Submitted:
03 April 2024
Posted:
04 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Method
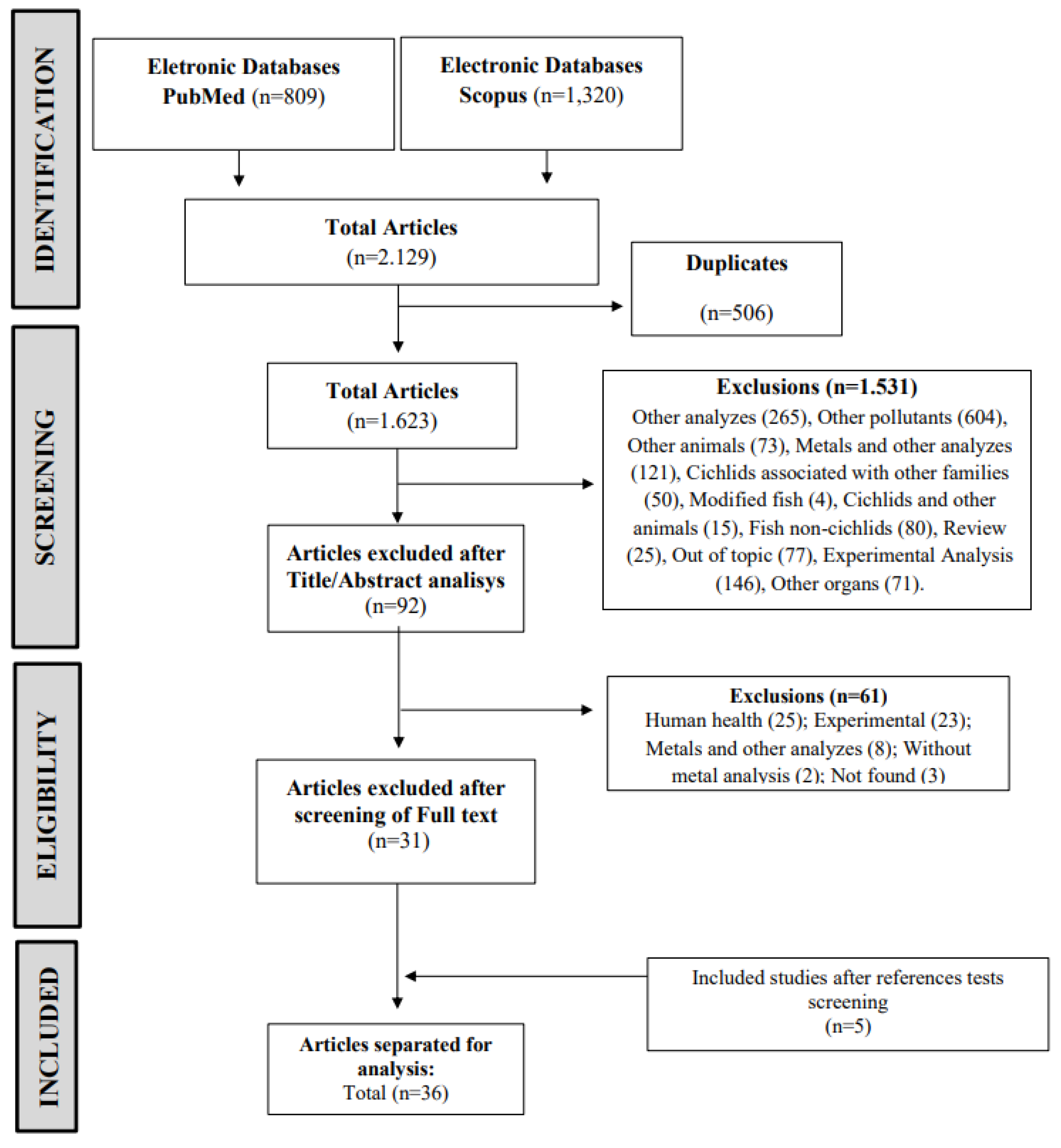
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- Studies in which at least one of the analyzes mentioned below were performed: quantification of the metal in the organ (bioaccumulation), histopathological analysis and oxidative status.
- (4)
- Studies that analyzed the effect of heavy metals on liver or gills or both.
2.3. Data Extraction and Management
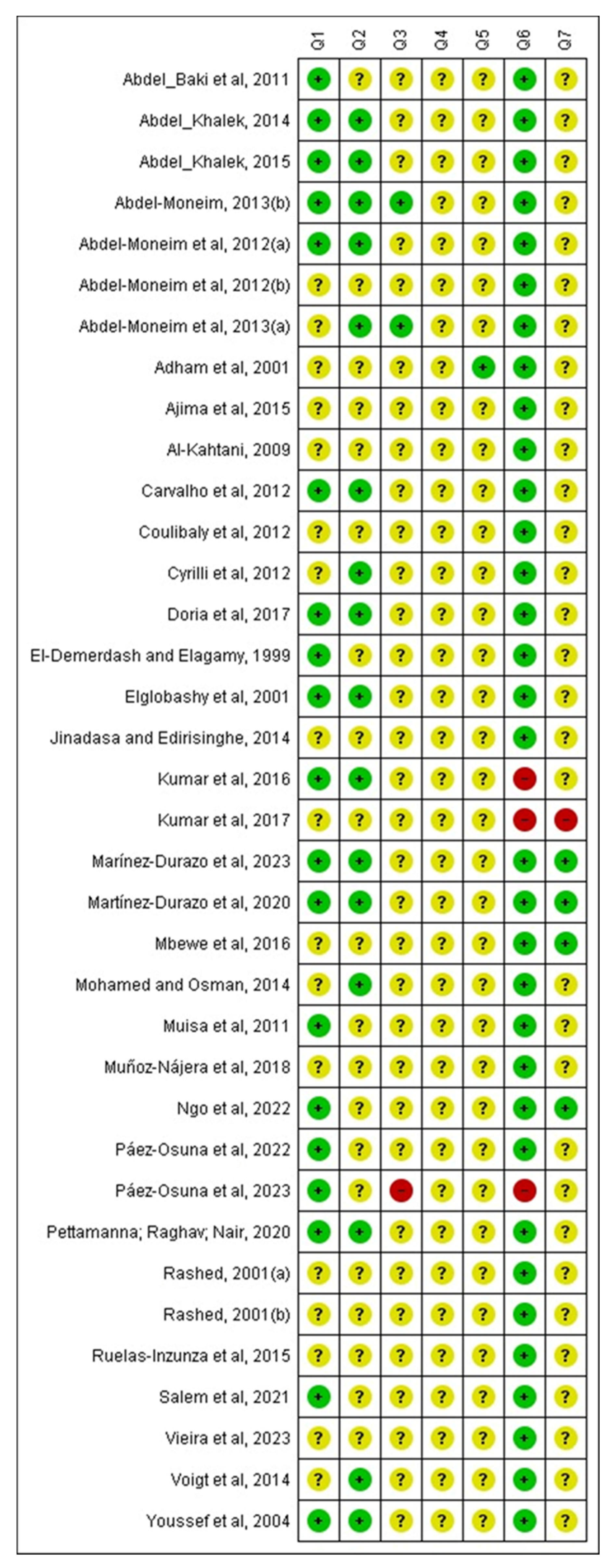
2.4. Bias Risk Assessment in the Included Studies
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Publications
3.2. Characteristics of Fish and Collecting Environments
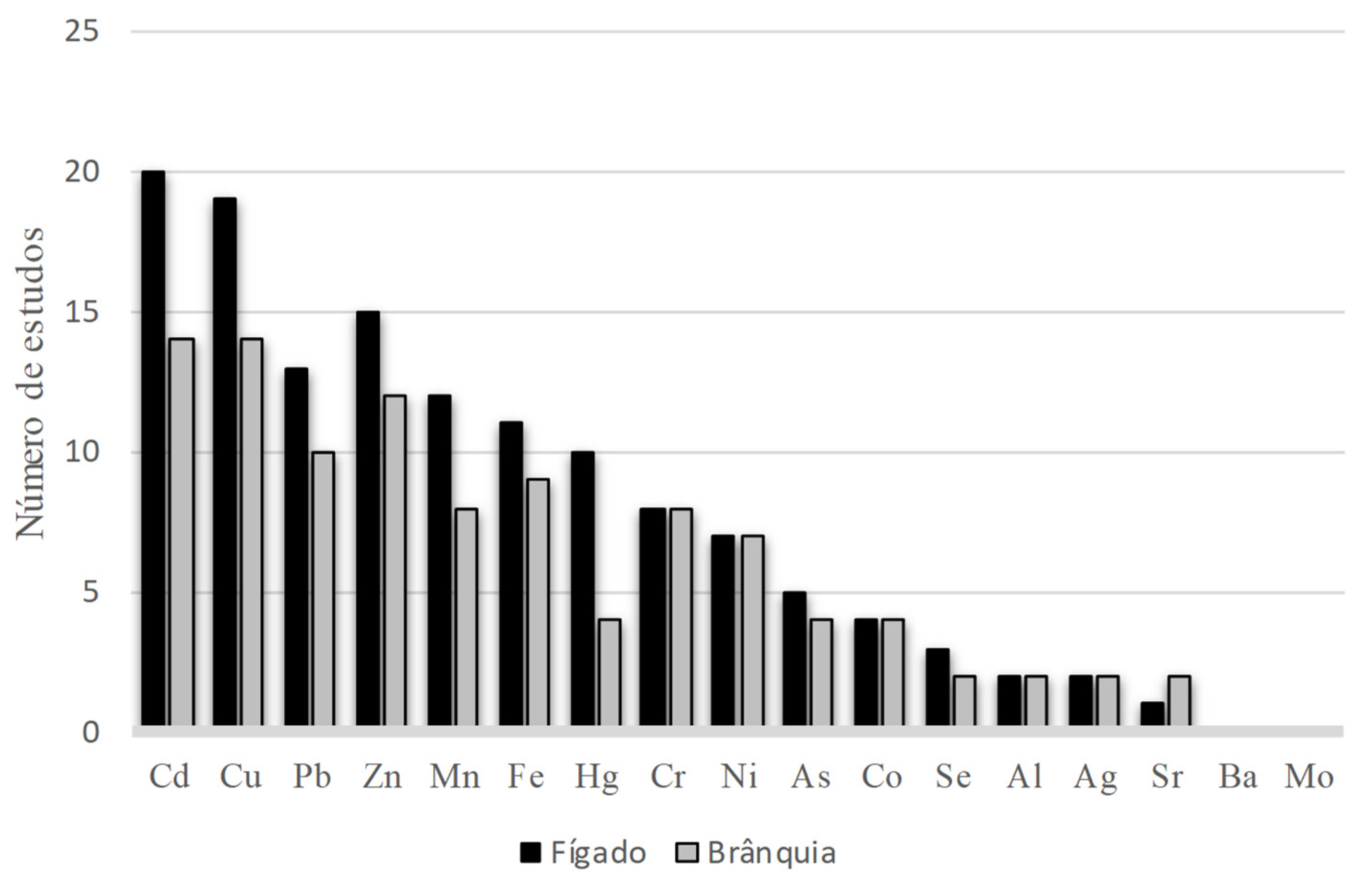
3.3. Characteristics of the Analyses
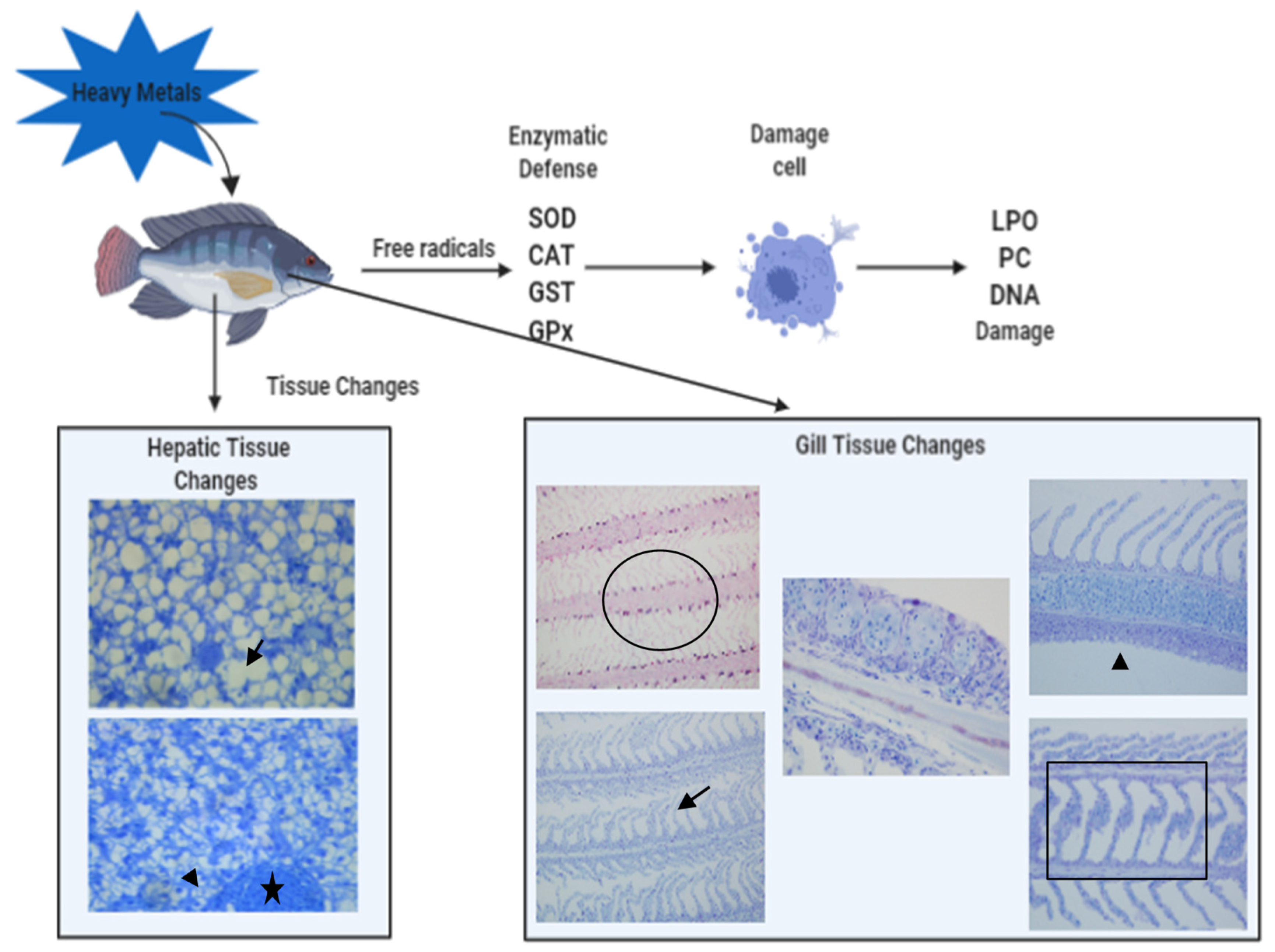
3.4. Ecotoxicological Effects of Heavy Metals on Fish
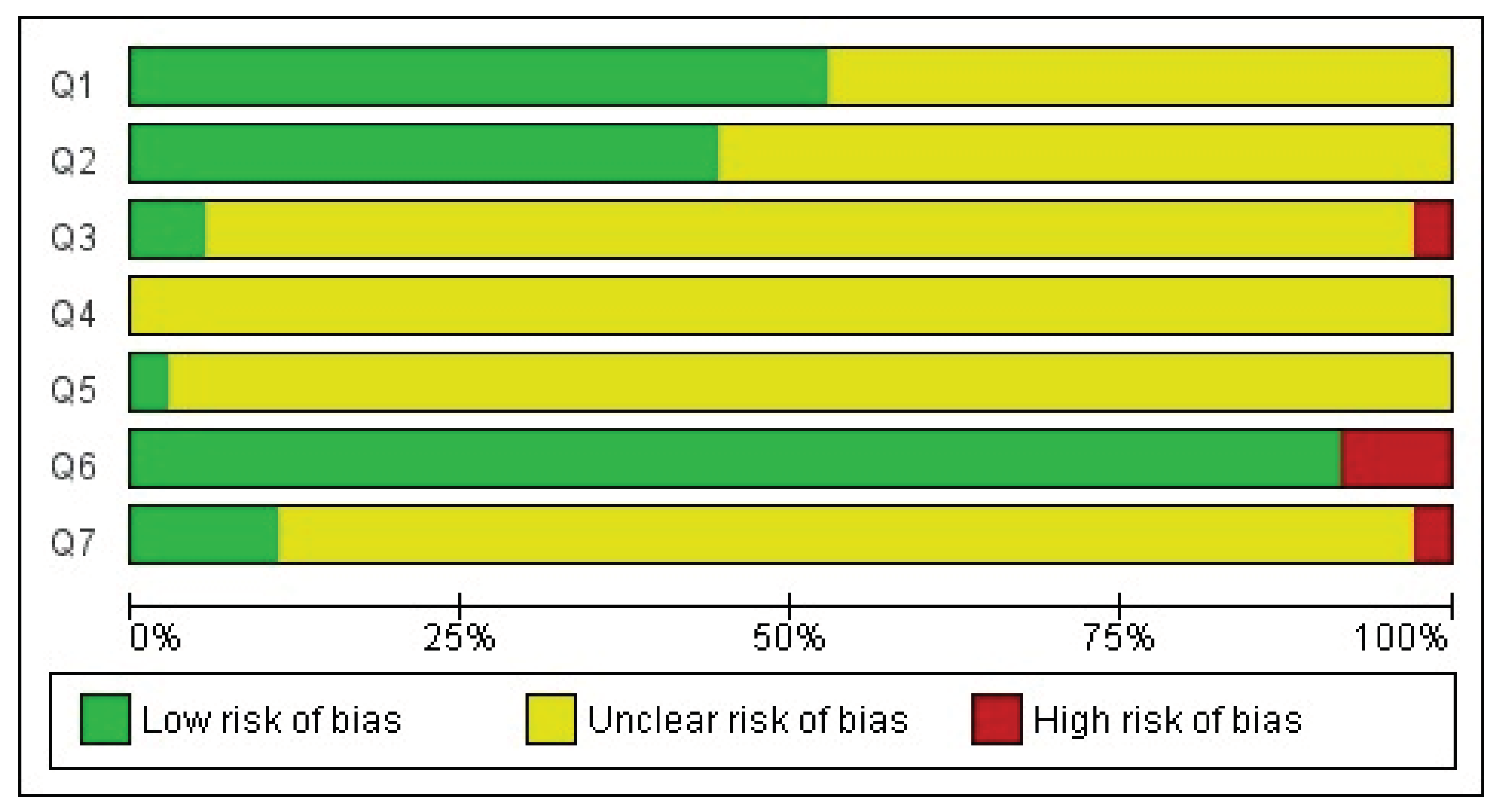
3.5. Bias Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
7. Highlights
- Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) is the most used animal model among cichlids;
- Heavy metals accumulate in the liver and gills, causing several morphofunctional changes, with greater bioaccumulation and greater liver damage;
- Of the metals most analyzed in the works, we highlight the bioaccumulation of cadmium, copper, lead, zinc, iron and manganese.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngo, H.T.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Le, T.T.; Nguyen, D.Q. Adverse Effects of Toxic Metal Pollution in Rivers on the Physiological Health of Fish. Toxics 2022, 10, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Rai, D.K.; Pandey, R.S.; Sharma, B. Analysis of some heavy metals in the riverine water, sediments and fish from river Ganges at Allahabad. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 157, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguère, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Hare, L.; McDonald, D.G.; Rasmussen, J.B. Influence of lake chemistry and fish age on cadmium, copper, and zinc concentrations in various organs of indigenous yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 1702–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Xiao, R.; Mi, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J. Spatial determinants of hazardous chemicals in surface water of Qiantang River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 24, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Biswas, A.K.; Qureshi, T.A.; Borana, K.; Virha, R. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish tissues of a freshwater lake of Bhopal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 160, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Durazo. ; Rivera-Domínguez, M.; García-Gasca, S.A.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Cruz-Acevedo, E.; Jara-Marini, M.E. Assessing metal(loid)s concentrations and biomarkers in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) of three ecosystems of the Yaqui River Basin, Mexico. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 166–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Dwivedi, P. Heavy metal water pollution-A case study. Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Baby, J.; Raj, J.; Biby, E.; Sankarganesh, P.; Jeevitha, M.; Ajisha, S.; Rajan, S. Toxic effect of heavy metals on aquatic environment. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, M.; Ulven, S.M.; Meltzer, H.M.; Alexander, J. Arsenic in the human food chain, biotransformation and toxicology – Review focusing on seafood arsenic. