Submitted:
09 April 2024
Posted:
09 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Types of Microneedles
2.1. Solid Microneedles
2.2. Coated Microneedles
2.3. Dissolving Microneedles
2.4. Hollow Microneedles
2.5. Hydrogel-forming Microneedles
3. Microneedles Design
3.1. Length
3.2. Needle-to-Needle Spacing
3.3. Tip Diameter and Tip Angle
3.4. Aspect Ratio
3.5. Needle Geometry
4. Microneedle Fabrication Methods
4.1. Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS)
4.2. Micromolding
4.3. Laser Cutting
4.4. Laser Ablation
4.5. Drawing-based Methods
4.6. Atomized Spraying Method
4.7. Injection Molding
4.8. Micro-Mechanical Machining
4.9. Additive Manufacturing
4.9.1. Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
4.9.2. Material Jetting (MJ)
4.9.3. Stereolithography (SLA)
4.9.4. Digital Light Processing (DLP)
4.9.5. Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP)
4.9.6. Two-Photon-Polymerization (2PP)
5. Microneedle Systems Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- C.M. Chuong, B.J. Nickoloff, P.M. Elias, L.A. Goldsmith, E. Macher, P.A. Maderson, J.P. Sundberg, H. Tagami, P.M. Plonka, K. Thestrup-Pedersen, B.A. Bernard, J.M. Schröder, P. Dotto, C.H. Chang, M.L. Williams, K.R. Feingold, L.E. King, A.M. Kligman, J.L. Rees, E. Christophers, What is the “true” function of skin?, Exp Dermatol 11 (2002) 159–160. [CrossRef]
- Y.W. Chien, J.C. Liu, Transdermal drug delivery systems, J Biomater Appl 1 (1986) 183–206. [CrossRef]
- W.F. Wong, K.P. Ang, G. Sethi, C.Y. Looi, Recent Advancement of Medical Patch for Transdermal Drug Delivery, Medicina (B Aires) 59 (2023). [CrossRef]
- L. Lasagna, D.J. Greenblatt, More than skin deep: transdermal drug-delivery systems, N Engl J Med 314 (1986) 1638–1639. [CrossRef]
- Q. Zhou, H. Li, Z. Liao, B. Gao, B. He, Bridging the Gap between Invasive and Noninvasive Medical Care: Emerging Microneedle Approaches, Anal Chem 95 (2023) 515–534. [CrossRef]
- T. Waghule, G. Singhvi, S.K. Dubey, M.M. Pandey, G. Gupta, M. Singh, K. Dua, Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 109 (2019) 1249–1258. [CrossRef]
- R.J. Pettis, A.J. Harvey, Microneedle delivery: clinical studies and emerging medical applications, Ther Deliv 3 (2012) 357–371. [CrossRef]
- K. Ahmed Saeed AL-Japairai, S. Mahmood, S. Hamed Almurisi, J. Reddy Venugopal, A. Rebhi Hilles, M. Azmana, S. Raman, Current trends in polymer microneedle for transdermal drug delivery, Int J Pharm 587 (2020) 119673. [CrossRef]
- G. Yan, K.S. Warner, J. Zhang, S. Sharma, B.K. Gale, Evaluation needle length and density of microneedle arrays in the pretreatment of skin for transdermal drug delivery, Int J Pharm 391 (2010) 7–12. [CrossRef]
- J. Xu, D. Xu, X. Xuan, H. He, Advances of Microneedles in Biomedical Applications, Molecules 26 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Sachan, R.J. Sachan, J. Lu, H. Sun, Y.J. Jin, D. Erdmann, J.Y. Zhang, R.J. Narayan, Injection molding for manufacturing of solid poly(l-lactide-co-glycolide) microneedles, MRS Adv 6 (2021) 61–65. [CrossRef]
- X. Jin, D.D. Zhu, B.Z. Chen, M. Ashfaq, X.D. Guo, Insulin delivery systems combined with microneedle technology, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 127 (2018) 119–137. [CrossRef]
- X. Luo, Q. Yu, Y. Liu, W. Gai, L. Ye, L. Yang, Y. Cui, Closed-Loop Diabetes Minipatch Based on a Biosensor and an Electroosmotic Pump on Hollow Biodegradable Microneedles, ACS Sens 7 (2022) 1347–1360. [CrossRef]
- D. Han, R.S. Morde, S. Mariani, A.A. La Mattina, E. Vignali, C. Yang, G. Barillaro, H. Lee, 4D Printing of a Bioinspired Microneedle Array with Backward-Facing Barbs for Enhanced Tissue Adhesion, Adv Funct Mater 30 (2020) 1909197. [CrossRef]
- Y.-C. Kim, J.-H. Park, M.R. Prausnitz, Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64 (2012) 1547–1568. [CrossRef]
- G. Lee, Y. Ma, Y. Lee, H. Jung, Clinical Evaluation of a Low-pain Long Microneedle for Subcutaneous Insulin Injection, Biochip J 12 (2018) 309–316. [CrossRef]
- R. Zhang, Q. Miao, D. Deng, J. Wu, Y. Miao, Y. Li, Research progress of advanced microneedle drug delivery system and its application in biomedicine, Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 226 (2023) 113302. [CrossRef]
- 18. R. Parhi, Recent advances in 3D printed microneedles and their skin delivery application in the treatment of various diseases, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 84 (2023) 104395. [CrossRef]
- G. Yang, Q. Chen, D. Wen, Z. Chen, J. Wang, G. Chen, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Q. Hu, L. Zhang, Z. Gu, A Therapeutic Microneedle Patch Made from Hair-Derived Keratin for Promoting Hair Regrowth, ACS Nano 13 (2019) 4354–4360. [CrossRef]
- L. Barnum, M. Samandari, T.A. Schmidt, A. Tamayol, Microneedle arrays for the treatment of chronic wounds, Expert Opin Drug Deliv 17 (2020) 1767–1780. [CrossRef]
- Than, C. Liu, H. Chang, P.K. Duong, C.M.G. Cheung, C. Xu, X. Wang, P. Chen, Self-implantable double-layered micro-drug-reservoirs for efficient and controlled ocular drug delivery, Nat Commun 9 (2018) 4433. [CrossRef]
- E. Ju, M. Peng, Y. Xu, Y. Wang, F. Zhou, H. Wang, M. Li, Y. Zheng, Y. Tao, Nanozyme-integrated microneedle patch for enhanced therapy of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by breaking the gap between H 2 O 2 self-supplying chemodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy, J Mater Chem B (2023).
- S. Shukla, K.B. Mamale, R.K.K. Arya, R.K. Kaundal, R. Shukla, Therapeutic potential of microneedles based delivery systems for the management of atopic dermatitis, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 84 (2023) 104493.
- X. Cheng, S. Hu, K. Cheng, Microneedle Patch Delivery of PROTACs for Anti-Cancer Therapy, ACS Nano (2023).
- W. Li, J.Y. Chen, R.N. Terry, J. Tang, A. Romanyuk, S.P. Schwendeman, M.R. Prausnitz, Core-shell microneedle patch for six-month controlled-release contraceptive delivery, Journal of Controlled Release 347 (2022) 489–499.
- Y. Kim, I.H. Park, J. Shin, J. Choi, C. Jeon, S. Jeon, J. Shin, H. Jung, Sublingual Dissolving Microneedle (SLDMN)-based Vaccine For Inducing Mucosal Immunity Against SARS-CoV-2, Adv Healthc Mater (2023) 2300889.
- L. Wang, L. Yang, F. Zhang, X. Liu, Q. Xie, Q. Liu, L. Yuan, T. Zhao, S. Xie, Q. Xu, A microneedle-based delivery system for broad-protection seasonal influenza A DNA nanovaccines, Cell Rep Phys Sci 4 (2023).
- M. Friedel, B. Werbovetz, A. Drexelius, Z. Watkins, A. Bali, K.W. Plaxco, J. Heikenfeld, Continuous Molecular Monitoring of Human Dermal Interstitial Fluid with Microneedle-Enabled Electrochemical Aptamer Sensors., Lab Chip (2023).
- J. Chen, X. Cai, W. Zhang, D. Zhu, Z. Ruan, N. Jin, Fabrication of Antibacterial Sponge Microneedles for Sampling Skin Interstitial Fluid, Pharmaceutics 15 (2023) 1730.
- V. Alimardani, S.S. Abolmaali, G. Yousefi, Z. Rahiminezhad, M. Abedi, A. Tamaddon, S. Ahadian, Microneedle Arrays Combined with Nanomedicine Approaches for Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics, J Clin Med 10 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Q.Y. Li, J.N. Zhang, B.Z. Chen, Q.L. Wang, X.D. Guo, A solid polymer microneedle patch pretreatment enhances the permeation of drug molecules into the skin, RSC Adv 7 (2017) 15408–15415. [CrossRef]
- A.M. de Groot, A.C.M. Platteel, N. Kuijt, P.J.S. van Kooten, P.J. Vos, A.J.A.M. Sijts, K. van der Maaden, Nanoporous Microneedle Arrays Effectively Induce Antibody Responses against Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoid , Frontiers in Immunology 8 (2017).
- J.K. Kim, M.R. Roh, G. Park, Y.J. Kim, I.K. Jeon, S.E. Chang, Fractionated microneedle radiofrequency for the treatment of periorbital wrinkles., J Dermatol 40 (2013) 172–176. [CrossRef]
- Abiandu, K. Ita, Transdermal delivery of potassium chloride with solid microneedles, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 53 (2019) 101216. [CrossRef]
- P. Bollella, S. Sharma, A.E.G. Cass, R. Antiochia, Minimally-invasive Microneedle-based Biosensor Array for Simultaneous Lactate and Glucose Monitoring in Artificial Interstitial Fluid, Electroanalysis 31 (2019) 374–382. [CrossRef]
- M. Senel, M. Dervisevic, N.H. Voelcker, Gold microneedles fabricated by casting of gold ink used for urea sensing, Mater Lett 243 (2019) 50–53. [CrossRef]
- R.S. Bhadale, V.Y. Londhe, Solid microneedle assisted transepidermal delivery of iloperidone loaded film: Characterization and Skin deposition studies, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 79 (2023) 104028. [CrossRef]
- K. van der Maaden, H. Yu, K. Sliedregt, R. Zwier, R. Leboux, M. Oguri, A. Kros, W. Jiskoot, J.A. Bouwstra, Nanolayered chemical modification of silicon surfaces with ionizable surface groups for pH-triggered protein adsorption and release: application to microneedles, J Mater Chem B 1 (2013) 4466–4477. [CrossRef]
- B.K. Meyer, M.A.F. Kendall, D.M. Williams, A.J. Bett, S. Dubey, R.C. Gentzel, D. Casimiro, A. Forster, H. Corbett, M. Crichton, S. Ben Baker, R.K. Evans, A. Bhambhani, Immune response and reactogenicity of an unadjuvanted intradermally delivered human papillomavirus vaccine using a first generation NanopatchTM in rhesus macaques: An exploratory, pre-clinical feasibility assessment, Vaccine X 2 (2019) 100030. [CrossRef]
- 40. P.E. Daddona, James.A. Matriano, J. Mandema, Y.-F. Maa, Parathyroid Hormone (1-34)-Coated Microneedle Patch System: Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics for Treatment of Osteoporosis, Pharm Res 28 (2011) 159–165. [CrossRef]
- S. Ross, N. Scoutaris, D. Lamprou, D. Mallinson, D. Douroumis, Inkjet printing of insulin microneedles for transdermal delivery, Drug Deliv Transl Res 5 (2015) 451–461. [CrossRef]
- M. Cormier, B. Johnson, M. Ameri, K. Nyam, L. Libiran, D.D. Zhang, P. Daddona, Transdermal delivery of desmopressin using a coated microneedle array patch system, Journal of Controlled Release 97 (2004) 503–511. [CrossRef]
- D. Al Sulaiman, J.Y.H. Chang, N.R. Bennett, H. Topouzi, C.A. Higgins, D.J. Irvine, S. Ladame, Hydrogel-Coated Microneedle Arrays for Minimally Invasive Sampling and Sensing of Specific Circulating Nucleic Acids from Skin Interstitial Fluid, ACS Nano 13 (2019) 9620–9628. [CrossRef]
- V Matadh, D. Jakka, S.G. Pragathi, K. Poornima, H.N. Shivakumar, R.N. Murthy, S. Rangappa, M. Shivanna, S.N. Murthy, Polymer coated polymeric microneedles for intravitreal delivery of dexamethasone, Exp Eye Res 231 (2023) 109467. [CrossRef]
- J.H. Han, C.R. Kim, C.H. Min, M.J. Kim, S.-N. Kim, H.B. Ji, S. Bin Yoon, C. Lee, Y. Bin Choy, Microneedles coated with composites of phenylboronic acid-containing polymer and carbon nanotubes for glucose measurements in interstitial fluids, Biosens Bioelectron 238 (2023) 115571. [CrossRef]
- I.K. Ramöller, I.A. Tekko, H.O. McCarthy, R.F. Donnelly, Rapidly dissolving bilayer microneedle arrays – A minimally invasive transdermal drug delivery system for vitamin B12, Int J Pharm 566 (2019) 299–306. [CrossRef]
- Y.-H. Chen, K.-Y. Lai, Y.-H. Chiu, Y.-W. Wu, A.-L. Shiau, M.-C. Chen, Implantable microneedles with an immune-boosting function for effective intradermal influenza vaccination, Acta Biomater 97 (2019) 230–238. [CrossRef]
- C. Dillon, H. Hughes, N.J. O’Reilly, C.J. Allender, D.A. Barrow, P. McLoughlin, Dissolving microneedle based transdermal delivery of therapeutic peptide analogues, Int J Pharm 565 (2019) 9–19. [CrossRef]
- W. Disphanurat, N. Sivapornpan, B. Srisantithum, J. Leelawattanachai, Efficacy of a triamcinolone acetonide-loaded dissolving microneedle patch for the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled split-scar study, Arch Dermatol Res 315 (2023) 989–997. [CrossRef]
- H. Wang, Y. Fu, P. Liu, F. Qu, S. Du, Y. Li, H. Du, L. Zhang, J. Tao, J. Zhu, Supramolecular Dissolving Microneedle Patch Loading Hydrophobic Glucocorticoid for Effective Psoriasis Treatment, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15 (2023) 15162–15171. [CrossRef]
- S. Lin, G. Quan, A. Hou, P. Yang, T. Peng, Y. Gu, W. Qin, R. Liu, X. Ma, X. Pan, H. Liu, L. Wang, C. Wu, Strategy for hypertrophic scar therapy: Improved delivery of triamcinolone acetonide using mechanically robust tip-concentrated dissolving microneedle array, Journal of Controlled Release 306 (2019) 69–82. [CrossRef]
- H. Yang, S. Kim, M. Jang, H. Kim, S. Lee, Y. Kim, Y.A. Eom, G. Kang, L. Chiang, J.H. Baek, J.H. Ryu, Y.E. Lee, J. Koh, H. Jung, Two-phase delivery using a horse oil and adenosine-loaded dissolving microneedle patch for skin barrier restoration, moisturization, and wrinkle improvement, J Cosmet Dermatol 18 (2019) 936–943. [CrossRef]
- H.X. Nguyen, B.D. Bozorg, Y. Kim, A. Wieber, G. Birk, D. Lubda, A.K. Banga, Poly (vinyl alcohol) microneedles: Fabrication, characterization, and application for transdermal drug delivery of doxorubicin, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 129 (2018) 88–103. [CrossRef]
- L. Dong, Y. Li, Z. Li, N. Xu, P. Liu, H. Du, Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, J. Zhu, G. Ren, J. Xie, K. Wang, Y. Zhou, C. Shen, J. Zhu, J. Tao, Au Nanocage-Strengthened Dissolving Microneedles for Chemo-Photothermal Combined Therapy of Superficial Skin Tumors, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10 (2018) 9247–9256. [CrossRef]
- Huh, S. Kim, H. Yang, M. Jang, G. Kang, H. Jung, Effects of two droplet-based dissolving microneedle manufacturing methods on the activity of encapsulated epidermal growth factor and ascorbic acid, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 114 (2018) 285–292. [CrossRef]
- I.M.N. Hamdan, I.A. Tekko, K.B. Matchett, L.G. Arnaut, C.S. Silva, H.O. McCarthy, R.F. Donnelly, Intradermal Delivery of a Near-Infrared Photosensitizer Using Dissolving Microneedle Arrays, J Pharm Sci 107 (2018) 2439–2450. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, F. Liu, C. Su, B. Yu, D. Liu, H.-J. Chen, D. Lin, C. Yang, L. Zhou, Q. Wu, W. Xia, X. Xie, J. Tao, Biodegradable Therapeutic Microneedle Patch for Rapid Antihypertensive Treatment, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11 (2019) 30575–30584. [CrossRef]
