1. Introduction
Plastic waste can be converted into different fuels or chemicals in order to generate value, and therefore reduce environmental pollution. Pyrolysis gained a lot attention in scientific and industrial branches as a promising technique for converting plastic waste into more valuable products, which gain economic value. However, it is still challenging to find an efficient pyrolysis process for commercial application [
1]. Pyrolysis is a thermal degradation process that takes place at temperatures between 300 and 900 °C in an inert atmosphere, with liquid oil as a mainly product [
2]. Polyolefin plastics decompose into heterogeneous products by a random-chain scission mechanism [
3,
4]. So, the wide range of products is produced on such a way, mostly linear paraffins and olefins. On the other hand, plastics, which have high viscosity and low heat transfer, produce more waxy products. Employment of catalysts reduces either the reaction temperature and time, as well as it lowers the activation energy of degradation (pyrolysis) and the boiling temperature. Therefore, the energy consumption is reduced and narrow ranged hydrocarbons are formed. Most common plastic waste streams contain HDPE, LDPE, PP, PS, PVC, and PET [
5]. In this investigation, Ahmad et al. studied the pyrolysis of polypropylene (PP) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) in a steel micro reactor, at different temperatures (250, 300, 350, and 400 °C) [
6]. PP oil yield increased as the temperature reached 300 °C (57.27% at 250 °C; 69.82% at 300 °C). On the other hand, further temperature rise caused oil yield to reduce (67.74% at 350 °C; 63.23% at 400 °C), by promoting secondary reactions (char formation). However, another study devoted to PP pyrolysis at temperatures of 300, 350 and 400 °C, in a 4.5 L steel batch reactor, showed an increase in the pyrolysis oil yield with increasing the temperature, with a maximum yield of 82.3% at 400 °C [
7]. Moreover, another study [
8], which examined the pyrolysis of PP at 450°C, 500°C, 550°C, and 600°C in a semi-continuous tubular reactor with sample of about 3 g, showed that the maximum oil yield is 97.6% at 450°C. A similar study [
9] investigated the pyrolysis of PP in a 1 L stirred semi-batch reactor shows maximum oil yield of 95.2 at 450°C, with 100 g sample and without the presence of a catalyst. On the other hand, Achilias et al. studied the pyrolysis of HDPE, LDPE and PP in a fixed bed reactor at 450 °C, with addition of FCC as catalysts [
10]. The results showed that the liquid oil yield from the PP pyrolysis at 450 °C without the presence of a catalyst is 49.3 wt%, while in the presence of FCC acting as a catalyst the liquid oil yield increased up to 67.3 wt%. Waste PP was pyrolyzed in a batch reactor at different temperatures (300, 350, 375 and 400 °C) with and without the FCC catalyst. The maximum oil yield was achieved in a thermal run at 400 °C [
11]: 83.3 wt%. In a review article by Vijayakumar and Sebastian [
12] summarized the pyrolysis potential of different types of plastics: it is generally confirmed that a temperature higher than 500°C leads to a decrease in pyrolysis oil.
Type of reactor, residence time, temperature, pressure, experimental conditions and feedstock are the most important factors that influence the pyrolysis process. Therefore, it is important to examine the limitations of the used unit in order to understand the most influencing parameters of the process [
13]. The influence of reactor temperature or, as it is often presented, the reaction temperature, on the yield and quality of pyrolysis products of various plastic materials has been relatively well investigated [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. However, by analyzing the published results, a significant variation in oil yield can be observed, even at the same or similar reaction temperatures, because each pyrolysis reactor or pyrolysis plant has different configuration, which influences the process products. Therefore, the effect of temperature on the distribution of pyrolysis products should be considered together with the influence of other process parameters, such as the carrier gas flow and the reaction time, the type of plastic, the composition of the plastic mixture and the effects due to the presence of a catalyst in order to evaluate their effect on the oil yield and its quality [
3,
19,
20,
21,
22].
Obviously, this result can be prescribed by different reactor designs, but what is missing and at the same time worth noting is that even with the same reactor designs, significant variations are possible in both the yield and quality of pyrolytic oil. In this study, it was assumed that different levels of reactor occupancy, expressed as the mass of raw material, will lead to pronounced non-uniformity of the temperature field inside the reactor, i.e., local overheating, which will lead to different yields and qualities of pyrolytic oil. Namely, the automatic temperature control of the reactor, trying to achieve the desired temperature in the layer of a raw material at the bottom of the reactor, performs overheating in the upper parts of the reactor, with a fixed layer [
16]. Namely, when the plastic melts, it descends towards the bottom of the reactor, leaving the middle part of the reactor free, thus causing overheating of this part in comparison with the bottom part of the reactor. The upper parts of the reactor are occupied by vapor phase, which in this case is overheated, leading to overcracking. In order to examine the aforementioned assumptions, to mathematically describe them, and quantify each of them, the Bex-Behnken design was used as a specific type of the Response Surface Methodology (RSM).
RSM is commonly applied in the description of various processes [
23,
24,
25,
26], especially in the description of pyrolysis of plastics [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
Pyrolysis was performed in a laboratory scale, fixed bed reactor at presented in
Figure 1. A washed and shredded polypropylene waste sample was placed in the reaction vessel (c), occupying approximately:
25% of reactor effective volume for 50 g feedstock mass;
50% of reactor effective volume for 100 g feedstock mass;
75% of reactor effective volume for 150 g feedstock mass.
