Submitted:
04 April 2024
Posted:
05 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
History of Obesogens and the Environmental Obesogens Hypothesis
Sources of Obesogens
| EDCs | Source | Route of Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol A (BPA) | Use in the manufacturing of various plastics such as food packaging, water bottles, water supply pipes, children’s toys, and electronic appliances [17]. | Inhalation, ingestion, or dermal contact [17]. |
| Phthalates | Belongs to the group of plasticizers used to make plastics more flexible and durable. Found in plastic packaging, children’s toys, personal care products, vinyl flooring materials, clothing, and medical devices [18]. | Inhalation, ingestion, or dermal contact [18]. |
| Dioxins | Unwanted by-products of industrial or (production of herbicides, smelting or bleaching of paper) natural processes (forest fires and volcanic eruptions) [19]. | Highest level of exposure is through food, especially dairy and meat products, shellfish and fish. They are mainly stored in the fat tissue of animals, thus accumulate in the food chain [19]. |
| Tributyltin (TBT) | Biocide used to control a broad spectrum of organisms and used in marine paints, wood preservation and industrial water systems [12]. | Most common contaminant of marine and freshwater ecosystems. Humans exposed through inhalation or consumption of contaminated seafood or water [20]. |
| Atrazine (ATZ) | One of the most widely used herbicides in the world, used to control grasses and broadleaf weeds in corn, sugarcane, and sorghum crops [21]. | Eating or drinking contaminated products, through inhalation or dermal contact [21]. |
| Perchlorate | Manufactured for use in fireworks, explosives, rocket fuel and road flares or naturally occurring in the environment in small amounts [22]. | Inhalation, ingestion, or dermal contact [22]. |
| Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) | Man-made chemicals resisting heat, water, oil, and grease. Therefore, they are widely used in fire-fighting foams, non-stick cooking pans, food packaging, textile coatings and household products [23]. | PFAS are known to persist in the environment longer than any other man-made chemicals as they break down very slowly. Humans are exposed by consuming PFAS contaminated food or water, through inhalation of contaminated air or by direct exposure with PFASs products [23]. |
| Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and Polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) | Chemicals used as flame retardants in wire insulation, electronic devices, upholstery, draperies, rugs, and furniture [24]. | Ingestion (particularly of food high in fat content), inhalation or dermal contact [24]. |
| Triclosan | Used as antibacterial in products such as soaps, toothpaste, body washes and cosmetics [25]. | Ingestion and dermal absorption [25]. |
| Parabens | Chemicals used as preservatives in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals [26]. | Ingestion and dermal absorption [26]. |
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) | Occur naturally in most fossil fuels (coal, gasoline, and crude oil) and are also by-products of incomplete combustion processes [27]. | Inhalation of contaminated air (motor vehicle exhaust, cigarette smoke etc), ingestion (grilled or charred meats or contaminated food) and in some cases dermal absorption [27]. |
Pathophysiology
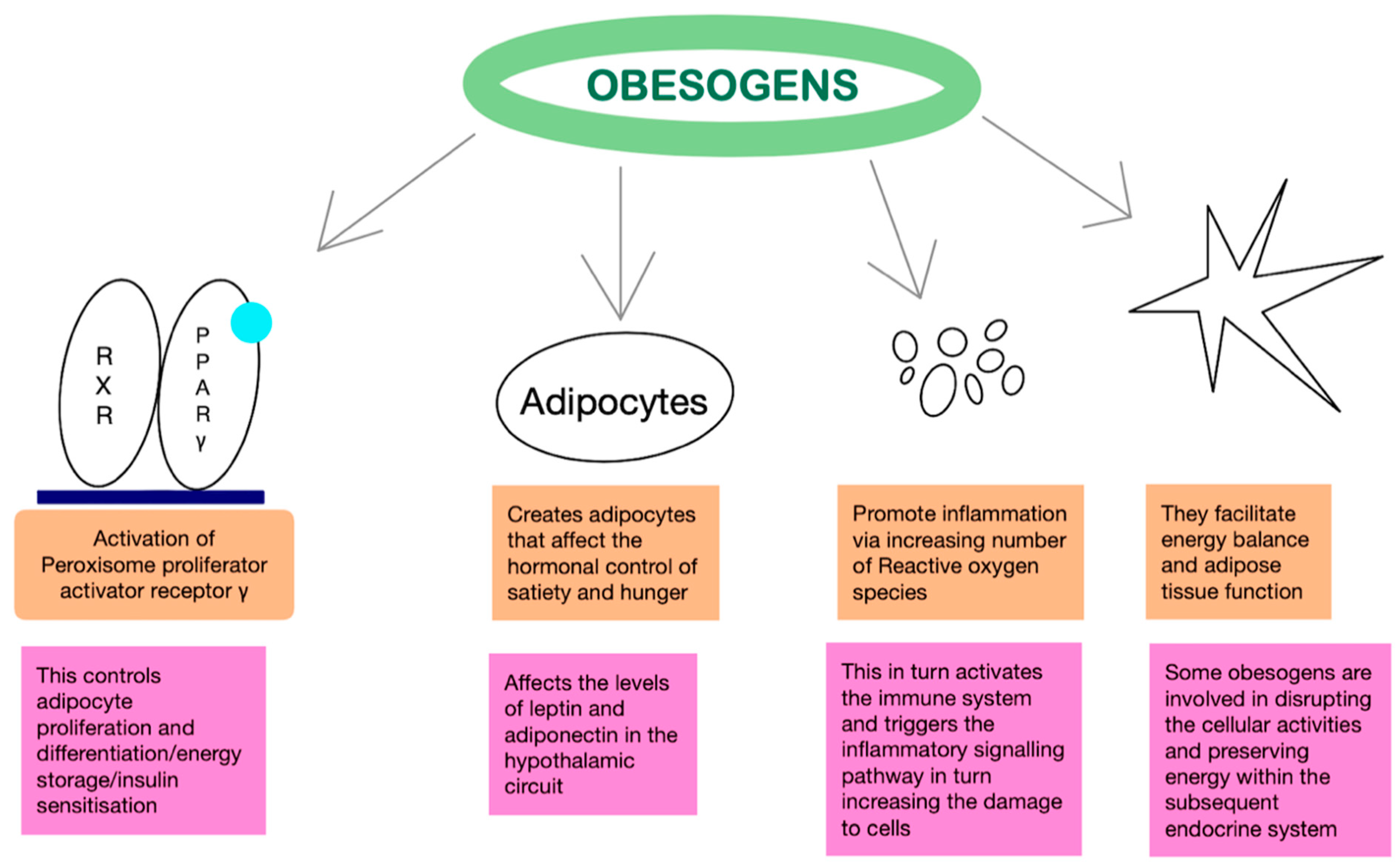
Mechanism of Action
Pre and Postnatal Effects
Epigenetics
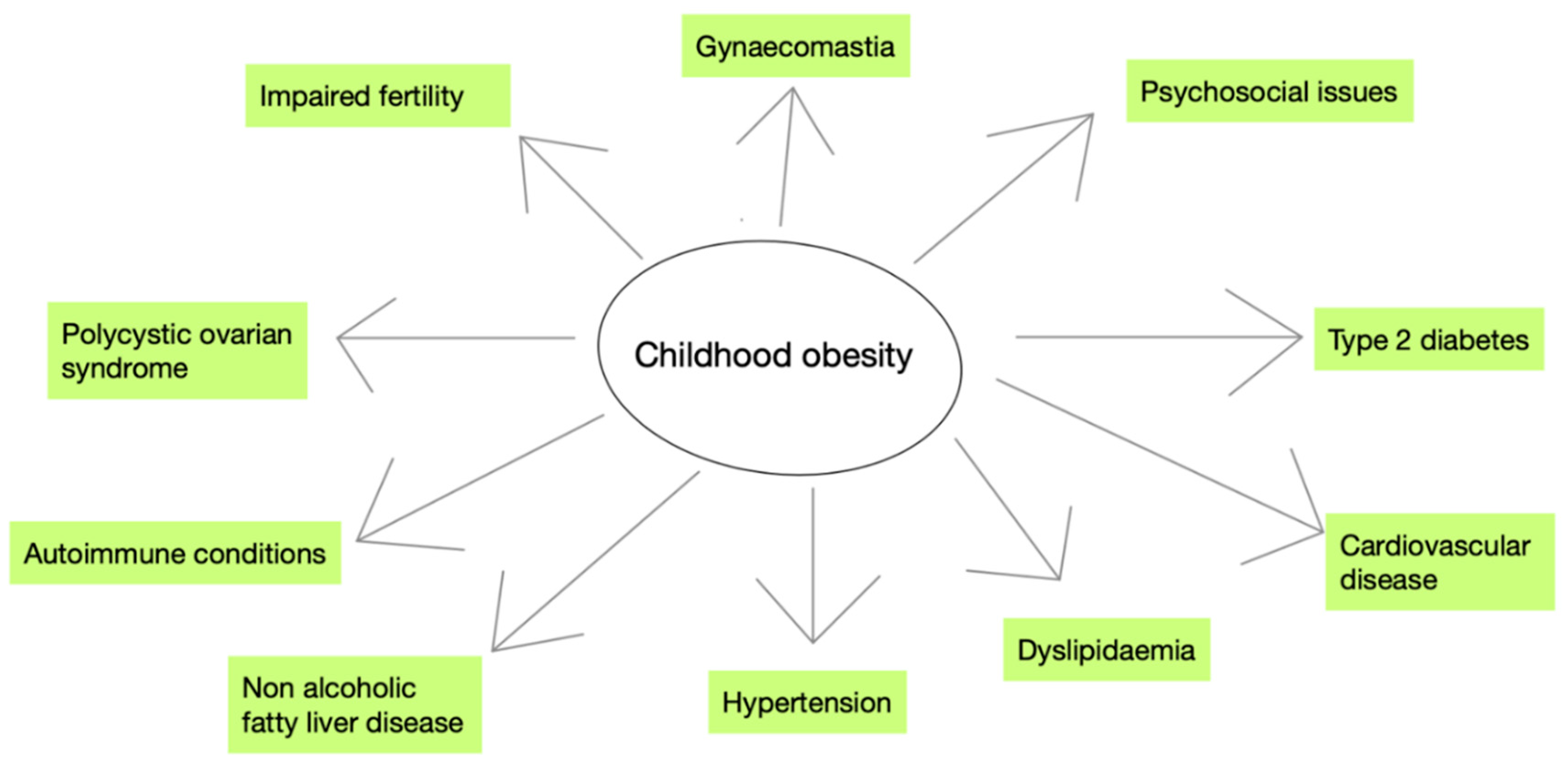
Long-Term Effects of Childhood Obesity
Prevention Strategies
Individual Actions
Healthcare Providers’ Actions
Community Actions
Discussion
Conclusions
Future Directions
References
- Jebeile H, Kelly AS, O’Malley G, Baur LA. Obesity in children and adolescents: Epidemiology, causes, assessment, and Management. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2022 May;10(5):351–65. [CrossRef]
- Defining child BMI categories [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2023 [cited 2023 Dec 13]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/childhood-defining.html.
- Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Acosta-Cazares B, Acuin C, et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. The Lancet. 2017 Dec;390(10113):2627–42. [CrossRef]
- Global atlas on childhood obesity [Internet]. [cited 2023 Dec 14]. Available from: https://www.worldobesity.org/membersarea/global-atlas-on-childhood-obesity.
- Pulgarón, ER. Childhood obesity: A review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clinical Therapeutics. 2013 Jan;35(1). [CrossRef]
- Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, Justice AE, Pers TH, Day FR, et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for Obesity Biology. Nature. 2015 Feb 11;518(7538):197–206. [CrossRef]
