Submitted:
04 April 2024
Posted:
05 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
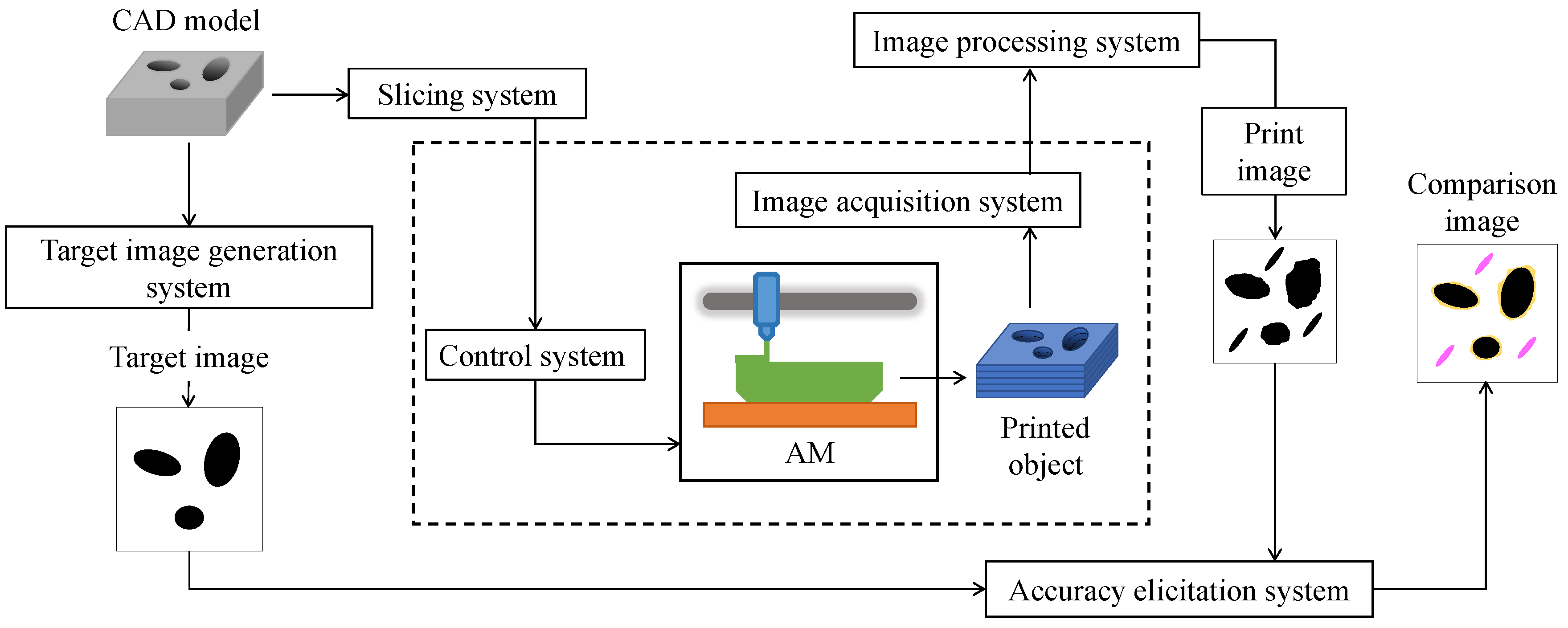
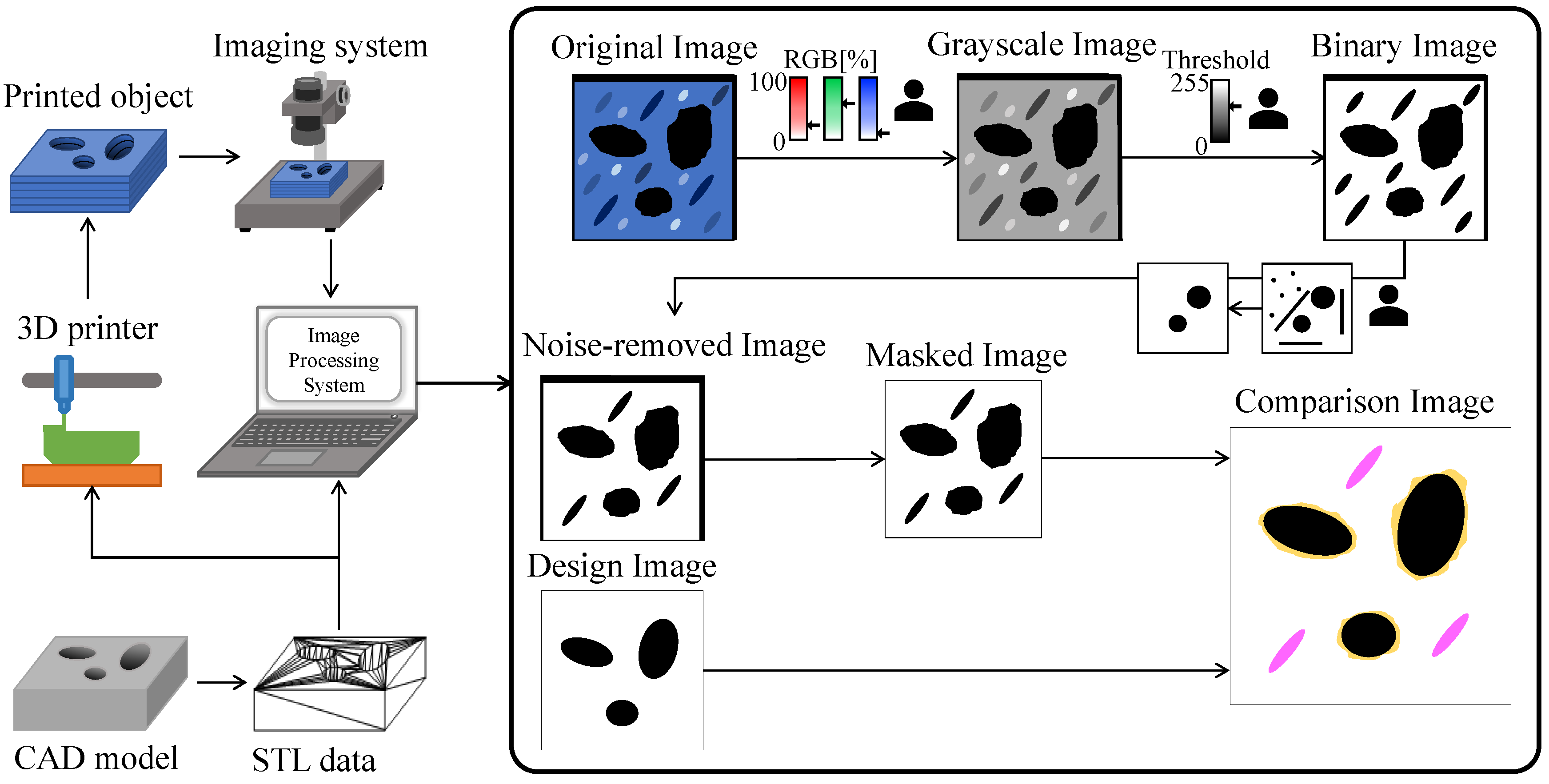
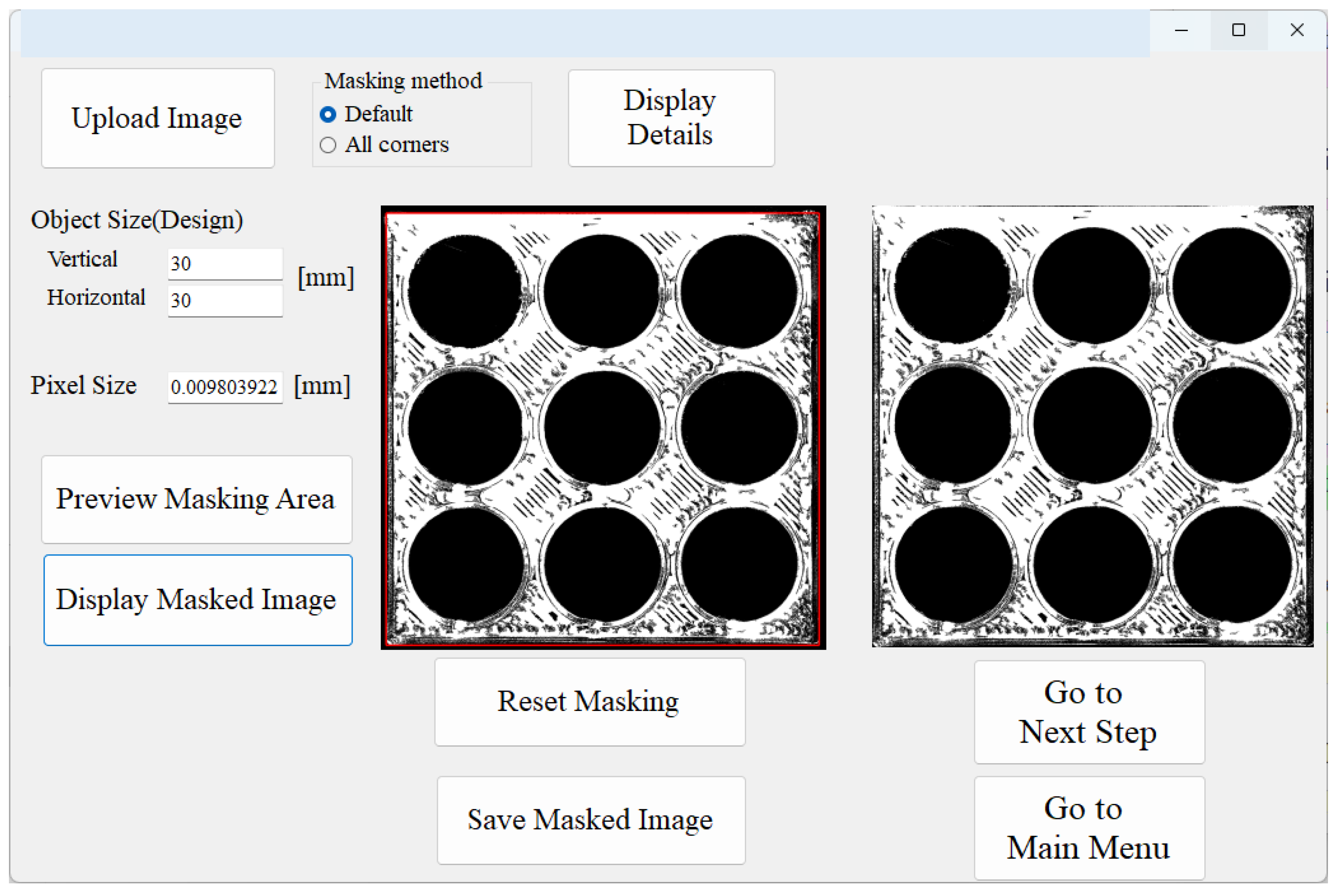
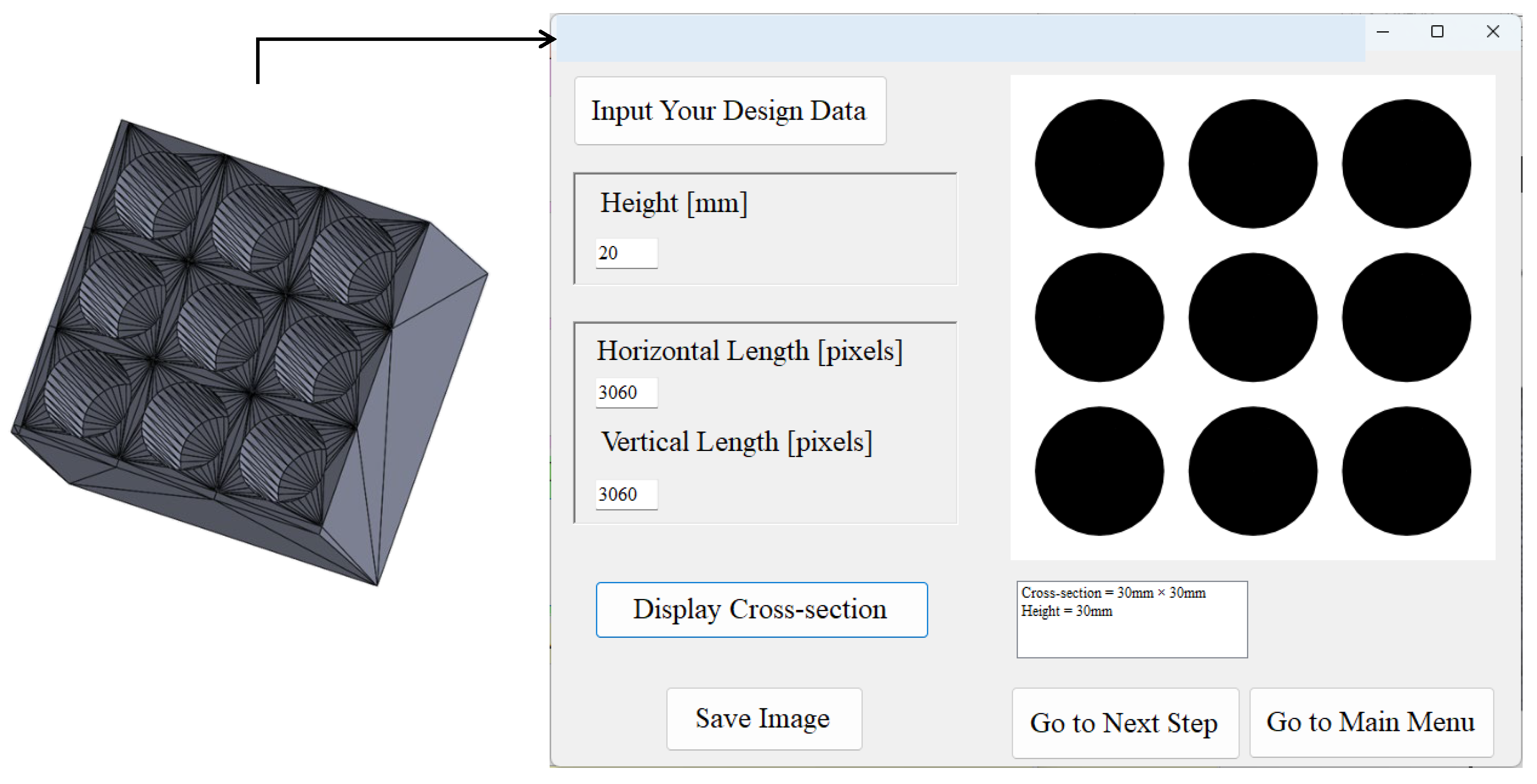
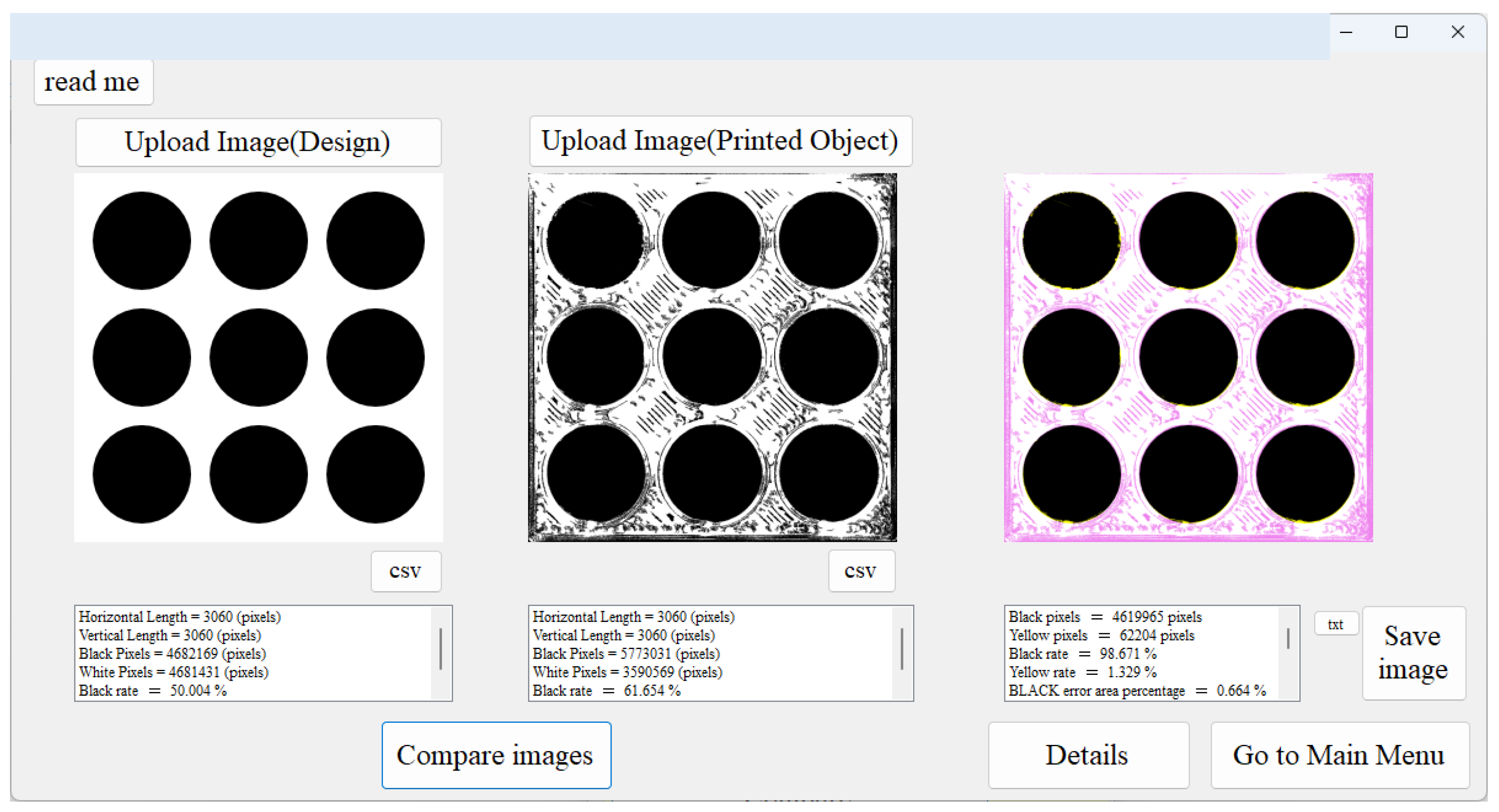
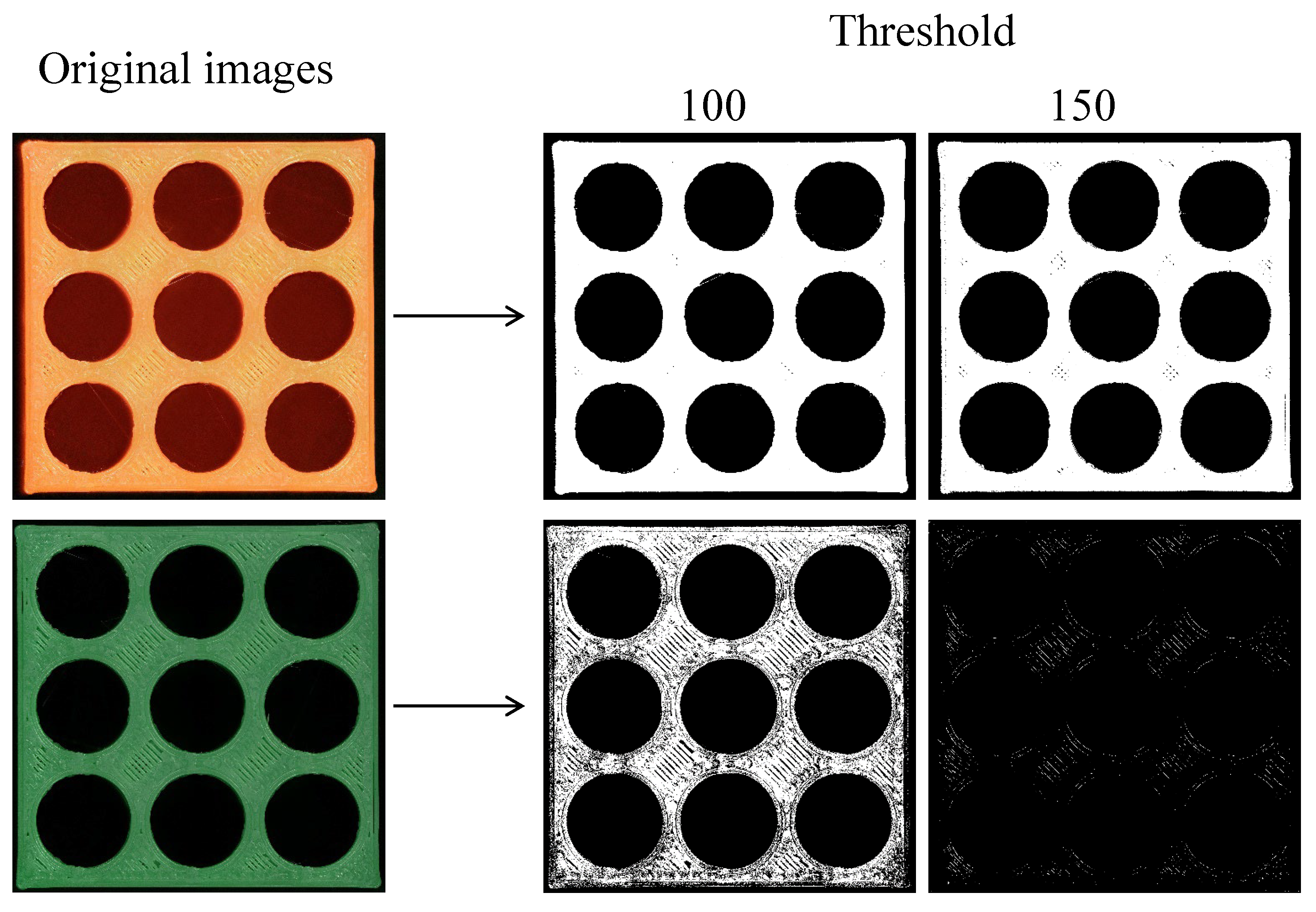
3. Image Processing System
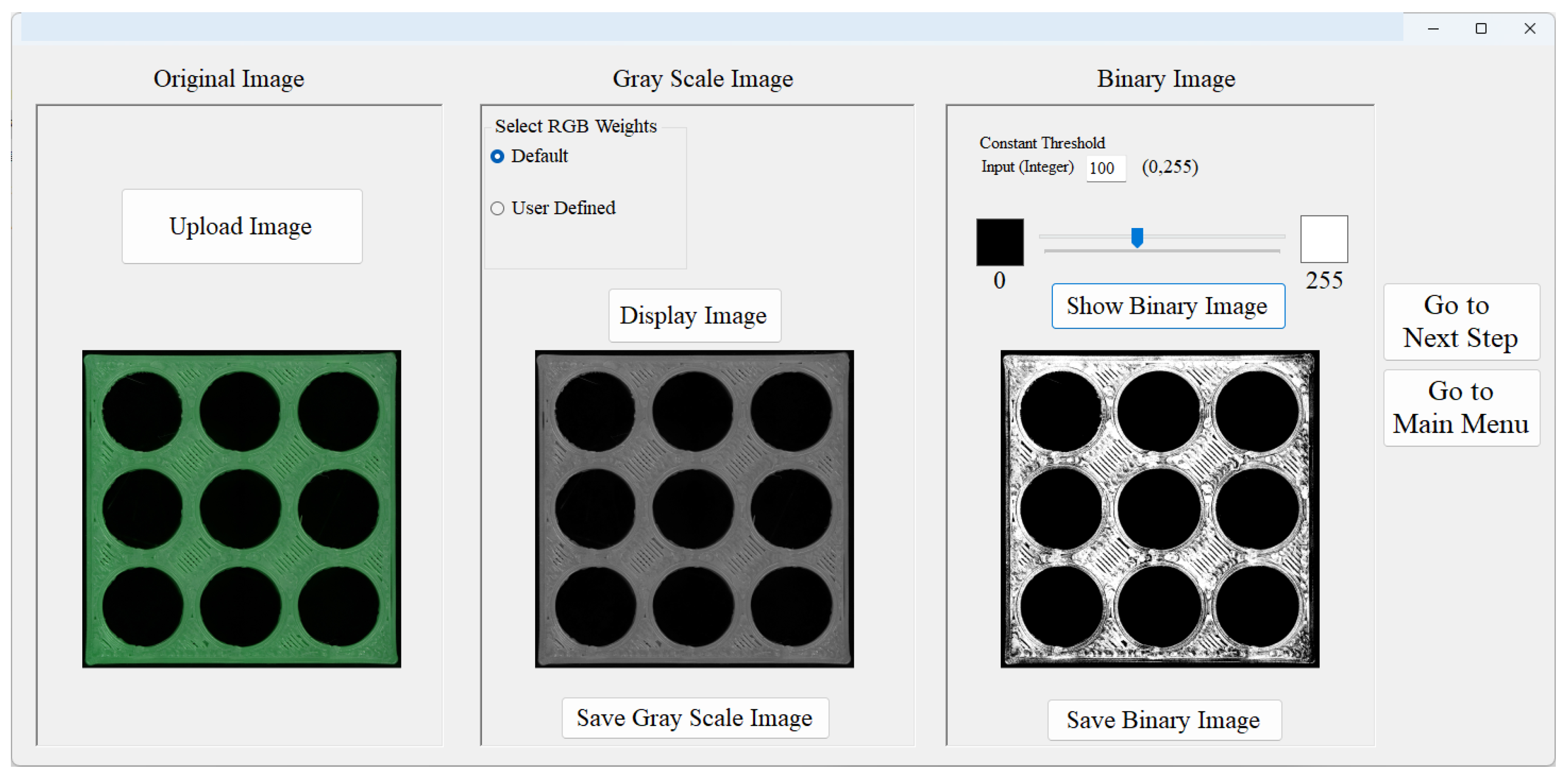
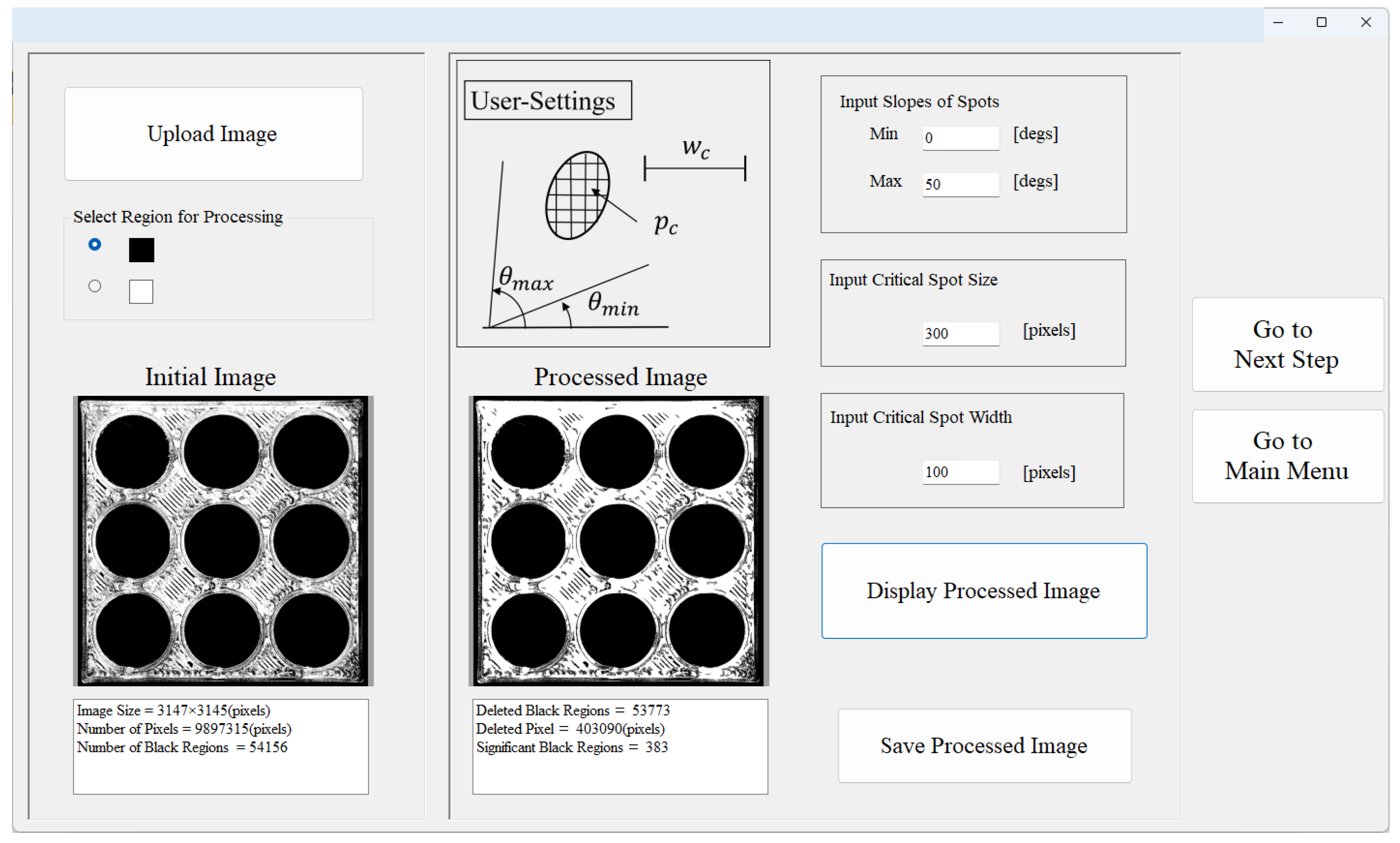
User Interfaces
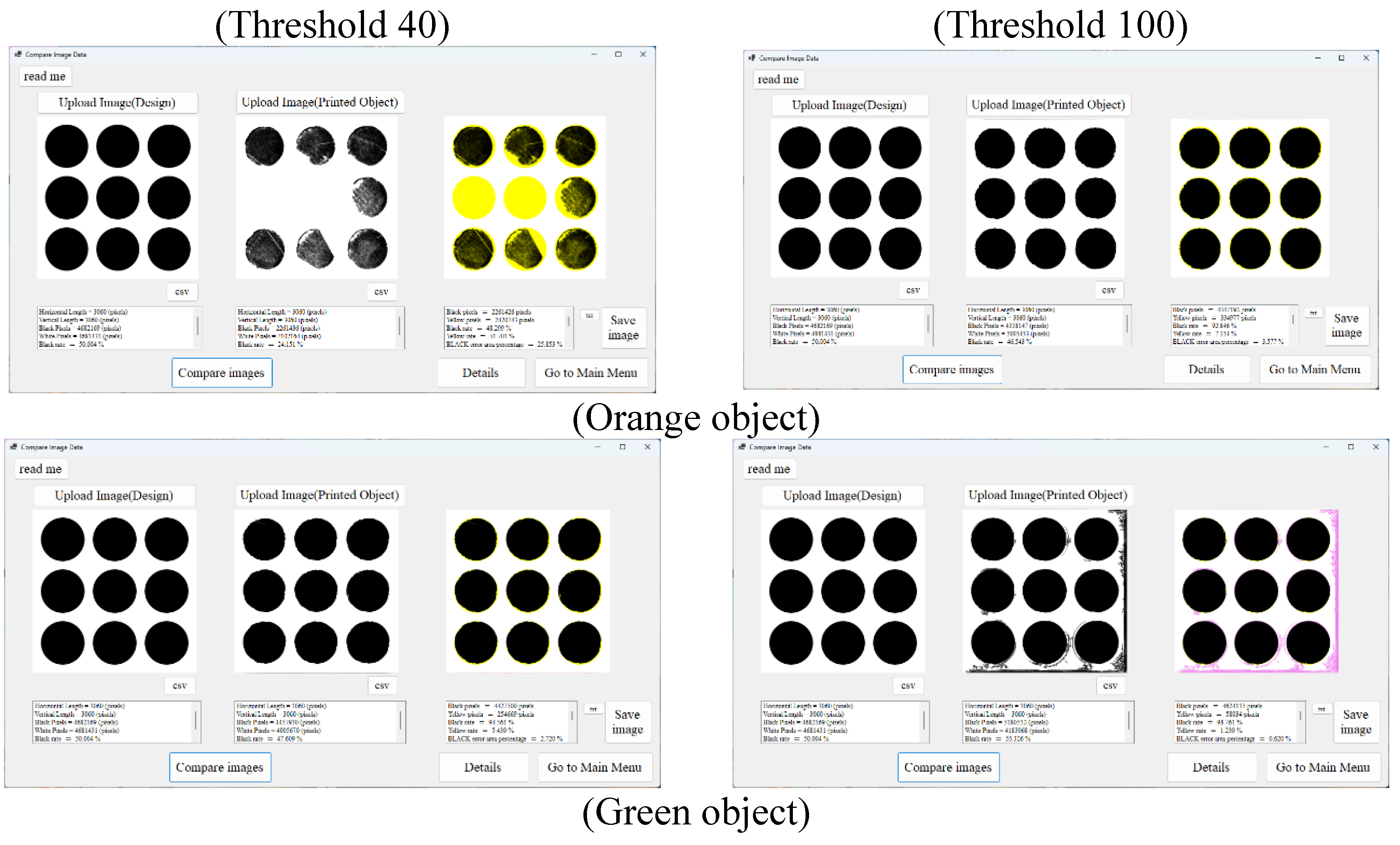
4. Accuracy of a Simple 3D-Printed Object
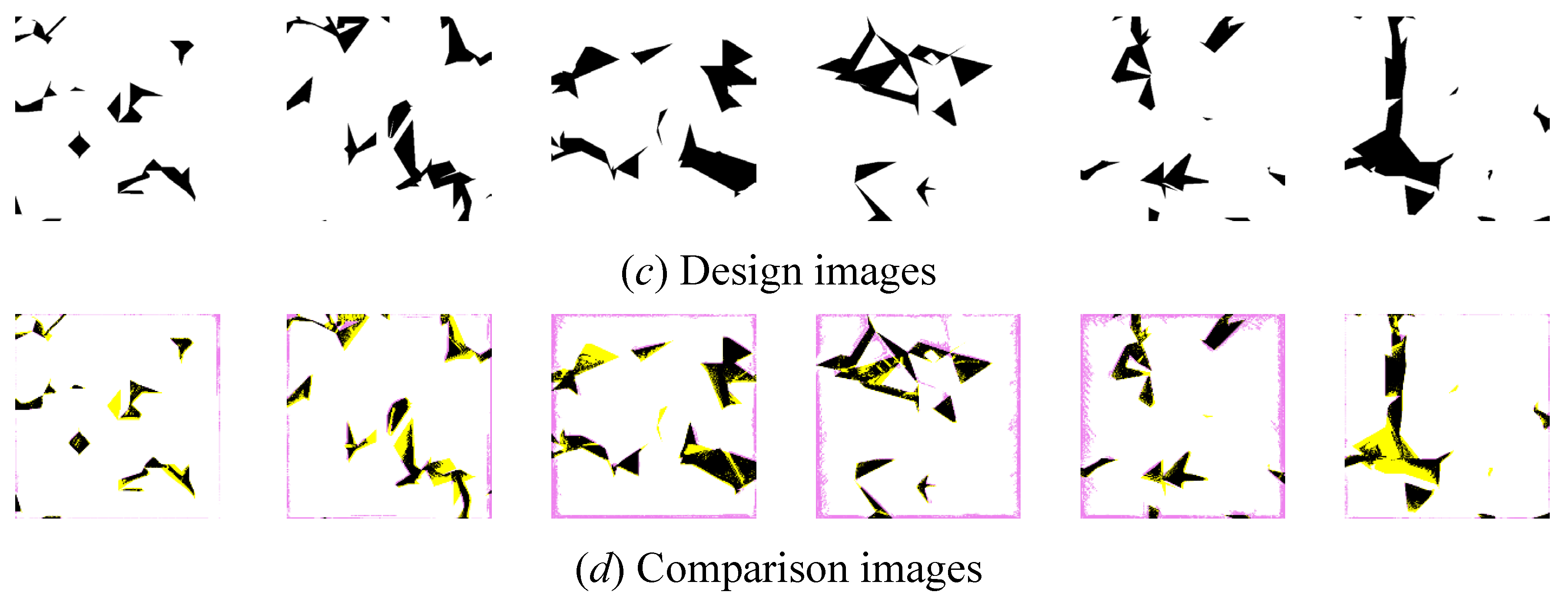
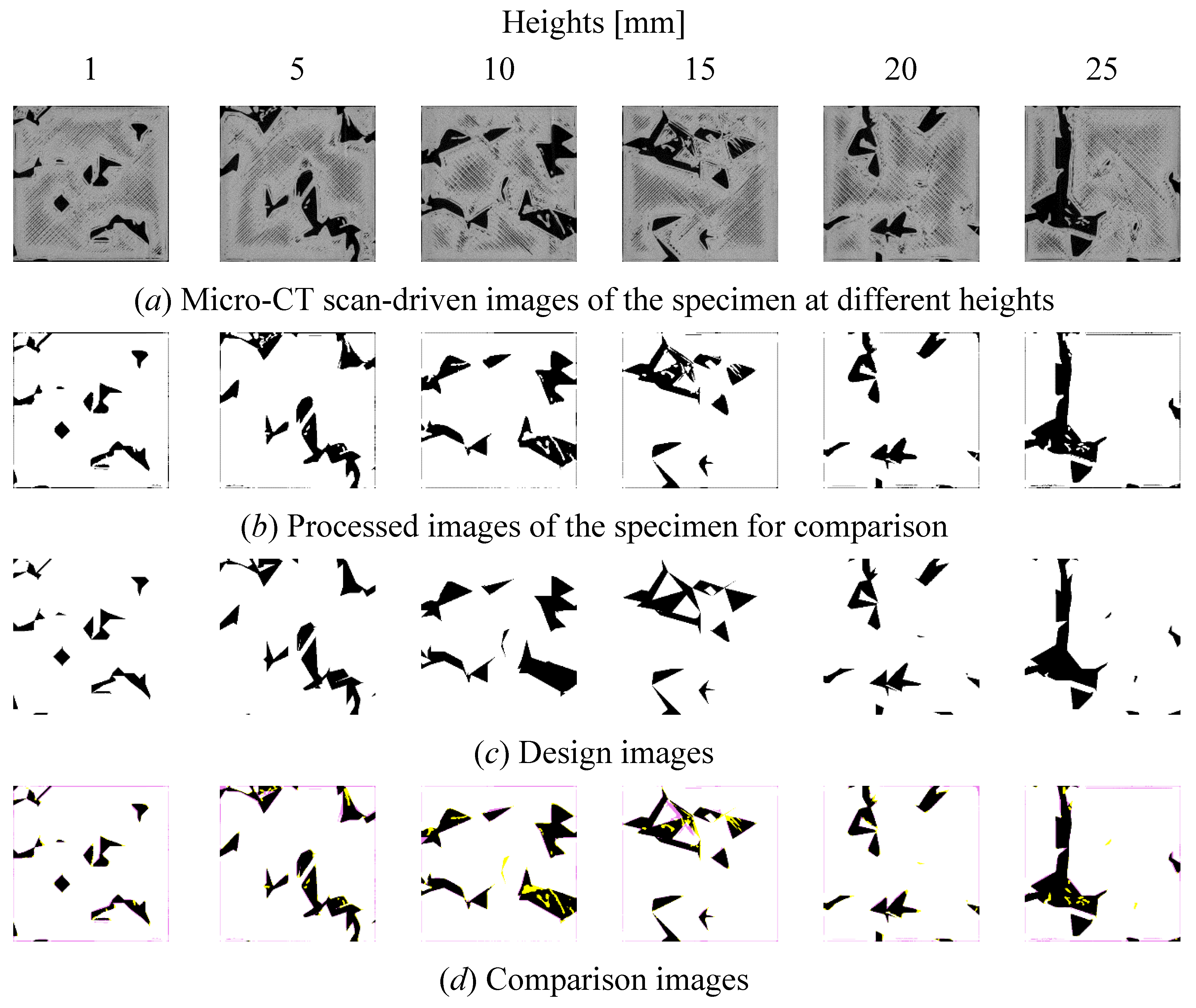
5. Accuracy of a 3D-Printed Porous Structure (Complex Object)
6. Concluding Remarks
References
- D. L. Bourell, D. W. Rosen, and M. C. Leu, The Roadmap for Additive Manufacturing and Its Impact, 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, Vol.1, No.1, pp. 6-9, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D. Rosen, B. Stucker. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D Printing, Rapid Prototyping, and Direct Digital Manufacturing, Springer, New York, NY, 2015.
- M. M. S. Ullah, Tashi, A. Kubo, K. H. Harib. Tutorials for Integrating 3D Printing in Engineering Curricula. Education Sciences. 2020; 10(8):194. [CrossRef]
- M. M. S. Ullah, D. M. D’Addona, K. H. Harib, T. Lin. Fractals and Additive Manufacturing, International Journal of Automation Technology, 2016, 10(2), pp. 222-230.
- M. M. S. Ullah, Hiroki Kiuno, Akihiko Kubo, Doriana Marilena D’Addona, A system for designing and 3D printing of porous structures, CIRP Annals, 69(1), 2020, pp. 113-116, 2020. [CrossRef]