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2015, 31, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimska, P.K.; Anna; Skóra, K. ; Namieśnik, J. Bioaccumulation of Metals in Tissues of Marine Animals, Part I: the Role and Impact of Heavy Metals on Organisms. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Bouraoui, Z.; Banni, M.; Ghedira, J.; Clerandeau, C.; Guerbej, H.; Narbonne, J.F.; Boussetta, H. Acute effects of cadmium on liver phase I and phase II enzymes and metallothionein accumulation on sea bream Sparus aurata. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 34, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaleh, S.B.; Banday, U.Z.; Usmani, N. Comparative study of biochemical, histological and molecular biomarkers of heavy metal contamination in Cyprinus carpio collected from warm-monomictic lake and government culture pond. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, D.D.P.; Marques, M.R.D.C.; Baptista, D.F.; Buss, D.F. Metal bioavailability and toxicity in freshwaters. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Saran, R.; Liu, J. Metal Sensing by DNA. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8272–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawuro, A.A.; Voegborlo, R.B.; Adimado, A.A. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Some Tissues of Fish in Lake Geriyo, Adamawa State, Nigeria. J. Environ. Public Heal. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, S.; Chang, J. Acute Toxicity, Respiratory Reaction, and Sensitivity of Three Cyprinid Fish Species Caused by Exposure to Four Heavy Metals. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e65282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.N. Cadmium and Lead Levels in Fish (Tilapia Nilotica) Tissues as Biological Indicator for Lake Water Pollution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 68, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblmüller, S.; Albertson, R.C.; Genner, M.J.; Sefc, K.M.; Takahashi, T. Preface: Advances in cichlid research: behavior, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Hydrobiologia 2015, 748, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Camacho, D.; Carleton, K.L. Sensory modalities in cichlid fish behavior. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 6, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, T.D. Adaptive evolution and explosive speciation: the cichlid fish model. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 22. Kullander,O. S. A phylogeny and classification of the South American Cichlidae (Teleostei: Perciformes)., Malabarba, L, R Reis, R, E Vari, R, P Lucena, Z, M, S Lucena, C, A, S Phylogeny Classif. Neotrop. Fishes.
- Galvão, T.F.; Pereira, M.G. Revisões sistemáticas da literatura: passos para sua elaboração. 23. [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, A.L.A.; Goulart, E. Ciclídeos neotropicais: Ecomorfologia trófica. Oecologia Aust. 2011, 15, 775–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehjbeen, J.; Nazura, U. Assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Ni, Fe, Co, Mn, Cr, Zn) in rivulet water, their accumulations and alterations in hematology of fish Channa punctatus. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Greco, G.M.Z.; Moreira, A.M.; Chagas, P.F.; Caldas, I.S.; Gonçalves, R.V.; Novaes, R.D. Applicability of plant-based products in the treatment ofTrypanosoma cruziandTrypanosoma bruceiinfections: a systematic review of preclinicalin vivoevidence. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Tillema, A.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M. Enhancing search efficiency by means of a search filter for finding all studies on animal experimentation in PubMed. Lab. Anim. 2010, 44, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Cochrane Collab. (2014).
