1. Introduction
In recent years, the rapid development of the metaverse, human-computer interaction, intelligent medical technology [
1], and other industries has propelled the advancement of flexible electronic device and actuators. As the foundation of flexible devices, various functional materials that are flexible and even stretchable are emerging rapidly, among which the dielectric elastomers are widely investigated due to their essential role in constructing flexible sensors, circuit [
2], transistors [
3], and artificial muscle. For example, thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) is considered a crucial component of the flexible capacitor [
4], which plays a vital role in pressure sensing [
5] and displacement measurement. Additionally, capacitors enable diverse functions such as tuning, by-passing, coupling, and filtering when employed within logic circuits [
6]. Moreover, the artificial muscle that made of dielectric elastomers could deform when an electric field is applied, which could be used for prosthetics [
7], surgical robots, and wearable devices [
5], as well as soft robots [
8] capable of locomotion and manipulation in natural environments or inside human body.
In the above scenario, dielectric elastomers typically need to operate while in deformation. Characterizing the dielectric properties during the strain process is not only beneficial for providing important reference for improving the tensile stability of flexible capacitors [
9], but also helps to improve the accuracy of modeling electrical parameters such as energy density, power density [
10,
11] for actuators under strain conditions. Due to the significant impact of different dielectric constants under strain on the electromechanical coupling of devices, studying the regulation of dielectric constants of dielectric elastomers under stress is crucial.
Previous studies have shown that the dielectric constant can indeed be affected by external strain [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. For example, Vu-Cong et al. [
19] and Wissler et al. [
20] experimentally found that the dielectric constant of VHB4910 decreased at stretching deformation. However, traditional approach of determining the dielectric constant upon stretching is ex situ and clumsy. In these approaches, the samples with predetermined area were stretched by clamping them in a frame, following which the electrodes were prepared and the capacitance was measured to determine the dielectric constant [
21,
22,
23]. Based on the above methods, the sample thickness measurement is not accurate, and the tensile strain is difficult to measure accurately [
18]. Therefore, it is highly demanded to construct an experimental setup that enables in situ and accurate determination of the dielectric constant upon stretching. In the theoretical aspects, many models have been constructed to predict the dielectric constant of elastomers under strain[
24,
25,
26], where the polarization degree [
27] and orientation distribution of dipoles [
28] in elastic materials were considered to process as factors. However, the experimental evidence of in-situ characterizing the structure evolution of an elastomer upon strain is still lacking. Herein, we proposed and designed a device capable of in situ measuring the permittivity of TPU under different strain states. We quantitatively determined its dielectric constant at different strain up to 400%. Moreover, by employing micro-polarization theory along with techniques such as wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS), small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FITR) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) analysis, a link between the evolution of dielectric constant and the microstructures under external strain was manifested. As TPU is mainly composed of soft segments (polyester, polyether polyol) and hard segments (diisocyanate) [
29], which are formed by chain extender polycondensation reaction. The results indicate that the average size of polarized hard domains decreases, and the molecular chains tends to align parallelly with the tensile stress. As the polarity of TPU is predominantly provided by the hard segment phase [
30,
31,
32], the electric diploes become harder to polarized upon stretching, which results in the decrease of dielectric constant in TPU.
Materials and Methods
2.1. Dielectric Elastomers
The TPU used in the experiments is commercially available from Jiaxin Plastic Material Company, with an average thickness of 0.08 mm.
2.2. Experimental Setup
The device for measuring the dielectric constant of elastomers under strain is mainly based on the principle of parallel plate capacitor proposed by Hermann von Helmholtz. The essence of this principle is to calculate the dielectric constant value of the material by measuring the capacitance and shape of the material:
εr = Cd/(ε0 S)
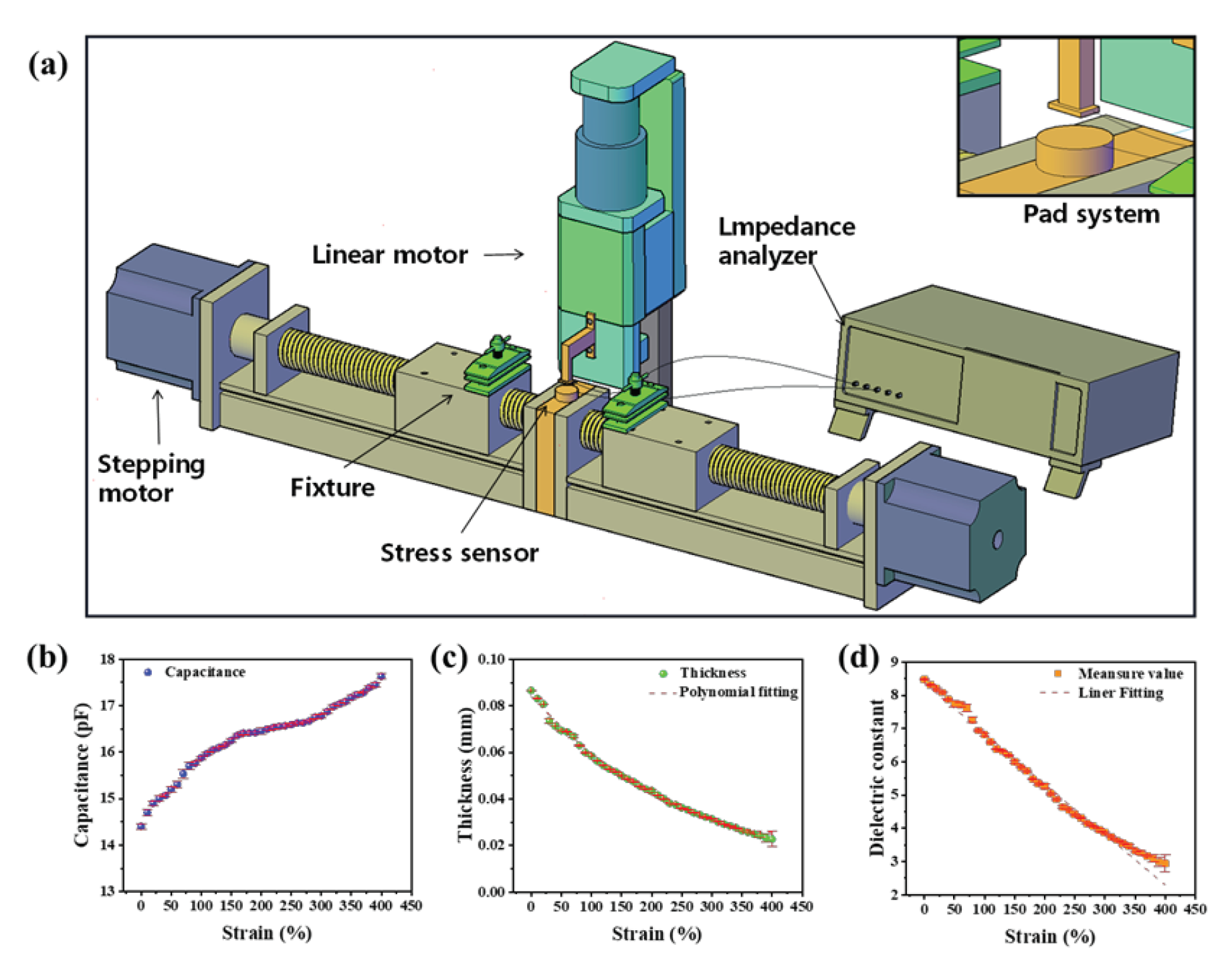
