Submitted:
09 April 2024
Posted:
10 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Bronchoalveolar Lavage
2.3. Clinical Biochemistry Assays and Real Time PCR (RT-PCR)
- hsa-miR-223-5p: CGUGUAUUUGACAAGCUGAGUU; (Assay ID 477984_mir)
- hsa-miR-16-5p: UAGCAGCACGUAAAUAUUGGCG; (Assay ID 477860_mir)
- hsa-miR-20a-5p: UAAAGUGCUUAUAGUGCAGGUAG; (Assay ID 478317_mir)
- hsa-miR-17-5p: CAAAGUGCUUACAGUGCAGGUAG; (Assay ID 478447_mir)
- hsa-miR-34a-5p: UGGCAGUGUCUUAGCUGGUUGU; (Assay ID 478048_mir)
- hsa-miR-106a-5p: AAAAGUGCUUACAGUGCAGGUAG; (Assay ID 478225_mir)
- U6 snRNA: GTGCTCGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAATTGGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGCATGGCCCCTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCAAATTCGTGAAGCGTTCCATATTTT; (AssayID: 001973).
2.4. In Silico Prediction of hsa-miRs Target Genes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
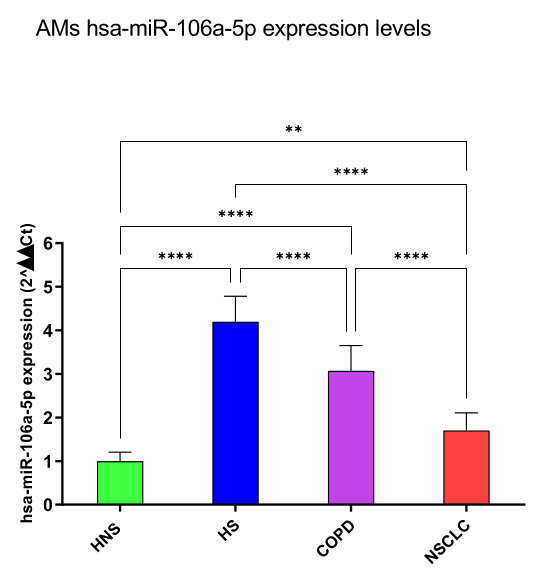
3.1. miRNA Expression Levels
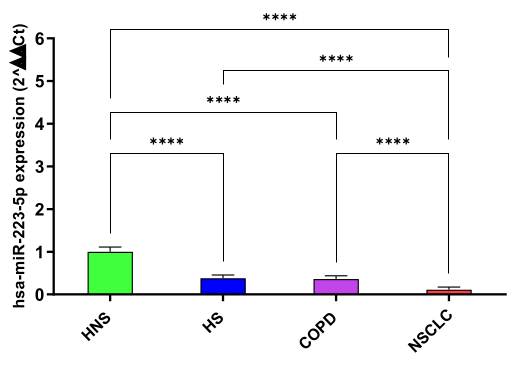
hsa-miR-223-5p
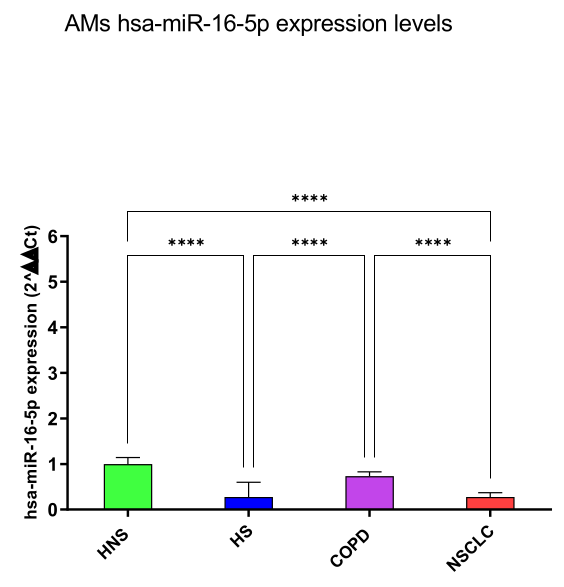
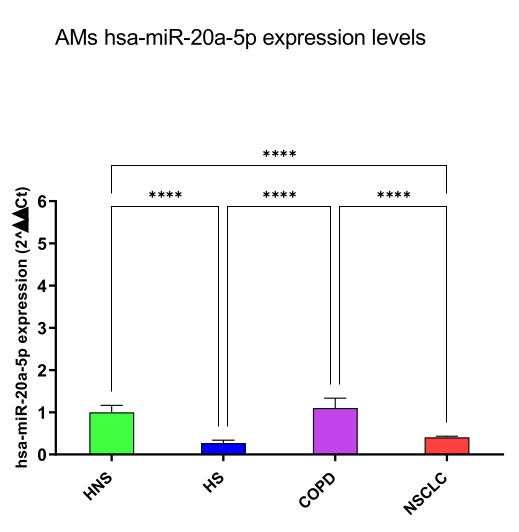
hsa-miR-16-5p and 20a-5p
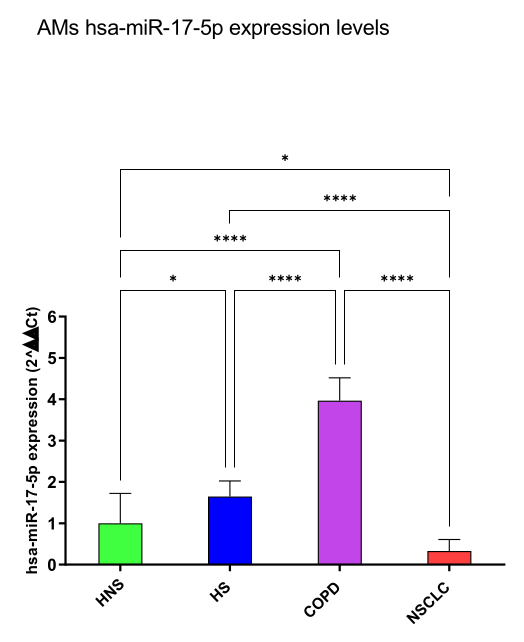
hsa-miR-17-5p
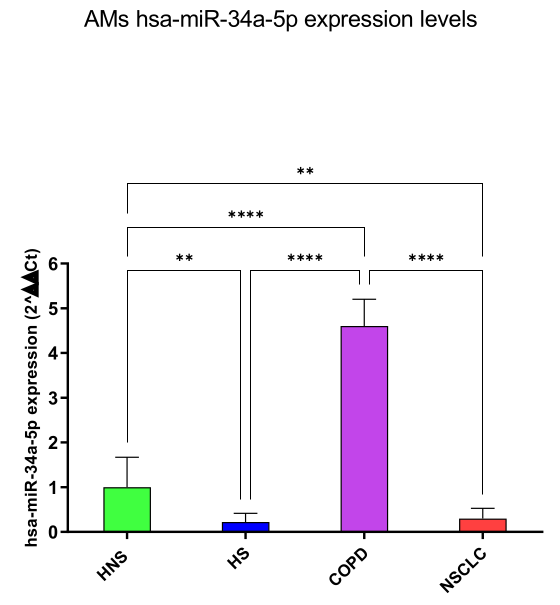
hsa-miR-34a-5p
3.2. In Silico Identification of Target mRNAs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest Statement
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Funding
References
- López-Campos, J.L.; Tan, W.; Soriano, J.B. Global burden of COPD. Respirology. 2016, 21(1):14-23. [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Noori, M.; Nejadghaderi, S. A.; Sullman, M. J. M.; Ahmadian Heris, J.; Ansarin, K.; Mansournia, M. A.; Collins, G. S.; Kolahi, A. A.; Kaufman, J. S. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ, 2022, 378:e069679. [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, R. A.; Rabe, K. F. Burden and Clinical Features of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). The Lancet 2004, 364 (9434), 613–620. [CrossRef]
- Kotlyarov, S. The Role of Smoking in the Mechanisms of Development of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Atherosclerosis. IJMS 2023, 24 (10), 8725. [CrossRef]
- Urbanek, K.; De Angelis, A.; Spaziano, G.; Piegari, E.; Matteis, M.; Cappetta, D.; Esposito, G.; Russo, R.; Tartaglione, G.; De Palma, R.; Rossi, F.; D’Agostino, B. Intratracheal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulates Tachykinin System, Suppresses Airway Remodeling and Reduces Airway Hyperresponsiveness in an Animal Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11 (7), e0158746. [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, B.; Advenier, C.; De Palma, R.; Gallelli, L.; Marrocco, G.; Abbate, G. F.; Rossi, F. The Involvement of Sensory Neuropeptides in Airway Hyper-Responsiveness in Rabbits Sensitized and Challenged to Parietaria Judaica: Sensory Neuropeptides in Airway Hyper-Responsiveness. Clinical & Experimental Allergy 2002, 32 (3), 472–479. [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, B.; Marrocco, G.; De Nardo, M.; Calò, G.; Guerrini, R.; Gallelli, L.; Advenier, C.; Rossi, F. Activation of the Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ Receptor Reduces Bronchoconstriction and Microvascular Leakage in a Rabbit Model of Gastroesophageal Reflux: N/OFQ Effects in the Airways in a GER Animal Model. British Journal of Pharmacology 2005, 144 (6), 813–820. [CrossRef]