Nitrogen was used as the inert gas (a). A gas-flow meter (b) was used to adjust the gas flow (100 ncm
3min
-1), and after 10 min, inert atmosphere was achieved. A PC (i) using CelciuX (EJ1N-TC4A-QQ) (Omron) thermal controller and CX-Thermo (Omron) were used for automatic control and regulation of the system (h) by turning on or off the electric heaters system (c) according to the control loop [
16,
18,
38,
39]. The T1 thermocouple measured the temperature at the bottom part of the reactor and served as a control sensor for the controlling loop of electric heaters i.e., as a control variable. The reactor temperature set point are 450, 475 and 500 °C. The time that feedstock spent on a set point temperature was considered to be a reaction time. After the chosen reaction time, the regulation system was turned off. As the reactor temperature fell below 100 °C, the reactor was taken apart and the reaction vessel was disconnected from the reactor (c). The reaction vessel was weighed before and after the occurrence of pyrolysis reaction and the solid residue was determined from the mass difference. The vessels for receiving condensate (f) were disconnected from the condensation system (e) and weighed as well, to determine the mass of condensable products, including the part of the condensate products mass from internal walls of the condensation system (e) [
18]. The reactor vessel is in the form of a vertical cylinder, whose sizes are 101.6×2 mm. The vessel consists of a body (lower part) and a body cover (upper part), with bolted flange joint with gaskets. The body is 200 mm high, representing a reaction vessel and it is separated from the upper part and serves as a dosing system. The design enables simple weighing of the raw material and solid residue after the process is completed, so that it is possible to set up the material balances relatively easily. A second cylindrical container is attached to the reactor body from the upper side - a cover with a total length of 40 mm. This cover carries three K-type thermocouples and three stainless steel tubes (A304) in which there are cartridge-electric heaters with a total power of 3×350 W. By connecting the cover to the reactor body, the electric heaters and thermocouples are placed in the reactor body. The heaters extend to the bottom of the reactor body, while three thermocouples are arranged in the reactor body, at different heights, as shown in
Figure 1. The thermocouples T1 (CH1) and T2 (CH2) are located: 7 and 90 mm from the bottom of the reactor body, respectively. The reactor is made of stainless steel (A304) and a 3 cm thick thermal insulation layer of stone wool is applied on the outer wall of the reactor. The reactor temperature changes were monitored at two characteristic points. All temperatures were measured by K-type thermocouples and recorded using CX-Thermo software package (Omron, Japan). Regulation of the operation of the heater, i.e., temperature control was performed using the temperature controller CelciuX (OMRON, Japan). Adjustment of the PID constants was carried out before the reaction started. In addition, the specified constants and other characteristic values in the regulation system were set by using the software. Inert gas flow was measured and regulated by a mass flow meter/regulator (MASS VIEW model MV-304 Mass Flow Regulator, Bronkhorst High-Tech BV, Nederland) with the measurement range 0.04 to 20 dm
3 min
-1 and the additional possibility of fine flow regulation. Nitrogen of 99.99 % purity was used as a carrier gas.
2.2. Design of an Experiment and Mathematical Modeling
Design of an experiment, development and assessment of mathematical models were performed using the BBD (Box-Behnken) type of the Response surface methodology (RSM), with support of Deign-Expert 11 software (Stat-Ease, Inc.). BBD is type of second-order designs based on three-level incomplete factorial designs. The following variables were used as independent variables: reactor temperature (Factor 1), feedstock mass (Factor 2) and reaction time (Factor 3). Liquid yield i.e., pyrolytic oil yield (Response 1) and rector solid residue (Response 2) were observed as dependent variables.
Table 1 presents the design of the experiments with the corresponding response measurement results. According to the used experimental design, a total of 16 experiments (design points), were carried out: i.e., 4 repetitions of the central point (475 °C; 100 g, 60 min) and 12 factorial points. This type of experimental design has proven to be reliable in testing the hypothesis of a complex interaction of 3 independent variables with minimal number of experiments. BBD design of experiment, but with different independent variables and waste plastic mixture as feedstock, was recently described [
32]. Moreover, Ore and Adebiyi [
33] chose a similar design of experiment and a related RSM in studying the effects of temperature, sample weight, and reaction time on the yield of non-condensable gases in the pyrolysis of waste tire in a fixed-bed reactor.
The models were developed by fitting numerical values of the Response 1 and Response 2 into corresponding equations, using method of the least squares.
The general form of a second-degree polynomial is:
where
Yiis the response (Response 2, Response 2);
Xi refers to dependent variables (A, B, C);
β0 is the constant coefficient;
β1,
β2 and
β3 are linear coefficients;
β12,
β13 and
β23are coefficients of interaction between the variables;
β11,
β22 and
β33 are quadratic coefficients, and e is the model error.
By selecting the BBD design, it was possible to test linear, two factor interaction (2FI) and quadratic equations, while cubic, and higher order equations in general, were aliased, i.e., there were not enough unique design points to estimate all the model coefficients that may result in contour plots with misleading shapes. Fit summary procedures (
Table 2) collect preliminary statistics about the tested polynomial models, which were used to identify the starting point for the final model, i.e., the model for further in-depth study. A preliminary selection of the tested models was carried out via Whitcomb Score, which uses the Sum of Squares p-value, Lack of Fit p-values, Adjusted and Predicted R-squared as parameters in a heuristic scoring system. The software labeled as “Suggested” the full-order model that met the criteria specified by Whitcomb Score. It was found that only the quadratic model describing the change of the pyrolytic oil yield (Response 1), and linear model describing the mass of solid residue (Response 2) could give significant values of all mentioned statistical parameters. Thus, the development and statistical proofing of these models are further described in this paper.
The statistical analysis of the developed mathematical models, i.e., the determination of their statistical significance, was conducted using the analysis of variance (ANOVA), i.e., the Fisher’s test (F-test), with alpha (significance) level of 0.05.
The analysis of variance determined the significance of the effect of each model parameter on the variance of the outcome, in comparison with the total variance of all the observed model parameters.