Where C is the capacitance, ε0 is the vacuum dielectric constant, εr is the relative dielectric constant, S is the area opposite the electrode plate, and d is the thickness of the dielectric layer. As is shown in Figure1 (a), the device has three main components: the mechanical stretching system, the thickness measurement system, and the capacitance measurement system. The mechanical stretching system consists of two stepper motors placed on the same axis with the same speed but opposite direction of motion. Each stepper motor is equipped with a DC programmable intelligent servo driver, and the two motors are controlled by a controller to achieve synchronous movement. The dielectric elastomer is fixed on each end of the stepper motor by a clap, and a transverse stretching is applied onto the sample in a controllable manner. The total effective tensile length of the system is 424 mm, and the tensile accuracy is 4±0.5 mm. To reduce the residual stress in the sample as much as possible, the samples are slowly stretched at a speed of 0.1 mm/s. In contrast to previous methods for measuring dielectric constants, our setup enables the measurement of elastomer dielectric constants under arbitrary tensile strains.
Accurate thickness measurement is another crucial issue in determining the dielectric constant. In order to accurately measure the thickness of an elastomer, the force is usually applied on the elastomer surface. In light of this situation, we integrated the pressure and displacement sensors into the upper and lower electrode plates, so as to measure the changes of elastomer thickness more accurately. The thickness measurement system consists of a pressure sensor, voice coil displacement sensor, control software program, and an L-shaped cantilever beam. The pressure sensor has a comprehensive accuracy of 0.5 F.S. and a repeatability error of less than 0.2% in the force range of up to 10 N. The voice coil displacement sensor has an accuracy of 0.001 mm with a selected motion rate of 0.1 mm/s. The working process involves initially zeroing the distance between the upper and lower plates. As the upper plate moves downward and gradually increases contact force up to a pre-set value of 0.1 N, it immediately stops moving. At this point, the voice coil displacement sensor allows us to estimate the change of sample thickness upon stretching.
In addition, the measurement of capacitance is also important for the measurement of permittivity, and the shape and material of the electrode plate directly affect the measurement of capacitance. As a result of the fact that flexible electrodes shall deform upon stretching, rigid electrodes were utilized. In addition, the upper electrode was composed of a rectangular brass copper of 14 mm×2.8 mm×1 mm, and the lower plate was composed of a circular brass sheet with a diameter of 20 mm attached on the surface of the pressure sensor. In this way, the area of the electrode is determined by the upper electrode plate. The capacitance value was recorded by using a Hioki IM3570 impedance analyzer. The photograph of the setup is shown in Fig. S1 (Supporting Information). Generally, the measured capacitance usually contains contributions from the sample and other factors such as air, stray capacitance, and conductors between the plates. In order to validate the reliability of the experimental setup, the setup was calibrated by using standard samples prior measurement, as is described in Note S1 (Supporting Information).
3. Results
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
3.1. Variation of the Dielectric Constant of TPU under Tensile Strain
After calibration, the device was used to measure the capacitance variation of TPU with strain and the thickness variation of TPU with strain, and the variation of relative permittivity with strain was calculated. Based on the experimental setup diagram
Figure 1(a), the relationship between TPU strain and capacitance was investigated
Figure 1(b). Under test conditions of temperature at 20 °C, frequency at 1 MHz, and voltage at 1 V, it was observed that the TPU capacitance gradually increased with increasing strain. When the strain was 0%, the initial capacitance obtained through calibration methods that exclude air and stray capacitance was 14.4 pF, with an error bar of 0.054. Meanwhile, the variation in TPU thickness during the stretching process was measured, as shown in
Figure 1(c). The initial thickness value was 0.0866 mm and gradually decreased to 0.0227 mm when the strain reached 400%. At a strain of 380%, the error bar of the thickness value suddenly increased, as the film thickness approached the limit of the sensor (0.001 mm). Therefore, a strain measurement range of 0% to 400% was chosen.
Finally, the variation of relative permittivity with strain was calculated using the parallel plate capacitor principle, as shown in
Figure 1(d). The results indicated that with increasing strain, the relative permittivity gradually decreased from 8.47 ± 0.01 (ε= 0%) to 2.94 ± 0.27 (ε= 400%). It was found that the relative permittivity of TPU decreased gradually with increasing strain. Linear fitting of the curve yielded a goodness of fit value of R
2 = 99.11%. The rate of thickness variation of the TPU film at different geometric positions was different, but the calibration process using standard samples demonstrated that when the electrode area was sufficiently small (S= 15.4 mm
2), the effect of air in the electrode gap could be compensated.
