Submitted:
08 April 2024
Posted:
08 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Data Collection
3. Major Sources of Dietary Polyphenols
| Polyphenols | Sources | References |
|---|---|---|
| Non-flavonoids | ||
| Lignans | Flaxseeds | [85] |
| Phenolic acids Hydroxybenzoic acids Hydroxycinnamic acids |
Black radish, onions, and tea Cereals, coffee, fruits, tea, vegetables and wine |
[86,87,88,89] |
| Stilbenes | Grapevines, peanuts and sorghums | [90] |
| Flavonoids | ||
| Anthocyanins Cyanidin Delphinidin Pelargonidin Peonidin Petunidin Malvidin |
Sweet and sour cherries, mulberries, black elderberries, chokeberries and red cabbage Eggplant, roselle, maqui berries and black currants Raspberries and strawberries Cranberries, blueberries and plums Chokeberries Acerola, blackberries and grapevines |
[46,51,58,64,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102] |
| Coumarins Umbelliferone Esculin |
Aegle marmelo Horse-chestnut barks |
[70,103,104] |
| Flavan-3-ols (+)-Catechin (-)-Epicatechin Epigallocatechin gallate |
Peaches, apricots, apples and green tea Apricots, sour cherries, apples, cholate, cocoa and green and black teas Green tea |
[71,86,105,106,107] |
| Flavonols Kaempferol Quercetin Myricetin Fisetin |
Onion leaves, papaya shoots, pumpkins, carrots and black tea Mentha pulegium L. Whortleberries, lingonberries, chokeberries and cranberries Strawberries, apples, persimmons, grapes, onions, and cucumbers |
[75,77,78,108,109,110,111] |
| Flavanones Hesperetin Naringin Eriodictyol |
Citrus fruits, namely, grapefruits, tangerines, oranges and lemons Citrus fruits, namely grapefruits and oranges Yerba Santa |
[112,113,114,115,116] |
| Flavonones Hesperidin Liquiritin Pinocembrin |
Citrus fruits Glycyrrhiza Glabra L. leaves and roots Honey and propolis |
[117,118,119,120] |
| Isoflavones | Soybeans | [68,121,122,123,124,125] |
4. Pharmacological Properties of Dietary Polyphenols
4.1. Antioxidant Capacity
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory Abilities
4.2.1. Anti-Rheumatoid Effects
In Vitro Studies
| Polyphenolic/ Plant | Model | Dose | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro studies | ||||
| Slibinin | RAW 264.7 cells | 50, 100 and 200 μM | Th17 cell differentiation inhibition NF-kB, SIRT1 and autophagy inhibition Macrophage M2 polarization induction Apoptotic events promotion |
[237] |
| Oleuropein | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of RA patient cells | 50, 100 and 200 µg/mL | ↑ IL-10 and TGF-β Shift CD4+ T cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of RA patients toward CD4+CD25+FoxP3 Tregs |
[238] |
| Extra virgin olive oil | Synovial fibroblasts | 12.5-50 µg/mL | ↓ IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2 and microsomal PGE synthase-1, and MAPK and NF-kB signalling pathways | [239] |
| Curcumin | Synovial sarcoma SW982 cells | 5 and 10 µM | ↓ MMP1 and TNF-α | [240] |
| Quercetin | RA-fibroblasts-like synoviocytes | 1, 5 and 25 µM | ↓ IL-17-stimulated RANKL production IL-17-stimulated Osteoclast formation Th17 differentiation Modulate bone destructive processes in RA |
[243] |
| Punicalagin | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 12.5-100 µM | ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17A, MMP-1 and MMP-13 | [244] |
| Syringaldehyde | Lymphoblastic leukemia T lymphocytes | 25, 50, 100, 250, and 500 µM | ↓ CD86, CD40, MHC II and IL-23 ↑ IL-10 and antigen phagocytosis Inhibition MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathways |
[245] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 1, 3 and 10 µg/mL | ↓ Sirt1 protein, MMP1 and MMP13 | [246] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 20 µM | Inhibition of phosphorylation and acetylation of p65, c-Jun, and Fos ↓ COX-2 expression |
[247] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 1-40 µM | ↑ Nrf2-2, heme oxygenase-1, and Bcl-2/Bax, apoptosis ↓ Keap1 expression and ROS, and MDA levels block NF-κB p6 translocation, Inhibit cell proliferation and migration |
[248,249] |
| Resveratrol | RSC-364 cells | 25 and 50 µmol/L | ↓ Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and activated phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase arrest cells at G0/G1 cell-cycle ↑ apoptosis |
[250] |
| Resveratrol | U251 glioma cells | 1-100 µM | Interference on PI3K/Akt/BAD signalling pathway Inhibition of cells growth and apoptosis | [251,252] |
| Resveratrol | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells | 20 µM | interference on PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK Induce FOXO transcriptional activity Inhibition of cell migration and capillary tube formation Prevent angiogenesis |
[253] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 50 µM | Block cells at the G2/M stage ↓ TNF-α and S phase cells ratio Promote serine-threonine kinase-p53 axis, and autophagy Cells apoptosis |
[254] |
| Resveratrol | Human RA synovial MH7A cells | 100 and 200 µM | ↓ cells viability Stimulate H2A.X phosphorylation and apoptosis events Mitochondrial membrane potentials disruption Stimulate cytochrome c release from the mitochondria to the cytosol Caspase-3 and caspase-9 activation Upregulate the expression of the NAD-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 mRNA Downregulate the expression of the Bcl-X(L) mRNA Hyperplasia suppression |
[255] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 200 µM/L |
Caspase-3 activation Inhibition of cells proliferation Induces cell apoptosis |
[256] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 25-200 µM | ↓ ROS and Bax ↑ Bcl-2 levels and apoptotic cells Regulate the expression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase |
[257] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 100 µM | ↓ MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9, RANKL, osteoprotegrin | [258] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 100 µM | ↓ TNF-α by interfering with SIRT1/cortistatin pathway | [259] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 100 µM | ↑ the expression of genes involved in mitosis, cell cycle, chromosome segregation and apoptosis | [260] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 5, 15 and 45 mg/kg | ↓ IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α ↑ IL-10 and apoptosis |
[261] |
| Resveratrol | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 10 and 20 µM | ↓ urban particulate matter-induced COX-2/PGE2 release Inhibition of the activation of NADPH oxidase/ROS/NF-κB |
[262] |
| Resveratrol | Mouse preosteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells | 1, 2, 3 and 5 µM |
Mediate SIRT-1 interactions with p300 Modulate NF-kB signaling activation Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis Prevent bone loss in bone-derived cells |
[263] |
| Resveratrol + methotrexate | Synovial mononuclear cells from RA patients | 25 µM resveratrol with 0.5 μg/mL methotrexate | ↓ monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 levels | [264] |
| Curcumin | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 25-100 µM |
Induce apoptosis PGE2 inhibition Downregulate anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and the X-linked inhibitor of the apoptosis protein Upregulate pro-apoptotic Bax expression |
[241] |
| Curcumin | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes and MH7A cells | 12.5-50 µM | ↓ IL-1β, PMA-induced IL-6 and VEGF-A expression, and cells viability Inhibition of NF-κB and induced dephosphorylation of ERK1/2 ↑ apoptosis |
[242] |
| Purified grape-derived compounds | 1, 10 and 100 µM | Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells | ↓ TNF-α, IL1, IL-6 and iNOS genes | [100] |
| Gallotannins | Human mast cells | 1, 1 and 10 µg/mL | Downregulate NF-kB expression | [265] |
| Ellagic acid | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 10, 25, 50 and 100 µM | ↓ IL-6, IL-1β, MDA and TNF-α ↑ Superoxide dismutase and apoptosis |
[266] |
| Gallic acid | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 0.1 and 1 µM | ↑ caspase-3 activity Regulate Bcl-2, Bax, p53 and pAkt productions ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, CCL-2/MCP-1, CCL-7/MCP-3, COX-2, and MMP-9 |
[267] |
| Rosmarinic acid nanoparticles | Macrophages | Not mentioned | ↓ RONS and pro-inflammatory cytokines | [191] |
| ρ-Coumaric acid encapsulated with mannosylated liposomes | Macrophages | Not mentioned | ↓ RONS and pro-inflammatory cytokines Inhibition of osteoclasts differentiation Downregulate the expression of MMP-9 and NFATc1 |
[268] |
| Ferulic acid | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes | 25-300 µM | ↓ IL-17-levels Inhibition of IL-17/IL-17RA/STAT-3 signalling cascade |
[269] |
| Ferulic acid | RAW 264.7 macrophages | 25, 50 and 100 µM | Attenuate RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation ↓ bone resorption activity Downregulate NFATc1, c-Fos, TRAP, Cathepsin K and MMP-9 levels |
[270] |
| Chlorogenic acid | T cells c1 | 10-50 µg/mL | Inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption Downregulate RANKL Suppress mRNA expression of NFATc1, TRAP and OSCAR |
[271] |
| Tea polyphenol carrier-enhanced dexamethasone | Umbilical vein endothelial, murine fibroblast cells L929 and murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells | Not mentioned | ↓ inflammatory | [272] |
| Tinospora cordifolia | RAW 264.7 cells | 100, 250 and 500 µg/mL | ↓ IL-6, TNF-α, PGE2, and NO, and iNOS and COX Modulate JAK/STAT pathway |
[273] |
| Blueberry polyphenols | HIG-82 rabbit synoviocytes | 100-200 µM | ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β, MMP3 and NF-kB levels | [274] |
| Cocoa polyphenols | Mouse epidermal cells | 10 and 20 µg/mL | ↓ TNF-α-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression Inhibition PI3K and MEK1 |
[275] |
| Catechin-7,4'-O-digallate from Woodfordia uniflora | Mouse macrophages | 5-80 µM | ↓ IL-6 and IL-1β levels Regulate NF-kB signalling pathway |
[276] |
| Salacia reticulata leaves | MTS-C H7 cells | IC50 score of ~850 μg/mL | Inhibition of cells proliferation | [277] |
| In vivo studies | ||||
| Slibinin | Rats with induced RA | 50, 100 and 150 mg/kg | ↓ IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α levels, and joint inflammation | [237] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 5 mg/kg, 15 mg/kg and 45 mg/kg | ↓ abnormal proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes, swelling degree of the paw and malondialdehyde levels ↑ superoxide dismutase activity, and glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase ratio |
[278] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | ↓ progression of periodontitis and rheumatoid factor amount | [182] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | ↓ Wnt5a, MAPK3, Src kinase, and STAT3 levels | [279] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α levels, atrial apoptosis and fibrosis, and activate the AMPK/PGC-1α pathway | [280] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | ↓ serum rheumatoid factor, MMP-3, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, IgG, antinuclear antibody, TNF-α, MPO, C-reactive protein and MDA ↑ IL-10 and glutathione |
[281] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 50 mg/kg | ↓ paw swelling, TNF-α, IL-1β, TBARs, and NOx Suppress NF-κB p65 expression |
[282] |
| Resveratrol | Rabbit inflammatory RA model | 10 µMol/kg | ↓ inflammatory responses Prevent the loss of matrix proteoglycan content in the cartilage in |
[283] |
| Resveratrol | Murine collagen-induced arthritis | 15 and 20 mg/kg | Inhibition of Th17 and B-cell function | [284] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with bovine type-II collagen-induced arthritis | 400 g/kg/bw | ↓ oxidative stress and inflammation, and MDA levels ↑ serum superoxide dismutase Suppress MAPK signalling pathways, and angiogenesis |
[250] |
| Resveratrol | Adjuvant arthritis rat model | 45 mg/kg | ↓ store-operated Ca2+ entry ↑ apoptosis Interference on ORAI1-STIM1 complex |
[285] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 12.5 mg/kg | Induce the noncanonical autophagy pathway ↓ p62 expression, caspase-3 expression and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, IL-1β, C-reactive protein, and prostaglandin E2,and NF-κB synovial tissue expression |
[286] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 12.5 mg/kg | ↓ PCNA, CD68, CD3, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 staining, cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 and the level of the marker of DNA damage, 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanine | [287] |
| Resveratrol | Collagen-induced arthritis rat model | 2.5 and 10 mg/kg | Suppress MMP1 and MMP13 amounts | [246] |
| Resveratrol | Adjuvant arthritis rats | 10 and 50 mg/kg | ↓ the proliferation of concanavalin A-stimulated spleen cells, articular cartilage degeneration with synovial hyperplasia and inflammatory cell infiltration Suppress the production of COX-2 and PGE2 |
[288] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | Alleviates adjuvant arthritis-interstitial lung disease | [289] |
| Resveratrol | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | Prevent the production of pro-inflammatory via modulating JAK/STAT/RANKL signalling pathway Ameliorate fibrosis via autophagy-lysosome pathway |
[186] |
| Resveratrol combined with methotrexate loaded-nanoemulsion | Rats with induced RA | Not mentioned | ↓ inflammation Better anti-arthritic effects potentiated by resveratrol |
[290] |
| QRu-PLGA-DS nanoparticles carried resveratrol | Arthritic rats | Not mentioned | Improvements the water solubility and targeting the effectiveness of this compound Ameliorate anti-inflammatory effects ↑ M2 type macrophages transformation ↓ the recruitment of the M1 type macrophages |
[291] |
| Ellagic acid | Arthritic rats | 5, 50 and 100 mg/kg | ↓ oxidative stress and inflammation ↑ serum superoxide dismutase Suppress MAPK signalling pathways, angiogenesis and MTA1/HDAC1-mediated Nur77 deacetylation |
[266] |
| Ellagic acid | Arthritic rats | 25 mg/kg | ↓ articular edema, NF-kB, and neutrophil elastase, neutrophil extracellular traps Interference on TLR-4, peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 enzyme and COX-2 |
[292] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | Ameliorate RA symptoms ↓ histological scores in arthritic mice, as well as reduce IgG2a antibodies Suppress T cell proliferation and relative frequencies of CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells and B cell subsets ↑ the frequency of CD4+-Foxp3+ Treg cells and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase expression by CD11b+ dendritic cells, NF-kB, Nrf-2 and heme oxygenase-1 |
[293] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | Collagen-induced arthritis rat model | 50 mg/kg | ↓ TNF-α, IL-17, Nrf-2 and MDA levels ↑ heme oxygenase-1, superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase levels |
[188] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | ↓ neuroinflammation, namely by activating caspase-3 | [294] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | Mice with collagen-induced arthritis | 50 mg/kg |
↓ arthritis index Protective effects against joint destruction Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis and TH17 cells activation ↑ the number of Treg cells |
[295] |
| Extracellular vesicles-encapsulated epigallocatechin gallate | Rats with induced RA | Not mentioned | Downregulate the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α Inhibition apoptosis of chondrocytes Promote the recovery of type II collagen ↓ joint swelling |
[296] |
| Epigallocatechin | Arthritic rats | Not mentioned | ↑ reduced elastic modulus, hardness and stiffness in cartilage | [297] |
| Epigallocatechin | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | Prevent cartilage destruction in at, by imbibing myeloperoxidase activity. Moreover, | [298] |
| Green tea | Rats with induced RA t | 2-12 g/L | ↓ RA severity and IL-17 levels ↑ IL-10 levels Suppress the anti-Bhsp65 antibody response |
[299] |
