1. Introduction
SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2) is a fatal coronavirus that appeared in late 2019. It generated the global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), an acute respiratory and systemic illness that endangers public health globally [
1]. Since the outbreak in 2019, the COVID-19 pandemic has been the centerpiece for studies on the signalosome [
2], therapeutic treatments [
3], and its potential role in other illnesses ([
4,
5]). Thousands of SARS-CoV-2 patients are suffering from a variety of post-COVID problems, including so-called "long COVID-19".
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC) is a multisystemic sickness with frequent significant signs that arise following an acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [
6]. According to a cautiously anticipated prevalence, with over 651 million reported COVID-19 cases worldwide, at least 10% of infected individuals have experienced long COVID [
6]. Studies have reported that 10-30% of non-hospitalized patients and 50-70% of hospitalized patients are impacted by PASC [
7]. Interestingly, it has been described that 10-12% of people who have received vaccinations have faced long COVID [
8]. Long-term COVID symptoms include brain fog, tiredness, insomnia, arthralgia, myalgia, pharyngitis, headaches, fever, digestive issues, skin rashes, and emotional symptoms such as sadness and anxiety, which are analogous to those reported during the early phase of infection [
9,
10,
11]. Severity of long COVID symptoms was shown to vary in different patients and this contrast was observed to be associated with the degree of the early infection [
12]. Several pathways have been proposed for protracted COVID pathogenesis, including immunological dysregulation, microbiome disruption, autoimmune, clotting, and endothelial abnormalities, and faulty neurological signaling [
13]. The effect of long COVID exceeds the individual limit and impacts the society as significant numbers of patients with lengthy COVID were reported to be unable to return to work [
14], which contributes to the labor shortages.
Long COVID is likely to have numerous causes, some of which may overlap. Several hypothesis have been proposed for its pathophysiology, including persistent reservoirs of SARS-CoV-2 in tissues [
15], immune deregulation [
16], reactivation of underlying infections, including herpesviruses like Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), among others [
17,
18], impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on the microbiota (including the virome) [
19,
20], autoimmunity [
21] and priming of the immune system from molecular mimicry [
20], microvascular blood clotting with endothelial dysfunction [
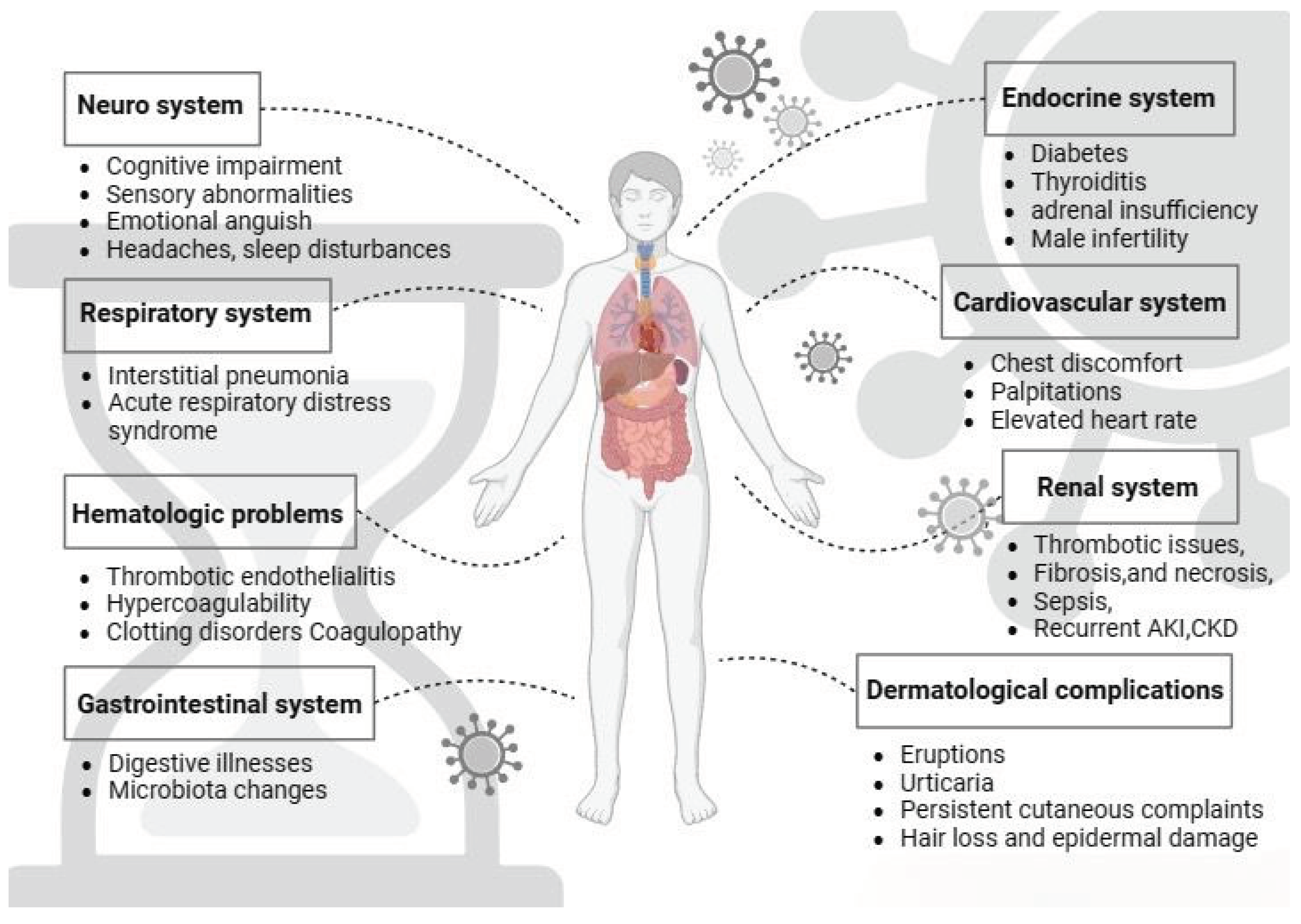
22]. The summary of organ systems affected by long COVID-19 is represented in
Figure 1.
For a long period of time researchers tried to observe the symptoms and manifestation of long COVID on various organ systems. It is known that long COVID participates in many organ systems including central nervous system (CNS), gastrointestinal system (GI), respiratory system, renal system, cardiovascular system (CVS), endocrine system, immunological system and on the skin. This review article seeks to thoroughly explore the emerging evidence and present understanding of the intricate interplay between various organ systems and long-term COVID-19 manifestations, shedding light on the potential implications on different physiological systems causing persistent symptoms.
2. Long COVID and the Nervous System
Long COVID is linked to a wide range of neuropsychiatric and neurological symptoms that may significantly disrupt daily activities, posing a significant public health issue [
23,
24,
25,
26].
The neurological and neuropsychiatric symptoms included in this category are cognitive impairment (brain fog), memory issues, ageusia (loss of taste), anosmia (loss of smell), headaches, sleep disturbances, depression, and anxiety [
23,
24,
26]. Based on the clinical case definition of long-COVID developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) using the Delphi methodology, the prevalence of all symptoms, including neuropsychiatric symptoms, was higher in hospitalized patients compared to non-hospitalized patients (53% vs 35%). Additionally, the prevalence was higher in women compared to men (49% vs 37%). The predominant neuropsychiatric symptom reported was brain fog, with a prevalence of 74%. This was followed by memory impairment (65%), sleep difficulties (62%), changed sense of smell (hyposmia) or taste (hypogeusia) (57%), headache (56%), and depression (50%) [
27].
COVID-19 Infection of the respiratory system leads to inflammation of the neurological system via systemic chemokines and increased microglial activity. The dysregulation of cytokines, chemokines, and reactive microglia in the central nervous system disrupts many kinds of neural cells. It also negatively affects the balance and adaptability of myelin which leads to dysregulation of blood brain barrier (BBB). In addition, it inhibits neurogenesis in the hippocampus, and triggers harmful astrocyte reactivity which causes the death of oligodendrocyte cells and vulnerable neurons. Hence, COVID-19 infection may have an adverse impact on the functioning of neural circuits and therefore cause cognitive impairment [
28].
One of the most common (20-35%) [
23] and most distressing neurological effects of long COVID is a syndrome called "brain fog" which refers to a chronic cognitive impairment and was even observed in those who had a moderate SARS-COV-2 infection. This condition is marked by difficulties in memory, concentration, information processing speed, attention, and executive function [
7,
26,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32]. A study conducted in Italy during the spring of 2020 examined patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia. The study found that 78% of these patients experienced cognitive impairment in at least one area three months after their infection. The most common cognitive impairments observed were related to executive function (50%), attention and information processing speed (33%), working memory (24%), and verbal memory (10%) [
33].
Another recent neuro-psychometric study conducted in a New York City hospital tracked patients with mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19 from spring 2020 to spring 2021. The study revealed that seven months after infection, there were noticeable declines in attention (10%), processing speed (18%), memory encoding (24%), and executive function (16%) among the patients [
34]. Longitudinal research performed in Spain aimed to assess neuropsychiatric symptoms in individuals with long COVID. The study reported that 46.8% of patients had cognitive impairment after one year [
35].
Additional potential processes that may contribute to neuropsychiatric symptoms associated with COVID-19 include: SARS-CoV-2 seldom has the ability to directly invade the neurological system; it has the potential to trigger an immune response that targets the neurological system, leading to an autoimmune reaction; reactivation of dormant herpesviruses, such as the Epstein-Barr virus, might potentially initiate neuropathological conditions; cerebrovascular and thrombotic illness may impede blood circulation, impair the function of the blood-brain barrier, and exacerbate neuroinflammation and ischemia in neural cells. The severe form of COVID-19 may lead to pulmonary and multi-organ malfunction resulting in hypoxemia, hypotension, and disruptions in metabolic processes. These conditions can also have detrimental effects on neuronal cells [
28].