3.2. Orientation Behavior of TPU during Tensile Strain
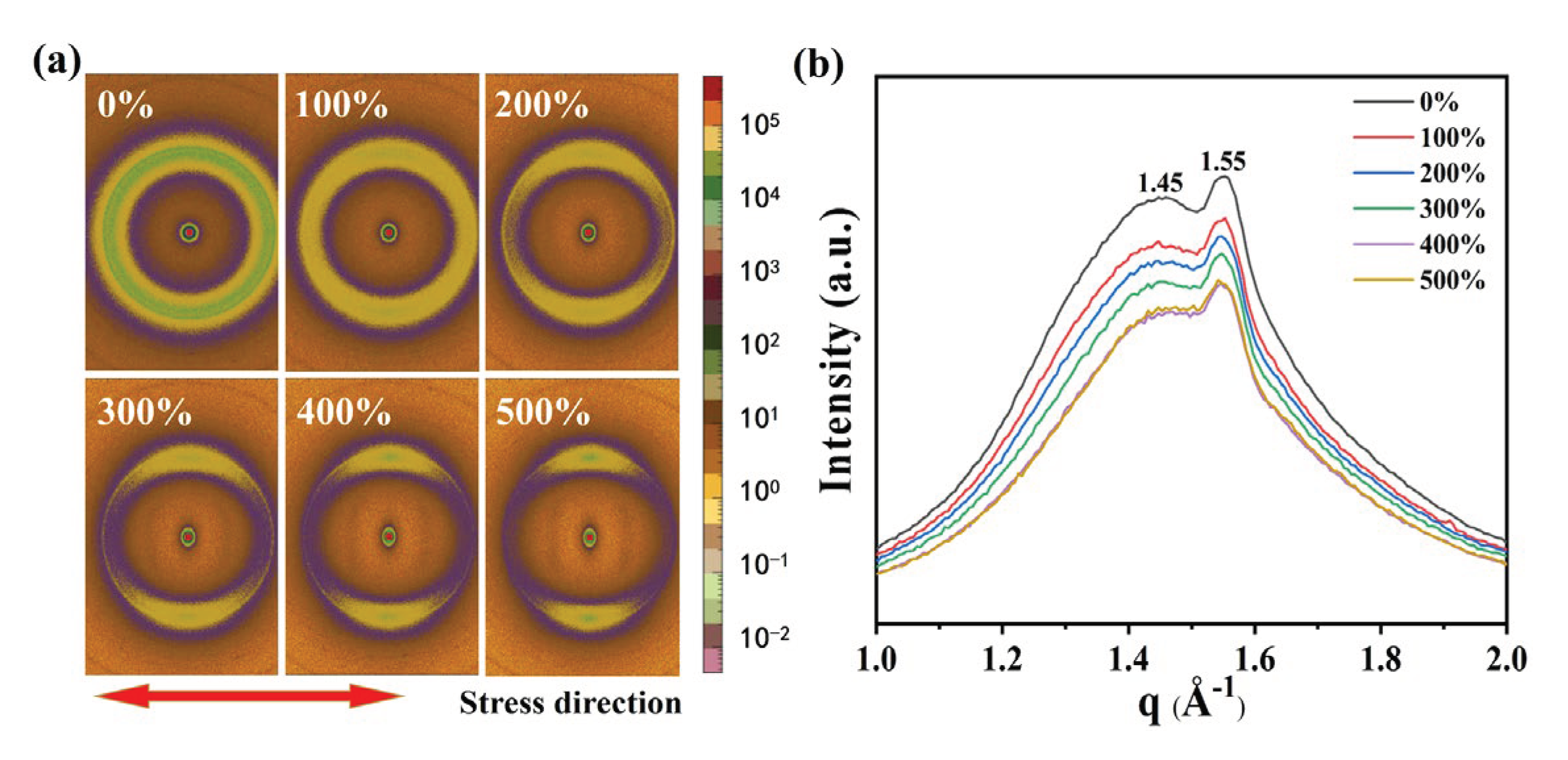
The dielectric constant is a macroscopic manifestation of the polarization ability of a material, and the polarization of the dielectric can take the form of orientation polarization, interface polarization, and composite polarization. These polarization behaviors are essentially caused by the difference in electronegativity between atoms at the ends of chemical bonds in the molecules. The polarization ability and dielectric constant can be influenced by the formation of crystallization or orientation in the molecular chains under certain conditions. The TPU molecule has a natural microphase separation structure due to the dispersed distribution of toluene diisocyanate (2,4TDI) and polyol groups with different polarities. To gain a deeper understanding of the orientation behavior of TPU during stretching, we used in-situ WAXS to test the microstructure of TPU in different stretching states. As shown in
Figure 2(a), when not stretched, the scattering ring of TPU is a concentric circular Debye ring, indicating an isotropic and disordered distribution of the molecular chains. As the strain reaches 100%, the scattering ring of TPU gradually becomes elliptical, indicating that there is orientation occurring between the molecular chains. According to the regions where scattering rings appear, it can be inferred that the molecular chains tend to orientate along the stretching direction. As the strain increases to 200%, diffuse spots appear in the scattering ring, and at 500%, more distinct diffraction spots concentrated in the direction perpendicular to the stretching direction can be observed, further indicating the occurrence of orientation behavior in the molecular chains of TPU after stretching.
Figure 2(b) displays the one-dimensional WAXS curve, which shows distribution of weak crystal scattering peaks under different stretching states. When the strain is 0%, two scattering peaks appear at q = 1.45 Å
-1 and q = 1.55 Å
-1, corresponding to interchain distances (d) of 4.310 Å and 4.043 Å, respectively. For the scattering peak at q = 1.45 Å
-1, when the strain increases, the interchain distance increases to 4.338Å at 100% strain, but it remains unchanged under further strain. Meanwhile, at q = 1.55 Å
-1, the scattering peak shows an increase in interchain distance to 4.072 Å at 500% strain. These results indicate that the molecular chains of TPU exhibit preferential orientation along the stretching direction after stretching, and the interchain distances corresponding to the two scattering peaks gradually increase, with an average increase of 0.031 Å.
