1. Introduction
The global under-five child mortality rates declined by 59% from 93 deaths per 1000 live births in 1990 to 38 in 2021. Despite this, improving child survival remains a matter of urgent concern. In 2021, roughly 13,800 under-five deaths occurred every day [
1]. In 2015, the UN General Assembly set SDGs of bringing down under-five child mortality to 25 deaths per 1000 live births by 2030 [
2]. Two regions- Sub-Saharan Africa (2.8 million under-five deaths) and South Asia (1.4 million under-five deaths) collectively accounted for 51% of the global under-five population.
In India, 26 million children are born every year. Children (0-6 years) comprise 13% of the country's total population [
3]. Studying the Under-Five Mortality Rate is important from a public health perspective.
India has shown a significant decline of three points from 2019 (32 per 1000 live births in 2020 against 35 per 1000 live births in 2019). It varies from 36 in rural areas to 21 in urban areas [
4].
Intending to improve the nutritional and health status of children in the age group 0-6 years, the government of India in 1975 launched ‘The Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)’; Anganwadi (AWCs) is part of it [
5]. Anganwadi is a community Daycare center started as part of the Integrated Child Development Service program to improve child health and malnutrition. A total of 1.396 million Anganwadi are registered in the country [
6]. Out of which 0.136 million are in urban areas whereas the rest are in rural areas of the country.
Over fifty percent of Indians (759 million) are active Internet users and this user base is expected to grow to 900 million by 2025. Out of 759 million active internet users in India for 2022, 399 million are from rural India while 360 million are urbans. Out of the total internet users, 54% are male users. However, it is interesting to know that 57% of all new users in 2022 were females [
7].
Burgeoning studies show that the Internet plays an important role in public health awareness and improvement [
8,
9,
10,
11]. A study shows that being female is positively associated with a preference for internet health information-seeking behaviors [
12,
13]. The COVID-19 pandemic has unearthed our reliance on broadband internet, not as a luxury but as an essential utility such as water and electricity [
14]. Broadband internet access is a super determinant of health because many other social determinants (e.g., education, health care, food, income) hinge on it [
15].
There is no study available to show whether there is any effect of internet access to women on reducing the under-five mortality rate. If there is any positive relation persists then the results may be used to frame strategic policies to provide targeted information in regional languages to these women. At the same time, there is no study available to show, how effective AWCs are in lessening the U5MR. This comparative analysis may help to understand the situation better and help frame policies to provide more health-related information access via the Internet by government and private companies. The results obtained and the policies framed can also be used for betterment in sub-Saharan and south-Asian countries.
2. Methods
2.1. Data:
We used anonymized, publicly available secondary data from the India National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5). The survey work for the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) was planned in two phases. The first phase was carried out for 17 states and 5 Union territories and the second phase has been completed in 11 States and 3 UTs. The data was collected from the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), Government of India.
A uniform sample design, which is representative at the national, state/union territory, and district levels was adopted for each round of the survey. The NFHS-5 survey protocol was reviewed and approved by the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) Institutional Review Board.
Data related to the number of Anganwadi centers per state has been collected from the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
2.2. Study Population:
Our sample consisted of 724,115 women in the age group of 15-49 years. The majority of India’s population growth comes from rural and underprivileged areas, while the rise in income comes from the urban privileged population. So, studying both populations were considered to help better understand the issue.
Population is divided into two sub-samples for study-Urban women, and rural women. For better analysis of data, the country is divided into regions- 1)The northern region- has six states- Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Uttarakhand, Haryana, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh; 2) The southern region contains five states- Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana; 3) Eastern region- is consisting of the states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal, 4)Western region states are Rajasthan, Maharashtra Gujarat and Goa; 5) Central region consists of two states- Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh 6)North-East region includes-eight States viz. Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura. Union territories (Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Lakshadweep, Puducherry, Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir) are grouped as per their geographical locations.
2.3. Ethics Statements:
2.3.1. Ethics Approval
Our study is based on the publicly available dataset of the NFHS-5 surveys with no identifiable information on the participants and can be freely accessed from the NFHS website. The ethical approval for the NFHS-5 surveys is obtained from the ethics review board of the International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai, India. These surveys are reviewed and approved by the ICF Institutional Review Board. Informed written consent for participation in this survey is obtained from the respondents during the survey. Each individual’s approval is sought before the patient interview, as per the consistent methodology followed in these national surveys.