| Tinospora cordifolia | Rats with induced RA | 150 mg/kg | ↓ erythema, paw edema, hyperplasia, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-17, NO and PGE2 levels phosphorylation of STAT3 and the expression of VEGF | [273] |
| Kalpaamruthaa | Rats with induced RA | 150 mg/kg | ↓ oxidative stress, myeloperoxidase and lipid peroxide and increase the activity of enzymic and non-enzymic antioxidants | [300] |
| Ribes orientale | Sprague Dawley rats with induced RA | 50, 100, 200 mg/kg | ↓ paw volume/diameter, and PGE2, COX-2, IL-1β, IL-6, NF-kB and TNF-α levels ↑ IL-4 and IL-10 |
[183] |
| Chebulanin | Collagen-induced arthritis mouse model | 80 mg/kg | suppress the progression and development of RA ↓ arthritis severity scores, paw swelling and joint destruction, IL-6 and TNF-α amounts, excised phosphorylated (p)-p38 and p-p65, phosphorylated-c-JUN N-terminal kinase and phosphorylated NF-κB and inhibitor alpha |
[185] |
| Punicalagin | Rats with induced RA | 50mg/kg/ | Prevent the translocation of p-65 Avoid the phosphorylation of IkK and Ik Bα, Modulate NF-kB pathway ↓ TNFα, IL-6, CD86, CCR7, CD40 and MHC II expression, Th1, Th17 and Th17/Th1-like ↑ IL-10 expression Suppress dendritic cells migration, which, in turn Promote the generation of Tregs via regulation of dendritic cells maturation |
[244] |
| Syringaldehyde | Rats with induced RA | 10, 25, 50 mg/kg | Alleviate paw and joint edema ↓ TNF-α and IL-6 levels ↑ IL-10 |
[245] |
| Syringaldehyde | Rats with induced RA | 100 and 200 mg/kg | ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α levels | [301] |
| Clitoria ternatea flower petals and its major compound, quercetin-3ß-D-glucoside | Rats with induced RA | 50 mg/kg Clitoria ternatea flower petals, and 2.5 mg/kg of quercetin-3ß-D-glucoside | ↓ MPO activity and pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, RNOS, and TNFR1, TLR2, iNOS, COX-2 and MMP-2 expression levels | [302] |
| Berberis orthobotrys Bien ex Aitch | Rats with induced RA | 150 mg/kg | Protection against arthritic lesions, oxidative damage and body weight alterations* Ameliorated altered hematological parameters, rheumatoid factor Contributed to positively modified radiographic and histopathological changes |
[303] |
| Diospyros malabarica (Desr.) Kostel fruits | Rats with induced RA | 250, 500 and 750 mg/kg | ↑ anti-inflammatory enzymes ↓ anti-inflammatory enzymes |
[304] |
| ρ-Coumaric acid | Rats with induced RA | 100 mg/kg | Suppress paw edema and body weight loss ↓ cartel | [272] |
| ρ-Coumaric acid | Rats with induced RA | 100 mg/kg | ↓ age, bone erosion, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17 and MCP-1, and the expression of RANKL and TRAP, iNOS and COX-2, JNK, p-JNK, and ERK1/2 Regulate the RANKL/OPG imbalance Inhibition the RANKL-induced NFATc-1 and c-Fos expression |
[192,305] |
| Chlorogenic acid | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | Attenuate liposaccharide-induced bone loss of rat femurs | [271] |
| Theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate | Collagen-induced RA mouse model | 10 mg/kg |
↓ IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, as well as MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-3 amounts Inhibition the activation of NF-kB and the phosphorylation of P38, JNK2, and ERK |
[184] |
| Cinnamtannin D1 | Rats with induced RA | 50 mg/kg | Alleviate the severity of RA ↓ clinical scores and paw swelling, inflammatory cell infiltration, cartilage damage in the joints, and IL-17, IL-6, and IL-1β levels, and the frequency of Th17 cells ↑ TGF-β and IL-10 levels and the frequence of Treg cells Inhibition of aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression and phospho-STAT3/RORγt |
[306] |
| Cinnamon barks | Mice with induced RA | 200 mg/kg | ↓ paw volume, weight loss, and IL-2, IL-4 and IFNγ levels | [307] |
| N-feruloylserotonin | Rats with induced RA | 3mg/kg | ↓ C-reactive protein, the activity of LOX, as well as mRNA transcription of TNF-α, iNOS IL-1β and IL-1β mRNA expression | [308] |
| Extra virgin olive oil | Mice with collagen-induced RA | 100 and 200 mg/kg | ↓ inflammatory markers, joint edema, cell migration, cartilage degradation and bone erosion, and also reducing COX-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 expression Inhibition c-Jun N-terminal kinase, p38, signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 |
[309] |
| Hydroxytyrosol acetate | Mice with collagen-induced RA | 0.05% | ↓ IgG1 and IgG2a, COMP, MMP-3, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-17A, and MAPKs JAK/STAT and NF-κB pathways ↑ Nrf-2 and heme oxygenase-1 |
[310] |
| mangiferin | Mice with induced RA | 50, 100 and 400 mg/kg | Inhibition of mRNA expression of cytokine genes in thymus and spleen, and also NF-κB and activating ERK1/2 ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and RANKL |
[311] |
| Sarcococca saligna | Rats with induced RA | 250 mg/kg | ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, prostaglandin E2, TNF-α and NF-κB levels, arthritic index and paw inflammation ↑ IL-4 and IL-10 levels |
[190] |
| Curcumin | Rats with induced RA | 10 mg/kg | ↓ TNF-α and IL-1β | [312] |
| Dichrostachys cinerea fruits | Rats with induced RA | 75.48 mg | ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and cortisol levels, lipid peroxidation and NOx production | [313] |
| Circaea mollis Sieb. & Zucc. plant | Freund's complete adjuvant-induced arthritis model in rats | 170-1350 mg/kg | ↓ paw and inflammatory swelling, arthritis index, TNF-α and IL-1β levels ↑ IL-10 levels |
[314] |
| Opuntia littoralis | Rats with induced RA | 10 and 20 mg/100 g bw | ↓ joint inflammation, paw swelling, edemas, MDA, and IL-1β, IL-6R, IL-6, IL-17, and IL-23, Ameliorated COX-2, NF-kB, STAT-3, PTEN, and RANKL expression Upregulate the expression of miR-28 and miR-199a |
[193] |
| Antrocaryon micraster seeds | Rats with induced RA | 25 and 100 mg/kg | ↓ cachexia, paw edema, infiltration of inflammatory cells, pannus formation, and synovium damage | [315] |
| Dried plums | Transgenic mice with induced-RA | + 20% dried plums in the normal diet | Protect articular cartilage ↓ synovitis, IL-1β, MCP1, MIP1α, MMP1 and MPP3, and RANKL expression Repress TNF-induced formation of osteoclasts and mRNA levels of cathepsin K and MMP9 Inhibition of NFATc1 expression and NF-κB activation |
[316] |
| Opuntia monacantha | Rats with induced RA | 750 mg/kg | ↓ paw edema, arthritic score, rheumatoid factor, inflammation, COX-2, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1, NF-kB, bone erosion and pannus formation Restore hemoglobin, white blood count and platelets parameters ↑ catalase and superoxide dismutase, IL-4 and IL-10 levels Inhibition of glutaminase 1 activity |
[317] |
| Solanum nigrum | Rats with induced RA | 800 mg/kg | ↓ paw edema Restore body weight, hematologic parameters, radiographic and histopathologic alterations |
[318] |
| Quercetin and quercetin-loaded chitosan | Rats with induced RA | 15 mg/kg quercetin and 10 and 20 mg/kg quercetin-loaded chitosan | ↓ TNF-α and IL-6 The nanoencapsulation of quercetin enhances its efficacy |
[319] |
| Grape polyphenols + propolis | Female rats with induced RA | 1.25 g/kg grape polyphenols mixed with 1.25 g/kg propolis | ↓ the intensity of cachexia and alleviate RA scores | [320] |
| Malvidin 3-O-β glucoside | Chronic rat adjuvant-induced arthritis with | 125 mg/kg | ↓ cachexia and arthritic paw scores | [100] |
| Phoenix dactylifera L. seeds | Rats with induced RA | 30 mg/kg | ↓ IL-1β levels, paw edema, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein | [321] |
| Liposomal drug delivery system for morin | Rats with induced RA | Not mentioned | ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, RANKL, STAT-3, p-STAT-3, VEGF, iNOS and NF-kB-p65 ↑ osteoprotegerin and murin uptake by rats synovial and spleen macrophages |
[189] |
| Clinical trials | ||||
| Low-calorie cranberry juice | 500 mL/day | Women with RA | ↓ anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies levels, pain intensity and swollen joints | [322] |
| Low-calorie cranberry juice + fish oil ω-3 fatty acids | 500 mL/day of low-calorie cranberry juice with 3 g of fish oil ω-3 fatty acids | People with rheumatoid arthritis | ↓ C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and related-pain | [323] |
| Pomegranate extract | 250 mg | RA patients | ↓ swollen, pain intensity and tender joints, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and morning stiffness ↑ glutathione peroxidase |
[324] |
| Resveratrol | 1 g | RA patients | ↓ joint swelling, tenderness, TNF-α, IL-6, protein C-reactive, MMP-3, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and undercarboxylated osteocalcin | [325] |
In Vivo Studies
Clinical Trials
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maity, S.; Wairkar, S. Dietary polyphenols for management of rheumatoid arthritis: Pharmacotherapy and novel delivery systems. Phytother Res 2022, 36, 2324–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, K.; Nossent, J.; Preen, D.; Keen, H.; Inderjeeth, C. The global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis based on a systematic review. Rheumatology International 2021, 41, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, D.; Antonucci, M.; Petrelli, F.; Bilia, S.; Alunno, A.; Puxeddu, I. One year in review 2020: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2020, 38, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silman, A.J.; Pearson, J.E. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2002, 4, S265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.; Liu, Q.; Yin, H.; Wang, K.; Diao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Guo, A. Prevalence Trends of Site-Specific Osteoarthritis From 1990 to 2019: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2022, 74, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Research 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzer, T.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Mysler, E.; Hochberg, M.C.; Doherty, M.; Ehrsam, E.; Gitton, X.; Krammer, G.; Mellein, B.; Matchaba, P.; et al. Comparison of lumiracoxib with naproxen and ibuprofen in the Therapeutic Arthritis Research and Gastrointestinal Event Trial (TARGET), reduction in ulcer complications: randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 2004, 364, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.; Niño, A.; Acosta-Guzmán, P.; Guevara-Pulido, J. Design and synthesis of a potential selective JAK-3 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis using predictive QSAR models. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2024, 45, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Banik, S. Pharmacotherapy Options in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinical Medicine Insights: Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 6, CMAMD–S5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.; Mousavi, M.J.; Jamalzehi, S.; Alimohammadi, R.; Bezvan, M.H.; Mohammadi, H.; Aslani, S. Strategies toward rheumatoid arthritis therapy; the old and the new. Journal of cellular physiology 2019, 234, 10018–10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Systematic Review: Comparative Effectiveness and Harms of Disease-Modifying Medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2008, 148, 124–134. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L. Side effects of methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2018, 158, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brickman, A.M.; Yeung, L.K.; Alschuler, D.M.; Ottaviani, J.I.; Kuhnle, G.G.C.; Sloan, R.P.; Luttmann-Gibson, H.; Copeland, T.; Schroeter, H.; Sesso, H.D.; et al. Dietary flavanols restore hippocampal-dependent memory in older adults with lower diet quality and lower habitual flavanol consumption. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2023, 120, e2216932120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamel, T.H.; Abdel-Aal, E.M.; Tucker, A.J.; Pare, S.M.; Faughnan, K.; O'Brien, C.D.; Dykun, A.; Rabalski, I.; Pickard, M.; Wright, A.J. Consumption of whole purple and regular wheat modestly improves metabolic markers in adults with elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein: a randomised, single-blind parallel-arm study. The British journal of nutrition 2020, 124, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, T.; Masumoto, S.; Moriichi, N.; Ohtake, Y.; Kanda, T. Administration of Apple Polyphenol Supplements for Skin Conditions in Healthy Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcusa, R.; Carrillo, J.; Xandri-Martínez, R.; Cerdá, B.; Villaño, D.; Marhuenda, J.; Zafrilla, M.P. Effects of a Fruit and Vegetable-Based Nutraceutical on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Status in the Plasma of a Healthy Population: A Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, and Randomized Clinical Trial. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, E.K.; Terwoord, J.D.; Litwin, N.S.; Vazquez, A.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Ghanem, N.; Michell, K.A.; Smith, B.T.; Grabos, L.E.; Ketelhut, N.B.; et al. Daily blueberry consumption for 12 weeks improves endothelial function in postmenopausal women with above-normal blood pressure through reductions in oxidative stress: a randomized controlled trial. Food & function 2023, 14, 2621–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-García, I.; Ortíz-Flores, R.; Badía, R.; García-Borrego, A.; García-Fernández, M.; Lara, E.; Martín-Montañez, E.; García-Serrano, S.; Valdés, S.; Gonzalo, M.; et al. Rich oleocanthal and oleacein extra virgin olive oil and inflammatory and antioxidant status in people with obesity and prediabetes. The APRIL study: A randomised, controlled crossover study. Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2023, 42, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackner, S.; Mahnert, A.; Moissl-Eichinger, C.; Madl, T.; Habisch, H.; Meier-Allard, N.; Kumpitsch, C.; Lahousen, T.; Kohlhammer-Dohr, A.; Mörkl, S.; et al. Interindividual differences in aronia juice tolerability linked to gut microbiome and metabolome changes-secondary analysis of a randomized placebo-controlled parallel intervention trial. Microbiome 2024, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.F.; Liao, Y.R.; Shen, Y.C.; Han, Y.C.; Golovinskaia, O.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; Hung, C.C.; Wang, C.K. Improvement on blood pressure and skin using roselle drink: A clinical trial. Journal of food biochemistry 2022, 46, e14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.-J.; Tzen, J.T.C. The Potential Role of Phenolic Acids from Salvia miltiorrhiza and Cynara scolymus and Their Derivatives as JAK Inhibitors: An In Silico Study. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23, 4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.Y.; Kim, K.D.; Yoo, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Hwangbo, C. Phytochemicals Targeting JAK–STAT Pathways in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Insights from Animal Models. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 26, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, C.; Almeida, L.; Barbosa, R.M.; Laranjinha, J. Luteolin suppresses the JAK/STAT pathway in a cellular model of intestinal inflammation. Food & function 2017, 8, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kour, G.; Choudhary, R.; Anjum, S.; Bhagat, A.; Bajaj, B.K.; Ahmed, Z. Phytochemicals targeting JAK/STAT pathway in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Is there a future? Biochemical Pharmacology 2022, 197, 114929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.R.; Flores-Félix, J.D.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Falcão, A.; Alves, G.; Silva, L.R. Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activities of Portuguese Prunus avium L. (Sweet Cherry) By-Products Extracts. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, Q.; Long, Y.; Qu, Q.; Qi, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Ai, K. microRNAs: critical targets for treating rheumatoid arthritis angiogenesis. Journal of Drug Targeting 2024, 32, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Costa, A.R.; Flores-Félix, J.D.; Falcão, A.; Alves, G.; Silva, L.R. Anti-Inflammatory and Antiproliferative Properties of Sweet Cherry Phenolic-Rich Extracts. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. Journal of Natural Products 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, H.A.M. Phenolic Compounds: Classification, Chemistry, and Updated Techniques of Analysis and Synthesis. In Phenolic Compounds; Farid, A.B., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2021; p. Ch. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Gaspar, D.; Flores-Félix, J.D.; Falcão, A.; Alves, G.; Silva, L.R. Effects of Functional Phenolics Dietary Supplementation on Athletes' Performance and Recovery: A Review. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Kitabatake, M.; Kayano, S.-i.; Ito, T. Dietary Phenolic Compounds: Their Health Benefits and Association with the Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carregosa, D.; Carecho, R.; Figueira, I.; N Santos, C. Low-Molecular Weight Metabolites from Polyphenols as Effectors for Attenuating Neuroinflammation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2020, 68, 1790–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capanoglu, E.; Chen, F. The interaction between food components and gut microbiota. Food chemistry 2024, 442, 138117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwumah, Y.; Walker, L.T.; Verghese, M. Peanut skin color: a biomarker for total polyphenolic content and antioxidative capacities of peanut cultivars. International journal of molecular sciences 2009, 10, 4941–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre, G.; Piccardo, D.; Sergio, G.-A.; Pérez-Navarro, J.; García-Romero, E.; Mena-Morales, A.; González-Neves, G. Stilbenes in grapes and wines of Tannat, Marselan and Syrah from Uruguay: This article is published in cooperation with the 11th OenoIVAS International Symposium, June 25–28 2019, Bordeaux, France. OENO One 2020, 54, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, V.S.; Cole, R.J. trans-Resveratrol Content in Commercial Peanuts and Peanut Products. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 1999, 47, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Göksel, Z.; Erdoğan, S.S.; Öztürk, A.; Atak, A.; Özer, C. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Content of Seed, Skin and Pulp Parts of 22 Grape (Vitis vinifera L.) Cultivars (4 Common and 18 Registered or Candidate for Registration). Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2015, 39, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.F.; Alcorn, J. Flaxseed Lignans as Important Dietary Polyphenols for Cancer Prevention and Treatment: Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, and Molecular Targets. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, F.; Janiak, M.A.; Sulewska, K.; Peiretti, P.G.; Karamać, M. Phenolic Compound Profile and Antioxidant Capacity of Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) Harvested at Different Growth Stages. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomah, B.D.; Kenaschuk, E.O.; Mazza, G. Phenolic Acids in Flaxseed. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 1995, 43, 2016–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.H.; Chung, S.J.; Lee, S.W.; Park, Y.B.; Lee, S.K.; Park, M.C. Gallic acid, a natural polyphenolic acid, induces apoptosis and inhibits proinflammatory gene expressions in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Joint bone spine 2013, 80, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Rodrigues, M.; Santos, A.O.; Alves, G.; Silva, L.R. Antioxidant Status, Antidiabetic Properties and Effects on Caco-2 Cells of Colored and Non-Colored Enriched Extracts of Sweet Cherry Fruits. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowska, M.; Gołębiewska, E.; Świderski, G.; Męczyńska-Wielgosz, S.; Lewandowska, H.; Pietryczuk, A.; Cudowski, A.; Astel, A.; Świsłocka, R.; Samsonowicz, M.; et al. Plant-Derived and Dietary Hydroxybenzoic Acids—A Comprehensive Study of Structural, Anti-/Pro-Oxidant, Lipophilic, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Activity in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Cell Lines. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawula, S.; Gokul, A.; Niekerk, L.-A.; Basson, G.; Keyster, M.; Badiwe, M.; Klein, A.; Nkomo, M. Insights into the Effects of Hydroxycinnamic Acid and Its Secondary Metabolites as Antioxidants for Oxidative Stress and Plant Growth under Environmental Stresses. Current Issues in Molecular Biology 2024, 46, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Campos, G.; Alves, G.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Moreno, D.A.; Silva, L.R. Physical and phytochemical composition of 23 Portuguese sweet cherries as conditioned by variety (or genotype). Food Chem 2021, 335, 127637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksuz, T.; Tacer-Caba, Z.; Nilufer-Erdil, D.; Boyacioglu, D. Changes in bioavailability of sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) phenolics and anthocyanins when consumed with dairy food matrices. Journal of food science and technology 2019, 56, 4177–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Rodrigues, M.; Flores-Félix, J.D.; Campos, G.; Nunes, A.R.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Silva, L.R.; Alves, G. Sweet cherry phenolics revealed to be promising agents in inhibiting P-glycoprotein activity and increasing cellular viability under oxidative stress conditions: in vitro and in silico study. Journal of food science 2022, 87, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, P.; Wojdyło, A.; Samoticha, J. Evaluation of phytochemicals, antioxidant capacity, and antidiabetic activity of novel smoothies from selected Prunus fruits. Journal of Functional Foods 2016, 25, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Ocampo, E.; Torrejón-Valqui, L.; Muñóz-Astecker, L.D.; Medina-Mendoza, M.; Mori-Mestanza, D.; Castro-Alayo, E.M. Antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content and phenolic compounds of pulp and bagasse of four Peruvian berries. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Félix, J.D.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Meirinho, S.; Nunes, A.R.; Alves, G.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Moreno, D.A.; Silva, L.R. Differential response of blueberry to the application of bacterial inoculants to improve yield, organoleptic qualities and concentration of bioactive compounds. Microbiological Research 2024, 278, 127544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellappan, S.; Akoh, C.C.; Krewer, G. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Georgia-grown blueberries and blackberries. J Agric Food Chem 2002, 50, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Młynarczyk, K.; Walkowiak-Tomczak, D.; Łysiak, G.P. Bioactive properties of Sambucus nigra L. as a functional ingredient for food and pharmaceutical industry. Journal of Functional Foods 2018, 40, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shi, C.; Shen, D.; Han, T.; Wu, W.; Lyu, L.; Li, W. Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanins and Non-Anthocyanin Flavonoids in Blackberry from Different Growth Stages. Foods 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, C.; Codină, G.G.; Héjja, M.; András, C.D.; Chetrariu, A.; Dabija, A. Study of Antioxidant Activity of Garden Blackberries (Rubus fruticosus L.) Extracts Obtained with Different Extraction Solvents. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Ranieri, M.; Lv, D.; Zhang, M.; Charles, M.T.; Tsao, R.; Rekika, D.; Khanizadeh, S. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Capacity of Newly Developed Strawberry Lines from British Columbia and Quebec. International Journal of Food Properties 2011, 14, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondheimer, E.; Karash, C.B. The Major Anthocyanin Pigments of the Wild Strawberry (Fragaria vesca). Nature 1956, 178, 648–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, T.; Patel, H.; Akande, O.E.; Galam, D.C.A. Total Anthocyanin Content of Strawberry and the Profile Changes by Extraction Methods and Sample Processing. Foods 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orak, H.H. Total antioxidant activities, phenolics, anthocyanins, polyphenoloxidase activities of selected red grape cultivars and their correlations. Scientia Horticulturae 2007, 111, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kőrösi, L.; Molnár, S.; Teszlák, P.; Dörnyei, Á.; Maul, E.; Töpfer, R.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Szabó, É.; Röckel, F. Comparative Study on Grape Berry Anthocyanins of Various Teinturier Varieties. Foods 2022, 11, 3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negro, C.; Aprile, A.; De Bellis, L.; Miceli, A. Nutraceutical Properties of Mulberries Grown in Southern Italy (Apulia). Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denev, P.; Kratchanova, M.; Petrova, I.; Klisurova, D.; Georgiev, Y.; Ognyanov, M.; Yanakieva, I. Black Chokeberry (<i>Aronia melanocarpa</i> (Michx.) Elliot) Fruits and Functional Drinks Differ Significantly in Their Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity. Journal of Chemistry 2018, 2018, 9574587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak-Drozd, K.; Oniszczuk, T.; Soja, J.; Gancarz, M.; Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.; Markut-Miotła, E.; Oniszczuk, A. The Efficacy of Black Chokeberry Fruits against Cardiovascular Diseases. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimerdová, B.; Bobríková, M.; Lhotská, I.; Kaplan, J.; Křenová, A.; Šatínský, D. Evaluation of Anthocyanin Profiles in Various Blackcurrant Cultivars over a Three-Year Period Using a Fast HPLC-DAD Method. Foods 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milić, A.; Daničić, T.; Tepić Horecki, A.; Šumić, Z.; Teslić, N.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P.; Pavlić, B. Sustainable Extractions for Maximizing Content of Antioxidant Phytochemicals from Black and Red Currants. Foods 2022, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiczkowski, W.; Szawara-Nowak, D.; Topolska, J. Red cabbage anthocyanins: Profile, isolation, identification, and antioxidant activity. Food Research International 2013, 51, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabek Uher, S.; Radman, S.; Opačić, N.; Dujmović, M.; Benko, B.; Lagundžija, D.; Mijić, V.; Prša, L.; Babac, S.; Šic Žlabur, J. Alfalfa, Cabbage, Beet and Fennel Microgreens in Floating Hydroponics—Perspective Nutritious Food? Plants 2023, 12, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujić, I.; Šertović, E.; Jokić, S.; Sarić, Z.; Alibabić, V.; Vidovic, S.S.; Zivkovic, J.V. Isoflavone content and antioxidant properties of soybean seeds. Croatian journal of food science and technology 2011, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanda, T.; Madan, V.K.; Beniwal, R. Quantitative analysis of phenols, flavonoids in different parts of Aegle marmelos (Bael) along with the evaluation of Antioxidant potential using different extracts. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 2020, 9, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, P.B.; Katekhaye, S.D.; Mulik, M.B.; Laddha, K.S. Rapid simultaneous determination of marmelosin, umbelliferone and scopoletin from Aegle marmelos fruit by RP-HPLC. Journal of food science and technology 2014, 51, 2251–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, C.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Silva, B.; Silva, L.R. Assessing the phenolic profile, antioxidant, antidiabetic and protective effects against oxidative damage in human erythrocytes of peaches from Fundão. Journal of Functional Foods 2018, 43, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, I.C.W.; van de Putte, B.; Hollman, P.C.H. Catechin Contents of Foods Commonly Consumed in The Netherlands. 2. Tea, Wine, Fruit Juices, and Chocolate Milk. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2000, 48, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almanza-Aguilera, E.; Ceballos-Sánchez, D.; Achaintre, D.; Rothwell, J.A.; Laouali, N.; Severi, G.; Katzke, V.; Johnson, T.; Schulze, M.B.; Palli, D.; et al. Urinary Concentrations of (+)-Catechin and (-)-Epicatechin as Biomarkers of Dietary Intake of Flavan-3-ols in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangkarn, S.; Grudpan, K.; Khanongnuch, C.; Pattananandecha, T.; Apichai, S.; Saenjum, C. Development of HPLC Method for Catechins and Related Compounds Determination and Standardization in Miang (Traditional Lanna Fermented Tea Leaf in Northern Thailand). Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miean, K.H.; Mohamed, S. Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J Agric Food Chem 2001, 49, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Kaempferol, a potential neuroprotective agent in neurodegenerative diseases: From chemistry to medicine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 165, 115215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbou, F.; Azzi, R.; Ouffai, K.; El Haci, I.A.; Belyagoubi-Benhammou, N.; Bensouici, C.; Benamar, H. Phenolic profile, antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory properties of phenolic-rich fractions from the aerial parts of Mentha pulegium L. South African Journal of Botany 2022, 146, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, S.H.; Kärenlampi, S.O.; Heinonen, I.M.; Mykkänen, H.M.; Törrönen, A.R. Content of the flavonols quercetin, myricetin, and kaempferol in 25 edible berries. J Agric Food Chem 1999, 47, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demonty, I.; Lin, Y.; Zebregs, Y.E.M.P.; Vermeer, M.A.; van der Knaap, H.C.M.; Jäkel, M.; Trautwein, E.A. The Citrus Flavonoids Hesperidin and Naringin Do Not Affect Serum Cholesterol in Moderately Hypercholesterolemic Men and Women. The Journal of Nutrition 2010, 140, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Avula, B.; Lee, J.; Upton, R.; Khan, I.A. Chemical characterization and quantitative determination of flavonoids and phenolic acids in yerba santa (Eriodictyon spp.) using UHPLC/DAD/Q-ToF. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2023, 234, 115570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Nicolás, M.; Ledesma-Escobar, C.A.; Priego-Capote, F. Spatial Distribution and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts from Citrus Fruits. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elezovic, A.; Uzunovic, A.; Hadzidedic, S.; Pilipovic, S.; Sapcanin, A. New and fast HPLC method for analysis of flavonoids in honey and propolis samples. Planta Med 2010, 76, P526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, G.; Chen, Z. Quality assessment of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) from different sources by multiple fingerprint profiles combined with quantitative analysis, antioxidant activity and chemometric methods. Food chemistry 2020, 324, 126854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guofang, X.; Xiaoyan, X.; Xiaoli, Z.; Yongling, L.; Zhibing, Z. Changes in phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity in rabbiteye blueberries during ripening. International Journal of Food Properties 2019, 22, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, I.E.; Hall, C.; Kubátová, A. Determination of lignans in flaxseed using liquid chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A 2009, 1216, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, K.; Nagel, C.W. Occurrence and content of hydroxycinnamic and hydroxybenzoic acid compounds in foods. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 1989, 28, 315–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramli; , N.; Yatim; , A.M.; Said; , M.; Hok, H.C. HPLC determination of methylxanthines and polyphenols levels In cocoa and chocolate products Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences 2001, 7, 377–386.