3.3. Changes in Hydrogen Bonding under Tensile Strain
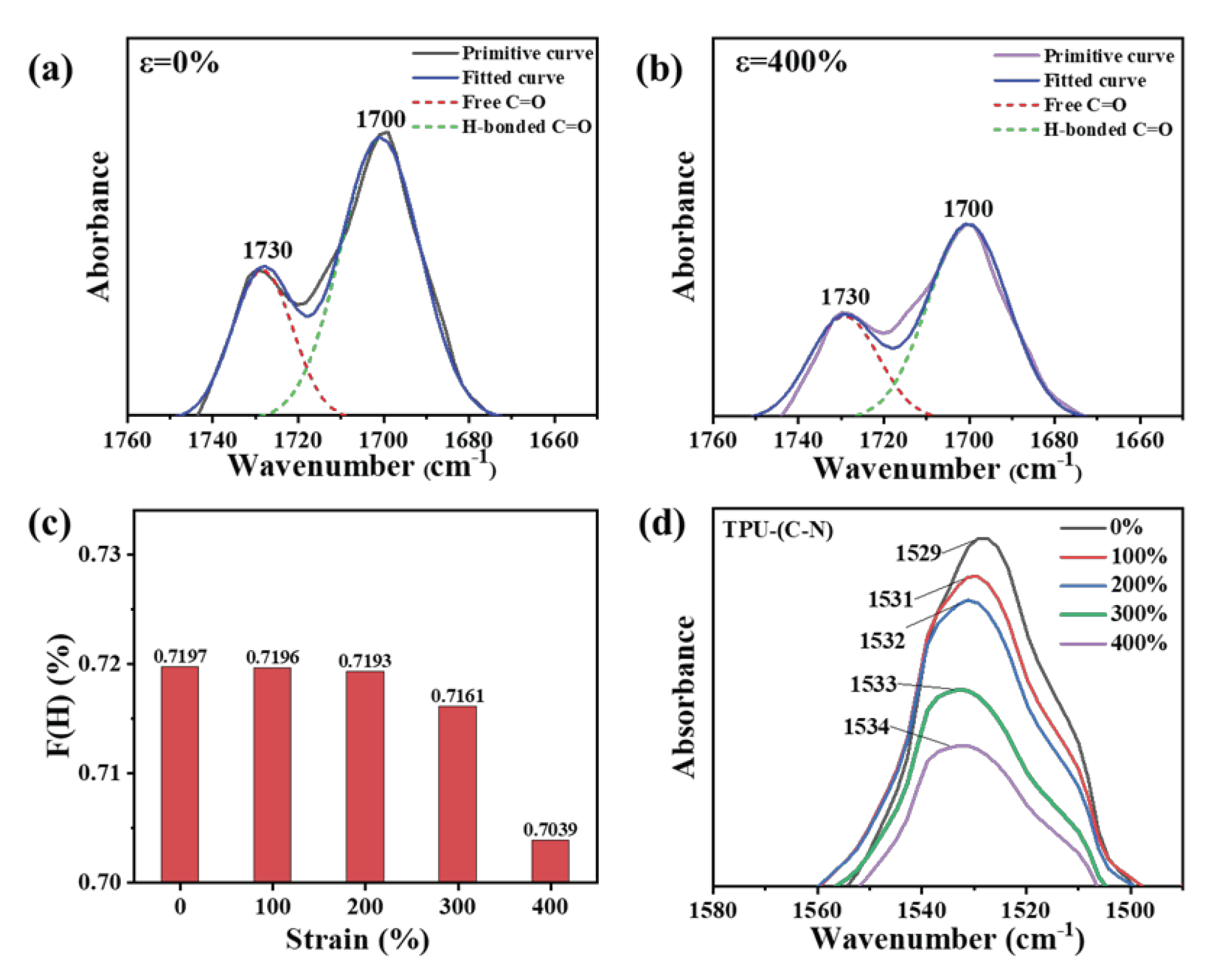
By observing changes in hydrogen bonds under strain, the variations in the structure of hard domains could be reflected. There are three types of hydrogen bonds in the molecular conformation of TPU. Firstly, the hydrogen bonds between the hard segments in the hard domain structure are typically reflected by the carbonyl peaks in the Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra, expressed as "H-bonded C=O". Secondly, the hydrogen bonds formed between the interactions of soft and hard domains are referred to as the hydrogen bonds between the hard and soft segments, which are usually reflected by the N-H peaks in the spectra, expressed as "H-bonded N-H". Thirdly, there are unconstrained free hydrogen bonds. Figure S4 (Supporting Information) shows the FTIR spectra of TPU under different states as the tensile strain increases from 0% to 400%. At ε = 0%, the C-O-C asymmetric and symmetric stretching peaks can be clearly observed at 1220 cm-1, indicating the presence of polyether-type polyurethane. For polyether-type polyurethanes, a large number of hydrogen bonds exist near the amino acid groups. The N-H bonds in the main hard segment structure, such as the urethane groups, act as bridges to form hydrogen bonds between the hard and soft segments, combined with the C=O bonds in the hard segments to form (C=O---N-H) hydrogen bonds, and combined with the C-O bonds in the soft segments to form (C-O---N-H) hydrogen bonds. Since the molecular polarity of the hard segment in TPU is much larger than that of the soft segment, and the overall polarity depends on the extent of the microphase separation constructed by hydrogen bonds, the degree of microphase separation determines the dielectric constant of TPU in the unstressed state. However, the stretching state often increases steric hindrance in the molecular chains, affecting the formation of these two types of hydrogen bonds. Therefore, we used the attenuated total reflectance (ATR) mode in FTIR to fit and analyze the C=O peak and investigate the microphase separation behavior.
As shown in
Figure 3a and 3b, the peak at 1700 cm
-1 is attributed to the hydrogen-bonded carbonyl stretching vibration, while the peak at 1730 cm
-1 is attributed to the free carbonyl stretching vibration (more data are displayed in Figure S5, Supporting Information). The areas (A) of these two peaks were obtained by fitting and calculating using Gaussian functions, and the fitted curves correspond well with the original curves. Here, the coefficient F(H) representing the degree of hydrogen bond formation was obtained using the formula: F(H)=A
1700/(A
1730+A
1700 )*100%. A
1700 is the spectral peak area at 1700 cm
-1, and A
1730 is the spectral peak area at 1730 cm
-1. As the strain increases from 0% to 400%, the values of F(H) gradually decrease (
Figure 3(c)), which indicates that as the strain increases, the ability of microphase separation increases, leading to the gradual disruption of hydrogen bonds in the hard segments. This forces the highly polar hard domain structures to disperse within the less polar soft domain structures.
