Submitted:
08 April 2024
Posted:
09 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
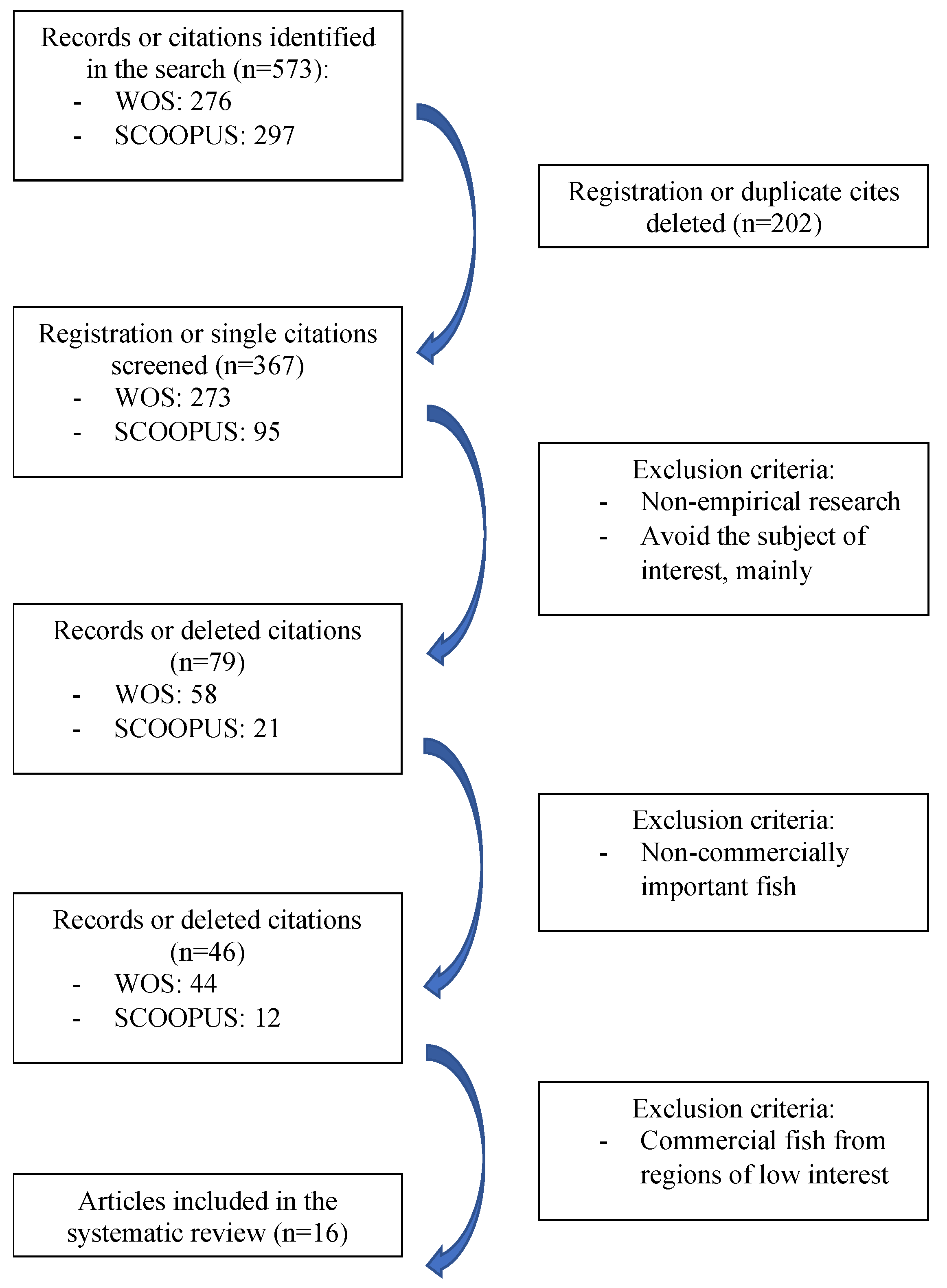
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehel J, Murphy S. Microplastics in the Food Chain: Food Safety and Environmental Aspects. In: De Voogt P, editor. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 259. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021. p. 1-49.
- Bajt O. From plastics to microplastics and organisms. FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Apr;11(4):954-966. [CrossRef]
- Matjašič T, Simčič T, Medvešček N, Bajt O, Dreo T, Mori N. Critical evaluation of biodegradation studies on synthetic plastics through a systematic literature review. Sci Total Environ. 2021 Jan 15;752:141959. [CrossRef]
- Ter Halle A, Ladirat L, Gendre X, Goudouneche D, Pusineri C, Routaboul C, Tenailleau C, Duployer B, Perez E. Understanding the Fragmentation Pattern of Marine Plastic Debris. Environ Sci Technol. 2016 Jun 7;50(11):5668-75. [CrossRef]
- Almroth BC, Eggert H. Marine Plastic Pollution: Sources, Impacts, and Policy Issues. Review of Environmental Economics and Policy. 2019;13(2):317-26.