Moreover, findings from a 1-year follow-up research indicate that being female and experiencing anxiety and depression at the 4-month point are strong indicators of developing anxiety and depressive symptoms after 12 months [
36].
Further longitudinal research done in Spain on assessing the neuropsychiatric symptoms in individuals with long COVID revealed that 45% of participants had mental morbidity, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder, after one year [
35].
Taquet et al. performed a retrospective cohort research including 236,379 individuals. The study found that 17.4% of the patients had anxiety disorder and 13.7% had a mood disorder within 6 months after being diagnosed with COVID-19 [
37]. Besides the neuropathological pathways, environmental and lifestyle disruptions, together with the global pandemic, are probable factors that have contributed to an overall decline in mental health. These disruptions include isolation, limited healthcare access, and significant and prolonged changes in daily living on a large scale [
23].
Additional frequently noticed neurological symptoms associated with long COVID include sleep disturbances with prevalence of 26% which have a bidirectional association between mental health problems [
38,
39,
40]. The reported sleep disturbances include trouble sleeping, nightmares, and lucid dreaming [
41].
Sensory impairments such as ageusia or dysgeusia and anosmia, have been documented as a symptom linked to long COVID. Interestingly, the incidence of these impairments did not vary based on the severity of the infection [
23,
42,
43]. A recent meta-analysis study performed by Trott et al. described that around 12.2% of patients have anosmia and 11.7% suffer from ageusia that lasts for more than 12 weeks after contracting COVID-19 [
44]. Another study conducted in Poland involving 2218 patients who had recovered from COVID-19, revealed that 98 patients (4.4%) experienced smell and taste disorders for up to 3 months after their infection [
45]. The etiology of these symptoms remains unknown; nevertheless, it is possible that inflammation and infection-induced immune system dysfunction may serve as the underlying mechanism [
23]. The summary of neurological complications can be seen in
Table 1.
The ongoing neurological symptoms and neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 pose a significant global health challenge, with long-lasting consequences potentially causing incapacitating effects. These symptoms can hinder resuming a normal lifestyle and potentially strain healthcare systems worldwide. Efficient treatments have been challenging to find in the first years of the epidemic. Identifying long-term neurological symptoms is crucial for perceptive medical practitioners, as it can guide clinical diagnosis and treatment, reducing unnecessary testing. Further research is expected to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction. It is also essential to monitor cognitive and neuropsychological abilities in those recovering from COVID-19 [
23,
46].
Table 1.
Relationship between long COVID and affected organ systems.
Table 1.
Relationship between long COVID and affected organ systems.
| Organ system |
Symptoms |
Pathology |
Ref. |
| Nervous system |
Cognitive impairment (brain fog),
memory issues, ageusia (loss of taste), anosmia (loss of smell), headaches, sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety |
|
[23,24,26] |
| Cardiovascular system |
Chest discomfort or tightness, palpitations, dizziness, rise in resting heart rate |
Myocarditis, Pericarditis, Coronary artery disease |
[47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] |
| Hematologic problems |
|
Persistent thrombotic endothelialitis, Systemic hypercoagulability, fibrinaloid microclots, platelet hyperactivation, endothelial dysfunction, clotting disorders, SARS-CoV-2-mediated immune thrombocytopenia, persistent lymphocytopenia, coagulation |
[59,60,61,62,63]
|
| Respiratory system |
Chest pain, breathlessness, cough, pulmonary dysfunction |
Diffusion impairment, restrictive ventilatory defects, reduction in diffusion capacity |
[64,65,66,67,68,69] |
| Renal system |
Decreased renal perfusion, hypotension, ischaemia, salt diuresis, sympathetic stimulation, increased salt and water retention |
Systemic inflammation, thrombotic issues, fibrosis, necrosis, sepsis, recurrent AKI, CKD |
[70,71,72,73,74,75] |
Immune
complications |
|
Systemic inflammation, immune dysregulation, debilitating condition, intravascular hyperinflammation with changes in angiogenesis and coagulation, comorbid hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, Guillain-Barre syndrome, quadriplegia and bilateral facial paresis, acute motor sensory axonal polyneuropathy, multisystem inflammatory, syndrome in children, hyperinflammatory immune responses |
[76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85] |
| Endocrine system |
|
Diabetes, autoimmune thyroiditis, adrenal insufficiency, male infertility, autoimmune hypothyreodism, steroid-induced diabetes mellitus, acute adrenal insufficiency |
[86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97] |
| Gastrointestinal system |
Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, loss of taste, abdominal pain |
Acid related disorders (dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease), motility disorders, belching, hepatic and biliary disease, functional intestinal disorders, rectal bleeding, liver damage, acute pancreatitis, cholangiopathy, irritable bowel syndrome, microbiota alterations |
[98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110] |
Dermatological complications
|
Itchy welts |
|
[111,112] |
| Mottled, purplish discoloration that forms a net-like pattern |
Livedo reticularis |
[113,114] |
| Petechiae and purpura |
[112,114,115,116] |
| Similarities to chickenpox or herpes infection |
Vesicular rash |
[117,118] |
| Discoloration of the toes and fingers to red or purple, swelling, Pain |
COVID toes |
[118] |
| |
Maculopapular rash, urticarial lesions, chilblains |
[119] |
| |
Skin rashes |
[38] |
| Absence of hair follicles, destruction of adipose tissue, damage to the epidermal layer |
Persistent cutaneous extracutaneous symptoms |
[120,121,122] |
| Livedo reticularis lesions, petechiae, painful acral red purple papules, |
Maculopapular exanthem (morbilliform), papulovesicular rash, urticaria, |
[123] |
| |
Morbilliform eruptions, urticaria, papulosquamous eruptions |
[120] |
| |
Pernio lesions |
[119] |
3. Long COVID and Cardiovascular System
The most prevalent cardiovascular (CV) symptoms reported in PACS are chest discomfort or tightness, palpitations, dizziness, and a rise in resting heart rate [
47]. However, the underlying pathophysiological relationship between PACS and the CV system has not been conclusively identified. Several CV disorders may be linked. The summary of cardiovascular issues can be found in
Table 1.
3.1. Myocarditis
A study of 29 previously hospitalized COVID-19 patients with unexplained increased troponin levels found that 45% had late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) suggestive of myocarditis-like patterns on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) about 27 days after discharge. Despite this, individuals did not have elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) or troponin levels, and their left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was normal with no wall motion abnormalities. However, no myocardial strain data was supplied [
48].
In another research based on Ohio State University athletes, 15% had CMR data that met the modified Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis diagnosis, which include myocardial edema and non-ischemic myocardial damage markers. This study received media attention, yet it lacked a control group and included patients lacking myocarditis characteristics [
49].
Huang et al. [
50] evaluated 26 COVID-19 recovered patients with residual cardiovascular symptoms and discovered abnormalities on CMR in 58% without using the new Lake Louise criteria. Notably, the control group's abnormality % was unknown, and there were no significant variations in troponin, brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), or CRP levels between individuals with normal and abnormal CMRs. Furthermore, several symptomatic individuals had normal CMR values.
Moulson et al. [
54] carried out a large-scale study of 19,378 college athletes who recovered from COVID-19. Seventeen percent (17%) tested positive for the virus. The majority had comprehensive cardiac screening, including electrocardiogram, transthoracic echocardiogram, and troponin level with CMR conducted as needed. Only 3.0% of individuals tested with CMR had pathology related to COVID-19. However, later analysis found that the existence of cardiovascular symptoms during illness or exercise, or aberrant findings in the first triad testing, significantly enhanced the risk of abnormal CMR outcomes. The authors recommended a progressive screening technique based on symptom intensity and aberrant triad test findings, which they projected would discover 82% of athletes with myocardial or pericardial involvement caused by COVID-19. A prospective study of 149 healthcare professionals in a non-athlete population found no changes in CMR features, troponin levels, or N-terminal pro-BNP at 6 months post-infection compared to age, sex, and ethnicity-matched seronegative controls [
51]. The study cohort had limited comorbidities, with only one patient having severe COVID-19.
3.2. Pericarditis
The majority of pericarditis cases in the general population are idiopathic, yet it is widely believed that these instances are the result of viral infections [
124]. One research found that 12% of hospitalized COVID-19 patients had diffuse acute ST alterations compatible with pericarditis [
52]. Puntmann et al. found that 20% of patients had a pericardial effusion >1 cm on CMR versus 7% in risk factor-matched controls, however no patients experienced symptoms [
53]. Moulson et al. [
54] and Kotecha et al. [
125] both observed a 5% incidence of pericardial effusion, which was usually modest in size.
3.3. Coronary Artery Disease
Approximately 20-30% of individuals hospitalized with COVID-19 will have elevated troponin levels, most commonly due to type 2 myocardial infarction [
55]. Type 2 myocardial infarction should not be neglected once the acute sickness has passed. Troponin levels above the 99th percentile in COVID-19 patients were linked to a 3-6 times higher risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) [
56]. Preliminary research by Nai Fovino et al. demonstrated a tendency for greater high-sensitivity troponin peak during COVID-19 admission in patients with a coronary artery calcium score > 400 than those with a score < 400 (1424 versus 419 ng/L, p = 0.084) [
57]. Interestingly, patients with COVID-19 had a threefold greater chance of a significant adverse cardiac event assessed at a median of 5 months post-discharge compared to age, gender, and risk factor-matched controls; however, these findings deserve more investigation [
58].