Simultaneously, the peak at 1529 cm
-1 is attributed to the hydrogen-bonded C-N stretching vibration in the hard domains, which is also an important indicator for estimating the proportion of hard domains. From
Figure 3(d), it is clear that the intensity of the C-N peak decreases with increasing tensile strain. The peak area decreases from 4.336 (ε = 0%) to 1.970 (ε = 400%), indicating a gradual decrease in the number of hydrogen bonds connected to C-N as the strain increases. Interestingly, besides the decrease in peak intensity, a peak shift towards higher wavenumbers also occurs, suggesting that after hydrogen bonds break in the hard segments, they transform into interactions between soft domains. As a result, the frequency of C-N stretching vibrations in the hard domains increases.
3.4. Variation in the Molecular Chain Long Period during Strains
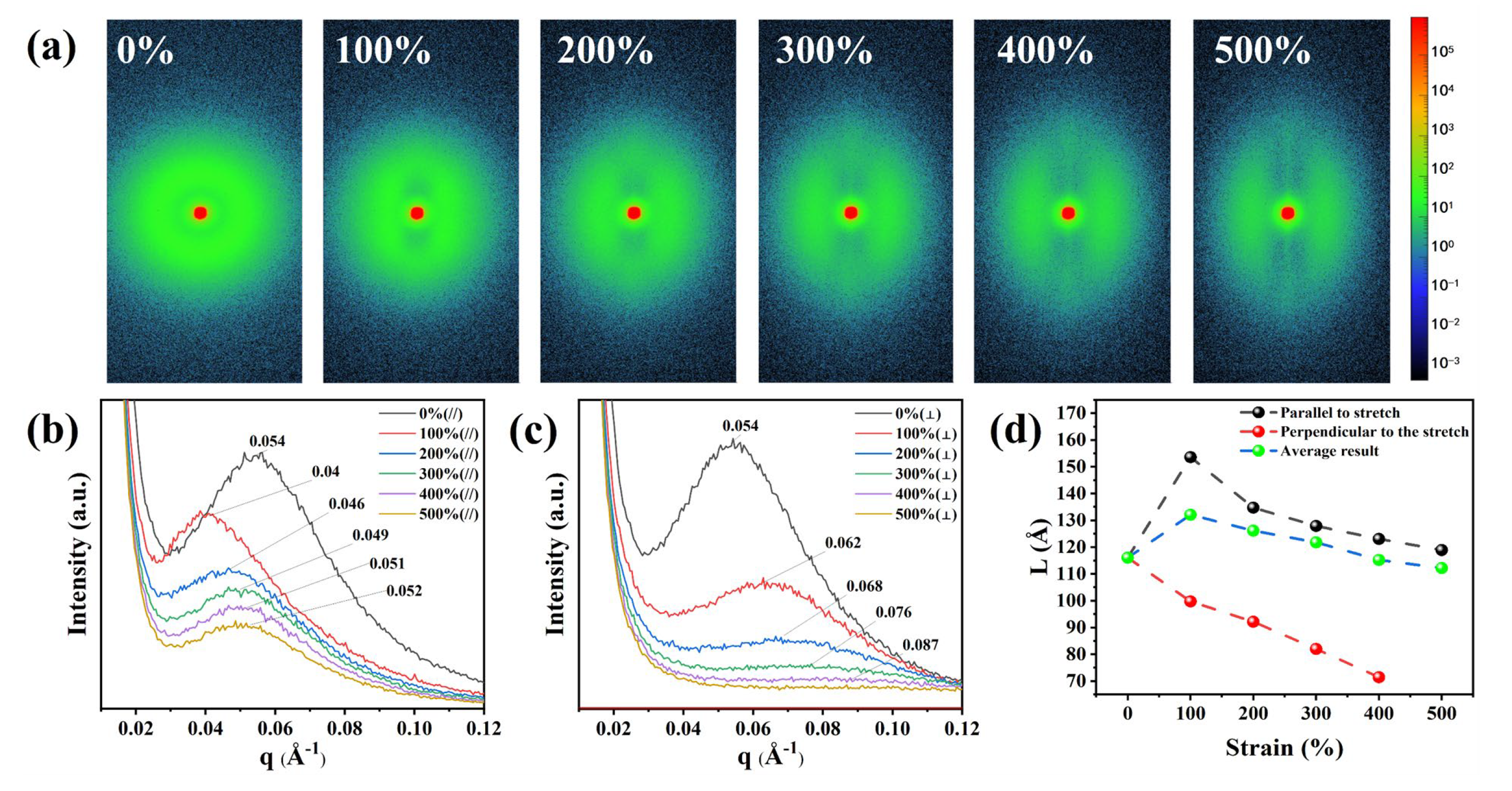
To analyze the reason for the smaller number of hydrogen bonds between highly polar hard domains in TPU under strain, we investigated the evolution of the distances between hard domains and that between hard and soft domains upon different strain states in TPU molecules. The variation of the molecular chain long period (L) in TPU was studied using small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) technique.
Figure 4(a) shows the 2D-SAXS patterns of TPU at various strain state. To obtain clear and accurate images, we performed the experiments under the conditions of 600 s exposure time and a stretching speed of 200 um/s. At zero strain, a uniform circular scattering ring is observed around the central red spot, indicating an isotropic arrangement between the hard segments and the soft segments. As the strain increases to 100%, the scattering pattern changes from circular to elliptical, indicating the occurrence of orientation behavior in the molecular chains and the appearance of striped scattering regions perpendicular to the stretching direction. In addition, a diffuse scattering pattern appears parallel to the stretching direction. As the strain increases, the width and intensity of the diffuse scattering increase, indicating a greater degree of dispersion, while the intensity of the striped scattering region becomes stronger, indicating an increase in the number of molecular chain segments oriented in the stretching direction.
To quantitatively determine the specific changes in the hard and soft domains in the microphase separation structure, we integrated the 2D-SAXS patterns parallel and perpendicular to the stretching direction to obtain the 1D-SAXS intensity distribution in
Figure 4(a). The molecular chain long period (L) was calculated using the formula L=2π/q
max (where q
max is the q value at the maximum intensity of the scattering peak).