- Agency EE. Contaminants in Europe’s Seas Moving Towards a Clean, Non-Toxic Marine Environment. 2019.
- Karbalaei S, Hanachi P, Walker TR, Cole M. Occurrence, sources, human health impacts and mitigation of microplastic pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Dec;25(36):36046-36063. [CrossRef]
- Soto AM, Sonnenschein C, Chung KL, Fernandez MF, Olea N, Serrano FO. The E-SCREEN assay as a tool to identify estrogens: An update on estrogenic environmental pollutants. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Oct;103 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):113-22. [CrossRef]
- Kannan K, Vimalkumar K. A Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights Into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 18;12:724989. [CrossRef]
- Ferrante M, Cristaldi A, Oliveri Conti G. Oncogenic Role of miRNA in Environmental Exposure to Plasticizers: A Systematic Review. J Pers Med. 2021 Jun 2;11(6):500. [CrossRef]
- Prata JC, da Costa JP, Lopes I, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci Total Environ. 2020 Feb 1;702:134455. [CrossRef]
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336-41. [CrossRef]
- Europe P. Plásticos –https://plasticseurope.org/es/knowledge-hub/plasticos-situacion-en-2020/.
- Gundogdu S, Cevik C, Atas NT. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tracts of some edible fish species along the Turkish coast. Turkish Journal of Zoology. 2020;44(4):312-23. [CrossRef]
- Digka N, Tsangaris C, Torre M, Anastasopoulou A, Zeri C. Microplastics in mussels and fish from the Northern Ionian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull. 2018 Oct;135:30-40. [CrossRef]
- Kılıç E, Yücel N. Microplastic occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract and gill of bioindicator fish species in the northeastern Mediterranean. Mar Pollut Bull. 2022 Apr;177:113556. [CrossRef]
- Ferrante M, Pietro Z, Allegui C, Maria F, Antonio C, Pulvirenti E, Favara C, Chiara C, Grasso A, Omayma M, Gea OC, Banni M. Microplastics in fillets of Mediterranean seafood. A risk assessment study. Environ Res. 2022 Mar;204(Pt C):112247. [CrossRef]
- Savoca S, Capillo G, Mancuso M, Bottari T, Crupi R, Branca C, Romano V, Faggio C, D'Angelo G, Spanò N. Microplastics occurrence in the Tyrrhenian waters and in the gastrointestinal tract of two congener species of seabreams. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2019 Apr;67:35-41. [CrossRef]
- Chenet T, Mancia A, Bono G, Falsone F, Scannella D, Vaccaro C, Baldi A, Catani M, Cavazzini A, Pasti L. Plastic ingestion by Atlantic horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus) from central Mediterranean Sea: A potential cause for endocrine disruption. Environ Pollut. 2021 Sep 1;284:117449. [CrossRef]
- Barboza LGA, Lopes C, Oliveira P, Bessa F, Otero V, Henriques B, Raimundo J, Caetano M, Vale C, Guilhermino L. Microplastics in wild fish from North East Atlantic Ocean and its potential for causing neurotoxic effects, lipid oxidative damage, and human health risks associated with ingestion exposure. Sci Total Environ. 2020 May 15;717:134625. [CrossRef]
- Gündogdu S, Rathod N, Hassoun A, Jamroz E, Kulawik P, Gokbulut C, Aït-Kaddour A, Özogul F. The impact of nano/micro-plastics toxicity on seafood quality and human health: Facts and gaps. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(23):6445-6463. [CrossRef]
- Santonicola S, Volgare M, Di Pace E, Cocca M, Mercogliano R, Colavita G. Occurrence of potential plastic microfibers in mussels and anchovies sold for human consumption: Preliminary results. Ital J Food Saf. 2021 Dec 22;10(4):9962. [CrossRef]
- Llorca M, Álvarez-Muñoz D, Ábalos M, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Santos LHMLM, León VM; et al. Microplastics in Mediterranean coastal area: Toxicity and impact for the environment and human health. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry. 2020;27:e00090. [CrossRef]
- Garrido Gamarro E, Ryder J, Elvevoll EO, Olsen RL. Microplastics in Fish and Shellfish–A Threat to Seafood Safety? Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology. 2020;29(4):417-25. [CrossRef]
- Smith M, Love DC, Rochman CM, Neff RA. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2018 Sep;5(3):375-386. [CrossRef]
- Jin M, Wang X, Ren T, Wang J, Shan J. Microplastics contamination in food and beverages: Direct exposure to humans. J Food Sci. 2021 Jul;86(7):2816-2837. [CrossRef]
- Barboza LGA, Dick Vethaak A, Lavorante BRBO, Lundebye AK, Guilhermino L. Marine microplastic debris: An emerging issue for food security, food safety and human health. Mar Pollut Bull. 2018 Aug;133:336-348. [CrossRef]
