1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) has witnessed over sixty years of development, with its progression leading to transformative applications that significantly impact various aspects of our lives. The core objective of AI is to emulate and augment human intelligence, resulting in the creation of intelligent machines [1, 2]. As AI systems rapidly evolve, their integration becomes increasingly prevalent in governance. Government and agency managers grapple with decision-making challenges involving vast amounts of data, necessitating the consideration of rational choices coupled with human experiential insights[
3].
The ability of managers to navigate rational decisions holds pivotal importance for their tactical and strategic choices, particularly within the domain of digital government. AI technology's growing significance in modern enterprises is chiefly attributed to its proven capacity to alleviate administrative burdens, enabling data-driven decisions as opposed to relying solely on intuition[
4]. While previous studies assert that AI can engage in rational thinking and actions [5-7], differing opinions highlight cautious approaches [8-11]. The scepticism revolves around AI's ability to surmount obstacles to practical reasoning.
Government research on AI is in its nascent stages, focusing on expected impacts and theoretical aspects. There exists substantial room for empirical research on natural and AI applications, especially in government sectors [8, 9, 12]. Alan Turing's Machine stands as a seminal intelligent computer model, playing a pivotal role in AI studies and inspiring the pursuit of "thinking machines" capable of human-like reasoning [1, 2, 13]. As AI holds immense potential across various government sectors, encompassing education, healthcare, transportation, telecommunications, infrastructure, data protection, finance, policymaking, legal systems, and research and development, governments are compelled to consider and incorporate AI to enhance the efficiency of their decision-making processes [10, 14]. This study focuses specifically on machine learning (ML), the most commonly used technique within AI. The field of machine learning, which falls under the umbrella of artificial intelligence, enables machines to enhance their performance by learning from available data eliminating the necessity for explicit programming. [15-17]. Supervised machine learning (Sup_Lea) and unsupervised machine learning (Uns_Lea) constitute the two main dimensions of ML, involving knowledge extraction from observed outcomes and discovering insights from data without predetermined results, respectively[15, 16, 18].
In the realm of ML research within the government sector, the field is still in its early stages, with primary emphasis on expected impacts and theoretical aspects. Stakeholders recognize the ample room for theoretical work on ML implementations and challenges[
13]. Furthermore, there is a growing need for a comprehensive understanding of AI-based applications, including associated problems and limitations[14, 15]. Budget allocation prioritizes maintaining legacy systems, and there is a notable gap in contextual ML knowledge among government employees, potentially affecting citizen trust and satisfaction with public services [
19].
In tackling the issue of insufficient contextual awareness within ML solutions, this research advocates for a sustainable approach that merges human expertise with machine capabilities, particularly within the domain of digital government. By integrating these two pillars, decision-making processes are enriched, fostering a holistic perspective that extends into the realm of administrative science studies. This aligns with Simon's decision-making model [
20] the research aims to determine how decision-making affected by ML best supports, identifying suitable ML techniques for RDM, emphasizing the importance of incorporating diverse perspectives and sustainable practices into our methodologies. By incorporating sustainability principles such as engaging stakeholders, continuous improvement, collaborative decision-making and knowledge sharing into our methodologies, we can ensure that our decision-making processes are not only more inclusive and equitable but also sustainable in the long term.
The primary inquiry under investigation for this research led to important question which is: "What is the effect of using machine learning (supervised learning and unsupervised learning) on rational decision-making with role of trust as a mediating in this relationship?" Addressing this, the study seeks insights into the impact of supervised and unsupervised ML on rational decision-making in the digital government transformation context of Jordanian e-government. It also investigates the impact of ML on Trust, the influence of Trust on RDM, and the mediating role of Trust in the ML, RDM relationship. By addressing this question, the study aims to provide valuable insights into the nuanced dynamics between machine learning, trust, and rational decision-making in the specific context of Jordanian digital government transformation, contributing to a deeper understanding of the effective utilization of AI technologies in this domain.
The remaining sections of this document are organized as follows: Initially, a comprehensive literature review is provided, followed by a discussion of the conceptual framework of the study and the development of hypotheses accordingly. Following this, the research methodology is explained, and the outcomes of the data analysis are then introduced. The next section delves into a discussion of the findings and explores their implications. Lastly, the document concludes with a discussion on limitations, future research prospects, and final conclusions.
2. Literature Review, Conceptual Framework and Hypotheses
2.1. Machine Learning
Machine learning, a dynamic domain of computational algorithms, seeks to emulate human intelligence through adaptation and learning from its surroundings. ML has emerged as a pivotal force in the age of big data. Its versatile applications extend across diverse domains, including pattern recognition, computer vision, spacecraft engineering, finance, entertainment, computational biology, biomedical applications, and beyond. [21-23].
Machine learning, both supervised and unsupervised, plays a crucial role in supporting decision-making processes across various domains, including digital government. Supervised Learning using Predictive Analytics where the algorithms can be used to make predictions based on historical data. For example, in finance, supervised learning models can predict stock prices or identify fraudulent transactions, assisting decision-makers in investment and risk management [
22]. Kureljusic and Metz [
15] focused on machine learning applications in decision taking for accounts receivables management, underlining the significance of data quality and model validation. Other supervised Classification algorithms as can classify data into predefined categories. For instance, in healthcare, predictive models can classify medical images to assist radiologists in diagnosing diseases, ultimately aiding in treatment decisions. Particularly in cancer treatment, where radiotherapy plays a pivotal role for over half of the patients in advanced stages, machine learning algorithms provide substantial advantages in optimizing and automating intricate tasks. These responsibilities encompass quality assurance in radiation physics, contouring, and treatment planning, as well as tasks such as image-guided radiotherapy, respiratory motion management, treatment response modeling, and outcomes prediction [
24]. Also, Personalization where supervised learning algorithms can personalize recommendations or services based on user behavior and preferences. This is commonly seen in e-commerce platforms, where recommendation systems suggest products based on past purchases, enhancing the customer experience and influencing purchasing decisions [
25].
Sen et al. [
26], offered a classification framework for machine learning algorithms, providing a comprehensive guide for researchers and practitioners. This framework contributes to understanding the types of supervised machine learning algorithms applicable in digital transformation, aiding decision-makers in e-government context. These studies enhance the comprehension of the role that supervised machine learning plays in decision-making processes
. Therefore, we hypothesize:
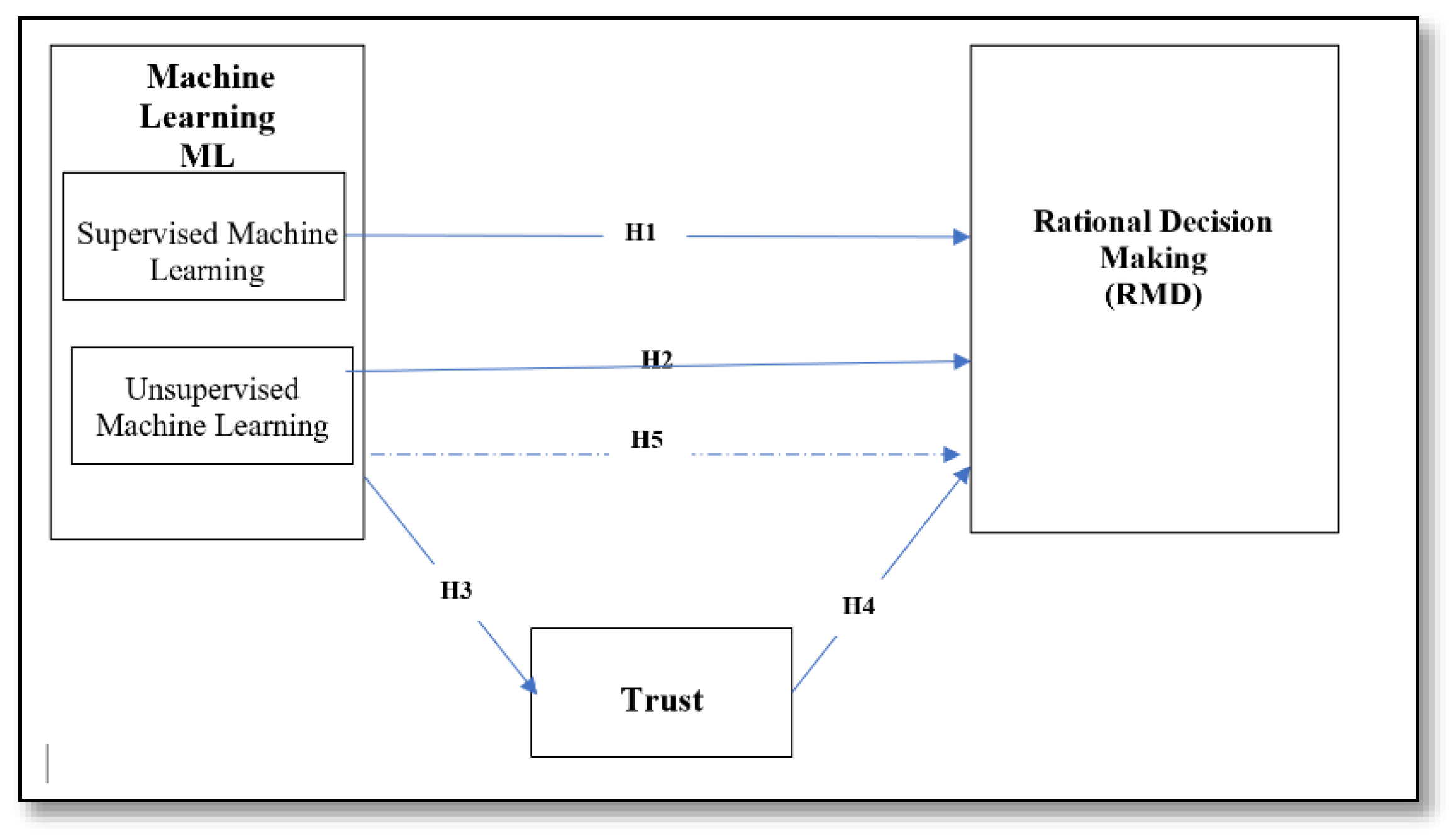
H1. “Supervised machine learning has a significant positive impact on rational decision-making”.
