Submitted:
09 April 2024
Posted:
10 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Migraine Patients
2.2. Tryptophan and Its Metabolites in Migraine Patients and Controls
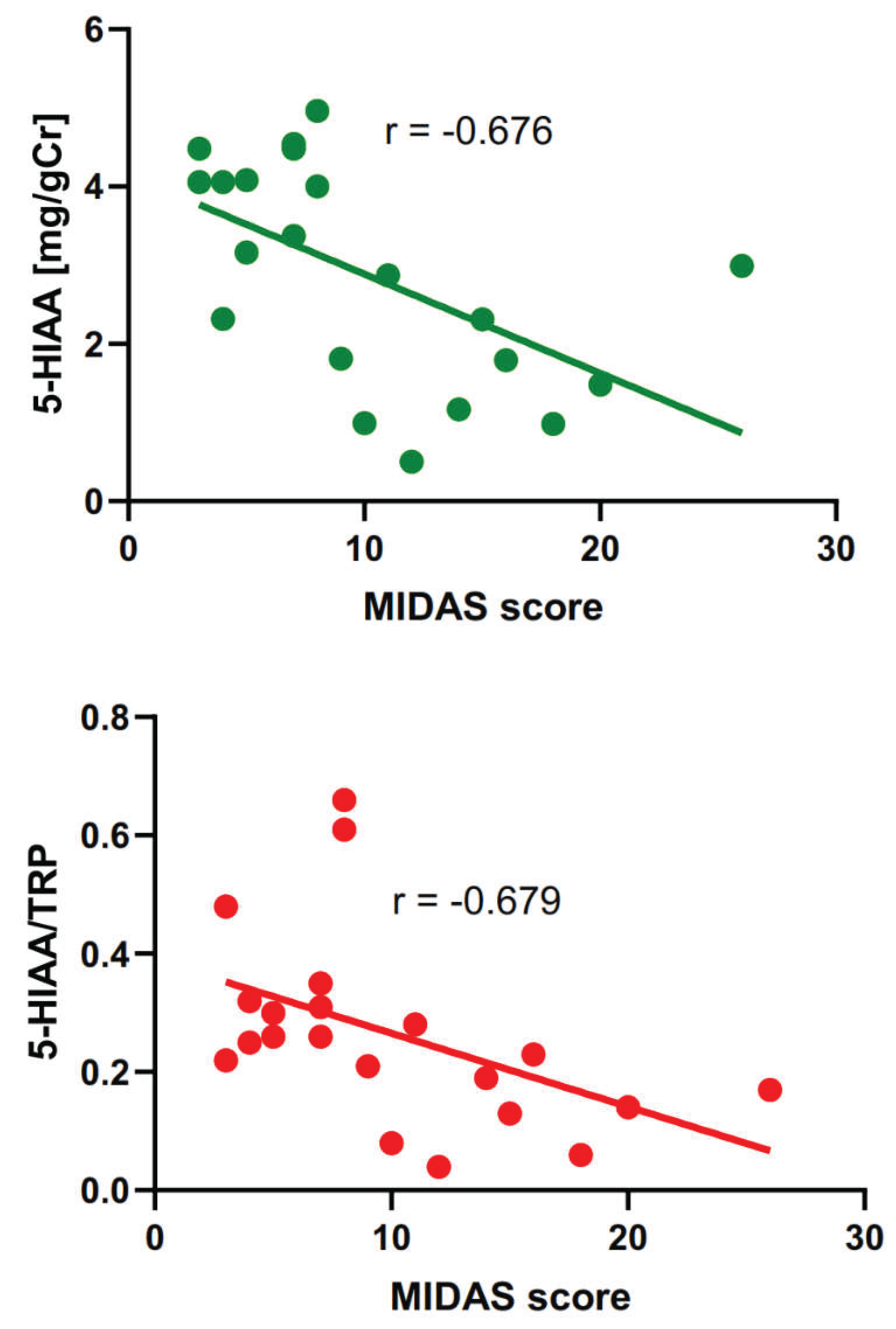
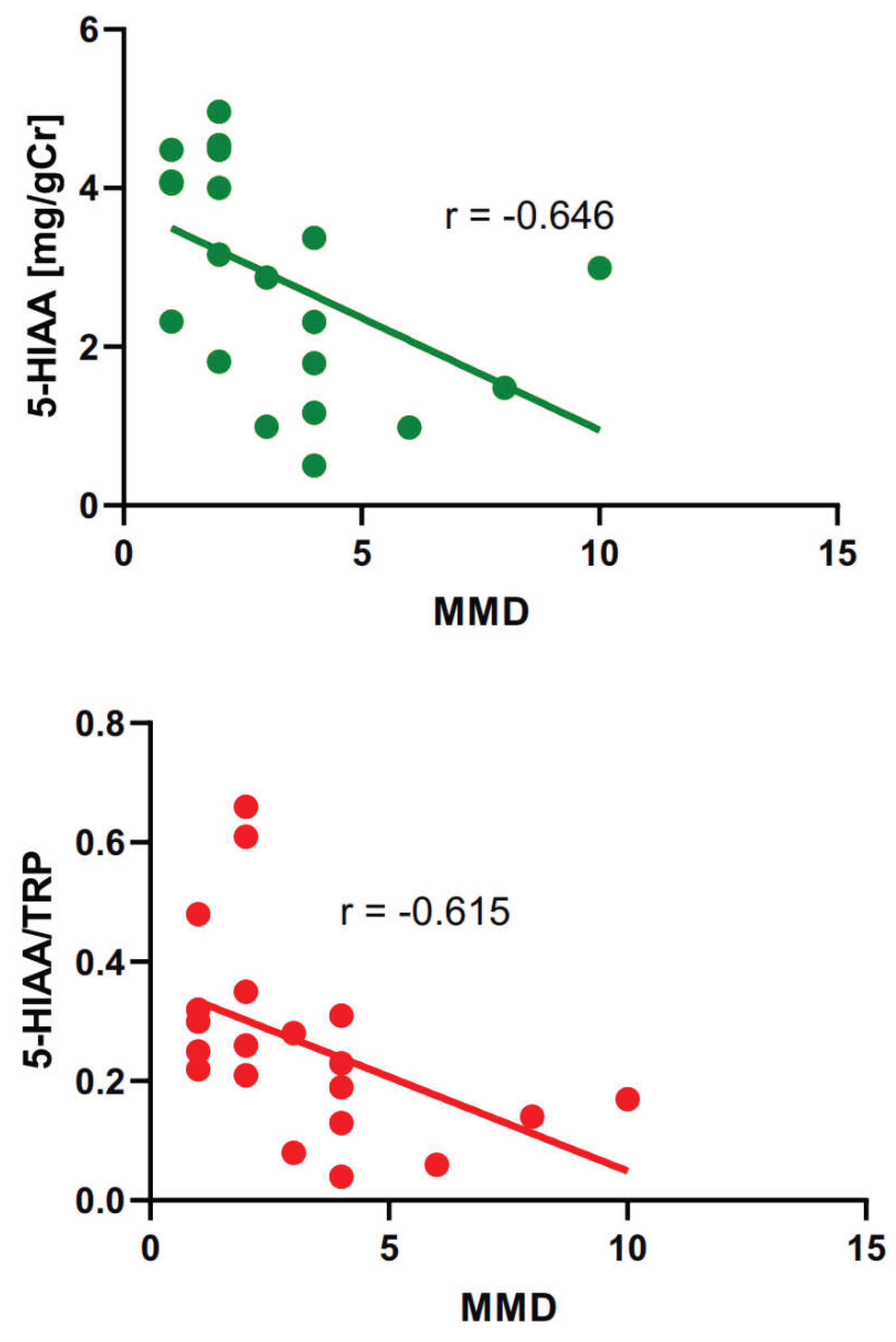
2.3. Associations of Migraine Severity and Timing with Tryptophan Metabolites
2.4. Association of Anxiety/Depression with Tryptophan Metabolites in Migraine Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Ethics
4.2. Diagnosis
4.3. Determination of TRP Metabolites
4.4. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eigenbrodt, A.K.; Ashina, H.; Khan, S.; Diener, H.C.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Sinclair, A.J.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Martelletti, P.; Ducros, A.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; et al. Diagnosis and management of migraine in ten steps. Nat Rev Neurol 2021, 17, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demartini, C.; Greco, R.; Francavilla, M.; Zanaboni, A.M.; Tassorelli, C. Modelling migraine-related features in the nitroglycerin animal model: Trigeminal hyperalgesia is associated with affective status and motor behavior. Physiology & Behavior 2022, 256, 113956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.D.; Goadsby, P.J.; Burstein, R.; Kurth, T.; Ayata, C.; Charles, A.; Ashina, M.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Dodick, D.W. Migraine. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2022, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashina, M.; Hansen, J.M.; Do, T.P.; Melo-Carrillo, A.; Burstein, R.; Moskowitz, M.A. Migraine and the trigeminovascular system-40 years and counting. Lancet Neurol 2019, 18, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yu, S.; Long, Y.; Shi, A.; Deng, J.; Ma, Y.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism: Mechanism-oriented therapy for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 985378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körtési, T.; Spekker, E.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the Tryptophan Metabolic Pathways in Migraine-Related Mechanisms. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razeghi Jahromi, S.; Togha, M.; Ghorbani, Z.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Khorsha, F.; Rafiee, P.; Shirani, P.; Nourmohammadi, M.; Ansari, H. The association between dietary tryptophan intake and migraine. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology 2019, 40, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Li, G.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Su, Y.; Chu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab 2023, 35, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenchner, J.R.; Santos, C. Biochemistry, 5 Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid. In StatPearls; StatPearls PublishingCopyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2024.