Figure 4(b) depicts the results along the stretching direction, from which the coherent scattering peak shifts to lower q values and L increases from 11.60 nm (ε = 0%) to 15.36 nm (ε = 100%) as the strain increases. As the strain further increases from 100% to 500%, the coherent scattering peak shifts back to higher q values and L gradually decreases to 11.89 nm (ε = 500%), indicating a phenomenon where the distance between hard domains in TPU initially increases and then decreases in the stretching direction. At the same time, the intensity of the coherent scattering peak gradually decreases, indicating a reduction in the scattering intensity in the hard domain region. One the other hand, the long period perpendicular to the stretching direction overall shows an increasing trend
Figure 4(c), with a small range of variation from 11.60 nm (ε = 0%) to 11.89 nm (ε = 500%), and the scattering intensity decreases significantly. According to the analysis of hydrogen bonding strength in the hard segment after 100% strain in FTIR, it can be inferred that this may be due to the elastic deformation of the molecules at the beginning of stretching, where hydrogen bonds are not broken and the distance between hard domains increases horizontally. However, as the hydrogen bonds are disrupted, the hard domains evolve. From the weakening of the coherent scattering peak intensity, it can be speculated that there is an increment the degree of microphase separation in TPU. All in all, the number of hard segments in the perpendicular direction significantly decreases, transforming into hard domains along the stretching direction. This change can also be seen from the change of azimuth angle as shown in Figure S6 (Supporting Information). At ε = 0%, the hard domains in TPU exhibit isotropic characteristics. For ε = 100%, by defining the stretching direction as 0°, then the hard domains are more likely to oriented in the directions of 45°, 132°, 227°, and 314°. For ε larger than 100%, more and more hard domains are concentrated in the parallel stretching direction, while a small number of hard domains are perpendicular to the stretching direction. For example, they peaked at 89° and 270° at ε = 500%. This is consistent with the results of the 2D-WSXS test, which show that the molecular chains in TPU exhibit a preferential orientation along the stretching direction.
3.5. Characterization of TPU Microphase Separation
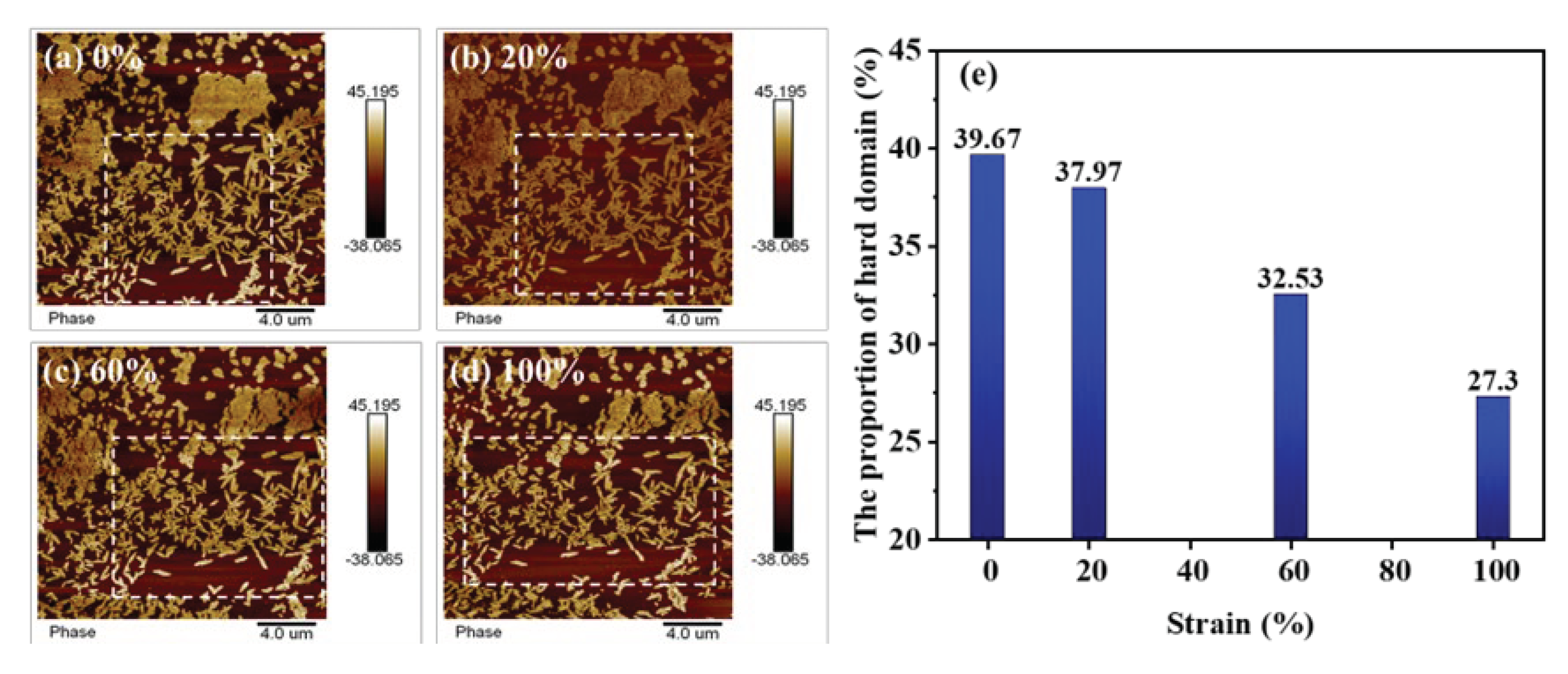
To characterize the microscopic phase separation upon strain in the TPU elastomers, the AFM technique was employed to map the phase images of TPU at various strain states. As can be seen from
Figure 5, the elastomer is composed of regions characterized by distinct bright and dark phase contrast. The bright regions show clear and regular edges, and could therefore be regarded as hard domains. The percentage of hard domains in the images were calculated by the image analysis software, and the number of hard domains in the stretching process was obtained quantitatively. In the unstretched initial state, the hard domain phases are typically of a few hundred nanometers in size and show leaflet-like patterns, with more agglomerates intertwined and fewer independently present in the soft domains. As the tensile strain increases, it is vividly observed that the agglomerated hard domains are gradually dispersed into smaller independent fragments, and the lateral distances between the original independent hard domains gradually increases. We estimated the proportion of hard domains in the same region (marked by dashed box), and found that it decreases from 39.67% to 27.30% as the strain increase from zero to 100%. Our observation also provides strong support for the analytical results of SAXS.
