 mm). Suhag and Nanda [
32] investigated the atomization of honey with the addition of ascorbic acid and Santana et al. [
33] the atomization of pequi, both studies reported that gum arabic also promoted high retention of ascorbic acid.
Chitosan had a negative linear effect on vitamin C retention, probably related to the high viscosity observed. The increasing viscosity increases particle formation time, especially for the smaller nozzle diameters (1.0 mm), leaving the component susceptible to degradation. A similar effect on vitamin C retention has also been reported for guavira pulp by Oliveira, Argandoña, and Oshiro [
23] and for curry phenolic compounds by Sablania et al. [
19] while the decreasing antioxidant activity of purple carrot was observed by Murali et al. [
34].
Figure 5.
Response surfaces for the Vitamin C (mg/100g) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters: 1.0 mm (j), 1.2 mm (k), and 1.5 mm (l).
Figure 5.
Response surfaces for the Vitamin C (mg/100g) obtained for the studied nozzle diameters: 1.0 mm (j), 1.2 mm (k), and 1.5 mm (l).
3.5. Microstructures
The microstructure of encapsulated products is an important parameter to be evaluated since it is related to the protection capacity offered by the different polymers while being affected by the integrity and porosity of the microparticles. Test 2 provided the microencapsulated guavira pulp with the highest vitamin C content and was, therefore, submitted to SEM to obtain the photomicrographs of the microstructures seen in
Figure 6a,b, and c for the 1.0, 1.2, and, 1.5 mm spray nozzles, respectively.
Particle average diameters were 93.94, 92.63, and, 118.99 μm for the 1.0, 1.2, and 1.5 mm nozzle diameters, respectively. In addition to nozzle diameter, particle size is probably related to the interaction between inlet temperature, feed rate, encapsulating agent, and feed composition [
35].
According to Oyewumi et al. [
36], powder particles are classified as macroparticles (> 100 µm), microparticles (1 to 1000 µm), and, nanoparticles (< 1µm). Based on this information, powdered guavira pulp yielded microparticles for the 1.0 and 1.2 mm spray nozzles. Regardless of the nozzle used, the microparticles were mostly wilted and irregular due to shrinkage during drying. The microparticles with irregular, wilted, or hollow structures are formed when the increased internal pressure of the drop causes the internal vapor flow to be trapped by the capsule, forming vapor bubbles within the particle [
37].
Microparticles serve as multiunit drug delivery systems with well-defined physiological and pharmacokinetic benefits to improve effectiveness, tolerability, and patient compliance [
38]. In this sense, the microparticles obtained in this study, we suggest that the microcapsules rich in vitamin C, originated from the guavira pulp, can be a potential product to be inserted in formulations, dietary supplements to be used with therapeutic and/or chemopreventive purposes for health.
Figure 6.
SEM micrographs of powdered guavira pulp containing 18% gum arabic, and 6% dehydrated green bocaiuva pulp obtained by spray-drying using the 1.0 mm (a), 1.2 mm (b), and 1.5 mm (c) diameter spray nozzle, at 200, 500 and 1500X resolution.
Figure 6.
SEM micrographs of powdered guavira pulp containing 18% gum arabic, and 6% dehydrated green bocaiuva pulp obtained by spray-drying using the 1.0 mm (a), 1.2 mm (b), and 1.5 mm (c) diameter spray nozzle, at 200, 500 and 1500X resolution.
3.6. Model Optimization and Verification
Optimization of the guavira atomization process from the response surface methodology (RSM) showed that the wall materials significantly affected (p <0.05) yield, solubility, hygroscopicity, and vitamin C content.
Table 6 shows the models able to predict the influence of encapsulating materials on the studied variables. The determination coefficients (R2) higher than 95% were considered efficient to explain the effect of adding the studied carrier agents on the response variables of the atomization process using different diameter spray nozzles.