- Obesity and overweight [Internet]. World Health Organization; [cited 2023 Dec 16]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
- Endocrine Society. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (edcs) [Internet]. Endocrine Society; 2022 [cited 2023 Dec 16]. Available from: https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/endocrine-library/edcs.
- Grün F, Blumberg B. Environmental obesogens: Organotins and endocrine disruption via nuclear receptor signaling. Endocrinology. 2006 Jun 1;147(6). [CrossRef]
- Baillie-Hamilton, PF. Chemical toxins: A hypothesis to explain the global obesity epidemic. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2002 Apr;8(2):185–92. [CrossRef]
- Grün F, Blumberg B. Endocrine disrupters as obesogens. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 2009 May 25;304(1–2):19–29. [CrossRef]
- PubChem [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2004-. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 3032732, Tributyltin; [cited 2023 Dec. 16]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tributyltin.
- PAR-11-171: Role of Environmental Chemical Exposures in the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome (R21) [Internet]. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; [cited 2023 Dec 20]. Available from: https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-11-171.html.
- Endocrine Society. Common edcs and where they are found [Internet]. Endocrine Society; 2019 [cited 2023 Dec 20]. Available from: https://www.endocrine.org/topics/edc/what-edcs-are/common-edcs.html.
- Micic, D. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and obesity: The evolving story of obesogens. Acta Endocrinologica (Bucharest). 2021;17(4):503–8. [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro G, Forcucci F, Chiarelli F. Endocrine disruptor chemicals and children’s health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023 Jan 31;24(3):2671. [CrossRef]
- Bisphenol A (BPA) [Internet]. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; [cited 2023 Dec 20]. Available from: https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/sya-bpa.
- Phthalates factsheet [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2021 [cited 2023 Dec 21]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/biomonitoring/Phthalates_FactSheet.html.