- 6. Yusuke Seto, AMM Sharif Ullah, Akihiko Kubo, Doriana Marilena D’Addona, Roberto Teti, On the Porous Structuring using Unit Cells, Procedia CIRP, 99, 2021, pp. 381-386. [CrossRef]
- S. Ullah, D. M. D’Addona, Y. Seto, S. Yonehara, A. Kubo. Utilizing Fractals for Modeling and 3D Printing of Porous Structures, Fractal and Fractional, 2021; 5(2):40. [CrossRef]
- Carew, R. M., Morgan, R. M. and Rando, C., A Preliminary Investigation into the Accuracy of 3D Modeling and 3D Printing in Forensic Anthropology Evidence Reconstruction, Journal of Forensic Sciences, Vol. 64, No. 2 (2019), pp. 342−352. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J. and Rogers, T., The Accuracy and Applicability of 3D Modeling and Printing Blunt Force Cranial Injuries, Journal of Forensic Sciences, Vol. 63, No. 3 (2018), pp. 683−691. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Y., Cho, J. W., Chang, N. Y., Chae, J. M., Kang, K. H., Kim, S. C. and Cho, J. H., Accuracy of three-dimensional printing for manufacturing replica teeth, Korean Journal of Orthodontics, Vol. 45, No. 5 (2015), pp. 217−2251. [CrossRef]
- Leng, S., McGee, K., Morris, J., Alexander, A., Kuhlmann, J., Vrieze, T., McCollough C. H., and Matsumoto, J. Anatomic modeling using 3D printing: quality assurance and optimization, 3D Printing in Medicine, Vol. 3 (2017) pp. 6. [CrossRef]