- Rouget, C.; Cui, Y. Y.; D’Agostino, B.; Faisy, C.; Naline, E.; Bardou, M.; Advenier, C. Nociceptin Inhibits Airway Microvascular Leakage Induced by HCl Intra-Oesophageal Instillation: Nociceptin and Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux. British Journal of Pharmacology 2004, 141 (6), 1077–1083. [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L.; D’Agostino, B.; Marrocco, G.; De Rosa, G.; Filippelli, W.; Rossi, F.; Advenier, C. Role of Tachykinins in the Bronchoconstriction Induced by HCl Intraesophageal Instillation in the Rabbit. Life Sciences 2003, 72 (10), 1135–1142. [CrossRef]
- Durham, A. L.; Adcock, I. M. The Relationship between COPD and Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90 (2), 121–127. [CrossRef]
- Papi, A. COPD Increases the Risk of Squamous Histological Subtype in Smokers Who Develop Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Thorax 2004, 59 (8), 679–681. [CrossRef]
- Young, R. P.; Hopkins, R. J. Link between COPD and Lung Cancer. Respiratory Medicine 2010, 104 (5), 758–759. [CrossRef]
- Schetter, A. J.; Heegaard, N. H. H.; Harris, C. C. Inflammation and Cancer: Interweaving MicroRNA, Free Radical, Cytokine and P53 Pathways. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31 (1), 37–49. [CrossRef]
- Caramori, G.; Adcock, I. M.; Casolari, P.; Ito, K.; Jazrawi, E.; Tsaprouni, L.; Villetti, G.; Civelli, M.; Carnini, C.; Chung, K. F.; Barnes, P. J.; Papi, A. Unbalanced Oxidant-Induced DNA Damage and Repair in COPD: A Link towards Lung Cancer. Thorax 2011, 66 (6), 521–527. [CrossRef]
- Schaible, A. M.; Filosa, R.; Temml, V.; Krauth, V.; Matteis, M.; Peduto, A.; Bruno, F.; Luderer, S.; Roviezzo, F.; Di Mola, A.; de Rosa, M.; D’Agostino, B.; Weinigel, C.; Barz, D.; Koeberle, A.; Pergola, C.; Schuster, D.; Werz, O. Elucidation of the Molecular Mechanism and the Efficacy in Vivo of a Novel 1,4-Benzoquinone That Inhibits 5-Lipoxygenase. Br J Pharmacol 2014, 171 (9), 2399–2412. [CrossRef]
- Schaible, A. M.; Filosa, R.; Krauth, V.; Temml, V.; Pace, S.; Garscha, U.; Liening, S.; Weinigel, C.; Rummler, S.; Schieferdecker, S.; Nett, M.; Peduto, A.; Collarile, S.; Scuotto, M.; Roviezzo, F.; Spaziano, G.; de Rosa, M.; Stuppner, H.; Schuster, D.; D’Agostino, B.; Werz, O. The 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor RF-22c Potently Suppresses Leukotriene Biosynthesis in Cellulo and Blocks Bronchoconstriction and Inflammation in Vivo. Biochemical Pharmacology 2016, 112, 60–71. [CrossRef]
- Mark, N. M.; Kargl, J.; Busch, S. E.; Yang, G. H. Y.; Metz, H. E.; Zhang, H.; Hubbard, J. J.; Pipavath, S. N. J.; Madtes, D. K.; Houghton, A. M. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Alters Immune Cell Composition and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2018, 197 (3), 325–336. [CrossRef]