The recent advancements in unsupervised machine learning have been facilitated by the creation of novel learning algorithms and accompanying theories, along with the continuous surge in easily accessible online data and cost-effective computing resources. The widespread application of unsupervised machine learning techniques permeates various sectors, such as science, technology, and commerce, heralding a new era of evidence-based decision-making across diverse domains [
27] where the unsupervised machine learning algorithms such as by Pattern Discovery, Anomaly Detection and Data Exploration can be applied. Used by Pattern Discovery where algorithms can uncover hidden patterns or structures within data. For instance, clustering algorithms can group similar customers together based on their purchasing behavior, helping businesses identify market segments and tailor marketing strategies accordingly which can have advanced the decisions taking regards the market segmentations [
28]. Also, the Anomaly Detection algorithms can detect unusual patterns or outliers in data, which may indicate anomalies or potential issues. In cybersecurity, anomaly detection algorithms can identify suspicious activities in network traffic, enabling quick response to security threats and informed decision-making to mitigate risks [
29]. And the Data Exploration where the unsupervised learning techniques like dimensionality reduction can help in visualizing high-dimensional data and identifying important features. This aids decision-makers in understanding the underlying relationships within the data and making informed decisions based on the insights gained [
30].
Merkert et al.[
18] and Wang et al. [
31], contributed to the understanding of machine learning algorithms, while Wang et al.[
31], focused on multivariate forecasting and deep feature learning, presenting a novel anomaly detection framework for smart manufacturing support. Merkert et al.[
18], Examined the utilization of machine learning in decision support systems, offering insights into different algorithms and their practical implications. Both studies delve into the application of machine learning in decision support, establishing a groundwork for comprehending its role in the context of digital transformation. Therefore, we hypothesize:
H2. “Unsupervised machine learning has a significant positive impact on rational decision-making”.
Alloghani et al. [
32] Conducted a systematic review of supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms within the realm of data science. This examination involved the identification of their respective strengths, weaknesses, and potential applications. This review informed the selection of appropriate algorithms for specific tasks in the e-government domain, supporting decision-making processes. Alexopoulos et al. [
33], explored the impact of machine learning on e-government, discussing its applications in service delivery, decision-making, and citizen engagement. Power et al. [
34] highlighted the importance of using data-driven analytics and evidence-based approaches to reduce bias and improve decision-making
By leveraging both supervised and unsupervised machine learning techniques, decision-makers can extract valuable insights from data, improve the accuracy of predictions, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately make more informed and effective decisions across a wide range of applications and industries [
35,
36].
2.2. Rational Decision Making
Rational decision-making stands as a pivotal element in human behavior, permeating various disciplines such as economics, psychology, and management [
37]. This literature review juxtaposes insights garnered from seminal works to recent studies, delving into diverse dimensions of rational decision-making. Herbert Simon's groundbreaking work in "Administrative Behavior" laid the groundwork by introducing the concept of bounded rationality[
37,
38,
39]. Herbert Simon's work indeed revolutionized our understanding of decision-making processes. By introducing the concept of bounded rationality, he highlighted the inherent cognitive limitations that individuals face when making decisions. This departure from the classical economic model of complete rationality has had profound implications across various disciplines [
40,
41].
Simon's insights have influenced subsequent research by shifting the focus towards understanding how individuals make decisions under constraints, rather than assuming perfect rationality. This approach acknowledges that decision-makers often operate with limited information, time, and cognitive resources, leading to satisficing rather than optimizing behavior [
42]. Furthermore, Simon's ideas have permeated fields beyond economics, including psychology and management. His emphasis on bounded rationality has led to a more nuanced understanding of human behavior in organizational settings, where decision-makers must navigate complex environments with imperfect information [
43].
Overall, Simon's contributions have enriched our understanding of decision-making processes, highlighting the importance of considering cognitive limitations and contextual factors in rational decision-making.
Julmi [
44] Exploration in "Rational Decision-Making in Organizations" shifts the focus toward the application of rational decision-making in organizational settings. This study scrutinizes how organizational structures and decision-making frameworks either facilitate or impede rational choices. Insights from this work shed light on the practical implications of rational decision-making theories. On other side, Power et al. [
34] comprehensive examination centers on the impact of information asymmetry on rational decision-making. This research underscores how unequal access to information can lead to suboptimal decisions. The study highlights the critical need to address information disparities to foster truly rational decision-making processes. The gap in Power et al.[
34] study covered by Cao et al. [
45] as they exploration of the role of technology in rational decision-making. Their study investigates how advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning influence decision-making processes. The findings provide contemporary insights into the integration of technology and its impact on rational decision-making, which is the more relevant study to our research.
Acciarini et al. [
46] Concentrating on the ethical dimensions of rational decision-making, these researchers introduced a moral layer to the discourse. Their investigation delves into the ethical considerations individuals encounter when engaging in rational decision-making. This study underscores the pivotal role of moral reasoning in the realm of rational decision-making. In contrast, Bag et al. [
47] explored the interplay between emotion and rational decision-making. Their research delves into how emotional states can both augment and hinder the rational decision-making process. This study offers a nuanced perspective on the often overlooked emotional dimensions in decision-making.
The theoretical landscape of rational decision-making is diverse, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of this field. From the classical economic model to bounded rationality, prospect theory, decision heuristics, behavioral economics, and institutional analyses, each theory contributes to a nuanced understanding of decision processes[
48]. Recognizing the complexities inherent in decision-making, scholars continue to refine and integrate these theories, fostering a comprehensive framework that addresses the dynamic nature of human choices across various contexts.
2.3. The Mediating Role of Trust between Machine Learning and Rational Decision Making
The integration of machine learning (ML) into rational decision-making processes has garnered significant attention in various domains, ranging from finance to healthcare side with government attention [
21,
35]. However, the successful implementation of ML systems relies not only on their technical capabilities but also on the trust users place in these systems that's why we explore the mediating role of trust in the utilization of ML for supporting rational decision making [
49].