- Fila, M.; Chojnacki, C.; Chojnacki, J.; Blasiak, J. The kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism in abdominal migraine in children - A therapeutic potential? Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2023, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fila, M.; Chojnacki, J.; Pawlowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Chojnacki, C.; Blasiak, J. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Migraine and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spekker, E.; Nagy-Grócz, G.; Vécsei, L. Ion Channel Disturbances in Migraine Headache: Exploring the Potential Role of the Kynurenine System in the Context of the Trigeminovascular System. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalón, C.M.; VanDenBrink, A.M. The Role of 5-Hydroxytryptamine in the Pathophysiology of Migraine and its Relevance to the Design of Novel Treatments. Mini Rev Med Chem 2017, 17, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Altamirano, J.L.; Olmos-Hernandez, A.; Jaime, H.B.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Bandala, C.; Reyes-Long, S.; Alfaro-Rodríguez, A. Review: 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 Receptors and their Role in the Modulation of Pain Response in the Central Nervous System. Curr Neuropharmacol 2018, 16, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Vécsei, L. Are 5-HT(1) receptor agonists effective anti-migraine drugs? Expert Opin Pharmacother 2021, 22, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre Leite, G.; Adriana Martini, F.; Reinaldo Teixeira, R.; Eliova, Z.; José, C.-N.; Mario Fernando Prieto, P. Randomised clinical trial comparing melatonin 3 mg, amitriptyline 25 mg and placebo for migraine prevention. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 2016, 87, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Ren, Z.; Xia, H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, T.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z. Associations between anxiety, depression with migraine, and migraine-related burdens. Front Neurol 2023, 14, 1090878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres, M.F.P.; Mercante, J.P.P.; Tobo, P.R.; Kamei, H.; Bigal, M.E. Anxiety and depression symptoms and migraine: a symptom-based approach research. J Headache Pain 2017, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervenka, I.; Agudelo, L.Z.; Ruas, J.L. Kynurenines: Tryptophan’s metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2017, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irimia, P.; Garrido-Cumbrera, M.; Santos-Lasaosa, S.; Aguirre-Vazquez, M.; Correa-Fernández, J.; Colomina, I.; Pozo-Rosich, P. Impact of monthly headache days on anxiety, depression and disability in migraine patients: results from the Spanish Atlas. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia : an international journal of headache 2013, 33, 629–808. [CrossRef]
- Al Ghadeer, H.A.; Al Salman, S.A.; Alshakhs, Z.M.; Alghanim, J.H.; Alneamah, A.A.; Almazyadi, H.S.; Alalawi, H.H.; AlHassan, M.I.; Alsuwailem, B.S.; Albonasser, A.A.; et al. Migraine Headache and the Risk of Depression. Cureus 2022, 14, e31081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreou, D.; Saetre, P.; Werge, T.; Andreassen, O.A.; Agartz, I.; Sedvall, G.C.; Hall, H.; Terenius, L.; Jönsson, E.G. Tryptophan hydroxylase gene 1 (TPH1) variants associated with cerebrospinal fluid 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid and homovanillic acid concentrations in healthy volunteers. Psychiatry Res 2010, 180, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifačić, D.; Aralica, M.; Sotošek Tokmadžić, V.; Rački, V.; Tuškan-Mohar, L.; Kučić, N. Values of vanillylmandelic acid and homovanillic acid in the urine as potential prognostic biomarkers in ischaemic stroke patients. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, S.I.; Schapiro, M.B.; May, C. Reduced Brain Delivery of Homovanillic Acid to Cerebrospinal Fluid During Human Aging. Archives of Neurology 2004, 61, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyasaikumar, K.V.; Tararina, M.; Wu, H.Q.; Neale, S.A.; Weisz, F.; Salt, T.E.; Schwarcz, R. Xanthurenic Acid Formation from 3-Hydroxykynurenine in the Mammalian Brain: Neurochemical Characterization and Physiological Effects. Neuroscience 2017, 367, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangasniemi, P.J. Changes in serotonin metabolism during migraine attacks. Monogr Neural Sci 1976, 3, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, L.; Lange, K.S.; Waliszewska-Prosół, M.; Onan, D.; Marschollek, K.; Wiels, W.; Mikulenka, P.; Farham, F.; Gollion, C.; Ducros, A.; et al. Genetics of migraine: where are we now? The Journal of Headache and Pain 2023, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cader, M.Z. The genetics of migraine and the path to precision medicine. Prog Brain Res 2020, 255, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.W.; Burch, R.C.; Frishberg, B.M.; Marmura, M.J.; Mechtler, L.L.; Silberstein, S.D.; Turner, D.P. Neuroimaging for Migraine: The American Headache Society Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guideline. Headache 2020, 60, 318–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berstad, J.R. Total 5-hydroxyindoles in blood related to migraine attacks. Acta Neurol Scand 1976, 54, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deanović, Z.; Iskrić, S.; Dupelj, M. Fluctuation of 5-hydroxy-indole compounds in the urine of migrainous patients. Biomedicine 1975, 23, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hyypp, M.T.; Kangasniemi, P. Variation of plasma free tryptophan and CSF 5-HIAA during migraine. Headache 1977, 17, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curzon, G.; Theaker, P.; Phillips, B. Excretion of 5-hydroxyindolyl acetic acid (5HIAA) in migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1966, 29, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.D.; Odink, J.; Tapparelli, C.; Van Kempen, G.M.; Pennings, E.J.; Bruyn, G.W. Serotonin metabolism in migraine. Neurology 1989, 39, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanović, D.D.; Majkić-Sing, N.; Mirković, D.; Pavlović, J. Plasma and urinary serotonin and 5-hydroxyindol-3-acetic acid in adults with migraine and tension-type headache. Advances in experimental medicine and biology 1999, 467, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.A.; Cotrim, M.D.; Morgadinho, M.T.; Ramos, M.I.; Santos, E.S.; de Macedo Tdos, R. Migraine, serum serotonin and platelet 5-HT2 receptors. Cephalalgia : an international journal of headache 1990, 10, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousser, M.G.; Elghozi, J.L.; Laude, D.; Soisson, T. Urinary 5-HIAA in migraine: evidence of lowered excretion in young adult females. Cephalalgia: an international journal of headache 1986, 6, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonaci, F.; Nappi, G.; Galli, F.; Manzoni, G.C.; Calabresi, P.; Costa, A. Migraine and psychiatric comorbidity: a review of clinical findings. J Headache Pain 2011, 12, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresler, T.; Caratozzolo, S.; Guldolf, K.; Huhn, J.I.; Loiacono, C.; Niiberg-Pikksööt, T.; Puma, M.; Sforza, G.; Tobia, A.; Ornello, R.; et al. Understanding the nature of psychiatric comorbidity in migraine: a systematic review focused on interactions and treatment implications. J Headache Pain 2019, 20, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommer, R.; Lateef, T.; He, J.P.; Merikangas, K. Headache and mental disorders in a nationally representative sample of American youth. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2022, 31, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Chung, P.W.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, M.J.; Park, J.W.; Chu, M.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Bae, D.W.; Song, T.J.; Sohn, J.H.; et al. The impact of remission and coexisting migraine on anxiety and depression in cluster headache. J Headache Pain 2020, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayamohananan, H.; Manoj Kumar, M.K. T, P.A. 5-HIAA as a potential biological marker for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Adv Pharm Bull 2019, 9, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, C.; Gąsiorowska, A.; Popławski, T.; Błońska, A.; Konrad, P.; Zajdler, R.; Chojnacki, J.; Blasiak, J. Reduced Intake of Dietary Tryptophan Improves Beneficial Action of Budesonide in Patients with Lymphocytic Colitis and Mood Disorders. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, C.; Popławski, T.; Chojnacki, J.; Fila, M.; Konrad, P.; Blasiak, J. Tryptophan Intake and Metabolism in Older Adults with Mood Disorders. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, C.; Popławski, T.; Konrad, P.; Fila, M.; Błasiak, J.; Chojnacki, J. Antimicrobial treatment improves tryptophan metabolism and mood of patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2022, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, C.; Popławski, T.; Konrad, P.; Fila, M.; Chojnacki, J.; Błasiak, J. Serotonin Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth-A Pilot Study with Patients Diagnosed with Lactulose Hydrogen Breath Test and Treated with Rifaximin. Journal of clinical medicine 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colín-González, A.L.; Maldonado, P.D.; Santamaría, A. 3-Hydroxykynurenine: An intriguing molecule exerting dual actions in the Central Nervous System. NeuroToxicology 2013, 34, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Tavasol, A.; Jazi, K.; Hajibeygi, R.; Shool, S.; Sodeifian, F.; Klegeris, A.; McElhinney, A.; et al. Dynamic changes in metabolites of the kynurenine pathway in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease: A systematic Review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 997240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, M.; Lionetto, L.; Negro, A.; Capi, M.; Perugino, F.; Fazio, F.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Simmaco, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Martelletti, P. Altered serum levels of kynurenine metabolites in patients affected by cluster headache. J Headache Pain 2015, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fila, M.; Chojnacki, C.; Chojnacki, J.; Blasiak, J. The kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism in abdominal migraine in children - A therapeutic potential? Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2024, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fila, M.; Chojnacki, J.; Pawlowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Chojnacki, C.; Blasiak, J. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Migraine and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuka, B.; Nyári, A.; Cseh, E.K.; Körtési, T.; Veréb, D.; Tömösi, F.; Kecskeméti, G.; Janáky, T.; Tajti, J.; Vécsei, L. Clinical relevance of depressed kynurenine pathway in episodic migraine patients: potential prognostic markers in the peripheral plasma during the interictal period. J Headache Pain 2021, 22, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.; Viktrup, L.; Nicholson, R.A.; Ossipov, M.H.; Vargas, B.B. The not so hidden impact of interictal burden in migraine: A narrative review. Front Neurol 2022, 13, 1032103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhon, S.; Gupta, V. Mood Disorder. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2024.
