1. Introduction
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a metabolite involved in lipid metabolism, is also known to induce a plethora of effects acting as a messenger in intercellular communication, i.e., it is a “bioactive lipid", exerting those actions through interaction with different receptors, mainly those of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily [
1,
2,
3]. Six of these receptors are generally considered to constitute the LPA receptor subfamily (LPA1-6). These receptors are expressed almost ubiquitously and frequently exhibit promiscuous interaction with various G proteins that activate many signaling pathways [
1,
2,
3].
The LPA
3 receptor, the subject of this work, has a vast expression in tissues, and it is particularly abundant in the heart, testicles, prostate, and pancreas, while it has lower expression in the lungs, brain, colon, duodenum, stomach, thyroid, and the gallbladder [
2]. This receptor participates in many physiological functions and pathological processes, including chemotaxis [
4], migration [
5], proliferation [
6], differentiation [
7], embryo implantations [
8], and determination of vertebrate left-right patterning during embryogenesis [
9], among many others. The relevant role of LPA and its receptors in cancer has been recently reviewed (see [
10] and references therein). In ovarian cancer, LPA
3 expression is considered a therapeutic target and a poor prognosis marker [
6,
11].
As expected for a G protein-coupled receptor, LPA
3 presents in its structure seven transmembrane domains, connected by three intracellular loops and three extracellular loops, an extracellular amino terminus, and an intracellular carboxyl terminus (Ctail). This receptor interacts mainly with two different G protein types, G
αi/o and G
αq/11, triggering different signaling processes via their α and βγ subunits (reviewed in [
1,
2,
3,
12,
13]). It is known that agonist activation increases calcium signaling, activation of protein kinase C (PKC), phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and the MAP kinase cascade, among other pathways (see [
14] and accompanying manuscript [
15]).
It is generally accepted that GPCR agonist activation promotes a series of conformational changes that expose sites that can be phosphorylated by a variety of protein kinases, including but not limited to G protein-coupled receptor kinases and those activated by second messengers, such as protein kinase A and PKC (reviewed in [
16,
17,
18,
19]). Such phosphorylation seems critical in defining interaction with the essential proteins, β-arrestins, which participate in receptor desensitization and internalization [
20,
21,
22]. It is worth mentioning that the phosphorylation state of a receptor is not only what it is functionally relevant but also the specific sites affected by this posttranslational modification. There is evidence that a given receptor can be phosphorylated at distinct sites, and it has been proposed that such difference can lead to distinct receptor functional outcomes, i.e., distinct routes of internalization, subcellular destinations, and different final actions. These ideas are known as the "phosphorylation barcode hypothesis" (reviewed in [
17,
18,
19,
23,
24,
25]).
In the accompanying manuscript [
15], we showed that agonist-stimulated LPA
3 receptors, expressed in Flp-In T-Rex HEK293 cells, were able to increase intracellular calcium, ERK 1/2 phosphorylation, induce LPA
3 phosphorylation, favor receptor interaction with β-arrestin-2 and receptor internalization. Similarly, the PKC activator, phorbol myristate acetate (PMA), induced LPA
3 receptor phosphorylation, interaction with β-arrestin-2, receptor desensitization, and internalization. In addition, we immunopurified the LPA
3 receptor and detected, using mass spectrometry, the sites phosphorylated in cellulo under baseline and stimulated conditions. Phosphorylated residues were detected in the intracellular loop 3 (IL3) (S221, T224, S225, and S229) and in the carboxyl terminus (Ctail) (S321, S325, S331, T333, S335, Y337, and S343) [
15]. In the present work, the function of the wild-type (WT) LPA
3-GFP receptor construct was compared to mutants in which the sites detected phosphorylated in the IL3, Ctail, or both domains (IL3/Ctail) were substituted by non-phosphorylatable amino acids (i.e., serine-alanine and threonine-valine substitutions). The data allowed us to observe that the sites in these domains play different roles in LPA
3 receptor signaling and regulation.
2. Results
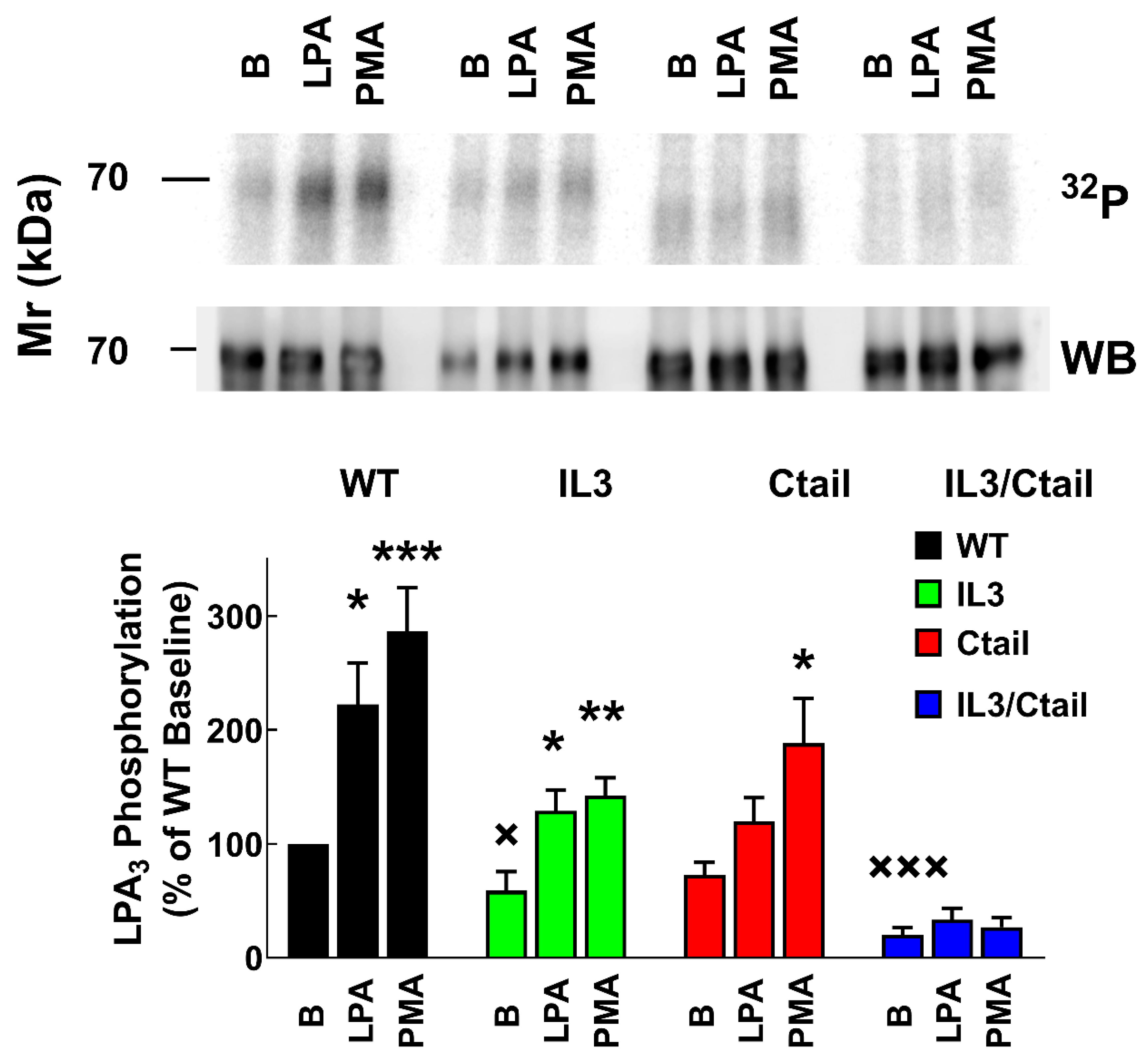
Receptor phosphorylation experiments were performed in cells expressing the WT or the mutant LPA
3 receptors. All these experiments were run in parallel and in the same gels and membranes to allow a proper comparison; cells were incubated without any agent or presence of 1 µM LPA or 1 µM PMA for 15 min (optimal time and agent concentrations [
15]). As shown in
Figure 1, in cells expressing the WT receptor, a light but well-defined baseline receptor phosphorylation was observed, which was markedly increased (2 to 3-fold) by incubation with the agonist, LPA, or the PKC activator, PMA, in agreement with previous results [
15,
26]. Baseline phosphorylation was hardly detectable in cells expressing the IL3/Ctail receptor mutant and no effect of LPA or PMA was observed (
Figure 1). In cells expressing the IL3 receptor mutant, baseline phosphorylation was decreased (≈ 50%) when compared to those expressing the WT, and the effects of LPA and PMA were observed but decreased (
Figure 1). In cells expressing the Ctail mutant, baseline receptor phosphorylation was slightly decreased (≈ 30 %; statistically insignificant) as compared to that in the WT-expressing cells; LPA induced a statistically insignificant increase, and PMA only marginally increased receptor phosphorylation (
Figure 1). It is worth mentioning that, as shown in
Figure 1 (representative image, samples run in the same gel) receptor migration was slightly faster in cells expressing the Ctail and IL3/Ctail mutants. The reason for this is unclear; the plasmids employed were sequenced again and found to be correct.