2.4. Statistical Analysis:
Linear regression analysis of national data was done for the internet access to women and U5MR. Linear regression is used to model the relationship between two variables and estimate the value of a response by using a line-of-best fit. Statistical software GraphPad has been used for the descriptive as well as linear regression analysis.
The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) is used to measure the strength of a linear association between two variables. Pearson Correlation Coefficient Calculator of Social Science Statistics
www.socscistatistics.com is used in this study.
3. Results:
Urban women of Himachal Pradesh (78.9%) have the highest number of women with internet access in the northern region of India (
Table 1). It is followed by Chandigarh (75.2%), Punjab (64.1%) and Delhi (63.7%). Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh have 50-60% of the women population with internet access. In all these states, rural women have comparatively lower internet access. Compared to data of NFHS-4, U5MR has reduced in every state of Northern India, but it is still substantial in rural Uttar Pradesh (62.5%). In northern India, Jammu and Kashmir (urban as well as rural) and Punjab (urban) have achieved the SDG target of achieving below 25 deaths per 1000 live births for under-five children.
In the northern region of India, Uttar Pradesh has shown the highest number of AWCs (189024) followed by Jammu and Kashmir (28119), Punjab (27314), Haryana (25963), Uttarakhand (20088), Himachal Pradesh (18925), and Delhi (10899). Union territories like Ladakh (1144), and Chandigarh (450) have a smaller number of AWCs. Despite having the highest number of AWCs in Uttar Pradesh, the state has reported 59.8 deaths per 1000 live births. The lowest number of deaths in U5MR is reported in Jammu and Kashmir (18.5) followed by the Union Territory of Ladakh (29.5).
In the southern part of India, urban women of Union territory of Puducherry (66.9%) are the largest group to have internet access followed by Kerala (64.9%), Lakshwadeep (61.8%), Tamil Nadu (55.8%), and Karnataka (50.1%). Less than 50% of urban women of Andhra Pradesh (33.9%) and Telangana (43.9%) have internet access. In the rural parts of most of these states other than Kerala and Puducherry, less than 50% of women are noticed for internet access. State of Kerala has only 5.2 U5MR and Union territory of Puducherry has 3.9 U5MR the lowest among the region. Compared to the data of NFHS-4, the U5MR has reduced in the entire southern region except for Andaman and Nicobar (
Table 2). In urban parts of southern India, except Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana have achieved the SDG target for U5MR. Kerala has made remarkable progress at urban (3.9 deaths for 1000 live births) as well as rural level (6.4 deaths for 1000 live births).
In the southern region, Karnataka has shown the highest number (65909) of AWCs followed by Andhra Pradesh (55615), Tamil Nadu (54442), Telangana (35693), and Kerala (33115). UTs like Puducherry (855), Andaman & Nicobar (720), and Lakshadweep (90) have comparatively very low numbers of AWCs. The UT of Puducherry has the highest number of women with Internet access with only 855 AWCs showing the lowest U5MR of 3.9 in the southern region.
In the Eastern region of India, West Bengal (122442) has the highest number of AWCs followed by Bihar (114989), Odisha (74157), and Jharkhand (38431). Jharkhand has the highest number of urban women with internet access (57.8%) followed by West Bengal (48.1%), Odisha (39.7%), and Bihar (38.4%). In rural parts of the region, less than 23 women out of 100 have access to the internet. Rural Bihar (57.4%) has the highest under-five child mortality in the region followed by urban Bihar (50.0%) whereas West Bengal, urban as well as rural has the lowest under-five mortality in the region. Compared to data of 2015-16 of NFHS-4, the under-five mortality has reduced in this region (
Table 3). In this region, only urban West Bengal has achieved the (23 deaths per 1000 live births) SDG target for U5MR.