Trust plays a crucial role in the acceptance and utilization of ML systems. Research suggests that individuals are more likely to rely on ML-generated insights and recommendations when they perceive the system as reliable, competent, and transparent. Moreover, trust acts as a mediator between the perceived usefulness of ML technology and users' willingness to adopt it for decision making [
49,
50].
Ferrario and Viganò [
50] present a multi-layer model of trust in human-AI interactions, highlighting factors such as transparency, explain ability, and accountability. Several factors influence the development of trust in ML systems. Users are more likely to trust ML algorithms that produce accurate and reliable results consistently. Additionally, transparent and explainable ML models instill confidence in users by providing insights into the decision-making process and underlying algorithms. Furthermore, establishing accountability mechanisms can enhance trust by ensuring that ML systems are held responsible for their decisions and actions [
50].
Araujo et al. [
51] investigate public perceptions of automated decision-making by AI, exploring the various factors that influence trust. Bag et al. [
47] propose an integrated AI framework for B2B marketing decision-making, leveraging AI technologies to enhance knowledge creation and firm performance. Cao et al. [
45] explore managers' attitudes toward using AI for decision-making in organizations, underscoring the importance of trust in AI systems.
Despite its importance, trust in ML systems is not always easily established or maintained. Challenges such as algorithmic bias, data privacy concerns, and lack of interpretability can undermine users' trust in ML technologies. Moreover, the black-box nature of some ML algorithms poses challenges to understanding how decisions are made, leading to skepticism and distrust among users. Understanding the mediating role of trust is crucial for the successful implementation of ML systems in decision-making contexts. Organizations must prioritize efforts to build trust in ML technologies through transparency, accountability, and ethical practices. Additionally, further research is needed to explore the complex interplay between trust, perceived usefulness, and adoption intentions in diverse settings and user populations [45, 47, and 50].
Janssen et al. [
52] put forth a decision-making framework for e-government utilizing AI and machine learning techniques, with a specific focus on data governance. Ingrams et al. [
53] examine citizen perceptions of AI in government decision-making, shedding light on the significant role of trust. The literature review underscores the potential benefits and challenges associated with applying machine learning in decision support systems, with a particular emphasis on factors such as data quality and interpretability. Trust in AI systems is highlighted as a crucial aspect in the literature [
49,
50], and the exploration of trust extends to the context of e-government decision-making [
51,
52,
53]. This introduces the third and fourth hypothesis. Therefore, we hypothesize:
H3. “Machine learning has a significant positive impact on trust”.
H3a: “Supervised machine learning has a significant positive impact on trust.”
H3b: “Unsupervised machine learning has a significant positive impact on trust.”
H4. “Trust has a significant positive impact on rational decision-making.”
Trust as mediating variable that might affect the relationship between ML and RDM is building on the literature suggesting that trust plays a crucial mediating role in AI systems [
49], and considering the potential influence of trust on decision-making. Therefore, we hypothesize:
H5. “Trust plays a mediating role in the relationship between machine learning and rational decision-making.”
H5a: “Trust plays a mediating role in the relationship between supervised machine learning and rational decision-making.”
H5b: “Trust plays a mediating role in the relationship between unsupervised machine learning and rational decision-making.”
The objective of this study was to examine and analyze the relationships among the variables ML (Machine Learning), RDM (Rational Decision-Making), and Trust, as illustrated by the conceptual framework presented in
Figure 1.
3. Research Methodology
The principal objective of this research is to construct a conceptual framework that provides a thorough understanding of the influence of machine learning on rational decision-making, taking into account trust as a mediating variable in this relationship. The study aims to validate the hypotheses formulated and examine the test results. It involves an inquiry into government perceptions regarding the role of machine learning in decision-making. The primary data for this research were collected utilizing the most suitable methodologies for data collection and sampling strategies.
3.1. Sample and Data Collection
The research focuses on Jordanian e-government employees in middle-level management as the target population. These individuals were purposefully selected due to their engagement in diverse tasks across various departments utilizing machine learning technology. The choice of middle-level management is intentional, given their tendency to make more rational day-to-day decisions compared to upper management, which is more involved in strategic decisions. The Ministry of Digital Economy and Entrepreneurship (MoDEE) was chosen as the research site, being the ideal entity for adopting new technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning. MoDEE serves as the umbrella organization for Jordanian e-government, representing the technical arm of the government.
The study aims to contribute significantly by exploring the role of machine learning (ML) and trust in rational decision-making (RDM) within the Jordanian government, this is a unique endeavor as no similar research has been conducted in Jordan. According to the 2023 human resources report of MoDEE, the total staff population was 245. The researchers utilized a quantitative research methodology, employing an electronically structured questionnaire as the means of collecting data. The survey strategy was chosen for its versatility in combining quantitative and qualitative aspects in business research.
The online survey was deemed appropriate due to the dispersed nature of the target population across various ministries and institutes, presenting challenges in time, cost, and potential non-response. This approach enabled communication with respondents who may have been difficult to reach through conventional methods. The study adhered to ethical principles by ensuring voluntary participation, maintaining the confidentiality of responses, and respecting participants' rights to privacy and anonymity. Before distributing the questionnaire, the researchers obtained permission from MoDEE authorities.
Collaboration with a reputable organization such as MoDEE, as recommended by Sekaran and Bougie [
54], was established to enhance response rates. MoDEE distributed the survey link to its staff, accompanied by a participant information sheet explaining the study's nature. The survey took place over three months (October–December) in the fall semester of 2023, the responses were gathered and systematically documented directly in private database. To determine the sample size, formulas recommended by Sekaran and Bougie [
54] were applied, considering a 95% confidence level and a 5% margin of error. With a population size of 245, the ideal sample size was calculated to be 152. The research employed a convenience sampling method, resulting in 141 usable responses out of 163 distributed questionnaires, representing an 86.5% response rate.
Demographic characteristics of respondents that have been captured in this research include four different aspects: age, educational level, experience period, and gender represented in
Table 1 categorizes the sample’s demographic characteristics into four groups. The survey findings revealed that 54.6% of the 141 participants were “female”, and 45.4% were “male”. Furthermore, 69.5.3% of the target responders were “between 25-44”, 66% held a “Bachelor’s degree”, and 36.2.6% had “>16 years” experience.
3.2. Variable Measurement
The research adopts a quantitative and cross-sectional model, employing a questionnaire comprising four sections and a total of 46 items: demographic information, the machine learning scale, the rational decision-making scale, and the trust scale. The study utilizes a five-point Likert scale, categorizing responses based on importance or the degree of agreement. The scale ranges from strong agreement at one extreme to strong disagreement at the other, with intermediate points. Each point on the scale carries a corresponding score, with (1) indicating the least agreement and (5) indicating the most agreement for each response.
The questionnaire's construction was informed by relevant literature, involving literature research and collaboration with subject matter experts in artificial intelligence (Machine Learning) to establish the content validity of the scale instrument. The items related to rational decision-making (10 items) were adapted from previous research [
55,
56,
57], while the six items measuring the trust variable were adapted from relevant literature [
58,
59]. To ensure clarity and understanding among respondents, two rounds of pre-testing were conducted. Initially, the questionnaire reviewed by academic researchers experienced in questionnaire design, and subsequently, it was piloted with artificial intelligence experts. The validity of the questionnaire tool was assessed through face validity and construct validity. Face validity involved evaluating the clarity, linguistic quality, and alignment of paragraphs with their intended dimensions. Specialized arbitrators in machine learning and academic experts in business administration were consulted, and their recommendations were incorporated into the final questionnaire.
Given that the questionnaire was initially developed in English, a back-translation process was carried out from English to Arabic and vice versa to verify the content's accuracy. The Arabic version underwent evaluation to ensure clarity and intelligibility, with specialists examining the material after amendments. The revised Arabic version was then used to pre-test with 33 participants before distributing the surveys to the larger population.