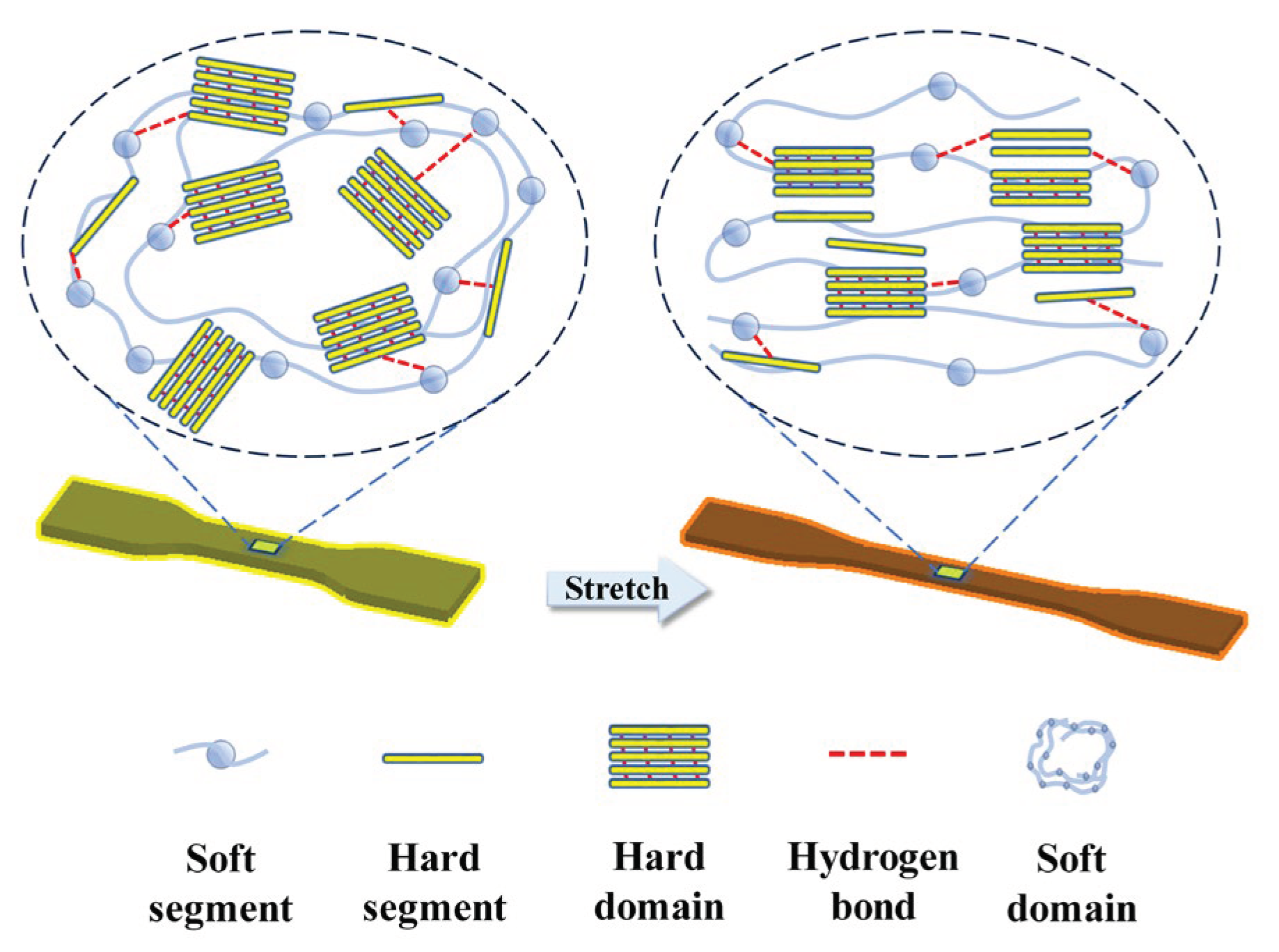
Finally,
Figure 6 summarizes a schematic diagram showing how the microstructure of TPU evolves upon the application of external strain. Although no evidence of strain-induced phase transition was observed in TPU, there is clear sign of re-orientation of the molecular chains aligning along the stretching direction. Furthermore, the hard domains, are gradually disrupted and enveloped by soft domains, giving rise to a simultaneous decrease of the density of the hard domains. As the hard domains contribute significantly to the dielectric constant, such convolution of hard domains shall lead to a decrease in the observed dielectric constant of TPU.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we designed a device based on the parallel plate capacitor principle for in situ measurement of the dielectric constant of elastomers under controllable strain conditions. We measured the evolution of dielectric constant of TPU at different strain states, and found that the dielectric constant gradually decreased from 8.47 ± 0.01 (ε = 0%) to 2.94 ± 0.27 (ε = 400%). To explain this interesting phenomenon, we characterized the effects of strain on TPU at the nanoscale by using microscopic characterization method to observe the molecular chain spacing, hydrogen bonding status, and molecular chain long period. Based on these characterizations, we revealed a decreased density and average size of polarized hard domains, along with a tendency of the molecular chains to align in parallel with the tensile stress, which results in a reduction of the dielectric constant in TPU.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Run-Wei Li; Formal analysis, Huali Yang; Funding acquisition, Huali Yang, Yali Xie and Run-Wei Li; Investigation, Yubo Wang; Methodology, Yubo Wang, Lili Pan, Dan Zhao, Jinxia Chen, Mengting Zou and Tian Tian; Project administration, Run-Wei Li; Resources, Xilai Bao, Dan Zhao, Tian Tian and Run-Wei Li; Software, Xilai Bao, Lili Pan, Jinxia Chen and Mengting Zou; Supervision, Huali Yang, Yali Xie, Tian Tian and Run-Wei Li; Validation, Huali Yang and Yali Xie; Writing – original draft, Yubo Wang; Writing – review & editing, Huali Yang, Yali Xie, Tian Tian and Run-Wei Li. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51931011, 52127803, 52371205, U23A20551), the K. C. Wong Education Foundation (No. GJTD-2020−11), the “Pioneer” and “Leading Goose” R&D Program of Zhejiang (No. 2022C01032), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LD24E010001), the Ningbo Key Scientific and Technological Project (Nos. 2022Z094, 2023Z076), and the Foundation of Director of Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2022SZZB0002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy and legal.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Xuke Li for assistance in the SAXS tests.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abramson, A.; Chan, C.T.; Khan, Y.; Mermin-Bunnell, A.; Matsuhisa, N.; Fong, R.; Shad, R.; Hiesinger, W.; Mallick, P.; Gambhir, S.S.; et al. A flexible electronic strain sensor for the real-time monitoring of tumor regression. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Gu, C.; Liu, S.; Zeng, M.; Wu, Y. Ultrashort 15-nm flexible radio frequency ITO transistors enduring mechanical and temperature stress. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eade4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, S.; Cao, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, B.; Xie, J.; Shu, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, A.; Dong, J.; et al. High performance flexible Sn-Pb mixed perovskite solar cells enabled by a crosslinking additive. npj Flex. Electron. 2023, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-B.; Li, B.; Yang, D.-D.; Liu, C.; Feng, S.; Chen, M.-L.; Sun, Y.; Tian, Y.-N.; Su, X.; Wang, X.-M.; et al. A flexible ultrasensitive optoelectronic sensor array for neuromorphic vision systems. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Man, Q.; Hu, C.; Asghar, W.; Li, F.; Yu, Z.; Shang, J.; Liu, G.; et al. A Skin-Inspired Tactile Sensor for Smart Prosthetics. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat0429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phadkule, S.S.; Sarma, S. Progress in nanocomposite based flexible temperature sensors: A review. Meas. Sensors 2023, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hou, J.; Xiao, X.; Wan, R.; Ge, G.; Zheng, W.; Chen, C.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Self-healing electrical bioadhesive interface for electrophysiology recording. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 654, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, H.; Qin, K.; Guo, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Qu, Y.; Yan, D.; Li, Z.; et al. Self-protection soft fluidic robots with rapid large-area self-healing capabilities. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyenucheya, B.; Allen, J.; Pierre, K.; Zirnheld, J.; Burke, K. Dielectric Elastomers: An Investigation in Strain Dependent Electrostatic Pressure of Soft Compliant Dielectric. 2019 IEEE Pulsed Power & Plasma Science (PPPS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–4.