- H. Choi, J. Hong, Y. Seo, S.-H. Joo, H. Lim, S.F. Lahiji, Y.-H. Kim, Self-Assembled Oligopeptoplex-Loaded Dissolving Microneedles for Adipocyte-Targeted Anti-Obesity Gene Therapy, Advanced Materials n/a (2024) 2309920. [CrossRef]
- W. Wan, Y. Li, J. Wang, Z. Jin, W. Xin, L. Kang, J. Wang, X. Li, Y. Cao, H. Yang, J. Wang, S. Gao, PLGA Nanoparticle-Based Dissolving Microneedle Vaccine of Clostridium perfringens ε Toxin, Toxins (Basel) 15 (2023). [CrossRef]
- X. Jiang, P. Chen, W. Niu, R. Fang, H. Chen, Y. An, W. Wang, C. Jiang, J. Ye, Preparation and evaluation of dissolving tofacitinib microneedles for effective management of rheumatoid arthritis, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 188 (2023) 106518. [CrossRef]
- J. Xie, X. Zhu, M. Wang, C. Liu, G. Ling, P. Zhang, Dissolving microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of flurbiprofen axetil-loaded pH-responsive liposomes for arthritis treatment, Chemical Engineering Journal 482 (2024) 148840. [CrossRef]
- H. Abd-El-Azim, H. Abbas, N.S. El Sayed, A.M. Fayez, M. Zewail, Non-invasive management of rheumatoid arthritis using hollow microneedles as a tool for transdermal delivery of teriflunomide loaded solid lipid nanoparticles, Int J Pharm 644 (2023) 123334. [CrossRef]
- S. Kawre, P. Suryavanshi, D.S. Lalchandani, M.K. Deka, P. Kumar Porwal, S. Kaity, S. Roy, S. Banerjee, Bioinspired labrum-shaped stereolithography (SLA) assisted 3D printed hollow microneedles (HMNs) for effectual delivery of ceftriaxone sodium, Eur Polym J 204 (2024) 112702. [CrossRef]
- S. Golombek, M. Pilz, H. Steinle, E. Kochba, Y. Levin, D. Lunter, C. Schlensak, H.P. Wendel, M. Avci-Adali, Intradermal Delivery of Synthetic mRNA Using Hollow Microneedles for Efficient and Rapid Production of Exogenous Proteins in Skin, Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 11 (2018) 382–392. [CrossRef]
- K. van der Maaden, J. Heuts, M. Camps, M. Pontier, A. Terwisscha van Scheltinga, W. Jiskoot, F. Ossendorp, J. Bouwstra, Hollow microneedle-mediated micro-injections of a liposomal HPV E743–63 synthetic long peptide vaccine for efficient induction of cytotoxic and T-helper responses, Journal of Controlled Release 269 (2018) 347–354. [CrossRef]
- F.S. Iliescu, J.C.M. Teo, D. Vrtacnik, H. Taylor, C. Iliescu, Cell therapy using an array of ultrathin hollow microneedles, Microsystem Technologies 24 (2018) 2905–2912. [CrossRef]
- S. Yin, Z. Yu, N. Song, Z. Guo, W. Li, J. Ma, X. Wang, J. Liu, M. Liang, A long lifetime and highly sensitive wearable microneedle sensor for the continuous real-time monitoring of glucose in interstitial fluid, Biosens Bioelectron 244 (2024) 115822. [CrossRef]
- A.-M. Drăgan, M. Parrilla, S. Cambré, J. Domínguez-Robles, U. Detamornrat, R.F. Donnelly, R. Oprean, C. Cristea, K. De Wael, Microneedle array-based electrochemical sensor functionalized with SWCNTs for the highly sensitive monitoring of MDMA in interstitial fluid, Microchemical Journal 193 (2023) 109257. [CrossRef]
- T. Abbasiasl, F. Mirlou, H. Mirzajani, M.J. Bathaei, E. Istif, N. Shomalizadeh, R.E. Cebecioğlu, E.E. Özkahraman, U.C. Yener, L. Beker, A Wearable Touch-Activated Device Integrated with Hollow Microneedles for Continuous Sampling and Sensing of Dermal Interstitial Fluid, Advanced Materials 36 (2024) 2304704. [CrossRef]
- A.Y.R. Aziz, N.A. Hasir, N.B.P. Imran, M.F. Hamdan, U. Mahfufah, N. Wafiah, A. Arjuna, R.N. Utami, A.D. Permana, Development of hydrogel-forming microneedles for transdermal delivery of albendazole from liquid reservoir, J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 34 (2023) 1101–1120. [CrossRef]
- D. Elim, A.M.N. Fitri, M.A.S. Mahfud, N. Afika, N.A.F. Sultan, Hijrah, R.M. Asri, A.D. Permana, Hydrogel forming microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of sildenafil citrate from polyethylene glycol reservoir: An ex vivo proof of concept study, Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 222 (2023) 113018. [CrossRef]
- E.M. Migdadi, A.J. Courtenay, I.A. Tekko, M.T.C. McCrudden, M.-C. Kearney, E. McAlister, H.O. McCarthy, R.F. Donnelly, Hydrogel-forming microneedles enhance transdermal delivery of metformin hydrochloride, Journal of Controlled Release 285 (2018) 142–151. [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, A.K. Banga, Novel in situ forming hydrogel microneedles for transdermal drug delivery, Drug Deliv Transl Res 7 (2017) 16–26. [CrossRef]
- Q.K. Anjani, A.D. Permana, Á. Cárcamo-Martínez, J. Domínguez-Robles, I.A. Tekko, E. Larrañeta, L.K. Vora, D. Ramadon, R.F. Donnelly, Versatility of hydrogel-forming microneedles in in vitro transdermal delivery of tuberculosis drugs, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 158 (2021) 294–312. [CrossRef]
- J. Leanpolchareanchai, N. Nuchtavorn, Response Surface Methodology for Optimization of Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles as Rapid and Efficient Transdermal Microsampling Tools, Gels 9 (2023). [CrossRef]
- J.A. Mikszta, J.B. Alarcon, J.M. Brittingham, D.E. Sutter, R.J. Pettis, N.G. Harvey, Improved genetic immunization via micromechanical disruption of skin-barrier function and targeted epidermal delivery., Nat Med 8 (2002) 415–419. [CrossRef]
- Sabri, J. Ogilvie, J. McKenna, J. Segal, D. Scurr, M. Marlow, Intradermal Delivery of an Immunomodulator for Basal Cell Carcinoma; Expanding the Mechanistic Insight into Solid Microneedle-Enhanced Delivery of Hydrophobic Molecules, Mol Pharm 17 (2020) 2925–2937. [CrossRef]
- N. Elahpour, F. Pahlevanzadeh, M. Kharaziha, H.R. Bakhsheshi-Rad, S. Ramakrishna, F. Berto, 3D printed microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: A brief review of two decades, Int J Pharm 597 (2021) 120301. [CrossRef]
- E. Larrañeta, R.E.M. Lutton, A.D. Woolfson, R.F. Donnelly, Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: Materials science, manufacture and commercial development, Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports 104 (2016) 1–32. [CrossRef]
- R.F. Donnelly, T.R.R. Singh, A.Z. Alkilani, M.T.C. McCrudden, S. O’Neill, C. O’Mahony, K. Armstrong, N. McLoone, P. Kole, A.D. Woolfson, Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays exhibit antimicrobial properties: Potential for enhanced patient safety, Int J Pharm 451 (2013) 76–91. [CrossRef]
- 81. R. Parhi, A review of three-dimensional printing for pharmaceutical applications: Quality control, risk assessment and future perspectives, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 64 (2021) 102571. [CrossRef]
- J. Gupta, H.S. Gill, S.N. Andrews, M.R. Prausnitz, Kinetics of skin resealing after insertion of microneedles in human subjects, Journal of Controlled Release 154 (2011) 148–155. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, B.Z. Chen, Q.L. Wang, X. Jin, X.D. Guo, Fabrication of coated polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery, Journal of Controlled Release 265 (2017) 14–21. [CrossRef]
- R.S.J. Ingrole, H.S. Gill, Microneedle Coating Methods: A Review with a Perspective, Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 370 (2019) 555 LP – 569. [CrossRef]
- Vrdoljak, M.G. McGrath, J.B. Carey, S.J. Draper, A.V.S. Hill, C. O’Mahony, A.M. Crean, A.C. Moore, Coated microneedle arrays for transcutaneous delivery of live virus vaccines, Journal of Controlled Release 159 (2012) 34–42. [CrossRef]
- R.H.E. Chong, E. Gonzalez-Gonzalez, M.F. Lara, T.J. Speaker, C.H. Contag, R.L. Kaspar, S.A. Coulman, R. Hargest, J.C. Birchall, Gene silencing following siRNA delivery to skin via coated steel microneedles: In vitro and in vivo proof-of-concept, Journal of Controlled Release 166 (2013) 211–219. [CrossRef]
- H.-J. Choi, D.-G. Yoo, B.J. Bondy, F.-S. Quan, R.W. Compans, S.-M. Kang, M.R. Prausnitz, Stability of influenza vaccine coated onto microneedles, Biomaterials 33 (2012) 3756–3769. [CrossRef]
- C.P.P. Pere, S.N. Economidou, G. Lall, C. Ziraud, J.S. Boateng, B.D. Alexander, D.A. Lamprou, D. Douroumis, 3D printed microneedles for insulin skin delivery, Int J Pharm 544 (2018) 425–432. [CrossRef]
- J. Li, M. Zeng, H. Shan, C. Tong, Microneedle Patches as Drug and Vaccine Delivery Platform, Curr Med Chem 24 (2017) 2413–2422. [CrossRef]
- P. Makvandi, A. Maleki, M. Shabani, A.R.J. Hutton, M. Kirkby, R. Jamaledin, T. Fang, J. He, J. Lee, B. Mazzolai, R.F. Donnelly, F.R. Tay, G. Chen, V. Mattoli, Bioinspired microneedle patches: Biomimetic designs, fabrication, and biomedical applications, Matter 5 (2022) 390–429. [CrossRef]
- J.-H. Park, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Polymer Microneedles for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery, Pharm Res 23 (2006) 1008–1019. [CrossRef]
- M.T.C. McCrudden, A.Z. Alkilani, C.M. McCrudden, E. McAlister, H.O. McCarthy, A.D. Woolfson, R.F. Donnelly, Design and physicochemical characterisation of novel dissolving polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal delivery of high dose, low molecular weight drugs, Journal of Controlled Release 180 (2014) 71–80. [CrossRef]
- L. Long, D. Ji, C. Hu, L. Yang, S. Tang, Y. Wang, Microneedles for in situ tissue regeneration, Mater Today Bio 19 (2023) 100579. [CrossRef]
- T. Bauleth-Ramos, N. El-Sayed, F. Fontana, M. Lobita, M.-A. Shahbazi, H.A. Santos, Recent approaches for enhancing the performance of dissolving microneedles in drug delivery applications, Materials Today 63 (2023) 239–287. [CrossRef]
- K. Lee, H. Jung, Drawing lithography for microneedles: A review of fundamentals and biomedical applications, Biomaterials 33 (2012) 7309–7326. [CrossRef]
- K. Lee, C.Y. Lee, H. Jung, Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug administration prepared by stepwise controlled drawing of maltose, Biomaterials 32 (2011) 3134–3140. [CrossRef]
- T. Miyano, Y. Tobinaga, T. Kanno, Y. Matsuzaki, H. Takeda, M. Wakui, K. Hanada, Sugar Micro Needles as Transdermic Drug Delivery System, Biomed Microdevices 7 (2005) 185–188. [CrossRef]
- G. Li, A. Badkar, S. Nema, C.S. Kolli, A.K. Banga, In vitro transdermal delivery of therapeutic antibodies using maltose microneedles., Int J Pharm 368 (2009) 109–115. [CrossRef]
- B. Yang, Y. Dong, Y. Shen, A. Hou, G. Quan, X. Pan, C. Wu, Bilayer dissolving microneedle array containing 5-fluorouracil and triamcinolone with biphasic release profile for hypertrophic scar therapy, Bioact Mater 6 (2021) 2400–2411. [CrossRef]
- S. Lin, G. Quan, A. Hou, P. Yang, T. Peng, Y. Gu, W. Qin, R. Liu, X. Ma, X. Pan, H. Liu, L. Wang, C. Wu, Strategy for hypertrophic scar therapy: Improved delivery of triamcinolone acetonide using mechanically robust tip-concentrated dissolving microneedle array, Journal of Controlled Release 306 (2019) 69–82. [CrossRef]
- S.Y. Choi, H.J. Kwon, G.R. Ahn, E.J. Ko, K.H. Yoo, B.J. Kim, C. Lee, D. Kim, Hyaluronic acid microneedle patch for the improvement of crow’s feet wrinkles, Dermatol Ther 30 (2017) e12546. [CrossRef]
- Y. Park, B. Kim, Skin permeability of compounds loaded within dissolving microneedles dependent on composition of sodium hyaluronate and carboxymethyl cellulose, Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 34 (2017) 133–138. [CrossRef]
- V. Zvezdin, T. Kasatkina, I. Kasatkin, M. Gavrilova, O. Kazakova, Microneedle patch based on dissolving, detachable microneedle technology for improved skin quality of the periorbital region. Part 2: Clinical Evaluation, Int J Cosmet Sci 42 (2020) 429–435. [CrossRef]
- E.P. Yalcintas, D.S. Ackerman, E. Korkmaz, C.A. Telmer, J.W. Jarvik, P.G. Campbell, M.P. Bruchez, O.B. Ozdoganlar, Analysis of In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Carbohydrate-Based Materials Used for Dissolvable Microneedle Arrays, Pharm Res 37 (2020) 33. [CrossRef]
- 105. G. Reineccius, 9 - Controlled release of flavour in food products, in: A. Taylor, J.B.T.-M.F. in F. Hort (Eds.), Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition, Woodhead Publishing, 2007: pp. 169–184. [CrossRef]
- B.-M. Lee, C. Lee, S.F. Lahiji, U.-W. Jung, G. Chung, H. Jung, Dissolving Microneedles for Rapid and Painless Local Anesthesia, Pharmaceutics 12 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Ono, S. Ito, S. Sakagami, H. Asada, M. Saito, Y.-S. Quan, F. Kamiyama, S. Hirobe, N. Okada, Development of Novel Faster-Dissolving Microneedle Patches for Transcutaneous Vaccine Delivery, Pharmaceutics 9 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Y. Huang, H. Yu, L. Wang, D. Shen, Z. Ni, S. Ren, Y. Lu, X. Chen, J. Yang, Y. Hong, Research progress on cosmetic microneedle systems: Preparation, property and application, Eur Polym J 163 (2022) 110942. [CrossRef]
- C.-L. Ke, F.-S. Deng, C.-Y. Chuang, C.-H. Lin, Antimicrobial Actions and Applications of Chitosan, Polymers (Basel) 13 (2021). [CrossRef]
- M.-C. Chen, S.-F. Huang, K.-Y. Lai, M.-H. Ling, Fully embeddable chitosan microneedles as a sustained release depot for intradermal vaccination, Biomaterials 34 (2013) 3077–3086. [CrossRef]
- Y.-H. Chiu, M.-C. Chen, S.-W. Wan, Sodium Hyaluronate/Chitosan Composite Microneedles as a Single-Dose Intradermal Immunization System, Biomacromolecules 19 (2018) 2278–2285. [CrossRef]
- T. Kean, M. Thanou, Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62 (2010) 3–11. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhang, R. Guo, S. Wang, X. Yang, G. Ling, P. Zhang, Fabrication, evaluation and applications of dissolving microneedles, Int J Pharm 604 (2021) 120749. [CrossRef]
- D.F.S. Fonseca, C. Vilela, A.J.D. Silvestre, C.S.R. Freire, A compendium of current developments on polysaccharide and protein-based microneedles, Int J Biol Macromol 136 (2019) 704–728. [CrossRef]