- Zhu, W.; Stevens, A.P.; Dettmer, K.; Gottfried, E.; Hoves, S.; Kreutz, M.; Holler, E.; Canelas, A.B.; Kema, I.; Oefner, P.J. Quantitative profiling of tryptophan metabolites in serum, urine, and cell culture supernatants by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 2011, 401, 3249–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.H.; Yoo, D.; Ahn, T.B.; Lee, W.; Hong, J. Profiling Analysis of Tryptophan Metabolites in the Urine of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Using LC-MS/MS. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
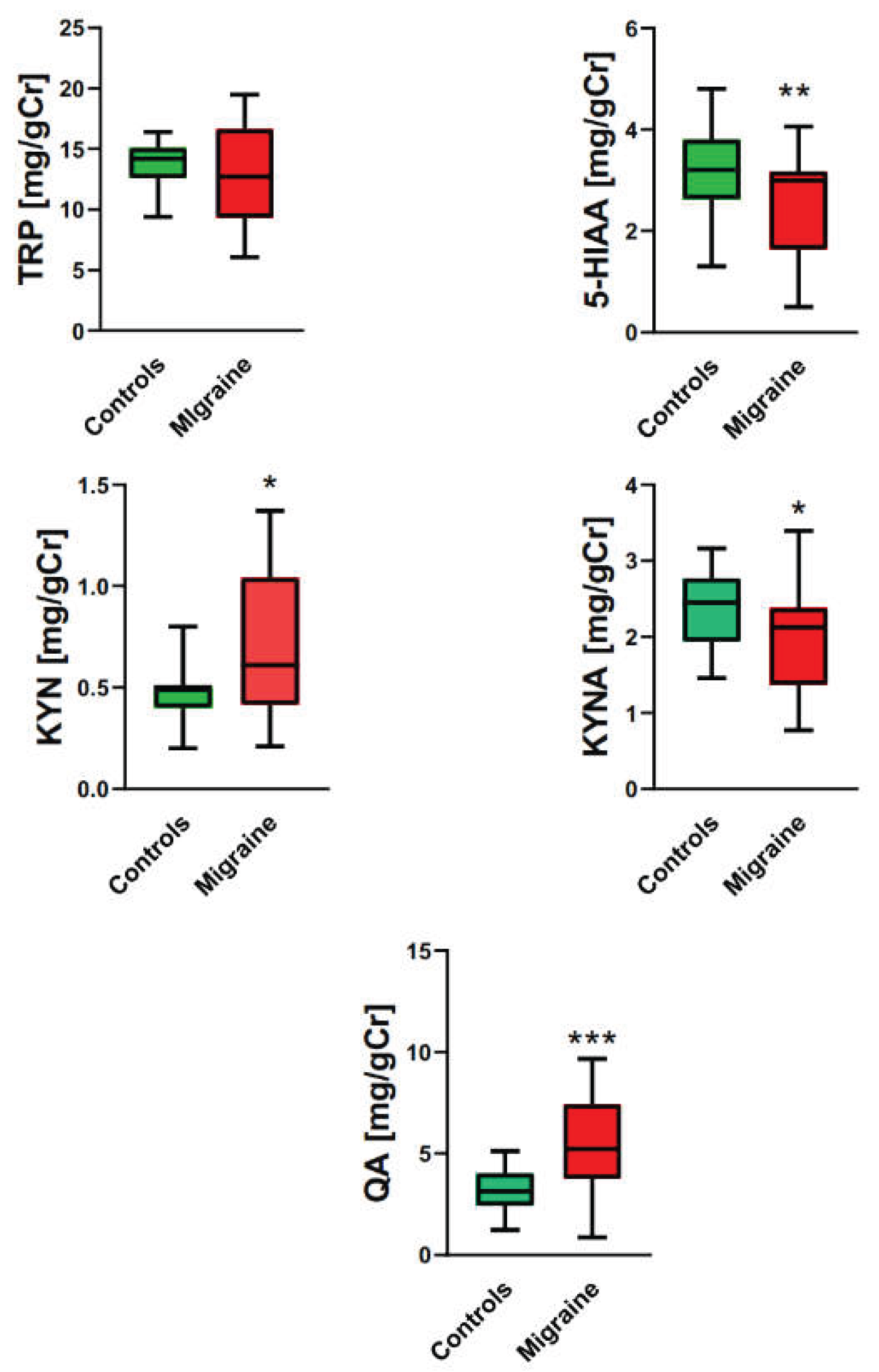
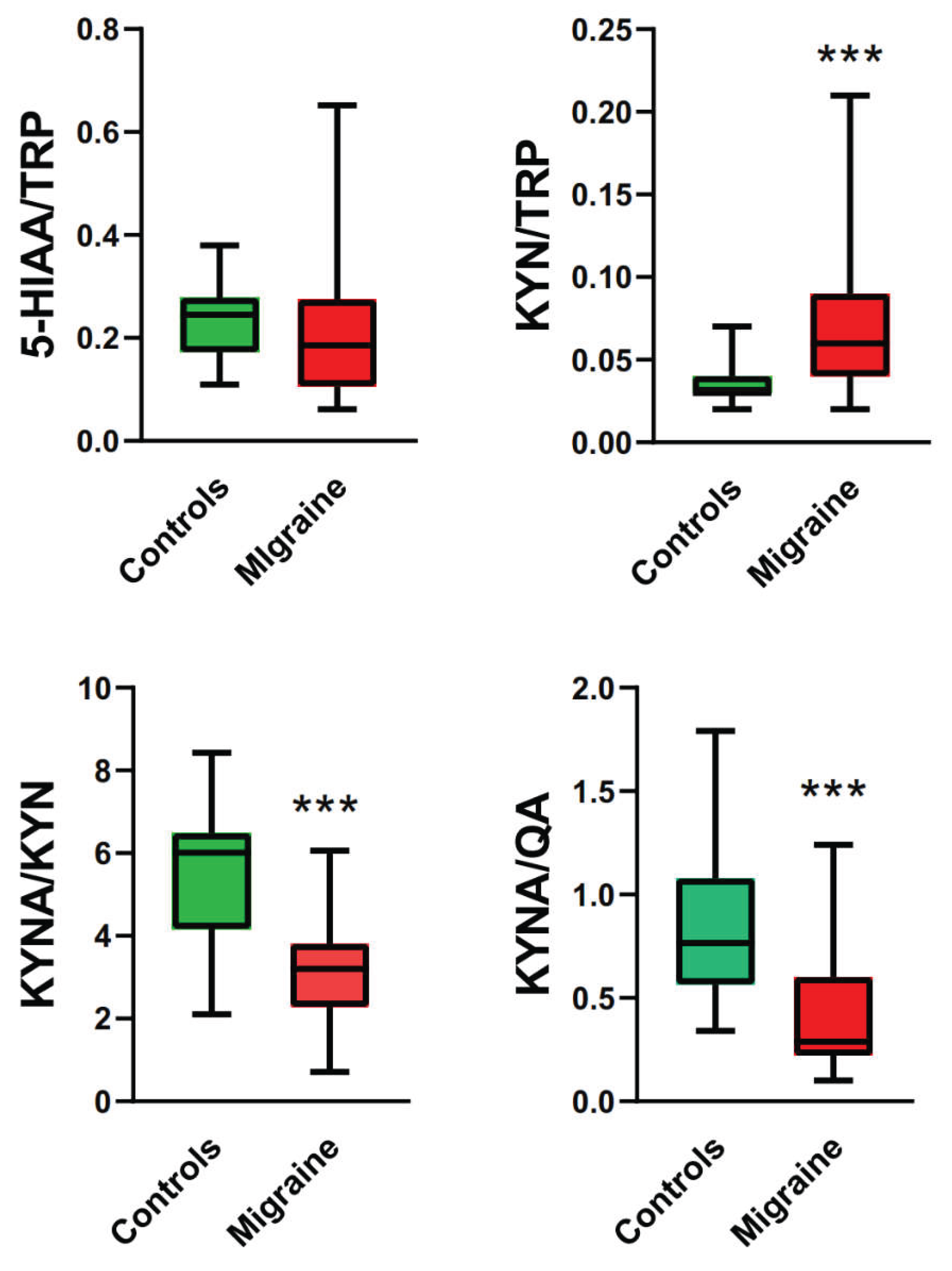