- Sova, M.; Saso, L. Natural Sources, Pharmacokinetics, Biological Activities and Health Benefits of Hydroxycinnamic Acids and Their Metabolites. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglett;, G.E.; Chen;, D.; Liu, S.X. Antioxidant Activities of Selective Gluten Free Ancient Grains. Food and Nutrition Sciences 2015, 6. [CrossRef]
- Reinisalo, M.; Kårlund, A.; Koskela, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Karjalainen, R.O. Polyphenol Stilbenes: Molecular Mechanisms of Defence against Oxidative Stress and Aging-Related Diseases. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2015, 2015, 340520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, S.; Li, Q.; Song, L.; Zhang, W.; Yu, P.; Xuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Delphinidins and Naringenin Chalcone Underlying the Fruit Color Changes during Maturity Stages in Eggplant. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usenik, V.; Štampar, F.; Veberič, R. Anthocyanins and fruit colour in plums (Prunus domestica L.) during ripening. Food chemistry 2009, 114, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariram Nile, S.; Hwan Kim, D.; Keum, Y.-S. Determination of Anthocyanin Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Different Grape Varieties. Ciência Téc. Vitiv. 2015, 30, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, V.K.; Hasna, C.K.; Muraleedharan, K. The natural food colorant Peonidin from cranberries as a potential radical scavenger – A DFT based mechanistic analysis. Food chemistry 2018, 262, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Hodun, G.; Gołba, M. Chemical Composition of 21 Cultivars of Sour Cherry (Prunus cerasus) Fruit Cultivated in Poland. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 25, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni;, A.; Amanda;, H.; Darwis, D. Characterization of pelargonidin compound from raspberry fruit (Rubus rosifolius Sm) with mass spectroscopy method. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research 2015, 7, 804–808.
- Alvarado, J.L.; Leschot, A.; Olivera-Nappa, Á.; Salgado, A.M.; Rioseco, H.; Lyon, C.; Vigil, P. Delphinidin-Rich Maqui Berry Extract (Delphinol®) Lowers Fasting and Postprandial Glycemia and Insulinemia in Prediabetic Individuals during Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests. BioMed research international 2016, 2016, 9070537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Shao, J.; Zheng, Y. Delphinidin-3-O-glucoside, an active compound of Hibiscus sabdariffa calyces, inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation in rabbits with atherosclerosis. Pharmaceutical biology 2022, 60, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera de Rosso, V.; Hillebrand, S.; Cuevas Montilla, E.; Bobbio, F.O.; Winterhalter, P.; Mercadante, A.Z. Determination of anthocyanins from acerola (Malpighia emarginata DC.) and açai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) by HPLC–PDA–MS/MS. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2008, 21, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decendit, A.; Mamani-Matsuda, M.; Aumont, V.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Moynet, D.; Boniface, K.; Richard, E.; Krisa, S.; Rambert, J.; Mérillon, J.M.; et al. Malvidin-3-O-β glucoside, major grape anthocyanin, inhibits human macrophage-derived inflammatory mediators and decreases clinical scores in arthritic rats. Biochem Pharmacol 2013, 86, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.R.; Queiroz, M. Bioactive compounds of red grapes from Dão region (Portugal): Evaluation of phenolic and organic profile. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 2016, 6, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-J.; Ko, M.-J.; Chung, M.-S. Anthocyanin Structure and pH Dependent Extraction Characteristics from Blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum) and Chokeberries (Aronia melanocarpa) in Subcritical Water State. Foods 2021, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lončar, M.; Jakovljević, M.; Šubarić, D.; Pavlić, M.; Buzjak Služek, V.; Cindrić, I.; Molnar, M. Coumarins in Food and Methods of Their Determination. Foods 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanic, G.; Jurisic, B.; Brkic, D. HPLC Analysis of Esculin and Fraxin in Horse-Chestnut Bark (Aesculus hippocastanum L.). Croatica Chemica Acta 1999, 72, 827–834. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Provan, G.J.; Helliwell, K. HPLC determination of catechins in tea leaves and tea extracts using relative response factors. Food chemistry 2003, 81, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, E.; Jayakumar, T.; Elanchezhian, R.; Sakthivel, M.; Geraldine, P.; Thomas, P.A. Green tea catechins, alleviate hepatic lipidemic-oxidative injury in Wistar rats fed an atherogenic diet. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2009, 180, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra, L.D.; Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.X.; Escobar, S.; Ruiz Pardo, R.Y. From controlled transformed cocoa beans to chocolate: Bioactive properties, metabolomic profile, and in vitro bioaccessibility. Food chemistry 2024, 433, 137321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, W.; Khan, H.; Shah, M.A.; Cauli, O.; Saso, L. Kaempferol as a Dietary Anti-Inflammatory Agent: Current Therapeutic Standing. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FIESCHI, M.; CODIGNOLA, A.; MOSCA, A.M.L. Mutagenic Flavonol Aglycones in Infusions and in Fresh and Pickled Vegetables. Journal of food science 1989, 54, 1492–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Syed, D.N.; Ahmad, N.; Mukhtar, H. Fisetin: a dietary antioxidant for health promotion. Antioxidants & redox signaling 2013, 19, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Saeed, F.; Hussain, G.; Imran, A.; Mehmood, Z.; Gondal, T.A.; El-Ghorab, A.; Ahmad, I.; Pezzani, R.; Arshad, M.U.; et al. Myricetin: A comprehensive review on its biological potentials. Food science & nutrition 2021, 9, 5854–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaze, F.I.; Gabrieli, C.; Kokkalou, E.; Georgarakis, M.; Niopas, I. Simultaneous reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of diosmin, hesperidin and naringin in different citrus fruit juices and pharmaceutical formulations. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2003, 33, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed Janabi, A.H.; Kamboh, A.A.; Saeed, M.; Xiaoyu, L.; BiBi, J.; Majeed, F.; Naveed, M.; Mughal, M.J.; Korejo, N.A.; Kamboh, R.; et al. Flavonoid-rich foods (FRF): A promising nutraceutical approach against lifespan-shortening diseases. Iranian journal of basic medical sciences 2020, 23, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannataro, R.; Fazio, A.; La Torre, C.; Caroleo, M.C.; Cione, E. Polyphenols in the Mediterranean Diet: From Dietary Sources to microRNA Modulation. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Food Supplement with Antioxidative Santa Herba Extract Modulates Energy Metabolism and Contributes to Weight Management. Journal of Medicinal Food 2021, 24, 1235–1242. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, O.K.; Chung, S.J.; Song, W.O. Estimated Dietary Flavonoid Intake and Major Food Sources of U.S. Adults1,2. The Journal of Nutrition 2007, 137, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S. Determination of Pinocembrin in Honey Using HPLC. Journal of Apicultural Research 1989, 28, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, T.; Feng, M.; Chen, H.; Zhuang, M.; Lin, L. Bioactive profiles, antioxidant activities, nitrite scavenging capacities and protective effects on H2O2-injured PC12 cells of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. leaf and root extracts. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2014, 19, 9101–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adham, A.N. Qualitative and quantitative estimation of hesperidin in peel and juice of citrus fruits by RP-HPLC method growing in Kurdistan region/Iraq. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research 2015, 33, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Volpi, N.; Bergonzini, G. Analysis of flavonoids from propolis by on-line HPLC–electrospray mass spectrometry. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2006, 42, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukutake, M.; Takahashi, M.; Ishida, K.; Kawamura, H.; Sugimura, T.; Wakabayashi, K. Quantification of genistein and genistin in soybeans and soybean products. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 1996, 34, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitani, K.; Narimatsu, S.; Kataoka, H. Determination of daidzein and genistein in soybean foods by automated on-line in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A 2003, 986, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, A.; Mine, W.; Nakada, M.; Yanase, E. Analysis of isoflavones and coumestrol in soybean sprouts. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 2016, 80, 2077–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.A.; Custer, L.J.; Wang, W.; Shi, C.Y. HPLC analysis of isoflavonoids and other phenolic agents from foods and from human fluids. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine (New York, N.Y.) 1998, 217, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoflavone Composition, Total Polyphenolic Content, and Antioxidant Activity in Soybeans of Different Origin. Journal of Medicinal Food 2010, 13, 657–664. [CrossRef]
- De Leo, M.; Iannuzzi, A.M.; Germanò, M.P.; D'Angelo, V.; Camangi, F.; Sevi, F.; Diretto, G.; De Tommasi, N.; Braca, A. Comparative chemical analysis of six ancient italian sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) varieties showing antiangiogenic activity. Food chemistry 2021, 360, 129999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnology Reports 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debelo, H.; Li, M.; Ferruzzi, M.G. Processing influences on food polyphenol profiles and biological activity. Current Opinion in Food Science 2020, 32, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneidy, R.A.; Zaki, E.R.; Gad, A.A.M.; Saleh, N.S.E.; Shokeer, A. Evaluation of Phenolic Content Diversity along with Antioxidant/Pro-Oxidant, Glutathione Transferase Inhibition, and Cytotoxic Potential of Selected Commonly Used Plants. Preventive nutrition and food science 2022, 27, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurzyńska-Wierdak, R. Phenolic Compounds from New Natural Sources-Plant Genotype and Ontogenetic Variation. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregziabher, B.S.; Zhang, S.; Ghosh, S.; Shaibu, A.S.; Azam, M.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Qi, J.; Agyenim-Boateng, K.G.; Htway, H.T.P.; Feng, Y.; et al. Origin, Maturity Group and Seed Coat Color Influence Carotenoid and Chlorophyll Concentrations in Soybean Seeds. Plants 2022, 11, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Immunology 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoph Jan, W.; Athanassios, F.; Agata, G.; Lars-Ove, B.; Yuet Wai, K.; Kaimin, C.; Joachim, H.; Sandra, F.-W.; Deike, V.; Sebastian, L.; et al. Role of oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis: insights from the Nrf2-knockout mice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2011, 70, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Bento, C.; Silva, B.M.; Silva, L.R. Sweet cherries from Fundão possess antidiabetic potential and protect human erythrocytes against oxidative damage. Food research international (Ottawa, Ont.) 2017, 95, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogi, S.; Guarino, I.; Flori, L.; Sirous, H.; Calderone, V. In Silico Identification of Natural Products and World-Approved Drugs Targeting the KEAP1/NRF2 Pathway Endowed with Potential Antioxidant Profile. Computation 2023, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, W.; Jie, F.; Wang, M.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lu, B. Discovery of Keap1-Nrf2 small-molecule inhibitors from phytochemicals based on molecular docking. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2019, 133, 110758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mili, A.; Birangal, S.; Nandakumar, K.; Lobo, R. A computational study to identify Sesamol derivatives as NRF2 activator for protection against drug-induced liver injury (DILI). Molecular Diversity 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Shu, H.; Mo, X.; Tian, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, H.-Y. Activation of the Nrf2 Antioxidant Pathway by Longjing Green Tea Polyphenols in Mice Livers. Natural Product Communications 2022, 17, 1934578X221139409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, M.; Kiese, S.; Herfellner, T.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. How Does the Phenol Structure Influence the Results of the Folin-Ciocalteu Assay? Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soobrattee, M.A.; Neergheen, V.S.; Luximon-Ramma, A.; Aruoma, O.I.; Bahorun, T. Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: mechanism and actions. Mutation research 2005, 579, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, M.; Kiese, S.; Herfellner, T.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Miesbauer, O.; Eisner, P. Common Trends and Differences in Antioxidant Activity Analysis of Phenolic Substances Using Single Electron Transfer Based Assays. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 26, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Yuan, Z.; Xueqing Zhao; Yin, Y.; Feng, L. COMPOSITION AND CONTENTS OF ANTHOCYANINS IN DIFFERENT POMEGRANATE CULTIVARS. Acta Horticulturae 2015, 1089, 35–41. [CrossRef]