3.3. Data Analysis
In this study, we employed SPSS and AMOS software to analyze the collected sample, utilizing a combination of multiple regression and A Confirmatory Factor Analysis approaches to scrutinize our hypotheses. Multiple regression in SPSS is considered a contemporary and effective alternative to traditional analysis tools, featuring advancements such as confirmatory analysis, exploration of non-linear impacts, and the examination of mediating and moderating effects [
60,
61]. Numerous scholars in the field have advocated for using multiple regression statistical methods to explore mediation effects, drawing on both primary and secondary data [
62]. We posited that multiple regression using SPSS would be the most suitable method for our study, aligning with previous research [
63] that investigated the mediation effect on decision-making.
A Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was employed to establish a measurement model for the entire self-rating scales through a convergent validity test. The modification index was then used to select variables for refinement [
64]. We prioritized removing components with the highest modification index values until the desired goodness of fits was attained. Although most goodness-of-fit indicators exceeded specified cutoff thresholds, a few factor loadings fell below the minimum requirement of 0.5. Consequently, these were excluded to ensure the validity of our data framework. All components of observed variables demonstrated factor loadings exceeding the critical point of 0.5, confirming their validity [
65].
4. Results
4.1. Testing Goodness-of-Fit, Model Validity, Reliability and Correlation Coefficients
Initially, the reliability of the scale and the validity of the questionnaire were assessed using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. As suggested by Sekaran and Bougie [
54], Cronbach’s alpha values exceeding (0.70) indicate high internal consistency in measuring variables, contributing to increased reliability. To evaluate the stability of the research instrument, Cronbach's internal consistency was computed—a recognized method for gauging the tool's stability. This approach evaluates the homogeneity of the tool's statements using Cronbach's Alpha, measuring the extent to which the units or items within the test relate to each other and to the scale as a whole. Cronbach’s alpha coefficients were employed to evaluate measurement reliability, and construct correlation was used to assess the validity of the sample [
65].
Table 2 presents the reliability coefficients (Cronbach alpha) for the various dimensions and fields of the study, ranging between 0.730 and 0.962. All these values are considered high, demonstrating strong internal consistency and indicating acceptability for practical application. It's worth noting that most studies consider a reliability coefficient acceptance threshold of 0.70 [
66].
In the second step of the analysis, a correlation analysis was performed to examine the positive relationships between variables. Correlation Analysis: A matrix of correlation coefficients between the study variables was extracted. By reviewing
Table 2 shows that the correlation coefficients between the sub-dimensions of the independent variable and the dependent variable ranged between (0. 643-0. 813), which is a statistically significant value at the level of (0.01). From reviewing the results, the correlation coefficients between the sub-dimensions of the independent variable and the dependent variable and the mediating variable ranged between (0. 795-0. 889), which is a statistically significant value at the level of (0.01). All correlation coefficients demonstrated positive correlations among themselves, with statistical significance at the 0.01 level and exhibiting medium-to-high power.
Thirdly, factor analysis was employed to identify principal components and assess whether the chosen factors in the study adequately capture the variables, as well as to determine the relationship between the questionnaire's factors and the variables. Hair et al. [
66] emphasized that Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) is utilized for data exploration, indicating the necessary number of factors for better data representation. EFA assigns each measured or observed variable to a factor based on the load estimation factor value. A key characteristic of EFA is that factors are derived solely from statistical outcomes, devoid of theoretical assumptions, and naming of factors occurs post-factor analysis. Essentially, EFA allows analysis without prior knowledge of the existing factors or the allocation of variables to constructs.
Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was employed to reduce observed variables and identify relationships between them. The principal components analysis (PCA) technique, along with Promax with Kaiser Normalization rotation, was used to extract factors. The analysis, applied to the Machine Learning items, revealed two sub-dimensions measured with (30) items. All item saturations (Loadings) ranged from (0.410 to 0.843) as shown in
Table 3, surpassing the threshold of 0.4. Orthogonal rotation resulted in the classification of questionnaire items into two factors. The two factors that the value of the matrix Determinant It is equal to (0.013) and exceeds the value of zero, which indicates that there is no autocorrelation problem between the elements of the variable.
Exploratory factor analysis reveals the rotation matrix for items related to Rational Decision Making, measured with (10) items. The EFA demonstrates that all item saturations (Loadings) fall within the range of (0.54 to 0.82) as shown in
Table 4, surpassing the threshold of 0.4. Through orthogonal rotation, the questionnaire items are categorized into one factor. Notably, the matrix Determinant value is calculated to be 0.011, exceeding zero, indicating the absence of an autocorrelation issue among the elements of the variable.
Also, exploratory factor analysis reveals the rotation matrix for items related to Trust, involving (6) items. The EFA demonstrates that all item saturations (Loadings) fall within the range of (0.647 to 0.820), surpassing the threshold of 0.4, as illustrated in
Table 5. Through orthogonal rotation, the questionnaire items are categorized into one factor. Notably, the matrix Determinant value is calculated to be 0.041, exceeding zero, indicating the absence of an autocorrelation issue among the elements of the variable.
To determine the absolute model fit index, a goodness-of-fit test was conducted to assess the alignment of the data sample with the connecting path map of the overall framework. Subsequently, we assessed the validity of the measurement model based on established reliability and validity tests. The goodness-of-fit evaluation, crucial for determining how well the model aligns with the dataset’s variance–covariance structure, indicated a favorable fit for both the CFA measurement and structural models.
Fourthly, to ensure the construct validity of the variable measurement items and their alignment with the respective constructs, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted. This aimed to validate the three measures in the study, assessing their convergent validity through the saturation values of each item. The study employed various indicators to ascertain a strong alignment for each measure and the overall study measure [
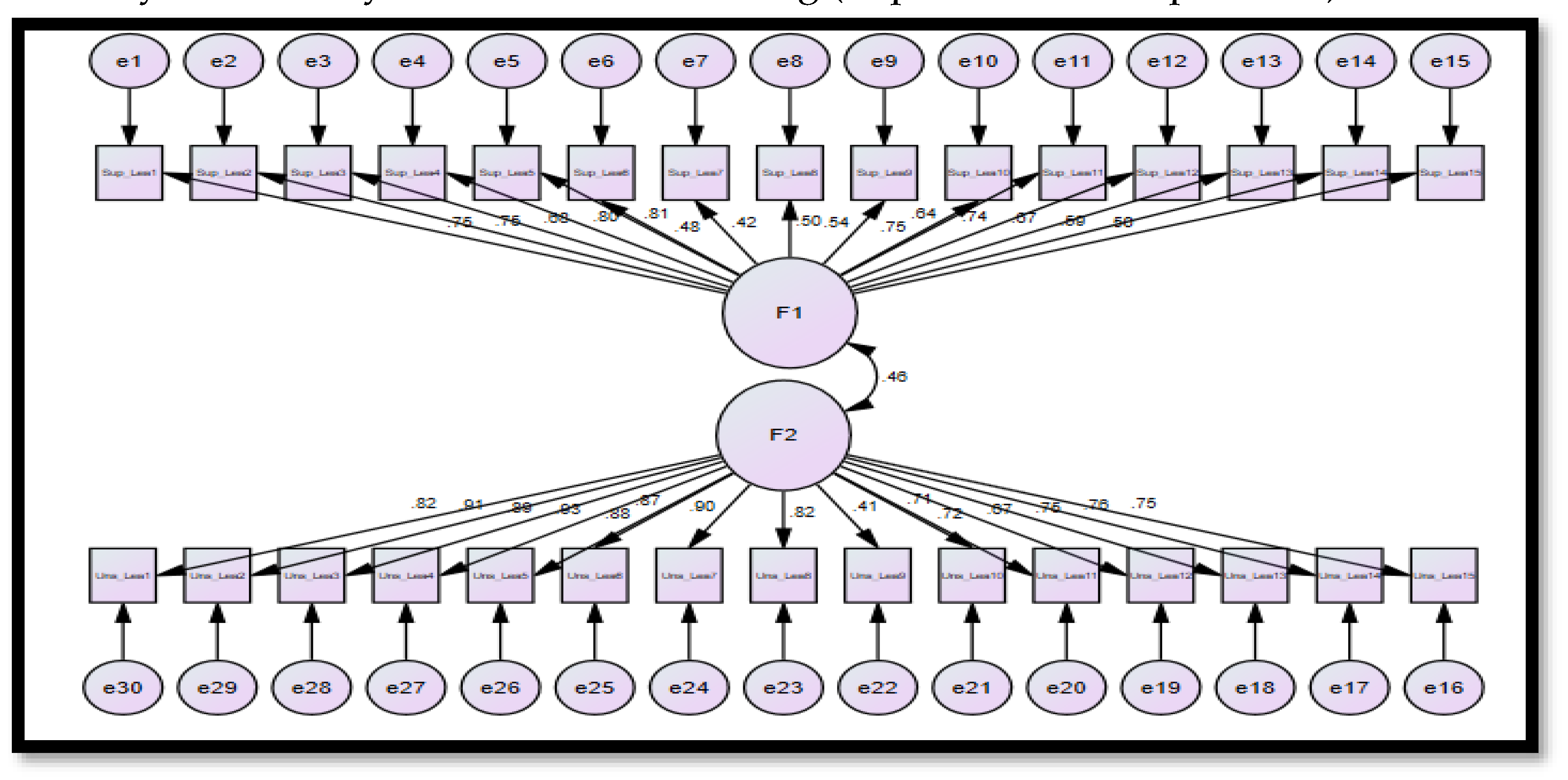
66]. The goal of using confirmatory factor analysis is to verify the validity of the proposed study model that contains the latent variable and the indicators used to measure it or the items used in the study tool to measure this variable. The assumption of construct validity is achieved if the standard regression weights are greater than (0.40), and
Figure 2 Confirmatory factor analysis of Machine Learning (Supervised/ Unsupervised).