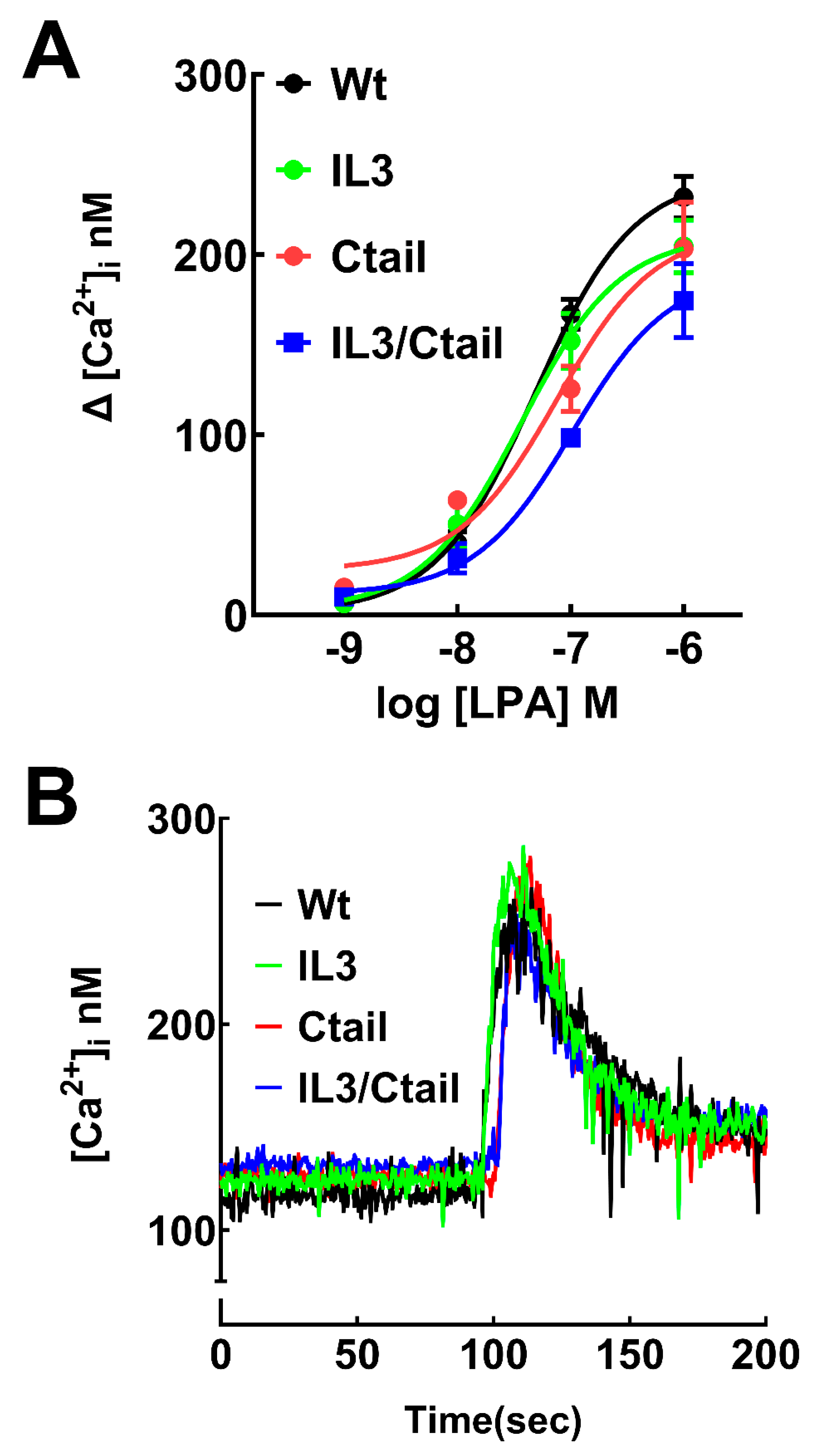
LPA was able to induce an increase in intracellular calcium concentration in cells expressing the WT and mutant LPA
3 receptors (
Figure 2). The response observed with 1 µM LPA was very similar in cells expressing the distinct receptors in the speed of the increases, the maxima reached, and the return toward baseline values, as shown in the representative calcium tracings (
Figure 2B). However, in the concentration-response curves a slight shift to the right was noticed, particularly in the IL3/Ctail mutant that did not reach an evident saturation at 1 µM LPA (
Figure 2A). Nevertheless, the changes were relatively small. We did not detect any change in the baseline calcium concentration in the distinct LPA
3
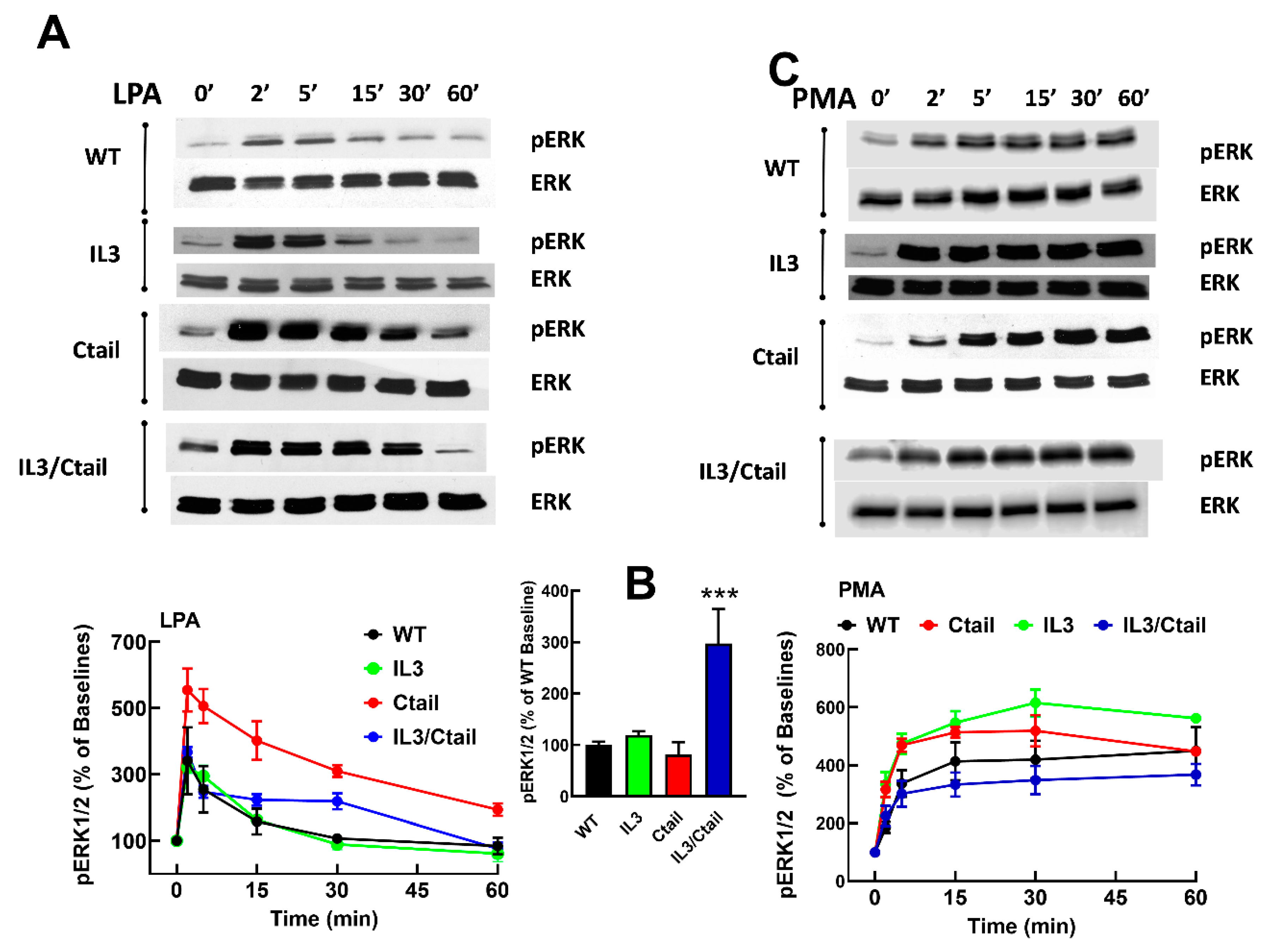
We previously observed that in cells expressing the LPA
3 receptor, LPA and PMA increase ERK 1/2 phosphorylation [
15,
26]. When the effects of LPA and PMA were tested in cells expressing the WT and mutant receptors, similar patterns of ERK phosphorylation were observed (
Figure 3). However, some differences were noticed. For example, the baseline ERK 1/2 phosphorylation state was noticeable but relatively small in WT receptor-expressing cells; however, in cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant, the baseline signal was consistently more intense (
Figure 3B, see also representative immunoblots in Figs. 3 and 4). In
Figure 3, the effects of LPA and PMA were calculated employing the baselines of cells expressing each receptor studied as a reference (100 %). We considered the possibility that the decreased LPA- and PMA-induced responses observed with cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant receptor could only be just apparent (i.e., due to the high baseline value).