In the Western region of India, urban as well as rural women of Goa are more in number in relation to access to the internet (
Table 4). Goa is followed by Maharashtra (38.0%), Rajasthan (36.9%), Dadra and Nagar Haveli (36.7%), and Gujrat (30.8%) for total women who have internet access. For under-five child mortality, Goa has the lowest value of 10.6 in the region whereas Rajasthan and Gujrat showed 37.6 deaths for 1000 live births. Compared to data of NFHS-4, the under-five child mortality has reduced in the region. In western India, only the state of Goa, urban as well as rural, has achieved the target of SDG for U5MR. The lowest number (10.6) of U5MR is found in Goa with only 1262 AWCs with 73.7% of women with Internet access.
In Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh of Central India, more than double the urban women have access to the Internet as compared to rural women (
Table 5). As far as child mortality in the region is concerned, approximately 50 children per 1000 live births die. This number is lower than the NFHS-4. States of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh of Central region have similar numbers of total women with internet access. At the same time, more or less similar U5MR is observed in children. Despite the considerable difference in the number of AWCs between the states, the comparable results might be due to access of the internet to women.
Urban Sikkim (90%), followed by Mizoram (83.8%) and Arunachal Pradesh (70.7%) have the highest number of women with internet access, not only in the North-East region but also in the other parts of the country (
Table 6). In rural parts of the states, this number is lower than in urban parts of the region. The state of Tripura has the lowest number of women with internet access in urban (36.6%) as well as in rural (17.7%) parts. When compared with NFHS4, Manipur, Meghalaya, and Tripura have shown an increase in under-five child mortality. In the North-East region, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh have achieved SDG targets in urban as well as rural areas. Whereas except Assam, urban parts of Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland have achieved the SDG target.
Sikkim has the lowest Under-five deaths (11.2) whereas Tripura has the highest deaths (43.3). Sikkim has only 1308 AWCs but 76.7% of women have internet access here. On the contrary, Tripura has 10146 AWCs but the lowest (22.9%) women population with Internet access in the Northeast region. It clearly shows Internet access to women is far more effective in bringing down U5MR if compared to the community-level approach of AWCs.
Table 6.
No. of operational AWCs, Women with Internet Access (%) and Child Mortality (U5MR) (per 1,000 live births) in the North-Eastern region of India.
Table 6.
No. of operational AWCs, Women with Internet Access (%) and Child Mortality (U5MR) (per 1,000 live births) in the North-Eastern region of India.
| States |
No. AWC operational |
Women with Internet Access (%) |
Child Mortality (U5MR)
(per 1,000 live births) |
U5MR in NFHS-4 |
| |
|
Urban |
Rural |
Total |
Urban |
Rural |
Total |
Total |
| Arunachal Pradesh |
5642 |
70.7 |
49.6 |
52.9 |
22.2 |
18.3 |
18.8 |
32.9 |
| Assam |
61738 |
49.0 |
24.4 |
28.2 |
33.0 |
39.9 |
39.1 |
56.5 |
| Manipur |
11509 |
50.8 |
40.4 |
44.8 |
17.1 |
36.2 |
30.0 |
25.9 |
| Meghalaya |
5896 |
57.8 |
28.0 |
34.7 |
23.4 |
42.6 |
40.0 |
39.6 |
| Mizoram |
2244 |
83.8 |
48.0 |
67.6 |
21.8 |
26.2 |
24.0 |
46.0 |
| Nagaland |
3980 |
66.5 |
40.3 |
49.9 |
22.5 |
36.8 |
33.0 |
37.5 |
| Sikkim |
1308 |
90.0 |
68.1 |
76.7 |
- |
17.8 |
11.2 |
32.2 |
| Tripura |
10146 |
36.6 |
17.7 |
22.9 |
24.4 |
49.0 |
43.3 |
32.7 |
| Mean |
12807.88 |
63.15 |
39.562 |
47.212 |
23.486 |
33.35 |
29.93 |
32.913 |
| Median |
5769 |
82.15 |
40.35 |
47.35 |
22.5 |
36.5 |
31.5 |
35.2 |
| Range |
60430 |
53.4 |
50.4 |
53.8 |
15.9 |
31.2 |
32.1 |
30.6 |
Table 7.
presents national-level data on internet access to women and the rate of under-five mortality (
Figure 1).