3. Results
The effects of independent variables (A, B, C) on the liquid yield (Response 1) and the reactor solid residue (Response 2) were examined using the values shown in
Table 1. The effects of the independent variables (A, B, C) on the liquid yield (Response) and the solid residue of the reactor (Response 2) were examined, through the numerical values shown in
Table 1. As far as the liquid yield is concerned, it can be seen that these effects are not linear, and that there are simultaneous interactions of several factors. For example, the highest liquid yield (66.54%) was obtained in run 6 (475 °C; 50 g; 60 min), which is slightly higher than the liquid yield (62.22%) obtained in run 3 (450 °C; 50 g; 60 min). However, one should keep in the mind that during the occurrence of run 3 the conversion in the reactor was incomplete due to very high solid residue in reactor, mainly consisted of unreacted plastic. On the other hand,
Table 1 shows that even with the same temperature, reaction time and quite similar solid residue, i.e., similar conversion of the reactor feed, significantly different liquid yields are obtained, only as a consequence of different feedstock mass. The most obvious examples of the former claim could be drawn from a simple pairwise comparison of run 3 vs. 4, or from a pairwise comparison of run 5 vs. 14 (
Table 1). Such a complex nature of the interaction of dependent variables justifies the application of RSM in the description of the mentioned phenomena. These interactions and their effects on liquid yield are described by a second order polynomial (equation 2 and 4) and related response surfaces (
Figure 2) and finally explained by temperature diagrams (
Figure 3, 4 and 5).
As for the effects of the dependent variables on response 2 (solid residual), the behavior of the system is clearer and expected, i.e., higher temperature, longer reaction time promote smaller amount of solid residue (higher reactor conversion rate). Therefore, such influences are described by a linear model (equations 3 and 5) without interaction factors (AB, AC, BC). In general, such a model could be developed with a less complex experimental design.
3.1. Models Development
By fitting the numerical values of Response 1 and Response 2 in the polynomials suggested by the
Table 2 the following empirical models were developed in terms of actual factors:
Liquid yield = –2339.348 + 8.889·T + 0,128·m + 10.041·t – 0.011·T·t – 0,005·m·t – 0.009·T
2 –
where T refer to the temperature (in °C), m refers to feedstock mass (in g), and t to the reaction time (in min). These equations can be used to make predictions about the response for given levels of each factor. Here, the levels should be specified in the original units for each factor. This equation should not be used to determine the relative impact of each factor because the coefficients are scaled to accommodate the units of each factor and the intercept is not at the center of the design space.
In order to compare the relative contributions of the independent variables to the dependent variables (Responses 1 and 2), it is convenient to express the independent variables in coded form. The coding law is given in
Table 3.
By fitting the numerical values of Response 1 and Response 2 into Equation 1, i.e., suggested equations from
Table 2, and expressing independent variables (A, B, C) in the coded form the fallowing empirical models were developed
Liquid yield = 57.51 - 2.55A - 7.62B + 5.09C - 0.6625AB - 4.17AC - 3.52BC - 5.48A² +
The equation in terms of the coded factors can be used to make predictions about the response for given levels of each factor. By default, the high levels of the factors are coded as +1 and the low levels are coded as -1. The coded equation is useful for identifying the relative impact of the factors by comparing the factor coefficients.
According to equation 4, i.e., the corresponding coefficients of factors A, B and C, it is obvious that the influence of factor B far exceeds factors A and C. This means that an increase in the reactor feed mass (B) leads to a relatively lower liquid yield than that caused by an increase in temperature (A) or reduction of reaction time (C). Usually such behavior is not expected. It is common sense to just leave enough time to allow complete conversion of a given mass of raw material at the chosen temperature, or to study temperature and time influence on some response of interests, which is common practice in many published studies [
14,
24,
30,
37].
The above statement is also proved by equation (5), from which it can be seen that a simple increase in temperature and reaction time leads to a decrease in the solid residue and finally to a minimal solid residue, i.e., a complete conversion of the raw material. In other words, the mass of the feedstock in the reactor does not affect the total conversion of the reactor at a given temperature and time, which excludes the possibility that the conversion itself affected the liquid yield. This is consistent with the conclusion that can be drawn from the previously described pairwise comparison (runs 3, 4, 5 and 14).
A fairly similar effect of feedstock mass on the yield of non-condensable gases in a fixed-bed reactor was observed in a tire waste pyrolysis study [
33]. A similar empirical model was developed and statistically confirmed. However, no further explanation of such behavior was given.
3.1.1. Statistical Testing
The developed models and all their coefficients were further proven by ANOVA (
Table 4) and general fit statistics (
Table 5).
Table 4 gives results of the Analysis of variance (ANOVA) regarding the developed empirical models (equation 4 and 5) determining the significance of the impact of each model parameter (A, B, C, AB, AC, BC, A2, B2) on the variance of results.
Based on the values of the statistical parameters shown in
Table 4 one can conclude that the quadratic model (equation 4) and the multilinear model (equation 5) are reliable in describing the relative influence of A, B and C on Response 1 and A, C on Response 2, respectively. Namely, the model F-value of 33.79 in case of Response 1 and Model F-value of 13.7 in case of Response 2 implies that the developed models are significant. There is only a 0.01% chance for Response 1 and 0.07% chance for response 2 that the F-values could occur due to noise. In general, P-values less than 0.0500 indicate that the model terms are significant. In case of Response 1 A, B, C, AC, BC, A², C² are the significant terms, while in case of response 2 these are A and C. Insignificant model terms (AB, and B
2) with respect to response 1 are not shown in the
Table 4. Generally, values greater than 0.1000 indicate that the model terms are not significant. The selection of the quadratic model for Response 1 is also supported by the Lack of fit test, according to which there is only an 14.77% % chance that such a large F-value of Lack of fit test due to noise could occur,
Furthermore, the values listed in
Table 5 support the significance of the selected models. Concerning Response 1, the Predicted R² of 0.7716 is in reasonable agreement with the Adjusted R² of 0.9387; i.e., the difference is less than 0.2. As far as Response 2 is concerned, the Predicted R² of 0.4514 is in reasonable agreement with the Adjusted R² of 0.6186; i.e., the difference is less than 0.2. The Parameter Adeq Precision measures the signal to noise ratio, being a ratio greater than 4 as desirable. In both cases the values of these parameter indicate an adequate signal. Thus, one can conclude that the developed models are reliable and can be used.