4. Long COVID and Hematologic Problems
Hematological disorders were observed to occur following the COVID-19 infection [
126]. Different alternation in blood composition can be observed in COVID-19 patients, serving as potential indicators for prognosis and treatment. While most individuals infected with COVID19 experience a return to normal hematological levels shortly after onset, a small percentage may continue to exhibit elevated parameters, leading to blood disorders, for an extended period of time, spanning months to years [
127]. The summary of hematological symptoms can be found in
Table 1.
During and post COVID19 infection, various pathophysiological mechanisms can cause long hematological conditions, such as: persistent thrombotic endothelialitis and systemic hypercoagulability, leading to the formation of fibrinaloid microclots, platelet hyperactivation, and endothelial dysfunction, ultimately contributing to a range of clotting disorders [
59]. One of such disorder is COVID-19-induced coagulopathy, which is characterized by an abnormal immune response leading to both blood clotting and bleeding events [
60,
61]. Elevated levels of D-dimer and fibrinogen, along with mild thrombocytopenia, modest prolongation of prothrombin time, and activated partial thromboplastin time, are important markers of coagulopathy that have been frequently observed in severely ill COVID-19 patients [
60]. Late-onset thrombocytopenia is a condition where the immune system becomes deregulated with time [
128,
129]. Detailed mechanisms through which SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to immune thrombocytopenia are not completely understood, needing additional investigation. However, potential mechanisms underlying SARS-CoV-2-mediated immune thrombocytopenia include immune system dysregulation, molecular mimicry, epitope spreading, and susceptibility mutations in suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene [
126]. A systematic analysis revealed that out of 45 individuals with immune thrombocytopenia caused by COVID-19, 20% experienced thrombocytopenia three weeks after the initial COVID-19 symptoms appeared, while 9% encountered a relapse after responding to treatment during the monitoring period [
62].
It is already known that during a severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, a cytokine storm occurs, with significantly elevated levels of interleukins (primarily IL-6, IL-2, IL-7, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, interferon-γ inducible protein 10, MCP-1, and MIP1-a) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, which can lead to lymphocyte apoptosis [
126]. It is noted that persistent lymphocytopenia may still be present even after 5 weeks from the onset of the disease, particularly in patients with severe acute COVID-19. A study conducted in China on 435 hospitalized COVID-19 patients revealed that lymphocytopenia was especially notable in CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD19+, and CD16/56+ lymphocyte subsets [
63].
A prospective cohort study on coagulation was conducted in 2023, with 102 individuals who had recovered from COVID-19. The results showed that 75% of the patients had a procoagulant state at the 3-month follow-up, while the percentages decreased to 50% at 6 months and 30% at 12-18 months. This association between persistent symptoms and a procoagulant state suggests that ongoing thrombi formation and/or persistent micro thrombosis may be responsible for the main physical symptoms experienced by long-COVID patients [
61].
5. Long COVID and Respiratory System
COVID-19 primarily impacts the respiratory system, causing a wide array of clinical and radiological indications. While around 80% of cases involve infection in the upper airways, in 20% of cases, the virus progresses to the alveoli, leading to the development of pulmonary infiltrates [
130]. Numerous studies have documented a range of persistent respiratory symptoms in individuals who have recovered from acute COVID-19. The summary of respiratory symptoms can be found in
Table 1. PASC is mainly characterized by respiratory symptoms such as chest pain, breathlessness, and cough. Scientific research has validated that even 1 to 3 months post-discharge, patients continued to exhibit radiological abnormalities indicative of pulmonary dysfunction, a reduction in the diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide, and weakened respiratory muscle strength [
64,
65,
66,
67]. However, these symptoms tend to decrease over time, with abnormalities in lung function or chest imaging being less common after 12 months compared to six months post-discharge [
131].
In COVID-19 infected patients, interstitial pneumonia is the primary reason for hospitalization, with the majority of cases being classified as mild to moderate. Nevertheless, approximately 5-10% of individuals experience a progression to severe respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [
132,
133,
134]. Even after recovering from COVID-19, many patients continue to suffer from respiratory symptoms, and multiple studies have indicated abnormalities in pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and chest CT images, even months following their hospital admission. The prevalence of these findings varies, influenced by the approach taken in the research and the duration of follow-up [
135,
136].
A large meta-analysis study conducted by Long et al. [
68], where a total of 4,478 COVID-19 patients from 16 cohort studies were included, showed that the prevalence of abnormalities in lung function was approximately 20%. The most common abnormality observed was diffusion impairment, followed by restrictive ventilatory defects [
68]. Similar findings have been reported by other studies, as for example in the study that evaluated a total of 1200 patients, with 83 suffering from post-COVID-19 pulmonary complications, exhibiting lung function abnormalities, emphasizing the potential long-term consequences on respiratory function [
137].
Further, patients who were not hospitalized during acute phase of the COVID infection, showed abnormal breathing pattern and respiratory movements, chest pain, reduced lung volumes, air flow, reduced respiratory muscle strength, physical capacity and thoracic expansion may be involved in long COVID [
138]. In 2023 a cohort study measured the diffusion capacity (DLCO) of nonhospitalized and hospitalized patients in University Hospitals of Umeå and Örebro, and Karlstad Central Hospital, Sweden. The measured DLCO among hospitalized patients was 20% reduced, compared to non-hospitalized patients which was 4%, indicating a significant difference among the analyzed patients [
69].
6. Long COVID and Renal System
COVID-19 may influence the kidney in a variety of ways, with the contribution of these variables changing over time. Many of the SARS-CoV-2 virus's direct and indirect effects may linger beyond hospital release, increasing the risk of sepsis, recurrent acute kidney injury (AKI), and chronic kidney disease (CKD). The summary of renal complications can be found in
Table 1. Furthermore, a new diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and deteriorating cardiovascular disease owing to COVID-19 may prolong AKI recovery. Second, the association between COVID-19 and CKD is likely to be bidirectional. Mild CKD may increase the risk of COVID-19 and related AKI, whereas severe AKI may be linked with chronic renal dysfunction, delayed recovery, and/or the requirement for long-term dialysis [
70].
US research that used electronic health data from the Veterans Health Administration to perform a complete assessment of lengthy COVID found that COVID-19 increased the risk of CKD, with the largest risk among individuals with severe disease [
71]. Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 had a comparable risk of CKD to those hospitalized with influenza.
The findings of Veterans Health Administration research were comparable to the results of a study based in China on COVID-19 patients, which indicated that 35% of patients had impaired kidney function (6 months after hospitalization) (estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <90 ml/min/1.73 m2). Additionally, 13% of patients who did not have AKI during hospitalization had a decrease in eGFR at follow-up [
38].
COVID-19 pathophysiological pathways may be accentuated in conjunction with deteriorating diabetes or hypertension control. Kidney disease development in COVID-19 is most likely complex and may be triggered by persistent inflammation, intrinsic tubular damage, or maladaptive repair, among other mechanisms. Novel kidney-specific plasma and urine biomarkers may aid in determining the primary underlying causes and predicting which individuals are most likely to develop CKD during COVID-19 hospitalization [
139].
A specific interaction between a receptor called angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 in different tissues has been identified [
140]. It is well known that SARS-CoV-2 gains cell entry through ACE2. When it comes to assessment of the mechanism, ACE2 is essential for regulating the cardiovascular and renal systems via the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS). Renal juxtaglomerular cells start releasing renin in response to certain situations, such as decreased renal perfusion, hypotension, ischemia, salt diuresis, and sympathetic stimulation, which changes liver-derived angiotensinogen to angiotensin I (ANGI) [
72]. ACE2 then converts ANGI to ANGII, which is further metabolized by ACE2 into ANG I-7. In cardiorenal illness patients, ANGII can modulate fibrosis, hypertrophy, and pro-oxidative hormone, resulting in increased salt and water retention [
73]. SARS-CoV-2 reaches the kidneys via the glomerular capillaries and arteries, where it infects the podocytes. SARS-CoV-2 penetrates tubular fluid and eventually reaches proximal tubule epithelial cells [
72]. SARS-CoV-2-induced ACE2 receptor internalization causes ACE2 insufficiency on cells, shifting the ANG I-7-Mas pathways to angiotensin II-angiotensin II type 1 receptor (ANGII-AT1R) and inducing a proinflammatory state [
141].
Furthermore, ACE2 controls the Kallikrein Kinin System. In this context, after generating kinin from bradykininogens, this metabolite works on both B1 and B2 receptors to cause inflammation and enhance vascular permeability [
74]. Furthermore, Kallikrein can cause a coagulation imbalance by activating factor 12 and plasmin. The renal alterations may increase systemic inflammation, thrombotic issues, fibrosis, and necrosis caused by COVID-19 in the kidneys, culminating in renal impairment [
74].
Ramamoorthy et al. [
75] reported for the first time that renal fibrosis might occur in the long term after infection. The observation of this study shows elevated mRNA levels of transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), interleukin 18 (IL-18), hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1-α), toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40), and β2 microglobulin (B2M) long after MHV-1 infection. Long-term post-MHV-1 infection was associated with increased protein levels of HIF1-α, TLR-2, and EGFR, as revealed by immunoblot investigations. Only keyboard input monitor 1 (KIM-1) and matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP-7) protein levels, as well as NGAL mRNA, rise during acute infection (7 days). Treatment of MHV-1 infected mice with a synthetic peptide, SPIKENET (SPK), which inhibits spike protein binding, lowered NGAL mRNA in acute infection and decreased TGF-β1, B-cell CLL/lymphoma 3 (BCL3) mRNA, as well as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), HIF1-α, and TLR-2 protein levels long-term post infection. These data clearly show that renal fibrosis may occur in the long-term following infection. As a result, tackling these parameters may lead the way to avoiding long-term COVID-19 problems [
75].