Atomization parameters of guavira pulp with added dehydrated green bocaiuva pulp were optimized to maximize yield, solubility, and vitamin C content and minimize the hygroscopicity of guavira pulp powder. The multiple response optimization indicated that the ideal guavira microcapsules resulted from the addition of 10.8% gum arabic and, 7.2% chitosan using the 1.0 mm diameter spray nozzle to form the resulting suspension containing 60% guavira pulp and, 6% dehydrated bocaiuva pulp. Under these conditions, the predicted values were 29.48% for powder yield, 82.96% for solubility, 15.90g/100g for hygroscopicity, and, 741.11mg/100g for vitamin C content.
To understand better how adding gum arabic and chitosan affects the process-dependent variables, the coded models that had the highest regression coefficient and represented the yield, solubility, hygroscopicity, and, vitamin C of the microencapsulated guavira pulp resulting from the guavira pulp drying process are shown in equations 1, 2, 3 and 4 below:
where G is Gum arabic and Q, Chitosan.
5. Conclusions
The results of the study indicate that dehydrated bocaiuva pulp associated with maltodextrin, gum arabic, and chitosan as wall materials provided powders with high vitamin C levels. The addition of gum arabic favored the powder yield and vitamin C retention, whereas maltodextrin increased powder solubility and decreased hygroscopicity. The response surface methodology defined the best conditions for guavira pulp atomization. The addition of gum arabic (10.8%) and chitosan (7.2%) provided the optimal results for the following parameters, 29.48% powder yield, 82.96% solubility, 15.90% hygroscopicity, and 741.11mg/100g vitamin C. In addition, the 1.0 mm diameter nozzle was considered the most suitable for obtaining guavira pulp microparticles with the highest ascorbic acid content.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Figure S1. Simplex Centroid Experimental Design.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.F.O. and E.J.S-A.; methodology, N.F.O.; V.S.M.; software, N.F.O.; validation, D.S.B. and D.A.G.; formal analysis, N.F.O.; V.S.M; and E.J.S-A. investigation, N.F.O. and V.S.M.; resources, E.J.S-A and S.S.Y.; data curation, N.F.O. and D.S.B; writing—original draft preparation, N.F.O.; writing—review and editing, N.F.O.; E.J.S-A. and D.S.B; visualization, D.S.B.; supervision, E.J.S-A.; project administration, E.J.S-A.; funding acquisition, E.J.S-A. and D.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Support Foundation for the Development of Teaching, Science and Technology of the State of Mato Grosso do Sul (FUNDECT -MS), grant number 888/2022 (SIAFEM 32425) and by National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq—407671/2013-7).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Higher-Level Staff Training Coordination (CAPES), the Postgraduate Program in Biotechnology and Biodiversity Pro-Centro-Oeste Network (PPGBB) for the granting of a scholarship and technical support and Otávio Maticoli Ferreira for his collaboration in the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Machado, W.; Guimarães, M.F.; Lira, F.F.; Santos, J.V.F.; Takahashi, L.S.A.; Leal, A.C.; Coelho, G.T.C.P. Evaluation of Two Fruit Ecotypes (Totai and Sclerocarpa) of Macaúba (Acrocomia Aculeata). Ind Crops Prod 2015, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.M.C.; Oliveira, D.M.; Costa, L.E.C. Macauba Palm— Acrocomia Aculeata. In Exotic Fruits; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.M.; Clemente, E.; da Costa, J.M.C. Bioactive Compounds and Physicochemical Parameters of Grugru Palm (Acrocomia Aculeata) from Brazil: Pulp and Powder. Food Sci Technol Res 2014, 20, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Nie, S.-P. The Functional and Nutritional Aspects of Hydrocolloids in Foods. Food Hydrocoll 2016, 53, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunco, A.J. Características Físicas, Químicas, Nutricionais e Funcionais de Frutos e Farinha de Acrocomia Aculeata (Jacq) Lodd. Em Diferentes Estádios de Maturação, Universidade Federal da Grande Dourados, Dourados. 2017. Available online: https://sucupira.capes.gov.br/sucupira/public/consultas/coleta/trabalhoConclusao/viewTrabalhoConclusao.jsf?popup=true&id_trabalho=5015970 (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Sá, S.; Chaul, L.T.; Alves, V.F.; Fiuza, T.S.; Tresvenzol, L.M.F.; Vaz, B.G.; Ferri, P.H.; Borges, L.L.; Paula, J.R. Phytochemistry and Antimicrobial Activity of Campomanesia Adamantium. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2018, 28, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.C.; Piccinelli, A.C.; Aquino, D.F.S.; de Souza, V.V.; Schmitz, W.O.; Traesel, G.K.; Cardoso, C.A.L.; Kassuya, C.A.L.; Arena, A.C. Toxicological Analysis and Antihyperalgesic, Antidepressant, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Campomanesia Adamantium Fruit Barks. Nutr Neurosci 2017, 20, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscardi, D.Z.; de Oliveira, V.S.; Arrigo, J.d.S.; Piccinelli, A.C.; Cardoso, C.A.L.; Maldonade, I.R.; Kassuya, C.A.L.; Sanjinez-Argandoña, E.J. Anti-Inflammatory, and Antinociceptive Effects of Campomanesia Adamantium Microencapsulated Pulp. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2017, 27, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, L.G.; Tessaro, E.P.; Eberlin, M.; Pastore, G.M.; Liu, R.H. Assessment of Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities and the Identification of Phenolic Compounds of Exotic Brazilian Fruits. Food Research International 2013, 53, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.C.; Torres, C.A.V.; Nunes, D.; Duarte, P.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A.M.; Fortunato, E.; Moldão-Martins, M.; da Costa, L.B.; Alves, V.D. Using a Bacterial Fucose-Rich Polysaccharide as Encapsulation Material of Bioactive Compounds. Int J Biol Macromol 2017, 104, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Battista, C.A.; Constenla, D.; Ramírez Rigo, M.V.; Piña, J. Process Analysis and Global Optimization for the Microencapsulation of Phytosterols by Spray Drying. Powder Technol 2017, 321, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Estevinho, B.N.; Santos, L. Preliminary Studies of Rosmarinic Acid Microencapsulation with Chitosan and Modified Chitosan for Topical Delivery. Powder Technol 2016, 297, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, F.M.; Lis, M.; Carmona, Ó.G.; Carmona, C.G.; Moisés, M.P.; Zanin, G.M.; Moraes, F.F. Assessment of the Delivery of Citronella Oil from Microcapsules Supported on Wool Fabrics. Powder Technol 2019, 343, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.B.A.C.; Costa, C.J.M.; Pomella, A.W.V.; Ribeiro, E.J.; Santos, L.D.; Zotarelli, M.F. Evaluation of Lethality Temperature and Use of Different Wall Materials in the Microencapsulation Process of Trichoderma Asperellum Conidias by Spray Drying. Powder Technol 2019, 347, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellone, G.; Salvo, A.; Costa, R.; Saija, E.; Bongiorno, D.; Di Stefano, V.; Calabrese, G.; Dugo, G. Investigation on the Influence of Spray-Drying Technology on the Quality of Sicilian Nero d’Avola Wines. Food Chem 2018, 240, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, D.; Pasquali, M.A.; Cavalcanti-Mata, M.; Duarte, M.E.; Lisboa, H.M. Influence of Spray Drying Conditions on the Properties of Avocado Powder Drink. Food Chem 2018, 266, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zotarelli, M.F.; da Silva, V.M.; Durigon, A.; Hubinger, M.D.; Laurindo, J.B. Production of Mango Powder by Spray Drying and Cast-Tape Drying. Powder Technol 2017, 305, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuschagne, P. Impact of Wall Material Physicochemical Characteristics on the Stability of Encapsulated Phytochemicals: A Review. Food Research International 2018, 107, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablania, V.; Bosco, S.J.D. Optimization of Spray Drying Parameters for Murraya Koenigii (Linn) Leaves Extract Using Response Surface Methodology. Powder Technol 2018, 335, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Bi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, R. Multi-Objective Optimization of Spray Drying of Jujube (Zizyphus Jujuba Miller) Powder Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Bioproc Tech 2014, 7, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussaid, S.; Chibane, M.; Madani, K.; Amrouche, T.; Achat, S.; Dahmoune, F.; Houali, K.; Rendueles, M.; Diaz, M. Optimization of the Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Scirpus Holoschoenus Using a Simplex Centroid Design for Antioxidant and Antibacterial Applications. LWT 2017, 86, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes Filho, M.L.; Busanello, M.; Prudencio, S.H.; Garcia, S. Soymilk with Okara Flour Fermented by Lactobacillus Acidophilus: Simplex-Centroid Mixture Design Applied in the Elaboration of Probiotic Creamy Sauce and Storage Stability. LWT 2018, 93, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinícius Soares de Oliveira; Eliana Janet, S. Argandoña; Ayd Mary Oshiro. Atomização e Liofilização Da Polpa de Campomanesia Adamantium: Influência Das Variáveis de Processo Na Retenção de Vitamina C Novas Edições Acadêmicas, 2018; Vol. 1.