Similarly, an increase in the LPA- and PMA-mediated ERK 1/2 phosphorylation was observed in cells expressing the Ctail mutant, but baseline ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in cells expressing this mutant was variable and relatively faint in most experiments. Despite these differences, the general pattern of the responses was similar in cells expressing the distinct LPA
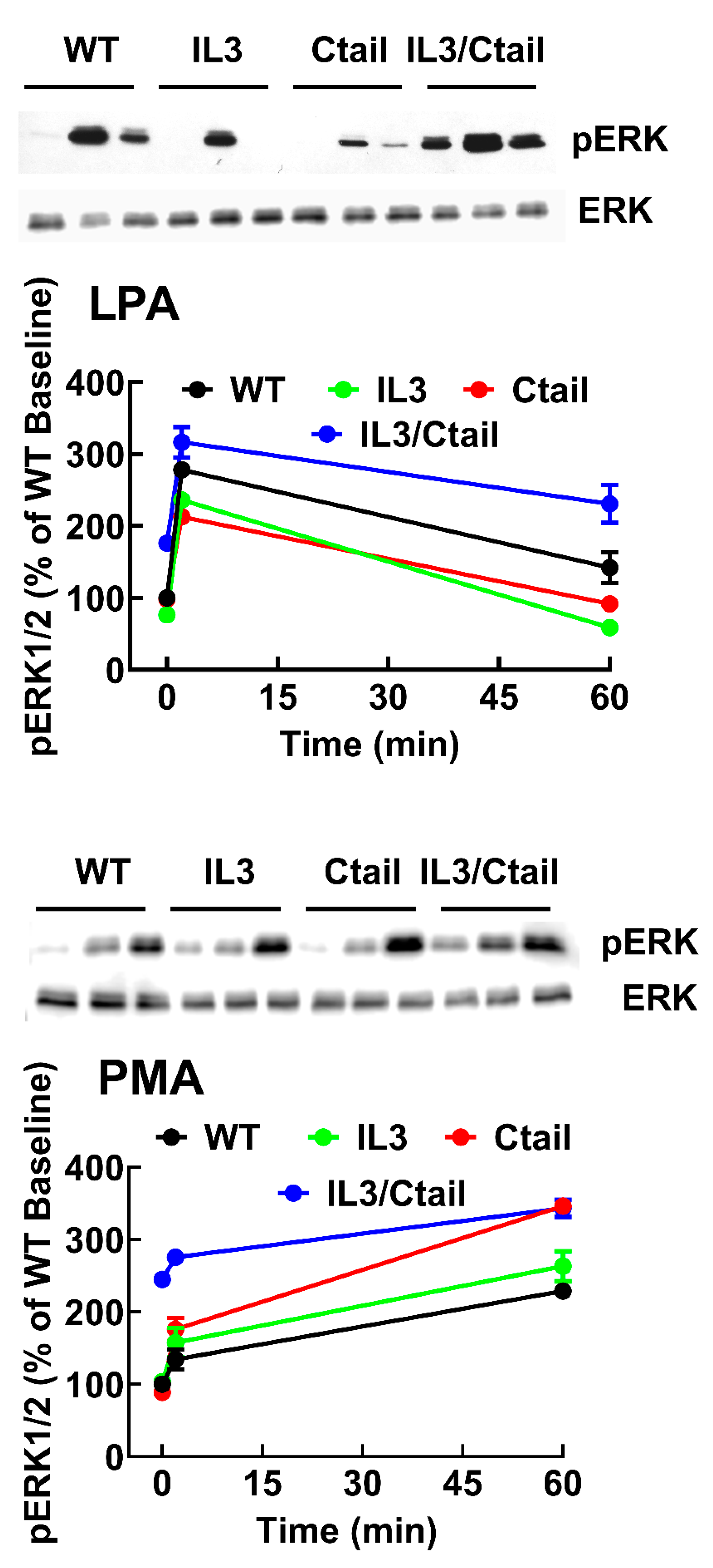
3 mutants. Experiments were performed simultaneously with cells expressing the distinct LPA
3 receptors (baseline and stimulations for 2 and 60 min), and samples were also run in the same gels; in these experiments, the baseline obtained with the WT-expressing cells was considered 100 %. These data confirmed that the baseline signal was more prominent in the IL3/Ctail mutant (p < 0.001) than in cells expressing the WT receptor. The data also evidenced the rapid and transient effect of LPA in the different mutants and the slower but more sustained action of PMA (
Figure 4). The general patterns of the responses were similar in cells expressing the distinct LPA
3 receptors.
As observed with many G protein-coupled receptors, LPA
3 agonist activation induces rapid recruitment of the β-arrestin 2, as evidenced by colocalization and FRET [
15]. We analyzed LPA
3 receptor-β-arrestin 2 interaction using FRET in cells expressing the distinct receptor mutants. As shown in Figs. 5 and 6, the baseline FRET index signal was low in cells expressing the WT receptor. Baseline FRET was slightly increased in cells expressing the Ctail mutant, whereas cells expressing receptors with the IL3 substitutions (i.e., the IL3 and the IL3/Ctail mutants) exhibited a more prominent baseline signal (Fig, 5A and representative images in Figs. 5 and 6). In agreement with our previous observation, 1 µM LPA rapidly (maximum at 2-5 min) increased the LPA
3-β-arrestin 2 FRET signal that decreased progressively at more extended times of incubation (
Figure 5). In cells expressing the IL3 receptor, a small signal was observed at 2 min of stimulation and decreased afterward. Ctail mutant-expressing cells showed an insignificant signal increase at 2 min of incubation with LPA but a more robust response at 30 and 60 min; i.e., a delayed but more sustained effect was detected in cells expressing the Ctail mutant; nevertheless, it was smaller than that observed in WT-expressing cells (
Figure 5). Cell expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant maintained the increased signal observed at the baseline in the presence of 1 µM LPA, and only a faint increase was detected at 60 min (
Figure 5).
In cells expressing the WT receptor, PMA also rapidly increased LPA
3-β-arrestin interaction, as indicated by the FRET index (
Figure 6); a decrease was observed after this initial signal peak. No apparent increase in receptor-β-arrestin interaction was observed in response to PMA in cells expressing the IL3 mutant. In cells expressing the Ctail mutant, a slight and brief increase (2 and 5 min) in FRET was observed which decreased afterward. In cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant, a similar slight and brief increase in FRET signal was observed, but in this case, it was followed by further increases at 30 and 60 min, reaching at the latter time a similar value than that observed with cells expressing the WT receptor, with the same treatment (
Figure 6). The general findings with LPA and PMA were also confirmed by direct observation with video recording (not shown, see [
15]).
We next examined the baseline and stimulated localization of the WT receptor and the distinct receptor mutants. As shown in
Figure 7, the cells expressing all these receptors showed marked fluorescence, patently delineating the plasma membrane; however, some differences were noticed. In cells expressing the WT LPA
3 receptors, only a fraction (≈ 25 %) of the cell’s fluorescence was located intracellularly. We scanned the cells (indicated with a red line in the images), and fluorescence profiles are indicated in the diagrams above the micrographs; as it can be observed, most fluorescence is present in the borders (plasma membrane) of the scan along the WT-expressing cell; some fluorescence in the cytoplasm was also noticed and evidenced as tiny peaks in the scan. It is worth mentioning that the large nucleus of these cells (see also [
15]) makes it challenging to select the region to be scanned. In cells expressing the IL3 receptor mutant, intracellular fluorescence increased (> 30 % of the total fluorescence detected), and this was evidenced in both the photograph and the scan (
Figure 7). Intracellular presence of fluorescence was even more intense in cells expressing the Ctail and IL3/Ctail mutants, reaching ≈ 50-60 % of the total (
Figure 7).
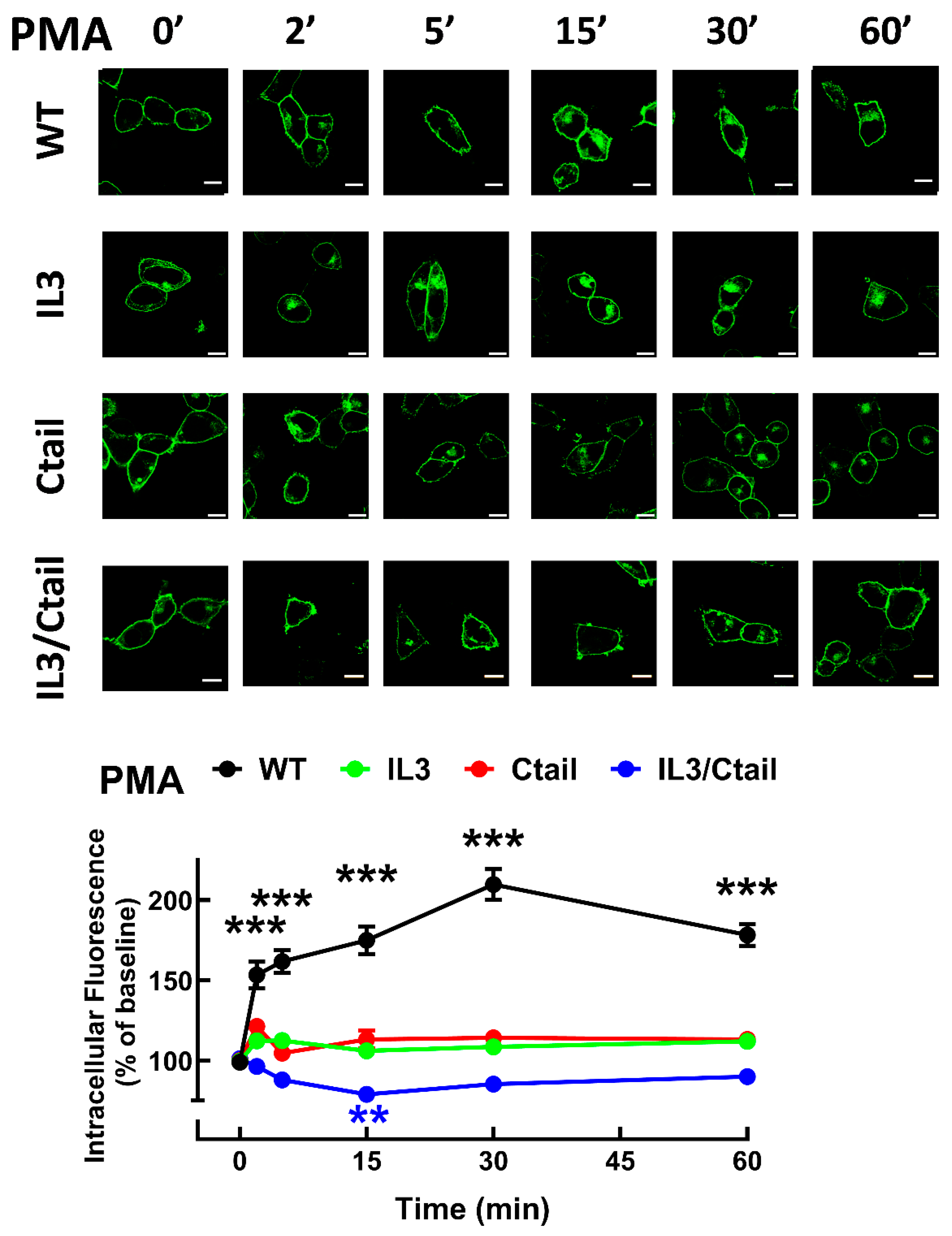
In cells expressing the LPA
3 WT receptor, 1 µM LPA induced a rapid receptor internalization (maximal at 2-5 min), which decreased at 15 min and increased again at 60 min; it was maintained above the initial level through the experiment (60 min) (
Figure 8). Cells expressing the IL3 and IL3/Ctail mutants showed minimal increases in intracellular fluorescence at early times that were maintained throughout the incubation. No LPA-induced change in intracellular fluorescence was observed in cells expressing the Ctail receptors. When cells expressing the WT receptor were challenged with 1 µM PMA, rapid receptor internalization was observed that slightly further increased at 30 min and was above baseline during the whole incubation period (
Figure 9). No PMA-induced internalization was observed in cells expressing the IL3 or Ctail mutants and, unexpectedly, in cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant a slight decrease in intracellular fluorescence was observed (
Figure 9).
