Submitted:
03 April 2024
Posted:
04 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
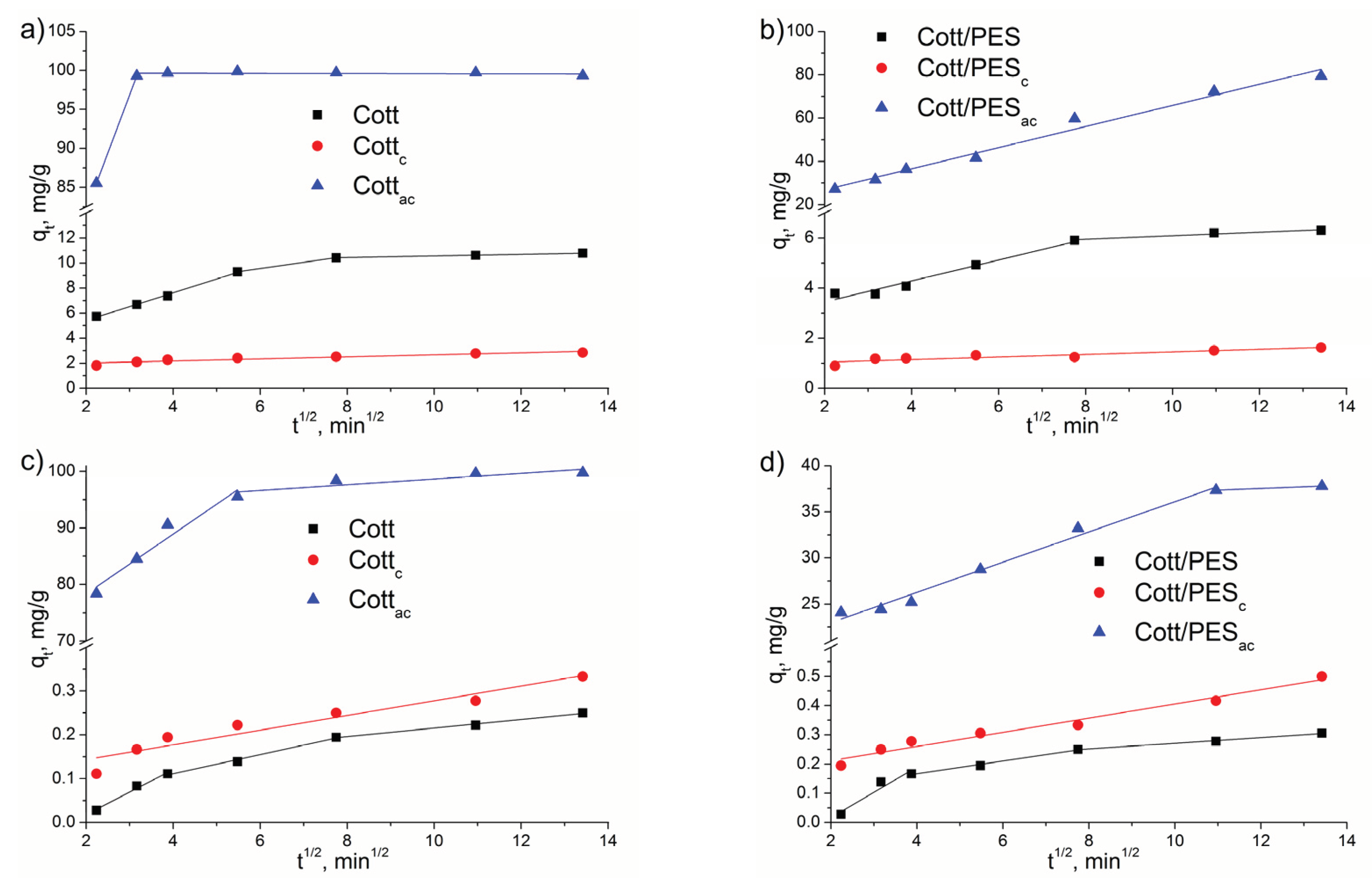
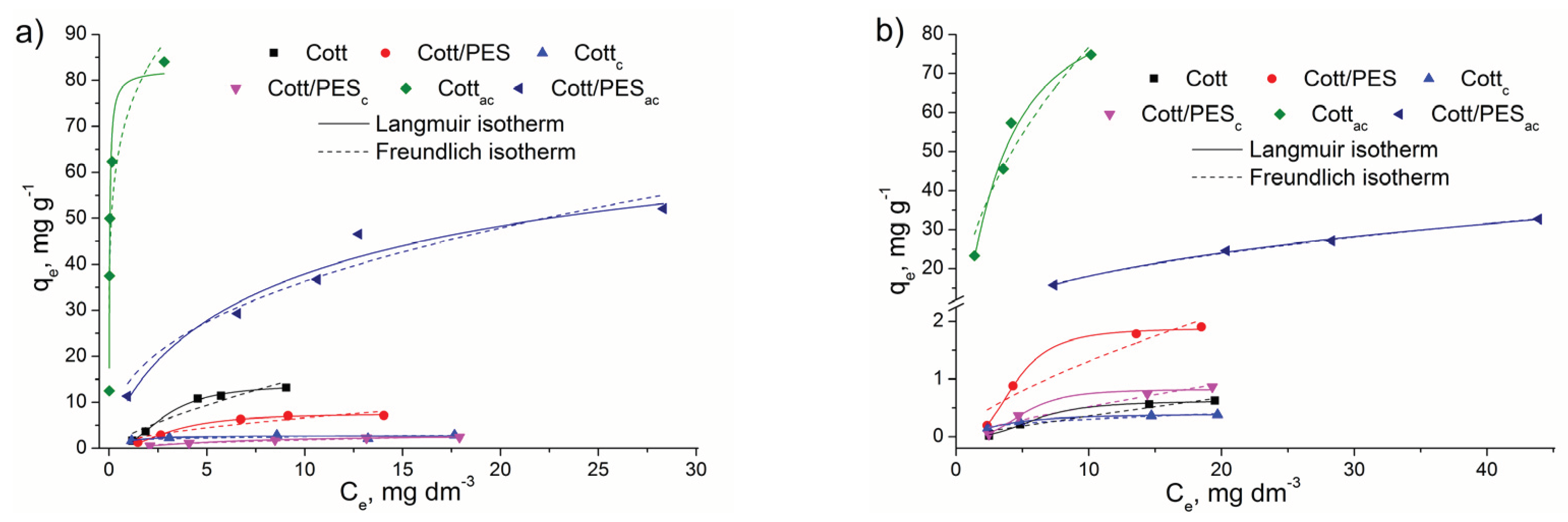
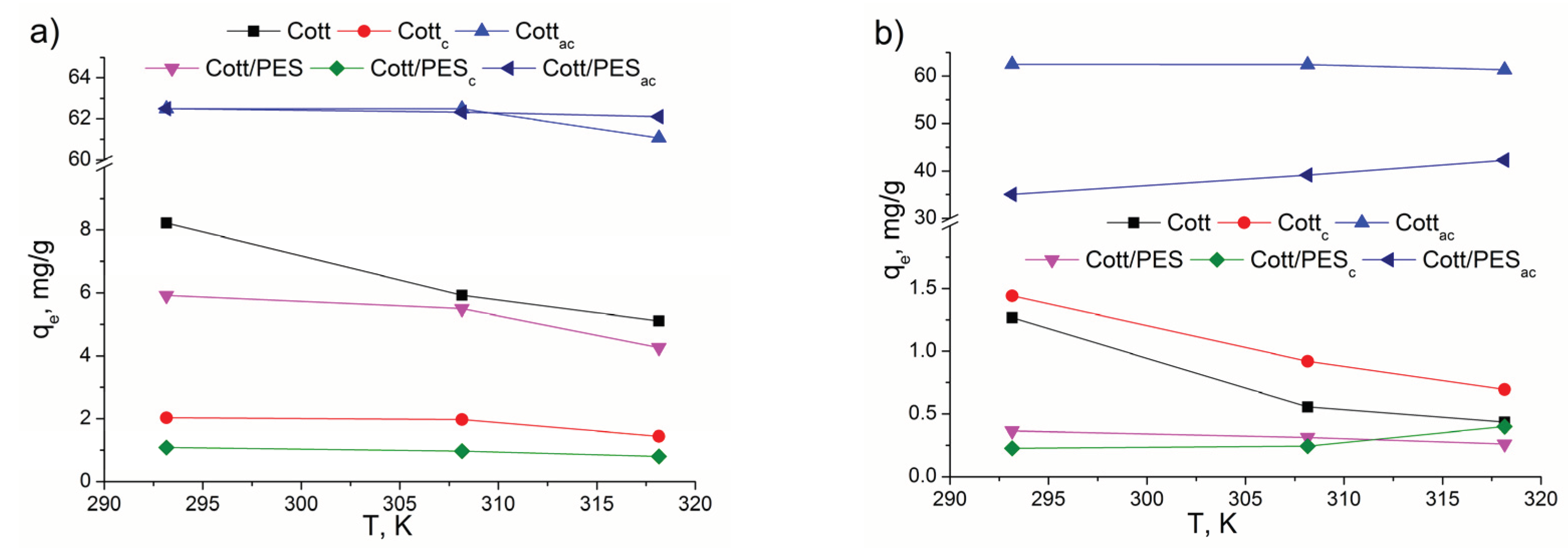
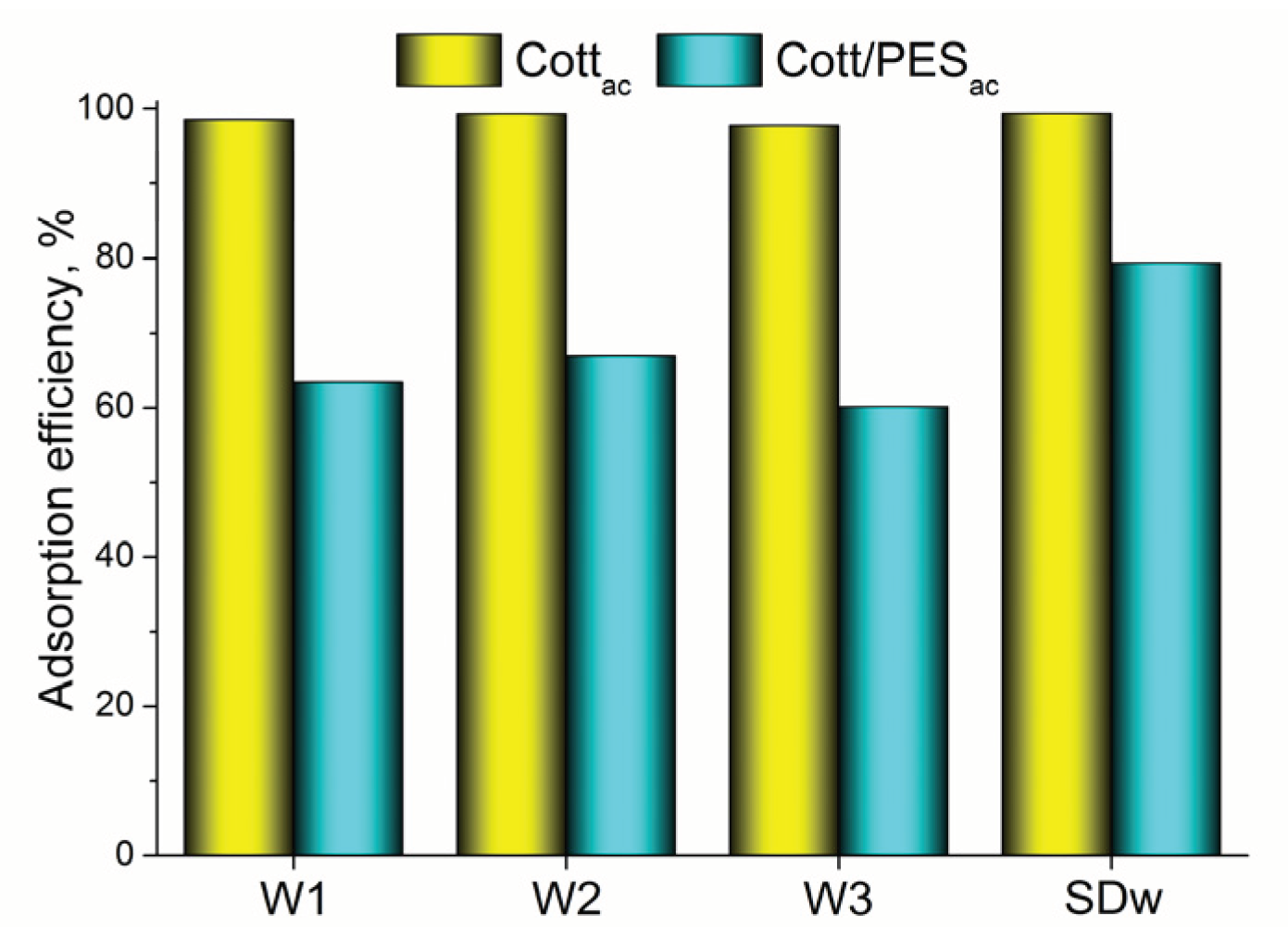
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Characterization
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaylarde, C.; Baptista-Neto, J.A.; Monteiro da Fonseca, E. Plastic microfibre pollution: how important is clothes’ laundering? Heliyon 2021, 7, e07105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaria, G.; Achtypi, A.; Perold, V.; Lee, J.R.; Pierucci, A.; Bornman, T.G.; Aliani, S.; Ryan, P.G. Microfibers in oceanic surface waters: A global characterization. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, M.; Som, C. Identifying the potential for circularity of industrial textile waste generated within Swiss companies, Resour. Conser. Recy. 2022, 182, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummino, M.L.; Varesano, A.; Copani, G.; Vineis, C. A Glance at Novel Materials, from the Textile World to Environmental Remediation. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 2826–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briga-Sá, A.; Nascimento, D.; Teixeira, N.; Pinto, J.; Caldeira, F.; Varum, H.; Paiva, A. Textile waste as an alternative thermal insulation building material solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Behera, B.; Militky, J. Recycling of textile waste into green composites: performance characterization. Polym. Composite 2014, 35, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.S.; Siddiqua, S.; Cherian, C. Sustainable applications of textile waste fiber in the construction and geotechnical industries: a retrospect. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 6, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z. Solvent-free synthesis of carboxylate-functionalized cellulose from waste cotton fabrics for the removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions. Cellulose 2014, 21, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihajlović, S.; Vukčević, M.; Pejić, B.; Perić, G.A.; Ristić, M. Application of waste cotton yarn as adsorbent of heavy metal ions from single and mixed solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2020, 27, 35769–35781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gu, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qi, R.; Chen, W. Synthesis of char-based adsorbents from cotton textile waste assisted by iron salts at low pyrolysis temperature for Cr(VI) removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2020, 27, 11012–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihajlović, S.; Vukčević, M.; Pejić, B.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Ristić, M.; Trivunac, K. Waste Cotton and Cotton/Polyester Yarns as Adsorbents for Removal of Lead and Chromium from Wastewater. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 19, 9860–9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, P.S.; Spessato, L.; Crespo, L.H.S.; Yokoyama, J.T.C.; Fonseca, J.M.; Bedin, K.C.; Ronix, A.; Cazetta, A.L.; Silva, T.L.; Almeida, V.C. Activated carbon fibers prepared from cellulose and polyester–derived residues and their application on removal of Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 289, 111150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, F.; Zhang, S.; Xv, H.; Xv, Z. Development of porosity and surface chemistry of textile waste jute-based activated carbon by physical activation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2018, 25, 9840–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed Jamaludin, S.I.; Ahmad Zaini, M.A.; Sadikin, A.N.; Abdol Jani, W.N.F. Textile waste valorization as potential activated carbon precursor for the removal of water contaminants: Commentary. Mater. Today: P. 2024, 96, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Adsorption in solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 384–410. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. Zur the orieder sogennanten adsorption geloester stoffe, Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solutions. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civil. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, C.; Ungarish, M. Kinetics of activated chemisorption. Part 1.—The non-elovichian part of the isotherm. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1. 1976, 72, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivunac, K.; Vukčević, M.; Maletić, M.; Karić, N.; Pejić, B.; Perić-Grujić, A. Waste materials as adsorbents for heavy metals removal from water: comparative analysis of modification techniques. Tekstilna industrija 2023, 71, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukčević, M.; Maletić, M.; Karić, N.; Pejić, B.; Trivunac, K.; Perić Grujić, A. Cellulose-based waste structure and chemical composition impact on the adsorption of pharmaceuticals. Tekstilna industrija 2023, 71, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Yoo, D.I.; Shin, Y.; Seo, G. FTIR analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ming, R.; Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Shao, H. Influence of alkali treatment on flax fiber for use as reinforcements in polylactide stereo complex composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbass, A.; Paiva, M.C.; Oliveira, D.V.; Lourenço, P.B.; Fangueiro, R. Insight into the Effects of Solvent Treatment of Natural Fibers Prior to Structural Composite Casting: Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Evaluation. Fibers 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portella, E.H.; Romanzini, D.; Coussirat Angrizani, C.; Campos Amico, S.; José Zattera, A. Influence of Stacking Sequence on the Mechanical and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Cotton/Glass Fiber Reinforced Polyester Composites. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.A. Evaluation of the flammability and thermal properties of a new flame retardant coating applied on polyester fabric. Egypt. J. Petrol. 2016, 25, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukčević, M.M.; Maletić, M.M.; Pejić, B.M.; Karić, N.V.; Trivunac, K.V.; Perić Grujić, A.A. Waste hemp and flax fibers and cotton and cotton/polyester yarns for removal of methylene blue from wastewater: Comparative study of adsorption properties. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2023, 88, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalijadis, A.; Ðorđević, J.; Trtić-Petrović, T.; Vukčević, M.; Popović, M.; Maksimović, V.; Rakočević, Z.; Laušević, Z. Preparation of boron-doped hydrothermal carbon from glucose for carbon paste electrode. Carbon 2015, 95, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P. On validity, physical meaning, mechanism insights and regression of adsorption kinetic models. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376, 121416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, L.; Forte, M.; Rossi, A.; Adamo, C.; Rossi, S.; Mita, D.G.; Guida, M.; Portaccio, M.; Godievargova, T.; Yavour, I.; Samir, M.; Eldin, M. Removal of 17-α Ethinylestradiol from water systems by adsorption on polyacrylonitrile beads: isotherm and kinetics studies. Peertechz. J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions with multi-walled carbon nanotubes: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Salehi, E. Adsorption of cations on nanofiltration membrane: Separation mechanism, isotherm confirmation and thermodynamic analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bery, H.M.; Saleh, M.; El-Gendy, R.A.; Saleh, M.R.; Thabet, S.M. High adsorption capacity of phenol and methylene blue using activated carbon derived from lignocellulosic agriculture wastes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah Omer, A.; El Naeem, G.A.; Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; Farahat, O.O.M.; El-Bardan, A.A.; Soliman, H.M.A.; Nayl, A.A. Adsorption of crystal violet and methylene blue dyes using a cellulose-based adsorbent from sugercane bagasse: characterization, kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
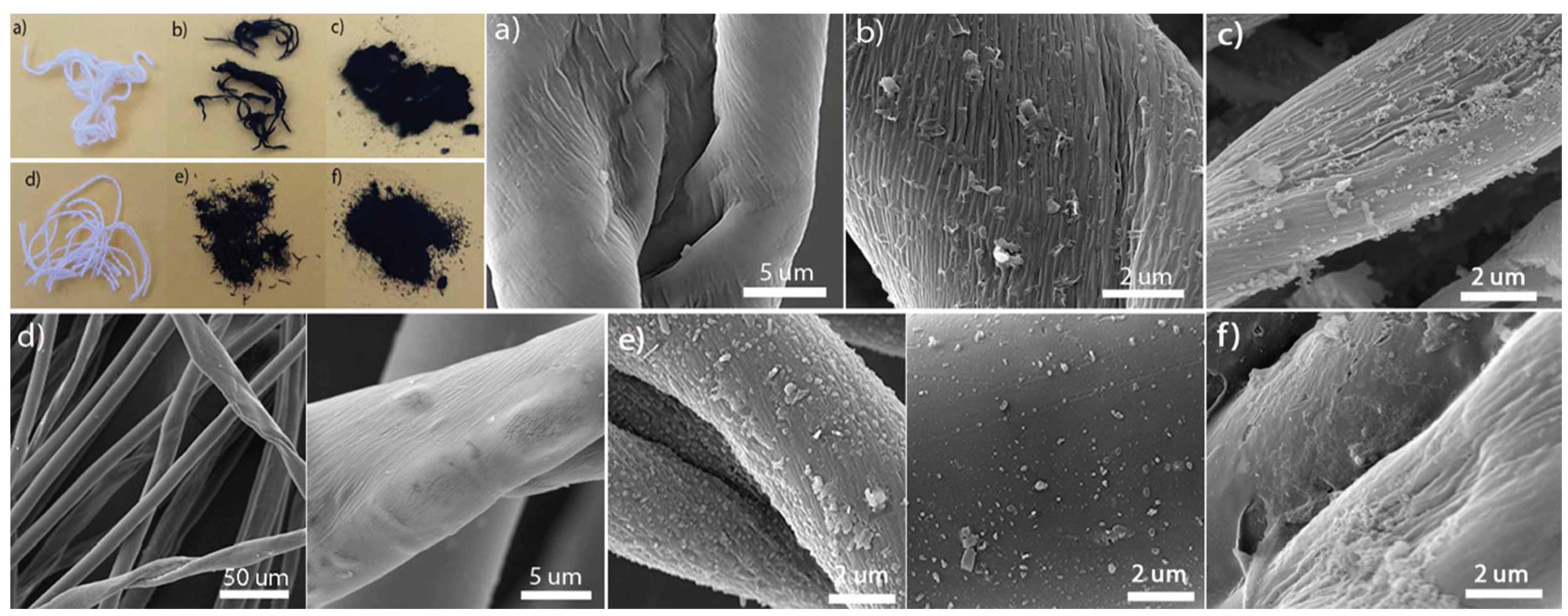
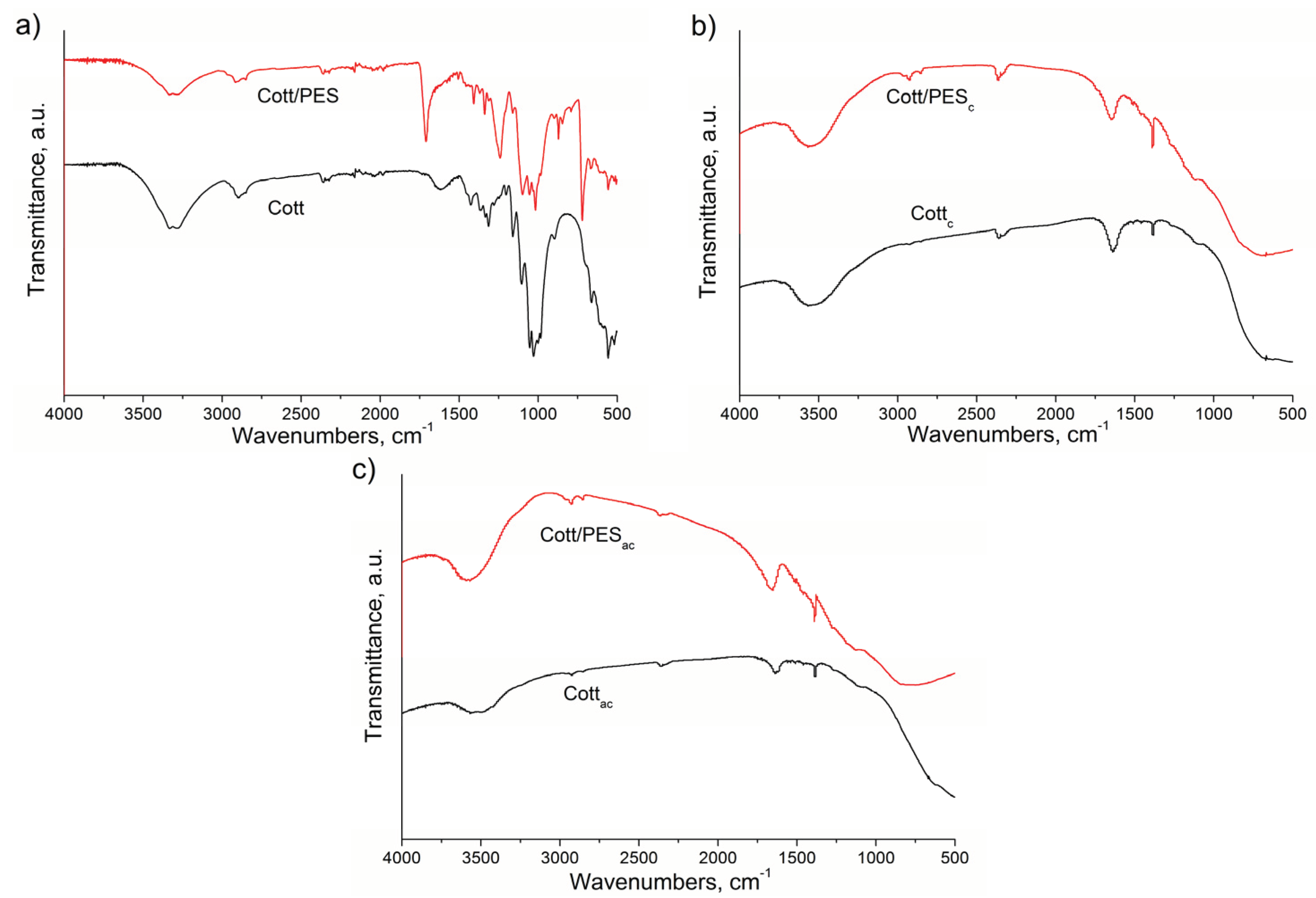
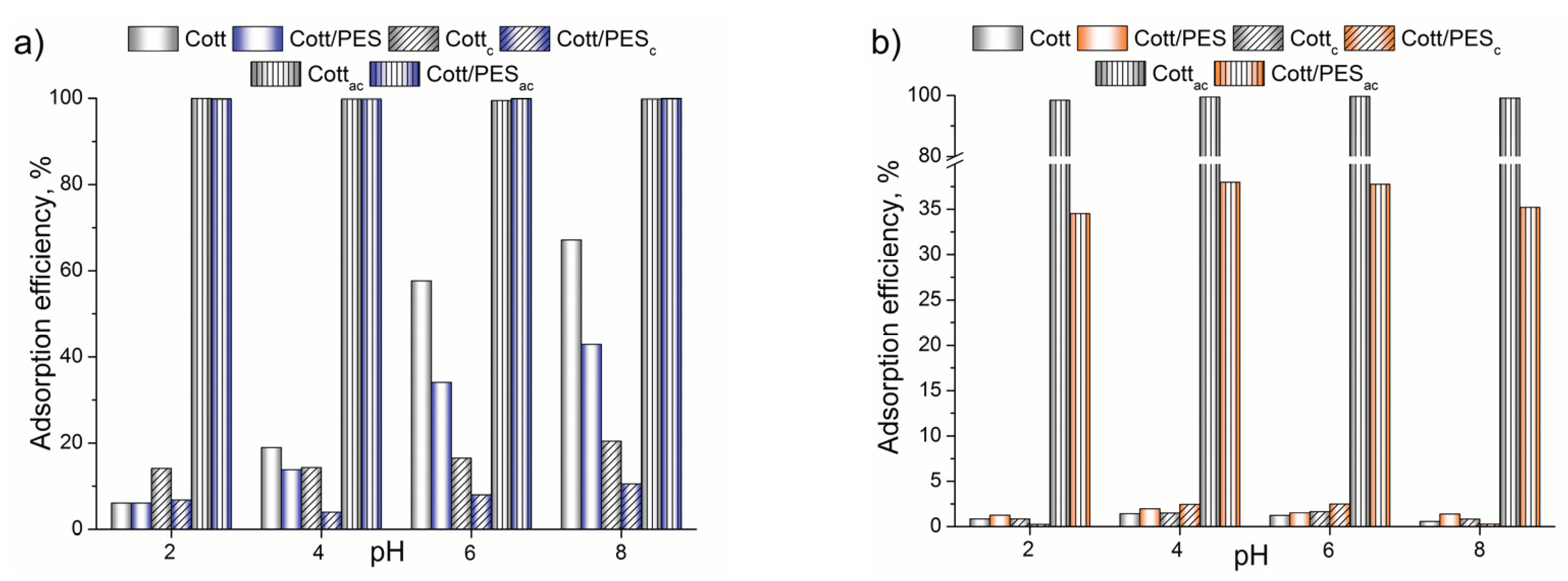
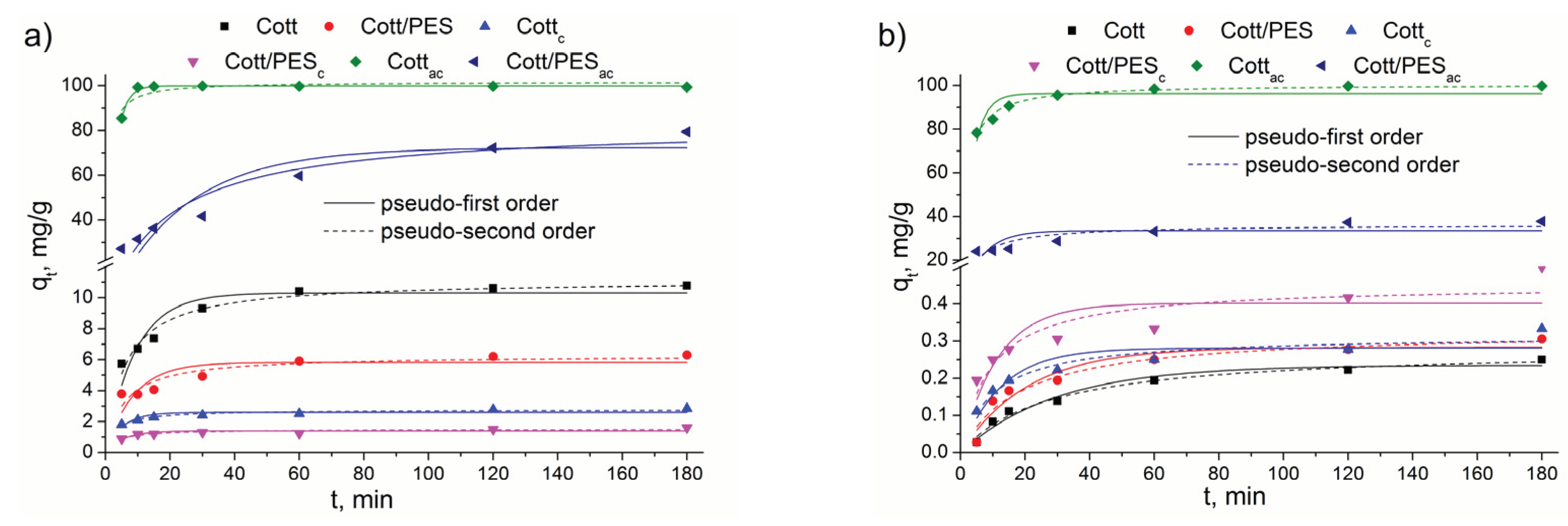
| Sample | SBET, m2/g | Sext, m2/g | Smicro, m2g−1 | Vtotal, cm3 g−1 | Vmicro, cm3 g−1 | Dm, nm | pHPZC |
| Cottc | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.001 | - | 8.71 |
| Cott/PESc | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 8.19 |
| Cottac | 885.8 | 222.5 | 663.3 | 0.518 | 0.359 | 4.57 | 5.11 |
| Cott/PESac | 913.1 | 157.0 | 756.1 | 0.511 | 0.404 | 4.07 | 6.43 |
| Dye | Sample | Cott | Cottc | Cottac | Cott/PES | Cott/PESc | Cott/PESac |
| Langmuir isotherm | |||||||
| MO | Q0, mg g−1 | 0.623 | 0.398 | 90.63 | 1.884 | 0.824 | 140.23 |
| MB | 13.91 | 2.637 | 82.57 | 7.555 | 2.813 | 79.45 | |
| MO | b | 0.004 | 0.142 | 0.217 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.048 |
| MB | 0.080 | 1.329 | 27.93 | 0.076 | 0.071 | 0.157 | |
| MO | R2 | 0.98528 | 0.99836 | 0.94448 | 0.99373 | 0.95600 | 0.99356 |