- C. Désévaux, P. Dubreuil, V. Lenaerts, C. Girard, Tissue reaction and biodegradation of implanted cross-linked high amylose starch in rats., J Biomed Mater Res 63 (2002) 772–779. [CrossRef]
- Y. Cao, B. Wang, Biodegradation of Silk Biomaterials, Int J Mol Sci 10 (2009) 1514–1524. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, M. Zhu, L. Zhao, D. Kuang, S.C. Kundu, S. Lu, Insulin-Loaded Silk Fibroin Microneedles as Sustained Release System, ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5 (2019) 1887–1894. [CrossRef]
- J. Lee, S.H. Park, I.H. Seo, K.J. Lee, W. Ryu, Rapid and repeatable fabrication of high A/R silk fibroin microneedles using thermally-drawn micromolds, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 94 (2015) 11–19. [CrossRef]
- M. Zhu, Y. Liu, F. Jiang, J. Cao, S.C. Kundu, S. Lu, Combined Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Insulin Delivery, ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6 (2020) 3422–3429. [CrossRef]
- K. Tsioris, W.K. Raja, E.M. Pritchard, B. Panilaitis, D.L. Kaplan, F.G. Omenetto, Fabrication of Silk Microneedles for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery, Adv Funct Mater 22 (2012) 330–335. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Stinson, W.K. Raja, S. Lee, H.B. Kim, I. Diwan, S. Tutunjian, B. Panilaitis, F.G. Omenetto, S. Tzipori, D.L. Kaplan, Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Transdermal Vaccine Delivery, ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3 (2017) 360–369. [CrossRef]
- J. Mao, H. Wang, Y. Xie, Y. Fu, Y. Li, P. Liu, H. Du, J. Zhu, L. Dong, M. Hussain, Y. Li, L. Zhang, J. Zhu, J. Tao, Transdermal delivery of rapamycin with poor water-solubility by dissolving polymeric microneedles for anti-angiogenesis, J Mater Chem B 8 (2020) 928–934. [CrossRef]
- K. Yu, X. Yu, S. Cao, Y. Wang, Y. Zhai, F. Yang, X. Yang, Y. Lu, C. Wu, Y. Xu, Layered dissolving microneedles as a need-based delivery system to simultaneously alleviate skin and joint lesions in psoriatic arthritis, Acta Pharm Sin B 11 (2021) 505–519. [CrossRef]
- E.M. Vicente-Perez, E. Larrañeta, M.T.C. McCrudden, A. Kissenpfennig, S. Hegarty, H.O. McCarthy, R.F. Donnelly, Repeat application of microneedles does not alter skin appearance or barrier function and causes no measurable disturbance of serum biomarkers of infection, inflammation or immunity in mice in vivo, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 117 (2017) 400–407. [CrossRef]
- W.S. Shim, Y.M. Hwang, S.G. Park, C.K. Lee, N.G. Kang, Role of Polyvinylpyrrolidone in Dissolving Microneedle for Efficient Transdermal Drug Delivery: In vitro and Clinical Studies, Bull Korean Chem Soc 39 (2018) 789–793. [CrossRef]
- E.P. on F.A. and F. (FAF), M. Younes, G. Aquilina, L. Castle, K.-H. Engel, P. Fowler, P. Fürst, R. Gürtler, U. Gundert-Remy, T. Husøy, M. Manco, W. Mennes, P. Moldeus, S. Passamonti, R. Shah, D.H. Waalkens-Berendsen, D. Wölfle, M. Wright, P. Boon, R. Crebelli, A. Di Domenico, M. Filipič, A. Mortensen, R. Woutersen, H. Van Loveren, A. Giarola, F. Lodi, A.M. Rincon, A. Tard, M.J. Frutos Fernandez, Re-evaluation of polyvinylpyrrolidone (E 1201) and polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (E 1202) as food additives and extension of use of polyvinylpyrrolidone (E 1201), EFSA Journal 18 (2020) e06215. [CrossRef]
- B.Z. Chen, M. Ashfaq, X.P. Zhang, J.N. Zhang, X.D. Guo, In vitro and in vivo assessment of polymer microneedles for controlled transdermal drug delivery, J Drug Target 26 (2018) 720–729. [CrossRef]
- X.P. Zhang, B.B. Wang, W.X. Li, W.M. Fei, Y. Cui, X.D. Guo, In vivo safety assessment, biodistribution and toxicology of polyvinyl alcohol microneedles with 160-day uninterruptedly applications in mice, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 160 (2021) 1–8. [CrossRef]
- J. Arya, S. Henry, H. Kalluri, D. V McAllister, W.P. Pewin, M.R. Prausnitz, Tolerability, usability and acceptability of dissolving microneedle patch administration in human subjects, Biomaterials 128 (2017) 1–7. [CrossRef]
- S.J. Schmidt, B.D. Holt, A.M. Arnold, S.A. Sydlik, Polyester functional graphenic materials as a mechanically enhanced scaffold for tissue regeneration, RSC Adv 10 (2020) 8548–8557. [CrossRef]
- J. Zhang, Y. Wang, J.Y. Jin, S. Degan, R.P. Hall, R.D. Boehm, P. Jaipan, R.J. Narayan, Use of Drawing Lithography-Fabricated Polyglycolic Acid Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Itraconazole to a Human Basal Cell Carcinoma Model Regenerated on Mice, JOM 68 (2016) 1128–1133. [CrossRef]
- W. Li, J. Tang, R.N. Terry, S. Li, A. Brunie, R.L. Callahan, R.K. Noel, C.A. Rodríguez, S.P. Schwendeman, M.R. Prausnitz, Long-acting reversible contraception by effervescent microneedle patch, Sci Adv 5 (2023) eaaw8145. [CrossRef]
- K.T.M. Tran, T.D. Gavitt, N.J. Farrell, E.J. Curry, A.B. Mara, A. Patel, L. Brown, S. Kilpatrick, R. Piotrowska, N. Mishra, S.M. Szczepanek, T.D. Nguyen, Transdermal microneedles for the programmable burst release of multiple vaccine payloads, Nat Biomed Eng 5 (2021) 998–1007. [CrossRef]
- J. Eum, Y. Kim, D.J. Um, J. Shin, H. Yang, H. Jung, Solvent-Free Polycaprolactone Dissolving Microneedles Generated via the Thermal Melting Method for the Sustained Release of Capsaicin, Micromachines (Basel) 12 (2021). [CrossRef]
- V. Sonetha, S. Majumdar, S. Shah, Step-wise micro-fabrication techniques of microneedle arrays with applications in transdermal drug delivery – A review, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 68 (2022) 103119. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhao, J. Mu, P. Du, H. Wang, Y. Mao, Y. Xu, X. Xin, F. Zang, Ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy in the diagnosis of neuroblastic tumors in children: a retrospective study on 83 cases, Pediatr Surg Int 33 (2017) 347–353. [CrossRef]
- D. Yang, M. Chen, Y. Sun, Y. Jin, C. Lu, X. Pan, G. Quan, C. Wu, Microneedle-mediated transdermal drug delivery for treating diverse skin diseases, Acta Biomater 121 (2021) 119–133. [CrossRef]
- S. Sharma, K. Hatware, P. Bhadane, S. Sindhikar, D.K. Mishra, Recent advances in microneedle composites for biomedical applications: Advanced drug delivery technologies, Materials Science and Engineering: C 103 (2019) 109717. [CrossRef]
- J.G. Turner, L.R. White, P. Estrela, H.S. Leese, Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles: Current Advancements and Future Trends, Macromol Biosci 21 (2021) 2000307. [CrossRef]
- N.N. Aung, T. Ngawhirunpat, T. Rojanarata, P. Patrojanasophon, B. Pamornpathomkul, P. Opanasopit, Fabrication, characterization and comparison of α-arbutin loaded dissolving and hydrogel forming microneedles, Int J Pharm 586 (2020) 119508. [CrossRef]
- K.J. Lee, S.S. Jeong, D.H. Roh, D.Y. Kim, H.-K. Choi, E.H. Lee, A practical guide to the development of microneedle systems – In clinical trials or on the market, Int J Pharm 573 (2020) 118778. [CrossRef]
- Z. Le, J. Yu, Y.J. Quek, B. Bai, X. Li, Y. Shou, B. Myint, C. Xu, A. Tay, Design principles of microneedles for drug delivery and sampling applications, Materials Today 63 (2023) 137–169. [CrossRef]
- M.R. Prausnitz, R. Langer, Transdermal drug delivery, Nat Biotechnol 26 (2008) 1261–1268. [CrossRef]
- K.A. Holbrook, G.F. Odland, Regional Differences in the Thickness (Cell Layers) of the Human Stratum Corneum: An Ultrastructural Analysis, Journal of Investigative Dermatology 62 (1974) 415–422. [CrossRef]
- V. Planz, C.-M. Lehr, M. Windbergs, In vitro models for evaluating safety and efficacy of novel technologies for skin drug delivery, Journal of Controlled Release 242 (2016) 89–104. [CrossRef]
- F.J. Verbaan, S.M. Bal, D.J. van den Berg, W.H.H. Groenink, H. Verpoorten, R. Lüttge, J.A. Bouwstra, Assembled microneedle arrays enhance the transport of compounds varying over a large range of molecular weight across human dermatomed skin, Journal of Controlled Release 117 (2007) 238–245. [CrossRef]
- R.F. Donnelly, M.J. Garland, D.I.J. Morrow, K. Migalska, T.R.R. Singh, R. Majithiya, A.D. Woolfson, Optical coherence tomography is a valuable tool in the study of the effects of microneedle geometry on skin penetration characteristics and in-skin dissolution, Journal of Controlled Release 147 (2010) 333–341. [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B. Al-Qallaf, D.B. Das, Transdermal drug delivery by coated microneedles: Geometry effects on effective skin thickness and drug permeability, Chemical Engineering Research and Design 86 (2008) 1196–1206. [CrossRef]
- M.M. Badran, J. Kuntsche, A. Fahr, Skin penetration enhancement by a microneedle device (Dermaroller®) in vitro: Dependency on needle size and applied formulation, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 36 (2009) 511–523. [CrossRef]
- X. Xiu, G. Gao, Y. Liu, F. Ma, Drug delivery with dissolving microneedles: skin puncture, its influencing factors and improvement strategies, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 76 (2022) 103653. [CrossRef]
- H.S. Gill, D.D. Denson, B.A. Burris, M.R. Prausnitz, Effect of Microneedle Design on Pain in Human Volunteers, Clin J Pain 24 (2008).
- J.S. Kochhar, T.C. Quek, W.J. Soon, J. Choi, S. Zou, L. Kang, Effect of Microneedle Geometry and Supporting Substrate on Microneedle Array Penetration into Skin, J Pharm Sci 102 (2013) 4100–4108. [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, D.B. Das, M.J. Garland, L. Belaid, R.F. Donnelly, Influence of Array Interspacing on the Force Required for Successful Microneedle Skin Penetration: Theoretical and Practical Approaches, J Pharm Sci 102 (2013) 1209–1221. [CrossRef]
- 154. M.R. Prausnitz, Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56 (2004) 581–587. [CrossRef]
- S.P. Davis, B.J. Landis, Z.H. Adams, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Insertion of microneedles into skin: measurement and prediction of insertion force and needle fracture force, J Biomech 37 (2004) 1155–1163. [CrossRef]
- S.M. Bal, A.C. Kruithof, R. Zwier, E. Dietz, J.A. Bouwstra, J. Lademann, M.C. Meinke, Influence of microneedle shape on the transport of a fluorescent dye into human skin in vivo, Journal of Controlled Release 147 (2010) 218–224. [CrossRef]
- J.-H. Park, Y.-K. Yoon, S.-O. Choi, M.R. Prausnitz, M.G. Allen, Tapered Conical Polymer Microneedles Fabricated Using an Integrated Lens Technique for Transdermal Drug Delivery, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54 (2007) 903–913. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Römgens, D.L. Bader, J.A. Bouwstra, F.P.T. Baaijens, C.W.J. Oomens, Monitoring the penetration process of single microneedles with varying tip diameters, J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 40 (2014) 397–405. [CrossRef]
- A.H. Sabri, Y. Kim, M. Marlow, D.J. Scurr, J. Segal, A.K. Banga, L. Kagan, J.B. Lee, Intradermal and transdermal drug delivery using microneedles – Fabrication, performance evaluation and application to lymphatic delivery, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 153 (2020) 195–215. [CrossRef]
- L. Bao, J. Park, G. Bonfante, B. Kim, Recent advances in porous microneedles: materials, fabrication, and transdermal applications, Drug Deliv Transl Res 12 (2022) 395–414. [CrossRef]
- Park, J. H., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2010). Analysis of Mechanical Failure of Polymer Microneedles by Axial Force. The journal of the Korean Physical Society, 56(4), 1223–1227. [CrossRef]
- Chang, K. T., Shen, Y. K., Fan, F. Y., Lin, Y., & Kang, S. C. (2020). Optimal design and fabrication of a microneedle arrays patch. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 54, 274-285. [CrossRef]
- Davis, S. P., Landis, B. J., Adams, Z. H., Allen, M. G., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2004). Insertion of microneedles into skin: measurement and prediction of insertion force and needle fracture force. Journal of biomechanics, 37(8), 1155-1163. [CrossRef]
- Gittard, S. D., Chen, B., Xu, H., Ovsianikov, A., Chichkov, B. N., Monteiro-Riviere, N. A., & Narayan, R. J. (2013). The effects of geometry on skin penetration and failure of polymer microneedles. Journal of adhesion science and technology, 27(3), 227-243. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, X. Hu, Z. Dong, Y. Chen, W. Zhao, Y. Wang, L. Zhang, M. Chen, C. Wu, Q. Wang, Dissolving Microneedle Arrays with Optimized Needle Geometry for Transcutaneous Immunization, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 151 (2020) 105361. [CrossRef]
- E.Z. Loizidou, N.T. Inoue, J. Ashton-Barnett, D.A. Barrow, C.J. Allender, Evaluation of geometrical effects of microneedles on skin penetration by CT scan and finite element analysis, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 107 (2016) 1–6. [CrossRef]
- S.H. Bariya, M.C. Gohel, T.A. Mehta, O.P. Sharma, Microneedles: an emerging transdermal drug delivery system, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 64 (2012) 11–29. [CrossRef]
- Tucak, M. Sirbubalo, L. Hindija, O. Rahić, J. Hadžiabdić, K. Muhamedagić, A. Čekić, E. Vranić, Microneedles: Characteristics, Materials, Production Methods and Commercial Development, Micromachines (Basel) 11 (2020). [CrossRef]
- A.R. Razali, Y. Qin, A Review on Micro-manufacturing, Micro-forming and their Key Issues, Procedia Eng 53 (2013) 665–672. [CrossRef]
- 170. E. Nuxoll, BioMEMS in drug delivery, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65 (2013) 1611–1625. [CrossRef]
- H. Kathuria, K. Kang, J. Cai, L. Kang, Rapid microneedle fabrication by heating and photolithography, Int J Pharm 575 (2020) 118992. [CrossRef]
- F. Pérennès, B. Marmiroli, M. Matteucci, M. Tormen, L. Vaccari, E. Di Fabrizio, Sharp beveled tip hollow microneedle arrays fabricated by LIGA and 3D soft lithography with polyvinyl alcohol, Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 16 (2006) 473. [CrossRef]
- 173. M.J. Madou, Fundamentals of microfabrication and nanotechnology, three-volume set, CRC Press, 2018.