Proliferation and migration, two long-term LPA actions, were also studied, considering the roles of the LPA
3 receptor in cancer. It was also observed that cells expressing the mutant receptors reach confluence in the Petri dishes more rapidly than those expressing the WT (
Figure 10A). We studied receptor proliferation using the MTT assay [
27], which determines the oxidative capacity of the culture, an index of cell number.
Both parenteral untransfected Flp-In-TREx HEK293 cells and cells transfected with the WT receptor but uninduced exhibited a reduced proliferation (≈ 45 % and ≈ 25 %, respectively) as compared to those expressing the WT receptor (considered as 100 %) (
Figure 10A). Cells expressing the distinct mutant LPA
3 receptors showed enhanced baseline proliferation (IL3, ≈ 1.7-fold; Ctail, ≈ 2.9-fold, and IL3/Ctail, ≈2-fold) (
Figure 10A). As anticipated when the WT receptor-expressing cells were incubated with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1 µM LPA, 1 µM PMA, or 100 ng/ml EGF, proliferation markedly increased (
Figure 10B). Despite the enhanced baseline proliferation, cells expressing the IL3 mutant receptor showed a similar pattern of enhanced proliferation in response to the agents tested (
Figure 10B). In cells expressing the Ctail or the IL3/Ctail mutants, no significant proliferation increases in response to serum or LPA was observed, which could be related to the enhanced baseline proliferation observed with these cells.
Similar experiments were carried out in cells incubated throughout the experiments (i.e., from induction to the end of the cell incubations) in the presence of 1 µM Ki16425, a well-known LPA
1,3 antagonist. Ki16425 decreased baseline proliferation by ≈ 35 % in cells expressing the WT receptors (
Figure 10C). Interestingly, during these experiments, it was observed that a) the baseline proliferation signal was no longer different among the cells expressing the distinct LPA
3 receptors, b) the actions of serum and LPA were essentially abolished, c) the action of PMA was only marginally detected in the IL3/Ctail expressing cells, and d) the ability of EGF to promote cell proliferation was robust and of a similar magnitude in the cells expressing the distinct LPA
3 receptors but diminished when compared to that in the absence of inhibitor (from 7-8-fold increases to only ≈ 3-fold increases).
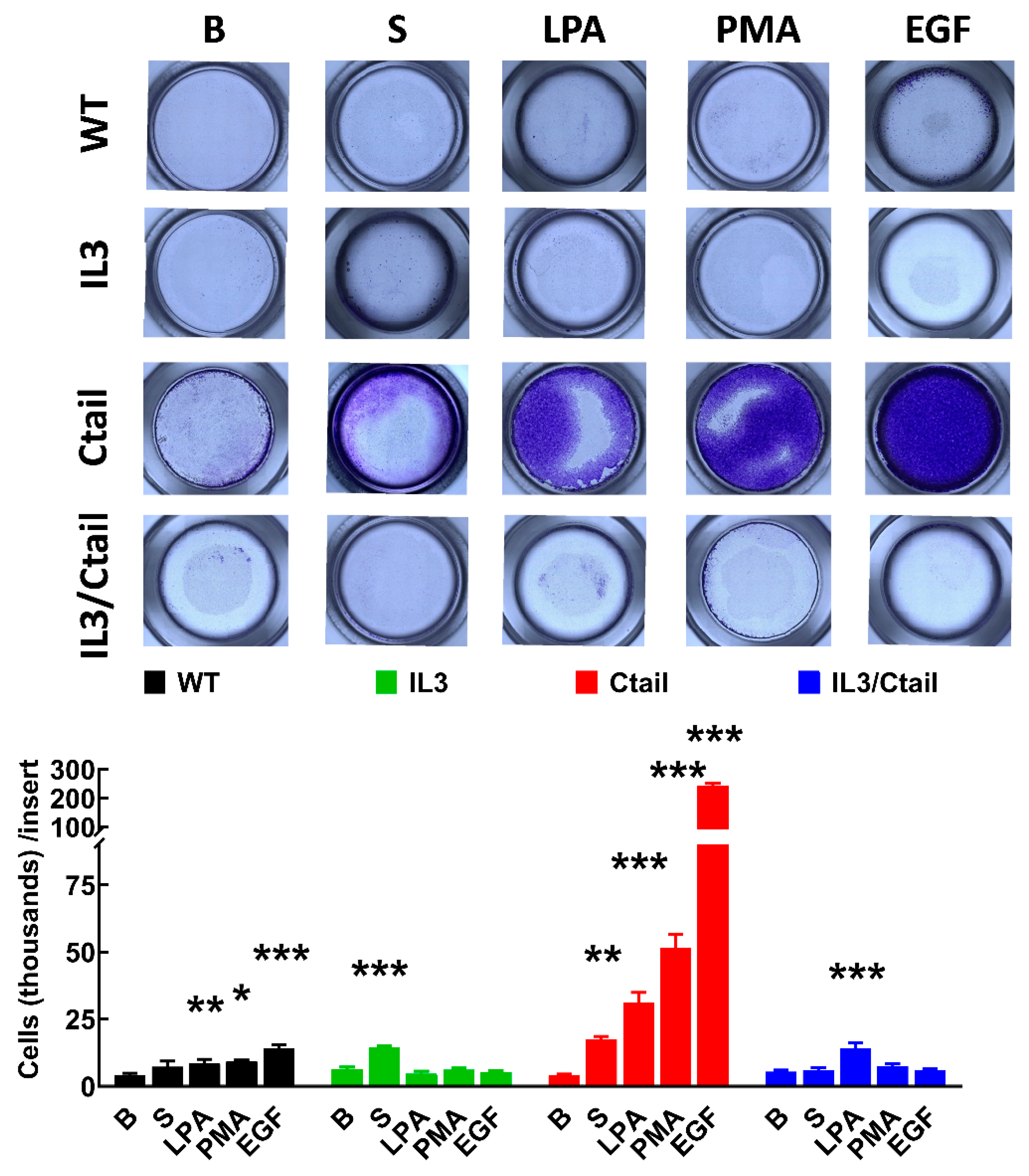
Cell migration was studied with Boyden chambers using the different LPA
3 receptors and serum, LPA, PMA, and EGF, as attractants (
Figure 11). In cells expressing the WT LPA
3 receptor, the different agents induced migration (although the effect of serum was small and did not reach statistical significance), EGF being the most effective. In cells expressing the IL3 mutant, only an effect of serum was observed, whereas, in cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant, only LPA increased migration (
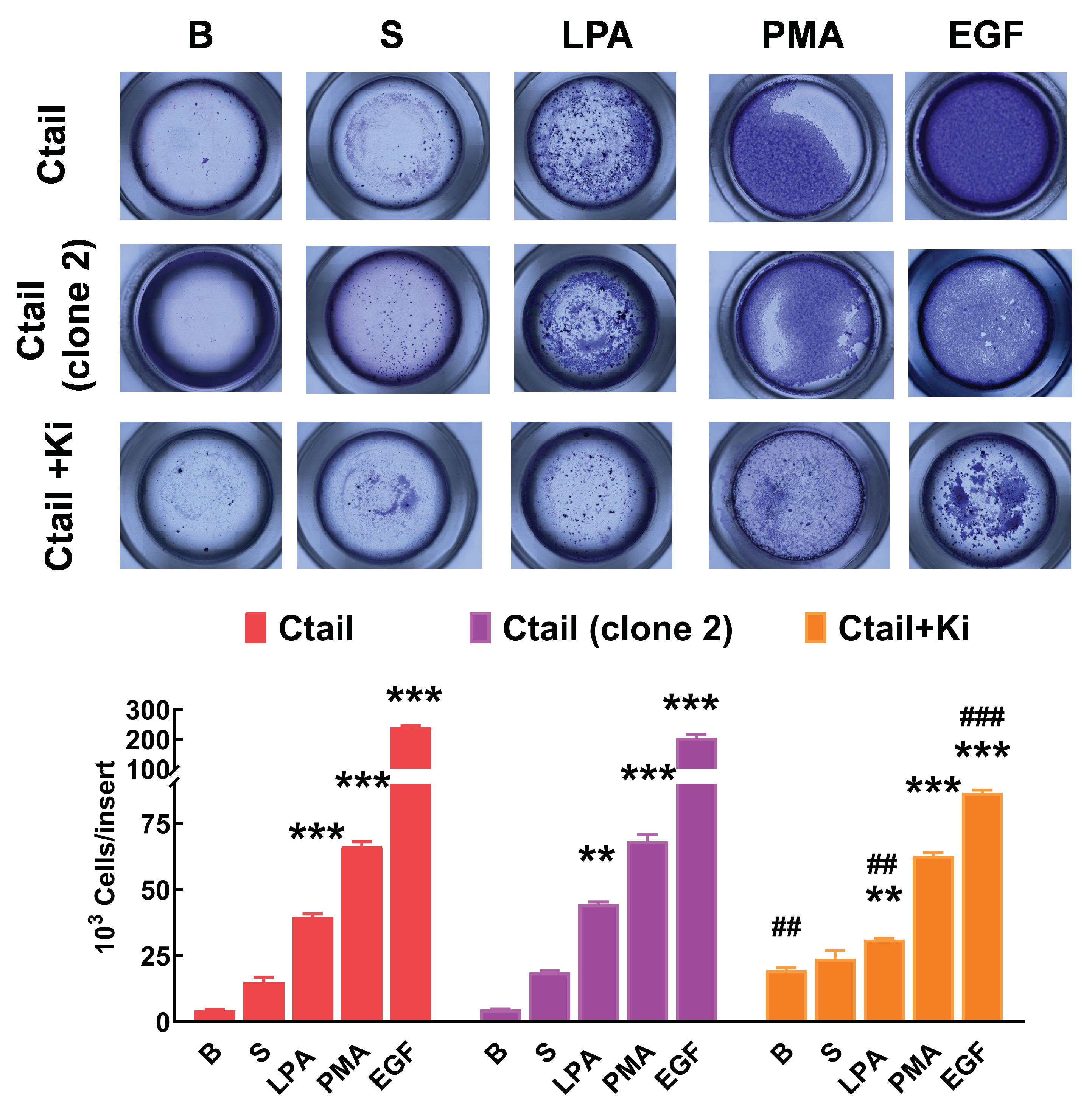
Figure 11). The figure also shows that in cells expressing the Ctail mutant, the effect of all attractants was much more prominent (as much as 10-fold in the case of EGF). We generated another line of cells expressing the Ctail mutant (named here clone 2), and similar effects were observed, discarding the possibility that such an effect could be due to a peculiarity of the cell line (
Figure 12). Incubation with Ki16425 increased by itself baseline migration. Additionally, this LPA
1-3 inhibitor decreased migration in response to LPA and EGF in cells expressing the Ctail mutant (first clone) (
Figure 12).