- Kalkan, F.; Vanga, S.K.; Murugesan, R.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Microencapsulation of Hazelnut Oil through Spray Drying. Drying Technology 2017, 35, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhalakshmy, S.; Don Bosco, S.J.; Francis, S.; Sabeena, M. Effect of Inlet Temperature on Physicochemical Properties of Spray-Dried Jamun Fruit Juice Powder. Powder Technol 2015, 274, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Corke, H. Production and Properties of Spray-dried Amaranthus Betacyanin Pigments. J Food Sci 2000, 65, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunniff, P.; Washington, D. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. 1995.
- Wang, S.; Langrish, T. A Review of Process Simulations and the Use of Additives in Spray Drying. Food Research International 2009, 42, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariod, A.A. Functional Properties of Gum Arabic. In Gum Arabic; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.A.; Cano-Higuita, D.M.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Telis, V.R.N. Influence of Different Combinations of Wall Materials on the Microencapsulation of Jussara Pulp (Euterpe Edulis) by Spray Drying. Food Chem 2016, 212, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.I.; Rodrigues, M.Z.; Ribeiro Pinto, M.R.M.; Lago Vanzela, E.S.; Stringheta, P.C.; Perrone, Í.T.; Ramos, A.M. Morphological Characterization of Pequi Extract Microencapsulated through Spray Drying. Int J Food Prop 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhag, Y.; Nanda, V. Optimization for Spray Drying Process Parameters of Nutritionally Rich Honey Powder Using Response Surface Methodology. Cogent Food Agric 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.A.; Kurozawa, L.E.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Park, K.J. Influence of Process Conditions on the Physicochemical Properties of Pequi Powder Produced by Spray Drying. Drying Technology 2013, 31, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Kar, A.; Mohapatra, D.; Kalia, P. Encapsulation of Black Carrot Juice Using Spray and Freeze Drying. Food Science and Technology International 2015, 21, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Rojas, D.F.; Souza, C.R.F.; Oliveira, W.P. Optimization of Spray Drying Conditions for Production of Bidens Pilosa L. Dried Extract. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 2015, 93, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewumi, M.O.; Kumar, A.; Cui, Z. Nano-Microparticles as Immune Adjuvants: Correlating Particle Sizes and the Resultant Immune Responses. Expert Rev Vaccines 2010, 9, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Higuita, D.M.; Villa-Vélez, H.A.; Telis-Romero, J.; Váquiro, H.A.; Telis, V.R.N. Influence of Alternative Drying Aids on Water Sorption of Spray Dried Mango Mix Powders: A Thermodynamic Approach. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2015, 93, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengyel, M.; Kállai-Szabó, N.; Antal, V.; Laki, A.J.; Antal, I. Microparticles, Microspheres, and Microcapsules for Advanced Drug Delivery. Sci Pharm 2019, 87, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).