- B.P. Chaudhri, F. Ceyssens, T. Guan, A. La Manna, H.P. Neves, C. Van Hoof, R. Puers, High Strength, Polymer Microneedles For Transdermal Drug Delivery, Procedia Eng 25 (2011) 1377–1380. [CrossRef]
- S.J. Moon, S.S. Lee, H.S. Lee, T.H. Kwon, Fabrication of microneedle array using LIGA and hot embossing process, Microsystem Technologies 11 (2005) 311–318. [CrossRef]
- H. Takahashi, Y. Jung Heo, N. Arakawa, T. Kan, K. Matsumoto, R. Kawano, I. Shimoyama, Scalable fabrication of microneedle arrays via spatially controlled UV exposure, Microsyst Nanoeng 2 (2016) 16049. [CrossRef]
- H. Takahashi, Y.J. Heo, I. Shimoyama, Scalable Fabrication of PEGDA Microneedles Using UV Exposure via a Rotating Prism, Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems PP (2017) 1–3. [CrossRef]
- 178. T. Tomono, A new way to control the internal structure of microneedles: a case of chitosan lactate, Mater Today Chem 13 (2019) 79–87. [CrossRef]
- S. Lyu, Z. Dong, X. Xu, H.-P. Bei, H.-Y. Yuen, C.-W. James Cheung, M.-S. Wong, Y. He, X. Zhao, Going below and beyond the surface: Microneedle structure, materials, drugs, fabrication, and applications for wound healing and tissue regeneration, Bioact Mater 27 (2023) 303–326. [CrossRef]
- S. Dharadhar, A. Majumdar, S. Dhoble, V. Patravale, Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: a systematic review, Drug Dev Ind Pharm 45 (2019) 188–201. [CrossRef]
- R.F. Donnelly, T.R.R. Singh, M.M. Tunney, D.I.J. Morrow, P.A. McCarron, C. O’Mahony, A.D. Woolfson, Microneedle Arrays Allow Lower Microbial Penetration Than Hypodermic Needles In Vitro, Pharm Res 26 (2009) 2513–2522. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, Y. Li, M. Liu, L. Cui, Y. Yu, Microneedle Electrode Array for Electrical Impedance Myography to Characterize Neurogenic Myopathy, Ann Biomed Eng 44 (2016) 1566–1575. [CrossRef]
- Y.-C. Li, S.-J. Feng, H.-X. Chen, Z.-L. Chen, D.-M. Zhang, Random vibration of train-track-ground system with a poroelastic interlayer in the subsoil, Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 120 (2019) 1–11. [CrossRef]
- N. Wilke, A. Mulcahy, S.-R. Ye, A. Morrissey, Process optimization and characterization of silicon microneedles fabricated by wet etch technology, Microelectronics J 36 (2005) 650–656. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, P.F. Eng, O.J. Guy, K. Roberts, H. Ashraf, N. Knight, Advanced deep reactive-ion etching technology for hollow microneedles for transdermal blood sampling and drug delivery, IET Nanobiotechnol 7 (2013) 59–62. [CrossRef]
- N. Roxhed, T.C. Gasser, P. Griss, G.A. Holzapfel, G. Stemme, Penetration-Enhanced Ultrasharp Microneedles and Prediction on Skin Interaction for Efficient Transdermal Drug Delivery, Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 16 (2007) 1429–1440. [CrossRef]
- S. Henry, D. V McAllister, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Microfabricated Microneedles: A Novel Approach to Transdermal Drug Delivery, J Pharm Sci 87 (1998) 922–925. [CrossRef]
- P.-C. Wang, B.A. Wester, S. Rajaraman, S.-J. Paik, S.-H. Kim, M.G. Allen, Hollow polymer microneedle array fabricated by photolithography process combined with micromolding technique., Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009 (2009) 7026–7029. [CrossRef]
- S.-J. Paik, S. Byun, J.-M. Lim, Y. Park, A. Lee, S. Chung, J. Chang, K. Chun, D. “Dan” Cho, In-plane single-crystal-silicon microneedles for minimally invasive microfluid systems, Sens Actuators A Phys 114 (2004) 276–284. [CrossRef]
- B. Ma, S. Liu, Z. Gan, G. Liu, X. Cai, H. Zhang, Z. Yang, A PZT insulin pump integrated with a silicon microneedle array for transdermal drug delivery, Microfluid Nanofluidics 2 (2006) 417–423. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, H. Wang, L. Lai, Y. Li, Preparation of Microneedle Array Mold Based on MEMS Lithography Technology, Micromachines (Basel) 12 (2021). [CrossRef]
- F.K. Aldawood, A. Andar, S. Desai, A Comprehensive Review of Microneedles: Types, Materials, Processes, Characterizations and Applications, Polymers (Basel) 13 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Z. Chen, J. He, J. Qi, Q. Zhu, W. Wu, Y. Lu, Long-acting microneedles: a progress report of the state-of-the-art techniques, Drug Discov Today 25 (2020) 1462–1468. [CrossRef]
- 194. K. Ita, Ceramic microneedles and hollow microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: Two decades of research, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 44 (2018) 314–322. [CrossRef]
- H. Chang, Y. Cui, Image Classification Algorithm Based on Big Data and Multilabel Learning of Improved Convolutional Neural Network, Wirel Commun Mob Comput 2021 (2021) 3138398. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Boks, W.W.J. Unger, S. Engels, M. Ambrosini, Y. van Kooyk, R. Luttge, Controlled release of a model vaccine by nanoporous ceramic microneedle arrays, Int J Pharm 491 (2015) 375–383. [CrossRef]
- S. Bystrova, R. Luttge, Micromolding for ceramic microneedle arrays, Microelectron Eng 88 (2011) 1681–1684. [CrossRef]
- S. Yang, Y. Feng, L. Zhang, N. Chen, W. Yuan, T. Jin, A scalable fabrication process of polymer microneedles., Int J Nanomedicine 7 (2012) 1415–1422. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, G. Jiang, W. Yu, D. Liu, B. Xu, Microneedles fabricated from alginate and maltose for transdermal delivery of insulin on diabetic rats, Materials Science and Engineering: C 85 (2018) 18–26. [CrossRef]
- J.-H. Park, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Biodegradable polymer microneedles: Fabrication, mechanics and transdermal drug delivery, Journal of Controlled Release 104 (2005) 51–66. [CrossRef]
- J. Lee, D.-H. Kim, K.J. Lee, I.H. Seo, S.H. Park, E.H. Jang, Y. Park, Y.-N. Youn, W. Ryu, Transfer-molded wrappable microneedle meshes for perivascular drug delivery, Journal of Controlled Release 268 (2017) 237–246. [CrossRef]
- K.A. Moga, L.R. Bickford, R.D. Geil, S.S. Dunn, A.A. Pandya, Y. Wang, J.H. Fain, C.F. Archuleta, A.T. O’Neill, J.M. DeSimone, Rapidly–Dissolvable Microneedle Patches Via a Highly Scalable and Reproducible Soft Lithography Approach, Advanced Materials 25 (2013) 5060–5066. [CrossRef]
- M.-T. Lee, I.-C. Lee, S.-W. Tsai, C.-H. Chen, M.-H. Wu, Y.-J. Juang, Spin coating of polymer solution on polydimethylsiloxane mold for fabrication of microneedle patch, J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 70 (2017) 42–48. [CrossRef]
- M.G. McGrath, S. Vucen, A. Vrdoljak, A. Kelly, C. O’Mahony, A.M. Crean, A. Moore, Production of dissolvable microneedles using an atomised spray process: Effect of microneedle composition on skin penetration, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 86 (2014) 200–211. [CrossRef]
- Vrdoljak, E.A. Allen, F. Ferrara, N.J. Temperton, A.M. Crean, A.C. Moore, Induction of broad immunity by thermostabilised vaccines incorporated in dissolvable microneedles using novel fabrication methods, Journal of Controlled Release 225 (2016) 192–204. [CrossRef]
- M.J. Kim, S.C. Park, B. Rizal, G. Guanes, S.-K. Baek, J.-H. Park, A.R. Betz, S.-O. Choi, Fabrication of Circular Obelisk-Type Multilayer Microneedles Using Micro-Milling and Spray Deposition, Front Bioeng Biotechnol 6 (2018). [CrossRef]
- H.S. Gill, M.R. Prausnitz, Coated microneedles for transdermal delivery, Journal of Controlled Release 117 (2007) 227–237. [CrossRef]
- W. Martanto, S.P. Davis, N.R. Holiday, J. Wang, H.S. Gill, M.R. Prausnitz, Transdermal Delivery of Insulin Using Microneedles in Vivo, Pharm Res 21 (2004) 947–952. [CrossRef]
- H.S. Gill, M.R. Prausnitz, Coating Formulations for Microneedles, Pharm Res 24 (2007) 1369–1380. [CrossRef]
- S. Indermun, R. Luttge, Y.E. Choonara, P. Kumar, L.C. du Toit, G. Modi, V. Pillay, Current advances in the fabrication of microneedles for transdermal delivery, Journal of Controlled Release 185 (2014) 130–138. [CrossRef]
- R. Nagarkar, M. Singh, H.X. Nguyen, S. Jonnalagadda, A review of recent advances in microneedle technology for transdermal drug delivery, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 59 (2020) 101923. [CrossRef]
- T. Omatsu, K. Chujo, K. Miyamoto, M. Okida, K. Nakamura, N. Aoki, R. Morita, Metal microneedle fabrication using twisted light with spin, Opt Express 18 (2010) 17967–17973. [CrossRef]
- T. Evens, O. Malek, S. Castagne, D. Seveno, A. Van Bael, A novel method for producing solid polymer microneedles using laser ablated molds in an injection molding process, Manuf Lett 24 (2020) 29–32. [CrossRef]
- S. Aoyagi, H. Izumi, Y. Isono, M. Fukuda, H. Ogawa, Laser fabrication of high aspect ratio thin holes on biodegradable polymer and its application to a microneedle, Sens Actuators A Phys 139 (2007) 293–302. [CrossRef]
- E. Albarahmieh, L. AbuAmmouneh, Z. Kaddoura, F. AbuHantash, B.A. Alkhalidi, A. Al-Halhouli, Fabrication of Dissolvable Microneedle Patches Using an Innovative Laser-Cut Mold Design to Shortlist Potentially Transungual Delivery Systems: In Vitro Evaluation., AAPS PharmSciTech 20 (2019) 215. [CrossRef]
- H.R. Nejad, A. Sadeqi, G. Kiaee, S. Sonkusale, Low-cost and cleanroom-free fabrication of microneedles, Microsyst Nanoeng 4 (2018) 17073. [CrossRef]
- K.T. Tu, C.K. Chung, Rapid prototyping of biodegradable microneedle arrays by integrating CO2 laser processing and polymer molding, Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 26 (2016) 65015. [CrossRef]
- Y.K. Demir, Z. Akan, O. Kerimoglu, Characterization of Polymeric Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery, PLoS One 8 (2013) e77289.
- G. Anbazhagan, S.B. Suseela, R. Sankararajan, Design, analysis and fabrication of solid polymer microneedle patch using CO2 laser and polymer molding, Drug Deliv Transl Res 13 (2023) 1813–1827. [CrossRef]
- E. Adarkwa, S. Desai, Scalable Droplet Based Manufacturing Using In-Flight Laser Evaporation, Journal of Nanoengineering and Nanomanufacturing 6 (2016) 87–92. [CrossRef]
- M. Yang, Z. Xu, S. Desai, D. Kumar, J. Sankar, Fabrication of Micro Single Chamber Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Using Photolithography and Pulsed Laser Deposition, J Fuel Cell Sci Technol 12 (2015). [CrossRef]
- T. Esho, S. Desai, Laser based microdroplet evaporation towards scalable micro and nano manufacturing, 62nd IIE Annual Conference and Expo 2012 (2012) 1750–1757.
- S.K. Parupelli, S. Desai, Understanding Hybrid Additive Manufacturing of Functional Devices, American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 10 (2017). [CrossRef]
- J. McKenzie, S. Desai, Investigating Sintering Mechanisms for Additive Manufacturing of Conductive Traces, American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 11 (2018). [CrossRef]
- S. Desai, M. Craps, T. Esho, Direct writing of nanomaterials for flexible thin-film transistors (fTFTs), The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 64 (2013) 537–543. [CrossRef]
- M.K. Ahmed, M.E. El-Naggar, A. Aldalbahi, M.H. El-Newehy, A.A. Menazea, Methylene blue degradation under visible light of metallic nanoparticles scattered into graphene oxide using laser ablation technique in aqueous solutions, J Mol Liq 315 (2020) 113794. [CrossRef]
- M. Moydeen, M. El-Newehy, A. M. Ismail, A. Anter, Enhancment the electrical conductivity of the synthesized polyvinylidene fluoride/polyvinyl chloride composite doped with palladium nanoparticles via laser ablation, Journal of Materials Research and Technology 9 (2020). [CrossRef]
- A.A. Menazea, M.H. El-Newehy, B.M. Thamer, M.E. El-Naggar, Preparation of antibacterial film-based biopolymer embedded with vanadium oxide nanoparticles using one-pot laser ablation, J Mol Struct 1225 (2021) 129163. [CrossRef]
- K.-Z. Tu, C.-K. Chung, Fabrication of biodegradable polymer microneedle array via CO2 laser ablation, 2015 IEEE 10th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, NEMS 2015 (2015) 494–497. [CrossRef]
- Y.-T. Chen, K.-J. Ma, A.A. Tseng, P.H. Chen, Projection ablation of glass-based single and arrayed microstructures using excimer laser, Opt Laser Technol 37 (2005) 271–280. [CrossRef]
- H.Y. Zheng, Y.C. Lam, C. Sundarraman, D. V Tran, Influence of substrate cooling on femtosecond laser machined hole depth and diameter, Applied Physics A 89 (2007) 559–563. [CrossRef]
- R.E.M. Lutton, E. Larrañeta, M.-C. Kearney, P. Boyd, A.D. Woolfson, R.F. Donnelly, A novel scalable manufacturing process for the production of hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays, Int J Pharm 494 (2015) 417–429. [CrossRef]
- M. Zaied, I. Miraoui, M. Boujelbene, E. Bayraktar, Analysis of Heat Affected Zone Obtained by CO2 Laser Cutting of Low Carbon Steel (S235), 2013. [CrossRef]
- Q.L. Wang, D.D. Zhu, Y. Chen, X.D. Guo, A fabrication method of microneedle molds with controlled microstructures, Materials Science and Engineering: C 65 (2016) 135–142. [CrossRef]
- B.Z. Chen, M.C. He, X.P. Zhang, W.M. Fei, Y. Cui, X.D. Guo, A novel method for fabrication of coated microneedles with homogeneous and controllable drug dosage for transdermal drug delivery, Drug Deliv Transl Res 12 (2022) 2730–2739. [CrossRef]
- P.M. Wang, M. Cornwell, J. Hill, M.R. Prausnitz, Precise Microinjection into Skin Using Hollow Microneedles, Journal of Investigative Dermatology 126 (2006) 1080–1087. [CrossRef]
- J. Gupta, E.I. Felner, M.R. Prausnitz, Rapid pharmacokinetics of intradermal insulin administered using microneedles in type 1 diabetes subjects., Diabetes Technol Ther 13 (2011) 451–456. [CrossRef]
- W. Martanto, J.S. Moore, O. Kashlan, R. Kamath, P.M. Wang, J.M. O’Neal, M.R. Prausnitz, Microinfusion Using Hollow Microneedles, Pharm Res 23 (2006) 104–113. [CrossRef]
- G. Mahadevan, H. Sheardown, P. Selvaganapathy, PDMS embedded microneedles as a controlled release system for the eye, J Biomater Appl 28 (2012) 20–27. [CrossRef]
- J.D. Kim, M. Kim, H. Yang, K. Lee, H. Jung, Droplet-born air blowing: Novel dissolving microneedle fabrication, Journal of Controlled Release 170 (2013) 430–436. [CrossRef]
- M. Wu, Y. Zhang, H. Huang, J. Li, H. Liu, Z. Guo, L. Xue, S. Liu, Y. Lei, Assisted 3D printing of microneedle patches for minimally invasive glucose control in diabetes, Materials Science and Engineering: C 117 (2020) 111299. [CrossRef]
- J. Kim, J. Bae, H. Kim, D. Jeong, Droplet-born Air Blowing (DAB) Technology for the Industrialization of Dissolving Microneedle, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Huh, S. Kim, H. Yang, M. Jang, G. Kang, H. Jung, Effects of two droplet-based dissolving microneedle manufacturing methods on the activity of encapsulated epidermal growth factor and ascorbic acid, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 114 (2018) 285–292. [CrossRef]
- L. Wu, N. Takama, J. Park, B. Kim, J. Kim, D. Jeong, Shadow mask assisted droplet-born air-blowing method for fabrication of dissoluble microneedle, 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS) (2017) 456–459.