- Kumar R, Manna C, Padha S, Verma A, Sharma P, Dhar A, Ghosh A, Bhattacharya P. Micro(nano)plastics pollution and human health: How plastics can induce carcinogenesis to humans? Chemosphere. 2022 Jul;298:134267. [CrossRef]
- Pellini G, Gomiero A, Fortibuoni T, Ferrà C, Grati F, Tassetti AN, Polidori P, Fabi G, Scarcella G. Characterization of microplastic litter in the gastrointestinal tract of Solea solea from the Adriatic Sea. Environ Pollut. 2018 Mar;234:943-952. [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Barragán P, Fitzsimmons C, Lloyd-Hartley H, Tinlin-Mackenzie A, Scott C, Sugden H. Fifty-year study of microplastics ingested by brachyuran and fish larvae in the central English North Sea. Environ Pollut. 2024 Feb 1;342:123060. [CrossRef]
- Mosconi G, Panseri S, Magni S, Malandra R, D'Amato A, Carini M, Chiesa L, Della Torre C. Plastic Contamination in Seabass and Seabream from Off-Shore Aquaculture Facilities from the Mediterranean Sea. J Xenobiot. 2023 Oct 25;13(4):625-640. [CrossRef]
- Simionov IA, Călmuc M, Iticescu C, Călmuc V, Georgescu PL, Faggio C, Petrea ŞM. Human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements and microplastics accumulation in products from the Danube River Basin fish market. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;104:104307. [CrossRef]
- Piskuła P, Astel AM. Microplastics in Commercial Fishes and By-Catch from Selected FAO Major Fishing Areas of the Southern Baltic Sea. Animals (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;13(3):458. [CrossRef]
- Yue Z, Liu X, Mei T, Zhang Y, Pi F, Dai H, Zhou Y, Wang J. Reducing microplastics in tea infusions released from filter bags by pre-washing method: Quantitative evidences based on Raman imaging and Py-GC/MS. Food Chem. 2024 Jul 1;445:138740. [CrossRef]
- Jalaudin Basha NN, Adzuan Hafiz NB, Osman MS, Abu Bakar NF. Unveiling the noxious effect of polystyrene microplastics in aquatic ecosystems and their toxicological behavior on fishes and microalgae. Front Toxicol. 2023 May 4;5:1135081. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Williams AM, Gordon EB, Rudolph SE, Longo BN, Li G, Kaplan DL. Biological effects of polystyrene micro- and nano-plastics on human intestinal organoid-derived epithelial tissue models without and with M cells. Nanomedicine. 2023 Jun;50:102680. [CrossRef]
- Wootton N, Reis-Santos P, Gillanders BM. Microplastic in fish A global synthesis. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries. 2021;31(4):753-71. [CrossRef]
- Wu H, Hou J, Wang X. A review of microplastic pollution in aquaculture: Sources, effects, removal strategies and prospects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Mar 1;252:114567. [CrossRef]
| Authors | Year | Impact Factor | Quartile | Objective | Method | Results | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gundogdu et al. [14] | 2020 | 0.673 | Q4 | Documenting the presence of MP in fish, especially edible fish in the Aegean, Marmara and Eastern Mediterranean Seas. | N=243. Raman μ-analysis. Pearson correlation analysis. | Approximately 39.2% of fish in the north-eastern Mediterranean, 40.5% in the Sea of Marmara and 61.6% in the Aegean Sea had MP. | The entry of plastics into the food chain means that they can become more concentrated at higher trophic levels and therefore for humans. |
| Digka et al. [15] | 2018 | 5.553 | Q1 | To assess the ingestion of MP in four highly commercial marine species from the Ionian Sea. | FT-IR | MP was found in 37 mussels, 17 sardines, 8 sea bream and 8 red mullets. The fragments were larger. | Filter feeding and pelagic species are more prone to MP contamination. |
| Kılıç et al. [16] | 2022 | 5.553 | Q1 | To test the existence in the MP present in the GIT and gills of fish from Iskenderun Bay and Samandağ. | N=153.FT-IR | MP abundance in the GIT was higher than in gills. A negative correlation was observed between body weight and gill MP abundance. | The abundance of MP in the gills depends mainly on the MP contamination in the surrounding environment. |
| Ferrante et al. [17] | 2022 | 6.498 | Q1 | To quantify the presence of MP in various edible seafood products from the southern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. | Estimated Dose in Humans (EDI) | MP has been found in all samples of all species studied. | Quantification and characterisation in the muscle tissue of marine organisms reflects the presence of MP in the aquatic environment. |