- George, E., Liacouras, P., Rybicki, F. J. and Mitsouras, D. Measuring and establishing the accuracy and reproducibility of 3D printed medical models, RadioGraphics, Vol. 37, No. 5 (2017), pp. 1424−1450. [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, C., Eshja, E., Peroni, C., Orlandi, M. A., Bizzotto, N. and Poggi, P., 3D printing of CT dataset: validation of an open source and consumer-available workflow, Journal of Digital Imaging, Vol. 29, No. 1 (2016), pp.14−21. [CrossRef]
- Herpel, C., Tasaka, A., Higuchi, S., Finke, D., Kühle, R., Odaka, K., Rues, S., Lux, C. J., Yamashita, S., Rammelsberg, P. and Schwindling, F. S., Accuracy of 3D Printing Compared with Milling—a Multi-Center Analysis of Try-In Dentures, Journal of Dentistry, Vol. 110 (2021), pp. 103681. [CrossRef]
- Cai, T., Rybicki, F. J., Giannopoulos, A. A., Schultz, K., Kumamaru, K. K., Liacouras, P., Demehri, S., Small, K. M. and Mitsouras, D., The residual STL volume as a metric to evaluate accuracy and reproducibility of anatomic models for 3D printing: application in the validation of 3D-printable models of maxillofacial bone from reduced radiation dose CT images, 3D Printing in Medicine, Vol. 1, No. 1 (2015), pp. 2. [CrossRef]
- Kim, T., Lee, S., Kim, G.B., Hong, D., Kwon, J., Park, J.W. and Kim, N., Accuracy of a simplified 3D-printed implant surgical guide, The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, Vol. 124, No. 2 (2020), pp. 195−201. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J., Kim, G.B., Kang, S., Byeon, Y., Sa, H.-S. and Kim, N., Accuracy of 3D printed guide for orbital implant, Rapid Prototyping Journal, Vol. 26, No. 8 (2020), pp. 1363−1370. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F., Sun, Y., Zhang, L. and Sun, Y., Accuracy of chair-side fused-deposition modelling for dental applications, Rapid Prototyping Journal, Vol. 25 No. 5 (2019), pp. 857−863. [CrossRef]