- Y.-H. Lin, I.-C. Lee, W.-C. Hsu, C.-H. Hsu, K.-P. Chang, S.-S. Gao, Rapid fabrication method of a microneedle mold with controllable needle height and width., Biomed Microdevices 18 (2016) 85. [CrossRef]
- R. Vecchione, S. Coppola, E. Esposito, C. Casale, V. Vespini, S. Grilli, P. Ferraro, P.A. Netti, Electro-Drawn Drug-Loaded Biodegradable Polymer Microneedles as a Viable Route to Hypodermic Injection, Adv Funct Mater 24 (2014) 3515–3523. [CrossRef]
- S. Lee, S. Fakhraei Lahiji, J. Jang, M. Jang, H. Jung, Micro-Pillar Integrated Dissolving Microneedles for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery, Pharmaceutics 11 (2019). [CrossRef]
- M.J. Kim, S.C. Park, S.-O. Choi, Dual-nozzle spray deposition process for improving the stability of proteins in polymer microneedles, RSC Adv 7 (2017) 55350–55359. [CrossRef]
- H. Juster, B. van der Aar, H. de Brouwer, A review on microfabrication of thermoplastic polymer-based microneedle arrays, Polym Eng Sci 59 (2019) 877–890. [CrossRef]
- M.S. Lhernould, M. Deleers, A. Delchambre, Hollow polymer microneedles array resistance and insertion tests, Int J Pharm 480 (2015) 152–157. [CrossRef]
- 251. K.J. Nair, Micro-injection molded microneedles for drug delivery., 2016.
- F. Sammoura, J. Kang, Y.-M. Heo, T. Jung, L. Lin, Polymeric microneedle fabrication using a microinjection molding technique, Microsystem Technologies 13 (2007) 517–522. [CrossRef]
- B. Bediz, E. Korkmaz, R. Khilwani, C. Donahue, G. Erdos, L.D. Falo, O.B. Ozdoganlar, Dissolvable Microneedle Arrays for Intradermal Delivery of Biologics: Fabrication and Application, Pharm Res 31 (2014) 117–135. [CrossRef]
- Malek-Khatabi, Z. Faraji Rad, M. Rad-Malekshahi, H. Akbarijavar, Development of dissolvable microneedle patches by CNC machining and micromolding for drug delivery, Mater Lett 330 (2023) 133328. [CrossRef]
- E. García-López, H.R. Siller, C.A. Rodríguez, Study of the fabrication of AISI 316L microneedle arrays, Procedia Manuf 26 (2018) 117–124. [CrossRef]
- S.K. Parupelli, S. Desai, A Comprehensive Review of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Processes, Applications and Future Potential, Am J Appl Sci 16 (2019). [CrossRef]
- E. Adarkwa, R. Kotoka, S. Desai, 3D printing of polymeric Coatings on AZ31 Mg alloy Substrate for Corrosion Protection of biomedical implants, Med Devices Sens 4 (2021) e10167. [CrossRef]
- B. Altubaishe, J. Clarke, C. McWilliams, S. Desai, Comparative Analysis of Risk Management Strategies for Additive Manufacturing Supply Chains, Am J Appl Sci 16 (2019). [CrossRef]
- F.K. Aldawood, S.X. Chang, S. Desai, Design and manufacture of a high precision personalized electron bolus device for radiation therapy, Med Devices Sens 3 (2020) e10077. [CrossRef]
- G. Haeberle, S. Desai, Investigating Rapid Thermoform Tooling Via Additive Manufacturing (3d Printing), Am J Appl Sci 16 (2019). [CrossRef]
- S.K. Parupelli, S. Desai, Hybrid additive manufacturing (3D printing) and characterization of functionally gradient materials via in situ laser curing, The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 110 (2020) 543–556. [CrossRef]
- S.N. Economidou, D.A. Lamprou, D. Douroumis, 3D printing applications for transdermal drug delivery, Int J Pharm 544 (2018) 415–424. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Alhnan, T.C. Okwuosa, M. Sadia, K.-W. Wan, W. Ahmed, B. Arafat, Emergence of 3D Printed Dosage Forms: Opportunities and Challenges, Pharm Res 33 (2016) 1817–1832. [CrossRef]
- W. Jamróz, J. Szafraniec, M. Kurek, R. Jachowicz, 3D Printing in Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications – Recent Achievements and Challenges, Pharm Res 35 (2018) 176. [CrossRef]
- L.K. Prasad, H. Smyth, 3D Printing technologies for drug delivery: a review, Drug Dev Ind Pharm 42 (2016) 1019–1031. [CrossRef]
- S.H. Lim, H. Kathuria, J.J.Y. Tan, L. Kang, 3D printed drug delivery and testing systems — a passing fad or the future?, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 132 (2018) 139–168. [CrossRef]
- J. Goole, K. Amighi, 3D printing in pharmaceutics: A new tool for designing customized drug delivery systems, Int J Pharm 499 (2016) 376–394. [CrossRef]
- Awad, S.J. Trenfield, S. Gaisford, A.W. Basit, 3D printed medicines: A new branch of digital healthcare, Int J Pharm 548 (2018) 586–596. [CrossRef]
- M. Camović, A. Biščević, I. Brčić, K. Borcak, S. Bušatlić, N. Ćenanović, A. Dedović, A. Mulalić, M. Osmanlić, M. Sirbubalo Šahinović, A. Tucak-Smajić, E. Vranic, Coated 3D Printed PLA Microneedles as Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems, in: 2020: pp. 735–742. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Luzuriaga, D.R. Berry, J.C. Reagan, R.A. Smaldone, J.J. Gassensmith, Biodegradable 3D printed polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery, Lab Chip 18 (2018) 1223–1230. [CrossRef]
- E.A. Allen, C. O’Mahony, M. Cronin, T. O’Mahony, A.C. Moore, A.M. Crean, Dissolvable microneedle fabrication using piezoelectric dispensing technology, Int J Pharm 500 (2016) 1–10. [CrossRef]
- H. Derakhshandeh, F. Aghabaglou, A. McCarthy, A. Mostafavi, C. Wiseman, Z. Bonick, I. Ghanavati, S. Harris, C. Kreikemeier-Bower, S.M. Moosavi Basri, J. Rosenbohm, R. Yang, P. Mostafalu, D. Orgill, A. Tamayol, A Wirelessly Controlled Smart Bandage with 3D-Printed Miniaturized Needle Arrays, Adv Funct Mater 30 (2020) 1905544. [CrossRef]
- L. Barnum, J. Quint, H. Derakhshandeh, M. Samandari, F. Aghabaglou, A. Farzin, L. Abbasi, S. Bencherif, A. Memic, P. Mostafalu, A. Tamayol, 3D-Printed Hydrogel-Filled Microneedle Arrays, Adv Healthc Mater 10 (2021) 2001922. [CrossRef]
- C. Yeung, S. Chen, B. King, H. Lin, K. King, F. Akhtar, G. Diaz, B. Wang, J. Zhu, W. Sun, A. Khademhosseini, S. Emaminejad, A 3D-printed microfluidic-enabled hollow microneedle architecture for transdermal drug delivery, Biomicrofluidics 13 (2019) 64125. [CrossRef]
- M.J. Uddin, N. Scoutaris, S.N. Economidou, C. Giraud, B.Z. Chowdhry, R.F. Donnelly, D. Douroumis, 3D printed microneedles for anticancer therapy of skin tumours, Materials Science and Engineering: C 107 (2020) 110248. [CrossRef]
- S.N. Economidou, C.P.P. Pere, A. Reid, Md.J. Uddin, J.F.C. Windmill, D.A. Lamprou, D. Douroumis, 3D printed microneedle patches using stereolithography (SLA) for intradermal insulin delivery, Materials Science and Engineering: C 102 (2019) 743–755. [CrossRef]
- K.J. Krieger, N. Bertollo, M. Dangol, J.T. Sheridan, M.M. Lowery, E.D. O’Cearbhaill, Simple and customizable method for fabrication of high-aspect ratio microneedle molds using low-cost 3D printing, Microsyst Nanoeng 5 (2019) 42. [CrossRef]
- C. Farias, R. Lyman, C. Hemingway, H. Chau, A. Mahacek, E. Bouzos, M. Mobed-Miremadi, Three-Dimensional (3D) Printed Microneedles for Microencapsulated Cell Extrusion, Bioengineering 5 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Xenikakis, M. Tzimtzimis, K. Tsongas, D. Andreadis, E. Demiri, D. Tzetzis, D.G. Fatouros, Fabrication and finite element analysis of stereolithographic 3D printed microneedles for transdermal delivery of model dyes across human skin in vitro, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 137 (2019) 104976. [CrossRef]
- S.D. Gittard, P.R. Miller, C. Jin, T.N. Martin, R.D. Boehm, B.J. Chisholm, S.J. Stafslien, J.W. Daniels, N. Cilz, N.A. Monteiro-Riviere, A. Nasir, R.J. Narayan, Deposition of antimicrobial coatings on microstereolithography-fabricated microneedles, JOM 63 (2011) 59–68. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lu, S.N. Mantha, D.C. Crowder, S. Chinchilla, K.N. Shah, Y.H. Yun, R.B. Wicker, J.-W. Choi, Microstereolithography and characterization of poly(propylene fumarate)-based drug-loaded microneedle arrays, Biofabrication 7 (2015) 45001. [CrossRef]
- N. El-Sayed, L. Vaut, M. Schneider, Customized fast-separable microneedles prepared with the aid of 3D printing for nanoparticle delivery, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 154 (2020) 166–174. [CrossRef]
- S.H. Lim, W.J. Tiew, J. Zhang, P.C.-L. Ho, N.N. Kachouie, L. Kang, Geometrical optimisation of a personalised microneedle eye patch for transdermal delivery of anti-wrinkle small peptide, Biofabrication 12 (2020) 35003. [CrossRef]
- A.R. Johnson, C.L. Caudill, J.R. Tumbleston, C.J. Bloomquist, K.A. Moga, A. Ermoshkin, D. Shirvanyants, S.J. Mecham, J.C. Luft, J.M. DeSimone, Single-Step Fabrication of Computationally Designed Microneedles by Continuous Liquid Interface Production, PLoS One 11 (2016) e0162518.