| MB | 0.99607 | 0.25795 | 0.93757 | 0.99396 | 0.99950 | 0.92797 | |
| Freundlich isotherm | |||||||
| MO | Kf,mg1−1/nL1/ng−1 | 0.042 | 0.126 | 24.52 | 0.253 | 0.078 | 7.192 |
| MB | 2.859 | 1.797 | 73.30 | 1.785 | 0.470 | 14.40 | |
| MO | 1/n | 0.930 | 0.382 | 0.496 | 0.714 | 0.826 | 0.400 |
| MB | 0.738 | 0.146 | 0.178 | 0.569 | 0.591 | 0.401 | |
| MO | R2 | 0.92697 | 0.91334 | 0.89728 | 0.89336 | 0.91379 | 0.99600 |
| MB | 0.86640 | 0.37184 | 0.75507 | 0.84106 | 0.93878 | 0.91954 | |
| Thermodynamic parameters | Dye | T, K | Cott | Cottc | Cottac | Cott/PES | Cott/PESc | Cott/PESac |
| ΔH0, kJ/mol | MO | -37.92 | -25.85 | -132.85 | -10.97 | 17.75 | 15.87 | |
| MB | -33.75 | -11.87 | -153.97 | -17.07 | -10.43 | -125.32 | ||
| ΔS0, kJ/molK | MO | -0.146 | -0.103 | -0.380 | -0.064 | 0.028 | 0.058 | |
| MB | -0.108 | -0.052 | -0.443 | -0.057 | -0.053 | -0.352 | ||
| ΔG0, kJ/mol | MO | 293.15 | -80.76 | 4.45 | -21.17 | 7.99 | 9.40 | -1.13 |
| 308.15 | -82.80 | 5.89 | -15.85 | 8.90 | 9.01 | -1.94 | ||
| 318.15 | -84.26 | 6.92 | -12.06 | 9.54 | 8.72 | -2.51 | ||
| MB | 293.15 | -2.05 | 3.34 | -23.62 | -0.41 | 5.16 | -21.64 | |
| 308.15 | -0.54 | 4.06 | -17.41 | 0.38 | 5.90 | -16.71 | ||
| 318.15 | 0.53 | 4.58 | -12.98 | 0.95 | 6.43 | -13.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