3. Discussion
Our present data confirm that the sites found phosphorylated in the mass spectrometry studies are those mainly involved in LPA
3 phosphorylation, as evidenced by the fact that substitution by non-phosphorylatable amino acids essentially abolished baseline and stimulated receptor phosphorylation [
15]. Receptor phosphorylation data using the partial substitutions (i.e., cells expressing either the IL3 or the Ctail mutants) indicate that both domains contribute to receptor phosphorylation. As indicated in the Results section, a somewhat faster migration was observed in extracts from cells expressing mutants containing the Ctail substitutions (i.e., the Ctail and IL3/Ctail mutants). After this finding, the plasmids were sequenced again and found to be correct. Therefore, such a faster migration was not due to any sequence change. The changes in receptor phosphorylation themselves could likely be responsible for the faster receptor migration. It could also be attributed to differences in posttranslational receptor modifications, such as changes in glycosylation or proteolysis, which cannot be discarded.
Changes in agonist-induced increases in calcium signaling were relatively small in the concentration-response curves and opposite to what we anticipated, based on similar experiments using the α
1B-adrenergic receptors [
28]. In cells expressing receptors with similar amino acid substitutions of this adrenergic receptor, we observed that cells expressing the IL3 or the Ctail mutants exhibited a shift to the left in the concentration-response curves, and this was even more pronounced in cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant [
28]. In these cells the maximal response was markedly increased, and the return toward baseline was slower [
28]. The data with the adrenergic receptor indicated that eliminating the phosphorylation sites allowed a fuller expression of the receptors' apparent efficacy and potency in these cells (in other words, amino acid substitution eliminates some constraints). The present data employing cells expressing the LPA
3 mutants were different and suggest that modification in the phosphorylation sites of this receptor might decrease the receptors’ affinity for LPA; the data also suggest that receptor phosphorylation might not be sufficient to desensitize the LPA
3 receptor, which is likely related to the difficulties to observe LPA-induced LPA
3 receptor desensitization, and the absence of effect on this parameter of GRK2 or GRK5 overexpression [
15]. It should be mentioned that we did not observe, in the distinct mutants, any change in the baseline calcium concentration. However, we cannot discard the possibility of some endogenous or unrestrained receptor activity, because cells adapt rapidly to maintain, within small margins, their calcium concentration.
It was also unexpected that cells expressing the IL3/Ctail LPA3 mutant receptor exhibited a consistently high ERK 1/2 baseline signal. Such an increase was hard to define due to the intrinsic difficulties of the Western blotting technique, even controlling the exposure time very carefully. For this reason, we recurred to running in parallel cells and samples from cells expressing the WT receptor with those of the mutants, and data were normalized with the WT baseline signal (100 %). The increased ERK phosphorylation of cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant was associated with enhanced baseline LPA3 receptor-β-arrestin interaction (FRET), baseline receptor internalization, and proliferation but not with cell migration. Interestingly, cells expressing the Ctail mutant showed a slight decrease in baseline ERK phosphorylation but a remarkable increase in attractant-induced migration.
The interaction of G protein-coupled receptors with β-arrestins seems to involve receptors’ acidic residues and phosphorylated sites [
21,
22]. Phosphorylation codes for β-arrestin recruitment by G protein-coupled receptors have been discovered [
29], which allows finding putative β-arrestin binding sites in receptors. The LPA
3 phosphorylation sites detected in the IL3 and Ctail [
15] were within putative interaction sites for β-arrestins [
29]. Therefore, we anticipated that cells expressing the mutants, these receptors would interact poorly with β-arrestin. Surprisingly, the baseline FRET signal was increased in cells expressing the mutant receptors. However, the rapid LPA- or PMA-induced receptor-β-arrestin interaction (FRET) was markedly reduced or absent. Only a delayed response to LPA was observed in the cells expressing the Ctail mutant, and a delayed response to PMA was observed in cells expressing the IL3/Ctail mutant.
Phosphorylation of G protein-coupled receptors promotes their interaction with β-arrestins, which plays a crucial role in receptor internalization [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34]. However, there is also evidence of phosphorylation-independent receptor desensitization and internalization [
35,
36]. Our experiments showed that LPA- and PMA-induced receptor-β-arrestin 2 interaction was markedly reduced in the LPA
3 mutants, paralleled with defective agonist- and PKC-induced internalization. It is worth mentioning that both the IL3 and Ctail mutants exhibited these defects, which is consistent but does not prove that phosphorylation sites in both domains participate in receptor-β-arrestin interaction and internalization. Additionally, a correlation seems to exist between the increased baseline FRET signal and the increased baseline intracellular density of fluorescence (receptors). It is possible that the amino acid substitutions performed might alter some steps of the receptor internalization/ recycling to the plasma membrane, but this remains to be explored in the future. Despite this limitation, our data indicate the importance of IL3 and Ctail phosphorylation sites in agonist- and PKC-mediated internalization.
Notably, the mutant receptors exhibit only a slight decrease in their apparent sensitivity to LPA to increase intracellular calcium. Similarly, the changes in LPA-induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation were relatively minor and generally maintained the same response pattern. The only marked change was the increased baseline signal in the IL3/Ctail mutant. These LPA effects are rapid, taking seconds (intracellular calcium) or minutes (ERK phosphorylation) to reach their maxima, and seem to be mediated through pertussis toxin-insensitive G proteins (likely G
q/11) [
15]. Substitution on the LPA
3 receptor residues found phosphorylated [
15] does not decrease these effects closely associated with G protein signaling.
Agonist effects that involve β-arrestin, such as LPA
3-β-arrestin interaction and receptor internalization, were markedly decreased. ERK phosphorylation exhibits two phases: a rapid initial phase, mediated mainly through G protein-initiated pathways, and a second, more sustained phase that involves β-arrestins. Our experiments found no relationship between agonist-induced LPA
3-β-arrestin interaction and ERK phosphorylation. There is evidence indicating that agonists can activate ERK phosphorylation in the absence or presence of β-arrestins [
37].
The mutant receptor-expressing cells had an increased baseline proliferation as evidenced in the MTT assay. It is noteworthy that the sole expression of the WT LPA3 receptor was able to promote baseline proliferation when compared to those with the receptor uninduced. The increased baseline proliferation observed in cells expressing the mutant receptor was abolished by the LPA1,3 antagonist, i.e., under these conditions all the cells expressing the mutant receptors baselines were essentially identical to that of WT receptor-expressing cells. It is possible that LPA traces present in the media or released by the cells might trigger receptor activity and that such activity could be less restrained in the mutant receptors. Additionally, in cells expressing the WT or the mutant receptors, Ki16425 markedly attenuated that the effect of serum, LPA, and PMA, but not that induced by EGF.
The cell migrations studies with the LPA3 mutants also provided some surprising data. In contrast to what took place in proliferation, cells expressing the WT or the mutant receptors exhibit similar baseline migration. The response to the distinct attractants observed in cells expressing the Ctail mutant was unexpectedly intense. Ki16425 reduced, as expected, the effect of LPA, but surprisingly, also that of EGF. The reason for such decrease is presently unknown. Cells expressing a mutated IL3 domain (i.e., IL3 and IL3/Ctail mutants) showed markedly decreased migration responses to PMA and EGF. In principle, the action of these agents could be independent of the LPA3 receptors. Therefore, the possibility that the modified IL3 domain might interfere with a fundamental step in the migration process should be considered.
Figure 1.
LPA- and PMA-induced LPA3 receptor phosphorylation. Cells expressing the WT and mutant receptors were challenged with 1 µM LPA or 1 µM PMA for 15 min. Receptor phosphorylation is expressed as the percentage of the WT baseline value. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-9 experiments performed on different days using different cell cultures. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 vs. baseline value. Representative autoradiographs (32P) and Western blots (WB) are presented above the graph.
Figure 1.
LPA- and PMA-induced LPA3 receptor phosphorylation. Cells expressing the WT and mutant receptors were challenged with 1 µM LPA or 1 µM PMA for 15 min. Receptor phosphorylation is expressed as the percentage of the WT baseline value. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-9 experiments performed on different days using different cell cultures. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 vs. baseline value. Representative autoradiographs (32P) and Western blots (WB) are presented above the graph.
Figure 2.
Increases in intracellular calcium in cells expressing WT or mutant LPA3 receptors. Panel A, Concentration-response curves in observed cells expressing the different LPA3 receptors. The abscissa indicates the increments in calcium concentration. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 5 experiments performed on different days and distinct cell cultures. Panel B; Cells expressing the WT and mutant receptors were challenged with 1 µM LPA (arrow). Representative calcium tracings are shown.
Figure 2.
Increases in intracellular calcium in cells expressing WT or mutant LPA3 receptors. Panel A, Concentration-response curves in observed cells expressing the different LPA3 receptors. The abscissa indicates the increments in calcium concentration. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 5 experiments performed on different days and distinct cell cultures. Panel B; Cells expressing the WT and mutant receptors were challenged with 1 µM LPA (arrow). Representative calcium tracings are shown.
Figure 3.