- El-Demerdash, F.; Elagamy, E. Biological effects in Tilapia nilotica fish as indicators of pollution by cadmium and mercury. Int. J. Environ. Heal. Res. 1999, 9, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M. Monitoring of environmental heavy metals in fish from Nasser Lake. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghobashy, H.; Zaghloul, K.; Metwally, M. EFFECT OF SOME WATER POLLUTANTS ON THE NILE TILAPIA, OREOCHROMISNILOTICUS COLLECTED FROM THE RIVER NILE AND SOME EGYPTIAN LAKES. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2001, 5, 251–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adham, K.G.; Hamed, S.S.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Saleh, R.A. Impaired Functions in Nile Tilapia,Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1757), from Polluted Waters. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2001, 29, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.H.; Tayel, F.T. Metal accumulation by threeTilapiaspp. from some Egyptian inland waters. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 20, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahtani, A. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis niloticus) from Al-Khadoud Spring, Al-Hassa, Saudi Arabia. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Baki, A.S.; Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Quraishy, S. Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals in tilapia fish relevant to their concentration in water and sediment of Wadi Hanifah, Saudi Arabia. African J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar]
- Muisa, N.; Hoko, Z.; Chifamba, P. Impacts of alum residues from Morton Jaffray Water Works on water quality and fish, Harare, Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M.; Abu El-Saad, A.M.; Hussein, H.K.; Dekinesh, S.I. Gill Oxidative Stress and Histopathological Biomarkers of Pollution Impacts in Nile Tilapia from Lake Mariut and Lake Edku, Egypt. J. Aquat. Anim. Heal. 2012, 24, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M.; Al-Kahtani, M.A.; Elmenshawy, O.M. Histopathological biomarkers in gills and liver of Oreochromis niloticus from polluted wetland environments, Saudi Arabia. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrille, Y.D.A.; Victor, K.; Sanogo, T.A.; Boukary, S.; Joseph, W. Cadmium Accumulation in Tissues of Sarotherodon melanotheron (Rüppel, 1852) from the Aby Lagoon System in Côte d’Ivoire. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2012, 9, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.d.S.; Bernusso, V.A.; de Araújo, H.S.S.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Fernandes, M.N. Biomarker responses as indication of contaminant effects in Oreochromis niloticus. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, S.; Atse, B.C.; Koffi, K.M.; Sylla, S.; Konan, K.J.; Kouassi, N.J. Seasonal Accumulations of Some Heavy Metal in Water, Sediment and Tissues of Black-Chinned Tilapia Sarotherodon melanotheron from Biétri Bay in Ebrié Lagoon, Ivory Coast. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M.; E Essawy, A.; El-Din, N.K.B.; El-Naggar, N.M. Biochemical and histopathological changes in liver of the Nile tilapia from Egyptian polluted lakes. Toxicol. Ind. Heal. 2013, 32, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M. Histopathological and ultrastructural perturbations in tilapia liver as potential indicators of pollution in Lake Al-Asfar, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 4387–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinadasa, B.; Edirisinghe, E. Cadmium, lead and total mercury in Tilapia sp. in Sri Lankan reservoirs. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2013, 7, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.H.A.; Osman, A.-R. Heavy Metals Concentration in Water, Muscles and Gills of Oreochromis niloticus Collected from the Sewage-Treated Water and the White Nile. Int. J. Aquac. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, C.L.; Da Silva, C.P.; Doria, H.B.; Randi, M.A.F.; Ribeiro, C.A.D.O.; De Campos, S.X. Bioconcentration and bioaccumulation of metal in freshwater Neotropical fish Geophagus brasiliensis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 8242–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalek, A.A. Antioxidant Responses and Nuclear Deformations in Freshwater Fish, Oreochromis niloticus, Facing Degraded Environmental Conditions. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalek, A.A. Risk Assessment, Bioaccumulation of Metals and Histopathological Alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Facing Degraded Aquatic Conditions. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 94, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajima, M.N.O.; Nnodi, P.C.; Ogo, O.A.; Adaka, G.S.; Osuigwe, D.I.; Njoku, D.C. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in Mbaa River and the impact on aquatic ecosystem. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelas-Inzunza, J.; Rojas-Ruiz, E.; Spanopoulos-Hernández, M.; Barba-Quintero, G. Mercury in the blue tilapia Oreochromis aureus from a dam located in a mining region of NW Mexico: seasonal variation and percentage weekly intake (PWI). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Krishnani, K.; Gupta, S.; Singh, N. Cellular stress and histopathological tools used as biomarkers in Oreochromis mossambicus for assessing metal contamination. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 49, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbewe, G.; Mutondo, M.; Maseka, K.; Sichilongo, K. Assessment of Heavy-Metal Pollution in Sediments and Tilapia Fish Species in Kafue River of Zambia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 71, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria, H.B.; Voigt, C.L.; Sandrini-Neto, L.; Campos, S.X.; de Oliveira-Ribeiro, C.A.; Randi, M.A.F. How and where to perform biomonitoring studies: different levels of toxic metal pollution are detected in the Alagados Reservoir in Southern Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13080–13094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Krishnani, K.; Meena, K.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, N. Oxidative and cellular metabolic stress of Oreochromis mossambicus as biomarkers indicators of trace element contaminants. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Nájera, M.A.; Barrera-Escorcia, G.; Ramírez-Romero, P.; Tapia-Silva, F.O.; Rosas-Cedillo, R. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in Oreochromis niloticus from Tenango Dam, Puebla, Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettamanna, A.; Raghav, D.; Nair, R.H. Hepatic Toxicity in Etroplus suratensis (Bloch 1790): An Economically Important Edible Fish in Vembanad Fresh Water Lake, Kerala, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Durazo. ; Cruz-Acevedo, E.