- Borgue, M. Panarotto, and O. Isaksson, “Fuzzy model-based design for testing and qualification of additive manufacturing components,” Design Science, vol. 8, p. e11, 2022, Art no. e11.
- T. Li, J. Li, X. Ding, X. Sun, and T. Wu, “An error identification and compensation method for Cartesian 3D printer based on specially designed test artifact,” The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, vol. 125, no. 9, pp. 4185-4199, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Holzmond and X. Li, “In situ real time defect detection of 3D printed parts,” Additive Manufacturing, vol. 17, pp. 135-142, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yu, X. Li, T. Zuo, Q. Wang, H. Wang, and Z. Liu, “High-accuracy DLP 3D printing of closed microfluidic channels based on a mask option strategy,” The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, vol. 127, no. 7, pp. 4001-4012, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Montgomery, F. Demoly, K. Zhou, and H. J. Qi, “Pixel-Level Grayscale Manipulation to Improve Accuracy in Digital Light Processing 3D Printing,” Advanced Functional Materials, vol. 33, no. 17, pp. 2213252, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ma, J. Potappel, M. A. I. Schutyser, R. M. Boom, and L. Zhang, “Quantitative analysis of 3D food printing layer extrusion accuracy: Contextualizing automated image analysis with human evaluations: Quantifying 3D food printing accuracy,” Current Research in Food Science, vol. 6, pp. 100511, 2023.