| Characteristic | Specification (Mean ± SD (range) or type and number) |
|---|---|
| Age | 39 ± 13 (26-65) |
| Sex | 14 F, 7 M |
| Migraine type | Episodic, 21 |
| Aura | 8 |
| Frequency of attacks (per month) | 1.2 ± 1.1 (0.3-4.0) |
| Frequency of attacks (per quarter) | 3.5 ± 2.9 (1-12) |
| Time since diagnosis (years) | 18 ± 12 (3-40) |
| Treatment | Abortive 16, prophylactic 5, both 3 |
| Pain intensity (NRS 1) | 7.0 ± 1.5 (5-10) |
| MIDAS | 10.0 ± 5.9 (3-26) |
| Monthly migraine days Monthly headache days |
3.2 ± 2.4 (1-10) 5.0 ± 3.1 (1-14) |
| Mood disorders | 8 |
| Anxiety (GAD-7 score) | 4.4 ± 3.1 (0-12) |
| Depression (PHQ-9 score) | 6.0 ± 3.2 (1-14) |
| MIDAS score and | rho-Spearman | p |
|---|---|---|
| TRP | 0.163 | 0.309 |
| 5-HIAA | – 0.676 | 0.001 |
| KYN | 0.242 | 0.304 |
| KYNA | – 0.050 | 0.835 |
| QA | 0.145 | 0.543 |
| 5-HIAA/TRP | – 0.679 | 0.001 |
| KYN/TRP | – 0.184 | 0.437 |
| KYNA/KYN | 0.077 | 0.748 |
| KYNA/QA | – 0.158 | 0.506 |
| MMD and | rho-Spearman | p |
|---|---|---|
| TRP | 0.195 | 0.410 |
| 5-HIAA | -0.646 | 0.002 |
| KYN | -0.188 | 0.427 |
| KYNA | 0.002 | 0.995 |
| QA | 0.143 | 0.548 |
| 5-HIAA/TRP | -0.615 | 0.003 |
| KYN/TRP | -0.116 | 0.627 |
| KYNA/KYN | 0.042 | 0.862 |
| KYNA/QA | -0.108 | 0.651 |
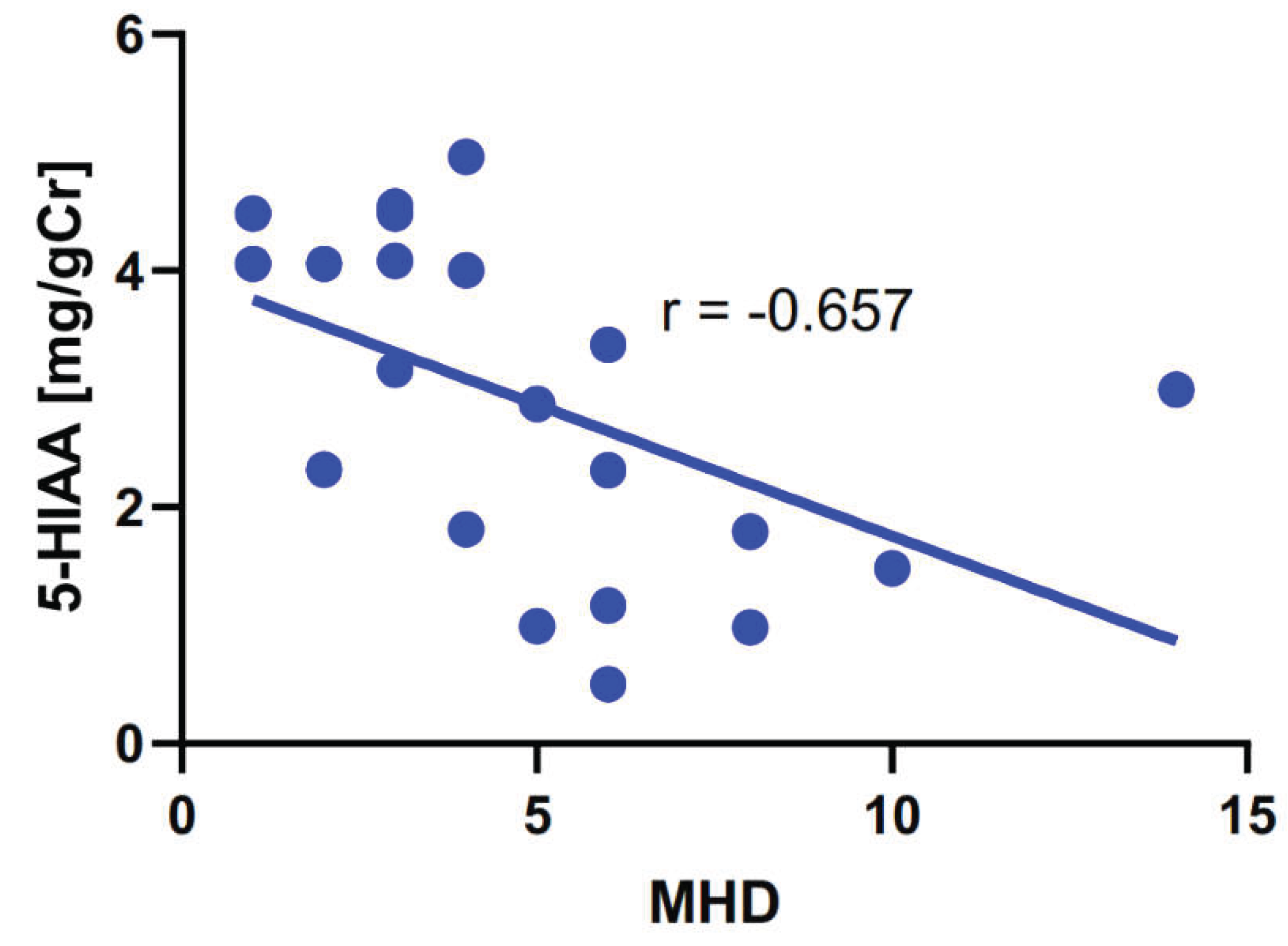
| MHD and | rho-Spearman | p |