3.2. Response Surfaces and Contour Plots
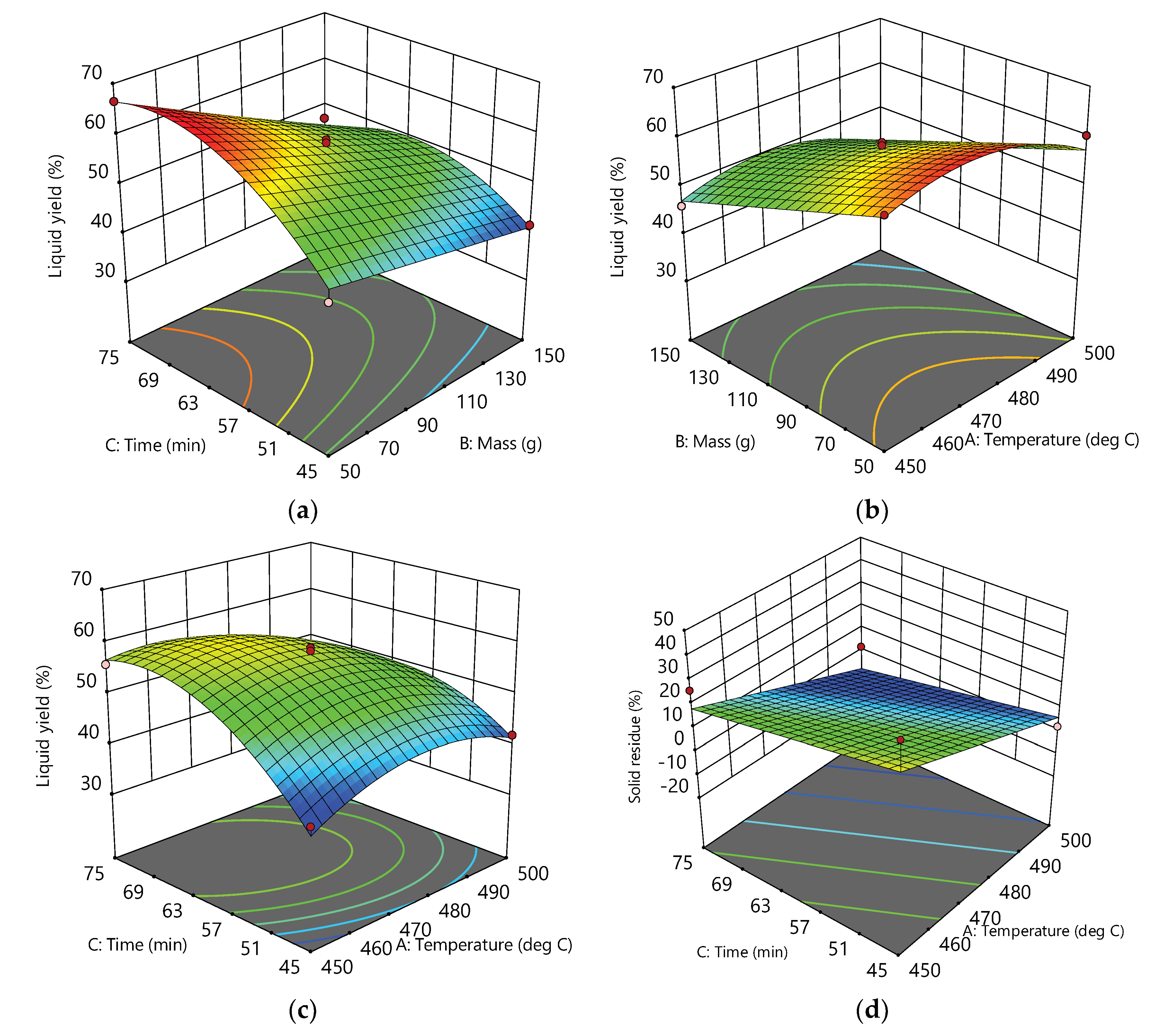
Graphical interpretations of the developed models are shown on
Figure 2. As it can been seen from the plots (a), (b) and (c), combined influence of the process variables i.e., factors A, B and C and their interaction performs a curvature of the plots surface. This clearly indicates the existence of a complex interaction among these factors. In all three diagrams and associated contours, the regions of the surfaces corresponding to the maximum liquid yield can be found. For example, from the plot (a) it can be seen that at a given temperature (475 °C) this area is in the range of 50-70 g of raw material mass, while the time is in the range of 57-75 min. Using the development equations, this yield can be further optimized by finding the best combination of factors to reach the maximum liquid yield.
On the other hand, the surface of the solid residue response graph is flat, or somewhat expected, which indicates that either the temperature and the time do not affect the total feed conversion in the reactor, that is, no influence on the amount of the solid residue. Alternatively, as it has already been emphasized, a simple increase in the temperature and reaction time leads to a decrease in the solid residue, and finally to a minimum solid residue.
