Submitted:
04 April 2024
Posted:
05 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
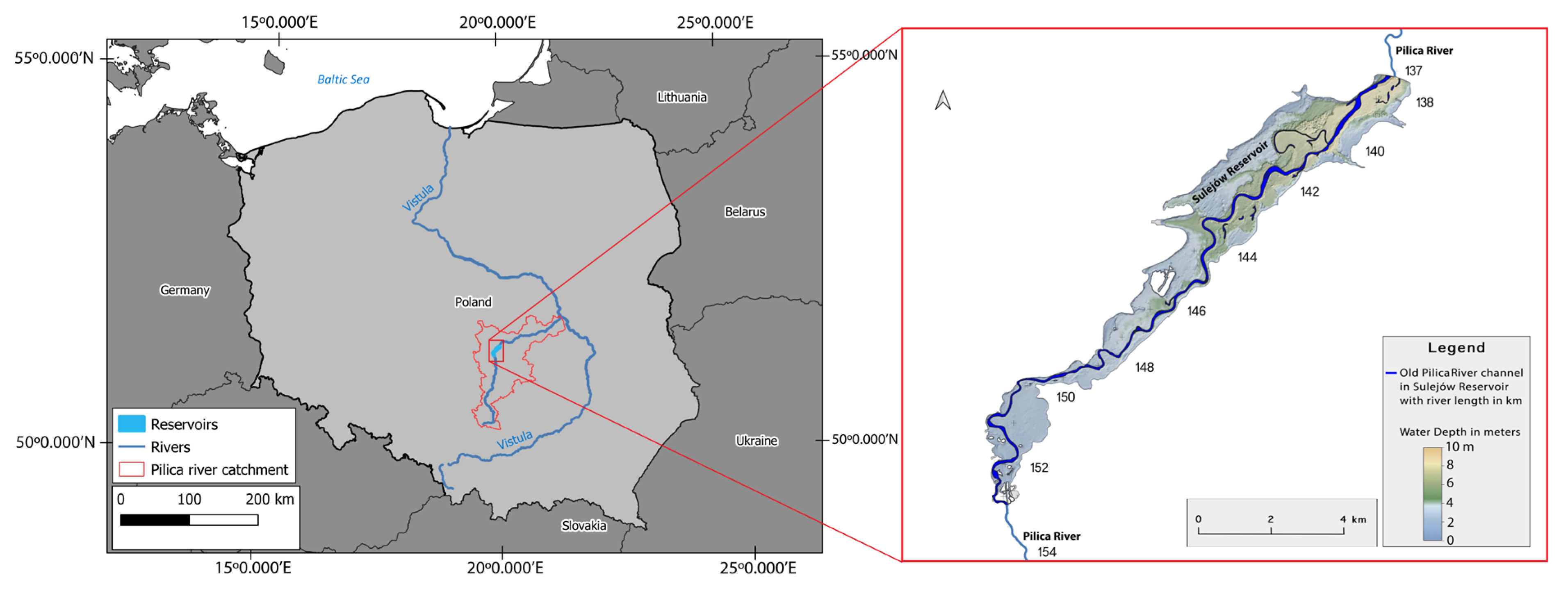
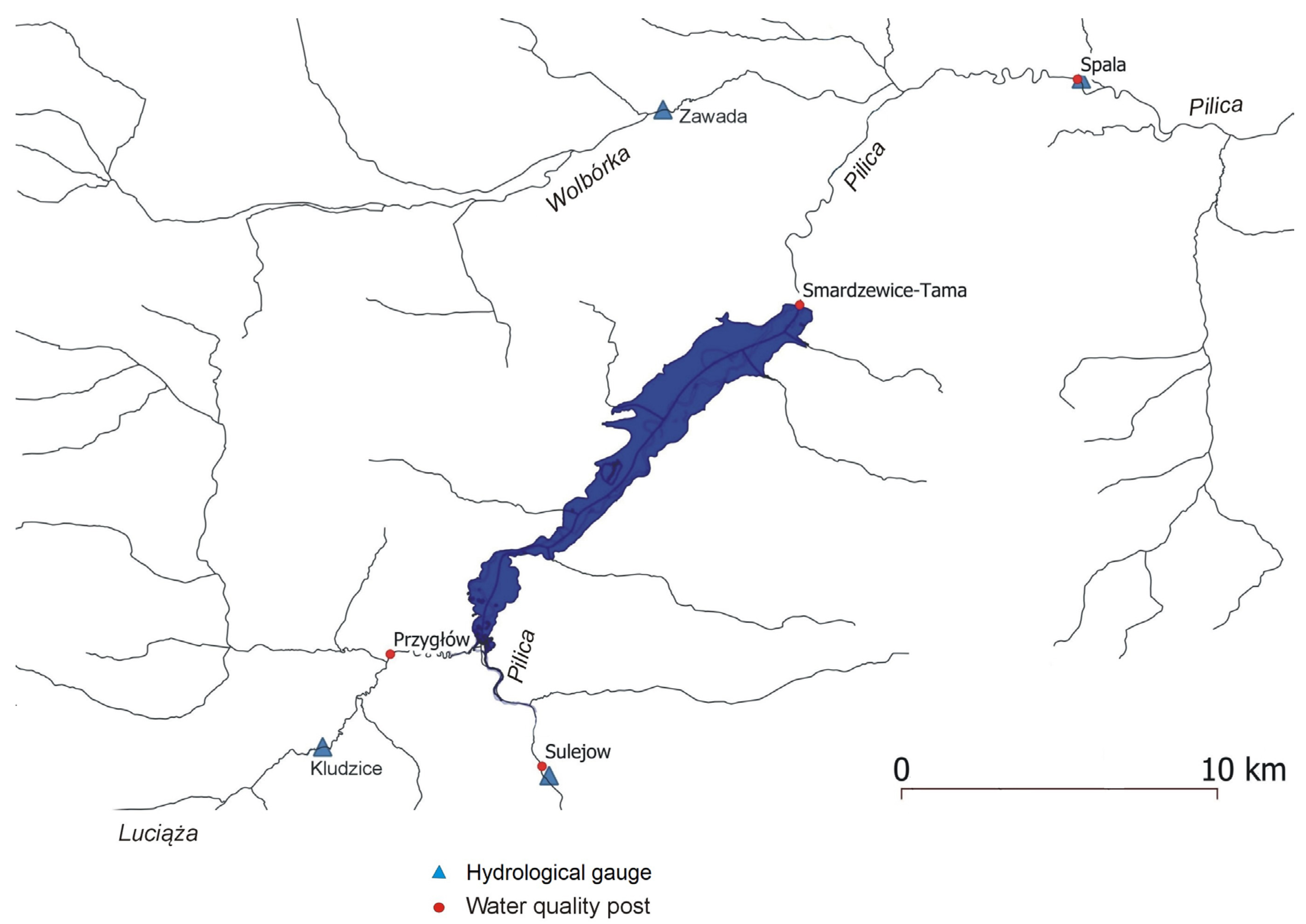
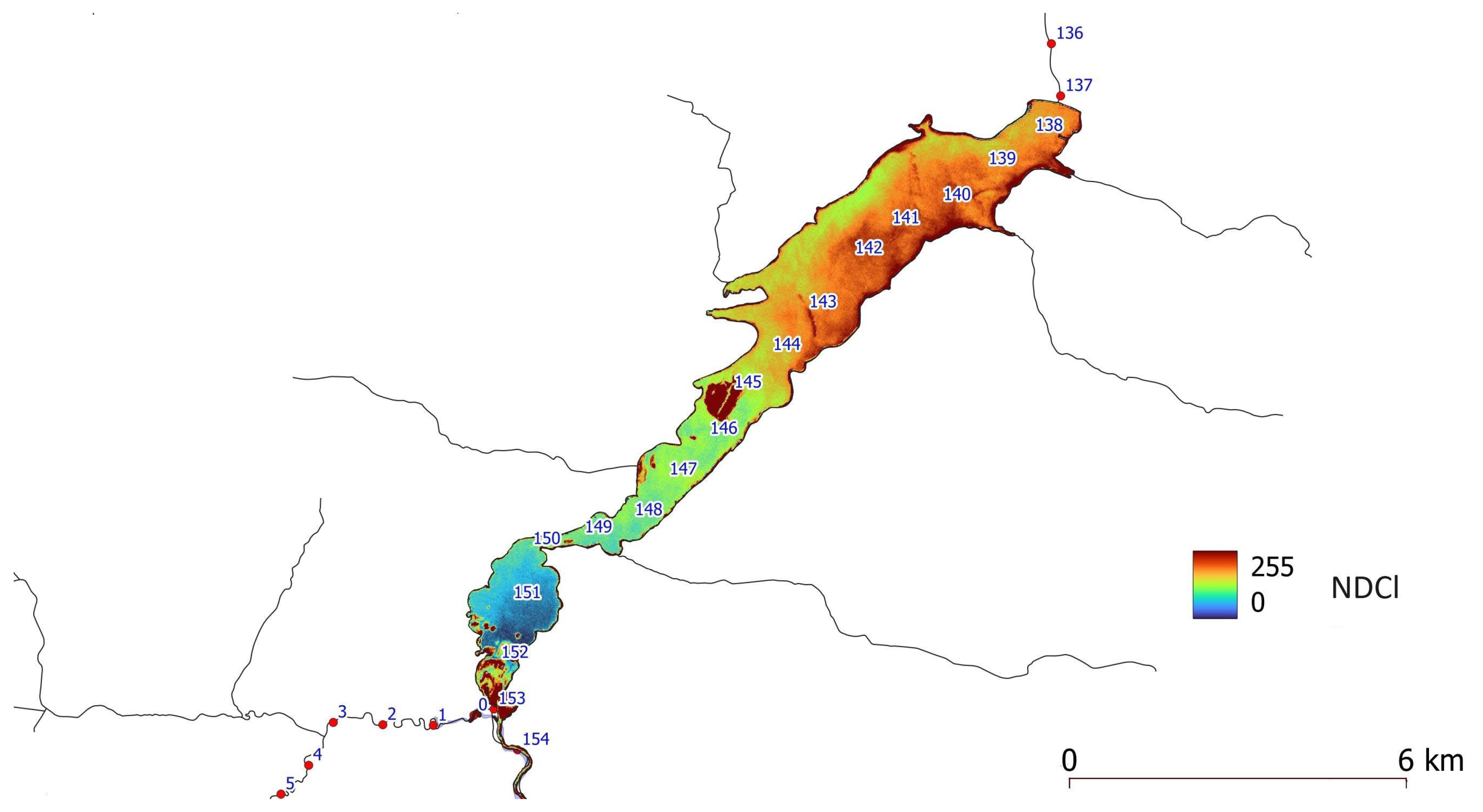
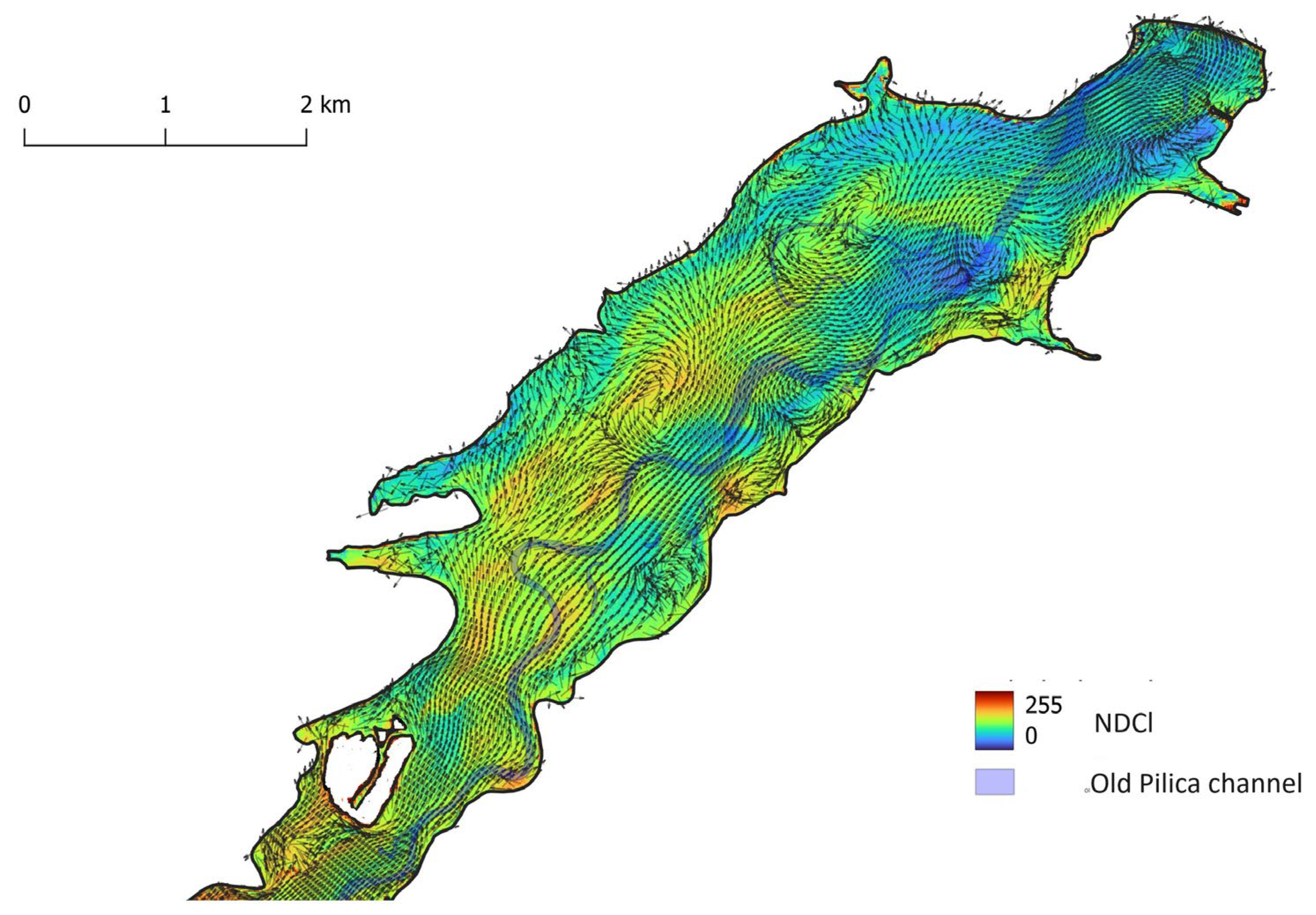
2.1. Study area
2.2. Remote sensing data
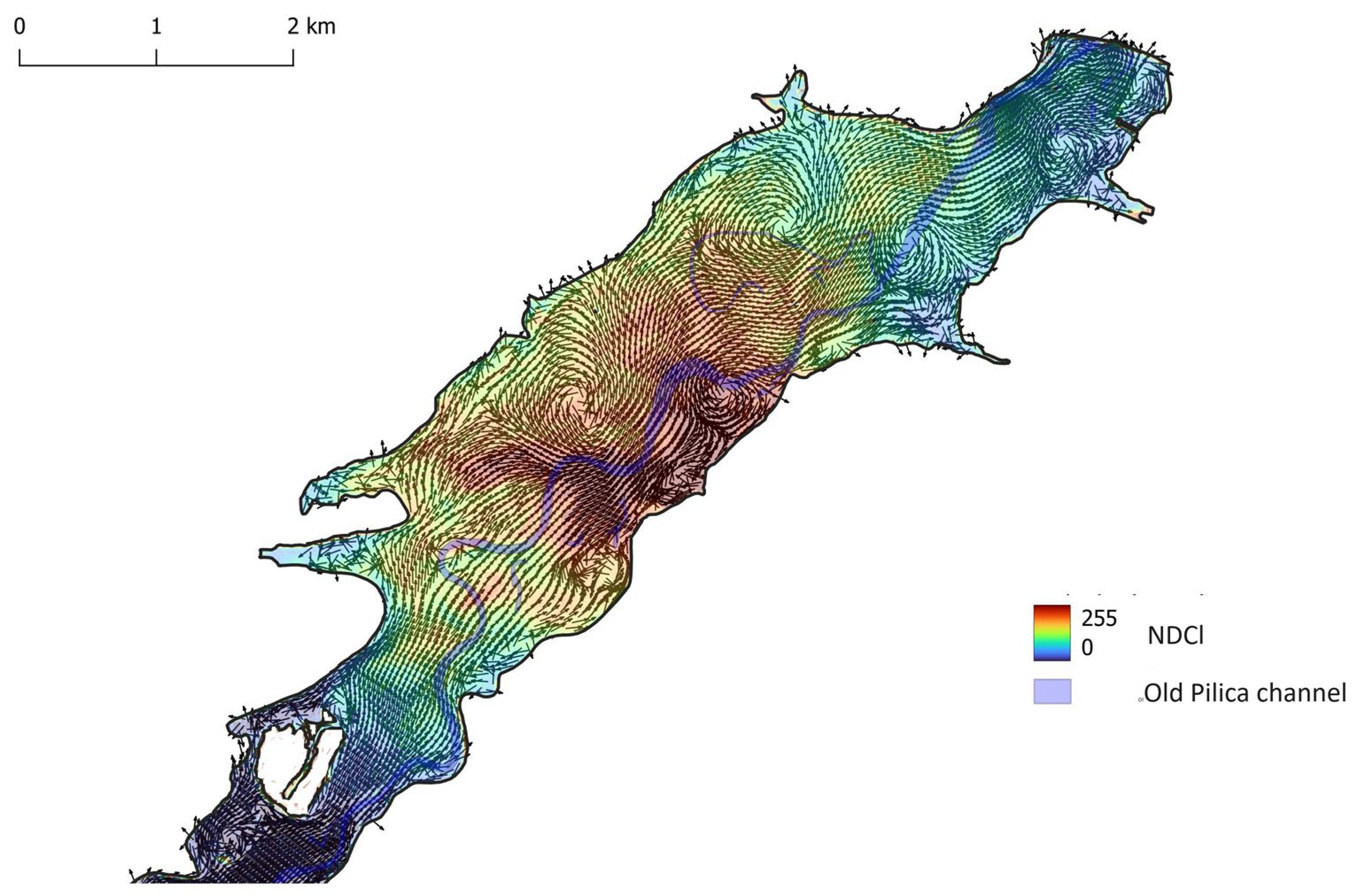
2.3. Hydrodynamic modelling
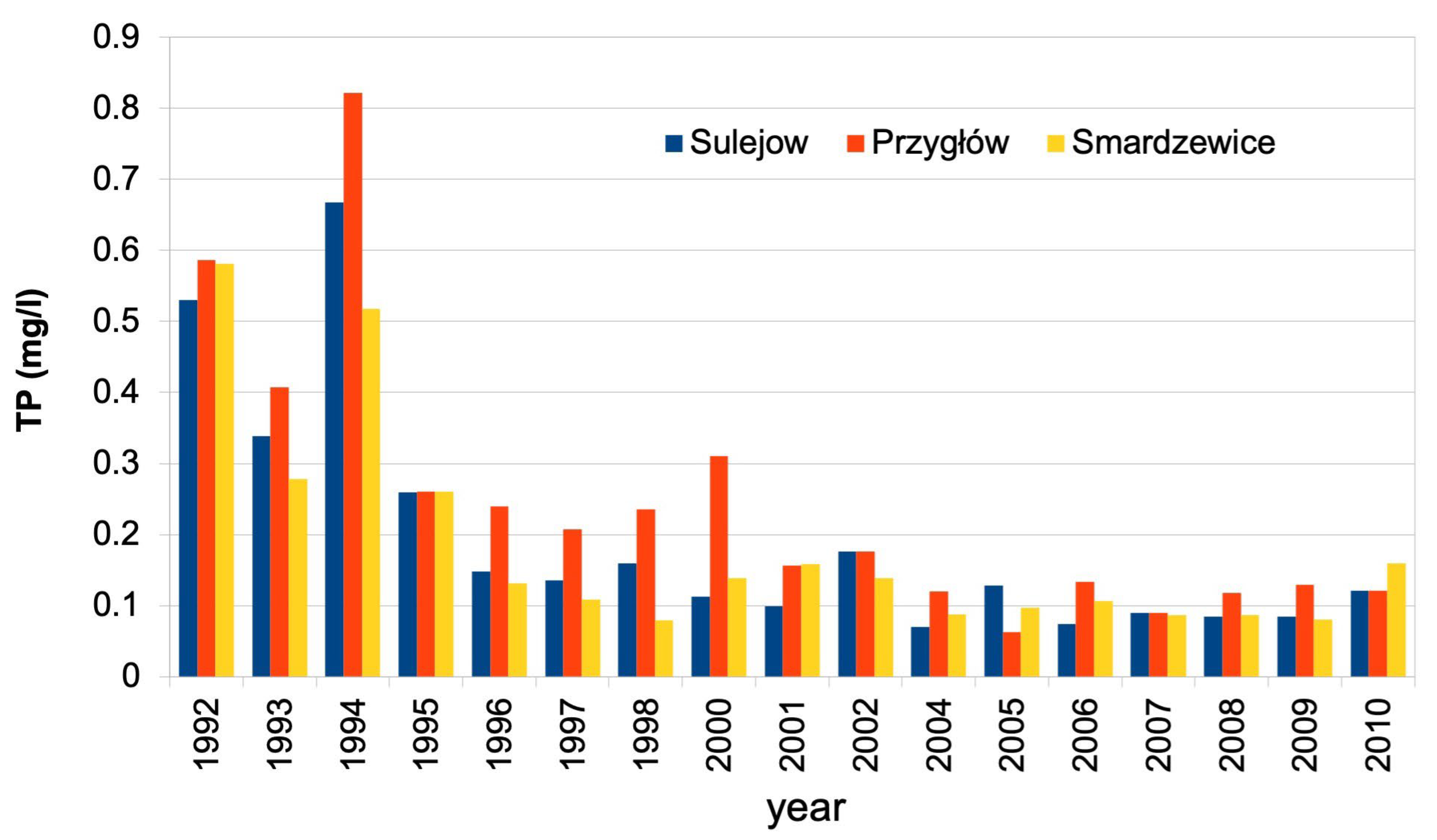
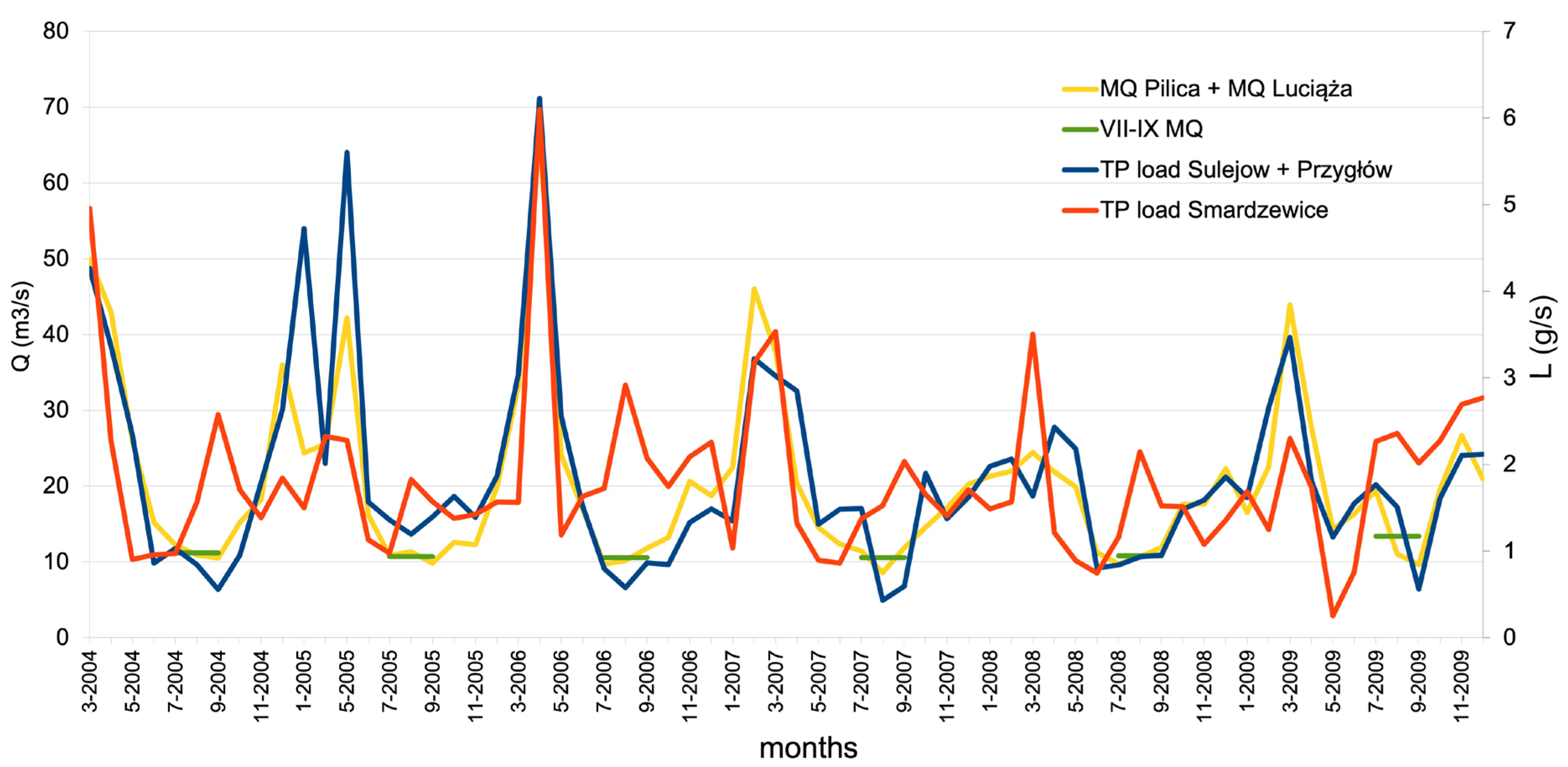
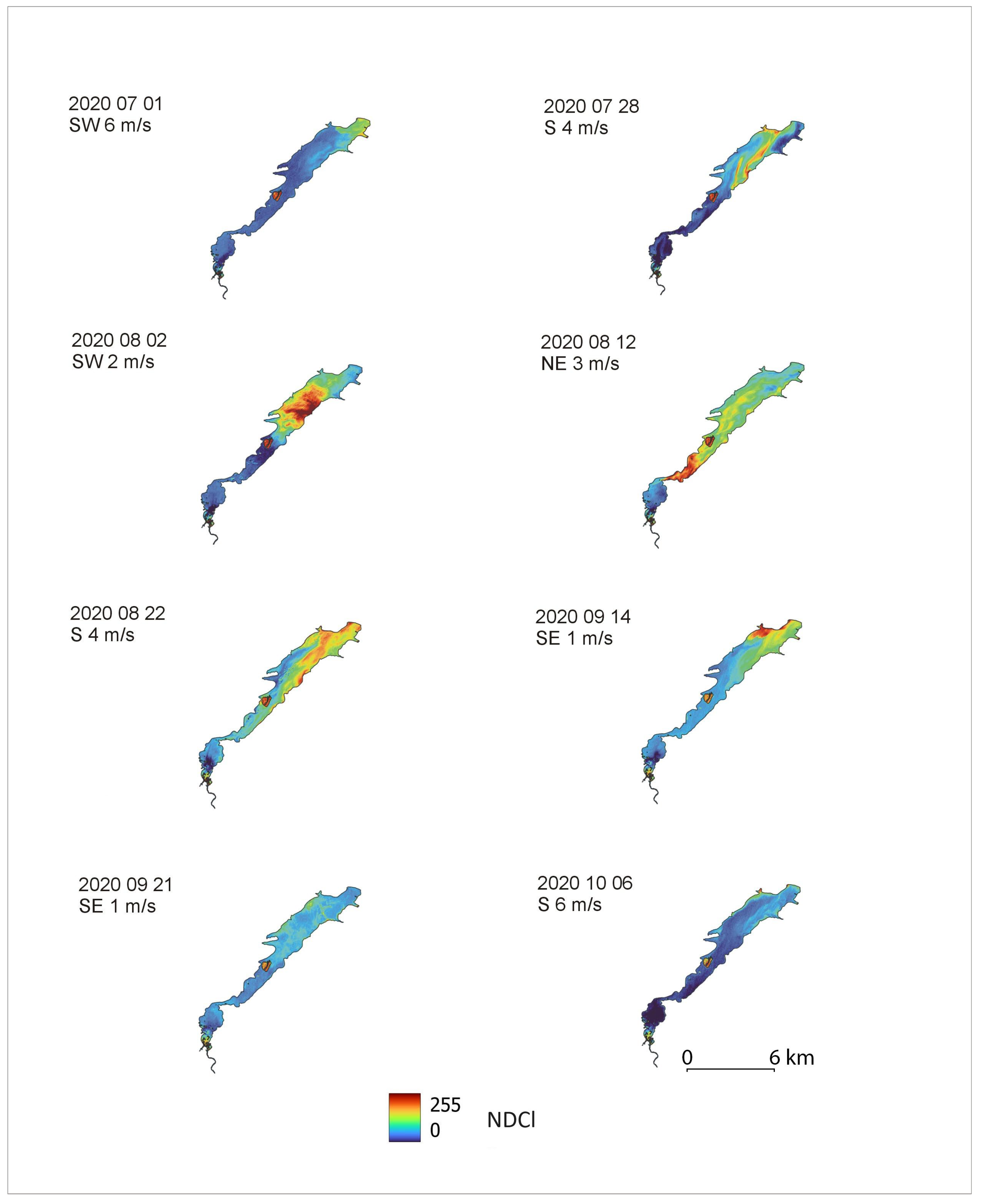
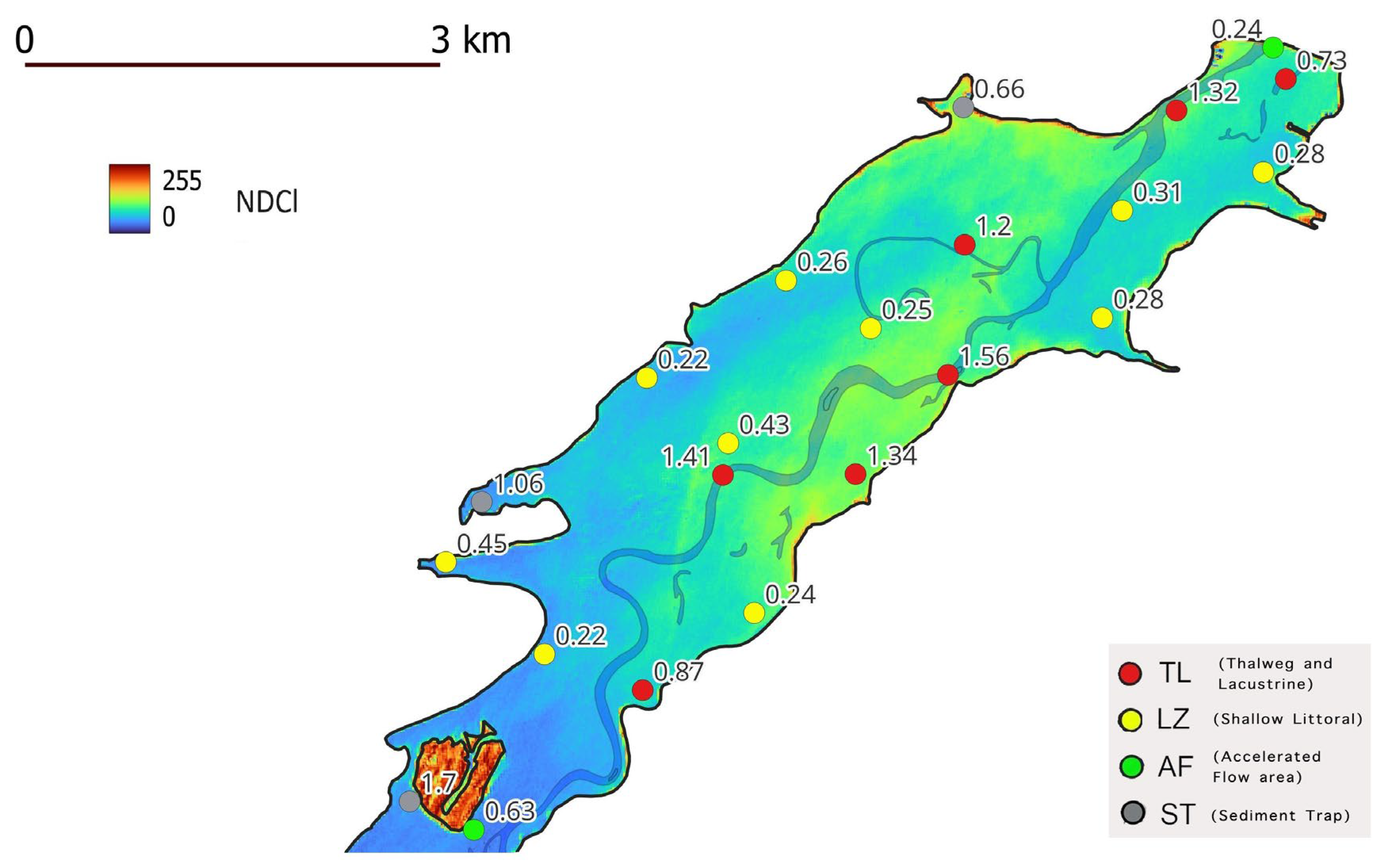
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harper, D.M. Eutrophication of Freshwaters: Rinciples, Problems, and Restoration; 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: London ; New York, 1992; ISBN 978-0-412-32970-8.