- N. Otsu, “A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 62-66, 1979. [CrossRef]
- N. Vidakis, C. David, M. Petousis, D. Sagris, and N. Mountakis, “Optimization of key quality indicators in material extrusion 3D printing of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene: The impact of critical process control parameters on the surface roughness, dimensional accuracy, and porosity,” Materials Today Communications, vol. 34, pp. 105171, 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. E. Eltes, L. Kiss, M. Bartos, Z. M. Gyorgy, T. Csakany, F. Bereczki, V. Lesko, M. Puhl, P. [28] P. Varga, and A. Lazary, “Geometrical accuracy evaluation of an affordable 3D printing technology for spine physical models,” Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, vol. 72, pp. 438-446, 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Nguyen, I. Stanislaus, C. McGahon, K. Pattabathula, S. Bryant, N. Pinto, J. Jenkins, and C. Meinert, “Quality assurance in 3D-printing: A dimensional accuracy study of patient-specific 3D-printed vascular anatomical models,” Frontiers in Medical Technology, vol. 5, 2023-February-07, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Huang, C. Xiang, C. Zeng, H. Ouyang, K. K. Wong, and W. Huang, Patient-specific geometrical modeling of orthopedic structures with high efficiency and accuracy for finite element modeling and 3D printing, Australasian Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine, vol. 38, no. 4, pp. 743-53, Dec, 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. Xia, B. Nematollahi, and J. Sanjayan, “Shape Accuracy Evaluation of Geopolymer Specimens Made Using Particle-Bed 3D Printing,” in Second RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication, Cham, F. P. Bos, S. S. Lucas, R. J. M. Wolfs, and T. A. M. Salet, Eds., 2020: Springer International Publishing, pp. 1011-1019.