Table 7.
presents national-level data on internet access to women and the rate of under-five mortality (
Figure 1).
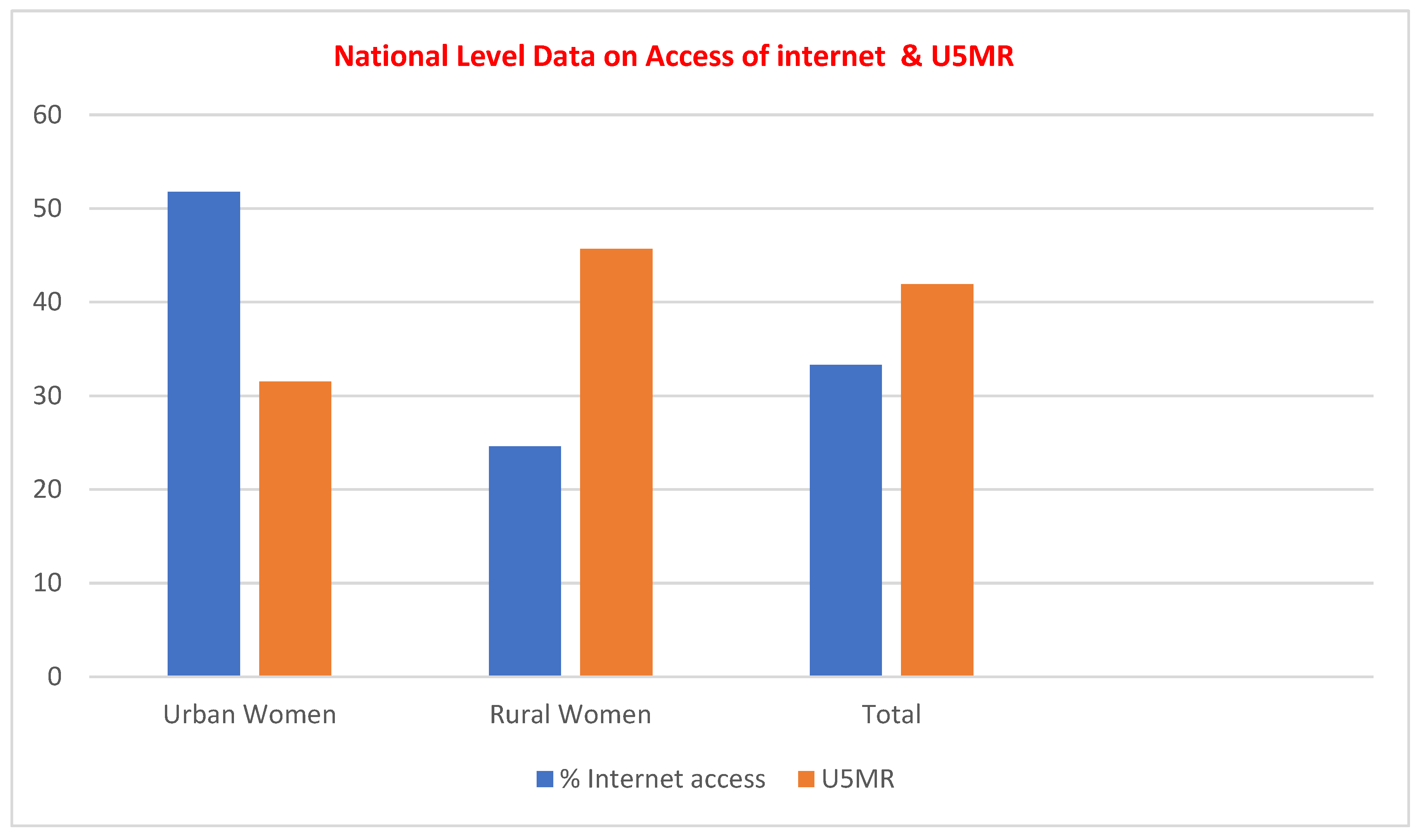
| National level data |
% of women with internet access |
Child Mortality U5MR
(per 1,000 live births) |
| Urban women |
51.8 |
31.5 |
| Rural Women |
24.6 |
45.7 |
| Total |
33.3 |
41.9 |
Figure 1.