For the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) results for all three variables (ML as independent, Trust as mediating, and RDM as the dependent variable) are above 0.001, as indicated in
Table 6. This implies that the sample size employed in this study is deemed sufficient. Additionally, the Chi-square test result, with a significant level of 0.000, is deemed satisfactory. In
Table 6, it is observed that the matrix determinant value is 0.013, surpassing zero, signifying the absence of an autocorrelation issue among the variable elements.
For the Machine Learning factor, the Keiser-Meyer-Oklin (KMO) test yielded a value of 0.84, surpassing the threshold of 0.50. This suggests that the sample size in the study is adequate for accurate measurement of the variable. Bartlett's Test produced a value of 5145.632 with a significance level of 0.000, indicating a significant relationship between the sub-elements of the variable. Similarly, for the Rational Decision Making factor, the KMO test resulted in a value of 0.80, exceeding 0.50, indicating an adequate sample size for precise variable measurement. Bartlett's Test yielded a value of 1190.304 with a significance level of 0.000, implying a significant relationship between the sub-elements of the variable. Regarding the Trust factor, the KMO test produced a value of 0.824, surpassing 0.50, indicating a sufficient sample size for accurate variable measurement. Bartlett's Test resulted in a value of 435.701 with a significance level of 0.000, suggesting a significant relationship between the sub-elements of the variable.
4.2. Statistical Assumption
Diagnostic tests play a crucial role in determining the adequacy of data for drawing conclusions, representing a vital requirement for researchers [
54]. The obtained results are outlined below:
4.2.1. Normality
The "Skewness and Kurtosis" tests were employed to assess the normality of the data distribution. The skewness and kurtosis coefficients fall within the acceptable minimum and maximum limits for a normal distribution. Specifically, the skewness values (-0.884, 0.196) fall within the range of -2 to 2, and the kurtosis coefficients values (-0.439, 2.412) fall within the range of -7 to 7. These results indicate that the data in the study exhibit a normal distribution. Consequently, the study data are deemed suitable for conducting subsequent statistical analyses.
4.2.2. Multicollinearity
The results were examined by calculating the "variance inflation factors (VIF)" and "tolerance" to ascertain the independence of the various independent variables. The outcomes indicate that there is no overlap among the independent variables in the study. Tolerance values, ranging from 0.159 to 0.362, all exceed the threshold of 0.10, and VIF values, ranging from 2.761 to 6.274, are below 10. These findings signify the absence of multicollinearity within the independent variables of the study [
54].
4.2.3. Independence
The results underwent testing using the "Durbin–Watson" statistic to assess whether residuals from the models exhibited autocorrelation. The findings indicate an absence of autocorrelation, as the Durbin-Watson values ranged between 1.660 and 1.922. These values, being less than 2.5 and more than 1.5, suggest that residuals are not significantly correlated with each other. Consequently, the independence of errors is not violated in the analysis.
4.3. Hypotheses Testing
Researchers using the SPSS program, complemented by a mediation analysis using AMOS software to test the research hypotheses, a software developed to help researchers test the relationships between variables that have a mediator or moderator [
65]. This research consists of five main hypotheses with sub-hypotheses.
Relationship between supervised machine learning and rational decision-making
According to the results of analysis shown in
Table 7, where the values of (Beta=0.770) and (T=14.208) were Positive and statistically significant; the (R-square) value was (5.14), a statistically significant value. Furthermore, the Lower Limit of Confidence Interval (LLCI) to Upper Limit of Confidence Interval (ULCI) range falls between 0.759 and 1.005, indicating significance as there are no zero values within this interval, therefore, the first main hypothesis H1 is accepted, where There is a positive impact for the Supervised machine learning to the rational decision-making in digital transformation at the e-government of Jordan.
Relationship between unsupervised machine learning and rational decision-making
According to the results of the analysis shown in
Table 7, there is a positive impact for the unsupervised machine learning the rational decision-making in digital transformation at the e-government of Jordan, where the values of (Beta=0.869) and (T=20.720) were Positive and statistically significant; the (R-square) value was (0.869), a statistically significant value. Furthermore, the Lower Limit of Confidence Interval (LLCI) to Upper Limit of Confidence Interval (ULCI) range falls between 0.693 and 0.840, indicating significance as there are no zero values within this interval, therefore, the main second hypothesis H2 is accepted.
Relationship between machine learning and trust
There is a positive impact of machine learning on the trust in digital transformation at the e-government of Jordan, where the values of (Beta=0.917) and (T=27.018) were Positive and statistically significant; the (R-square) value was (0.840), a statistically significant value. Furthermore, the Lower Limit of Confidence Interval (LLCI) to Upper Limit of Confidence Interval (ULCI) range falls between 0.823 and 0.953, indicating significance as there are no zero values within this interval, therefore, the H3 hypothesis is accepted.
There is a positive impact of the supervised machine learning on the trust in digital transformation at the e-government at the e-government of Jordan, where the values of (Beta=0.795) and (T=15.425) were Positive and statistically significant; the (R-square) value was (0.631), a statistically significant value. Furthermore, the Lower Limit of Confidence Interval (LLCI) to Upper Limit of Confidence Interval (ULCI) range falls between 0.7 and 0.91, indicating significance as there are no zero values within this interval, therefore, the sub-hypothesis H3a is accepted.
There is a positive impact of the unsupervised machine learning on the trust in digital transformation at the e-government at the e-government of Jordan, where the values of (Beta=0.862) and (T=20.004) were Positive and statistically significant; the (R-square) value was (0.742), a statistically significant value. Furthermore, the Lower Limit of Confidence Interval (LLCI) to Upper Limit of Confidence Interval (ULCI) range falls between 0.605 and 0.737, indicating significance as there are no zero values within this interval, therefore, the sub-hypothesis H3b is accepted.
Relationship between trust and rational decision-making
There is a positive impact of trust on in rational decision-making in digital transformation at the e-government of Jordan, where the values of (Beta=0.949) and (T=35.643) were Positive and statistically significant; the (R-square) value was (0.901), a statistically significant value. Furthermore, the Lower Limit of Confidence Interval (LLCI) to Upper Limit of Confidence Interval (ULCI) range falls between 1.02 and 1.13, indicating significance as there are no zero values within this interval, therefore, the H4 hypothesis is accepted.
The mediating role of trust on the effect of Machine Learning on the Rational Decision Making
To test this hypothesis, structural equation analysis was used using the Amos program supported by SPSS to verify the direct and indirect effect of machine learning on decision-making in digital transformation through trust as a mediating variable.