Time-course of LPA- and PMA-induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in cells expressing WT or mutant LPA3 receptors. Cells were stimulated with 1 µM LPA (Panel A) or 1 µM PMA (Panel C). Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed in the same cells. Panel B shows the comparative baseline values normalized to that of cells expressing the WT receptor (100%). The mean is plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 5 experiments performed on different days using distinct cell cultures. ***p < 0.0001 vs. WT baseline value. Representative Western blots are presented above the figure.
Figure 3.
Time-course of LPA- and PMA-induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in cells expressing WT or mutant LPA3 receptors. Cells were stimulated with 1 µM LPA (Panel A) or 1 µM PMA (Panel C). Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed in the same cells. Panel B shows the comparative baseline values normalized to that of cells expressing the WT receptor (100%). The mean is plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 5 experiments performed on different days using distinct cell cultures. ***p < 0.0001 vs. WT baseline value. Representative Western blots are presented above the figure.
Figure 4.
Time-course of LPA- and PMA-induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in cells ex pressing WT or mutant LPA3 receptors. Experiments were run in parallel with cells expressing WT and mutant receptors to compare the effects properly. Cells were stimulated with 1 µM LPA (Panel A) or 1 µM PMA (Panel B) for 0, 2, and 60 min. Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed in cells expressing the WT receptor. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 5-7 experiments performed on different days using distinct cell cultures. Representative Western blots are presented above the figure.
Figure 4.
Time-course of LPA- and PMA-induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in cells ex pressing WT or mutant LPA3 receptors. Experiments were run in parallel with cells expressing WT and mutant receptors to compare the effects properly. Cells were stimulated with 1 µM LPA (Panel A) or 1 µM PMA (Panel B) for 0, 2, and 60 min. Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed in cells expressing the WT receptor. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 5-7 experiments performed on different days using distinct cell cultures. Representative Western blots are presented above the figure.
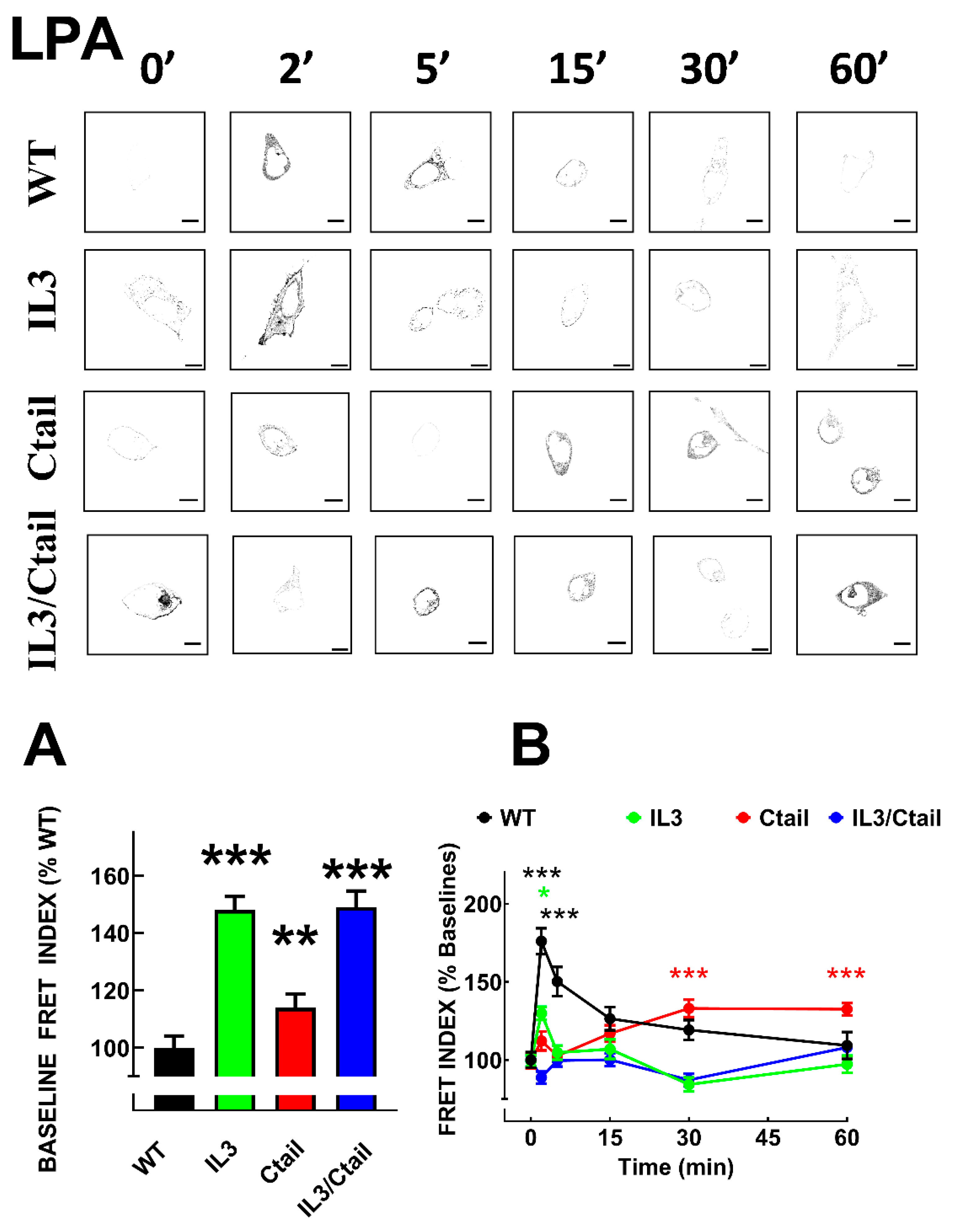
Figure 5.
Time-course of LPA-induced LPA3-β-arrestin interaction in cells expressing WT or mutant receptors. Panel A. Baseline FRET index observed in cells expressing the distinct LPA3 receptors. The baseline WT FRET index was considered as 100%. Panel B. Cells were incubated for the times indicated with 1µM LPA. Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed with cells expressing each receptor. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed for each condition in each experiment. In Panel A, ***p < 0.001 and **p < 0.01 vs. WT value; in Panel B, ***p < 0.001 and *p < 0.05 vs. respective baseline FRET value. Representative FRET index images are presented above the graph. Bars 10 µm.
Figure 5.
Time-course of LPA-induced LPA3-β-arrestin interaction in cells expressing WT or mutant receptors. Panel A. Baseline FRET index observed in cells expressing the distinct LPA3 receptors. The baseline WT FRET index was considered as 100%. Panel B. Cells were incubated for the times indicated with 1µM LPA. Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed with cells expressing each receptor. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed for each condition in each experiment. In Panel A, ***p < 0.001 and **p < 0.01 vs. WT value; in Panel B, ***p < 0.001 and *p < 0.05 vs. respective baseline FRET value. Representative FRET index images are presented above the graph. Bars 10 µm.
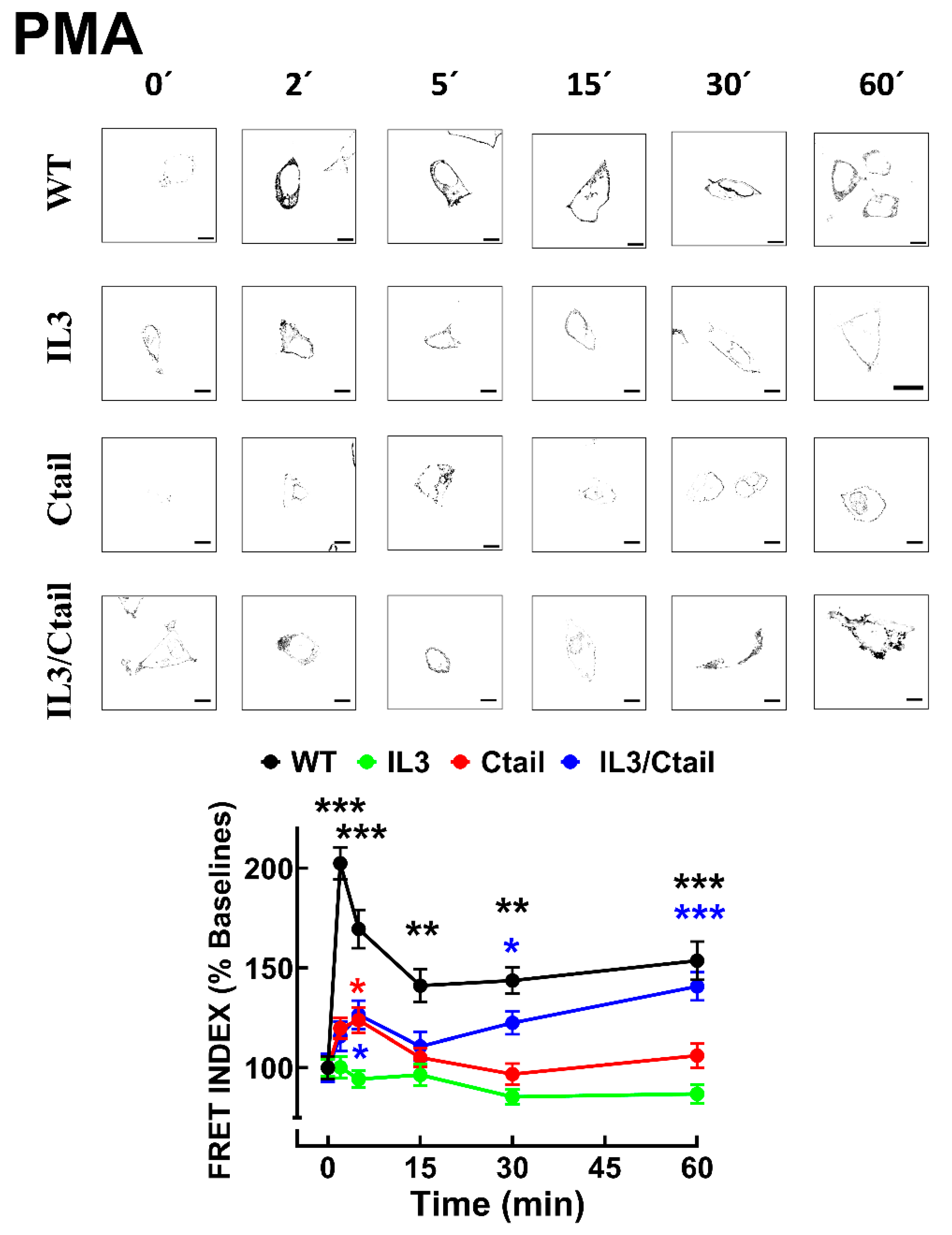
Figure 6.