- Dioxins [Internet]. World Health Organization; [cited 2023 Dec 22]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dioxins-and-their-effects-on-human-health.
- Bandara KRV, Chinthaka SDM, Yasawardene SG, Manage PM. Modified, optimized method of determination of tributyltin (TBT) contamination in coastal water, sediment and biota in Sri Lanka. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2021 May;166:112202. [CrossRef]
- Atrazine [Internet]. Environmental Protection Agency; [cited 2023 Dec 23]. Available from: https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/atrazine.
- Niziński P, Błażewicz A, Kończyk J, Michalski R. Perchlorate – properties, toxicity and human health effects: An updated review. Reviews on Environmental Health. 2020 Sept 4;36(2):199–222. [CrossRef]
- Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) [Internet]. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; [cited 2023 Dec 23]. Available from: https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/pfc.
- Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (pbdes) and polybrominated biphenyls (pbbs) factsheet [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2017 [cited 2024 Jan 3]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/biomonitoring/PBDEs_FactSheet.html.
- Commissioner O of the. 5 things to know about triclosan [Internet]. FDA; 2019 [cited 2024 Jan 3]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/5-things-know-about-triclosan.
- Parabens factsheet [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2023 [cited 2024 Jan 3]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/biomonitoring/Parabens_FactSheet.html.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (pahs): Where are pahs found? [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2023 [cited 2024 Jan 3]. Available from: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/csem/polycyclicaromatic-hydrocarbons/where_are_pahs_found.html.
- Griffin MD, Pereira SR, DeBari MK, Abbott RD. Mechanisms of action, chemical characteristics, and model systems of obesogens. BMC Biomedical Engineering. 2020 Apr 30;2(1). [CrossRef]
- Tyagi S, Sharma S, Gupta P, Saini A, Kaushal C. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor: A family of nuclear receptors role in various diseases. Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research. 2011;2(4):236. [CrossRef]
- Soccio RE, Chen ER, Lazar MA. Thiazolidinediones and the promise of insulin sensitization in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metabolism. 2014 Oct;20(4):573–91. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994 Dec;372(6505):425–32. [CrossRef]
- Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF. A novel serum protein similar to C1Q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995 Nov;270(45):26746–9. [CrossRef]
- Yan H, Guo H, Cheng D, Kou R, Zhang C, Si J. Tributyltin reduces the levels of serum adiponectin and activity of Akt and induces metabolic syndrome in male mice. Environmental Toxicology. 2018 Apr 20;33(7):752–8. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt J-S, Schaedlich K, Fiandanese N, Pocar P, Fischer B. Effects of di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) on female fertility and adipogenesis in C3H/N mice. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2012 Aug;120(8):1123–9. [CrossRef]
- MacKay H, Patterson ZR, Abizaid A. Perinatal exposure to low-dose bisphenol-a disrupts the structural and functional development of the hypothalamic feeding circuitry. Endocrinology. 2017 Feb 7;158(4):768–77. [CrossRef]
- Shahnazaryan U, Wójcik M, Bednarczuk T, Kuryłowicz A. Role of obesogens in the pathogenesis of obesity. Medicina. 2019 Aug 21;55(9):515. [CrossRef]
- Bateman ME, Strong AL, McLachlan JA, Burow ME, Bunnell BA. The effects of endocrine disruptors on adipogenesis and osteogenesis in Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2017 Jan 9;7. [CrossRef]
- Ricote M, Li AC, Willson TM, Kelly CJ, Glass CK. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature. 1998 Jan;391(6662):79–82. [CrossRef]
- Heindel JJ, Blumberg B, Cave M, Machtinger R, Mantovani A, Mendez MA, et al. Metabolism disrupting chemicals and metabolic disorders. Reproductive Toxicology. 2017 Mar;68:3–33. [CrossRef]
- Griffin MD, Pereira SR, DeBari MK, Abbott RD. Mechanisms of action, chemical characteristics, and model systems of obesogens. BMC Biomedical Engineering. 2020 Apr 30;2(1). [CrossRef]
- Knudsen N, Laurberg P, Rasmussen LB, Bülow I, Perrild H, Ovesen L, et al. Small differences in thyroid function may be important for body mass index and the occurrence of obesity in the population. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2005 Jul;90(7):4019–24. [CrossRef]
- Heindel JJ, Blumberg B. Environmental obesogens: Mechanisms and controversies. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2019 Jan 6;59(1):89–106. [CrossRef]
- Barker DJ, Gluckman PD, Godfrey KM, Harding JE, Owens JA, Robinson JS. Fetal nutrition and cardiovascular disease in adult life. Lancet. 1993 Apr 10;341(8850):938-41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritzen HB, Larose TL, Øien T, Sandanger TM, Odland J, van de Bor M, et al. Prenatal exposure to persistent organic pollutants and child overweight/obesity at 5-year follow-up: A prospective cohort study. Environmental Health. 2018 Jan 18;17(1). [CrossRef]
- Egusquiza, Riann & Blumberg, Bruce. (2020). Environmental Obesogens and Their Impact on Susceptibility to Obesity: New Mechanisms and Chemicals. Endocrinology. 161. 10.1210/endocr/bqaa024.