- Punturieri, A.; Szabo, E.; Croxton, T. L.; Shapiro, S. D.; Dubinett, S. M. Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Needs and Opportunities for Integrated Research. JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2009, 101 (8), 554–559. [CrossRef]
- Hodge, S.; Hodge, G.; Ahern, J.; Jersmann, H.; Holmes, M.; Reynolds, P. N. Smoking Alters Alveolar Macrophage Recognition and Phagocytic Ability: Implications in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2007, 37 (6), 748–755. [CrossRef]
- de Groot, L. E. S.; van der Veen, T. A.; Martinez, F. O.; Hamann, J.; Lutter, R.; Melgert, B. N. Oxidative Stress and Macrophages: Driving Forces behind Exacerbations of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease? American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2019, 316 (2), L369–L384. [CrossRef]
- Vlahos, R. Role of Alveolar Macrophages in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5. [CrossRef]
- Finicelli, M.; Digilio, F. A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Emerging Role of Macrophages in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: The Potential Impact of Oxidative Stress and Extracellular Vesicle on Macrophage Polarization and Function. Antioxidants 2022, 11 (3), 464. [CrossRef]
- Polverino, F.; Mirra, D.; Yang, C. X.; Esposito, R.; Spaziano, G.; Rojas-Quintero, J.; Sgambato, M.; Piegari, E.; Cozzolino, A.; Cione, E.; Gallelli, L.; Capuozzo, A.; Santoriello, C.; Berrino, L.; de-Torres, J. P.; Hackett, T. L.; Polverino, M.; D’Agostino, B. Similar Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression Profile in Patients with Mild COPD and Lung Cancer. Sci Rep 2022, 12 (1), 22402. [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Schoneveld, O.; Georgakilas, A. G.; Panayiotidis, M. I. Oxidative Stress, DNA Methylation and Carcinogenesis. Cancer Letters 2008, 266 (1), 6–11. [CrossRef]
- Kabesch, M.; Adcock, I. M. Epigenetics in Asthma and COPD. Biochimie 2012, 94 (11), 2231–2241. [CrossRef]
- Molina-Pinelo, S.; Pastor, M. D.; Suarez, R.; Romero-Romero, B.; Gonzalez De la Pena, M.; Salinas, A.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; De Miguel, M. J.; Rodriguez-Panadero, F.; Carnero, A.; Paz-Ares, L. MicroRNA Clusters: Dysregulation in Lung Adenocarcinoma and COPD. European Respiratory Journal 2014, 43 (6), 1740–1749. [CrossRef]
- Mirra, D.; Cione, E.; Spaziano, G.; Esposito, R.; Sorgenti, M.; Granato, E.; Cerqua, I.; Muraca, L.; Iovino, P.; Gallelli, L.; D’Agostino, B. Circulating MicroRNAs Expression Profile in Lung Inflammation: A Preliminary Study. JCM 2022, 11 (18), 5446. [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.-F.; Liston, A. MicroRNA in the Immune System, MicroRNA as an Immune System. Immunology 2009, 127 (3), 291–298. [CrossRef]
- Iannone, F.; Montesanto, A.; Cione, E.; Crocco, P.; Caroleo, M. C.; Dato, S.; Rose, G.; Passarino, G. Expression Patterns of Muscle-Specific MiR-133b and MiR-206 Correlate with Nutritional Status and Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2020, 12 (2), 297. [CrossRef]