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Jara-Marini, M.E. Comparative Assessment of Metal Bioaccumulation in Tilapia and Largemouth Bass from Three Dams of the Yaqui River. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 199, 3112–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.S.; Hagras, A.E.; El-Baghdady, H.A.M.; El-Naggar, A.M. Biomarkers of Exposure and Effect in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Environmentally Exposed to Multiple Stressors in Egypt. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Osuna, F.; Bergés-Tiznado, M.E.; Fregoso-López, M.G.; Valencia-Castañeda, G.; León-Cañedo, J.A.; Alarcón-Silvas, S.G.; Fierro-Sañudo, J.F.; Ramírez-Rochín, J. High accumulation of metals and metalloids in the liver of the blue tilapia (Oreochromis aureus) during a massive mortality event induced by a mine tailing spill. Environ. Geochem. Heal. 2022, 45, 3155–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.C.S.; Braga, C.P.; de Queiroz, J.V.; Cavecci-Mendonça, B.; de Oliveira, G.; de Freitas, N.G.; Fernandes, A.A.H.; Fernandes, M.d.S.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Adamec, J.; et al. The effects of mercury exposure on Amazonian fishes: An investigation of potential biomarkers. Chemosphere 2023, 316, 137779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, E.; Rajagopalsamy, C.; Ahilan, B.; Jeevagan, I.; Renuhadevi, M. Tilapia—An excellent candidate species for world aquaculture: A review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2019, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjoun, K.; Rosentrater, K.; Brown, M.L. TILAPIA: Profile and Economic Importance, South Dakota Coop. Ext. Servi. 2010, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.; Diniz, Y.; Marques, S.; Faine, L.; Ribas, B.; Burneiko, R.; Novelli, E. The use of the oxidative stress responses as biomarkers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to in vivo cadmium contamination. Environ. Int. 2002, 27, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lin, H.; Yang, W. The effects of maternal Cd on the metallothionein expression in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) embryos and larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, K.; Atli, G.; Canli, M. Effects of Metal (Cd, Cu, Zn) Interactions on the Profiles of Metallothionein-Like Proteins in the Nile Fish Oreochromis niloticus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelgrom, S.; Lamers, L.; Lock, R.; Balm, P.; Bonga, S. Interactions between copper and cadmium modify metal organ distribution in mature tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 90, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husen, A.; Sharma, S. Efficacy of anesthetics for reducing stress in fish during aquaculture practices: a review. Kathmandu Univ. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 10, 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Flik, G.; Klaren, P.H.; Burg, E.H.V.D.; Metz, J.R.; Huising, M.O. CRF and stress in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 146, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, N. The endocrinology of stress in fish: An environmental perspective. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 170, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross Lindsay G., R. Barbara, Anaesthetic and sedative techniques for aquatic animals, 2008.