Time-course of PMA-induced LPA3-β-arrestin interaction in cells expressing WT or mutant receptors. Cells were incubated for the times indicated with 1µM PMA. Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed with cells expressing each receptor. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed for each condition in each experiment. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and *p <0.05 vs. respective baseline FRET value. Representative FRET index images are presented above the graph. Bars 10 µm.
Figure 6.
Time-course of PMA-induced LPA3-β-arrestin interaction in cells expressing WT or mutant receptors. Cells were incubated for the times indicated with 1µM PMA. Data are presented as the percentage of the baseline observed with cells expressing each receptor. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed for each condition in each experiment. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and *p <0.05 vs. respective baseline FRET value. Representative FRET index images are presented above the graph. Bars 10 µm.
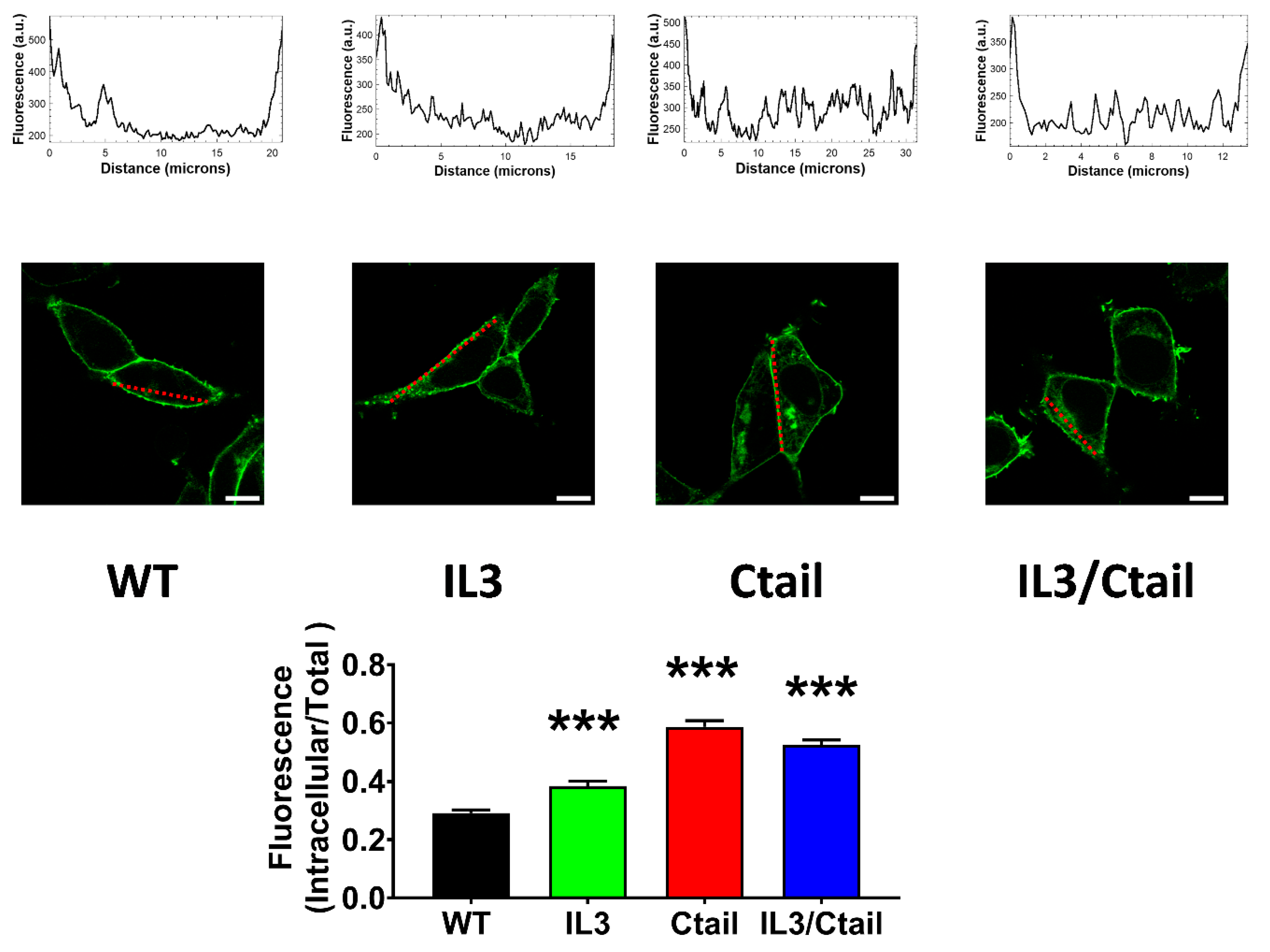
Figure 7.
Baseline intracellular fluorescence of cells expressing WT and mutant LPA3 receptors. Cells expressing the different LPA
3 receptor constructs were analyzed before any stimulation. Total fluorescence and that not located in the plasma membrane region were quantified, and the ratio was obtained. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed (i.e., 49 to 64). ***p <0.001 vs. WT. Representative images are presented above the graph (Bars 10 µm); a red line indicates the region in which the fluorescence scan was performed (notice that the large nucleus was avoided (see also [
15])). The fluorescence scans are presented above the cell images.
Figure 7.
Baseline intracellular fluorescence of cells expressing WT and mutant LPA3 receptors. Cells expressing the different LPA
3 receptor constructs were analyzed before any stimulation. Total fluorescence and that not located in the plasma membrane region were quantified, and the ratio was obtained. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed (i.e., 49 to 64). ***p <0.001 vs. WT. Representative images are presented above the graph (Bars 10 µm); a red line indicates the region in which the fluorescence scan was performed (notice that the large nucleus was avoided (see also [
15])). The fluorescence scans are presented above the cell images.
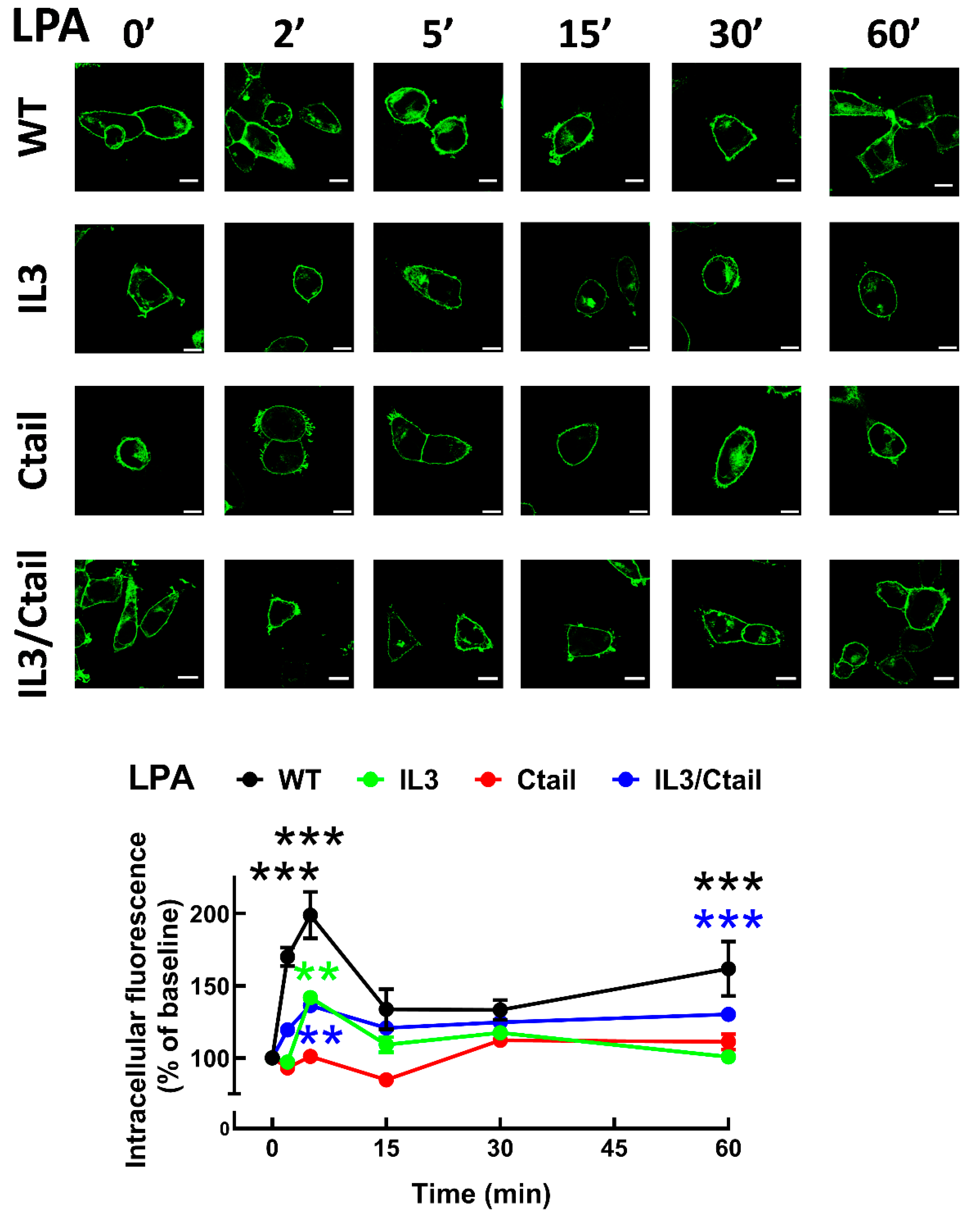
Figure 8.