- C. Caudill, J.L. Perry, K. Iliadis, A.T. Tessema, B.J. Lee, B.S. Mecham, S. Tian, J.M. DeSimone, Transdermal vaccination via 3D-printed microneedles induces potent humoral and cellular immunity, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118 (2021) e2102595118. [CrossRef]
- S.D. Gittard, A. Ovsianikov, B.N. Chichkov, A. Doraiswamy, R.J. Narayan, Two-photon polymerization of microneedles for transdermal drug delivery, Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7 (2010) 513–533. [CrossRef]
- Trautmann, G.-L. Roth, B. Nujiqi, T. Walther, R. Hellmann, Towards a versatile point-of-care system combining femtosecond laser generated microfluidic channels and direct laser written microneedle arrays, Microsyst Nanoeng 5 (2019) 6. [CrossRef]
- Aksit, D.N. Arteaga, M. Arriaga, X. Wang, H. Watanabe, K.E. Kasza, A.K. Lalwani, J.W. Kysar, In-vitro perforation of the round window membrane via direct 3-D printed microneedles, Biomed Microdevices 20 (2018) 47. [CrossRef]
- L. Wu, J. Park, Y. Kamaki, B. Kim, Optimization of the fused deposition modeling-based fabrication process for polylactic acid microneedles, Microsyst Nanoeng 7 (2021) 58. [CrossRef]
- L. Antonara, P.P. Dallas, D.M. Rekkas, A novel 3D printing enabled method for fast and reliable construction of polymeric microneedles using experimental design, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 68 (2022) 102888. [CrossRef]
- J.M. Loh, Y.J.L. Lim, J.T. Tay, H.M. Cheng, H.L. Tey, K. Liang, Design and fabrication of customizable microneedles enabled by 3D printing for biomedical applications, Bioact Mater 32 (2024) 222–241. [CrossRef]
- E.A. Allen, C. O’Mahony, M. Cronin, T. O’Mahony, A.C. Moore, A.M. Crean, Dissolvable microneedle fabrication using piezoelectric dispensing technology, Int J Pharm 500 (2016) 1–10. [CrossRef]
- M.J. Uddin, N. Scoutaris, P. Klepetsanis, B. Chowdhry, M.R. Prausnitz, D. Douroumis, Inkjet printing of transdermal microneedles for the delivery of anticancer agents, Int J Pharm 494 (2015) 593–602. [CrossRef]
- H. Derakhshandeh, F. Aghabaglou, A. McCarthy, A. Mostafavi, C. Wiseman, Z. Bonick, I. Ghanavati, S. Harris, C. Kreikemeier-Bower, S.M. Moosavi Basri, J. Rosenbohm, R. Yang, P. Mostafalu, D. Orgill, A. Tamayol, A Wirelessly Controlled Smart Bandage with 3D-Printed Miniaturized Needle Arrays, Adv Funct Mater 30 (2020) 1905544. [CrossRef]
- L. Barnum, J. Quint, H. Derakhshandeh, M. Samandari, F. Aghabaglou, A. Farzin, L. Abbasi, S. Bencherif, A. Memic, P. Mostafalu, A. Tamayol, 3D-Printed Hydrogel-Filled Microneedle Arrays, Adv Healthc Mater 10 (2021) 2001922. [CrossRef]
- T.D. Ngo, A. Kashani, G. Imbalzano, K.T.Q. Nguyen, D. Hui, Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges, Compos B Eng 143 (2018) 172–196. [CrossRef]
- V. Yadav, P.K. Sharma, U.S. Murty, N.H. Mohan, R. Thomas, S.K. Dwivedy, S. Banerjee, 3D printed hollow microneedles array using stereolithography for efficient transdermal delivery of rifampicin, Int J Pharm 605 (2021) 120815. [CrossRef]
- S. Choo, S. Jin, J. Jung, Fabricating High-Resolution and High-Dimensional Microneedle Mold through the Resolution Improvement of Stereolithography 3D Printing, Pharmaceutics 14 (2022). [CrossRef]
- K.B. Vinayakumar, M.D. Silva, A. Martins, S. Mundy, P. González-Losada, S. Sillankorva, Levofloxacin-Loaded Microneedles Produced Using 3D-Printed Molds for Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm Control, Adv Ther (Weinh) 6 (2023) 2200320. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yang, W. Zhong, Y. Liu, R. Hou, Y. Wu, Q. Yan, G. Yang, 3D-printed morphology-customized microneedles: Understanding the correlation between their morphologies and the received qualities, Int J Pharm 638 (2023) 122873. [CrossRef]
- J.G. Turner, M. Laabei, S. Li, P. Estrela, H.S. Leese, Antimicrobial releasing hydrogel forming microneedles, Biomaterials Advances 151 (2023) 213467. [CrossRef]
- W. Yao, D. Li, Y. Zhao, Z. Zhan, G. Jin, H. Liang, R. Yang, 3D Printed Multi-Functional Hydrogel Microneedles Based on High-Precision Digital Light Processing, Micromachines (Basel) 11 (2020). [CrossRef]
- E. Mathew, G. Pitzanti, A.L. Gomes dos Santos, D.A. Lamprou, Optimization of Printing Parameters for Digital Light Processing 3D Printing of Hollow Microneedle Arrays, Pharmaceutics 13 (2021). [CrossRef]
- D. Shin, J. Hyun, Silk fibroin microneedles fabricated by digital light processing 3D printing, Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 95 (2021) 126–133. [CrossRef]
- R. Sachan, A.K. Nguyen, J. Lu, D. Erdmann, J.Y. Zhang, R.J. Narayan, Digital light processing-based 3D printing of polytetrafluoroethylene solid microneedle arrays, MRS Commun 11 (2021) 896–901. [CrossRef]
- X. Wu, Q. Sun, W. Qiao, J. Cui, L. Chen, Rapid fabrication of customizable microneedle molds using digital light processing 3D printing methods, in: Proc.SPIE, 2021: p. 118500N. [CrossRef]
- P.K. Monou, E.G. Andriotis, K. Tsongas, E.K. Tzimtzimis, O.L. Katsamenis, D. Tzetzis, P. Anastasiadou, C. Ritzoulis, I.S. Vizirianakis, D. Andreadis, D.G. Fatouros, Fabrication of 3D Printed Hollow Microneedles by Digital Light Processing for the Buccal Delivery of Actives, ACS Biomater Sci Eng 9 (2023) 5072–5083. [CrossRef]
- H. Erkus, T. Bedir, E. Kaya, G.B. Tinaz, O. Gunduz, M.-C. Chifiriuc, C.B. Ustundag, Innovative transdermal drug delivery system based on amoxicillin-loaded gelatin methacryloyl microneedles obtained by 3D printing, Materialia (Oxf) 27 (2023) 101700. [CrossRef]
- B.J. Lee, K. Hsiao, G. Lipkowitz, T. Samuelsen, L. Tate, J.M. DeSimone, Characterization of a 30 µm pixel size CLIP-based 3D printer and its enhancement through dynamic printing optimization, Addit Manuf 55 (2022) 102800. [CrossRef]
- N.U. Rajesh, I. Coates, M.M. Driskill, M.T. Dulay, K. Hsiao, D. Ilyin, G.B. Jacobson, J.W. Kwak, M. Lawrence, J. Perry, C.O. Shea, S. Tian, J.M. DeSimone, 3D-Printed Microarray Patches for Transdermal Applications, JACS Au 2 (2022) 2426–2445. [CrossRef]
- Doraiswamy, C. Jin, R.J. Narayan, P. Mageswaran, P. Mente, R. Modi, R. Auyeung, D.B. Chrisey, A. Ovsianikov, B. Chichkov, Two photon induced polymerization of organic–inorganic hybrid biomaterials for microstructured medical devices, Acta Biomater 2 (2006) 267–275. [CrossRef]
- Z. Faraji Rad, P.D. Prewett, G.J. Davies, Rapid prototyping and customizable microneedle design: Ultra-sharp microneedle fabrication using two-photon polymerization and low-cost micromolding techniques, Manuf Lett 30 (2021) 39–43. [CrossRef]
- M.M. Pillai, S. Ajesh, P. Tayalia, Two-photon polymerization based reusable master template to fabricate polymer microneedles for drug delivery, MethodsX 10 (2023) 102025. [CrossRef]
- E. Fakeih, A.A. Aguirre-Pablo, S.T. Thoroddsen, K.N. Salama, Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Microneedles for Enhanced Fluid Injection and Suction: A Two-Photon Polymerization Approach, Adv Eng Mater 25 (2023) 2300161. [CrossRef]
- Z. He, F. Chen, S. He, Fabrication of microneedles using two photon-polymerization with low numerical aperture, Opt Commun 553 (2024) 130093. [CrossRef]
- Caudill, J.L. Perry, K. Iliadis, A.T. Tessema, B.J. Lee, B.S. Mecham, S. Tian, J.M. DeSimone, Transdermal vaccination via 3D-printed microneedles induces potent humoral and cellular immunity, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118 (2021) e2102595118. [CrossRef]
- S.N. Economidou, Md.J. Uddin, M.J. Marques, D. Douroumis, W.T. Sow, H. Li, A. Reid, J.F.C. Windmill, A. Podoleanu, A novel 3D printed hollow microneedle microelectromechanical system for controlled, personalized transdermal drug delivery, Addit Manuf 38 (2021) 101815. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Rodgers, M.T.C. McCrudden, Eva.M. Vincente-Perez, A. V Dubois, R.J. Ingram, E. Larrañeta, A. Kissenpfennig, R.F. Donnelly, Design and characterisation of a dissolving microneedle patch for intradermal vaccination with heat-inactivated bacteria: A proof of concept study, Int J Pharm 549 (2018) 87–95. [CrossRef]
- V Boopathy, A. Mandal, D.W. Kulp, S. Menis, N.R. Bennett, H.C. Watkins, W. Wang, J.T. Martin, N.T. Thai, Y. He, W.R. Schief, P.T. Hammond, D.J. Irvine, Enhancing humoral immunity via sustained-release implantable microneedle patch vaccination., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116 (2019) 16473–16478. [CrossRef]
- J. Park, Y.-C. Kim, Topical delivery of 5-fluorouracil-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles using microneedles for keloid treatment, Drug Deliv Transl Res 11 (2021) 205–213. [CrossRef]
- T. Zhang, B. Sun, J. Guo, M. Wang, H. Cui, H. Mao, B. Wang, F. Yan, Active pharmaceutical ingredient poly(ionic liquid)-based microneedles for the treatment of skin acne infection, Acta Biomater 115 (2020) 136–147. [CrossRef]