- Yoshimura, S. Rapid Entrophication within Recent Years of Lake Haruna, Gunma, Japan. Jpn. J. Geol. Geogr. 1933, 11, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kornijów, R. Eutrophication and Derivative Concepts. Origins, Compatibility and Unresolved Issues. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2023; S1642359323000708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. The Dilemma of Controlling Cultural Eutrophication of Lakes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4322–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczukocki, D.; Krawczyk, B.; Dałkowski, R.; Juszczak, R.; Miekoś, E.; Zieliński, M.; Cieśliński, R.; Jereczek-Korzeniewska, K. Monitoring hydrochemiczny zbioeników zaporowych województw łódzkiego; Problemy badań wody w XX I XXI wieku.; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Gdańskiego: Gdańsk, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchett, G.; Oliveira-Filho, E. Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins: From Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystems and Human Health to Anticarcinogenic Effects. Toxins 2013, 5, 1896–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarczyńska, M.; Osiecka, R.; Kątek, R.; Błaszczyk, A.; Zalewski, M. Przyczyny i konsekwencje powstawania toksycznych zakwitów sinicowych w zbiornikach; Zastosowanie biotechnologii ekosystemalnych do poprawy jakości wód.; Instytut Ekologii PAN, Człowiek i środowisko, 1997; Vol. 18;
- Ryan, J.; Greenfield, D.; Marin, R., Iii; Preston, C.; Roman, B.; Jensen, S.; Pargett, D.; Birch, J.; Mikulski, C.; Doucette, G.; et al. Harmful Phytoplankton Ecology Studies Using an Autonomous Molecular Analytical and Ocean Observing Network. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 1255–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Clayton, C. Assessment of Temporal Variations of Water Quality in Inland Water Bodies Using Atmospheric Corrected