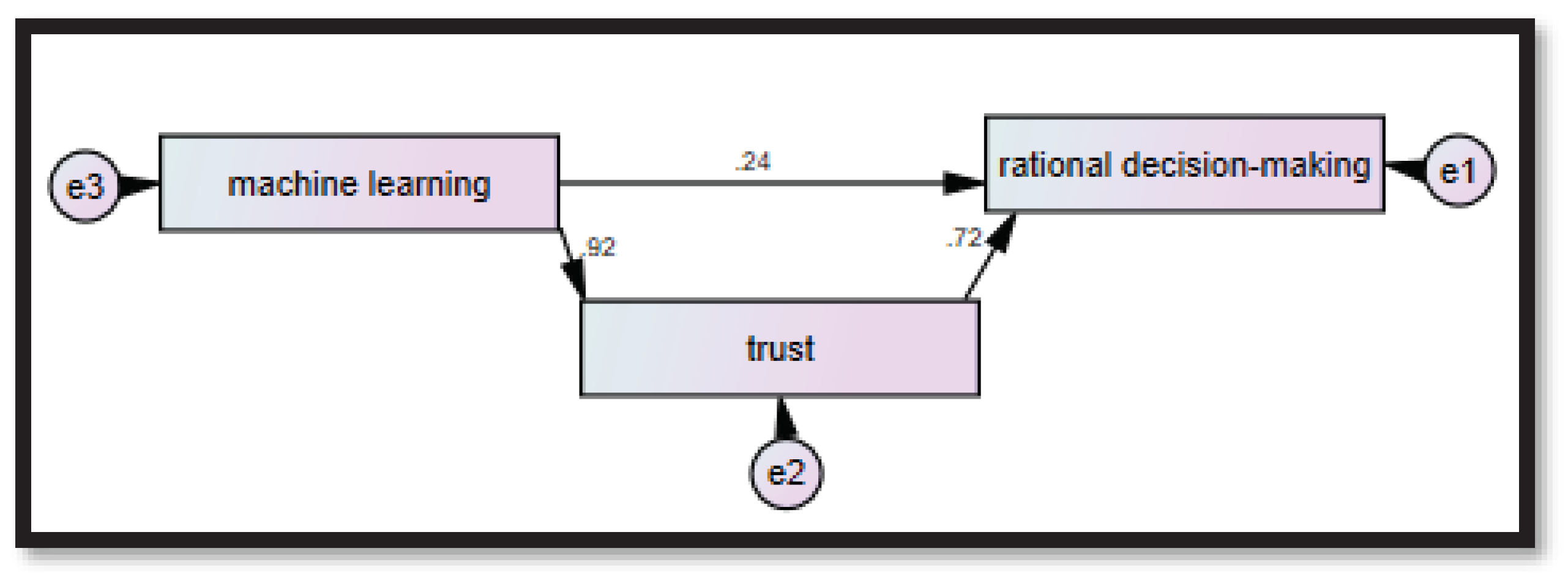
By reviewing the values of the direct effects in
Table 8, it is clear that the value of the impact of the independent variable on the dependent reached (0.245), the value of the effect of the independent variable on The mediator was (0.917), and the value of the direct effect of the mediator on the dependent was (0.725), These effects were expressed using standard values, as it is noted that all the values of these effects (coefficients) were statistically significant, as they were all less than 0.05, and at the same time they were less than 0.001, therefore It is symbolized by the symbol (***), which means that there is an indirect effect of the mediating variable, given that all values of the significance level were statistically significant, which indicates that there are partial mediators of trust (as a mediating variable) on the relationship between machine learning and rational decision-making in digital transformation. That leads to the H5 hypothesis being accepted.
Figure 3 shows the role of trust as a mediating variable in the relationship between machine learning and rational decision-making in digital transformation.
For testing the sub hypotheses By reviewing the values of the direct effects in
Table 9, it is clear that the value of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent reached (0.047), and the value of the effect of the independent variable on The mediator was (0.795), and the value of the direct effect of the mediator on the dependent was (0.917). These effects were expressed using standard values, as it is noted that all the values of these effects (coefficients) were statistically significant, as they were all less than 0.05, and at the same time, they were less than 0.001, Except for the values related to the influence of the independent on the dependent, which means that there is an indirect effect of the mediating variable, given that all values of the significance level were statistically significant, which indicates that there are full mediators of trust (as a mediating variable) on the relationship between supervised machine learning and rational decision-making in digital transformation. The sub-hypothesis (H5a) is accepted.
By reviewing the values of the direct effects in
Table 9, it is clear that the value of the impact of the independent variable on the dependent reached (0.199), and the value of the impact of the independent variable on the mediator was (0.862). The value of the direct impact of the mediator on the dependent was (0.778), which means that there is an indirect effect of the mediating variable, given that all values of the significance level were statistically significant, which indicates that there are partial mediators of trust (as a mediating variable) on the relationship between machine learning and rational decision-making in digital transformation. The sub-hypothesis (H5b) is accepted.
5. Discussion
The rapid evolution of technology, marked by advanced algorithms, vast datasets, and enhanced processing capabilities, has propelled the integration of machine learning (ML) into systems supporting various applications [
15,
32]. This integration has a pro-found impact on decision-making processes. Recognizing the growing demand for in-sights in the field of IT system social science, our study addresses the imperative to comprehend and analyze the influence of ML on decision-making. By contributing to both practical success and theoretical advancements in AI applications, our research seeks to identify and examine indirect factors that may shape the relationship between ML and rational decision-making (RDM) in the context of digital government transformation undertaken by Jordanian e-government [
56].
Given the escalating prevalence of Machine Learning (ML) in the digital transformation of e-government, our study offers empirical evidence supporting the idea that the practical and widespread utilization of ML has a significate positive impact on governance and fa-ciliates decision-making within the domain of digital government.
The validation of our first and second hypotheses (H1, H2), anticipating a significant relationship between (supervised/unsupervised) machine learning and rational decision-making, is substantiated by robust empirical evidence. Leveraging SPSS, AMOS software, and various tests outlined in the data analysis section, we assessed the strength and significance of these relationships, uncovering a substantial and positive correlation. The first hypothesis accepted and supported with results of similar studies in different areas of research as the results shows a significant positive impact of using supervised machine learning on supporting and influencing the decision making process specially in rational decisions taken in finance field [
15,
22], healthcare in radioecology uses [
24], supporting the e-commerce decisions [
25] and in government sector [
2] similar to our study.
Where the unsupervised machine learning algorithms examined in different fields too, we found that the second hypothesis is supported by a similar impact founded for using of unsupervised machine learning that positively influence the rational decision making in all phases; which supported by previous studies by Usama et al., [
27] focused on the impact of using unsupervised machine learning involves learning from the sur-rounding for intelligent decision-making and reliable communication. Arunachalam and Kumar, found that using cluster technique enhance the consumer segmentation decisions too [
28] .The same for the studies used unsupervised ML to support the decisions taken in in the fields of cybersecurity [
30] and smart manufacturing [
31].
Moreover, our third and fourth hypotheses (H3, H4), predicting a direct influence of ML (supervised (H3a) and unsupervised (H3b)) on trust and a direct influence of trust on rational decision-making, were empirically validated and both hypotheses were accepted with the hypotheses to as it is consistent with existing research results [
49,
50,
53]. The fifth hypothesis, suggesting a mediating role of trust on the relationship between machine learning and rational decision-making, was also confirmed through our comprehensive investigation and previous research [
49].In conclusion, our experimental evidence firmly establishes trust as a potent and substantial mediating factor between ML and rational decision-making, aligning with our initial hypotheses.
These findings not only contribute to a deeper understanding of the intricate dynamics associated with integrating ML into decision-making processes but also highlight the importance of sustainability considerations in building and maintaining trust in ML-driven systems. By prioritizing sustainability principles such as transparency, accountability, and ethical practices, organizations can foster enduring trust relationships that support the long-term adoption and utilization of ML technology. These insights hold significant implications for both academic research and practical applications, guiding policymakers and practitioners in leveraging ML to enhance governance and facilitate wise decision-making in a sustainable manner.