National-level data on access to internet to women (%) and Under-Five Mortality Rate.
Figure 1.
National-level data on access to internet to women (%) and Under-Five Mortality Rate.
The results for Pearson Correlation Coefficient analysis have shown the value of R is (-0.7379). This is a moderate negative correlation, which means there is a tendency for high % women with internet access (X variable scores) to go with low Y variable scores-U5MR (and vice versa). The value of R2, the coefficient of determination, is 0.5445. The P-Value is < .00001. The result is significant at p < .10, <0.05, and <0.01
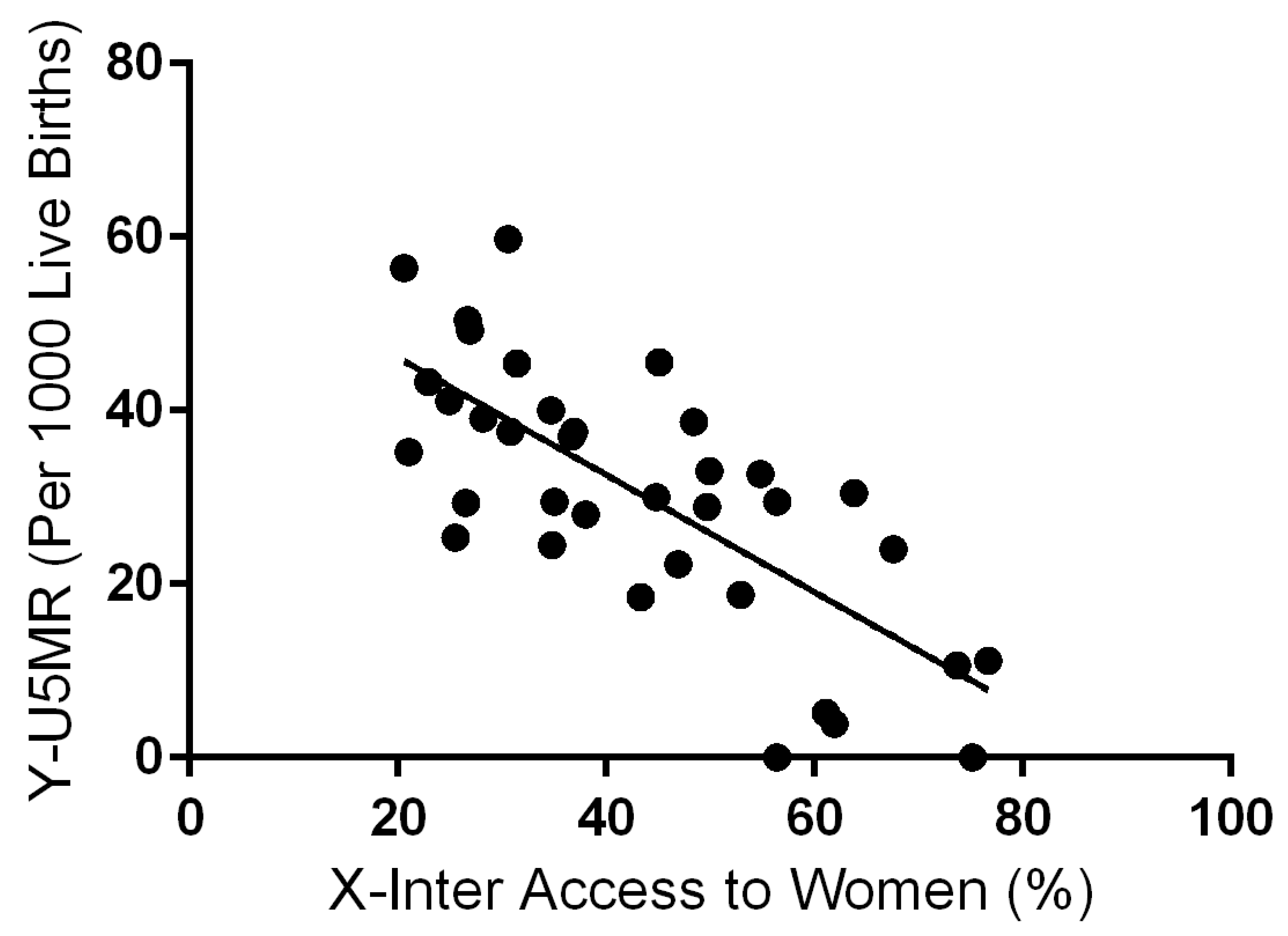
The linear regression analysis was carried out in this study shows a linear correlation between the variables of internet access to women and the under-five mortality rate in India (
Figure 2). The analysis shows Goodness of Fit with an R square value of 0.5444. The P-Value is < .0001. The result is significant.