3.3. Study of Temperature Diagrams
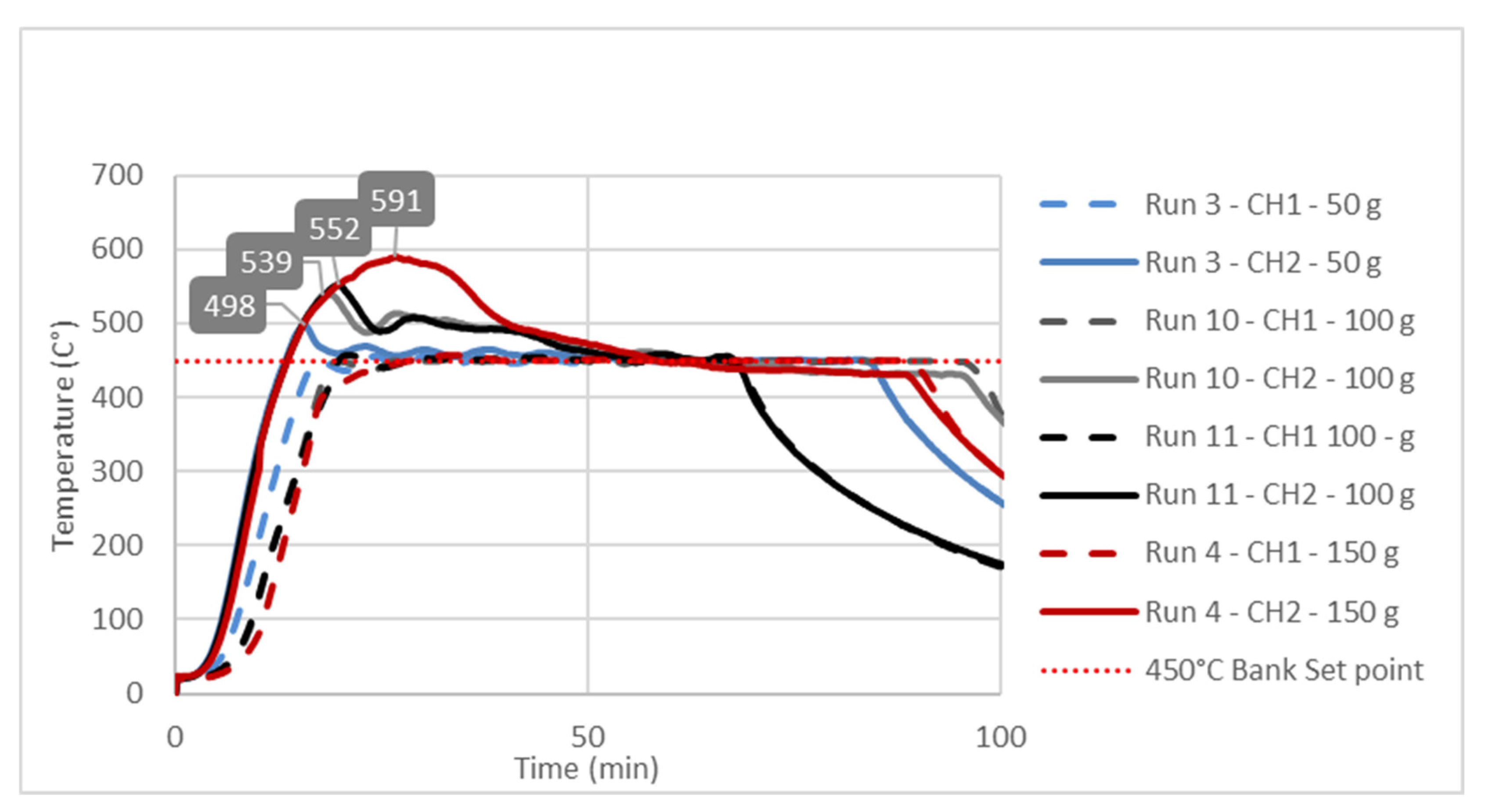
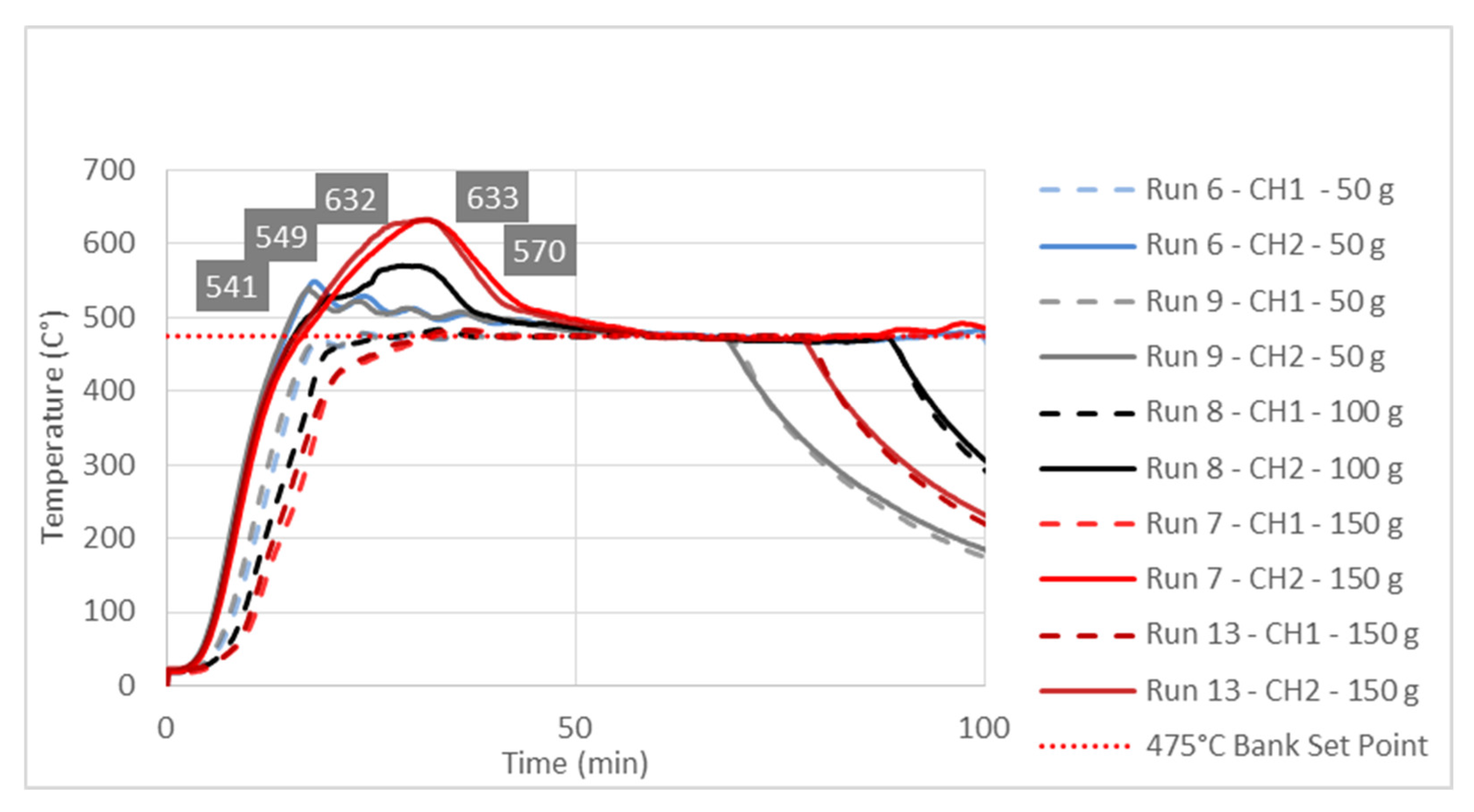
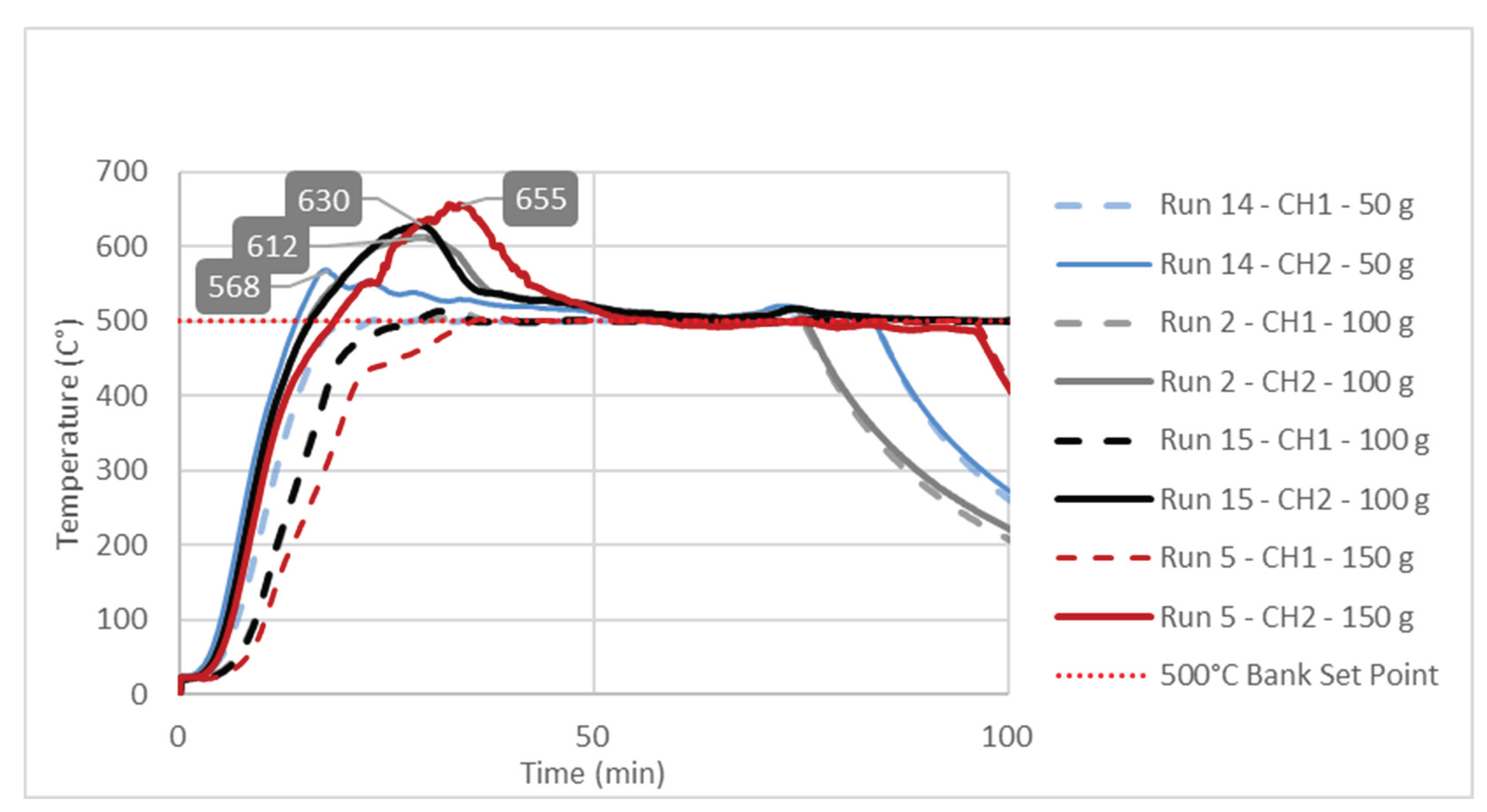
The observed significant effect of the factor B or feedstock mass on the Response 1 i.e., liquid yield could be explained by studying temperature change at characteristic point inside reactor during pyrolysis process. Temperature diagrams on
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 show simultaneous temperature changes at the bottom of the reactor (CH1), and in the middle part of the reactor (CH2), during the pyrolysis process at the preset bank temperatures of 450, 475 and 500 °C, respectively.
From all three diagrams it is clearly observed that at bottom part of the reactor (dashed lines corresponding to CH1 temperatures) the desired temperature almost ideally is reached. Certainly, this is the consequence of the suitable PID temperature control loop, based on the temperature probe located at the bottom of the reactor. On the other hand, in all cases the temperatures in the middle part of the reactor, whose trendlines correspond to CH2 temperatures, far exceed the preset temperatures (Bank Set Point). This excessive exceeding of the preset temperature is as more evident as the feedstock mass in the reactor is higher. In all three diagrams the highest excessive exceeding temperatures were observed during the experiments with the reactor loaded with 150 g of feedstock, while the lowest excessive exceeding temperatures are observed in those experiments with a minimum reactor loading: i.e., 50 g of feedstock mass. Namely, the temperature control loop, trying to achieve the desired temperature in the layer of the raw material at the bottom of the reactor, causes overheating in the upper parts of the reactor with a feedstock fixed layer [
16]. The upper parts of the reactor are occupied by the vapor phase, which in this case is overheated, leading to its overcracking, and consequently reducing the pyrolysis oil yield. The temperature profile and the related heat transfer are decisive factors that determine the effective reactor performance, being the thermal craking the most important step in producing the pyrolysis oil [
40,
41,
42].