6. Implications
The study's principal conclusions, asserting that investing in Machine Learning (ML) will fortify and enrich the Rational Decision-Making (RDM) of Jordanian e-government in the digital transformation process and underscoring the critical role of Trust as a mediator, bear substantial implications for both theoretical comprehension and practical applications. For the theoretical Implications, this research makes noteworthy contributions to the evolution of decision-making theories, particularly within the e-government domain. The study advances our theoretical understanding of the intricate interplay between technological advancements and decision-making capabilities in government settings. Furthermore, the findings bridge the realms of technology (ML) and decision sciences, offering insights into the nuanced relationship between technological progress and decision-making processes. This integration is pivotal for the development of comprehensive theories that encapsulate the evolving dynamics of decision-making in the digital age. The confirmation of Trust as a mediator in the connection between Machine Learning (ML) and rational decision-making (RDM) contributes significant substance to the broader conversation about the role of Trust in influencing decision-making processes. This is especially relevant in environments shaped by technological advancements. The uniqueness of this study lies in its theoretical contribution, as it addresses a gap in the existing literature by empirically assessing the mediating role of trust between ML and RDM in the government sector. Notably, this research is groundbreaking in Jordan, being the first of its kind and thus making a noteworthy contribution to the existing body of knowledge.
From Practical Implications; for practitioners in the digital government sector in Jordan, the study suggests strategic investments in ML technologies to augment decision-making processes during digital transformation initiatives. This involves the thoughtful adoption and integration of ML tools that align with the specific needs and challenges of the e-government. Recognizing the pivotal role of Trust as a mediator, practitioners should prioritize initiatives that cultivate and sustain trust among stakeholders. Transparent communication, ethical AI practices, and measures to address algorithmic bias and data privacy concerns become imperative in this context. In the workforce, the practical implications extend to the need for tailored training programs. Government officials and decision-makers must be equipped with the necessary skills to harness ML technologies effectively, ensuring they can leverage these tools for informed and rational decision-making. Moreover, the study suggests the development of a comprehensive framework for systematically integrating ML into decision-making processes within the e-government sector. Such a framework should consider the specific characteristics of the government context, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and ethical standards.
In summary, these theoretical and practical implications underscore the significance of informed ML investments and the critical role of Trust in shaping decision-making processes in the dynamic landscape of Jordanian digital government transformation. These insights provide a foundation for future research, policy development, and strategic planning in the realm of technology-driven governance.
7. Conclusions, Future Research and Limitations
Artificial intelligence technology, specifically machine learning (ML), has demonstrated its efficacy across diverse industries. The increasing prominence of ML, driven by factors like big data, advanced algorithms, and enhanced processing capabilities, is reshaping digital systems and exerting a substantial influence on rational decision-making.
This evolution underscores the imperative for researchers in social science and information systems to delve into the implications of ML on decision-making. It calls for a comprehensive understanding and active contribution to the academic and empirical advancements in ML technologies. This study addresses this need by scrutinizing and accentuating the remedial role of Trust in the interplay between ML and Rational Decision-Making (RDM). The exploration emphasizes pivotal issues and delineates potential avenues for future research.
The formulation of five research hypotheses directs attention toward the utilization and impact of ML on rational decision-making, with Trust serving as a mediator in this intricate relationship. The multiple regression results, facilitated by SPSS, indicate a significant influence of ML on both Trust and rational decision-making within the digital transformation landscape of e-government. Moreover, statistical evidence affirms Trust's substantial and crucial mediating role in shaping the interaction between ML and RDM While the primary focus of these hypotheses centers on the study of ML for RDM and trust mediation, their applicability extends beyond this specific domain. They provide valuable insights that can inform broader research endeavors, spanning the application and effects of ML across various industries. Furthermore, the significance of analyzing these relationships in diverse contexts, incorporating interaction variables, opens avenues for intriguing outcomes.
Limitations of machine learning in decision-making research include the early stage of development, which primarily focuses on theoretical aspects rather than empirical studies. While there is potential for extensive research on machine learning applications and challenges, particularly within the government sector, there is a lack of attention to the rapid technological changes worldwide and their synchronization with the slow adoption of technology within the government sector. This study faces several limitations, including the early stage of AI research in government, which primarily examines expected effects rather than practical implementations. Furthermore, the implementation of AI-based systems incurs high costs, as it is a time, cost, and resource-intensive process. Without proper validation during training, machine learning models may suffer from overfitting, leading to the retention of noise rather than relevant data, thereby hindering generalization. Additionally, the resistance to change among human poses and lack of trust in technologies are significant barrier to the adoption of new technologies, further limiting the effectiveness of machine learning in decision-making processes. Responses to questionnaires may be biased due to various factors such as social desirability bias, respondent mood, or misunderstanding of questions. Decision-making processes can be complex and influenced by a multitude of factors, including emotions, cognitive biases, and situational context.
In conclusion, this study contributes to the understanding of ML's impact on rational decision-making and the mediating role of Trust and lays the groundwork for future research endeavors. It urges researchers to explore the multifaceted relationships between ML, decision-making, and trust in varied contexts, fostering a richer comprehension of these dynamics for both theoretical advancements and practical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, resources, A.M.S; data curation, A.M.S and M.K.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.S.; writing—review and editing, S.Z.E. and A.M.S.; supervision, S.Z.E.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval to conduct the study was granted by the Scientific Research Ethics Committee of Near East University (NEU/SS/2023/1661), date: 9 October 2023.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work is based on the first author’s doctoral dissertation, titled ‘‘Assessing the Impact of Using Machine Learning on Rational Decision Making in Digital Transformation. A Case Study of e-Government in Jordan”. The planned submission date is October 2024. The dissertation supervisor is the 2nd author of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Duan, Y.; Edwards, J.S.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial intelligence for decision making in the era of Big Data–evolution, challenges and research agenda. International journal of information management 2019, 48, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.D.; Yadav, A.; Chopra, R. Artificial intelligence and effective governance: A review, critique and research agenda. Sustainable Futures 2020, 2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, R.D. Adaptive governance: integrating science, policy, and decision making; Columbia University Press: New York City, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shneiderman, B.H. , Human-centered AI; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mushayt, O.S. Automating E-government services with artificial intelligence. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146821–146829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.; Hartog, M.; Matheus, R.; Yi Ding, A.; Kuk, G. . Will algorithms blind people? The effect of explainable AI and decision-makers’ experience on AI-supported decision-making in government. Social Science Computer Review 2022, 40, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscopo, A.; Siebes, R.; Hardman, L. Predicting sense of community and participation by applying machine learning to open government data. Policy & Internet 2017, 9, 55–75. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhwaldi, A.; Kamala, M.; Qahwaji, R. From e-govemment to cloud-government: Challenges of Jordanian citizens' acceptance for public services. In Proceedings of the ICITST 2017. 12th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST) Cambridge, UK, (December 2017). [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, G.V.; Macadar, M.A.; Luciano, E.M.; Testa, M.G. Delivering public value through open government data initiatives in a Smart City context. Information Systems Frontiers 2017, 19, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.Q.; Medaglia, R. Mapping the challenges of Artificial Intelligence in the public sector: Evidence from public healthcare. Government Information Quarterly 2019, 36, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, B.W.; Müller, W.M. An integrated artificial intelligence framework for public management. Public Management Review 2019, 21, 1076–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulou, A.; Karacapilidis, N.; Loukis, E.; Charalabidis, Y. Transforming the communication between citizens and government through AI-guided chatbots. Government information quarterly 2019, 36, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, W.G.; de Melo, E.R.P.; Bermejo, P.H.D.S.; Farias, R.A.S.; Gomes, A.O. How and where is artificial intelligence in the public sector going? A literature review and research agenda. Government Information Quarterly 2019, 36, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaweh, M.J. Artificial intelligence government (Gov. 3.0): the UAE leading model. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 2018, 62, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kureljusic, M.; Metz, J. The applicability of machine learning algorithms in accounts receivables management. Journal of Applied Accounting Research 2023, 24, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.; Verma, Y.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Churi, P.P. A systematic survey on deep learning and machine learning approaches of fake news detection in the pre-and post-COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics 2021, 14, 617–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbka, J.; Rowland, Z. Using artificial intelligence in company management. In Digital Age: Chances, Challenges and Future; Ashmarina, S., Vochozka, M., Mantulenko, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 84, pp. 422–429. [Google Scholar]
- Merkert, J.; Mueller, M.; Hubl, M. A survey of the application of machine learning in decision support systems.In Twenty-Third European Conference on Information Systems, Münster, Germany (29-05-2015).