7. Long COVID-19 and Immune Complications
Oxidative stress and hyper-inflammation emerge as crucial elements in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 and the long-COVID-19 syndrome [
142]. The impact of free radicals is associated with the progression of cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, endocrine diseases, inflammatory conditions, and infections, including COVID-19. Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in COVID-19, acting as a significant cause of harm through reactive oxygen species (ROS) and serving as a vital indicator of disease severity. In the acute phase of COVID-19, the observed variations in ROS and oxidative stress levels suggest significant structural alterations in macromolecules, the formation of non-functional derivatives, and substantial harm to cellular components in moderate and critical cases of COVID-19 [
143]. Other studies have shown that the immune response against COVID-19 infection is connected to the adaptive immunity [
76,
144]. Today, long COVID related individuals exhibited systemic inflammation and immune dysregulation. As evidence, the global variations in the distribution of CD4+ T and CD8+ T in human cells, indicate ongoing immune responses [
76]. Patients also display higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and a lack of coordination between their SARS-CoV-2-specific T and B cell responses. These findings suggest an improper communication between cellular and humoral adaptive immunity in long COVID patients, which can result in immune dysregulation, inflammation, and the clinical symptoms associated with this debilitating condition [
77]. Further, a distinct cytokine profile is linked to various factors observed during the critical phase of this illness, encompassing the initiation of interferon synthesis, secretion of interleukin (ILs) 2 and 7, and the triggering of granulocyte activation and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) production [
145]. The cytokine profile causes intravascular hyperinflammation with changes in angiogenesis and coagulation [
78]. Others studies haves show that SARS-CoV-2 can trigger secondary diseases associated with an immunosuppression profile, such as comorbid hypertension (COPD) [
79] and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [
80]. Several reported studies indicated that individuals with pre-existing COPD tended to experience more severe outcomes when infected with SARS-CoV-2 [
146]. Based on the available evidence, hypertension was frequently observed in individuals with COVID-19, but it did not independently contribute to the occurrence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or the progression of COVID-19 [
79]. The summary of immunological symptoms can be seen in the
Table 1.
The COVID-19 infection significantly affected rare genetic disorders, as shown in the Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS). In the GBS disorder your "own immune system” attacks your nerve cells [
147]. The first symptoms are usually weakness and tingling in hands and feet. These sensations can quickly spread, eventually paralyzing the whole body [
147]. Several studies have confirmed that GBS also occurs in late COVID patients [
81,
82,
83]. One of the first studies explaining COVID19 effect on GBS patients was published in 2020, where the authors revealed that two weeks after COVID-19 infection, quadriplegia and bilateral facial paresis occurred. Further, the electrodiagnostic findings of patient demonstrated acute motor sensory axonal polyneuropathy [
82]. It is known that hypoxemic pneumonia generally emerges around two weeks post-infection, a minority of children and young adults experience the onset of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) approximately four weeks after being infected by SARS-CoV-2. This condition shares characteristics with both Kawasaki disease and toxic shock syndrome mediated by superantigens [
84]. Immunological examinations have unveiled hyperinflammatory immune responses, differing from those observed in acute COVID-19 and Kawasaki disease. There is also evidence of T-cell activation, potentially triggered by a superantigen associated with SARS-CoV-19 [
85]. A study conducted in 2023, indicated that among 2246, 151 patients harbored at least one ultra-rare variant of RTEL1 (regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1), chosen as a distinctive marker for acute severity in diseases correlated to liver functions causing lung fibrosis [
148].
8. Long COVID-19 and Endocrine System
ACE2 receptor has been found in several endocrine glands, including the pancreas, thyroid gland, ovaries, and testes. The presence of ACE2 receptor on endocrine system suggests that SARS-CoV-2 may cause alternations in endocrine function. Up to date several endocrine disorders such as diabetes, autoimmune thyroiditis, adrenal insufficiency, and male infertility have been reported in association with post COVID-19 disease [
86,
87,
88,
89].
Study by Szczerbiński et al. [
90] investigated long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the endocrine system in two distinct groups of patients. First group of patients (n=39) or case group was examined six months after COVID-19 and the control group, consisted of age and sex matched individuals before the COVID 19 pandemic. According to the obtained results they found significantly higher levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and anti-thyroid peroxidase (aTPO) antibodies and lower free triiodothyronine (FT3) and FT4 levels in case group compared to controls, indicating a potential autoimmune hypothyreodism in patients recovered from COVID-19. In a group of 334 COVID-19 patients who underwent TSH and FT4 measurements at the admission, showed normal levels and were euthyroid (86.5%). However, when these results were compared to non-COVID-19 cases (n=122), a small reduction in TSH and FT4 levels was observed. Patients with COVID-19 had a reduction in TSH and FT4 levels when compared to their results from 2019, which was not observed in patients without COVID-19 [
95]. COVID-19 genome-wide association studies were used to analyze the effect of COVID-19 on thyroid dysfunction, the results identified that COVID-19 susceptibility and its severity might increase the risk of hypothyroidism [
96].
It is well known that extensive use of steroids can lead to steroid-induced diabetes mellitus [
97]. Patients with severe COVID-19 typically receive an 8–10 days course of dexamethasone, with the possibility of prolonged steroid therapy for an extended duration. It has been observed that after the prolonged use of steroids for several weeks to treat COVID-19 in some cases has led to acute adrenal insufficiency [
88]. Given that SARS-CoV-2 can be found in the adrenal glands of deceased COVID-19 patients and can infect adrenal cells in laboratory settings, it is reasonable to assume that COVID-19 may cause damage to the adrenal glands [
88]. A significant cohort study utilizing the US Department of Veterans Affairs national database assembled a group of 181 280 individuals who tested positive for COVID-19. The study found that, with a median follow-up period of 352 days, COVID-19 patients exhibited a heightened risk of developing diabetes compared to the control group [
94].
Additionally, male patients recovered from COVID-19 had significantly lower levels of testosterone [
90]. Evaluation of the male reproductive health after three months from COVID-19 infection showed the presence of erectile dysfunction in one-third of tested subjects, however this study showed that COVID-19 didn’t significantly affect testosterone levels with only five subjects (6.2%) having testosterone levels below the laboratory reference range [
91]. In a study involving 358 patients with Covid-19 and 92 patients without COVID-19, it was found that serum total testosterone levels were notably reduced in individuals with COVID-19 compared to those without the virus. Moreover, upon stratifying patients with COVID-19 based on disease severity, individuals with severe cases exhibited lower total testosterone levels in contrast to those with mild to moderate Covid-19 [
92]. After a 7-month follow-up in men who recovered from COVID-19, overall testosterone increased in almost 90% of patients and further decreased in 10% of entire cohort. However, 55% of men had subnormal testosterone levels suggestive for hypogonadism [
93]. The summary of endocrine complications related to long COVID-19 are shown in
Table 1.
9. Long-COVID-19 and Gastrointestinal System
Studies have shown that patients with prolonged COVID-19 are at greater risk of developing digestive diseases [
149,
150]. It is well-known at this point that SARS-CoV-2 has adverse effects on different parts of digestive system [
98,
105]. Epithelial cells of Gastrointestinal (GI) have shown the most expression of ACE2 receptor in patients infected with COVID-19 [
140].
It has been shown that the degree of GI symptoms in patients with severe COVID-19 was higher [
150]. Also, the presence of GI symptoms has prolonged the duration of hospitalization for infected patients compared to those who had not experienced any GI symptoms [
151]. Accumulating evidence demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 genome was detected in faces of almost half of the infected patients over time [
152], suggesting an interaction between digestive system and the virus that could leave the patient with long term sequelae [
98,
105,
152,
153,
154,
155].
Choudhury et al. has reported that 12% of patients after COVID-19 and 22% as part of long COVID have shown GI symptoms [
100]. Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, loss of taste, irritable bowel syndrome, and abdominal pain are the main common GI symptoms among patients in early stages and even post-infection of the disease [
98,
99,
100,
105]. During the acute phase of the disease GI symptoms were mostly led by diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain respectively [
98,
101,
102]. One study has observed that even12 weeks after diagnosis diarrhea was present [
103].
Different studies have indicated a significant link between COVID-19 and elevation in risk of developing digestive system disorders in a long term [
104,
150]. These conditions include acid related disorders (dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease), motility disorders, belching, hepatic and biliary disease, functional intestinal disorders, rectal bleeding, liver damage, acute pancreatitis, and cholangiopathy [
99,
104,
105].
A meta-analysis performed by Cheung et al. [
152], which includes 60 studies demonstrates that among 4243 patients the commonness of GI symptoms was 17.6%. Comprising 11.8% of non-severe and 17.1% severe case of COVID-19 [
152].
In another study, Weng et al. [
99] has investigated the prevalence of GI symptoms with long COVID-19 among 117 patients who have been contacted 90 days after discharge. 15 of the patients were diagnosed with GI symptoms on admission and 49 of them during hospitalization. After 90 days 52 of patients reported GI symptoms. Among them 15 patients had GI symptoms on admission day and during hospitalization, 34 patients reported GI symptoms during hospitalization and 3 after discharge [
99].
GI tract is home to most human microbiota and it has been found that long Covid-19 could alter the population of this ecosystem [
106,
107]. Based on studies, this alteration has mostly affected oral and gut microbiome even after recovery from COVID-19 [
108,
109,
110]. Zhang et al. [
156] has compared this effect in patients with and without GI symptoms of long COVID-19. Patients who did not report GI symptoms showed little difference in the gut and oral microbiota compared to healthy controls. However, collected samples from patients with GI symptoms at baseline and 3 months period confirmed significant difference and ectopic colonization of the oral cavity by gut microbes. Their results have shown expression of serum metabolites such as 4-chlorophenylacetic acid, 5-sulfoxymethylfurfural, and estradiol valerate with potential toxicity which could be related to the differentially abundant of bacteria including Neisseria, Lautropia, and Agrobacterium [
156]. The summary of gastro-intestinal complications related to long COVID-19 are represented in the
Table 1.