- Cannataro, R.; Caroleo, M. C.; Fazio, A.; La Torre, C.; Plastina, P.; Gallelli, L.; Lauria, G.; Cione, E. Ketogenic Diet and MicroRNAs Linked to Antioxidant Biochemical Homeostasis. Antioxidants 2019, 8 (8), 269. [CrossRef]
- Leidinger, P.; Keller, A.; Borries, A.; Huwer, H.; Rohling, M.; Huebers, J.; Lenhof, H. P.; Meese, E. Specific peripheral miRNA profiles for distinguishing lung cancer from COPD. Lung cancer 2011, 74(1), 41–47. [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Fehlmann, T.; Ludwig, N.; Kahraman, M.; Laufer, T.; Backes, C.; Vogelmeier, C.; Diener, C.; Biertz, F.; Herr, C.; Jörres, R. A.; Lenhof, H. P.; Meese, E.; Bals, R., COSYCONET Study Group. Genome-wide MicroRNA Expression Profiles in COPD: Early Predictors for Cancer Development. Genomics, proteomics bioinformatics 2018, 16(3), 162–171. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 Family: A Potential Tumor Suppressor and Therapeutic Candidate in Cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2019, 38 (1), 53. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. MiR-223-5p Suppresses OTX1 to Mediate Malignant Progression of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 2021, 2021, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luo, Y.; Lin, M.; Peng, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, D.; Yang, Z. Serum Exosomal miR -16-5p Functions as a Tumor Inhibitor and a New Biomarker for PD-L1 Inhibitor-dependent Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating PD-L1 Expression. Cancer Medicine 2022, 11 (13), 2627–2643. [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Changyu, S.; Limeng, Z.; Yuan, P. Clinical Significance of MiRNA - 106a in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Who Received Cisplatin Combined with Gemcitabine Chemotherapy. Cancer Biology & Medicine 2018, 15 (2), 157. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, F.; Bian, H.; Tang, B.; Fang, X. MicroRNA-20a-5p Suppresses Tumor Angiogenesis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer through RRM2-Mediated PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 2021, 476 (2), 689–698. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, P.; Ma, Z. Biology of MiR-17-92 Cluster and Its Progress in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15 (13), 1443–1448. [CrossRef]
- Sweat, Y.; Ries, R. J.; Sweat, M.; Su, D.; Shao, F.; Eliason, S.; Amendt, B. A. MiR-17 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor by Negatively Regulating the MiR-17-92 Cluster. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 1148–1158. [CrossRef]
- Fathinavid, A.; Ghobadi, M.Z.; Najafi, A.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. Identification of Common MicroRNA between COPD and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer through Pathway Enrichment Analysis. BMC Genom. Data 2021, 22, 41.
- Sokolowski, J.W., Jr.; Burgher, L.W.; Jones, F.L., Jr.; Patterson, J.R.; Selecky, P.A. Guidelines for fiberoptic bronchoscopy in adults. American Thoracic Society guidelines. Medical Section of the American Lung Association. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 136, 1066.