Satellite Remotely Sensed Image Data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 159, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote Sensing of Inland Waters: Challenges, Progress and Future Directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Metsamaa, L.; Strömbeck, N.; Vahtmäe, E. Monitoring Cyanobacterial Blooms by Satellite Remote Sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized Difference Chlorophyll Index: A Novel Model for Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Productive Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Anderson, D.A.; Gentien, P.; Graneli, E.; Sellner, K.G. The Global, Complex Phenomena of Harmful Algal Blooms. Oceanogr. Soc. 2005, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Nuisance Phytoplankton Blooms in Coastal, Estuarine, and Inland Waters1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrick, H.J.; Worth, D.; Marshall, M.L. The Influence of Water Circulation on Chlorophyll-Turbidity Relationships in Lake Okeechobee as Determined by Remote Sensing. J. Plankton Res. 1994, 16, 1117–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawara, O.; Yura, E.; Fujii, S.; Matsumoto, T. A Study on the Role of Hydraulic Retention Time in Eutrophication of the Asahi River Dam Reservoir. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufford, D.L.; McKellar, H.N. Spatial and Temporal Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Modeling Analysis of a Large Reservoir on the South Carolina (USA) Coastal Plain. Ecol. Model. 1999, 114, 137–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhozina, V.A.; Kozhova, O.M.; Kusner, Yu.S. Hydrodynamics as a Limiting Factor in the Lake Baikal Ecosystem. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama Karim, P.; Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Magnuszewski, A. Hydraulic Properties of Sulejów Reservoir in Poland as a Driving Factor of Sedimentation Processes. In GeoPlanet: Earth and Planetary Sciences; Springer International Publishing, 2023; p. (in Press).