- X. Ning, C. Wiraja, W.T.S. Chew, C. Fan, C. Xu, Transdermal delivery of Chinese herbal medicine extract using dissolvable microneedles for hypertrophic scar treatment, Acta Pharm Sin B 11 (2021) 2937–2944. [CrossRef]
- Z. Chen, X. Hu, Z. Lin, H. Mao, Z. Qiu, K. Xiang, T. Ke, L. Li, L. Lu, L. Xiao, Layered GelMA/PEGDA Hydrogel Microneedle Patch as an Intradermal Delivery System for Hypertrophic Scar Treatment, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15 (2023) 43309–43320. [CrossRef]
- S. Meng, Q. Wei, S. Chen, X. Liu, S. Cui, Q. Huang, Z. Chu, K. Ma, W. Zhang, W. Hu, S. Li, Z. Wang, L. Tian, Z. Zhao, H. Li, X. Fu, C. Zhang, MiR-141-3p-Functionalized Exosomes Loaded in Dissolvable Microneedle Arrays for Hypertrophic Scar Treatment, Small n/a (2023) 2305374. [CrossRef]
- Y. Huang, J. Li, Y. Wang, D. Chen, J. Huang, W. Dai, P. Peng, L. Guo, Y. Lei, Intradermal delivery of an angiotensin II receptor blocker using a personalized microneedle patch for treatment of hypertrophic scars, Biomater Sci 11 (2023) 583–595. [CrossRef]
- H. Wang, Y. Fu, P. Liu, F. Qu, S. Du, Y. Li, H. Du, L. Zhang, J. Tao, J. Zhu, Supramolecular Dissolving Microneedle Patch Loading Hydrophobic Glucocorticoid for Effective Psoriasis Treatment, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 15 (2023) 15162–15171. [CrossRef]
- W. Zhao, L. Zheng, J. Yang, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, T. Ma, Q. Wang, Dissolving microneedle patches-mediated percutaneous delivery of tetramethylpyrazine for rheumatoid arthritis treatment, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 184 (2023) 106409. [CrossRef]
- H. Ding, Y. Cui, J. Yang, Y. Li, H. Zhang, S. Ju, X. Ren, C. Ding, J. Zhao, ROS-responsive microneedles loaded with integrin avβ6-blocking antibodies for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis, Journal of Controlled Release 360 (2023) 365–375. [CrossRef]
- N. Ben David, Y. Richtman, A. Gross, R. Ibrahim, A. Nyska, Y. Ramot, B. Mizrahi, Design and Evaluation of Dissolvable Microneedles for Treating Atopic Dermatitis, Pharmaceutics 15 (2023). [CrossRef]
- G. Ye, R. Jimo, Y. Lu, Z. Kong, Y. Axi, S. Huang, Y. Xiong, L. Zhang, G. Chen, Y. Xiao, P. Li, K. Gou, R. Zeng, Multifunctional natural microneedles based methacrylated Bletilla striata polysaccharide for repairing chronic wounds with bacterial infections, Int J Biol Macromol 254 (2024) 127914. [CrossRef]
- L. Long, W. Liu, L. Li, C. Hu, S. He, L. Lu, J. Wang, L. Yang, Y. Wang, Dissolving microneedle-encapsulated drug-loaded nanoparticles and recombinant humanized collagen type III for the treatment of chronic wound via anti-inflammation and enhanced cell proliferation and angiogenesis, Nanoscale 14 (2022) 1285–1295. [CrossRef]
- Y. Cai, X. Xu, M. Wu, J. Liu, J. Feng, J. Zhang, Multifunctional zwitterionic microneedle dressings for accelerated healing of chronic infected wounds in diabetic rat models, Biomater Sci 11 (2023) 2750–2758. [CrossRef]
- M. Lu, X. Zhang, D. Xu, N. Li, Y. Zhao, Encoded Structural Color Microneedle Patches for Multiple Screening of Wound Small Molecules, Advanced Materials 35 (2023) 2211330. [CrossRef]
- P.P. Samant, M.M. Niedzwiecki, N. Raviele, V. Tran, J. Mena-Lapaix, D.I. Walker, E.I. Felner, D.P. Jones, G.W. Miller, M.R. Prausnitz, Sampling interstitial fluid from human skin using a microneedle patch., Sci Transl Med 12 (2020). [CrossRef]
- J. Xiao, S. Zhang, Q. Liu, T. Xu, X. Zhang, Microfluidic-based plasmonic microneedle biosensor for uric acid ultrasensitive monitoring, Sens Actuators B Chem 398 (2024) 134685. [CrossRef]
- L. Zheng, D. Zhu, Y. Xiao, X. Zheng, P. Chen, Microneedle coupled epidermal sensor for multiplexed electrochemical detection of kidney disease biomarkers, Biosens Bioelectron 237 (2023) 115506. [CrossRef]
- Q. He, J. Zhao, S. Du, D. Li, Z. Luo, X. You, J. Liu, Reverse iontophoresis generated by porous microneedles produces an electroosmotic flow for glucose determination, Talanta 267 (2024) 125156. [CrossRef]
- H. Huang, M. Qu, Y. Zhou, W. Cao, X. Huang, J. Sun, W. Sun, X. Zhou, M. Xu, X. Jiang, A microneedle patch for breast cancer screening via minimally invasive interstitial fluid sampling, Chemical Engineering Journal 472 (2023) 145036. [CrossRef]
- W. Park, S.-W. Maeng, J.W. Mok, M. Choi, H.J. Cha, C.-K. Joo, S.K. Hahn, Hydrogel Microneedles Extracting Exosomes for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer, Biomacromolecules 24 (2023) 1445–1452. [CrossRef]
- H. Abd-El-Azim, I.A. Tekko, A. Ali, A. Ramadan, N. Nafee, N. Khalafallah, T. Rahman, W. Mcdaid, R.G. Aly, L.K. Vora, S.J. Bell, F. Furlong, H.O. McCarthy, R.F. Donnelly, Hollow microneedle assisted intradermal delivery of hypericin lipid nanocapsules with light enabled photodynamic therapy against skin cancer, Journal of Controlled Release 348 (2022) 849–869. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ma, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, P. Gao, Transdermal codelivery system of resveratrol nanocrystals and fluorouracil@ HP-β-CD by dissolving microneedles for cutaneous melanoma treatment, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 91 (2024) 105257. [CrossRef]
- R. Xu, H. Guo, X. Chen, J. Xu, Y. Gong, P. Cao, C. Wei, F. Xiao, D. Wu, W. Chen, L. Wang, Z. Wang, Smart hydrothermally responsive microneedle for topical tumor treatment, Journal of Controlled Release 358 (2023) 566–578. [CrossRef]

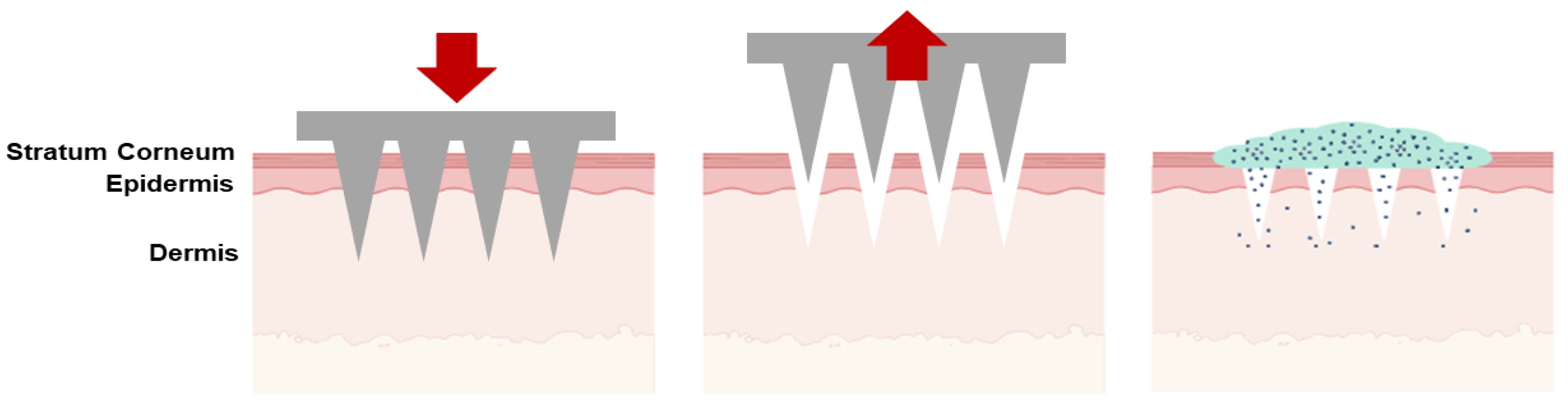
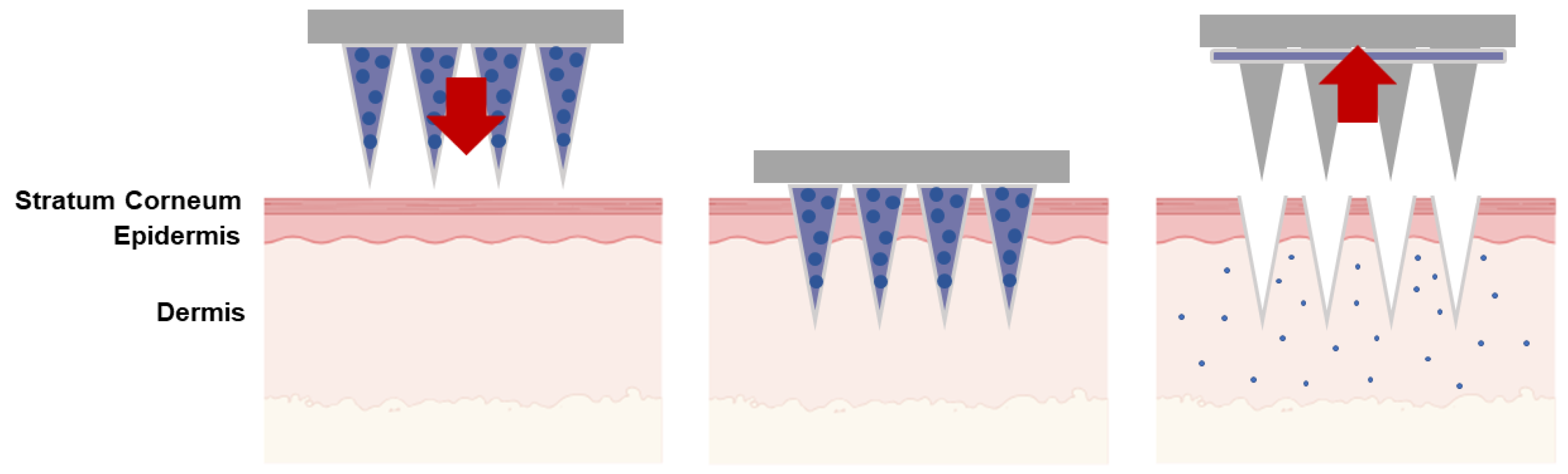
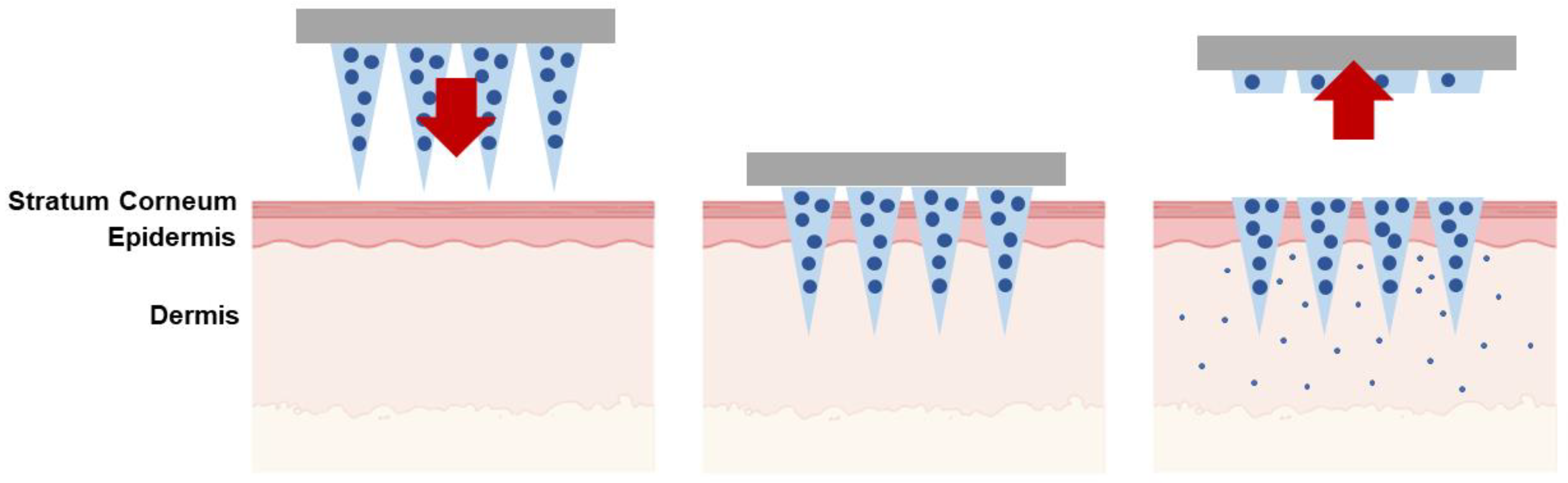
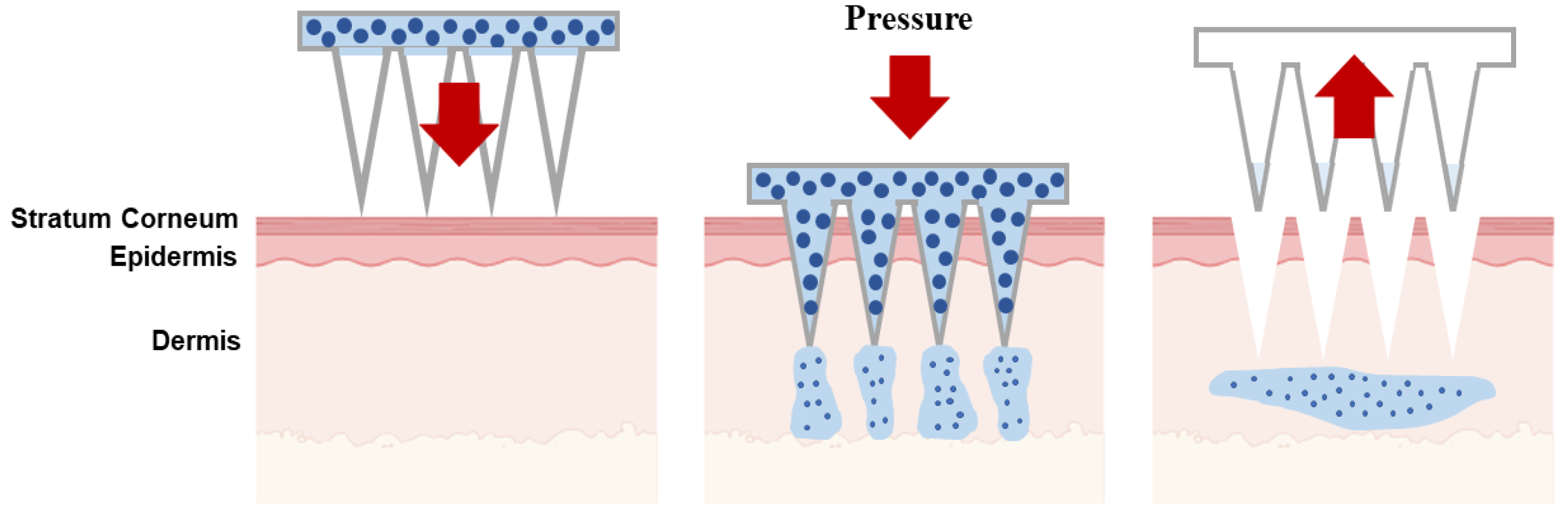
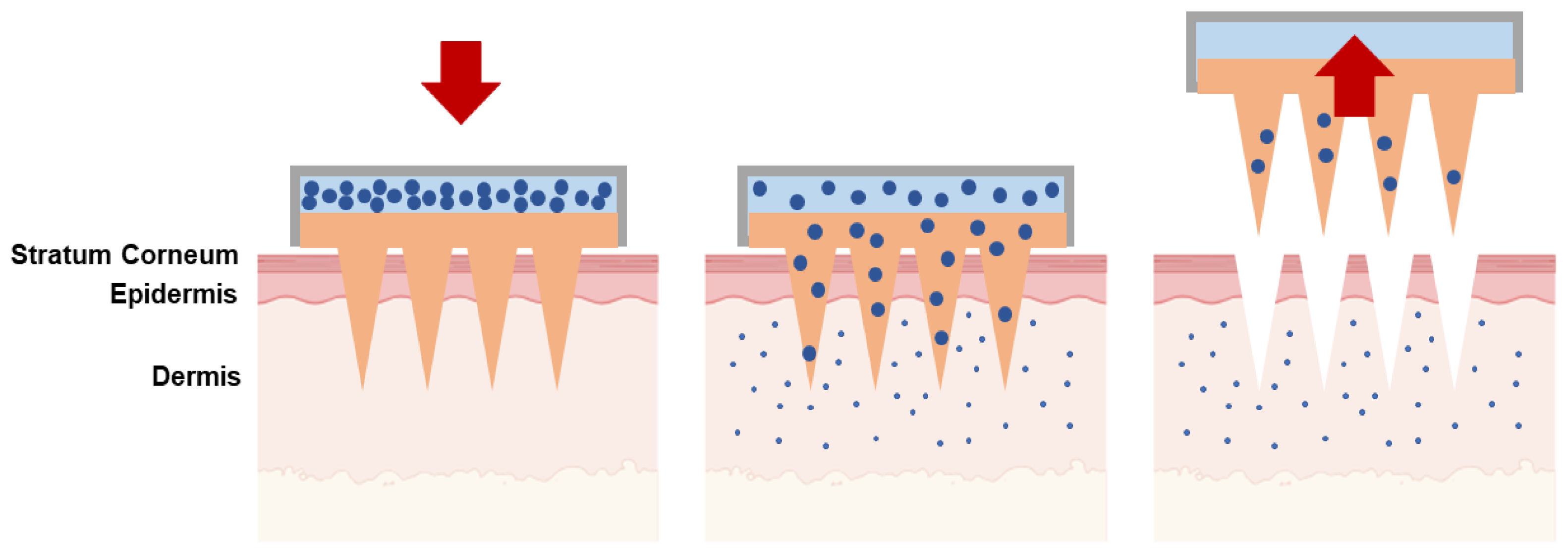
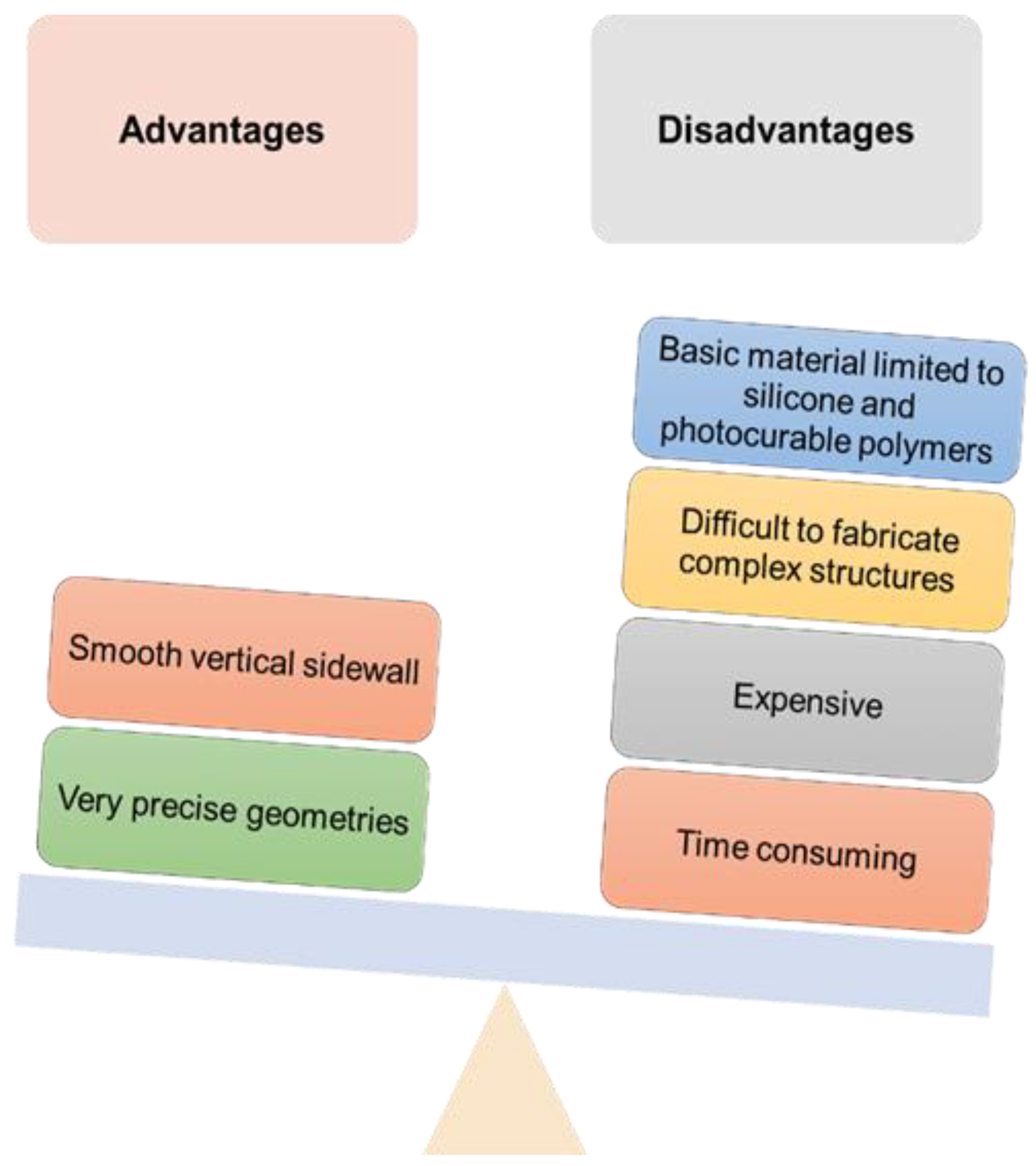
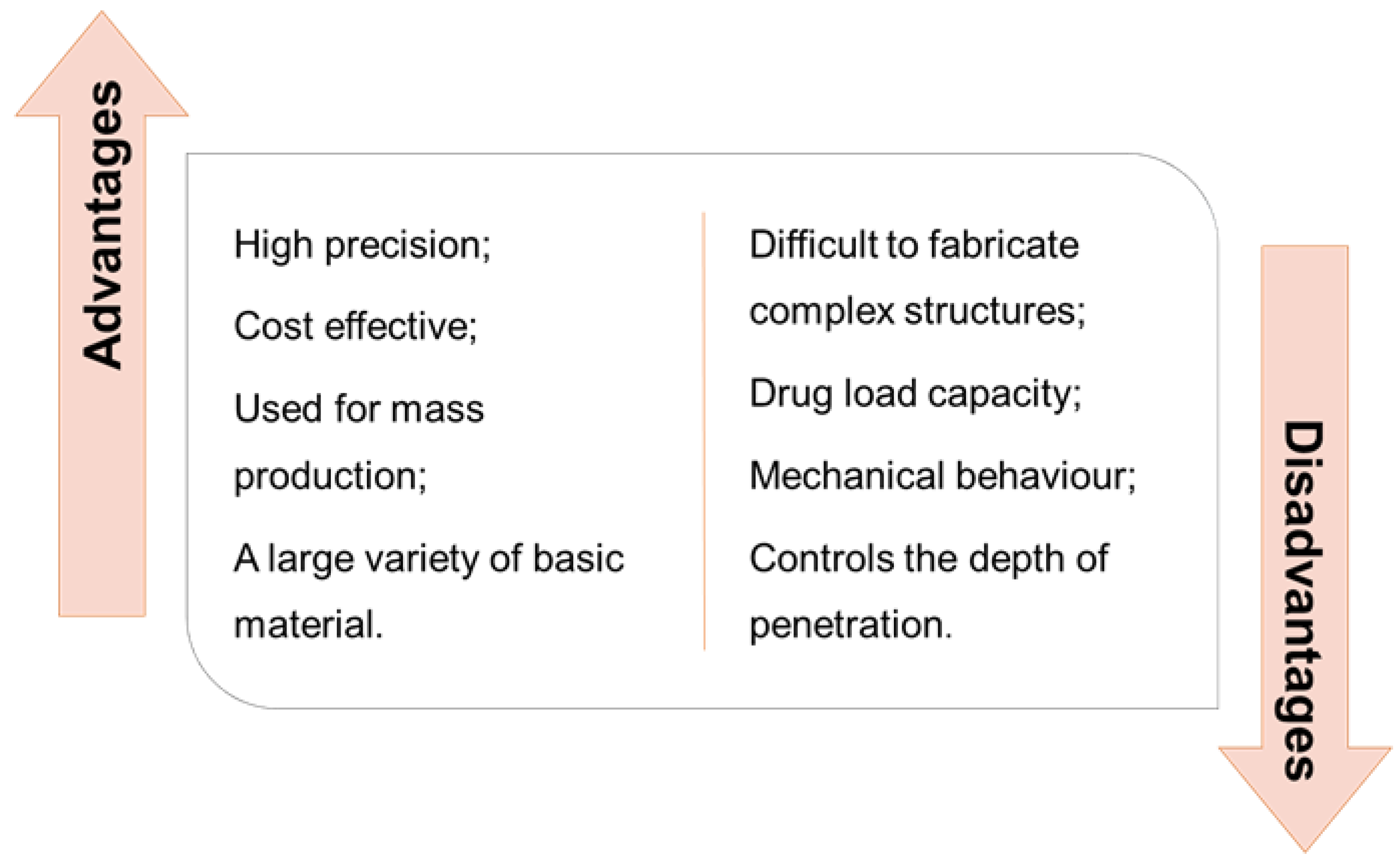
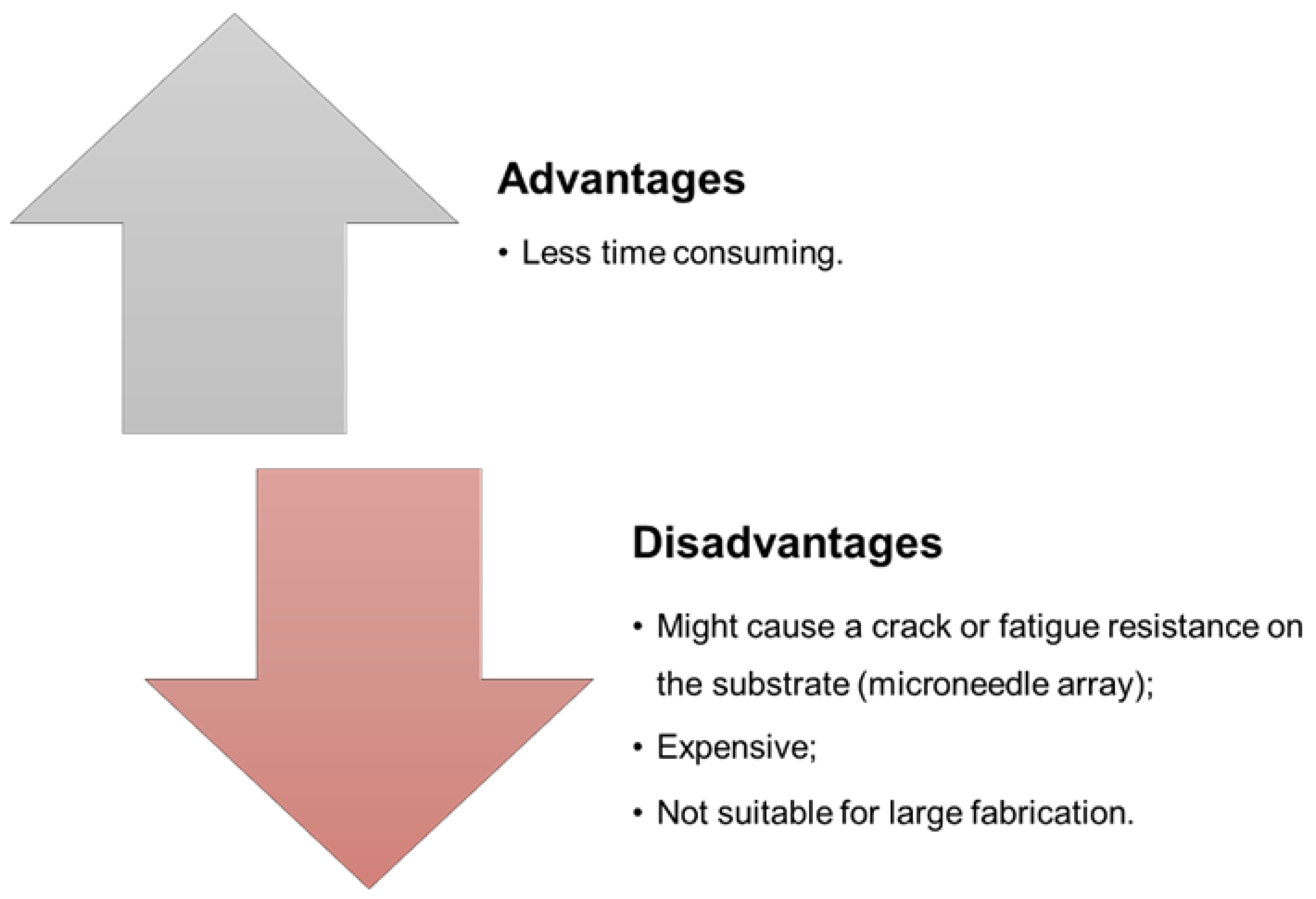

| Type of Microneedles |
Delivery Strategies | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid | The poke-and-patch method involves the application of numerous microneedles to create pores as a preparatory step. Following this, a traditional drug formulation is applied to the skin surface. | Skin pre-treatment for the delivery of potassium chloride, insulin, vaccines, cosmetics, antipsychotic medication; monitoring of glucose and lactate levels; urea sensing. | [31,32,33,34,35,36,37] |
| Coated | The coat-and-poke technique involves applying a water-soluble drug coating on solid microneedles. This coating dis-solves during administration, depositing the drug directly into the skin. | Delivery of proteins, vaccines, parathyroid hormone, insulin, desmopressin, dexamethasone; sampling, isolation and identification of biomarkers; monitoring of glucose. | [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] |
| Dissolving | The poke-and-dissolve method utilizes biodegradable or water-soluble microneedles encapsulating drugs. These microneedles dissolve upon application, releasing their therapeutic payload into the skin. | Delivery of vitamin B12, vaccines, therapeutic peptides, adenosine, doxorubicin, triamcinolone acetonide, near-IR photosensitizer (Redaporfin™), genes, sodium nitroprusside in combination with sodium thiosulfate, tofacitinib, flurbiprofen axetil, epidermal growth factor and ascorbic acid. | [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55], [56,57,58,59,60,61] |
| Hollow | The poke-and-flow method involves microneedles with a hole in the center or side of their structure, allowing the drug to flow across the skin. | Delivery of teriflunomide, ceftriaxone sodium, mRNA, vaccines; cell therapy; monitoring of glucose; synthetic amphetamine-type substance sensing; dermal interstitial fluid sampling and sensing. | [62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69] |
| Hydrogel-forming | The poke-and-release method utilizes water-insoluble microneedles injected into the skin, gradually releasing the encapsulated therapeutic molecule. The patch remains on the skin after application. | Delivery of albendazole, sildenafil citrate, metformin hydrochloride, methotrexate, tuberculosis drugs; dermal interstitial fluid sampling. | [70,71,72,73,74,75] |
| Materials | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maltose | Biocompatible; No dermatological issues were noted on the human skin following insertion; High mechanical strength; Easy degradation; Fast dissolution; Controllable viscosity; Drug stability enhancer; Efficiently deliver protein drugs; Accelerate drug delivery. | High melting point is unfavorable for heat-sensitive drugs; The use of microneedles in a humid environment is limited due to the poor moisture resistance. | [95,96,97,98] |