- de Torres, J.P.; Marín, J.M.; Casanova, C.; Cote, C.; Carrizo, S.; Cordoba-Lanus, E.; Baz-Dávila, R.; Zulueta, J.J.; Aguirre-Jaime, A.; Saetta, M.; et al. Lung Cancer in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Incidence and Predicting Factors. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 913–919.
- Park, H.Y.; Kang, D.; Shin, S.H.; Yoo, K.-H.; Rhee, C.K.; Suh, G.Y.; Kim, H.; Shim, Y.M.; Guallar, E.; Cho, J.; et al. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Lung Cancer Incidence in Never Smokers: A Cohort Study. Thorax 2020, 75, 506–509.
- Lofdahl, J. M. Bronchoalveolar Lavage in COPD: Fluid Recovery Correlates with the Degree of Emphysema. European Respiratory Journal 2005, 25 (2), 275–281. [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A. B.; Campbell, J. D.; Liu, G.; Elashoff, D.; Dubinett, S.; Smith, K.; Whitney, D.; Lenburg, M. E.; Spira, A. Alterations in Bronchial Airway MiRNA Expression for Lung Cancer Detection. Cancer Prevention Research 2017, 10 (11), 651–659. [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Han, K.; Xiao, M.; Lv, F. MiR-223-5p Suppresses Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Targeting E2F8. oncol res 2019, 27 (2), 261–268. [CrossRef]
- Roffel, M. P.; Bracke, K. R.; Heijink, I. H.; Maes, T. MiR-223: A Key Regulator in the Innate Immune Response in Asthma and COPD. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 196. [CrossRef]
- Schembri, F.; Sridhar, S.; Perdomo, C.; Gustafson, A. M.; Zhang, X.; Ergun, A.; Lu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Bowers, J.; Vaziri, C.; Ott, K.; Sensinger, K.; Collins, J. J.; Brody, J. S.; Getts, R.; Lenburg, M. E.; Spira, A. MicroRNAs as Modulators of Smoking-Induced Gene Expression Changes in Human Airway Epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2009, 106 (7), 2319–2324. [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Pan, C.; Yao, G.; Liu, B.; Ma, T.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. MiR-106b-5p Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis by Regulating BTG3 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017, 44 (4), 1545–1558. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, M.; Ahmad, T.; Mabalirajan, U.; Aich, J.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, B. Antagonism of Mmu-Mir-106a Attenuates Asthma Features in Allergic Murine Model. Journal of Applied Physiology 2012, 113 (3), 459–464. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Xiong, F.; Ge, J.; Xiang, B.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Xiong, W.; Guo, C.; Zeng, Z. Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-Mediated Tumor Immune Escape. Mol Cancer 2019, 18 (1), 10. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Jia, A.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Xiao, B. MicroRNA-16 Inhibits the Proliferation and Metastasis of Human Lung Cancer Cells by Modulating the Expression of YAP. J BUON 2020, 25(2):862-868.
- Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, T.; Guo, Y.; Nelson, R.; Tong, T. R.; Pangeni, R.; Salgia, R.; Raz, D. J. Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 22 Is Critical to in Vivo Angiogenesis, Growth and Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Commun Signal 2019, 17 (1), 167. [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhan, T.; Ke, T.; Huang, X.; Ke, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, H. Increased Expression of RRM2 by Human Papillomavirus E7 Oncoprotein Promotes Angiogenesis in Cervical Cancer. Br J Cancer 2014, 110 (4), 1034–1044. [CrossRef]
- Mirra, D.; Esposito, R.; Spaziano, G.; La Torre, C.; Vocca, C.; Tallarico, M.; Cione, E.; Gallelli, L.; D’Agostino, B. Lung MicroRNAs Expression in Lung Cancer and COPD: A Preliminary Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11 (3), 736. [CrossRef]
- Danov, O.; Wolff, M.; Bartel, S.; Böhlen, S.; Obernolte, H.; Wronski, S.; Jonigk, D.; Hammer, B.; Kovacevic, D.; Reuter, S.; Krauss-Etschmann, S.; Sewald, K. Cigarette Smoke Affects Dendritic Cell Populations, Epithelial Barrier Function, and the Immune Response to Viral Infection With H1N1. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 571003. [CrossRef]
- Barclay, A. N.; Brown, M. H. The SIRP Family of Receptors and Immune Regulation. Nat Rev Immunol 2006, 6 (6), 457–464. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Pan, C.; Li, L.; Bian, Z.; Lv, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Gu, H.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Zen, K. MicroRNA-17/20a/106a Modulate Macrophage Inflammatory Responses through Targeting Signal-Regulatory Protein α. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2013, 132 (2), 426-436.e8. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yu, M.; Yao, X. MicroRNA-17 and the Prognosis of Human Carcinomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8 (5), e018070. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Goswami, S.; Grudo, A.; Song, L.; Bandi, V.; Goodnight-White, S.; Green, L.; Hacken-Bitar, J.; Huh, J.; Bakaeen, F.; Coxson, H. O.; Cogswell, S.; Storness-Bliss, C.; Corry, D. B.; Kheradmand, F. Antielastin Autoimmunity in Tobacco Smoking–Induced Emphysema. Nat Med 2007, 13 (5), 567–569. [CrossRef]
- Polverino, F.; Laucho-Contreras, M.; Rojas Quintero, J.; Divo, M.; Pinto-Plata, V.; Sholl, L.; de-Torres, J. P.; Celli, B. R.; Owen, C. A. Increased Expression of A Proliferation-Inducing Ligand (APRIL) in Lung Leukocytes and Alveolar Epithelial Cells in COPD Patients with Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Possible Link between COPD and Lung Cancer? Multidiscip Respir Med 2016, 11 (1), 17. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Chen, G.; Cui, Q. Towards the Understanding of MicroRNA and Environmental Factor Interactions and Their Relationships to Human Diseases. Sci Rep 2012, 2 (1), 318. [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Park, D.; Sica, G. L.; Deng, X. Bcl2-Induced DNA Replication Stress Promotes Lung Carcinogenesis in Response to Space Radiation. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41 (11), 1565–1575. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wei, X. Unraveling the Potential of Senescence-Related Genes in Guiding Clinical Therapy of Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Funct Integr Genomics 2023, 23 (2), 188. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wan, S.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Lou, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, S. Expression and Prognostic Value of E2F3 Transcription Factor in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol Lett 2021, 21 (5), 411. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, J.; Xia, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Delayed Apoptosis by Neutrophils from COPD Patients Is Associated with Altered Bak, Bcl-Xl, and Mcl-1 MRNA Expression. Diagn Pathol 2012, 7 (1), 65. [CrossRef]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Sriratanasak, N.; Nonpanya, N. C-Myc Contributes to Malignancy of Lung Cancer: A Potential Anticancer Drug Target. Anticancer Res 2020, 40 (2), 609–618. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, N.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Q. MFN2 Deficiency Affects Calcium Homeostasis in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Downregulation of UCP4. FEBS Open Bio 2023, 13 (6), 1107–1124. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Ye, X.; Shou, F.; Cheng, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, G. RNF115-Mediated Ubiquitination of P53 Regulates Lung Adenocarcinoma Proliferation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2020, 530 (2), 425–431. [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Xie, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L. SENP1 Inhibition Suppresses the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells through Activation of A20-Mediated Ferroptosis. Ann Transl Med 2022, 10 (4), 224–224. [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Yao, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, P. 5-Hydroxytryptamine Activates a 5-HT/c-Myc/SLC6A4 Signaling Loop in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 2022, 1866 (4), 130093. [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Jiang, K.; Ou, L.; Shen, M.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Xu, W. Targeting Sphingosine Kinase 1/2 by a Novel Dual Inhibitor SKI-349 Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Growth. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13 (7), 602. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhi, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, C.; Qi, Y.; Gao, W.; He, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Fan, S.; Chen, H.; Piao, H.-L.; Qiao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Yin, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. RBMS1 Regulates Lung Cancer Ferroptosis through Translational Control of SLC7A11. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2021, 131 (22), e152067. [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, M.; Hoeksema, M. D.; Shiota, M.; Qian, J.; Harris, B. K.; Chen, H.; Clark, J. E.; Alborn, W. E.; Eisenberg, R.; Massion, P. P. SLC1A5 Mediates Glutamine Transport Required for Lung Cancer Cell Growth and Survival. Clinical Cancer Research 2013, 19 (3), 560–570. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Feng, G.; Chen, Z.; Fan, S. MiR-145 Modulates the Radiosensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Suppression of TMOD3. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43 (3), 288–296. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, S.; Fa, X. Upregulated miR-17 Regulates Hypoxia-Mediated Human Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis by Targeting Mitofusin 2. Med Sci Monit 2016, 22, 3301–3308. [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, N. R.; Shalgi, R.; Frankel, L. B.; Leucci, E.; Lees, M.; Klausen, M.; Pilpel, Y.; Nielsen, F. C.; Oren, M.; Lund, A. H. (2010). p53-independent upregulation of miR-34a during oncogene-induced senescence represses MYC. Cell Death Differ 2010, 17(2), 236–245. [CrossRef]
| Healthy Never Smokers |
Healthy Smokers |
COPD | NSCLC | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Partecipants (N) | 9 | 11 | 11 | 12 | |
| Age (SD) | 70.5 (15.2) | 52.5 (8.3) | 63.5 (6) | 75 (16.9) | NS |
| Gender (M/F) | 5/4 | 6/5 | 5/6 | 6/6 | NS |
| Smoking history (pack years) | NA | 35 | 28.3 | 31 | <0.001 |
|
Smoking habit (current/former smoker) |
NA | 8/3 | 11/0 | 6/6 | 0.0133 |
| FEV1 (% predicted) | 96% (3.2) | 91% (12) | 66% (14) | 88% (11) | 0.0438 |
| FEV/FVC | 76.1 (2.5) | 75 (1.4) | 59 (1.7) | 74 (3) | <0.0001 |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Hypertension (%) | 5 (55.5%) | 5 (45.4%) | 3 (27.2%) | 5 (41.6%) | 0.0152 |
| Other cardiovascluar diseases (%) | 2 (22.2%) | 0 | 3 (27.2%) | 1 (12.5%) | NS |
| Diabetes Mellitus (%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.8%) | NS |
| Medications | |||||
| Inhaled corticosteroids (N, %) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NS |
| LABA/SABA/LAMA (N, %) | 0 | 0 | 11 (100%) | 3 (25%) | <0.0001 |
| Number of Target Genes | ||
|---|---|---|
| miRNA | miR Target Link 2.0 | DIANA Tools |
| hsa-miR-223-5p | 551 | 10 |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | 2,279 | 455 |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | 1,659 | 611 |
| hsa-miR-17-5p | 1,817 | 136 |
| hsa-miR-34a-5p | 968 | 324 |
| hsa-miR-106a-5p | 1,166 | 435 |
| Abbreviation | Gene Name | Methods | Tissues | References(PMID) |
| BCL2 | BCL2 Apoptosis Regulator | Luciferase reporter assay, qRT-PCR, Western blot, Reporter assay, Proteomics analysis, Immunohistochemistry, Microarray, Sequencing, HITS-CLIP, Immunoblot, Immunoprecipitaion |