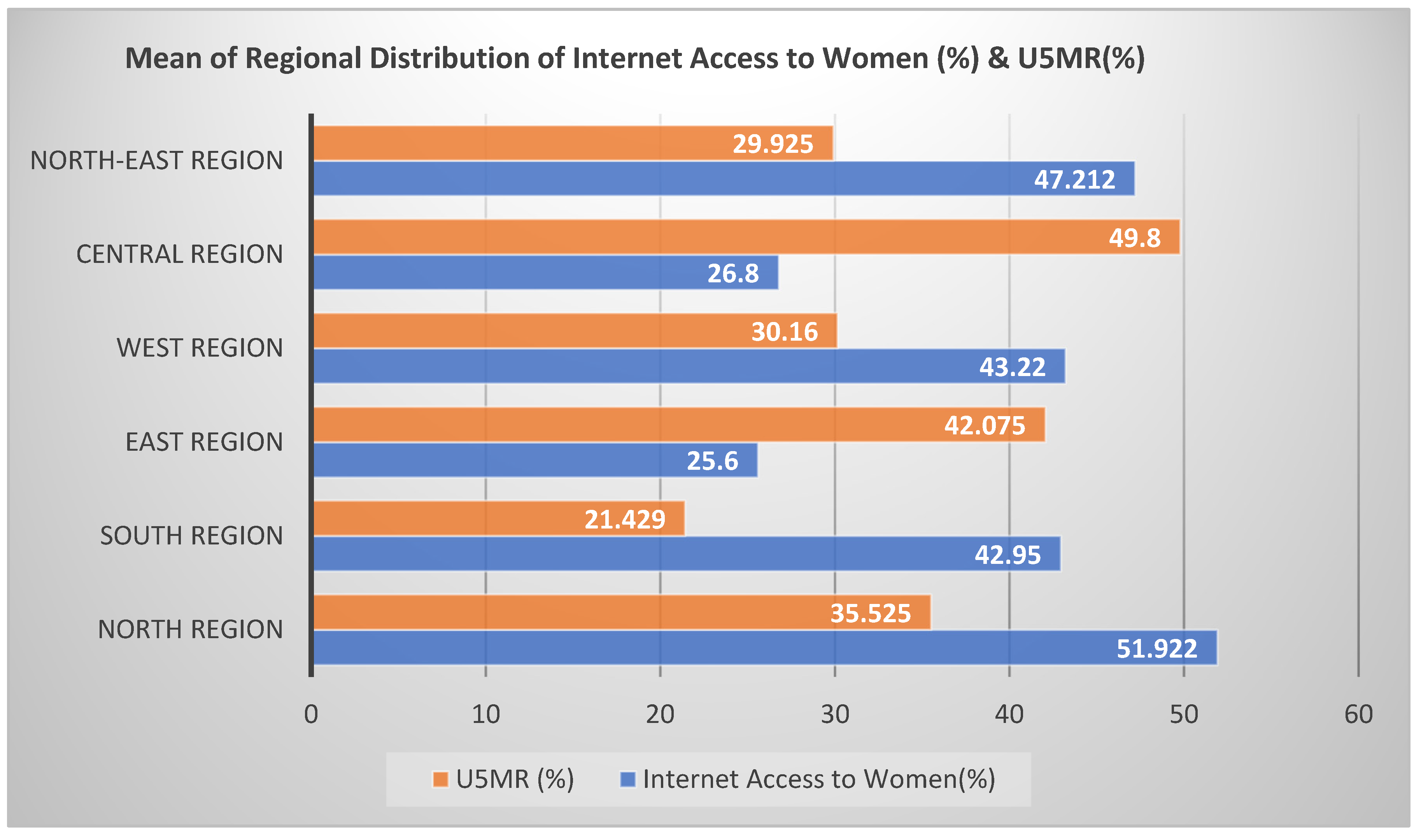
Mean/average were compared for regional situation for percentage of women with internet access and U5MR (
Figure 3). Region of north India has shown highest percentage of women (51.92%) in India with internet access. It is followed by north-east India (47.21%), western India (43.22%), south India (42.95%), central India (26.8%) and eastern India (25.6%). On average, highest U5MR is observed in central India (49.8%) followed by eastern India (42.08%), north India (35.525%), western India (30.16%), north-east India (29.9%), and south India (21.429%).