- Sink, T.D.; Strange, R.J.; Sawyers, R.E. Clove Oil Used at Lower Concentrations is Less Effective than MS-222 at Reducing Cortisol Stress Responses in Anesthetized Rainbow Trout. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2007, 27, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, E.F.d.M.; Uehara, S.A.; Rodrigues, E.C.; Palheta, G.D.A.; de Melo, N.F.A.C.; Freire, L.d.S.; Takata, R. Menthol and eugenol as natural anesthetics for early juveniles of curimba. Rev. Bras. de Zootec. 2018, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, S. Sodium Bicarbonate and Clove Oil as Potential Anesthetics for Nonsalmonid Fishes. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1998, 18, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.N.; Singer, T.D.; McKinley, R.S. The ability of clove oil and MS-222 to minimize handling stress in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; Wolf, J.C. Morphologic Effects of the Stress Response in Fish. ILAR J. 2009, 50, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaey, M.M.; Li, D. Transport Stress Changes Blood Biochemistry, Antioxidant Defense System, and Hepatic HSPs mRNA Expressions of Channel Catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AIgwegbe, O.; Negbenebor, C.A.; Chibuzo, E.C.; Badau, M.H.; Agbara, G.I. Effects of Season and Fhis Smoking on Heavy Metal Contents of Selected Fish Species from Thess Locations in State of Nigeria. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Hatje, V.; Pedreira, R.M.A.; de Rezende, C.E.; Schettini, C.A.F.; De Souza, G.C.; Marin, D.C.; Hackspacher, P.C. The environmental impacts of one of the largest tailing dam failures worldwide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.F.; Barbosa, S.C.T.; Barletta, M.; Dantas, D.V.; Kehrig, H.A.; Seixas, T.G.; Malm, O. Seasonal differences in mercury accumulation in Trichiurus lepturus (Cutlassfish) in relation to length and weight in a Northeast Brazilian estuary. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, M.; Lucena, L.; Costa, M.; Barbosa-Cintra, S.; Cysneiros, F. The interaction rainfall vs. weight as determinant of total mercury concentration in fish from a tropical estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 167, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, D.P. Assessment of contamination by heavy metals in water and fish from the Cassiporé, Amapá, Amazonas, Brazil basin. Diss. Mestr. 2013, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Rainbow, P.S. Trace metal bioaccumulation: Models, metabolic availability and toxicity. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleksic, V.; Mitrovic-Tutundzic, V. Fish gills as a monitor of sublethal and chronic effects of pollution. In: Sublethal and Chronic Effects of Pollutants on Freshwater Fish. Sublethal Chronic Eff. Pollut, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir, R.A.; Movahedinia, A.; Rastgar, S. American Journal of Toxicology Fish Liver Biomarkers for Heavy Metal Pollution : A Review Article. Am. J. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hedayati, A. Liver as a Target Organ for Eco-Toxicological Studies. J. Coast. Zone Manag. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakankun, O.A.; Babayemi, J.O.; Akosil, S.O. Evaluation of fish gills as potential target organ for accumulation of heavy metals. Africa J. Anim. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Oost, D.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in en v ironmental risk assessment : a re v iew, 2003, 13. 13.
- T.E.M. Parente, R.A. 89. T.E.M. Parente, R.A. Hauser-davis, The Use of Fish Biomarkers, Pollut. Fish Heal. Trop. Ecosyst. (. [CrossRef]
- Sevcikova, M.; Modra, H.; Slaninova, A.; Svobodova, Z. Metals as a cause of oxidative stress in fish: a review. 56. [CrossRef]
- Kroon, F.; Streten, C.; Harries, S. A protocol for identifying suitable biomarkers to assess fish health: A systematic review. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0174762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authman, M.M. Use of Fish as Bio-indicator of the Effects of Heavy Metals Pollution. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, I.D.; Nascimento, A.A.; Sales, A.; Araújo, F.G. Can fish gill anomalies be used to assess water quality in freshwater Neotropical systems?. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 5523–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Khaled, S.; Imed, M. Cadmium: Bioaccumulation, Histopathology and Detoxifying Mechanisms in Fish, Ali Annabi, Khaled Said. Imed Messaoudi. 2013, 1, 60–79. [Google Scholar]
- Habuer; Nakatani, J. ; Moriguchi, Y. Time-series product and substance flow analyses of end-of-life electrical and electronic equipment in China. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Fernandes, A.; Ferreira-Cardoso, J.V.; Garcia-Santos, S.; Monteiro, S.M.; Carrola, J.; Matos, P.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A. Histopathological changes in liver and gill epithelium of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, exposed to waterborne copper. 27. [CrossRef]
- Papagiannis, I.; Kagalou, I.; Leonardos, J.; Petridis, D.; Kalfakakou, V. Copper and zinc in four freshwater fish species from Lake Pamvotis (Greece). Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrilah, S.N.; Sabullah, M.K.; Shukor, M.Y.A.; Yasid, N.A.; Shamaan, N.A.; Ahmad, S.A. Toxicity effects of fish histopathology on copper accumulation. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2018, 41, 519–540. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado, N.E.; Quesada, I.; Hylland, K.; Marigómez, I.; Soto, M. Quantitative changes in metallothionein expression in target cell-types in the gills of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) exposed to Cd, Cu, Zn and after a depuration treatment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzyzewska, E.; Szarek, J.; Babinska, I. Morphologic evaluation of the gills as a tool in the diagnostics of pathological conditions in fish and pollution in the aquatic environment: a review. 61. [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, D.C.M.; da Matta, S.L.P.; de Oliveira, J.A.; dos Santos, J.A.D. Histological alterations in gills of Astyanax aff. bimaculatus caused by acute exposition to zinc. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalaka, S.E. Heavy metals bioaccumulation and histopathological changes in Auchenoglanis occidentalis fish from Tiga dam, Nigeria. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, C.B.R.; Nagae, M.Y.; Zaia, C.T.B.V.; Zaia, D.A.M. Acute morphological and physiological effects of lead in the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Braz. J. Biol. 2004, 64, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Risso, W.E.; Fernandes, M.N.; Martinez, C.B.R. Lead accumulation and its effects on the branchial physiology of Prochilodus lineatus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 40, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Durazo. ; Rivera-Domínguez, M.; García-Gasca, S.A.