Baseline intracellular fluorescence of cells expressing WT and mutant LPA3 receptors. Cells expressing the different LPA
3 receptor constructs were analyzed before any stimulation. Total fluorescence and that not located in the plasma membrane region were quantified, and the ratio was obtained. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed (i.e., 49 to 64). ***p <0.001 vs. WT. Representative images are presented above the graph (Bars 10 µm); a red line indicates the region in which the fluorescence scan was performed (notice that the large nucleus was avoided (see also [
15])). The fluorescence scans are presented above the cell images.
Figure 8.
Baseline intracellular fluorescence of cells expressing WT and mutant LPA3 receptors. Cells expressing the different LPA
3 receptor constructs were analyzed before any stimulation. Total fluorescence and that not located in the plasma membrane region were quantified, and the ratio was obtained. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed (i.e., 49 to 64). ***p <0.001 vs. WT. Representative images are presented above the graph (Bars 10 µm); a red line indicates the region in which the fluorescence scan was performed (notice that the large nucleus was avoided (see also [
15])). The fluorescence scans are presented above the cell images.
Figure 9.
PMA-induced LPA3 receptor internalization. Cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs were stimulated with 1 µM PMA, and intracellular fluorescence was quantified; data were normalized to the baseline obtained for each receptor construct. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed (i.e., 49 to 64). ***p <0.001 vs. respective baseline value. Representative images are presented above the graph (Bars 10 µm).
Figure 9.
PMA-induced LPA3 receptor internalization. Cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs were stimulated with 1 µM PMA, and intracellular fluorescence was quantified; data were normalized to the baseline obtained for each receptor construct. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 7-8 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures; 7-8 images were analyzed (i.e., 49 to 64). ***p <0.001 vs. respective baseline value. Representative images are presented above the graph (Bars 10 µm).
Figure 10.
Proliferation of cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs. Panel A. Cell proliferation was determined using the MTT assay indicated in Material and Methods. Panel A: Baseline proliferation observed in µ Flp-In T-Rex HEK293 cells (PAR), cells transfected with the WT plasmid (but not induced; WT NI), and cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs. Data were normalized to the value obtained with cells expressing the WT receptor (100%). The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 12 experiments in duplicate performed on different days and cell cultures. *p< 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs. WT baseline. Panel B: Cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs were challenged with no agent (Baseline), 10 % serum, 1 µM LPA, 1 µM PMA, or 100 ng/ml EGF. Data were normalized to the baseline obtained with cells expressing the WT receptor (100%). The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 8 experiments in duplicate performed on different days and cell cultures. *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 vs. the baseline or each cell line. Panel C: Baseline proliferation in cells expressing the WT receptor incubated in the absence (100%) or presence of 1 µM Ki16425. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 8 experiments performed in duplicate on different days and cell cultures. ***p < 0.001 vs. absence of inhibitor. Panel D: Experiments were performed as indicated for Panel B, but all samples contained 1 µM Ki16425. Other indications as in Panel B.
Figure 10.
Proliferation of cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs. Panel A. Cell proliferation was determined using the MTT assay indicated in Material and Methods. Panel A: Baseline proliferation observed in µ Flp-In T-Rex HEK293 cells (PAR), cells transfected with the WT plasmid (but not induced; WT NI), and cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs. Data were normalized to the value obtained with cells expressing the WT receptor (100%). The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 12 experiments in duplicate performed on different days and cell cultures. *p< 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs. WT baseline. Panel B: Cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs were challenged with no agent (Baseline), 10 % serum, 1 µM LPA, 1 µM PMA, or 100 ng/ml EGF. Data were normalized to the baseline obtained with cells expressing the WT receptor (100%). The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 8 experiments in duplicate performed on different days and cell cultures. *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 vs. the baseline or each cell line. Panel C: Baseline proliferation in cells expressing the WT receptor incubated in the absence (100%) or presence of 1 µM Ki16425. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 8 experiments performed in duplicate on different days and cell cultures. ***p < 0.001 vs. absence of inhibitor. Panel D: Experiments were performed as indicated for Panel B, but all samples contained 1 µM Ki16425. Other indications as in Panel B.
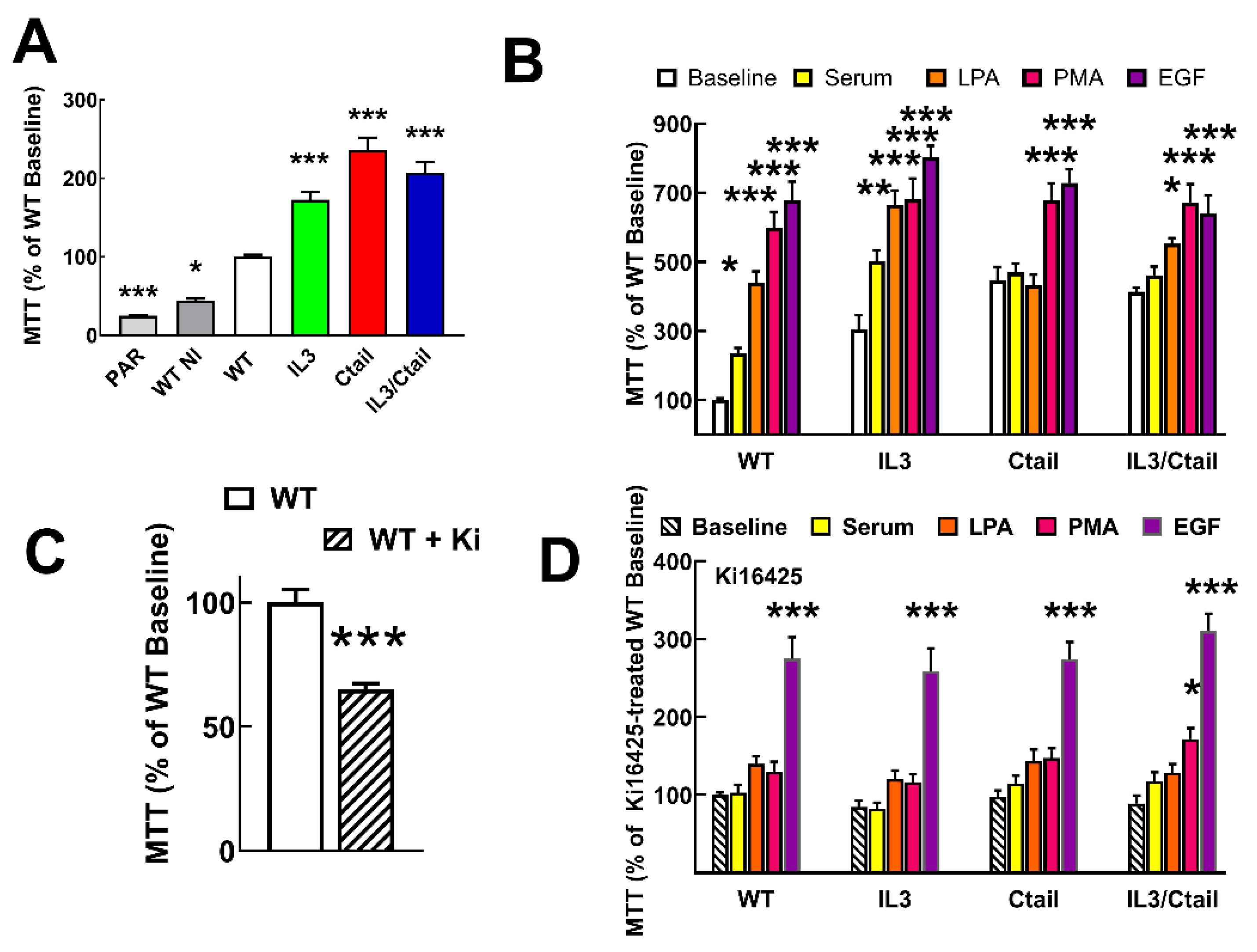
Figure 11.
Migration of cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs. Cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs were plated in Boyden Chambers, and the attractants were tested; i.e., absence of attractant (B, baseline), 10 % serum (S), 1 µM LPA, 1 µM PMA or 100 ng/ml EGF. Data are expressed as thousands of cells/ inserts. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 4 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures. ***p < 0.001, **p <0.01, and *p <0.01 vs. their respective baseline values. Above the graph, a photograph of the inserts of a representative experiment is shown.
Figure 11.
Migration of cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs. Cells expressing the different LPA3 receptor constructs were plated in Boyden Chambers, and the attractants were tested; i.e., absence of attractant (B, baseline), 10 % serum (S), 1 µM LPA, 1 µM PMA or 100 ng/ml EGF. Data are expressed as thousands of cells/ inserts. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 4 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures. ***p < 0.001, **p <0.01, and *p <0.01 vs. their respective baseline values. Above the graph, a photograph of the inserts of a representative experiment is shown.
Figure 12.
Migration of two different cell lines expressing the Ctail LPA3 receptor and effect of Ki16425. Cells were plated in Boyden chambers, and experiments were performed as described in
Figure 11. In the left group of columns (red), the original cell line was employed, and in the middle group (purple), a cell line generated on a different day also expressing the same Ctail LPA
3 receptor construct was used. The original cell line was employed in the right group of columns (orange), but the cells were incubated in media containing 1 µM Ki16425. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 3 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures. ***p < 0.001 and **p <0.01, *p <0.01 vs. their respective baseline values. ## p< 0.01 and ### p< 0.001 vs. cells of the original group incubated without Ki16425.
Figure 12.
Migration of two different cell lines expressing the Ctail LPA3 receptor and effect of Ki16425. Cells were plated in Boyden chambers, and experiments were performed as described in
Figure 11. In the left group of columns (red), the original cell line was employed, and in the middle group (purple), a cell line generated on a different day also expressing the same Ctail LPA
3 receptor construct was used. The original cell line was employed in the right group of columns (orange), but the cells were incubated in media containing 1 µM Ki16425. The means are plotted, and vertical lines indicate the SEM of 3 experiments performed on different days and cell cultures. ***p < 0.001 and **p <0.01, *p <0.01 vs. their respective baseline values. ## p< 0.01 and ### p< 0.001 vs. cells of the original group incubated without Ki16425.