When comparing the results for the range of access to the internet for women and U5MR, the variation is observed among the various regions of India. North-East India has shown a higher value for the range (53.8%) of access to women. This means in North-East India; some states have a higher percentage of women with Internet access whereas some states have a very low number of women with Internet access. The declining range was followed by north India (44.6%), west India (42.9%), south India (40.9%), east India (10.8%) and central India (0.2%). As far as U5MR is concerned, the highest value is noticed for north India (41.3%) followed by North-east India (32.1%), south India (31.3%), east India (31%), west India (27%) and central India (1.2%).
4. Discussion:
AWCs provide a combination of services like community-managed growth monitoring, supplementary nutrition, basic healthcare, and preschool education for children below 6 years. As the health and nutritional needs of children cannot be addressed in isolation from the mother, the program also extends to pregnant and lactating mothers. For the rural population getting the right healthcare is a challenge [
16] as most people are unaware of the government or community programs they can benefit from. Our study shows a clear link between internet access to women and low U5MR.
The internet is one of the most popular sources for health information. The highest number of internet users are in the age group of 25-34 years. Studies on the internet in public health improvement have been mainly conducted during the COVID-19 outbreak. There has been a dearth of evidence on the role of internet access to women and public health outcomes like under-five child mortality.
Our study suggests that more urban women have access to the Internet in India as compared to rural women. Child mortality is higher in rural areas as compared to urban areas. If compared to NFHS-4 (2015-16) under-five mortality has reduced in almost every state of the country.
Our study results are in tandem with the study carried out in China to evaluate the role of the Internet in public health governance [
17]. This study says the digital gap between regions, urban and rural areas, and user structures has a role in public health. The development of the internet and better urban management is significant in responding to public health emergencies.
Women are more likely to be frequent internet and health app users [
18] primarily because women are more often concerned with child rearing than men [
19]. Women with greater health needs or concerns are more likely to use the Internet. This is common in women with higher levels of income and education [
20]. These studies support our finding that higher internet penetration among women and lower child mortality in urban areas of India.
Our study shows some states in India have already achieved the SDG target of ending preventable deaths of under-five children to at least as low as 25 per 1000 live births. These states are Jammu and Kashmir, Kerala, Goa, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh. Some states like Manipur, Meghalaya, and Tripura have shown an increase in under-five deaths as compared to NFHS-4.
Some states like Punjab, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, West Bengal, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Nagaland have achieved the SDG target in their urban parts but not in rural ones. This disparity in achieving the target of reducing under-five child mortality at urban and rural levels is the reason behind the intra-state as well as inter-state disparity.
A study carried out for child mortality in the Indian population using earlier National Family Health Surveys concluded that geographic regions that were underprivileged in child nutrition or wealth or female literacy are likely to be disadvantaged in terms of infant and child survival irrespective of the state to which they belong [
21].
A study carried out using NFHS5 data for urban and rural divide related to under-five child mortality also highlights wealth and education as the determinants for urban-rural mortality gaps [
22]. These studies support our observation that the financial status of the mother and her education level can help her to avail and access the internet for health which can eventually bring down U5MR.