- S. Yonehara and A.S. Ullah, Elucidating accuracy of 3D printed porous structure by analyzing images of designed and printed structures, Proceedings of the International Conference on Design and Concurrent Engineering 2021 & Manufacturing Systems Conference 2021 (iDECON/MS2021), JSME, September 3-4, 2021, Virtual, Paper ID: 17.
- T. Okamoto, S. Yonehara, S. Ura and A.K. Ghosh, A Metrological System for 3D-Printed Objects, Proceedings of the 38th American Society for Precision Engineering Annual Meeting, Boston, Massachusetts, USA, November 12-17, 2023.
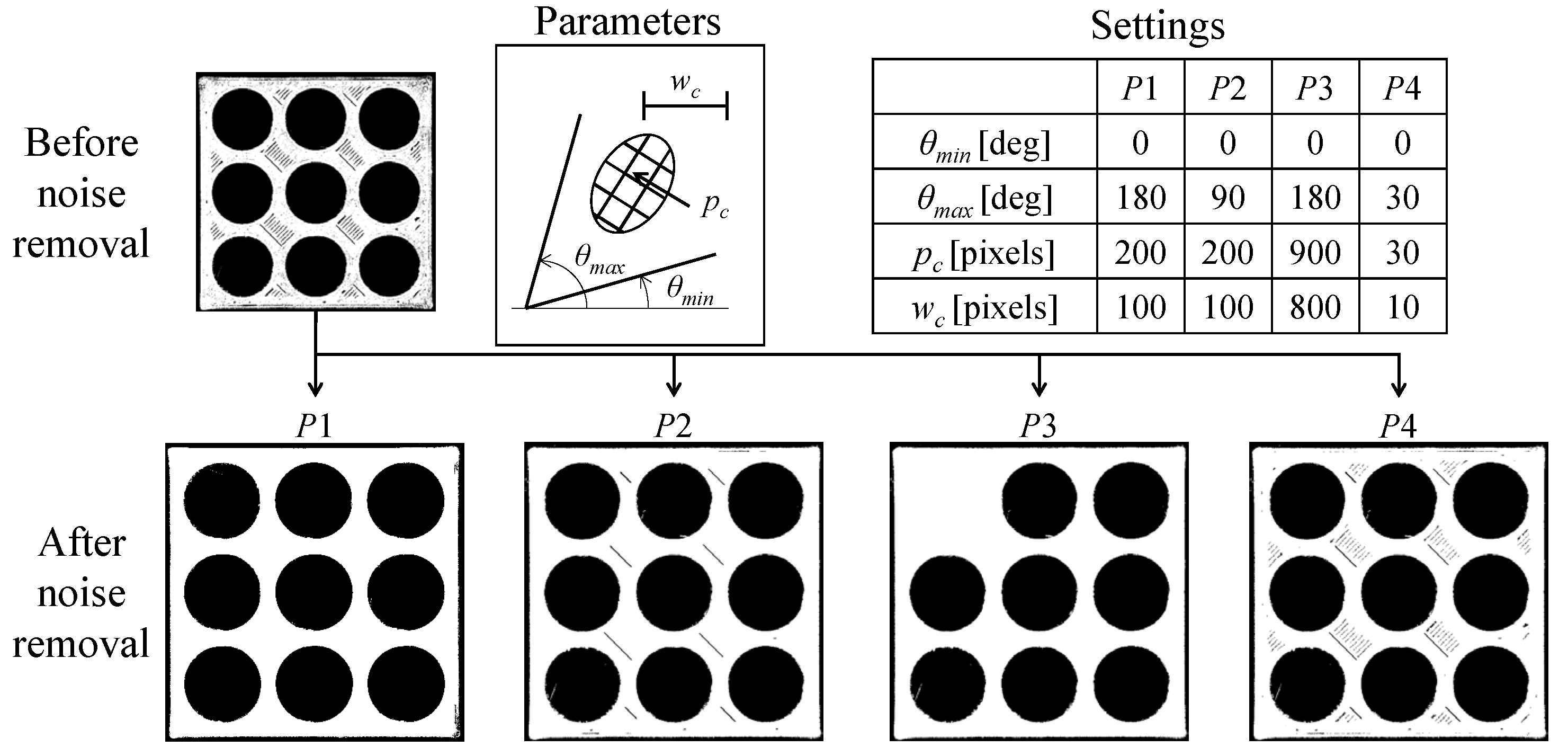

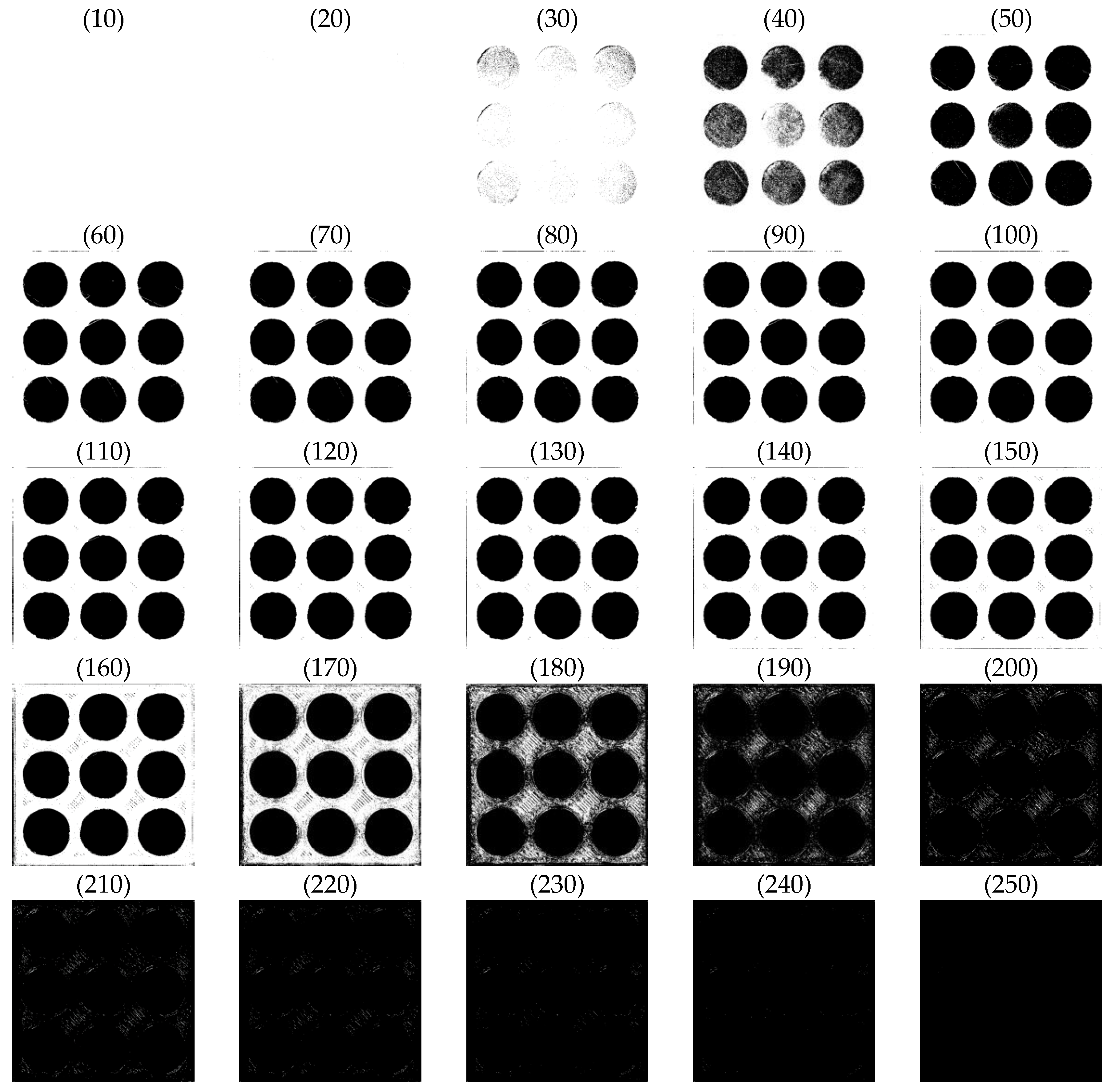
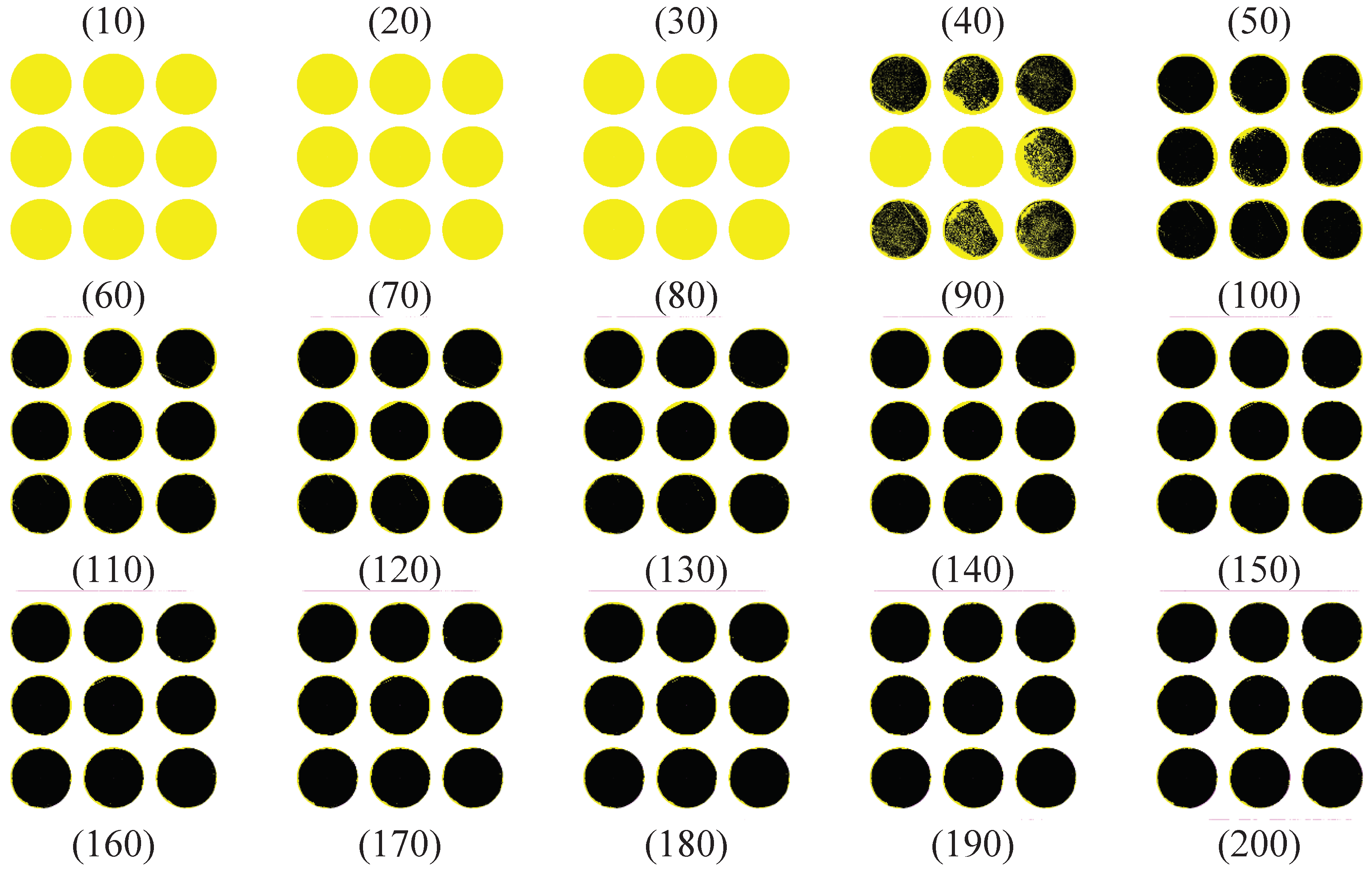
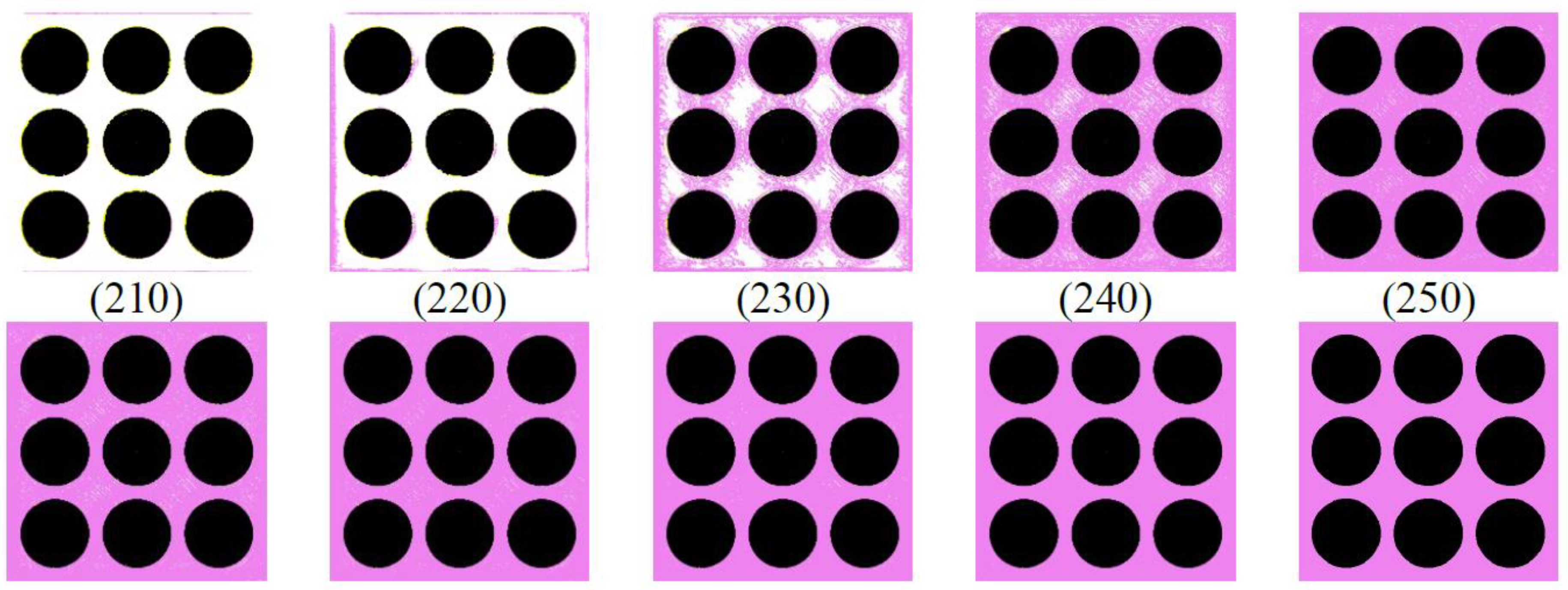
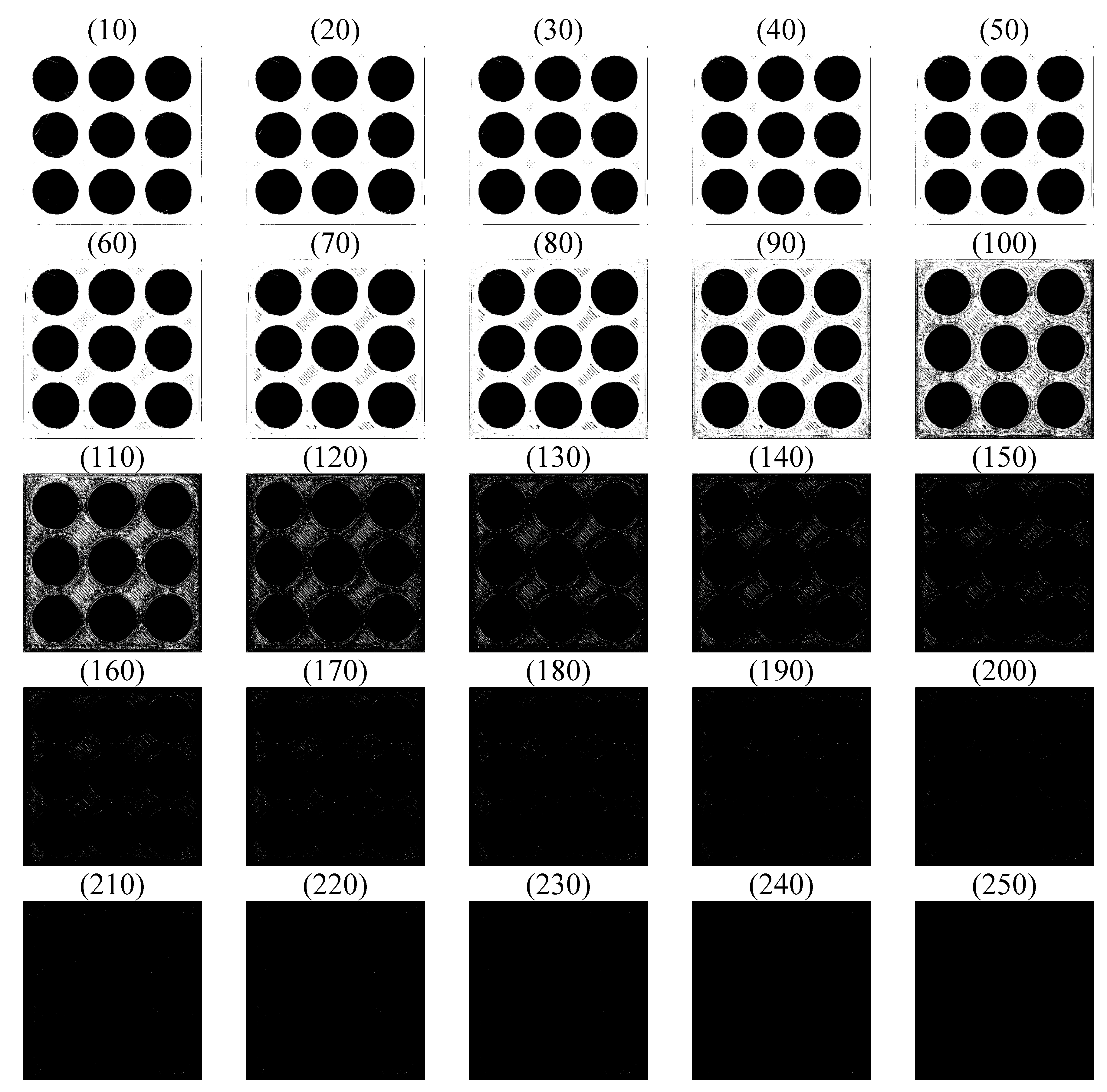
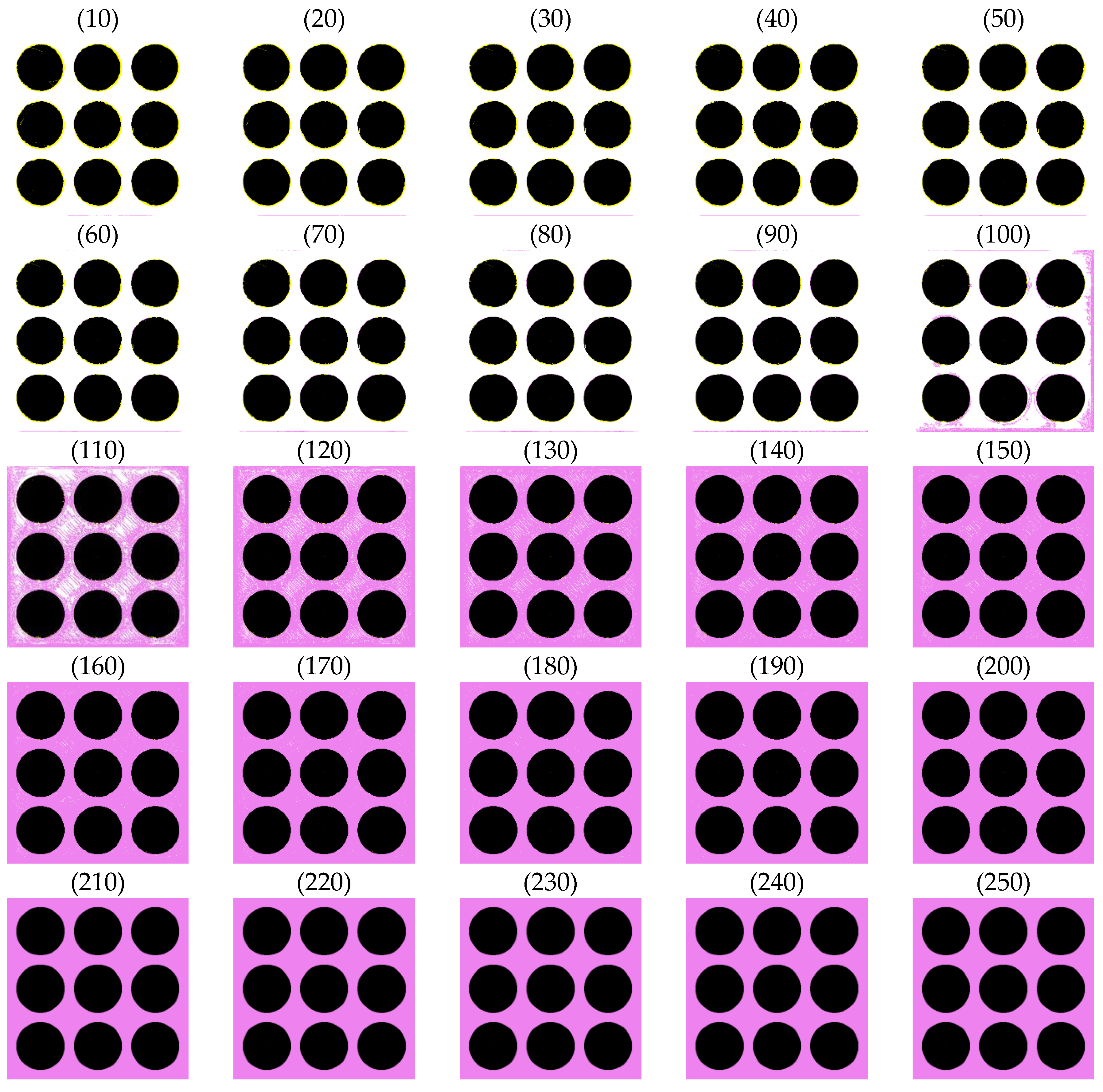
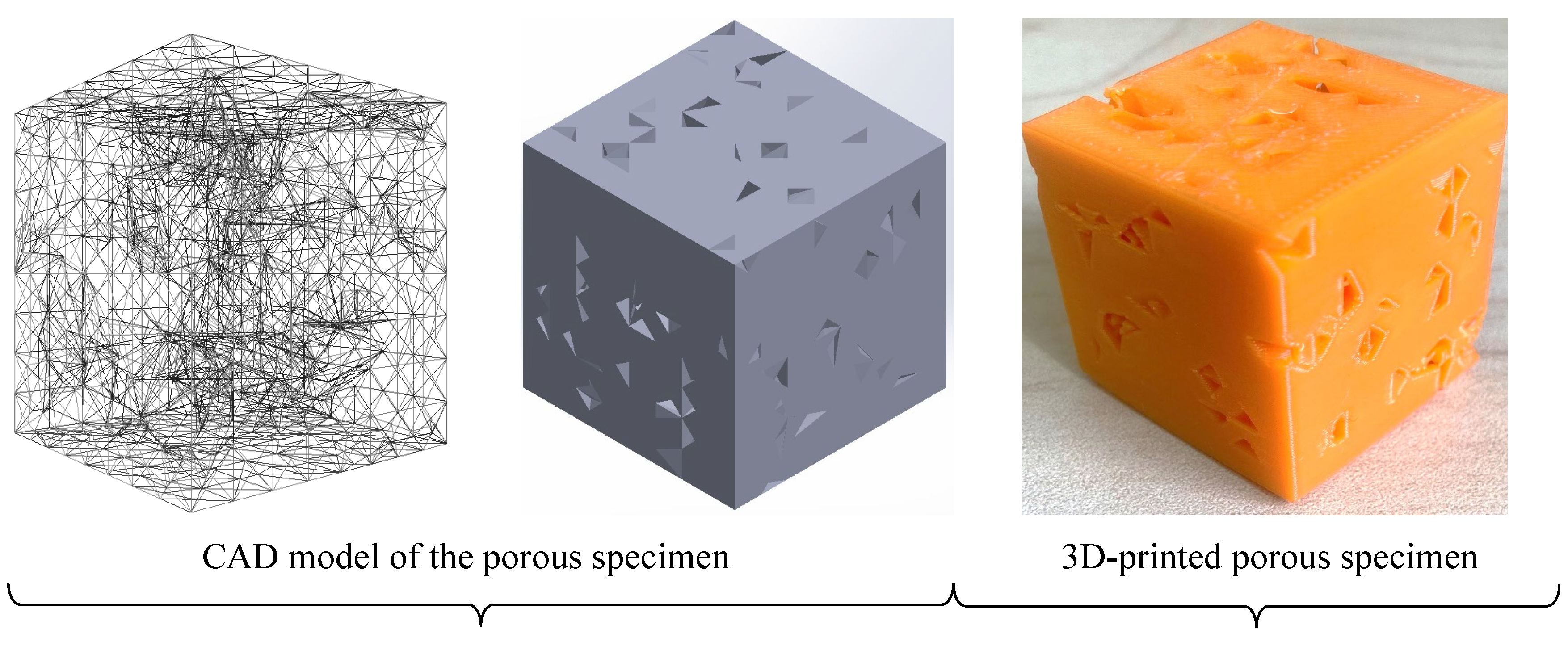
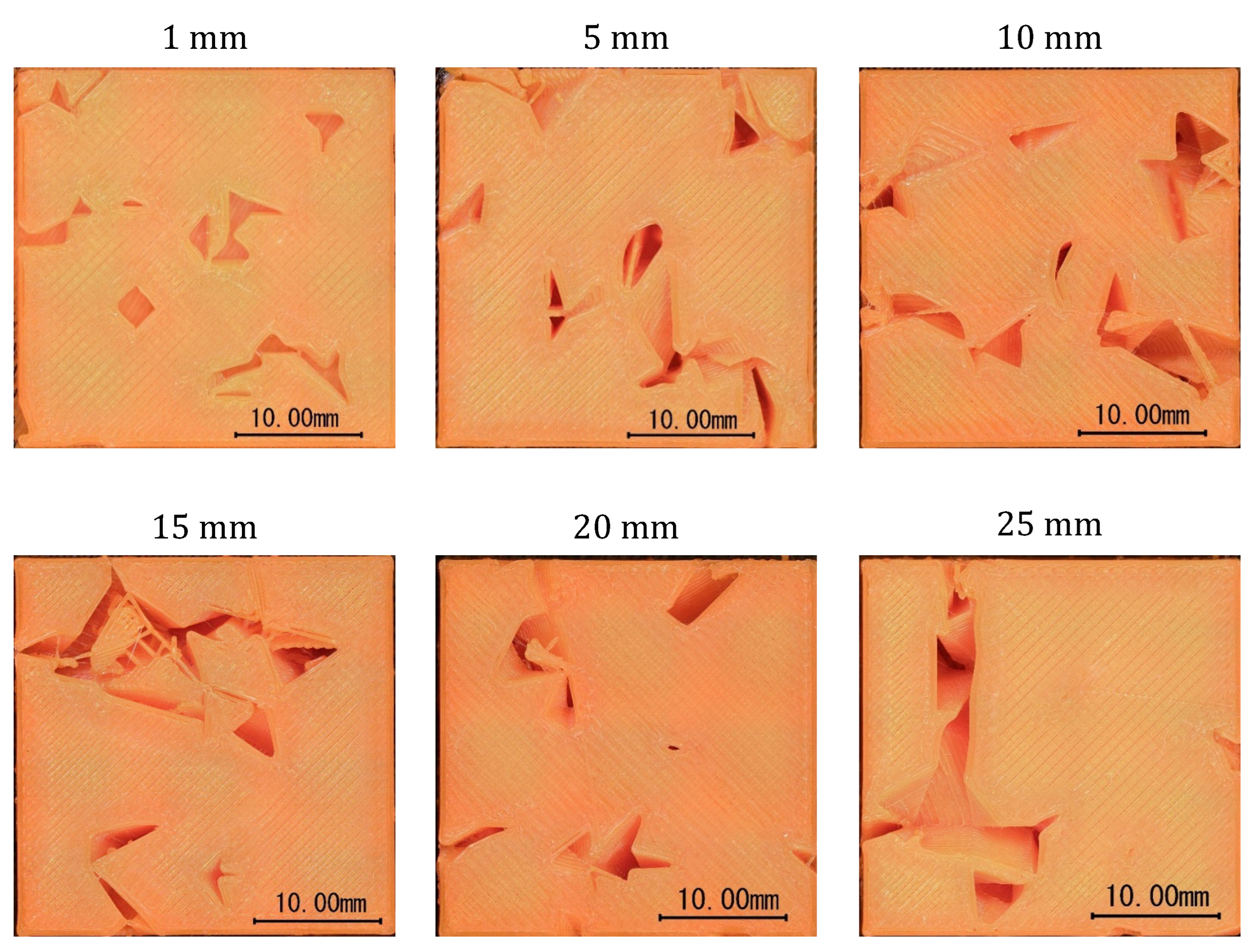
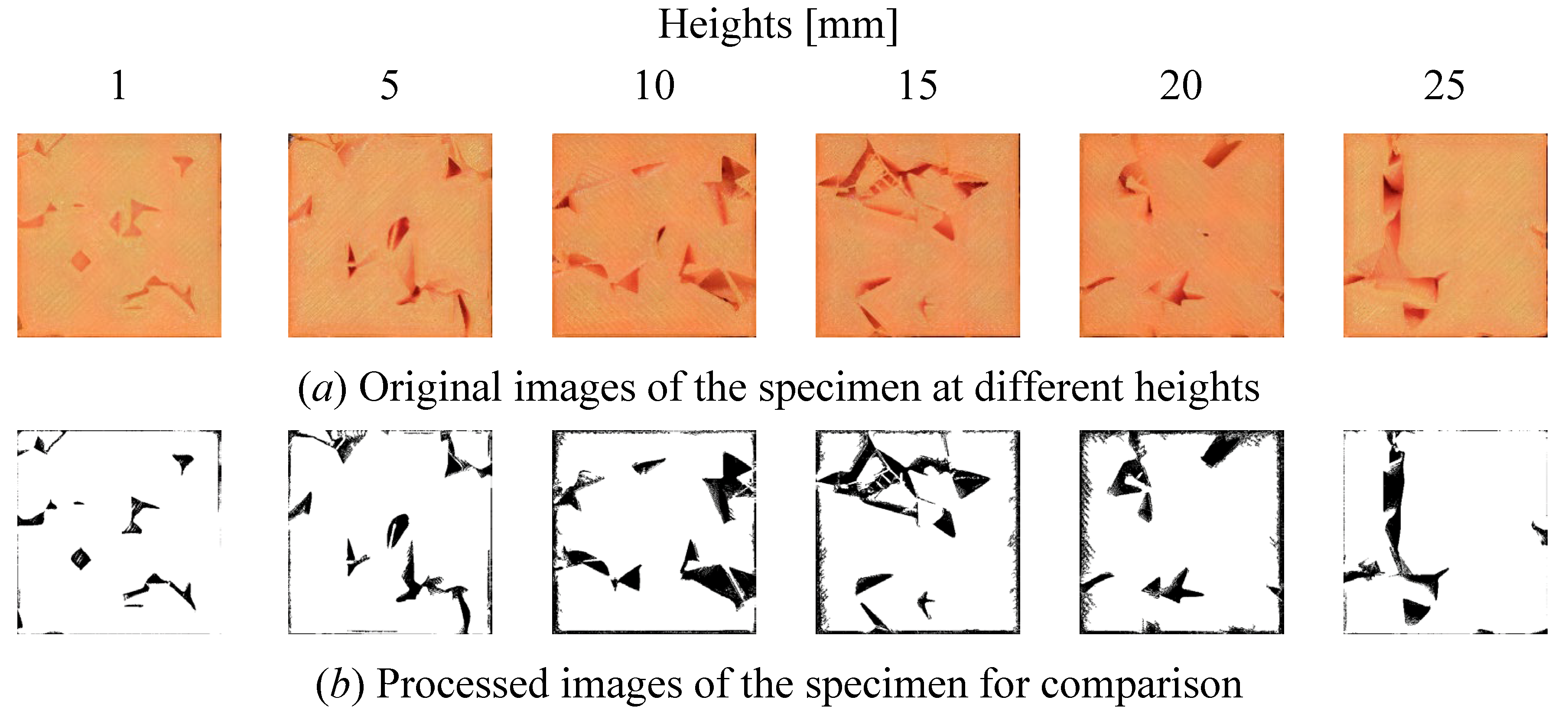

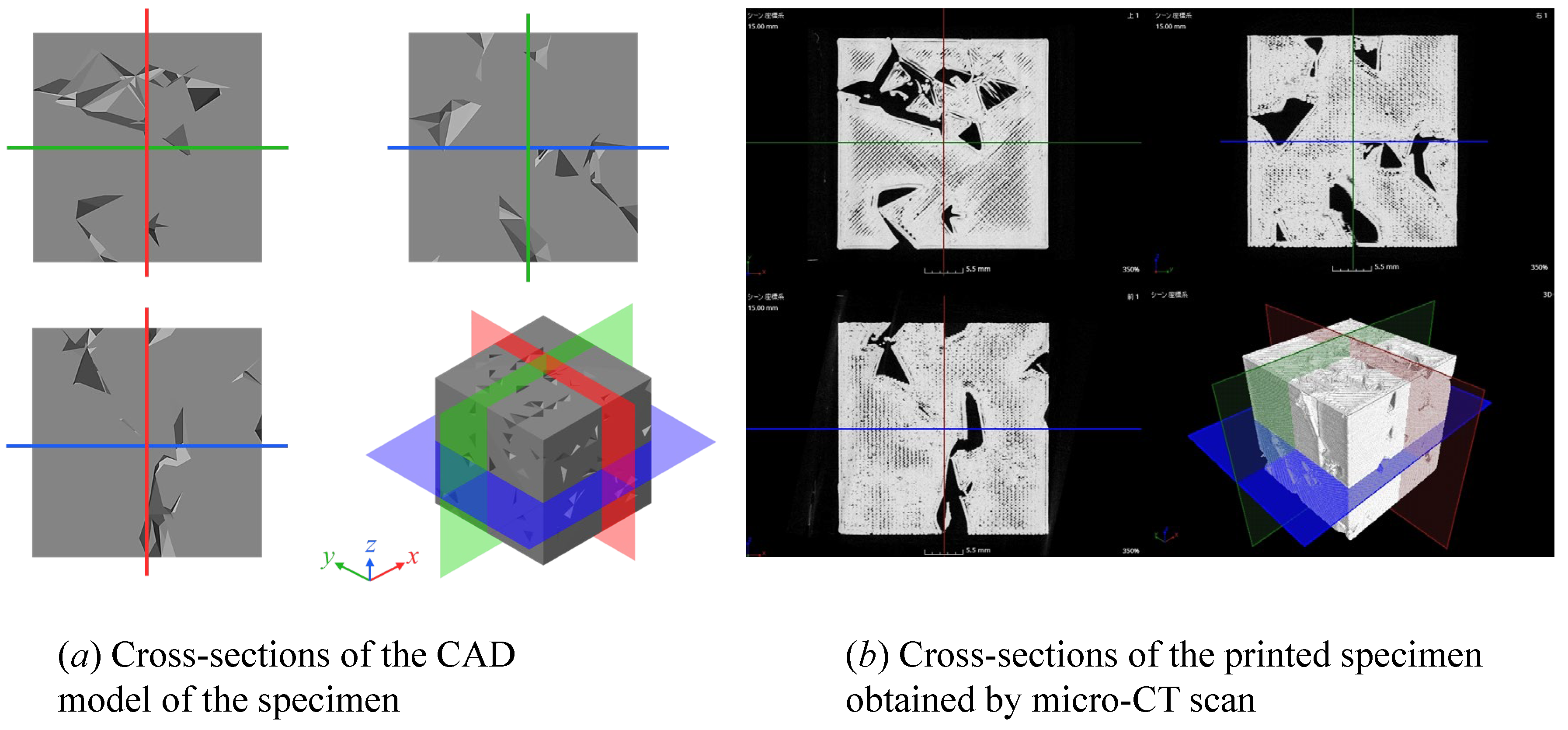

| Material | Thermoplastic filament made of Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA) |
| Printing technology | Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) |