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Cruz-Acevedo, E.; Jara-Marini, M.E. Assessing metal(loid)s concentrations and biomarkers in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) of three ecosystems of the Yaqui River Basin, Mexico. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 166–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, N.R.; Walker, P.A.; Glover, C.N. Nutritive metal uptake in teleost fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Barman, A.S.; Devi, A.L.; Devi, A.G.; Pandey, P.K. Iron mediated hematological, oxidative and histological alterations in freshwater fish Labeo rohita. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 170, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, M.; Usmani, N. Histopathology and Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals (Cr, Ni and Pb) in Fish (Channa striatus and Heteropneustes fossilis) Tissue: A Study for Toxicity and Ecological Impacts. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.; Fernandes, L.S.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Monteiro, S.; Pacheco, F. The impact of freshwater metal concentrations on the severity of histopathological changes in fish gills: A statistical perspective. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 599–600, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiger, J.; Wanke, R.; Adam, S.; Pawert, M.; Honnen, W.; Triebskorn, R. The use of histopathological indicators to evaluate contaminant-related stress in fish. J. Aquat. Ecosyst. Stress Recover. 1997, 6, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadag, H.; Fırat. ; Fırat,. Use of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Cyprinus carpio L. for the Evaluation of Water Pollution in Ataturk Dam Lake (Adiyaman, Turkey). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 92, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Oost, R.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansilla-Rivera, I.; Rodríguez-Sierra, C.J. Metal Levels in Fish Captured in Puerto Rico and Estimation of Risk from Fish Consumption. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 60, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| References | Country | Species | Weight (g)/ Size (cm) | Number of animals | Groups of animals | Collection Period/ Station | |Analysis | Metals | Tissues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
El-Demerdash and Elagamy, 1999 [30] |
Egypt |
Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis nilótica) |
200-250/ 15-20 | 20 | Test + Control | Yes/ ? | Metals in tissues and water, oxidative status, biochemical markers | Cd, Hg | Liver, Brain |
|
Rashed, 2001(a) [31] |
Egypt |
Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis nilótica) |
440-1020/ ? | 50 | Tests (animal ages) | ? | Metals in tissues, water, sediment and aquatic plant | Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Sr, Zn | Liver, Gills, Muscle, Stomach, Intestine, Vertebral Column, Scales |
|
Rashed, 2001(b) [18] |
Egypt |
Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis nilótica) |
440-1020/ ? | 50 | Tests (animal ages) + Control | ? | Metals in tissues, water, sediment and aquatic plant | Pb, Cd | Liver, Gills, Muscle, Stomach, Intestine, Vertebral Column, Scales |
|
Elghobashy et al., 2001 [32] |
Egypt | Oreochromis niloticus | 150 ± 5/ ? | 30 | Tests (collection sites) + Control | Yes/ Summer | Metals in tissues, metals and physical-chemical parameters in water, oxidative status, biochemical markers | Fe, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd | Liver, Gills, Kidney, Muscle |
|
Adham et al., 2001 [33] |
Egypt | Oreochromis niloticus | 150 ± 16,0/ 14,00 ± 1,4 | 200 | Tests (collection sites) + Control | Yes/ Fall-Winter, Spring-Summer | Metals and physical-chemical parameters in water, histopathology, biochemical markers | Pb, Cu, Mn, Zn, Fe, Ni, Hg | Liver, Gills, Blood |
|
Youssef et al., 2004 [34] |
Egypt | Oreochromis spp/ Sarotherodon galilaues | O. niloticus: 60-431/ 14,5-27 S. galilaeus: 3,6-37,5/ 8,0-11,5O. oreus: 21-151,8/ 10.5-20 | ? | Tests (animal species) | ? | Metals in tissues | Cu, Zn, Fe, Mn, Cd | Liver, Gills, Kidney, Muscle, Brain, Gonad |
|
Al-Kahtani, 2009 [35] |
Arabia | Oreochromis niloticus | 40-60/ 12-19 | ? | Tests (collection stations) | Yes/ Fall, Winter, Spring, Summer | Metals in tissues, metals and physical-chemical parameters in water | Fe, Zn, Cu, Pb, Mn, Cd | Liver, Muscle |
|
Abdel-Baki et al., 2011 [36] |
Saudi Arabia |
Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis nilótica) |
?/ ? | 10 | Test | Yes/ Summer | Metals in tissues and water | Pb, Cd, Hg, Cu, Cr | Liver, Kidney, Intestine, Gills, Muscle |
|
Muisa et al., 2011 [37] |
Zimbabwe | Oreochromis niloticus | ?/ ? | ? | Tests (collection periods and sites) | Yes/ 2 periods | Metals in tissues, water and sediment | Al | Liver, Gills, Muscle, Kidney |
|
Abdel-Moneim et al., 2012(a) [38] |
Egypt | Oreochromis niloticus | 85-150/ 18-25 | 108 | Tests (collection sites) + Control | Yes/ ? | Metals in water, histopathology, oxidative status | Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, Zn, Cr, Hg, Co, Ni | Gills |
|
Abdel-Moneim et al., 2012(b) [39] |
Saudi Arabia | Oreochromis niloticus | 90-130/ 18-22 | 120 | Tests (collection sites) | Yes/ ? | Metals and physical-chemical parameters in water, histopathology | Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni, Cd, Pb, Cr, Co, Hg | Liver, Gills |
|
Cyrille et al., 2012 [40] |
Ivory Coast | Sarotherodon melanotheron | Juvenile: 15,1-15,8/ ? Adult: 19,5-25,0/ ? | 15 | Tests (juvenile and adult animals) | Yes/ Dry, Rainy, Swelling | Metals in tissues, water physical-chemical parameters | Cd | Liver, Gills, Muscle |
|
Carvalho et al., 2012 [41] |
Brazil | Oreochromis niloticus | 90-200/ 15-20 | 32 | Tests (collection stations) + Control | Yes/ Fall, Winter, Spring, Summer | Metals and physical-chemical parameters in water, oxidative status, biochemical markers | Cr, Cd, Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe | Liver, Gills, Muscle |
|
Coulibaly et al., 2012 [42] |
Ivory Coast | Sarotherodon melanotheron | ?/ ? | 60 | Tests (collection stations) | Yes/ Dry, Rainy, Swelling | Metals in tissues, water and sediment | Cd, Cu, Pb, Hg, Zn | Liver, Kidney, Muscle, Brain |
|
Abdel-Moneim et al., 2013a [43] |
Egypt | Oreochromis niloticus | 125-210/ 20-26 | 120 | Test + Control | Yes/ ? | Metals in tissues and water, oxidative status, histopathology | Cd, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn, Mn | Liver |