A study on the Brazilian population shows identical results where urban houses, women, younger population, and higher income were the determinants of internet access and healthcare [
23]. Like India, Brazil is a country with economic inequality and uneven population distribution and faces challenges in achieving internet access to all. Internet was mainly assessed via cell phone here. Lack of interest, knowledge, availability, and cost were the reasons for not using the Internet in different regions of Brazil. Similar results for not using the Internet are also supported by other studies [
24]. This study has also highlighted the prevalence of varied internet access among different races where white people have more access compared to black, multi-racial, and other survey respondents. India is also a country with cultural and geographical diversity, and such kind of detailed study needs to be carried out for the Indian population.
This study also shows, that living in cities with population 100,000 to 499,999 residents, higher education, and being female are the factors associated with the use of the internet for health purposes. In that case, India has 40 cities with more than a million population, 396 cities with between 1,00,000 and 1 million population, and 2500 cities with between 10,000 and 1,00,000 population [
25]. On a priority basis, providing internet access to these cities can not only help to reduce child mortality and improve maternal health but to improve overall public health in these cities.
Over the past few years, with the rapid advancement of information technology, the penetration of the internet in India has been considerably improved everywhere, but our study highlights, that there are still significant regional differences, urban and rural differences, and user structure differences.
Other reasons might be the need for content in regional languages, difficulty with English as a foreign language, need for digital literacy across socio-economic layers specifically among women are the main challenges for penetration of the internet in different layers of socio-economic classes [
26]. How these characteristics affect India’s maternal health and child mortality should be studied in detail.
A study was carried out on Polish adults to assess the public attitudes towards the use of the Internet for health purposes as well as to identify the factors associated with the use of the Internet for health purposes [
27]. It suggests, that searching for information on drugs and their effects is the most common use of the internet. The internet is also used to search for information about doctors and medical services or medical facilities, to check online reviews of doctors, and to order drugs and dietary supplements.
Existing studies proved that information dissemination plays an important role of internet in public health. Social media sites like YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, and so on are becoming an important source of information for health protection due to low cost, fast dissemination, and user interaction in developed countries [
28,
29,
30]. In India, 25 million children are born every year. The share of children (0-6 years) accounts for 13% of the country's total population [
31]. Providing online health information possibly in regional languages by improving Internet access to women can help maternal health as well as children’s health.
The global internet penetration rates vary from 98% in Northern Europe to 25% in Middle Africa. Compared to the worldwide average, India has less than 50% internet penetration whereas 99% population of countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Norway have internet access. The digital gap observed in India might be similar to the Chinese situation where the development of the Internet remains uneven between urban areas and rural areas because of the dualistic nature of China’s urban–rural distribution [
32].
Half of all under-five deaths in 2020 occurred in just five countries, India, Pakistan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Nigeria, and Ethiopia. Nigeria and India alone account for almost a third of all deaths [
33].
India accounts for nearly one-fifth of the world’s annual childbirths [
34]. To address the issue of internet access in rural areas and to reduce the inequalities not only in U5MR but overall maternal health and child care it requires targeted measures as India’s diverse regions have different demographic distributions, house characteristics, and internet infrastructure.
ICDS is a package of six services including supplementary nutrition, pre-school non-formal education, immunization, nutrition and health education, health checkup, and referral services. Anganwadi workers deliver these services through AWCs. This program’s scale is huge and covers every village in the country. Our results are supported by the earlier findings where most of the AWCs were found inefficient and an improvement in the infrastructure and logistics is suggested to improve the efficiency of AWCs [
35,
36]. Our findings have shown the states where lower numbers of AWCS are located but because of a higher number of women in the population with internet access, the lower U5MR is noticed.
In a major initiative by the government of India, the work of Anganwadi is being digitized by providing a smartphone App to the Anganwadi workers to record data to integrate it with the health ministry. An app written in English, repeated crashes of this App, lack of mobile network reception, and electricity were the problems faced by the workers in the smooth implementation of this initiative [
37].
Based on the characteristics of the digital gap between different regions and different users of the internet in India, this paper provides an in-depth examination of the heterogeneity of the internet’s impact on reducing U5MR which will help India to tailor its future internet development and public health policies to local conditions.