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.; Eirug, A.; Galanos, V. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management 2021, 57, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.A. , Rational Decision Making in Business Organizations. The American Economic Review 1979, 69, 493–513. [Google Scholar]
- Adadi, A. A survey on data-efficient algorithms in big data era. Journal of Big Data 2021, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broby, D. , The use of predictive analytics in finance. The Journal of Finance and Data Science. 2022, 8, pp.145-161.
- Zhou, L.; Pan, S. ;Wang, J; Vasilakos, A. V. Machine learning on big data: Opportunities and challenges. Neurocomputing 2017, 237, 350–361. [Google Scholar]
- El Naqa, I.; Murphy, M. J. What Are Machine and Deep Learning? In Machine and Deep Learning in Oncology, Medical Physics and Radiology, I. El Naqa, M.J. Murphy, Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Loukili, M.; Messaoudi, F.; El Ghazi, M. Machine learning based recommender system for e-commerce. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence. 2023, 12(4), pp.1803-1811.
- Sen, P.C.; M. Hajra; Ghosh, M. Supervised Classification Algorithms in Machine Learning: A Survey and
Review. In Emerging Technology in Modelling and Graphics : Proceedings of IEM Graph, Singapore (2020).
- Usama, M.; Qadir, J.; Raza, A.; Arif, H.; Yau, K. l. A. Y. Elkhatib, K. l. A.; Hussain, A.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Unsupervised Machine Learning for Networking: Techniques, Applications and Research Challenges. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 65579–65615. [Google Scholar]
- Arunachalam, D.; Kumar, N. Benefit-based consumer segmentation and performance evaluation of clustering approaches: An evidence of data-driven decision-making. Expert Systems with Applications 2018, 111, pp.11-34.
- Fotiadou, K.; Velivassaki, T.H.; Voulkidis, A.; Skias, D.; Tsekeridou, S.; Zahariadis, T. Network traffic anomaly detection via deep learning. Information 2021, 12(5), 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesha, S.; Hanif, M.K.; Talib, R. Overview and comparative study of dimensionality reduction techniques for high dimensional data. Information Fusion. 2020, 59, pp.44-58.
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, R. X.; Wu, D. Deep learning for smart manufacturing: Methods and applications. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2018, 48, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloghani, M.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Mustafina, J.; Hussain, A.; Aljaaf, A. J. A Systematic Review on Supervised and Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms for Data Science. In Supervised and Unsupervised Learning for Data Science; Berry, M., Mohamed, A., Yap, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany,2020 ; pp. 3-21.
- Alexopoulos, C.; Zoi,L.; Aggeliki , A.; Vasiliki , D.; Yannis C.; Michalis,A.L. How Machine Learning is Changing e-Government. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Theory and Practice of Electronic Governance, Melbourne, VIC, Australia ( April 2019).
- Power, D.J.; Cyphert, D.; Roth, R.M. Analytics, bias, and evidence: the quest for rational decision making. Journal of Decision Systems 2019, 28, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuziemski, M.; Misuraca, G. AI governance in the public sector: Three tales from the frontiers of automated decision-making in democratic settings. Telecommunications Policy 2020, 44, 101976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, R.; Regondi, S.; Marini, R. Machine learning-based approach: global trends, research directions, and regulatory standpoints. Data Science and Management 2021, 4, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.A. Administrative behavior, 4th ed. Simon and Schuster: New York City, USA, 2013.
- March, J.G. Primer on decision making: How decisions happen, Simon and Schuster: New York City, USA, 1994.
- Thaler, R.H. ,. Misbehaving: The making of behavioral economics. WW Norton & Company.
- Beshears, J. , Kosowsky, H.Nudging: Progress to date and future directions. Organizational behavior and human decision processes, 2020,161,3-19.
- Gigerenzer, G. ; Selten, R. eds., Bounded rationality: The adaptive toolbox; MIT press, 2002.
- Keeney, R.L.; Raiffa, H. Decisions with multiple objectives: preferences and value trade-offs. Cambridge university press: Cambridge, UK, 1993.
- Hammond, J.S.; Keeney, R.L.; Raiffa, H. Smart choices: A practical guide to making better decisions. Harvard Business Review Press: Brighton, Massachusetts,USA, 2015.
- Julmi, C. , When rational decision-making becomes irrational: a critical assessment and re-conceptualization of intuition effectiveness. Business Research 2019, 12, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Duan, Y.; Edwards, J. S.; Dwivedi, Y. K. Understanding managers’ attitudes and behavioral intentions towards using artificial intelligence for organizational decision-making. Technovation 2021, 106, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciarini, C.; Brunetta, F.; Boccardelli, P. Cognitive biases and decision-making strategies in times of change: a systematic literature review. Management Decision 2021, 59, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, A.; Sivarajah, U. An integrated artificial intelligence framework for knowledge creation and B2B marketing rational decision making for improving firm performance. Industrial Marketing Management 2021, 92, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, S.; Hacker, P. , Theories of choice: the social science and the law of decision making. Oxford University Press : Oxford, UK, 2021.
- Yu, L. and Li, Y. Artificial intelligence decision-making transparency and employees’ trust: The parallel multiple mediating effect of effectiveness and discomfort. Behavioral Sciences 2022, 12(5), p.127.
- Ferrario, A.; Loi, M.; Viganò, E. In AI We Trust Incrementally: a Multi-layer Model of Trust to Analyze Human-Artificial Intelligence Interactions. Philosophy & Technology 2020, 33, 523–539. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, T.; Helberger, N.; Kruikemeier, S.; Vreese, C. H. In AI we trust? Perceptions about automated decision-making by artificial intelligence. AI & SOCIETY, 2020, 35, 611–623. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, M.; Brous, P.; Estevez, E.; Barbosa, L.S.; Janowski, T. Data governance: Organizing data for trustworthy Artificial Intelligence. Government Information Quarterly 2020, 37, 101493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrams, A.; Kaufmann, W.; Jacobs, D. In AI we trust? Citizen perceptions of AI in government decision making. Policy & Internet 2022, 14, 390–409. [Google Scholar]
- Sekaran, U.; Bougie, R. Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons.: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, S.G.; Bruce, R.A. Decision-making style: The development and assessment of a new measure. Educational and psychological measurement 1995, 55, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, D.P.; Sadler-Smith, E. An examination of the general decision making style questionnaire in two UK samples. Journal of Managerial Psychology 2005, 20, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, S.A.A. ; Myeong S. Use of artificial intelligence in smart cities for smart decision-making: A social innovation perspective. Sustainability, 2022. 14, 620-637.
- Abu-Shanab, E. Antecedents of trust in e-government services: an empirical test in Jordan. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy 2014, 8, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongena, Y. P.; Haan, M.; Yakar, D.; Kwee, T.C. Patients’ views on the implementation of artificial intelligence in radiology: development and validatiofn of a standardized questionnaire. European radiology 2020, 30, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albright, J.J.; Marinova, D.M. Estimating Multilevel Models Using SPSS, Stata, SAS and R; Indiana University: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rosopa, P.J. ; Stone-Romero, E.F. Problems with detecting assumed mediation using the hierarchical multiple regression strategy. Human Resource Management Review, 2008, 18, 294-310.
- Hayes, A.F. Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Communication monographs. 2009, 76,408-420. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, U.; Robles-Flores, J.A.; Popovič, A. Business intelligence capability: The effect of top management and the mediating roles of user participation and analytical decision making orientation. Journal of the Association for Information Systems 2017, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.; Khurshid, M.K.; Mahmood, S.; Ali, A. Factors effecting investment decision making behavior: The mediating role of information searches. Eur. Online J. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2018, 7, 758–767. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakol, M.; Dennick, R. Making sense of Cronbach's alpha. International journal of medical education, 2011, 2, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F. Multivariate Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).