|---|---|---|
| TRP | 0.149 | 0.518 |
| 5-HIAA | -0.657 | 0.001 |
| KYN | -0.206 | 0.369 |
| KYNA | -0.051 | 0.826 |
| QA | 0.159 | 0.491 |
| 5-HIAA/TRP | -0.418 | 0.060 |
| KYN/TRP | -0.152 | 0.510 |
| KYNA/KYN | 0.032 | 0.890 |
| KYNA/QA | -0.136 | 0.556 |
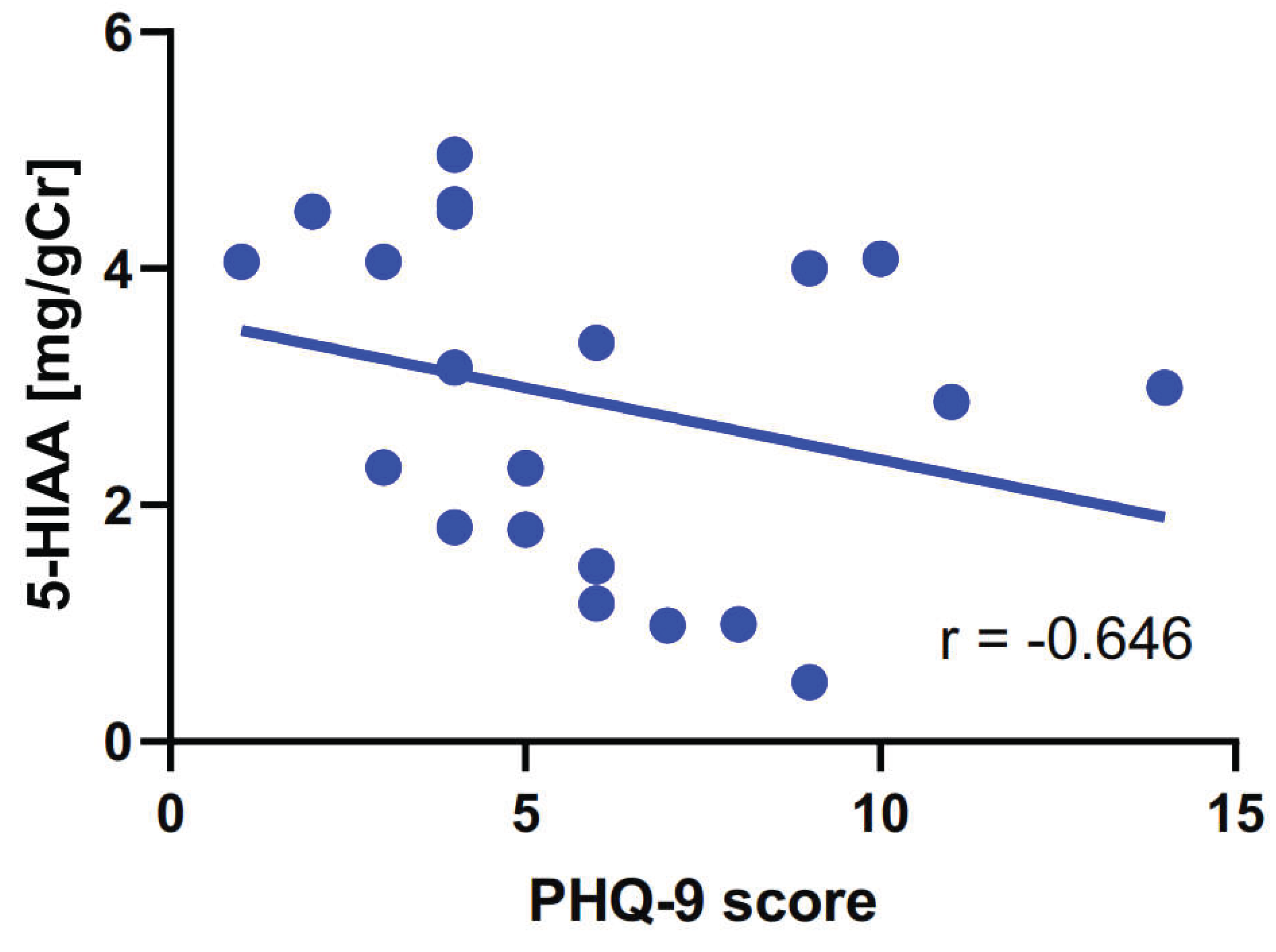
| PHQ-9 score and | rho-Spearman | p |
|---|---|---|
| TRP | 0.004 | 0.987 |
| 5-HIAA | -0.427 | 0.048 |
| KYN | -0.334 | 0.139 |
| KYNA | -0.160 | 0.489 |
| QA | 0.216 | 0.347 |
| 5-HIAA/TRP | -0.307 | 0.176 |
| KYN/TRP | 0.042 | 0.862 |
| KYNA/KYN | 0.238 | 0.299 |
| KYNA/QA | -0.198 | 0.390 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