| Hyaluronic acid (HA) |
FDA-approved; Biocompatible; Biodegradable; Water solubility; Faster rate of dissolving; Enhance mechanical strength of dissolving microneedles; Quickly release drugs; Nontoxic and non-irritant; HA can be utilized for extended durations; No hypersensitivity effects or side effects associated with HA microneedles were identified in clinical studies. | Poor moisture resistance; Easy to shrink after microneedles fabrication. | [99,100,101,102,103,104] |
| 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) |
Improve the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs by forming inclusion compounds; Enhance mechanical strength of dissolving microneedles. | Selective inclusion. | [99,100,105] |
| Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) |
FDA-approved; Biocompatible; Biodegradable; Dissolve quickly in water; Can achieve slow and controllable release of drugs; In vitro cytotoxicity analysis and in vivo tissue response test didn’t show any side effects after treatment with CMC microneedles. | Poor moisture resistance; Poor mechanical strength. | [91,106,107] |
| Chitosan | Biocompatible, biodegradable and nontoxic; It can either be cleared by the kidneys in vivo or degraded into fragments that are subsequently cleared by the kidneys; Antibacterial properties; Sufficient mechanical strength to penetrate porcine cadaver skin; Strong adsorption ability. | Limited raw materials; Negative water solubility. | [108,109,110,111,112] |
| Starch | Non-cytotoxic; Biodegradable; Higher mechanical strength than CMC. | Pure starch is more rigid, prone to fracturing, and exhibits inferior film-forming characteristics. | [113,114,115] |
| Gelatin | Excellent biodegradability, biocompatibility, film formation, gelation, emulsification, water retention and drug loading ability; Provides high safety and slow release. | Toughness of gelatin is poor, and it is easy to fracture; Low melting point and poor stability. | [108,113] |
| Silk fibroin | FDA-approved biomaterial; Non-cytotoxic, biocompatible and the in vivo degradation products are non-inflammatory; Adequate mechanical force to pierce mouse skin for drug delivery; High tensile strength and toughness; Excellent mechanical characteristics, efficient gradual release of drugs, and favorable processing conditions. | Long fabrication time. | [116,117,118,119,120,121] |
| Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) |
Sufficient strength to pierce mouse skin; Enables the avoidance of organic solvents and high temperatures, aiding in the preservation of the drug's stability and efficacy; Biocompatible and biodegradable; Low oral and transdermal toxicity; Non-irritating to skin; No adverse effects related to treatment were observed in a 6-month study. | Poor moisture resistance. | [113,122,123,124,125,126] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) |
Sufficient strength to penetrate both porcine cadaver skin and mouse skin; FDA-approved material; Biocompatible; Biodegradable; Good viscosity and toughness; Low cytotoxicity; Dissolve quickly in water. | Poor moisture resistance. | [108,127,128,129] |
| Polylactic acid (PLA) |
FDA-approved biomaterial for the use of implants in humans; Biocompatible; Biodegradable; The in vivo degradation products are nontoxic; Excellent mechanical strength; High modulus of elasticity. | Fabrication of microneedles typically necessitates high temperatures (exceeding 170°C) or organic solvents. | [31,108,130] |
| Polyglycolic acid (PGA) |
FDA-approved biomaterial; Biocompatible; Biodegradable; The in vivo degradation products are nontoxic; Excellent mechanical strength to penetrate the regenerated human skin. | Fabrication of microneedles typically necessitates high temperatures or organic solvents. | [131] |
| Poly(lactide-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) |
Outstanding mechanical strength to pierce the murine skin; FDA-approved biomaterial; Biocompatible; Biodegradable; The in vivo degradation products are nontoxic. | Fabrication of microneedles typically necessitates high temperatures or organic solvents. | [130,132,133] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) |
FDA-approved biomaterial; Biocompatible; Biodegradable; Non-cytotoxic; The in vivo degradation products are nontoxic; Sufficient mechanical strength to penetrate porcine cadaver skin for drug delivery. | The processing temperature is comparatively lower than PLA, PGA, and PLGA, yet still above 50°C, which poses a constraint on incorporating heat-sensitive drugs such as insulin. | [130,134] |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical force drawing | Cost effective | Time consuming Low precision Unable to produce complex structures Restricted to thermoplastic materials |
| Contact drawing | Cost effective Rapid |
Low precision Unable to produce complex structures Viscosity of basic material requires adjustment |
| Electro-drawing | Cost effective Rapid |
Low precision Unable to produce complex structures Conductivity of basic material requires adjustment |
| Centrifugal drawing | Cost effective Rapid |
Low precision Unable to produce complex structures |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Fused deposition modelling (FDM) |
Cost effective Less time consuming |
Low precision Cannot fabricate complex structures Needs post treatment |
| Stereolithography (SLA) |
Less time consuming Able to fabricate complex structures |
Average precision |
| Two-photon polymerization (2PP) |
High precision Easy to fabricate complex structures |
Expensive Time consuming Difficult to fabricate objects with large volume |
| Microneedle system | Active ingredient / Sampling | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric microneedles | Ovalbumin and CpG | Vaccine delivery | [316] |
| Hollow microneedles | Insulin | Vaccine delivery | [317] |
| Dissolving microneedle patches | Heat-inactivated bacteria | Vaccine delivery | [318] |
| Solid pyramidal microneedle | Stabilized HIV envelope trimer immunogen and adjuvant | Vaccine delivery | [319] |
| Microneedle patches | Acetyl-hexapeptide-3 | Wrinkle | [283] |
| Stainless solid microneedles | 5-fluorouracil | Keloids | [320] |
| Poly(ionic liquid)-based microneedle patches | Salicylic acid | Acne | [321] |
| Dissolvable hyaluronic acid microneedles | Shikonin | Hypertrophic scars | [322] |
| Methacrylate gelatin/polyethylene glycol diacrylate double-network hydrogel microneedle patch | Betamethasone | Hypertrophic scars | [323] |
| Dissolving microneedle array | MiRNA-modified functional exosomes | Hypertrophic scars | [324] |
| Dissolving gelatin and starch microneedle patches | Losartan | Hypertrophic scars | [325] |
| Dissolving microneedle | Triamcinolone acetonide | Psoriasis | [326] |
| Dissolving microneedle patches | Tetramethylpyrazine | Rheumatoid arthritis | [327] |
| Hydrogen peroxide-responsive microneedle | Integrin αvβ6-blocking antibody | Pulmonary fibrosis | [328] |
| Dissolvable microneedles | Dexamethasone | Atopic dermatitis | [329] |
| Natural antimicrobial material microneedles | Peony leaf extract | Chronic wounds | [330] |
| Hyaluronic acid microneedle | Recombinant humanized collagen type III and naproxen loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticle | Chronic wounds | [331] |
| Zwitterionic microneedle dressings | Zinc oxide nanoparticles and asiaticoside | Chronic wounds | [332] |
| Encoded structural color microneedle patches | Photonic crystals | Wound biomarker detection | [333] |
| Microneedles patches | Interstitial fluid | Sampling of interstitial fluid | [334] |
| Microfluidic−based wearable plasmonic microneedle sensor | Interstitial fluid | Uric acid monitoring | [335] |
| Polymeric microneedle coupled electrochemical sensor array | Interstitial fluid | Diagnosis of chronic kidney disease | [336] |
| Ion-conductive porous microneedle-based glucose sensing device combined with reverse ion electroosmosis | Interstitial fluid | Glucose determination (management of chronic diseases) | [337] |
| Gelatin methacrylate-acrylic acid microneedle patch | Interstitial fluid | Breast cancer screening | [338] |
| Hydrogel microneedles | Interstitial fluid | Colorectal cancer diagnosis | [339] |
| AdminPen™ hollow microneedles array | Hypericin lipid nanocapsules | Non-melanoma skin cancer | [340] |
| Dissolvable microneedle patch | Resveratrol nanocrystals and fluorouracil@hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin | Cutaneous melanoma | [341] |
| Hydrothermally responsive multi-round acturable microneedle | Docetaxel | Subcutaneous tumours | [342] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