- Magnuszewski, A.; Moran, S.; Yu, G. Modelling Lowland Reservoir Sedimentation Conditions and the Potential Environmental Consequences of Dam Removal: Wloclawek Reservoir, Vistula River, Poland. IAHS Publ. 2010, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Magnuszewski, A.; Sabat, A.; Jarocińska, A.; Sławik, Ł. Application of the AISA Hyperspectral Image for Verification of Sediment Transport Results Obtained from CCHE2D Hydrodynamic Model—Zegrze Reservoir Case Study, Poland. In Free Surface Flows and Transport Processes; Kalinowska, M.B., Mrokowska, M.M., Rowiński, P.M., Eds.; GeoPlanet: Earth and Planetary Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 103–112. ISBN 978-3-319-70913-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Polańczyk, A.; Zbiciński, I. 3-D CFD Simulations of Hydrodynamics in the Sulejow Dam Reservoir. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuszewski, A.; Kiedrzyńska, E.; Kiedrzyński, M.; Moran, S. Gis Approach to Estimation of the Total Phosphorous Transfer in the Pilica River Lowland Catchment. Quaest. Geogr. 2014, 33, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieron, Ł.; Absalon, D.; Habel, M.; Matysik, M. Inventory of Reservoirs of Key Significance for Water Management in Poland—Evaluation of Changes in Their Capacity. Energies 2021, 14, 7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiedrzyńska, E.; Kiedrzyński, M.; Urbaniak, M.; Magnuszewski, A.; Skłodowski, M.; Wyrwicka, A.; Zalewski, M. Point Sources of Nutrient Pollution in the Lowland River Catchment in the Context of the Baltic Sea Eutrophication. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, M.; Kiedrzyńska, E.; Zalewski, M. The Role of a Lowland Reservoir in the Transport of Micropollutants, Nutrients and the Suspended Particulate Matter along the River Continuum. Hydrol. Res. 2012, 43, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Imbierowicz, E.; Jaskulski, M.; Szmidt, A. Assessment of the Chemical State of Bottom Sediments in the Eutrophied Dam Reservoir in Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama Karim, P.; Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Magnuszewski, A. Hydraulic Control on Sedimentation Processes and Bottom Sediments Chemistry of Sulejów Reservoir in Poland. Misc. Geogr. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowska, M.B.; Rowiński, P.M.; Kubrak, J.; Mirosław-Świątek, D. Scenarios of the Spread of a Waste Heat Discharge in a River — Vistula River Case Study. Acta Geophys. 2012, 60, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, M.B.; Rowiński, P.M. Uncertainty in Computations of the Spread of Warm Water in a River – Lessons from Environmental Impact Assessment Case Study. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4177–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinakar, M.; Czernuszenko, W.; Rowiński, P.; Wang, S. Computational Modeling for the Development of Sustainable Water-Resources Systems in Poland. US-Poland Technology Transfer Program; E; Institute of Geophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences: Warsaw, 2005; Vol. E-5 (387);
- Jia, Y; Wang, S. CCHE2D : Two-Dimensional Hydrodynamic and Sediment Transport Model for Unsteady Open Channel Flows over Loose Bed, Technical Report No. NCCHE-TR-2001-1 2001.
- Jaskulski, M.; Szmidt, A.; Zbiciński, I.; Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Adamiec, J. Konstrukcja mapy batymetrycznej na podstawie badań sonarowych sztucznego zbiornika wodnego na przykładzie Zalewu Sulejowskiego. Teledetekcja Śr. 2018, 59, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mohn, C.; White, M. Remote Sensing and Modelling of Bio-Physical Distribution Patterns at Porcupine and Rockall Bank, Northeast Atlantic. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1875–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soontiens, N.; Binding, C.; Fortin, V.; Mackay, M.; Rao, Y.R. Algal Bloom Transport in Lake Erie Using Remote Sensing and Hydrodynamic Modelling: Sensitivity to Buoyancy Velocity and Initial Vertical Distribution. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R.; Kjerfve, B.; Ramsey, E.W.; Magill, K.E.; Medeiros, C.; Sneed, J.E. Remote Sensing and Numerical Modeling of Suspended Sediment in Laguna de Terminos, Campeche, Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 28, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouts, T.; Sipelgas, L.; Savinits, N.; Raudsepp, U. Environmental Monitoring of Water Quality in Coastal Sea Area Using Remote Sensing and Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE US/EU Baltic International Symposium; IEEE: Klaipeda, Lithuania, May, 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sabat-Tomala, A.; Jarocińska, A.M.; Zagajewski, B.; Magnuszewski, A.S.; Sławik, Ł.M.; Ochtyra, A.; Raczko, E.; Lechnio, J.R. Application of HySpex Hyperspectral Images for Verification of a Two-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