Cervix cells, gastric cells, Bone cells, Marrow cells, spleen, liver, kidney, lymph node, tracheal/bronchial epithelial cells, breast cells, ovary cells, embryonic kidney cells, gastric cancer cells, B cells, mesothelial cell, glioma cells |
17877811 18449891 18362358 17351108 17707831 20643754 20876285 19269153 16166262 19903841 20371350 23907579 22473208 24148817 25435430 26397135 26722459 |
| CYCS | Cytochrome C, Somatic |
Proteomics, PAR-CLIP, PCR array |
Breast cells, brain and liver |
18668040 23446348 28097098 |
| E2F3 | E2F Transcription Factor 3 |
CLASH. HITS-CLIP, luciferase reporter assay, Western blot |
Human embryonic kidney cells, B cells, stem cells | 23622248 22473208 17252019 |
| MCL1 |
MCL1 Apoptosis Regulator, BCL2 Family Member |
HITS-CLIP, microarray, Immunohistochemistry, Luciferase reporter assay, qRT-PCR, Western blot, PCR array | Human embryonic kidney cells, leukemic cells, liver | 22473208 18362358 23594563 28097098 |
| MFN2 |
Mitofusin 2 |
Proteomics, luciferase reporter assay, western blot, CLASH |
Breast cells, lungs, Human embryonic kidney cells | 18668040 27640178 23622248 |
| MYC | MYC Proto-Oncogene, BHLH Transcription Factor |
TRAP, Western blot, CLASH, Luciferase reporter assay, Western blot, Reporter assay; Western blot, qRT-PCR, Microarray; Sequencing. |
Bone cells, mouse embryonic fibroblasts, breast cells, kidney cells, cervical cells, human fibroblasts, oral ephitilium, stem cells, lymphoblastoid cells, bladder cells |
24510096 18695042 23622248 19696787 21294122 21297663 22159222 20371350 25572695 |
| RNF115 |
Ring Finger Protein 115 | HITS-CLIP | Kidney cells, cervical cells, Neuroblastoma cells, mouse embryonic fibroblasts, glial cells | 23313552 23824327 |
| SENP1 |
SUMO Specific Peptidase 1 |
HITS-CLIP, MIRT025428, PAR-CLIP |
Human embryonic kidney cells |
22473208 20371350 21572407 |
| SLC1A5 | Solute Carrier Family 12 Member 6 | HITS-CLIP | Neuronal mouse cells, mouse Primary Embryonic Fibroblasts | 23313552 |
| SLC6A4 |
Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 4 |
qRT-PCR, western blot, HITS-CLIP |
Lungs, brain |
22940131 23313552 23313552 |
| SLC7A11 |
Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 | PAR-CLIP HITS-CLIP |
Cervix cells, mouse neural progenitor cells, human retinal epithelial cells, primary mouse embryo fibroblasts, Human Embryonic Stem Cells, kidney cells | 23313552 22012620 20371350 21572407 |
| TMOD3 | Tropomodulin 3 | HITS-CLIP Proteomics |
Cervical cells colorectal cells |
23313552 21566225 |
| Biochemical Pathways |
miRNA | Validated target genes |
|---|---|---|
| DNA replication- apoptosis | hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-17-5p hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p |
BCL2 |
| DNA damage telomere stress - senescence pathways |
hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-17-5p hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p |
CYCS |
|
Uncontrolled tumor growth and invasion |
hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-17-5p hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p |
E2F3 |
|
Apoptosis- Bcl2 pathway-drug resistance |
hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-17-5p hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p |
MCL1 |
| Promotion of tumor growth- drug resistance-poor survival |
hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-17-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p hsa-miR-106a-5p |
MFN2 |
| Cancer cell growth and survival-drug resistance-poor survival |
hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-17-5p hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p |
MYC |
|
p53 pathway- proliferation and energy metabolism |
hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-106a-5p hsa-miR-223-5p |
RNF115 |
| Cell cycle deregulation and cell proliferation-drug resistance | hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p hsa-miR-223-5p |
SENP1 |
| Cellular transformation and growth | hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p hsa-miR-106a-5p |
SLC1A5 |
| C-MYC pathway-poor survival | hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-106a-5p |
SLC6A4 |
| Ferroptosis- tumor progression | hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-106a-5p hsa-miR-223-5p |
SLC7A11 |
| Cancer progression- EGFR/PI3K/AKT or MAPK/ ERK signaling pathways | hsa-miR-20a-5p hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-34a-5p hsa-miR-106a-5p |
TMOD3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