Since the most heat demanding (endothermic) process takes place in the lower part of the reactor, the heating and evaporation of molten plastic is a common practice to monitor and control the temperature in that part. However, this leads to overheating and excessive cracking of the steam in the upper sections occupied only by the pyrolysis vapors, as seen in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. By considering all these aspects, this means that if the temperature in the middle section of the fixed bed reactor is not monitored, different yields of the liquid for apparently the same temperature, i.e., temperature at the bottom of the reactor, are achieved. In general, such practice leads to uncertainty in the results, especially compared to other studies, which usually involve different masses of the raw material, different filling volume of the reactor and, in general, different reactor settings.
As this study demonstrates, complex temperature changes can occur in the vapor phase only as a consequence of the mass of the raw material, i.e., the different reactor occupancy and the related non-uniformity of the temperature field in the fixed bed reactor. In order to achieve a uniform temperature field within a fixed bed reactor, and thus a more consistent and comparable liquid yield, it is of utmost importance to develop even a more complex and precise temperature control. This temperature control should consist of at least two independent temperature control loops, one located close to the bottom and one close to the middle part of the reactor.
4. Conclusions
The effects of feedstock mass, temperature and time were analyzed during the occurrence of a plastic pyrolysis process in a fixed bed reactor in terms of liquid yield.
By means of the RSM methodology mathematical model that describe these effects are developed. Significance of the developed models and all it terms are proved by statistic tests.
A developed second-order polynomial equation shows that there is a complex interaction among the feedstock mass, the temperature and time on pyrolysis oil yield. The developed multi-linear model shows that either the temperature and time influence the yield of solid residue, while the mass of the raw material does not have such an influence.
The effect of feedstock mass far exceeds influence of the time and mass on the liquid yield in the fixed bed pyrolysis of waste plastic. This influence could be explained by studying the temperature change at the bottom and middle part of the fixed bed reactor.
The recorded temperature diagrams show that with greater masses of feedstock, local overheating occurs in the middle part of the reactor, which leads to overcracking of vapor products, and consequently to an increased formation of non-condensable gases, thus reducing the yield of pyrolytic oil.
In the near future, our efforts will be focused on proving how this advanced control loop leads to a significantly higher liquid yield, with negligible overheating, i.e., with a uniform reactor temperature field.
In this research, we used polypropylene only as a model sample, representing any other plastic waste. Namely, the observed findings would be the same for all other types of plastic materials because we proved that the thermal behavior of the system is dominantly influenced by the mass of the raw material in combination with the developed temperature control system and the associated heating of the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P. and S.V.C; methodology, S.P. and S.V.C; software, S.P.; validation, S.P., S.V.C. and M.D.; formal analysis, S.P. and J.D.; investigation, S.P., J.D, M.D.; resources, S.P.; data curation, S.P., S.V.C., M.D; writing—original draft preparation, S.P., S.V.C., M.D.; writing—review and editing, S.P., S.V.C., M.D.; visualization, S.P., S.V.C., M.D supervision, S.P., S.V.C.; project administration, S.P.; funding acquisition, S.P., J.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dai, L.; Zhou, N.; Lv, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cobb, K.; Chen, P.; Lei, H.; Ruan, R. Pyrolysis technology for plastic waste recycling: A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 93, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miandad, R.; Rehan, M.; Barakat, M.A.; Aburiazaiza, A.S.; Khan, H.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Dhavamani, J.; Gardy, J.; Hassanpour, A.; Nizami, A.-S. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Plastic Waste: Moving Toward Pyrolysis Based Biorefineries. Front. Energy Res. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuga, S.; Djurdjevic, M.; Ciccioli, A.; Ciprioti, S.V. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Plastic Waste and Molecular Symmetry Effects: A Review. Symmetry 2022, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouvoudi, E.C.; Rousi, A.T.; Achilias, D.S. Effect of the catalyst type on pyrolysis products distribution of polymer blends simulating plastics contained in waste electric and electronic equipment. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, S.H.; Sendeku, M.G.; Bahri, M. Recent Trends in the Pyrolysis of Non-Degradable Waste Plastics. ChemistryOpen 2021, 10, 1202–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, H.; Ishaq, M.; Tariq, R.; Gul, K.; Ahmad, W. Pyrolysis Study of Polypropylene and Polyethylene Into Premium Oil Products. Int. J. Green Energy 2014, 12, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebe, J.; Kryzevicius, Z.; Majauskiene, R.; Dulevicius, M.; Kosychova, L.; Zukauskaite, A. Use of polypropylene pyrolysis oil in alternative fuel production. Waste Manag. Res. J. a Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2022, 40, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafar, Y.; Abdelouahed, L.; El Hage, R.; El Samrani, A.; Taouk, B. Pyrolysis of common plastics and their mixtures to produce valuable petroleum-like products. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 195, 109770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas-Abadi, M.S.; Haghighi, M.N.; Yeganeh, H.; McDonald, A.G. Evaluation of pyrolysis process parameters on polypropylene degradation products. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 109, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilias, D. Recycling techniques of polyolefins from plastic wastes. Glob. NEST: Int. J. 2013, 10, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisien, E.T.; Otuya, I.C.; Aisien, F.A. Thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of waste polypropylene plastic using spent FCC catalyst. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Sebastian, J. Pyrolysis process to produce fuel from different types of plastic – a review. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 396, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Antelava, A.; Constantinou, A.; Manos, G.; Dutta, A. A review on thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of plastic solid waste (PSW). J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Abdullah, N.; Novianti, A.; Hakim, I.I.; Putra, N.; A Koestoer, R. Influence of temperature on conversion of plastics waste (polystyrene) to liquid oil using pyrolysis process. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 105, 12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar Sharuddin, S.D.; Abnisa, F.; Wan Daud, W.M.A.; Aroua, M.K. A review on pyrolysis of plastic wastes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurdjevic, M.; Papuga, S.; Kolundzija, A. Analysis of the thermal behavior of a fixed bed reactor during the pyrolysis process. Chem. Ind. 2023, 24–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maafa, I.M. Pyrolysis of Polystyrene Waste: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papuga, S.V.; Gvero, P.M.; Vukić, L.M. Temperature and time influence on the waste plastics pyrolysis in the fixed bed reactor. Therm. Sci. 2016, 20, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.; Cafiero, L.; De Angelis, D.; Tuffi, R.; Ciprioti, S.V. Valorization of the plastic residue from a WEEE treatment plant by pyrolysis. Waste Manag. 2020, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsella, E.; Aguado, R.; De Stefanis, A.; Olazar, M. Comparison of catalytic performance of an iron-alumina pillared montmorillonite and HZSM-5 zeolite on a spouted bed reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 130, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchi, M.; De Angelis, D.; Mazzeo, L.; Nardozi, P.; Piemonte, V.; Tuffi, R.; Ciprioti, S.V. Catalytic Pyrolysis of a Residual Plastic Waste Using Zeolites Produced by Coal Fly Ash. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaal, R.M.; Abdulaaima, D.A. Valuable oil recovery from plastic wastes via pressurized thermal and catalytic pyrolysis. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2023, 20, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-Z.; Li, B.-X.; Wu, H.; Shao, W. Multi-objective shape optimization of double pipe heat exchanger with inner corrugated tube using RSM method. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 90, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Salmah, S.; Sanusi, M.; Yuhazri, M.; Mohamad, N.; Azam, M.A.; Abdullah, Z.; Mohamad, E. Surface Roughness Optimization in Drilling Process Using Response Surface Method (RSM). J. Teknol. 2014, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M. J.K.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Aziz, S.Q.; Aun, N.C. , Sethupathi, S. Wastewater Treatment Processes Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Compared with Conventional Methods: Review and Comparative Study. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 2015, 23 (2), 244-252.
- Said, K.A.M.; Amin, M.A.M. Overview on the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) in Extraction Processes. J. Appl. Sci. Process. Eng. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, N.; Mondal, P.; Gupta, A. Optimization of process parameters using response surface methodology for maximum liquid yield during thermal pyrolysis of blend of virgin and waste high-density polyethylene. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R. Optimization of process parameters by response surface methodology (RSM) for catalytic pyrolysis of waste high-density polyethylene to liquid fuel. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.-L.; Tan, G.-Y.A.; Wang, J.-Y. Enhanced styrene recovery from waste polystyrene pyrolysis using response surface methodology coupled with Box–Behnken design. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.; Paradela, F.; Gulyurtlu, I.; Ramos, A.M. Prediction of liquid yields from the pyrolysis of waste mixtures using response surface methodology. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 116, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaganapathy, T.; Muthuvelayudham, R.; Jayakumar, M. Process parameter optimization study on thermolytic polystyrene liquid fuel using response surface methodology (RSM). Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 26, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, F.; Rasul, M.G.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Jahirul, I. Optimisation of Process Parameters to Maximise the Oil Yield from Pyrolysis of Mixed Waste Plastics. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ore, O.T.; Adebiyi, F.M. Process modelling of waste tyre pyrolysis for gas production using response surface methodology. Unconv. Resour. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonglhueng, N.; Sirisangsawang, R.; Sukpancharoen, S.; Phetyim, N. Optimization of iodine number of carbon black obtained from waste tire pyrolysis plant via response surface methodology. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada, L.; Pérez, A.; Godoy, V.; Peula, F.; Calero, M.; Blázquez, G. Optimization of the pyrolysis process of a plastic waste to obtain a liquid fuel using different mathematical models. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 188, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirawan, R.P.; Farizal Plastic Waste Pyrolysis Optimization to Produce Fuel Grade Using Factorial Design. In Proceedings of The 4th international conference on energy, environment, epidemiology and Information System (ICENIS 2019), E3S Web Conference, 28 October 2019. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 125, 13005. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Aguilar, A.M.; Cabrera-Madera, V.P.; Vera-Rozo, J.R.; Riesco-Ávila, J.M. Effects of Heating Rate and Temperature on the Thermal Pyrolysis of Expanded Polystyrene Post-Industrial Waste. Polymers 2022, 14, 4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuga, S.; Djurdjevic, M.; Tomović, G.; Ciprioti, S.V. Pyrolysis of Tyre Waste in a Fixed-Bed Reactor. Symmetry 2023, 15, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, I.; Tomić, T.; Katančić, Z.; Erceg, M.; Papuga, S.; Vuković, J.P.; Schneider, D.R. Catalytic pyrolysis of mechanically non-recyclable waste plastics mixture: Kinetics and pyrolysis in laboratory-scale reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartulistiyoso, E.; Sigiro, F.A.; Yulianto, M. Temperature Distribution of the Plastics Pyrolysis Process to Produce Fuel at 450oC. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Cho, Y.-J.; Song, P.-S.; Kang, Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, M.-J. Effects of temperature distribution on the catalytic pyrolysis of polystyrene waste in a swirling fluidized-bed reactor. Catal. Today 2003, 79-80, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyono, M.S.; Fenti, U.I. Influence of Heating Rate and Temperature on the Yield and Properties of Pyrolysis Oil Obtained from Waste Plastic Bag. Conserv. J. Energy Environ. Stud. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).