| Savoca et al. [18] | 2019 | 4.86 | Q1 | Add new data on the occurrence and diffusion of MP in marine waters and commercial teleosts in the Tyrrhenian Sea. | Ramany FT-IR spectroscopies | 39 specimens of Pagellus spp. were examined, analyses revealed that there were stomach remains in 4 specimens. (9,1%). | MP in the Mediterranean Sea and in marine biota underlined. |
| Chenet et al. [19] | 2021 | 8.071 | Q1 | To assess the presence of plastics in the GIT content of Atlantic horse mackerel and their adverse health effects. | N=92 | MP was found in 90.6% of all specimens. Almost all plastic products have been found to leach disruptive chemicals. | The southern central Mediterranean region is heavily affected by the presence of anthropogenic waste. |
| Barboza et al. [20] | 2020 | 7.963 | Q1 | To investigate the presence of MP in commercially important fish in the North-East Atlantic Ocean and to estimate human exposure to MP through fish consumption. | N= 150 FTIR and ATR-FTIR. | MP was found in 49 % of the fish examined. The estimated human intake of MP through consumption ranged from 518 MP items/year/capita (Brazil) to 3078 MP items/year/capita (Portugal). | The presence of MP in edible fish tissues, highlights the need for further assessment of contamination of human food. Exposure is higher in countries where fish consumption is high. |
| Gündogdu et al. [21] | 2022 | 11.176 | Q1 | Review the different sources of MP, their characterisation, as well as new estimation methods. | Review | Mussels may be an important route of human exposure to MP. MP concentrations are highest in the TGI of small fish. | Environmental contamination and the resulting contamination of seafood with MP pose a potential threat to consumers. |
| Santonicola et al. [22] | 2021 | 0.34 | Q4 | To assess the presence of plastic microfibres in mussels and anchovies from the Tyrrhenian Sea. | N=30 | Santonicola et al. [22] | |
| Llorca et al. [23] | 2020 | 9.6 | Q1 | It focuses on the Mediterranean Sea and summarises the main problems and shortcomings associated with MP and NP analyses. | Review | The average concentration of floating plastics was 175 elements/km2, and for floating MP it was 127,000 particles/km2. | The risks to the environment and human health due to the presence of MP associated with complex mixtures of pollutants need to be assessed. |
| Garrido Gamarro et al. [24] | 2020 | 1.767 | Q4 | Assess the knowledge on MP in seafood in relation to a potential threat to seafood safety. | Review | MP have been reported in products such as table and sea salt, beer, honey and sugar. Drinking water and seafood products seem to be more studied. | Bivalves, which are most often eaten whole, may contribute to the amount of MP ingested. Small pelagic fish appear to make a limited contribution. Concern about PM containing hazardous POPs. |
| Smith et al. [25] | 2018 | 7.122 | Q1 | Describe the evidence on human exposure to MP through seafood and discuss possible health effects. | Systematic review, PubMed, Google Scholar. | Human health effects depend on exposure concentrations. Chemical additives in plastic can cause toxic effects. | Smith et al. [25] |
| Jin et al. [26] | 2021 | 3.167 | Q2 | To examine our current knowledge on human exposure to MP through daily intake of food and beverages. | WOS Systematic Review | Fish is the main route of human exposure to MP through the consumption of fish or fishery products. | Aquatic foodstuffs, salt and drinking water, sources of MP come from the marine and contaminated freshwater system. |
| Barboza et al. [27] | 2018 | 5.553 | Q1 | Review the evidence of contamination of seafood by MP and the consequences of its presence in the marine environment. | Review | In the marine environment, MP can act as a vehicle for chemicals. | No information is available on the fate of MP in the human body after ingestion. |
| Kumar et al. [28] | 2022 | 7.086 | Q1 | To highlight the pathways of MP and NP into food chains and how these plastic particles can cause risks to human health. | Review | The high accumulation of MP in marine organisms at lower trophic levels poses potential risks to human health. | PS and PVC can cause cancer, through inhalation and dermal exposure. The health consequences in different organisms from ingestion of MP and NP are alarming. |
| Pellini et al. [29] | 2018 | 8.071 | Q1 | To address the occurrence and characterisation of MP in the contents of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of common sole. | N=423. FT-IR. | MP was recorded in 95 % of the 533 fish sampled in 2014 and 2015, and more than one element of MP was found in 80 % of the specimens. | The main reason for the presence or absence of MP in the GIT is the spatial distribution and abundance of MP. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