- Passafiume, R.; Perrone, A.; Sortino, G.; Gianguzzi, G.; Saletta, F.; Gentile, C.; Farina, V. Chemical–physical characteristics, polyphenolic content and total antioxidant activity of three Italian-grown pomegranate cultivars. NFS Journal 2019, 16, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, P.C.; Långvik, O.K.; Wärnå, J.P.; Salmi, T.O.; Willför, S.M.; Sjöholm, R.E. Chemical studies on antioxidant mechanisms and free radical scavenging properties of lignans. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2005, 3, 3336–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rühlmann, A.; Antovic, D.; Müller, T.J.J.; Urlacher, V.B. Regioselective Hydroxylation of Stilbenes by Engineered Cytochrome P450 from Thermobifida fusca YX. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 2017, 359, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Flores-Félix, J.D.; Costa, A.R.; Falcão, A.; Alves, G.; Silva, L.R. Hepatoprotective Effects of Sweet Cherry Extracts (cv. Saco). Foods 2021, 10, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simić, A.; Manojlović, D.; Segan, D.; Todorović, M. Electrochemical behavior and antioxidant and prooxidant activity of natural phenolics. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2007, 12, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alov, P.; Tsakovska, I.; Pajeva, I. Computational studies of free radical-scavenging properties of phenolic compounds. Current topics in medicinal chemistry 2015, 15, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliak, M.M.; Burdyliuk, N.I.; Lushchak, V.I. Effects of pH on antioxidant and prooxidant properties of common medicinal herbs. Open Life Sciences 2016, 11, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Sofic, E.; Prior, R.L. Antioxidant and Prooxidant Behavior of Flavonoids: Structure-Activity Relationships. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1997, 22, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, J.F.; Klucas, R.V.; Grayer, R.J.; Abian, J.; Becana, M. Complexes of Iron with Phenolic Compounds from Soybean Nodules and Other Legume Tissues: Prooxidant and Antioxidant Properties. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1997, 22, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniyah, N.; Alam, M.B.; Javed, A.; Alshammari, F.H.; Choi, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H. In silico and docking studies on the binding activities of Keap1 of antioxidant compounds in non-oilseed legumes. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2023, 16, 104414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Bian, C.; Ma, Z. In vitro and in silico perspectives on the activation of antioxidant responsive element by citrus-derived flavonoids. Frontiers in Nutrition 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, T.; Selvaraj, M.; Poomalai, S. Epigallocatechin gallate potentially abrogates fluoride induced lung oxidative stress, inflammation via Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway in rats: An in-vivo and in-silico study. International Immunopharmacology 2016, 39, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.G.; Han, S.S.; Toborek, M.; Hennig, B. EGCG protects endothelial cells against PCB 126-induced inflammation through inhibition of AhR and induction of Nrf2-regulated genes. Toxicology and applied pharmacology 2012, 261, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.H.; Cho, S.S.; Kim, J.H.; Xu, J.; Seo, K.; Ki, S.H. 5-Caffeoylquinic acid ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated cell death via Nrf2 activation in hepatocytes. Pharmaceutical biology 2020, 58, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Paital, B.; Jena, S.; Swain, S.S.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, M.K.; Chainy, G.B.N.; Samanta, L. Possible activation of NRF2 by Vitamin E/Curcumin against altered thyroid hormone induced oxidative stress via NFĸB/AKT/mTOR/KEAP1 signalling in rat heart. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Lahlou, R.A.; Alves, G.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Moreno, D.A.; Silva, L.R. Potential Activity of Abrantes Pollen Extract: Biochemical and Cellular Model Studies. Foods 2021, 10, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, F.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Alves, G.; Silva, L.R. Exploring the phenolic profile, antioxidant, antidiabetic and anti-hemolytic potential of Prunus avium vegetal parts. Food Res Int 2019, 116, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyarzún, J.E.; Andia, M.E.; Uribe, S.; Núñez Pizarro, P.; Núñez, G.; Montenegro, G.; Bridi, R. Honeybee Pollen Extracts Reduce Oxidative Stress and Steatosis in Hepatic Cells. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A.C.; Nunes, A.R.; Meirinho, S.; Ayuso-Calles, M.; Roca-Couso, R.; Rivas, R.; Falcão, A.; Alves, G.; Silva, L.R.; Flores-Félix, J.D. Exploring the Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Antimicrobial Capacity of Phenolics from Blueberries and Sweet Cherries. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Shinoda, A.; Takagi, C.; Ohno, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Ogura, K.; Hiratsuka, A. Procyanidins from Cinnamomi Cortex promote proteasome-independent degradation of nuclear Nrf2 through phosphorylation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in A549 cells. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2017, 635, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.-S. Suppression of Nrf2 Activity by Chestnut Leaf Extract Increases Chemosensitivity of Breast Cancer Stem Cells to Paclitaxel. Nutrients 2017, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Sun, L. Agrimoniin sensitizes pancreatic cancer to apoptosis through ROS-mediated energy metabolism dysfunction. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2022, 96, 153807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Sánchez, A.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Ruiz-Torres, V.; Agulló-Chazarra, L.; Herranz-López, M.; Valdés, A.; Cifuentes, A.; Micol, V. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) extract causes ROS-induced necrotic cell death and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C.; Cheng, M.-J.; Yen, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.A.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chen, I.-S.; Chang, H.-S. Chemical Constituents with GNMT-Promoter-Enhancing and NRF2-Reduction Activities from Taiwan Agarwood Excoecaria formosana. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 25, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.-M.; Ke, Z.-P.; Shi, F.; Sun, G.-C.; Chen, H. Chrysin enhances sensitivity of BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin by suppressing PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and ERK/Nrf2 pathway. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2013, 206, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Bai, X.; Gou, X.; Zeng, H.; Xia, C.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, M.; Jin, J. 3′,4′,5′,5,7-Pentamethoxyflavone Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant A549 Cells to Cisplatin by Inhibition of Nrf2 Pathway. Molecules and Cells 2015, 38, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Y-J, L.; J-H, I.; DM, L.; J-S, P.; SY, W.; M-K, C.; al., e. Synergistic inhibition of mesothelioma cell growth by the combination of clofarabine and resveratrol involves Nrf2 downregulation. BMB Reports 2012, 45, 647–652. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Jin, P.; Feng, L.; Song, J.; Sun, E.; Liu, W.; Shu, L.; Jia, X. Protective effect of luteolin on cigarette smoke extract-induced cellular toxicity and apoptosis in normal human bronchial epithelial cells via the Nrf2 pathway. Oncol Rep 2014, 31, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, K.; Hu, Y.; Su, F.; Gao, Z.; Hu, T.; Yang, Y.; Cao, X.; Qian, F. Schisantherin A induces cell apoptosis through ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human gastric cancer cells. Biochemical Pharmacology 2020, 173, 113673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Hou, X.; Yuan, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, N.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, P.; Dong, Z.; et al. Wedelolactone protects human bronchial epithelial cell injury against cigarette smoke extract-induced oxidant stress and inflammation responses through Nrf2 pathway. International Immunopharmacology 2015, 29, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnuma, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Itoi, A.; Kawana, A.; Nishiyama, T.; Ogura, K.; Hiratsuka, A. Enhanced sensitivity of A549 cells to the cytotoxic action of anticancer drugs via suppression of Nrf2 by procyanidins from Cinnamomi Cortex extract. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2011, 413, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnuma, T.; Anzai, E.; Suzuki, Y.; Shimoda, M.; Saito, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Ogura, K.; Hiratsuka, A. Selective antagonization of activated Nrf2 and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation by procyanidins from Cinnamomi Cortex extract. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2015, 585, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-Y.; Khor, T.O.; Saw, C.L.L.; Loh, S.C.; Chen, A.I.; Lim, S.S.; Park, J.H.Y.; Cai, L.; Kong, A.-N.T. Anti-inflammatory/Anti-oxidative Stress Activities and Differential Regulation of Nrf2-Mediated Genes by Non-Polar Fractions of Tea Chrysanthemum zawadskii and Licorice Glycyrrhiza uralensis. The AAPS Journal 2011, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, S.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Cianciosi, D.; Pistollato, F.; Zhang, J.; Pacetti, M.; Amici, A.; Reboredo-Rodríguez, P.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Bompadre, S.; et al. Strawberry tree honey as a new potential functional food. Part 2: Strawberry tree honey increases ROS generation by suppressing Nrf2-ARE and NF-кB signaling pathways and decreases metabolic phenotypes and metastatic activity in colon cancer cells. Journal of Functional Foods 2019, 57, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dutta, N.; Banerjee, P.; Gajbhiye, R.L.; Sareng, H.R.; Kapse, P.; Pal, S.; Burdelya, L.; Mandal, N.C.; Ravichandiran, V.; et al. Induction of monoamine oxidase A-mediated oxidative stress and impairment of NRF2-antioxidant defence response by polyphenol-rich fraction of Bergenia ligulata sensitizes prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2021, 172, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, I.; Demir, S.; Yaman, S.O.; Canbolat, D.; Mentese, A.; Aliyazicioglu, Y. An Investigation of the Antiproliferative Effect of Rhododendron luteum Extract on Cervical Cancer (HeLa) Cells via Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Nutrition and Cancer 2022, 74, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pterostilbene Decreases the Antioxidant Defenses of Aggressive Cancer Cells In Vivo: A Physiological Glucocorticoids- and Nrf2-Dependent Mechanism. Antioxidants & redox signaling 2016, 24, 974–990. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, M.G.; Pires, P.R.; Ribeiro, F.V.; Pimentel, S.P.; Cirano, F.R.; Napimoga, M.H.; Casati, M.Z.; Casarin, R.C.V. Systemic treatment with resveratrol reduces the progression of experimental periodontitis and arthritis in rats. PloS one 2018, 13, e0204414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uttra, A.M.; Alamgeer; Shahzad, M.; Shabbir, A.; Jahan, S.; Bukhari, I.A.; Assiri, A.M. Ribes orientale: A novel therapeutic approach targeting rheumatoid arthritis with reference to pro-inflammatory cytokines, inflammatory enzymes and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2019, 237, 92–107. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, J. Theaflavin-3, 3'-Digallate Attenuates Rheumatoid Inflammation in Mice Through the Nuclear Factor-κB and MAPK Pathways. Archivum immunologiae et therapiae experimentalis 2019, 67, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, S.; Lv, J.; Sun, F.; Weng, B.; Liu, S.; Xia, P. Chebulanin exerts its anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects via inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation in collagen-induced arthritis mice. International Immunopharmacology 2020, 88, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Ye, J.; Liu, N.; Shao, Y.; Li, W.; Fan, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, X. Resveratrol Ameliorates Fibrosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease via the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Lin, J.-K. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Blocks the Induction of Nitric Oxide Synthase by Down-Regulating Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Activity of Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor-κB. Molecular Pharmacology 1997, 52, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, A.; Dagli, A.F.; Orhan, C.; Gencoglu, H.; Ozgen, M.; Sahin, N.; Sahin, K.; Koca, S.S. Epigallocatechin 3-gallate attenuates arthritis by regulating Nrf2, HO-1, and cytokine levels in an experimental arthritis model. Biotechnology and applied biochemistry 2020, 67, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, F.; Neog, M.K.; Rasool, M. Targeted delivery of morin, a dietary bioflavanol encapsulated mannosylated liposomes to the macrophages of adjuvant-induced arthritis rats inhibits inflammatory immune response and osteoclastogenesis. European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics : official journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik e.V 2017, 115, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrukh, M.; Saleem, U.; Qasim, M.; Manan, M.; Shah, M.A. Sarcococca saligna extract attenuates formaldehyde-induced arthritis in Wistar rats via modulation of pro-inflammatory and inflammatory biomarkers. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Li, C.; Jing, L.; Zhuang, F.; Xiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B. Rosmarinic acid nanomedicine for rheumatoid arthritis therapy: Targeted RONS scavenging and macrophage repolarization. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society 2023, 362, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neog, M.K.; Joshua Pragasam, S.; Krishnan, M.; Rasool, M. p-Coumaric acid, a dietary polyphenol ameliorates inflammation and curtails cartilage and bone erosion in the rheumatoid arthritis rat model. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 2017, 43, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almansour, Z.H.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Hamad, R.S.; Abd El-Moaty, H.I. Phenolic-Compound-Rich Opuntia littoralis Ethyl Acetate Extract Relaxes Arthritic Symptoms in Collagen-Induced Mice Model via Bone Morphogenic Markers. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Qin, W.; Lin, Y.; Ma, S.; Liang, J. Homoplantaginin Inhibits Palmitic Acid-induced Endothelial Cells Inflammation by Suppressing TLR4 and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 2016, 67, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Gurley, E.C.; Zhou, H. Flavonoid apigenin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through multiple mechanisms in macrophages. PloS one 2014, 9, e107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Wu, D.M.; Li, M.Q.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.F.; Cheng, W.; Shan, Q. Luteoloside suppresses proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. PloS one 2014, 9, e89961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, F.M.; Kong, L.D. Quercetin and allopurinol ameliorate kidney injury in STZ-treated rats with regulation of renal NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipid accumulation. PloS one 2012, 7, e38285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.J.; Lim, Y. Resveratrol ameliorates hepatic metaflammation and inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Metabolism: clinical and experimental 2014, 63, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruna, R.; Geetha, A.; Suguna, P. Rutin modulates ASC expression in NLRP3 inflammasome: a study in alcohol and cerulein-induced rat model of pancreatitis. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2014, 396, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Ku, S.K.; Bae, J.S. Inhibitory effects of kaempferol-3-O-sophoroside on HMGB1-mediated proinflammatory responses. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2012, 50, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.J.; Lee, W.; Ku, S.K.; Song, K.S.; Bae, J.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of oleanolic acid on HMGB1 activated HUVECs. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2012, 50, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Gao, P.; Wu, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, R.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Jin, X. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates neointimal hyperplasia in a rat model of carotid artery injury by inhibition of high mobility group box 1 expression. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2017, 14, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Yuan, K.; Ji, B.; Han, Y.; Li, J. Protective effects of curcumin against neuroinflammation induced by Aβ25-35 in primary rat microglia: modulation of high-mobility group box 1, toll-like receptor 4 and receptor for advanced glycation end products expression. Annals of translational medicine 2020, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Popper, B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol downregulates inflammatory pathway activated by lymphotoxin α (TNF-β) in articular chondrocytes: Comparison with TNF-α. PloS one 2017, 12, e0186993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, A.; Orhan, C.; Tuzcu, M.; Şahin, N.; Özercan, İ.H.; Koca, S.S.; Juturu, V.; Şahin, K. Mango ginger (curcuma amada) inhibits collagen-induced arthritis by modulatinginflammatory cytokine levels in rats,. Turkich Journal of Medical Sciences 2020, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of taraxasterol on iNOS and COX-2 expression in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2014, 155, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyol, S.; Ozturk, G.; Ginis, Z.; Armutcu, F.; Yigitoglu, M.R.; Akyol, O. In vivo and in vitro antıneoplastic actions of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE): therapeutic perspectives. Nutr Cancer 2013, 65, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, G.G.; Carrasquedo, F.; Delfino, J.M.; Keen, C.L.; Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I. Epicatechin, catechin, and dimeric procyanidins inhibit PMA-induced NF-kappaB activation at multiple steps in Jurkat T cells. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2004, 18, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.D.; Choi, C.H.; Bark, H.; Son, H.Y.; Park, H.H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.W.; Park, E.K.; Shin, H.I.; Kim, S.H. Quercetin inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK in HMC-1 human mast cell line. Inflammation research : official journal of the European Histamine Research Society... [et al.] 2007, 56, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-C.; Ho, F.-M.; Pei-Dawn Lee, C.; Chen, C.-P.; Jeng, K.-C.G.; Hsu, H.-B.; Lee, S.-T.; Wen Tung, W.; Lin, W.-W. Inhibition of iNOS gene expression by quercetin is mediated by the inhibition of IκB kinase, nuclear factor-kappa B and STAT1, and depends on heme oxygenase-1 induction in mouse BV-2 microglia. European journal of pharmacology 2005, 521, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, P.A.; Braune, A.; Hölzlwimmer, G.; Quintanilla-Fend, L.; Haller, D. Quercetin inhibits TNF-induced NF-kappaB transcription factor recruitment to proinflammatory gene promoters in murine intestinal epithelial cells. J Nutr 2007, 137, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Sapkota, K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.J. Kaempferol acts through mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein kinase B/AKT to elicit protection in a model of neuroinflammation in BV2 microglial cells. British journal of pharmacology 2011, 164, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.H.; Bae, Y.; Kim, S.H. Galangin attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2013, 57, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.S.; Catravas, J.D.; Odoms, K.; Denenberg, A.; Malhotra, V.; Wong, H.R. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a green tea-derived polyphenol, inhibits IL-1 beta-dependent proinflammatory signal transduction in cultured respiratory epithelial cells. J Nutr 2004, 134, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, D.; Matsui, A.; Imai, M.; Sonoda, Y.; Kasahara, T. Effect of various catechins on the IL-12p40 production by murine peritoneal macrophages and a macrophage cell line, J774.1. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin 2004, 27, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Gupta, S.; Adhami, V.M.; Mukhtar, H. Green tea constituent epigallocatechin-3-gallate selectively inhibits COX-2 without affecting COX-1 expression in human prostate carcinoma cells. International journal of cancer 2005, 113, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.L.; Lin, J.K. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks the induction of nitric oxide synthase by down-regulating lipopolysaccharide-induced activity of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB. Mol Pharmacol 1997, 52, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, S.; Hao, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z. Genistein suppresses LPS-induced inflammatory response through inhibiting NF-κB following AMP kinase activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. PloS one 2012, 7, e53101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitani, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshida, M.; Azuma, T.; Kanazawa, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Mizuno, M. Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of luteolin: role of the aglycone in NF-κB inactivation in macrophages co-cultured with intestinal epithelial cells. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 2013, 39, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Peng, W.H.; Tsai, K.D.; Hsu, S.L. Luteolin suppresses inflammation-associated gene expression by blocking NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation pathway in mouse alveolar macrophages. Life sciences 2007, 81, 1602–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gründemann, C.; Gruber, C.W.; Hertrampf, A.; Zehl, M.; Kopp, B.; Huber, R. An aqueous birch leaf extract of Betula pendula inhibits the growth and cell division of inflammatory lymphocytes. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2011, 136, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carluccio, M.A.; Siculella, L.; Ancora, M.A.; Massaro, M.; Scoditti, E.; Storelli, C.; Visioli, F.; Distante, A.; De Caterina, R. Olive oil and red wine antioxidant polyphenols inhibit endothelial activation: antiatherogenic properties of Mediterranean diet phytochemicals. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2003, 23, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeram, N.P.; Momin, R.A.; Nair, M.G.; Bourquin, L.D. Cyclooxygenase inhibitory and antioxidant cyanidin glycosides in cherries and berries. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2001, 8, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; del Pilar Terrón, M.; Garrido, M.; Barriga, C.; Espino, J.; Paredes, D.S.; Rodríguez, B.A. Jerte Valley cherry-based product modulates serum inflammatory markers in rats and ringdoves. Journal of Applied Biomedicine 2012, 10, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, S.; Kwon, G.T.; Lee, E.; Jang, W.J.; Yang, H.; Kim, J.H.; Thimmegowda, N.R.; Chung, M.-Y.; Kwon, J.Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Gingerenone A, a polyphenol present in ginger, suppresses obesity and adipose tissue inflammation in high-fat diet-fed mice. Molecular nutrition & food research 2017, 61, 1700139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Parks, J.S.; Kang, H.W. Quercetin alleviates high-fat diet-induced inflammation in brown adipose tissue. Journal of Functional Foods 2021, 85, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, E.M.; Harbourne, N.; Marete, E.; Martyn, D.; Jacquier, J.; O'Riordan, D.; Gibney, E.R. Inhibition of proinflammatory biomarkers in THP1 macrophages by polyphenols derived from chamomile, meadowsweet and willow bark. Phytotherapy research : PTR 2013, 27, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.; Lee, J.; Yoon, S.; Kim, W.J. Tannic acid-based nanogel as an efficient anti-inflammatory agent. Biomaterials Science 2020, 8, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.M.; Cui, X.; Wu, R.; Dong, W.; Zhou, M.; Hu, M.; Simms, H.H.; Wang, P. The anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin in an experimental model of sepsis is mediated by up-regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Critical care medicine 2006, 34, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-P.; Matteliano, M.L.; Middleton, E. Effect of quercetin on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomal enzyme release and phospholipid metabolism. Life sciences 1982, 31, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusman, G.S.; Campana, P.R.V.; Castro, L.C.; Castilho, R.O.; Teixeira, M.M.; Braga, F.C. Evaluation of the Effects of Some Brazilian Medicinal Plants on the Production of TNF-<b><i>α</i></b> and CCL2 by THP-1 Cells. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2015, 2015, 497123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ping, S.; Huang, S.; Hu, L.; Xuan, H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, F. Molecular mechanisms underlying the in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of a flavonoid-rich ethanol extract from chinese propolis (poplar type). Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM 2013, 2013, 127672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.R.; Ho, Y.L.; Huang, S.C.; Huang, T.H.; Lai, S.C.; Tsai, J.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Huang, G.J.; Chang, Y.S. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative activities of Kalanchoe gracilis (L.) DC stem. The American journal of Chinese medicine 2011, 39, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.I.; Kang, S.R.; Park, H.S.; Lee, D.H.; Nagappan, A.; Kim, J.A.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, W.S.; Chung, H.J.; et al. Regulation of Proinflammatory Mediators via NF-κB and p38 MAPK-Dependent Mechanisms in RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Polyphenol Components Isolated from Korea Lonicera japonica THUNB. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM 2012, 2012, 828521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essafi-Benkhadir, K.; Refai, A.; Riahi, I.; Fattouch, S.; Karoui, H.; Essafi, M. Quince (Cydonia oblonga Miller) peel polyphenols modulate LPS-induced inflammation in human THP-1-derived macrophages through NF-κB, p38MAPK and Akt inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012, 418, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, R.A.; Spinozzi, G.M.; Simon, V.A.; Kelley, D.S.; Prior, R.L.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Kader, A.A. Consumption of Cherries Lowers Plasma Urate in Healthy Women. The Journal of Nutrition 2003, 133, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.W.; Zhang, C.; Hong, T.; Liu, D.H.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; He, X.K.; Xu, W.D. Silibinin alleviates inflammation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and has a therapeutic effect on arthritis in rats. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, Z.; Mirsanei, Z.; Bitaraf, F.S.; Mahdavi, S.; Mirzaii, M.; Jafari, R. Dose-dependent effects of oleuropein administration on regulatory T-cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An in vitro approach. International journal of immunopathology and pharmacology 2022, 36, 3946320221086084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosillo, M.Á.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.; Castejón, M.L.; Montoya, T.; Cejudo-Guillén, M.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M. Polyphenolic extract from extra virgin olive oil inhibits the inflammatory response in IL-1β-activated synovial fibroblasts. British Journal of Nutrition 2018, 121, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Więcek, K.; Kupczyk, P.; Chodaczek, G.; Woźniak, M. The Impact of Curcumin on the Inflammatory Profile of SW982 Cells in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Model. Journal of immunology research 2022, 2022, 1208970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Moon, D.O.; Choi, I.W.; Choi, B.T.; Nam, T.J.; Rhu, C.H.; Kwon, T.K.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Choi, Y.H. Curcumin induces apoptosis and inhibits prostaglandin E(2) production in synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. International journal of molecular medicine 2007, 20, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloesch, B.; Becker, T.; Dietersdorfer, E.; Kiener, H.; Steiner, G. Anti-inflammatory and apoptotic effects of the polyphenol curcumin on human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int Immunopharmacol 2013, 15, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, B.M.; Won, J.Y.; Lee, K.A.; Ko, H.M.; Kang, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Quercetin, a Plant Polyphenol, Has Potential for the Prevention of Bone Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Med Food 2019, 22, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Wu, K.; Zeng, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, T.; Chen, Z.; Lin, L.; Chen, D.; Ouyang, H. Punicalagin Inhibited Inflammation and Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Through NF-κB Pathway in the Experimental Study of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of inflammation research 2021, 14, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, X.; Han, P.; Aimaier, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Syringaldehyde ameliorates mouse arthritis by inhibiting dendritic cell maturation and proinflammatory cytokine secretion. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 121, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Wan, Y.; Xiao, J.; Tang, Q.; Deng, H.; Chen, L. A study of Sirt1 regulation and the effect of resveratrol on synoviocyte invasion and associated joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Molecular medicine reports 2017, 16, 5099–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.M.; Chen, Y.W.; Chi, P.L.; Lin, C.C.; Hsiao, L.D. Resveratrol inhibits BK-induced COX-2 transcription by suppressing acetylation of AP-1 and NF-κB in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol 2017, 132, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, T.; Cao, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Nrf2-Keap1 pathway-mediated effects of resveratrol on oxidative stress and apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-treated rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2019, 1457, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Xie, X.; Yuan, L.; Qiu, J.; Duan, W.; Xu, B.; Chen, X. Resveratrol ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis via activation of SIRT1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 2020, 46, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Chang, C.C.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Xu, L.; Ho, C.T.; Li, S. Resveratrol Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis via Reducing ROS and Inflammation, Inhibiting MAPK Signaling Pathways, and Suppressing Angiogenesis. J Agric Food Chem 2018, 66, 12953–12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Xie, X.; Du, J.; Wang, J.; Mao, N. [Effects of resveratrol on proliferation and apoptosis of TNF-alpha induced rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes]. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China journal of Chinese materia medica 2010, 35, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Chen, J.W.; Gao, J.S.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Resveratrol inhibits TNF-α-induced IL-1β, MMP-3 production in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via modulation of PI3kinase/Akt pathway. Rheumatol Int 2013, 33, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Unterman, T.G.; Shankar, S. FOXO transcription factors and VEGF neutralizing antibody enhance antiangiogenic effects of resveratrol. Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2010, 337, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Du, J.; Gan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, J.; Ling, G.; Li, F. Resveratrol promotes apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis through regulation of autophagy and the serine-threonine kinase-p53 axis. Archives of medical science : AMS 2024, 20, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Yaguchi, T.; Yoshiya, S.; Nishizaki, T. Resveratrol induces apoptosis MH7A human rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells in a sirtuin 1-dependent manner. Rheumatol Int 2012, 32, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.L.; Gao, J.S.; Chen, X.R.; Xie, X. [Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on the proliferation of synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis and its mechanism in vitro]. Zhong nan da xue xue bao. Yi xue ban = Journal of Central South University. Medical sciences 2006, 31, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W.; Chen, X. Effect of lentivirus-mediated overexpression or silencing of MnSOD on apoptosis of resveratrol-treated fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. European journal of pharmacology 2019, 844, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glehr, M.; Breisach, M.; Walzer, S.; Lohberger, B.; Fürst, F.; Friesenbichler, J.; Rinner, B.; Avian, A.; Windhager, R.; Leithner, A. The influence of resveratrol on the synovial expression of matrix metalloproteinases and receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung. C, Journal of biosciences 2013, 68, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.M.; Guo, Y.J.; Ling, H.W.; Zeng, R. The Effect of Resveratrol in Sirt1/CST Pathway to Inhibit TNF-α Induced Inflammatory Response in Rat Primary Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin 2023, 46, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glehr, M.; Fritsch-Breisach, M.; Lohberger, B.; Walzer, S.M.; Moazedi-Fuerst, F.; Rinner, B.; Gruber, G.; Graninger, W.; Leithner, A.; Windhager, R. Influence of resveratrol on rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes analysed with gene chip transcription. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2013, 20, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W.; Chen, X.; Fang, S. Resveratrol alleviates inflammatory injury and enhances the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Molecular medicine reports 2019, 20, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Hsu, L.-F.; Lee, C.-W.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Lee, M.-H.; How, J.-M.; Wu, C.-M.; Huang, C.-L.; Lee, I.T. Resveratrol inhibits urban particulate matter-induced COX-2/PGE2 release in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes via the inhibition of activation of NADPH oxidase/ROS/NF-κB. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 2017, 88, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakibaei, M.; Buhrmann, C.; Mobasheri, A. Resveratrol-mediated SIRT-1 interactions with p300 modulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) activation of NF-kappaB signaling and inhibit osteoclastogenesis in bone-derived cells. The Journal of biological chemistry 2011, 286, 11492–11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomholt, S.; Mellemkjaer, A.; Iversen, M.B.; Pedersen, S.B.; Kragstrup, T.W. Resveratrol displays anti-inflammatory properties in an ex vivo model of immune mediated inflammatory arthritis. BMC rheumatology 2018, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, H.H.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, Y.H.; Jun, C.D.; Kim, S.H. Allose gallates suppress expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-kappaB in human mast cells. Planta Med 2007, 73, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Wu, H.; Dong, J.; Huang, S.; Ye, J.; Liu, R. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis in Rats through Inhibiting MTA1/HDAC1-Mediated Nur77 Deacetylation. Mediators of inflammation 2021, 2021, 6359652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kafaween, M.A.; Alwahsh, M.; Mohd Hilmi, A.B.; Abulebdah, D.H. Physicochemical Characteristics and Bioactive Compounds of Different Types of Honey and Their Biological and Therapeutic Properties: A Comprehensive Review. Antibiotics (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neog, M.K.; Rasool, M. Targeted delivery of p-coumaric acid encapsulated mannosylated liposomes to the synovial macrophages inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorption in the rheumatoid arthritis animal model. European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics : official journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik e.V 2018, 133, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, R.; Rasool, M. Ferulic acid inhibits interleukin 17-dependent expression of nodal pathogenic mediators in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of cellular biochemistry 2019, 120, 1878–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doss, H.M.; Samarpita, S.; Ganesan, R.; Rasool, M. Ferulic acid, a dietary polyphenol suppresses osteoclast differentiation and bone erosion via the inhibition of RANKL dependent NF-κB signalling pathway. Life sciences 2018, 207, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.C.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, H.M.; So, H.S.; Lee, M.S.; Rho, M.C.; Oh, J. Chlorogenic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by down-regulation of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand-induced nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 expression. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin 2013, 36, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Ran, Y.; Chen, X.; Tong, Q.; Ma, L.; Tan, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, X. Tea polyphenol carrier-enhanced dexamethasone nanomedicines for inflammation-targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of materials chemistry. B 2023, 11, 11505–11518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, G.; Shyni, G.L.; Mohan, S.; Abraham, B.; Nisha, P.; Ranjith, S.; Rajankutty, K.; Raghu, K.G. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effect of Tinospora cordifolia via modulation of JAK/STAT pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- South, S.; Lucero, J.; Vijayagopal, P.; Juma, S. Anti-Inflammatory Action of Blueberry Polyphenols in HIG-82 Rabbit Synoviocytes. J Med Food 2019, 22, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Son, J.E.; Jung, S.K.; Kang, N.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J. Cocoa polyphenols suppress TNF-α-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression by inhibiting phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-1 (MEK1) activities in mouse epidermal cells. The British journal of nutrition 2010, 104, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Seo, J.B.; Yu, J.S.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.S.; Choi, J.U.; Lee, C.M.; Rashan, L.; Kim, K.H.; Cho, Y.C. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Polyphenol, Catechin-7,4'-O-Digallate, from Woodfordia uniflora by Regulating NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mouse Macrophages. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Mano, H.; Nakatani, S.; Shimizu, J.; Kobata, K.; Wada, M. Anti-proliferative effects of Salacia reticulata leaves hot-water extract on interleukin-1β-activated cells derived from the synovium of rheumatoid arthritis model mice. BMC research notes 2012, 5, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Cao, W.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Autophagy and mitochondrial dysfunction in adjuvant-arthritis rats treatment with resveratrol. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 32928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, B.; Yildirim, A.; Yolbas, S.; Celik, Z.B.; Etem, E.O.; Deniz, G.; Akin, M.; Akar, Z.A.; Karatas, A.; Koca, S.S. Resveratrol inhibits Src tyrosine kinase, STAT3, and Wnt signaling pathway in collagen induced arthritis model. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 2019, 45, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Sheng, L.; Li, Y. Resveratrol prevents atrial fibrillation by inhibiting atrial structural and metabolic remodeling in collagen-induced arthritis rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's archives of pharmacology 2018, 391, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahba, M.G.; Messiha, B.A.; Abo-Saif, A.A. Protective effects of fenofibrate and resveratrol in an aggressive model of rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Pharmaceutical biology 2016, 54, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ghazaly, M.A.; Fadel, N.A.; Abdel-Naby, D.H.; Abd El-Rehim, H.A.; Zaki, H.F.; Kenawy, S.A. Amelioration of adjuvant-induced arthritis by exposure to low dose gamma radiation and resveratrol administration in rats. International journal of radiation biology 2020, 96, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmali, N.; Baysal, O.; Harma, A.; Esenkaya, I.; Mizrak, B. Effects of resveratrol in inflammatory arthritis. Inflammation 2007, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuzhu, G.; Komai-Koma, M.; Leung, B.P.; Howe, H.S.; McSharry, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Xu, D. Resveratrol modulates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 and B-cell function. Ann Rheum Dis 2012, 71, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, S.; Chen, X. Resveratrol reduces store-operated Ca(2+) entry and enhances the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in adjuvant arthritis rats model via targeting ORAI1-STIM1 complex. Biological research 2019, 52, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, J.A.; Almonte-Becerril, M.; Ramil-Gómez, O.; Hermida-Carballo, L.; Viñas-Diz, S.; Vela-Anero, Á.; Concha, Á.; Camacho-Encina, M.; Blanco, F.J.; López-Armada, M.J. Autophagy Activation by Resveratrol Reduces Severity of Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis. Molecular nutrition & food research 2021, 65, e2000377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riveiro-Naveira, R.R.; Valcárcel-Ares, M.N.; Almonte-Becerril, M.; Vaamonde-García, C.; Loureiro, J.; Hermida-Carballo, L.; López-Peláez, E.; Blanco, F.J.; López-Armada, M.J. Resveratrol lowers synovial hyperplasia, inflammatory markers and oxidative damage in an acute antigen-induced arthritis model. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 2016, 55, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, J.; An, M.; Ma, Z.; Zong, H.; Yang, J. Anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol on adjuvant arthritis rats with abnormal immunological function via the reduction of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2. Molecular medicine reports 2014, 9, 2592–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lyu, L.; Wang, X.; Bao, L.; Lyu, B.; Lin, Z. Systemic treatment with resveratrol alleviates adjuvant arthritis-interstitial lung disease in rats via modulation of JAK/STAT/RANKL signaling pathway. Pulmonary pharmacology & therapeutics 2019, 56, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, N.; Lather, V.; Kaur, B.; Kirthanashri, S.V.; Pandita, D. Optimization and Development of Methotrexate- and Resveratrol-Loaded Nanoemulsion Formulation Using Box-Behnken Design for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Assay and drug development technologies 2020, 18, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Ma, L.; Lin, A.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, G.; Liu, J. A core-shell structure QRu-PLGA-RES-DS NP nanocomposite with photothermal response-induced M2 macrophage polarization for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18209–18223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xiao, G.; Ao, J. Resveratrol Attenuates Rheumatoid Arthritis Induce Neutrophil Extracellular Traps via TLR-4 Mediated Inflammation in C57BL/6 Mice. Physiological research 2024, 73, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.Y.; Yan, M.; Kim, S.B.; Ravikumar, S.; Kwon, S.R.; Vanarsa, K.; Kim, H.Y.; Davis, L.S.; Mohan, C. Green Tea Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Suppresses Autoimmune Arthritis Through Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase Expressing Dendritic Cells and the Nuclear Factor, Erythroid 2-Like 2 Antioxidant Pathway. Journal of inflammation (London, England) 2015, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.S.; Tsai, B.C.; Sitorus, M.A.; Kuo, C.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Chen, T.S.; Fu, C.Y.; Ho, T.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Ju, D.T. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Pretreatment Improves Autologous Adipose-derived Stem Cells Against Rheumatoid Arthritis-induced Neuroinflammation in the Brain of Collagen-induced Rats. Neurotoxicity research 2022, 40, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Jung, Y.O.; Ryu, J.-G.; Oh, H.-J.; Son, H.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, J.-E.; Kim, E.-K.; Park, M.-K.; Park, S.-H.; et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates autoimmune arthritis by reciprocal regulation of T helper-17 regulatory T cells and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting STAT3 signaling. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 2016, 100, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Xu, S.; Chang, L.; Zhao, X.; Mei, X.; Ren, X.; Chen, Z. Preparation of EGCG decorated, injectable extracellular vesicles for cartilage repair in rat arthritis. Regenerative biomaterials 2021, 8, rbab067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, M.P.; Ward, S.H.; Perry, B.; Mann, A.; Freeman, J.W.; Tiku, M.L. Intra-articular injection of epigallocatechin (EGCG) crosslinks and alters biomechanical properties of articular cartilage, a study via nanoindentation. PloS one 2022, 17, e0276626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leichsenring, A.; Bäcker, I.; Furtmüller, P.G.; Obinger, C.; Lange, F.; Flemmig, J. Long-Term Effects of (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) on Pristane-Induced Arthritis (PIA) in Female Dark Agouti Rats. PloS one 2016, 11, e0152518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Rajaiah, R.; Wu, Q.L.; Satpute, S.R.; Tan, M.T.; Simon, J.E.; Berman, B.M.; Moudgil, K.D. Green tea protects rats against autoimmune arthritis by modulating disease-related immune events. J Nutr 2008, 138, 2111–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mythilypriya, R.; Shanthi, P.; Sachdanandam, P. Restorative and synergistic efficacy of Kalpaamruthaa, a modified Siddha preparation, on an altered antioxidant status in adjuvant induced arthritic rat model. Chem Biol Interact 2007, 168, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Sannigrahi, S.; Majumdar, S.; Ghosh, B.; Sarkar, B. Resveratrol regulates antioxidant status, inhibits cytokine expression and restricts apoptosis in carbon tetrachloride induced rat hepatic injury. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2011, 2011, 703676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikary, R.; Sultana, S.; Bishayi, B. Clitoria ternatea flower petals: Effect on TNFR1 neutralization via downregulation of synovial matrix metalloproteases. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2018, 210, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamgeer; Uttra, A.M.; Hasan, U.H. Anti-arthritic activity of aqueous-methanolic extract and various fractions of Berberis orthobotrys Bien ex Aitch. BMC complementary and alternative medicine 2017, 17, 371. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, S.; Saleem, M.; Asif, M.; Hussain, K.; Butt, B.Z. Diospyros malabarica (Desr.) Kostel fruits extract attenuated acute and chronic inflammation through modulation of the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory biomarkers in rat models. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 2211–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pragasam, S.J.; Venkatesan, V.; Rasool, M. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effect of p-coumaric acid, a common dietary polyphenol on experimental inflammation in rats. Inflammation 2013, 36, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, B.; Jia, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Cinnamtannin D1 attenuates autoimmune arthritis by regulating the balance of Th17 and treg cells through inhibition of aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression. Pharmacological research 2020, 151, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathi, B.; Bodhankar, S.; Mohan, V.; Thakurdesai, P. Ameliorative Effects of a Polyphenolic Fraction of Cinnamomum zeylanicum L. Bark in Animal Models of Inflammation and Arthritis. Scientia pharmaceutica 2013, 81, 567–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pašková, Ľ.; Kuncírová, V.; Poništ, S.; Mihálová, D.; Nosáľ, R.; Harmatha, J.; Hrádková, I.; Čavojský, T.; Bilka, F.; Šišková, K.; et al. Effect of N-Feruloylserotonin and Methotrexate on Severity of Experimental Arthritis and on Messenger RNA Expression of Key Proinflammatory Markers in Liver. Journal of immunology research 2016, 2016, 7509653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillo, M.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.; Ferrándiz, M.L. Anti-inflammatory and joint protective effects of extra-virgin olive-oil polyphenol extract in experimental arthritis. J Nutr Biochem 2014, 25, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillo, M.A.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; González-Benjumea, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.G.; Lubberts, E.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Preventive effects of dietary hydroxytyrosol acetate, an extra virgin olive oil polyphenol in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Molecular nutrition & food research 2015, 59, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Kino, T.; Itoh, T.; Imano, M.; Tanabe, G.; Muraoka, O.; Satou, T.; Nishida, S. Mangiferin suppresses CIA by suppressing the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and RANKL through inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and ERK1/2. American journal of translational research 2015, 7, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Cai, H. The effect of curcumin and its nanoformulation on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Drug design, development and therapy 2015, 9, 4931–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiki, G.; Pop, R.M.; Sabin, O.; Bocsan, I.C.; Chedea, V.S.; Socaci, S.A.; Pârvu, A.E.; Finsia, E.; Francis, T.; Mathieu, Z.; et al. Polyphenols from Dichrostachys cinerea Fruits Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic, and Antioxidant Capacity in Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Arthritic Rat Model. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; et al. Anti-arthritic activities of ethanol extracts of Circaea mollis Sieb. & Zucc. (whole plant) in rodents. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2018, 225, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumatia, E.K.; Baffour, P.K.; Bolah, P. Antiarthritic and Antioxidant Activities of Antrocaryon micraster Seed Extract and Its Fractions. BioMed research international 2024, 2024, 8838626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, F.; Lorenzo, J.; Drissi, H.; Lee, F.Y.; Soung, D.Y. Dried plum alleviates symptoms of inflammatory arthritis in TNF transgenic mice. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry 2018, 52, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, F.; Saleem, M.; Jamshaid, T.; Jamshaid, U.; Youssef, F.S.; Diri, R.M.; Elhady, S.S.; Ashour, M.L. Opuntia monacantha: Validation of the anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity of its polyphenolic rich extract in silico and in vivo via assessment of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2024, 326, 117884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamgeer; Shanila, A.; Ambreen Malik, U.; Umme Habiba, H. Alkaloids, flavonoids, polyphenols might be responsible for potent antiarthritic effect of Solanum nigrum. Journal of traditional Chinese medicine = Chung i tsa chih ying wen pan 2019, 39, 632–641.
- Hannan, A.; Akhtar, B.; Sharif, A.; Anjum, F.; Pasha, I.; Khan, A.; Akhtar, M.F.; Saleem, A. Quercetin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles ameliorate adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats by regulating anti-oxidant enzymes and downregulating pro- and inflammatory cytokines. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossalayi, M.D.; Rambert, J.; Renouf, E.; Micouleau, M.; Mérillon, J.M. Grape polyphenols and propolis mixture inhibits inflammatory mediator release from human leukocytes and reduces clinical scores in experimental arthritis. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2014, 21, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhlali, E.d.T.; Hmidani, A.; Bourkhis, B.; Khouya, T.; Ramchoun, M.; Filali-Zegzouti, Y.; Alem, C. Phenolic profile and anti-inflammatory activity of four Moroccan date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seed varieties. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimóteo, N.S.B.; Iryioda, T.M.V.; Alfieri, D.F.; Rego, B.E.F.; Scavuzzi, B.M.; Fatel, E.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Simão, A.N.C.; Dichi, I. Cranberry juice decreases disease activity in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.) 2019, 60, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatel, E.C.S.; Rosa, F.T.; Alfieri, D.F.; Flauzino, T.; Scavuzzi, B.M.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Iriyoda, T.M.V.; Simão, A.N.C.; Dichi, I. Beneficial effects of fish oil and cranberry juice on disease activity and inflammatory biomarkers in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.) 2021, 86, 111183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavipour, M.; Sotoudeh, G.; Tavakoli, E.; Mowla, K.; Hasanzadeh, J.; Mazloom, Z. Pomegranate extract alleviates disease activity and some blood biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis patients. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2017, 71, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khojah, H.M.; Ahmed, S.; Abdel-Rahman, M.S.; Elhakeim, E.H. Resveratrol as an effective adjuvant therapy in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a clinical study. Clinical rheumatology 2018, 37, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
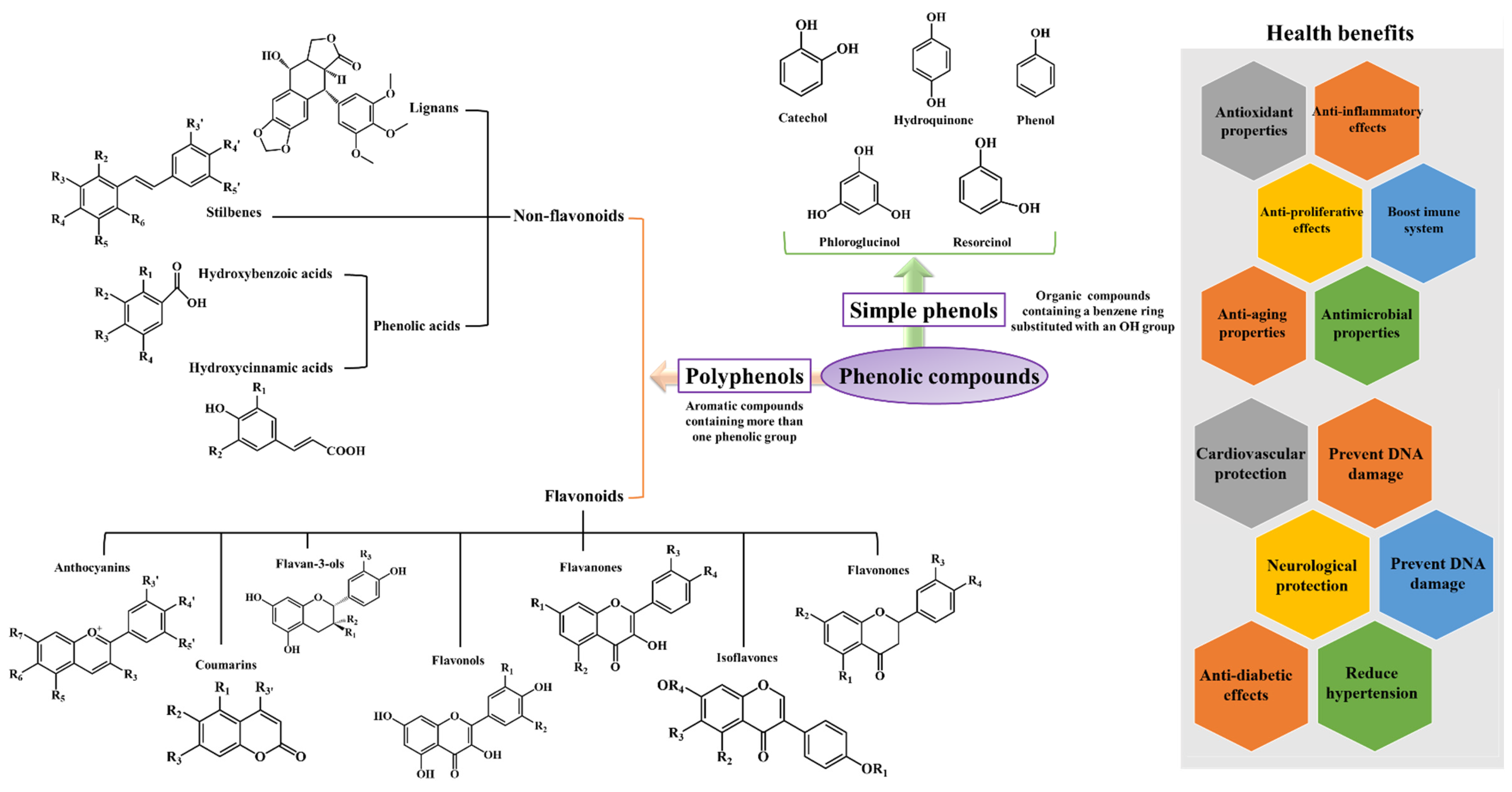
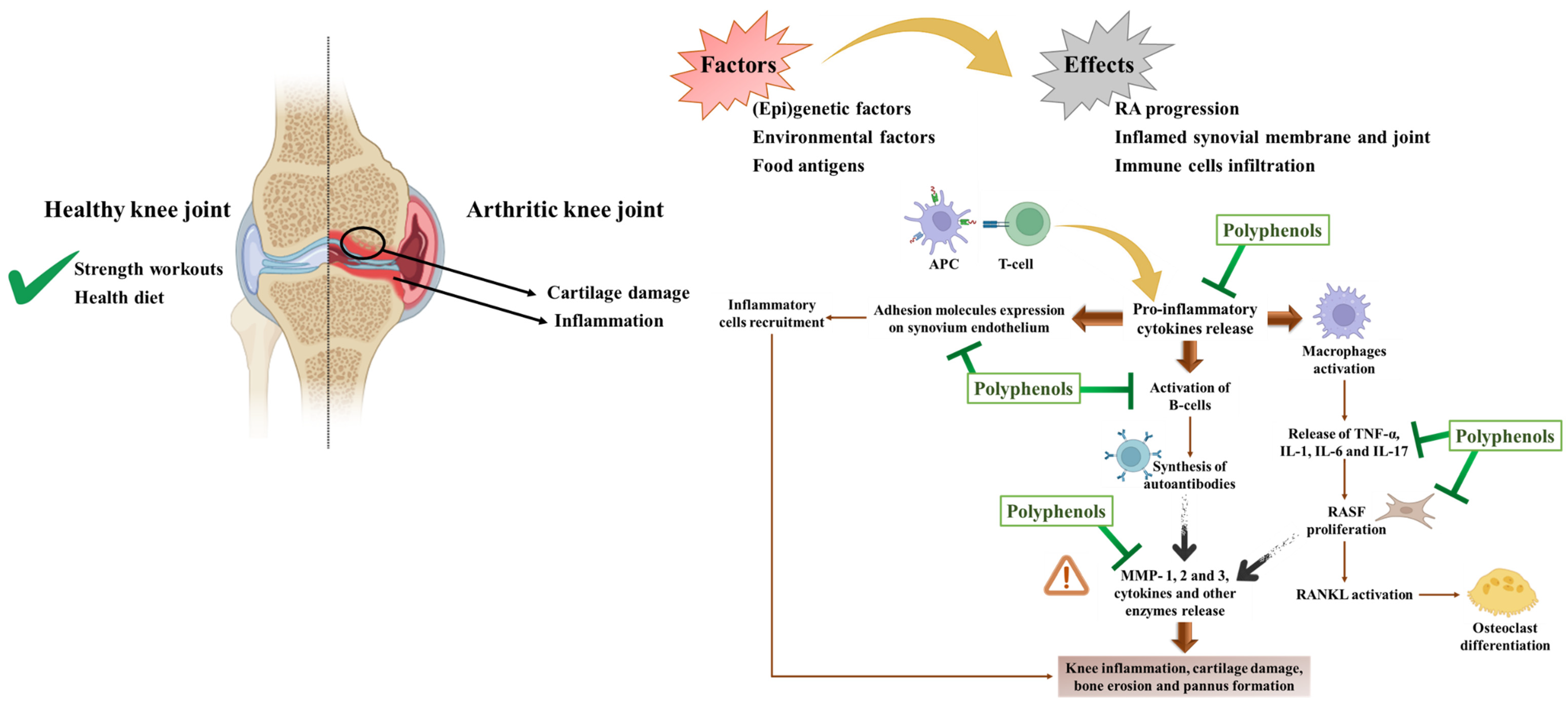
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