- Lotfiani, A.; Yi, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Parkestani, A.N. Analytical modeling and optimization of a corrugated soft pneumatic finger considering the performance of pinch and power grasps. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2021, 44, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Zhao, H. Speeding up soft pneumatic actuators through pressure and flow dynamics modeling and optimization. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2022, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, B.; Sahu, R. K.; Bhaumik, S.; Patra, K.; Pandey, A. K.; Setua, D. K. , Experimental study on permittivity of acrylic dielectric elastomer. In 2012 IEEE 10th International Conference on the Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials, Bangalore, India, 2012; pp 1-4.
- Tröls, A.; Kogler, A.; Baumgartner, R.; Kaltseis, R.; Keplinger, C.; Schwödiauer, R.; Graz, I.; Bauer, S. Stretch dependence of the electrical breakdown strength and dielectric constant of dielectric elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Calleja, R.; Riande, E. Comments on the influence of stretching on the permittivity of dielectric elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.R.; Jung, K.; Chuc, N.H.; Jung, M.; Koo, I.; Koo, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Nam, J.; Cho, M.; et al. Effects of prestrain on behavior of dielectric elastomer actuator. Smart Structures and Materials. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 283–291.
- Kofod, G.; Sommer-Larsen, P.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R. Actuation Response of Polyacrylate Dielectric Elastomers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2003, 14, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Gao, X. Effect of the deformation dependent permittivity on the actuation of a pre-stretched circular dielectric actuator. Mech. Res. Commun. 2019, 101, 103420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Patra, K. Proposal of a generic constitutive model for deformation-dependent dielectric constant of dielectric elastomers. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Cong, T.; Nguyen-Thi, N.; Jean-Mistral, C.; Sylvestre, A. , How does static stretching decrease the dielectric constant of VHB 4910 elastomer? In ELECTROACTIVE POLYMER ACTUATORS AND DEVICES (EAPAD) 2014, San Diego, California, United States, 2014; Vol. 9056.
- Srivastava, A.K.; Basu, S. Exploring the performance of a dielectric elastomer generator through numerical simulations. Sensors Actuators A: Phys. 2020, 319, 112401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Liang, Y.; Xining, Z. ; H. Results in Physics 2021, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, D.; Patra, K. Experimental and theoretical analysis of laterally pre-stretched pure shear deformation of dielectric elastomer. Polym. Test. 2019, 75, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Kang, G. Experimental study on uniaxial ratchetting of VHB 4910 dielectric elastomer. Polym. Test. 2022, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlögl, T.; Leyendecker, S. A polarisation based approach to model the strain dependent permittivity of dielectric elastomers. Sensors Actuators A: Phys. 2017, 267, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, H.; Qiang, J.; Zhou, J. A model for conditional polarization of the actuation enhancement of a dielectric elastomer. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.M.; McMeeking, R.M. Deformation dependent dielectric permittivity and its effect on actuator performance and stability. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 2013, 57, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedberg, I.Z.; Debotton, G. Electroelasticity of copolymer networks. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2023, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Mistral, C.; Sylvestre, A.; Basrour, S.; Chaillout, J.-J. Dielectric properties of polyacrylate thick films used in sensors and actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, Q.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, J. Asynchronous fracture of hierarchical microstructures in hard domain of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer: Effect of chain extender. Polymer 2018, 138, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.-S.; Zha, J.-W.; Yang, Y.; Han, P.; Hu, C.-H.; Wen, Y.-Q.; Dang, Z.-M. Polyurethane induced high breakdown strength and high energy storage density in polyurethane/poly(vinylidene fluoride) composite films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 252902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, R.; Kline, W.; Wang, C.; Ramprasad, R.; Sotzing, G. The rational design of polyurea & polyurethane dielectric materials. Polymer 2013, 54, 3529–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, J.; Yin, F.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y. Flexible and stretchable MXene/Polyurethane fabrics with delicate wrinkle structure design for effective electromagnetic interference shielding at a dynamic stretching process. Compos. Commun. 2020, 19, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).