| Extrusion width [mm] | 0.4 |
| Extruder temperature [℃] | 205 |
| Printing speed [mm/s] | 50.0 |
| Infill speed [mm/s] | 80.0 |
| Layer height [mm] | 0.25 |
| Infill density [%] | 15 |
| Infill pattern | Grid |
| Infill angles [°] | 45, 135 |
| Printer | Raise3D Pro2™ |
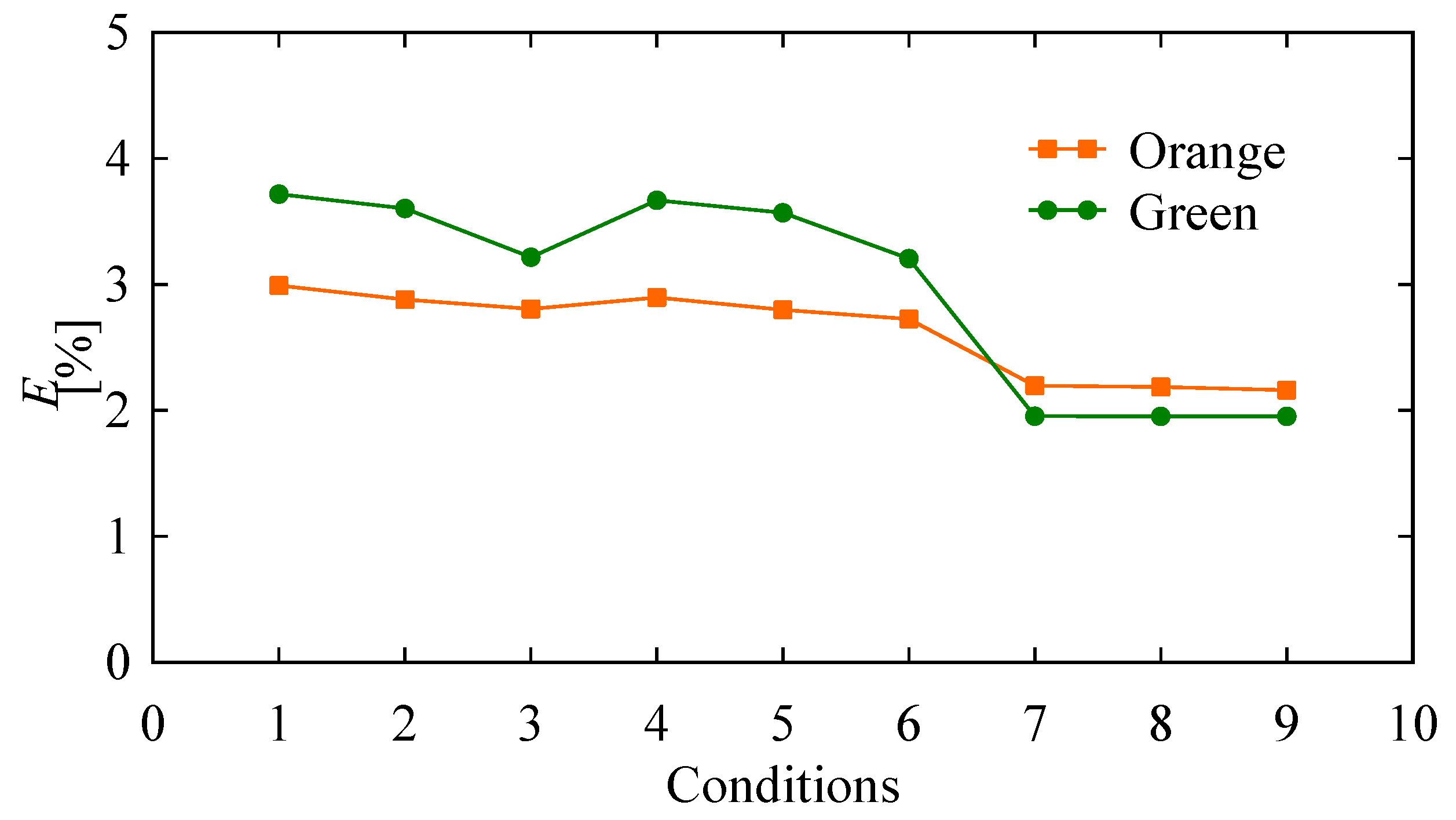
| Conditions | θmin | θmax | pc | wc | Thresholds |
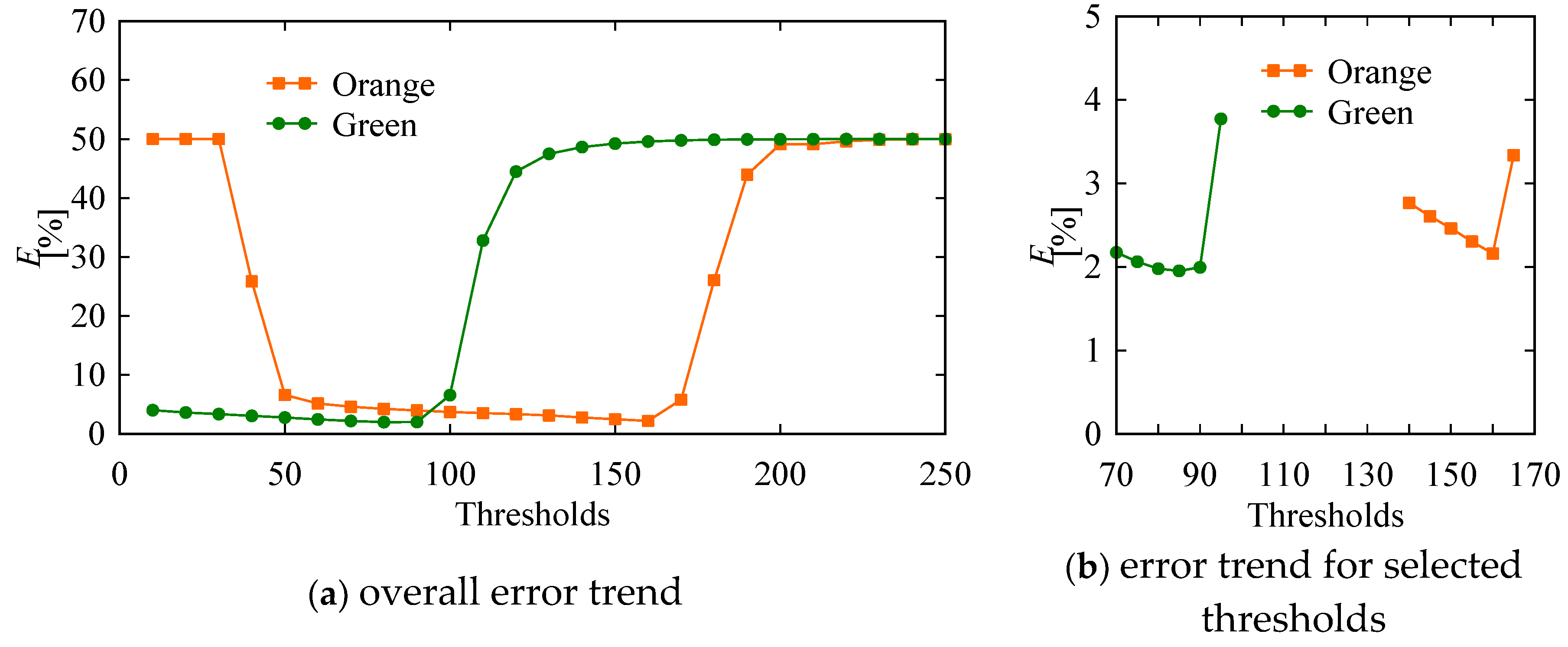
| C1 | 0 | 45 | 100 | 50 | For the orange object 160 For the green object 85 |
| C2 | 200 | 100 | |||
| C3 | 500 | 250 | |||
| C4 | 90 | 100 | 50 | ||
| C5 | 200 | 100 | |||
| C6 | 500 | 250 | |||
| C7 | 180 | 100 | 50 | ||
| C8 | 200 | 100 | |||
| C9 | 500 | 250 |
| Height [mm] | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| E [%] | 3.85 | 9.29 | 10.89 | 10.50 | 10.74 | 6.90 |
| Height [mm] | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| E [%] | 2.86 | 3.55 | 4.06 | 3.55 | 2.18 | 3.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