|
Abdel-Moneim, 2013b [44] |
Saudi Arabia | Oreochromis niloticus | 75-152/ 15-21 | ? | Tests (collection sites) + Control | Yes/ ? | Metals in water, histopathology | Ni, Fe, Zn, Co, Ba, Pb, Cu, Cd | Liver |
|
Jinadasa and Edirisinghe, 2014 [45] |
Sri Lanka | Tilapia sp | 216.6 ± 162,1/ 21,1 ± 4,0 | 80 | Tests (collection sites) | ? | Metals in tissues | Cd, Pb, Hg | Liver, Gills, Muscle |
|
Mohamed and Osman, 2014 [46] |
Sudan | Oreochromis niloticus | ?/ ~13 | ? | Tests (collection sites) | ? | Metals in tissues and water | Cd, Cr, Ni, Pb, Cu, Zn, Fe, Sr | Muscle, Gills |
|
Voigt et al., 2014 [47] |
Brazil | Geophagus brasiliensis | Male: 59,5-278,0/ 145-250 Female: 64,6-145,4/ 150-190 | Male:38 Female:17 | Tests (gender, weight and size of animals) | Yes/ Summer | Metals in tissues, water and sediment | Cu, Mn, Zn, Fe, Co, Cd, Cr, Ag, Ni | Liver, Gills, Muscle |
|
Abdel-Khalek, 2014 [48] |
Egypt | Oreochromis niloticus | 160-180/ 18,5-24,8 | 36 | Tests (collection sites) + Contol | Yes/ Summer | Metals in tissues and water, histopathology | Cu, Zn, Pb, Fe, Mn, Cd | Liver, Gills, Kidney, Muscle |
|
Abdel-Khalek, 2015 [49] |
Egypt | Oreochromis niloticus | 160-180/ 18,5-24,8 | 36 | Tests (collection sites) + Control | Yes/ Summer | Metals and physical-chemical parameters in water, oxidative status | Cu, Zn, Pb, Fe, Mn, Cd | Liver, Gills, Blood |
|
Ajima et al., 2015 [50] |
Nigeria |
Pelmatochromis guentheri/ Pelmatochromis pulcher |
35 ± 0,05/ ? | 18 | Tests (animal species) | ? | Metals in tissues, water and sediment | Pb, Zn, Cd, Cu, Fe | Gills, Muscle, Intestine |
|
Ruelas-Inzunza et al., 2015 [51] |
Mexico | Oreochromis aureus | Rainy station: 506,8 ± 100,5/ 30,9±2,4 Dry station: 563,4 ± 93,9/ 31,0±2,8 | 80 | Tests (collection stations) | Yes/ Dry, Rainy |
Metals in tissues | Hg | Liver, Muscle, Kidney |
|
Kumar et al., 2016 [52] |
India | Oreochromis mossambicus | ? | 54 | Tests (collection sites) | Yes/ ? | Metals in muscle, histopathology, oxidative status, biochemical markers | Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Cd, Hg, Pb | Liver, Gills, Kidney, Muscle, Brain, Gonad |
|
Mbewe et al., 2016 [53] |
Zambia |
Tilapia andersonii/ T. rendalli/ Oreochromis niloticus |
T.rendalli: 170-250/ ? O.niloticus: 150-300/ ?T.andersonii: 390/ ? | 3/ 4/ 3 | Tests (animal species and collection sites) | Yes/ ? | Metals in tissues and sediment | Cu, Cd, Pb, Mn, Cr, Ni, Fe | Liver, Gonads, Muscle, Intestines, Head. |
|
Doria et al., 2017 [54] |
Brazil | Geophagus brasiliensis | 148,8 ± 8,89/ 19,97 ± 2,87 | 55 | Tests (collection sites) | Yes/ Summer | Metals in tissues, histopathology, oxidative status, biochemical markers | Cu, Mn, Zn, Co, Cd, Cr, Ag, Pb, Ni, Al, As | Liver, Gills, Blood, Muscle, Brain |
|
Kumar et al., 2017 [55] |
India | Oreochromis mossambicus | ?/ ? | ? | Tests (collection sites) | Yes/ ? | Metals in tissues, water and sediment, oxidative status, biochemical markers | Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Cd, Hg, Pb | Liver, Gills, Kidney, Muscle, Brain, Gonad |
|
Muñoz-Nájera et al., 2018 [56] |
Mexico | Oreochromis niloticus | ?/ ? | 150 | Tests (collection periods) | Yes/ 5 periods | Metals in tissues, metals and physical-chemical parameters in water, biochemical markers | Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb | Liver, Muscle |
|
Pettamanna; Raghav; Nair, 2020 [57] |
Índia | Etroplus suratensis | 65,7-83,1/11-14,5 | 15 | Test + Control | Yes/Winter | Metals and physical-chemical parameters in water, histopathology, biochemical markers | Cu, Fe | Liver |
|
Martínez-Durazo et al., 2020 [58] |
Mexico |
Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis niloticus) Largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) |
461,8-619,6/26,98-34,51 45,1-1.182,0/30,17-40,10 |
21-30 21-30 |
Tests (animal species) | Yes/Dry and Rainy | Metals in tissues. | Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni,Zn | Liver, gills, stomach, gonads and muscle |
|
Salem et al., 2021 [59] |
Egypt |
Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis nilótica) |
80±5/17±2 | 16 males | Tests (collection sites) | Yesyear all | Metals in tissues, metals and physical-chemical in water, quantitative, biochemical markers Real-Time PCR. | Cd, Fe, Mn, Co e Pb | Liver |
|
Ngo et al., 2022 [1] |
Vietname |
common Carp (Cyprinus carpio), silver Carp (Hypothalmic molitrix), Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis niloticus) |
? | 240/240/240 | Tests (animal species) | Yes/four seasons | Metals in tissues and wate, oxidative status, biochemical markers. | Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd | Livers, kidneys, gills |
|
Páez-Osuna et al., 2022 [60] |
Mexico | Oreochromis aureus | 200-840/22.2-41.3 | 15 | Tests (collection periods) | Yes/spring | Metals in tissues, sediments, metals and physical-chemical parameters in water and risk assessment. | As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Se, Zn | Liver, muscle, and guts |
|
Vieira et al., 2023 [61] |
Brazil |
Tucunare (Cichla sp). Piraíba (Braquiplatystoma filamentosum) Jaraqui (Semaprochilodus sp) |
? | 10/10/10 | Tests (animal species) | ? | Metals in tissues, oxidative status, biochemical markers and bioinformatic. | Hg | Liver, muscle |
|
Martínez-Durazo et al., 2023 [6] |
Mexico |
Tilapia nilótica (Oreochromis niloticus) Largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides |
? | 20/20/20 | Tests (animal species) + control | Yes/Dry and Rainy | Metals in tissues, histopathology. | Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn Ni, Zn, As, Hg, Se. | Liver, gills, muscle, gonads |
|
Páez-Osuna, et al., 2023 [62] |
Mexico |
Carpa mon (Cyprinus carpio) Tilápia azul (Oreochromis aureus) Robalo (Micropterus salmoides) |
C.carpio 36,5-47/625/1.725 O. aureus 21-34/165-670 M. salmoides 24-38/170/740 |
7/22/16 | Tests (animal species) | ? | Metals in tissues, risk assessment. | As, Cd, Cu, Zn | Liver, gills, muscle, guts |
| Organ | Analyses | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | Histopathologies | Cell lesions and degenerations Circulatory changes Cell proliferative changes Ultramorphological changes |
| Oxidative stress | SOD: ↑, GPx: ↑, CAT: ↑, MDA:↑, GSH: ↑, GST: ↑, LPO: ↑, PC: ↑ SOD: ↓, GPx: ↓, CAT: ↓ | |
| Bioaccumulation | Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, Fe, Cr, Hg, Ni, Co, Ag, As, Se, Ba, Mo, Al | |
| Gill | Histopathologies | Cell proliferative changes Cell lesions and degenerations Circulatory changes Ultramorphological changes |
| Oxidative stress | SOD: ↑, GPx: ↑, CAT: ↑, MDA:↑, GSH: ↑, GST: ↑, LPO: ↑SOD: ↓, GPx: ↓, GSH: ↓, GR: ↓ |
|
| Bioaccumulation | Cd, Cu, Pb, Fe, Zn, Mn, Cr, Ni, Co, Ag, Hg, Al, Sr, As, Se, Ba, Mo |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