- Valvi D, Casas M, Mendez MA, Ballesteros-Gómez A, Luque N, Rubio S, et al. Prenatal bisphenol A urine concentrations and early rapid growth and overweight risk in The offspring. Epidemiology. 2013 Nov;24(6):791–9. [CrossRef]
- Cano-Sancho G, Salmon AG, La Merrill MA. Association between exposure to p,p′-DDT and its metabolite p,p′-DDE with obesity: Integrated systematic review and meta-analysis. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2017 Sept 22;125(9). [CrossRef]
- Dupont C, Armant D, Brenner C. Epigenetics: Definition, mechanisms, and clinical perspective. Seminars in Reproductive Medicine. 2009 Aug 26;27(05):351–7. [CrossRef]
- Gore AC, Chappell VA, Fenton SE, Flaws JA, Nadal A, Prins GS, et al. EDC-2: The endocrine society’s second scientific statement on endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Endocrine Reviews. 2015 Dec 1;36(6). [CrossRef]
- Egusquiza RJ, Blumberg B. Environmental obesogens and their impact on susceptibility to obesity: New mechanisms and chemicals. Endocrinology. 2020 Feb 18;161(3). [CrossRef]
- Robinson N, Brown H, Antoun E, Godfrey KM, Hanson MA, Lillycrop KA, et al. Childhood DNA methylation as a marker of early life rapid weight gain and subsequent overweight. Clinical Epigenetics. 2021 Jan 12;13(1). [CrossRef]
- Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2000 Mar 1;23(3):381–9. [CrossRef]
- Simmonds M, Llewellyn A, Owen CG, Woolacott N. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews. 2015 Dec 23;17(2):95–107. [CrossRef]
- Anderson EL, Howe LD, Jones HE, Higgins JP, Lawlor DA, Fraser A. The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE. 2015 Oct 29;10(10). [CrossRef]
- Marcus C, Danielsson P, Hagman E. Pediatric obesity—long-term consequences and effect of weight loss. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2022 Aug 5;292(6):870–91. [CrossRef]
- Neumark-Sztainer D, Falkner N, Story M, Perry C, Hannan P, Mulert S. Weight-teasing among adolescents: Correlations with weight status and disordered eating behaviors. International Journal of Obesity. 2002 Jan;26(1):123–31. [CrossRef]
- Karnehed N, Rasmussen F, Hemmingsson T, Tynelius P. Obesity and attained education: Cohort Study of more than 700,000 Swedish men. Obesity. 2006 Aug;14(8):1421–8. [CrossRef]
- Health service delivery framework for prevention and management of obesity. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023.
- Lobstein T, Brownell KD. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and obesity risk: A review of recommendations for obesity prevention policies. Obesity Reviews. 2021; 22(11):e13332. [CrossRef]
- Braun, JM. Early-life exposure to EDCs: role in childhood obesity and neurodevelopment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(3):161-173. [CrossRef]
- FDA Removes Harmful Chemicals From Food Packaging - Medscape - February 29, 2024.
- Fernandez-Twinn DS, Hjort L, Novakovic B, Ozanne SE, Saffery R. Intrauterine programming of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2019;62(10):1789-1801. [CrossRef]
- Russ K, Howard S. Developmental exposure to environmental chemicals and metabolic changes in children. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2016;46(8):255-285. [CrossRef]
- Heindel JJ, Howard S, Agay-Shay K, Arrebola JP, Audouze K, Babin PJ, et al. Obesity II: Establishing causal links between chemical exposures and Obesity. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2022 May; 199:115015. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases in the WHO European Region 2016– 2025. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; 2016.
- Heindel JJ, Blumberg B. Environmental obesogens: Mechanisms and controversies. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2019 Jan 6;59(1):89–106. [CrossRef]
- Horizon 2020 [Internet]. European Commission; [cited 2024 Mar 28]. Available from: https://research-and-innovation.ec.europa.eu/funding/funding-opportunities/funding-programmes-and-open-calls/horizon-2020_en.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