10. Long COVID-19 and Dermatological Complications
Investigations have revealed an association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and skin changes in post infection stage [
117,
118]. However, this viral infection could result in various cutaneous clinical patterns throughout the disease [
157]. Interestingly, accumulated evidence demonstrates that some of the cutaneous patterns are considered as prodromal sing and could possibly represent as early indicator of infection or the only symptom of asymptomatic carriers [
157,
158].
More than 30 different skin eruptions caused by COVID-19 virus have been described [
159] and the characteristics manifestation of these dermatological conditions varies between individuals [
117,
118]. For instance, urticaria with itchy welts on the skin could be presented jointly with other COVID-19 symptoms [
111,
112]. Livedo reticularis, a condition that characterizes with mottled, purplish discoloration that forms a net-like pattern has also been reported specially among infected patients with pre-existing vascular issues [
113,
114]. Other conditions such as petechiae and purpura have been found to be related to COVID-19 infection particularly in severe cases which could be due to coagulation abnormalities [
112,
114,
115,
116]. Also, there have been diagnosis of vesicular rash, with similarities to chickenpox or herpes infection, in some patients with COVID-19 [
117,
118]. Discoloration of the toes and fingers to red or purple, along with swelling, and pain are symptoms of COVID toes which was found to be a rare condition presented in infected patients [
118]. Recent analysis has shown that the most commonly reported manifestations of COVID-19 are maculopapular rash, urticarial lesions, and chilblains [
119].
Huang et al. have studied 1655 hospitalized Chinese patients 6 months after infection onset and reported that only 47 patients (3%) had reported skin rashes [
38]. In addition, other information on long term COVID-19 have declared persistent cutaneous and extracutaneous symptoms such as absence of hair follicles, destruction of adipose tissue, damage to the epidermal layer [
120,
121,
122].
Sachdeva et al. [
123] have conducted three case reports and a literature review on different manifestations in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. The result of the study demonstrates that maculopapular exanthem (morbilliform) was reported by 36.1% of the patients making it the most common cutaneous condition related to COVID-19, followed by papulovesicular rash (34.7%), urticaria (9.7%), painful acral red purple papules (15.3%), livedo reticularis lesions (2.8%) and petechiae (1.4%) [
123].
McMahon et el. [
120] have investigated dermatological conditions in individuals from 41 countries who were laboratory confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients and cases who only were diagnosed with the skin condition. Their results showed that the median duration of morbilliform eruptions was 7 days. Urticaria lasted a median of 4 days, and the maximum duration of this condition was 28 days. Also, the longest median of duration belonged to papulosquamous eruptions which lasted 20 days and one case was reported to last for 70 days [
120].
Ica et al. [
119] have published review research on skin lesions in COVID-19 patients in short term and in the long term. The study has not identified any lesions that were more likely to long term persistence. Moreover, no pattern was detected to demonstrate if a chronic skin disease would be a result of a long term COVID-19. However, perniosiform lesions were pointed out as the most evaluated lesions in the long term [
119]. It also needs to be noted that as novel virus variants arise, new cutaneous patterns will be expected in long COVID-19 syndrome [
159]. The summary of dermatological complications can be seen in
Table 1.
11. Conclusions
PASC presents complex health issues with significant public health implications. Neuropsychiatric and neurological symptoms, such as cognitive impairment, sensory abnormalities, headaches, and sleep disturbances, are common, especially among hospitalized individuals and specially women. Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to neurological inflammation, affecting neuronal functioning and cognitive abilities. Autoimmune responses, viral reactivation, and cerebrovascular issues contribute to these symptoms, alongside persistent cognitive impairments, and mental health concerns such as anxiety and depression. Taking into consideration impact of the virus, cardiovascular symptoms like chest pain, palpitations, and elevated heart rate are observed in long-term COVID patients, with unclear pathophysiological links. Persistent hematological problems contribute to clotting disorders and coagulopathy, posing serious risks. Respiratory issues persist post-COVID, including chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and cough, with some experiencing severe respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Kidney involvement raises the risk of sepsis and renal complications, including fibrosis. On the other hand, endocrine glands are affected, resulting in post-COVID diseases like diabetes, thyroiditis, and adrenal insufficiency. Long COVID may also impact male reproductive health, with reduced testosterone levels and erectile problems post-recovery. The digestive system experiences symptoms post-infection, potentially leading to acid-related illnesses, motility problems, and pancreatitis. Changes in the oral and gut microbiota are noted among patients with GI symptoms, indicating potential risks. Skin abnormalities, ranging from urticaria to COVID toe, are common, with long-term consequences like hair loss and epidermal damage. However, no definitive patterns indicate chronic skin illnesses caused by long-term COVID-19.
In summary, long COVID poses a complicated set of health difficulties, mostly impacting the neurological, cardiovascular, pulmonary, endocrine, digestive, and dermatological systems, with significant consequences for public health. The persistence of neuropsychiatric symptoms, cardiovascular complications, respiratory issues, endocrine disruptions, gastrointestinal disturbances, and skin abnormalities emphasizes the multifaceted nature of Long COVID and the urgent need for additional research and holistic approaches to its management and mitigation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H.J. and V.N.U.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G., A.H.J., J.Š., O.A., P.A., T.B.; writing—review and editing, E.M.R., A.R.C., V.N.U., A.H.J.; visualization, M.G.; supervision, A.H.J., V.N.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K.; Hromic-Jahjefendic, A.; Bilajac, E.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Baralic, K.; Sabri, N.A.; Shehata, E.M.; Raslan, M.; Ferreira, A.; Orlandi, L.; et al. COVID-19 signalome: Pathways for SARS-CoV-2 infection and impact on COVID-19 associated comorbidity. Cell Signal 2023, 101, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K.; Hromic-Jahjefendic, A.; Bilajac, E.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Baralic, K.; Sabri, N.A.; Shehata, E.M.; Raslan, M.; Raslan, S.A.; Ferreira, A.; et al. COVID-19 signalome: Potential therapeutic interventions. Cell Signal 2023, 103, 110559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromic-Jahjefendic, A.; Barh, D.; Uversky, V.; Aljabali, A.A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Alshammeri, S.; Lundstrom, K. Can COVID-19 Vaccines Induce Premature Non-Communicable Diseases: Where Are We Heading to? Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromic-Jahjefendic, A.; Barh, D.; Ramalho Pinto, C.H.; Gabriel Rodrigues Gomes, L.; Picanco Machado, J.L.; Afolabi, O.O.; Tiwari, S.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Serrano-Aroca, A.; et al. Associations and Disease-Disease Interactions of COVID-19 with Congenital and Genetic Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Viruses 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballering, A.V.; van Zon, S.K.R.; Olde Hartman, T.C.; Rosmalen, J.G.M.; Lifelines Corona Research, I. Persistence of somatic symptoms after COVID-19 in the Netherlands: an observational cohort study. Lancet 2022, 400, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceban, F.; Ling, S.; Lui, L.M.W.; Lee, Y.; Gill, H.; Teopiz, K.M.; Rodrigues, N.B.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Di Vincenzo, J.D.; Cao, B.; et al. Fatigue and cognitive impairment in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav Immun 2022, 101, 93–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Bowe, B.; Xie, Y. Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med 2022, 28, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.J.; Deeks, S.G. Early clues regarding the pathogenesis of long-COVID. Trends Immunol 2022, 43, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, E.; Janvier, P.; Kherabi, Y.; Le Bot, A.; Hamon, A.; Gouze, H.; Doucet, L.; Berkani, S.; Oliosi, E.; Mallart, E.; et al. Post-discharge persistent symptoms and health-related quality of life after hospitalization for COVID-19. J Infect 2020, 81, e4–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Knight, M.; A'Court, C.; Buxton, M.; Husain, L. Management of post-acute covid-19 in primary care. BMJ 2020, 370, m3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hadrawi, D.S.; Al-Rubaye, H.T.; Almulla, A.F.; Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Maes, M. Lowered oxygen saturation and increased body temperature in acute COVID-19 largely predict chronic fatigue syndrome and affective symptoms due to Long COVID: A precision nomothetic approach. Acta Neuropsychiatr 2023, 35, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.E.; Assaf, G.S.; McCorkell, L.; Wei, H.; Low, R.J.; Re'em, Y.; Redfield, S.; Austin, J.P.; Akrami, A. Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 38, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swank, Z.; Senussi, Y.; Manickas-Hill, Z.; Yu, X.G.; Li, J.Z.; Alter, G.; Walt, D.R. Persistent Circulating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Is Associated With Post-acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sequelae. Clin Infect Dis 2023, 76, e487–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetsouphanh, C.; Darley, D.R.; Wilson, D.B.; Howe, A.; Munier, C.M.L.; Patel, S.K.; Juno, J.A.; Burrell, L.M.; Kent, S.J.; Dore, G.J.; et al. Immunological dysfunction persists for 8 months following initial mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Immunol 2022, 23, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durstenfeld, M.S.; Peluso, M.J.; Peyser, N.D.; Lin, F.; Knight, S.J.; Djibo, A.; Khatib, R.; Kitzman, H.; O'Brien, E.; Williams, N.; et al. Factors Associated with Long Covid Symptoms in an Online Cohort Study. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubchenko, S.; Kril, I.; Nadizhko, O.; Matsyura, O.; Chopyak, V. Herpesvirus infections and post-COVID-19 manifestations: a pilot observational study. Rheumatol Int 2022, 42, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes de Almeida, V.; Engel, D.F.; Ricci, M.F.; Cruz, C.S.; Lopes, I.S.; Alves, D.A.; d' Auriol, M.; Magalhaes, J.; Machado, E.C.; Rocha, V.M.; et al. Gut microbiota from patients with COVID-19 cause alterations in mice that resemble post-COVID symptoms. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2249146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proal, A.D.; VanElzakker, M.B. Long COVID or Post-acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC): An Overview of Biological Factors That May Contribute to Persistent Symptoms. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 698169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.M.; Forrest, J.C.; Boehme, K.W.; Kennedy, J.L.; Owens, S.; Herzog, C.; Liu, J.; Harville, T.O. Development of ACE2 autoantibodies after SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0257016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, E.; Venter, C.; Laubscher, G.J.; Kotze, M.J.; Oladejo, S.O.; Watson, L.R.; Rajaratnam, K.; Watson, B.W.; Kell, D.B. Prevalence of symptoms, comorbidities, fibrin amyloid microclots and platelet pathology in individuals with Long COVID/Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC). Cardiovasc Diabetol 2022, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, A.B.; Greene, C.; Dayaramani, C.; Rauchman, S.H.; Stecker, M.M.; De Leon, J.; Pinkhasov, A. Long COVID, the Brain, Nerves, and Cognitive Function. Neurol Int 2023, 15, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Henry, B.M. COVID-19 and its long-term sequelae: what do we know in 2023? Pol Arch Intern Med 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Mahoney, L.L.; Routen, A.; Gillies, C.; Ekezie, W.; Welford, A.; Zhang, A.; Karamchandani, U.; Simms-Williams, N.; Cassambai, S.; Ardavani, A.; et al. The prevalence and long-term health effects of Long Covid among hospitalised and non-hospitalised populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 55, 101762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasserie, T.; Hittle, M.; Goodman, S.N. Assessment of the Frequency and Variety of Persistent Symptoms Among Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw Open 2021, 4, e2111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. The Lancet infectious diseases 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, M.; Iwasaki, A. The neurobiology of long COVID. Neuron 2022, 110, 3484–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. More than 50 long-term effects of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, T.J.; Neumann, C.; Bahmer, T.; Chaplinskaya-Sobol, I.; Endres, M.; Geritz, J.; Haeusler, K.G.; Heuschmann, P.U.; Hildesheim, H.; Hinz, A.; et al. Fatigue and cognitive impairment after COVID-19: A prospective multicentre study. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 53, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, S.; Rivas Zozaya, N.; Murillo, N.; Garcia-Molina, A.; Figueroa Chacon, C.A.; Kumru, H. Multidisciplinary outpatient rehabilitation of physical and neurological sequelae and persistent symptoms of covid-19: a prospective, observational cohort study. Disabil Rehabil 2022, 44, 6833–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badenoch, J.B.; Rengasamy, E.R.; Watson, C.; Jansen, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Sundaram, R.D.; Hafeez, D.; Burchill, E.; Saini, A.; Thomas, L.; et al. Persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms after COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Commun 2022, 4, fcab297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, M.G.; Palladini, M.; De Lorenzo, R.; Magnaghi, C.; Poletti, S.; Furlan, R.; Ciceri, F.; group, C.-B.O.C.S.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Benedetti, F. Persistent psychopathology and neurocognitive impairment in COVID-19 survivors: Effect of inflammatory biomarkers at three-month follow-up. Brain Behav Immun 2021, 94, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.H.; Lin, J.J.; Doernberg, M.; Stone, K.; Navis, A.; Festa, J.R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Assessment of Cognitive Function in Patients After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw Open 2021, 4, e2130645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, R.; Balanza-Martinez, V.; Luperdi, S.C.; Estrada, I.; Latorre, A.; Gonzalez-Jimenez, P.; Bouzas, L.; Yepez, K.; Ferrando, A.; Reyes, S.; et al. Long-term neuropsychiatric outcomes in COVID-19 survivors: A 1-year longitudinal study. J Intern Med 2022, 291, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramaglia, C.; Gattoni, E.; Gambaro, E.; Bellan, M.; Balbo, P.E.; Baricich, A.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Pirisi, M.; Binda, V.; Feggi, A.; et al. Anxiety, Stress and Depression in COVID-19 Survivors From an Italian Cohort of Hospitalized Patients: Results From a 1-Year Follow-Up. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13, 862651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taquet, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Husain, M.; Luciano, S.; Harrison, P.J. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Gu, X.; Kang, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X.; et al. 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study. Lancet 2021, 397, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premraj, L.; Kannapadi, N.V.; Briggs, J.; Seal, S.M.; Battaglini, D.; Fanning, J.; Suen, J.; Robba, C.; Fraser, J.; Cho, S.M. Mid and long-term neurological and neuropsychiatric manifestations of post-COVID-19 syndrome: A meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci 2022, 434, 120162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, V.; Stefanou, M.I.; Demetriou, M.; Siafakas, N.; Makris, M.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Kympouropoulos, S.P.; Tsoporis, J.N.; Spandidos, D.A.; et al. Long COVID and neuropsychiatric manifestations (Review). Exp Ther Med 2022, 23, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpelli, S.; Nadorff, M.R.; Bjorvatn, B.; Chung, F.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Espie, C.A.; Inoue, Y.; Matsui, K.; Merikanto, I.; Morin, C.M.; et al. Nightmares in People with COVID-19: Did Coronavirus Infect Our Dreams? Nat Sci Sleep 2022, 14, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trecca, E.M.C.; Cassano, M.; Longo, F.; Petrone, P.; Miani, C.; Hummel, T.; Gelardi, M. Results from psychophysical tests of smell and taste during the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2022, 42, S20–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanou, M.I.; Palaiodimou, L.; Bakola, E.; Smyrnis, N.; Papadopoulou, M.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Rizos, E.; Boutati, E.; Grigoriadis, N.; Krogias, C.; et al. Neurological manifestations of long-COVID syndrome: a narrative review. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2022, 13, 20406223221076890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, M.; Driscoll, R.; Pardhan, S. The prevalence of sensory changes in post-COVID syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 980253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudzik, M.; Babicki, M.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Kapusta, J. Persisting Smell and Taste Disorders in Patients Who Recovered from SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection-Data from the Polish PoLoCOV-CVD Study. Viruses 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.W.; Leonard, B.E.; Helmeste, D.M. Long COVID, neuropsychiatric disorders, psychotropics, present and future. Acta Neuropsychiatr 2022, 34, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, N.M.; Churchill, A.; Nsair, A.; Hsu, J.J. Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome and the cardiovascular system: What is known? Am Heart J Plus 2021, 5, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, D.S.; Kotecha, T.; Razvi, Y.; Chacko, L.; Brown, J.T.; Jeetley, P.S.; Goldring, J.; Jacobs, M.; Lamb, L.E.; Negus, R.; et al. COVID-19: Myocardial Injury in Survivors. Circulation 2020, 142, 1120–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpal, S.; Tong, M.S.; Borchers, J.; Zareba, K.M.; Obarski, T.P.; Simonetti, O.P.; Daniels, C.J. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Findings in Competitive Athletes Recovering From COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Cardiol 2021, 6, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, P.; Tang, D.; Zhu, T.; Han, R.; Zhan, C.; Liu, W.; Zeng, H.; Tao, Q.; Xia, L. Cardiac Involvement in Patients Recovered From COVID-2019 Identified Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2020, 13, 2330–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, G.; Artico, J.; Kurdi, H.; Seraphim, A.; Lau, C.; Thornton, G.D.; Oliveira, M.F.; Adam, R.D.; Aziminia, N.; Menacho, K.; et al. Prospective Case-Control Study of Cardiovascular Abnormalities 6 Months Following Mild COVID-19 in Healthcare Workers. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2021, 14, 2155–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, F.; Spanevello, A.; De Ponti, R.; Visca, D.; Marazzato, J.; Palmiotto, G.; Feci, D.; Reboldi, G.; Fabbri, L.M.; Verdecchia, P. Electrocardiographic features of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Eur J Intern Med 2020, 78, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntmann, V.O.; Carerj, M.L.; Wieters, I.; Fahim, M.; Arendt, C.; Hoffmann, J.; Shchendrygina, A.; Escher, F.; Vasa-Nicotera, M.; Zeiher, A.M.; et al. Outcomes of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients Recently Recovered From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol 2020, 5, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulson, N.; Petek, B.J.; Drezner, J.A.; Harmon, K.G.; Kliethermes, S.A.; Patel, M.R.; Baggish, A.L.; Outcomes Registry for Cardiac Conditions in Athletes, I. SARS-CoV-2 Cardiac Involvement in Young Competitive Athletes. Circulation 2021, 144, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majure, D.T.; Gruberg, L.; Saba, S.G.; Kvasnovsky, C.; Hirsch, J.S.; Jauhar, R.; Northwell Health, C.-R.C. Usefulness of Elevated Troponin to Predict Death in Patients With COVID-19 and Myocardial Injury. Am J Cardiol 2021, 138, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, H.A.; Atici, A.; Sahin, I.; Alici, G.; Aktas Tekin, E.; Baycan, O.F.; Ozturk, F.; Oflar, E.; Tugrul, S.; Yavuz, M.B.; et al. Prognostic significance of cardiac injury in COVID-19 patients with and without coronary artery disease. Coron Artery Dis 2021, 32, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nai Fovino, L.; Cademartiri, F.; Tarantini, G. Subclinical coronary artery disease in COVID-19 patients. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2020, 21, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubkhani, D.; Khunti, K.; Nafilyan, V.; Maddox, T.; Humberstone, B.; Diamond, I.; Banerjee, A. Post-covid syndrome in individuals admitted to hospital with covid-19: retrospective cohort study. BMJ 2021, 372, n693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Khan, M.A.; Putrino, D.; Woodcock, A.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Long COVID: pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of coagulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2023, 34, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.; Yazdi, M.H.H.; Mowlavi, A.A.; Ceberg, S.; Aznar, M.C.; Tabrizi, F.V.; Salek, R.; Ghodsi, A.; Jamali, F. Surface guided 3DCRT in deep-inspiration breath-hold for left sided breast cancer radiotherapy: implementation and first clinical experience in Iran. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 2022, 27, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, M.; Baryshnikova, E.; Anguissola, M.; Pugliese, S.; Falco, M.; Menicanti, L. The Long Term Residual Effects of COVID-Associated Coagulopathy. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Banerjee, M. Immune Thrombocytopenia Secondary to COVID-19: a Systematic Review. SN Compr Clin Med 2020, 2, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, T.; Zhili, N.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, R.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y. Dynamic changes in peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in adult patients with COVID-19. Int J Infect Dis 2020, 98, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Shang, Y.M.; Song, W.B.; Li, Q.Q.; Xie, H.; Xu, Q.F.; Jia, J.L.; Li, L.M.; Mao, H.L.; Zhou, X.M.; et al. Follow-up study of the pulmonary function and related physiological characteristics of COVID-19 survivors three months after recovery. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 25, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Tan, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Yuan, S.; et al. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on pulmonary function in early convalescence phase. Respir Res 2020, 21, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P.M.; Barratt, S.L.; Condliffe, R.; Desai, S.R.; Devaraj, A.; Forrest, I.; Gibbons, M.A.; Hart, N.; Jenkins, R.G.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Respiratory follow-up of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Thorax 2020, 75, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Vasconcello-Castillo, L.; Alsina-Restoy, X.; Solis-Navarro, L.; Burgos, F.; Puppo, H.; Vilaro, J. Respiratory function in patients post-infection by COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Z. Follow-Ups on Persistent Symptoms and Pulmonary Function Among Post-Acute COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 702635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorsell, T.; Sundh, J.; Lange, A.; Ahlm, C.; Forsell, M.N.E.; Tevell, S.; Blomberg, A.; Edin, A.; Normark, J.; Cajander, S. Risk factors for impaired respiratory function post COVID-19: A prospective cohort study of nonhospitalized and hospitalized patients. J Intern Med 2023, 293, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, H.C.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Blackwood, B.; Calandra, T.; Chlan, L.L.; Choong, K.; Connolly, B.; Dark, P.; Ferrucci, L.; Finfer, S.; et al. Understanding and Enhancing Sepsis Survivorship. Priorities for Research and Practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019, 200, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Xie, Y.; Bowe, B. High-dimensional characterization of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. Nature 2021, 594, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faour, W.H.; Choaib, A.; Issa, E.; Choueiry, F.E.; Shbaklo, K.; Alhajj, M.; Sawaya, R.T.; Harhous, Z.; Alefishat, E.; Nader, M. Mechanisms of COVID-19-induced kidney injury and current pharmacotherapies. Inflamm Res 2022, 71, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, S.; Li, C.; Siragy, H.M. Intrarenal Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: the Old and the New. Curr Hypertens Rep 2017, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, P.R.; Sirois, P.; Fernandes, P.D. The role of kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems in COVID-19 infection. Peptides 2021, 135, 170428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, R.; Hussain, H.; Ravelo, N.; Sriramajayam, K.; Di Gregorio, D.M.; Paulrasu, K.; Chen, P.; Young, K.; Masciarella, A.D.; Jayakumar, A.R.; et al. Kidney Damage in Long COVID: Studies in Experimental Mice. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Peluso, M.J.; Luo, X.; Thomas, R.; Shin, M.G.; Neidleman, J.; Andrew, A.; Young, K.C.; Ma, T.; Hoh, R.; et al. Long COVID manifests with T cell dysregulation, inflammation and an uncoordinated adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2. Nat Immunol 2024, 25, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydyznski Moderbacher, C.; Ramirez, S.I.; Dan, J.M.; Grifoni, A.; Hastie, K.M.; Weiskopf, D.; Belanger, S.; Abbott, R.K.; Kim, C.; Choi, J.; et al. Antigen-Specific Adaptive Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Acute COVID-19 and Associations with Age and Disease Severity. Cell 2020, 183, 996–1012.e1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, J.L.; Galindo, M.; Carmona, L.; Lledo, A.; Retuerto, M.; Blanco, R.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Martinez-Lopez, D.; Castrejon, I.; Alvaro-Gracia, J.M.; et al. Clinical outcomes of hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and chronic inflammatory and autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a multicentric matched cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 2020, 79, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, G.; Calvez, V.; Savoia, C. Hypertension and COVID-19: Current Evidence and Perspectives. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 2022, 29, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olloquequi, J. COVID-19 Susceptibility in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Clin Invest 2020, 50, e13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Abdelhak, A.; Foschi, M.; Tumani, H.; Otto, M. Guillain-Barre syndrome spectrum associated with COVID-19: an up-to-date systematic review of 73 cases. J Neurol 2021, 268, 1133–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, Z.; Karimi, N. Guillain Barre syndrome associated with COVID-19 infection: A case report. J Clin Neurosci 2020, 76, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keh, R.Y.S.; Scanlon, S.; Datta-Nemdharry, P.; Donegan, K.; Cavanagh, S.; Foster, M.; Skelland, D.; Palmer, J.; Machado, P.M.; Keddie, S.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination and Guillain-Barre syndrome: analyses using the National Immunoglobulin Database. Brain 2023, 146, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consiglio, C.R.; Cotugno, N.; Sardh, F.; Pou, C.; Amodio, D.; Rodriguez, L.; Tan, Z.; Zicari, S.; Ruggiero, A.; Pascucci, G.R.; et al. The Immunology of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 968–981.e967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodin, P.; Casari, G.; Townsend, L.; O'Farrelly, C.; Tancevski, I.; Loffler-Ragg, J.; Mogensen, T.H.; Casanova, J.L.; Effort, C.H.G. Studying severe long COVID to understand post-infectious disorders beyond COVID-19. Nat Med 2022, 28, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Karim, M.; Gupta, V.; Goel, H.; Jain, R. A Comprehensive Review of COVID-19-Associated Endocrine Manifestations. South Med J 2023, 116, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, F.; Amiel, S.A.; Zimmet, P.; Alberti, G.; Bornstein, S.; Eckel, R.H.; Mingrone, G.; Boehm, B.; Cooper, M.E.; Chai, Z.; et al. New-Onset Diabetes in Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Cozma, D.; Kamel, M.; Hamad, M.; Mohammad, M.G.; Khan, N.A.; Saber, M.M.; Semreen, M.H.; Steenblock, C. Long-COVID, Metabolic and Endocrine Disease. Horm Metab Res 2022, 54, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Qiao, F.; Chen, Y.; Chan, D.Y.L.; Yim, H.C.H.; Fok, K.L.; Chen, H. SARS-CoV-2 and male infertility: from short- to long-term impacts. J Endocrinol Invest 2023, 46, 1491–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczerbinski, L.; Okruszko, M.A.; Szablowski, M.; Solomacha, S.; Sowa, P.; Kiszkiel, L.; Goscik, J.; Kretowski, A.J.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Kaminski, K. Long-term effects of COVID-19 on the endocrine system - a pilot case-control study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1192174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, D.; Pallotti, F.; Anzuini, A.; Bianchini, S.; Caponecchia, L.; Carraro, A.; Ciardi, M.R.; Faja, F.; Fiori, C.; Gianfrilli, D.; et al. Male reproductive health after 3 months from SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicentric study. J Endocrinol Invest 2023, 46, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinislioglu, A.E.; Cinislioglu, N.; Demirdogen, S.O.; Sam, E.; Akkas, F.; Altay, M.S.; Utlu, M.; Sen, I.A.; Yildirim, F.; Kartal, S.; et al. The relationship of serum testosterone levels with the clinical course and prognosis of COVID-19 disease in male patients: A prospective study. Andrology 2022, 10, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonia, A.; Pontillo, M.; Capogrosso, P.; Gregori, S.; Carenzi, C.; Ferrara, A.M.; Rowe, I.; Boeri, L.; Larcher, A.; Ramirez, G.A.; et al. Testosterone in males with COVID-19: A 7-month cohort study. Andrology 2022, 10, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022, 10, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, B.; Tan, T.; Clarke, S.A.; Mills, E.G.; Patel, B.; Modi, M.; Phylactou, M.; Eng, P.C.; Thurston, L.; Alexander, E.C.; et al. Thyroid Function Before, During, and After COVID-19. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021, 106, e803–e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, T.; Lv, Y. Causal associations between thyroid dysfunction and COVID-19 susceptibility and severity: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 961717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathallah, N.; Slim, R.; Larif, S.; Hmouda, H.; Ben Salem, C. Drug-Induced Hyperglycaemia and Diabetes. Drug Saf 2015, 38, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkas, T. Gastrointestinal involvement in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Gastroenterol 2020, 33, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Shen, L.; Zhu, L.; Liang, Y.; Lin, X.; Jiao, N.; Cheng, S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Gastrointestinal sequelae 90 days after discharge for COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021, 6, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.; Tariq, R.; Jena, A.; Vesely, E.K.; Singh, S.; Khanna, S.; Sharma, V. Gastrointestinal manifestations of long COVID: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2022, 15, 17562848221118403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasa, S.; Desai, M.; Thoguluva Chandrasekar, V.; Patel, H.K.; Kennedy, K.F.; Roesch, T.; Spadaccini, M.; Colombo, M.; Gabbiadini, R.; Artifon, E.L.A.; et al. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Fecal Viral Shedding in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3, e2011335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Qiu, Y.; He, J.S.; Tan, J.Y.; Li, X.H.; Liang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhu, L.R.; Chen, Y.; Iacucci, M.; et al. Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020, 5, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goertz, Y.M.J.; Van Herck, M.; Delbressine, J.M.; Vaes, A.W.; Meys, R.; Machado, F.V.C.; Houben-Wilke, S.; Burtin, C.; Posthuma, R.; Franssen, F.M.E.; et al. Persistent symptoms 3 months after a SARS-CoV-2 infection: the post-COVID-19 syndrome? ERJ Open Res 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, E.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Long-term gastrointestinal outcomes of COVID-19. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogariu, A.M.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Digestive involvement in the Long-COVID syndrome. Med Pharm Rep 2022, 95, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wan, Y.; Zuo, T.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Lu, W.; Xu, W.; Lui, G.C.Y.; et al. Prolonged Impairment of Short-Chain Fatty Acid and L-Isoleucine Biosynthesis in Gut Microbiome in Patients With COVID-19. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 548–561.e544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paine, S.K.; Rout, U.K.; Bhattacharyya, C.; Parai, D.; Alam, M.; Nanda, R.R.; Tripathi, D.; Choudhury, P.; Kundu, C.N.; Pati, S.; et al. Temporal dynamics of oropharyngeal microbiome among SARS-CoV-2 patients reveals continued dysbiosis even after Viral Clearance. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestad, B.; Ueland, T.; Lerum, T.V.; Dahl, T.B.; Holm, K.; Barratt-Due, A.; Kasine, T.; Dyrhol-Riise, A.M.; Stiksrud, B.; Tonby, K.; et al. Respiratory dysfunction three months after severe COVID-19 is associated with gut microbiota alterations. J Intern Med 2022, 291, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, S.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, D.; Guo, J.; Wu, W.R.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.J.; et al. Six-month follow-up of gut microbiota richness in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2022, 71, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.Y.; Rao, B.C.; Zeng, Z.H.; Wang, X.M.; Ren, T.; Wang, H.Y.; Luo, H.; Ren, H.Y.; Liu, C.; Ding, S.Y.; et al. Characterization of oral and gut microbiome and plasma metabolomics in COVID-19 patients after 1-year follow-up. Mil Med Res 2022, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, I.A.; Pintea, I.; Bocsan, I.C.; Dobrican, C.T.; Deleanu, D. COVID-19 Disease Leading to Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Exacerbation: A Romanian Retrospective Study. Healthcare (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameni, F.; Hajikhani, B.; Yaslianifard, S.; Goudarzi, M.; Owlia, P.; Nasiri, M.J.; Shokouhi, S.; Bakhtiyari, M.; Dadashi, M. COVID-19 and Skin Manifestations: An Overview of Case Reports/Case Series and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence Studies. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 573188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahara, T.; Yokota, K. Livedo Reticularis Associated with COVID-19. Intern Med 2022, 61, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.W.; Tam, Y.C.; Oh, C.C. Skin manifestations of COVID-19: A worldwide review. JAAD Int 2021, 2, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, M.B.; Kumar, M.P.; Bhardwaj, A. The trend of cutaneous lesions during COVID-19 pandemic: lessons from a meta-analysis and systematic review. Int J Dermatol 2020, 59, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. The coagulopathy, endotheliopathy, and vasculitis of COVID-19. Inflamm Res 2020, 69, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, M.; Long, B. Dermatologic manifestations and complications of COVID-19. Am J Emerg Med 2020, 38, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.C.; Huang, A.; Desai, A.; Safai, B.; Marmon, S. "COVID toes": A true viral phenomenon or a diagnosis without a leg to stand on? JAAD Int 2022, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ica, O.M.; Mitroi, G.; Ianosi, S.L.; Tutunaru, C.V.; Leru, P.M.; Matei, D.; Avramescu, E.T.; Tanasie, C.A.; Mitroi, I.B.; Neagoe, C.D.; et al. Defining the short-term and long-term skin manifestations of COVID-19: insights after more than three years of the pandemic. Rom J Morphol Embryol 2023, 64, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.E.; Gallman, A.E.; Hruza, G.J.; Rosenbach, M.; Lipoff, J.B.; Desai, S.R.; French, L.E.; Lim, H.; Cyster, J.G.; Fox, L.P.; et al. Long COVID in the skin: a registry analysis of COVID-19 dermatological duration. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, 21, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, P.; Frumholtz, L.; Jaume, L.; De Masson, A.; Jachiet, M.; Begon, E.; Sulimovic, L.; Petit, A.; Bachelez, H.; Bagot, M.; et al. Frequency of relapse and persistent cutaneous symptoms after a first episode of chilblain-like lesion during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021, 35, e566–e568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, H.; Paidas, M.J.; Rajalakshmi, R.; Fadel, A.; Ali, M.; Chen, P.; Jayakumar, A.R. Dermatologic Changes in Experimental Model of Long COVID. Microorganisms 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, M.; Gianotti, R.; Shah, M.; Bradanini, L.; Tosi, D.; Veraldi, S.; Ziv, M.; Leshem, E.; Dodiuk-Gad, R.P. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: Report of three cases and a review of literature. J Dermatol Sci 2020, 98, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandaker, M.H.; Espinosa, R.E.; Nishimura, R.A.; Sinak, L.J.; Hayes, S.N.; Melduni, R.M.; Oh, J.K. Pericardial disease: diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc 2010, 85, 572–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, T.; Knight, D.S.; Razvi, Y.; Kumar, K.; Vimalesvaran, K.; Thornton, G.; Patel, R.; Chacko, L.; Brown, J.T.; Coyle, C.; et al. Patterns of myocardial injury in recovered troponin-positive COVID-19 patients assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Eur Heart J 2021, 42, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korompoki, E.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Fotiou, D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Terpos, E. Late-onset hematological complications post COVID-19: An emerging medical problem for the hematologist. Am J Hematol 2022, 97, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechuga, G.C.; Morel, C.M.; De-Simone, S.G. Hematological alterations associated with long COVID-19. Front Physiol 2023, 14, 1203472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, M.G.; Alanazi, N.; Yousef, A.; Alanazi, N.; Alotaibi, B.; Aljurf, M.; El Fakih, R. COVID-19 associated with immune thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Hematol 2022, 15, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Thrombosis and thrombocytopenia in COVID-19 and after COVID-19 vaccination. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2022, 32, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, V.; Vitale, C.; Rispoli, A.; Izzo, C.; Virtuoso, N.; Ferruzzi, G.J.; Santopietro, M.; Melfi, A.; Rusciano, M.R.; Maglio, A.; et al. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: Involvement and Interactions between Respiratory, Cardiovascular and Nervous Systems. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daines, L.; Zheng, B.; Pfeffer, P.; Hurst, J.R.; Sheikh, A. A clinical review of long-COVID with a focus on the respiratory system. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2022, 28, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zeng, W.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; Xiang, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; et al. CT imaging changes of corona virus disease 2019(COVID-19): a multi-center study in Southwest China. J Transl Med 2020, 18, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, A.; Pellegrino, D.; Messina, E.; Siena, L.M.; Baccolini, V.; D'Antoni, L.; Landini, N.; Baiocchi, P.; Villari, P.; Catalano, C.; et al. The Role of Pulmonary Function Testing and Lung Imaging in the Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Respiration 2023, 102, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerum, T.V.; Aalokken, T.M.; Bronstad, E.; Aarli, B.; Ikdahl, E.; Lund, K.M.A.; Durheim, M.T.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Meltzer, C.; Tonby, K.; et al. Dyspnoea, lung function and CT findings 3 months after hospital admission for COVID-19. Eur Respir J 2021, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, N.; Khanum, I.; Kazi, M.A.I.; Riaz, S.U.; Khawaja, U.A.; Awan, S.; Irfan, M.; Zubairi, A.B.S.; Khan, J.A. Post-COVID-19 sequelae of the respiratory system. A single-centre experience reporting the compromise of the airway, alveolar and vascular components. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2022, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagevik Olsén, M.; Lannefors, L.; Nygren-Bonnier, M.; Johansson, E.-L. Long COVID–respiratory symptoms in non-hospitalised subjects–a cross-sectional study. European Journal of Physiotherapy 2023, 25, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthumana, J.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Xu, L.; Coca, S.G.; Garg, A.X.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bhatraju, P.K.; Ikizler, T.A.; Siew, E.D.; Ware, L.B.; et al. Biomarkers of inflammation and repair in kidney disease progression. J Clin Invest 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Feng, Z.; Rao, S.; Xiao, C.; Xue, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, W. Diarrhoea may be underestimated: a missing link in 2019 novel coronavirus. Gut 2020, 69, 1141–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, E.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Razi Soofiyani, S.; Abediazar, S.; Shoja, M.M.; Ardalan, M.; Zununi Vahed, S. Covid-19 and kidney injury: Pathophysiology and molecular mechanisms. Rev Med Virol 2021, 31, e2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventura, A.; Vecchie, A.; Dagna, L.; Martinod, K.; Dixon, D.L.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dentali, F.; Montecucco, F.; Massberg, S.; Levi, M.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, E.; Ananiev, J.; Yovchev, Y.; Arabadzhiev, G.; Abrashev, H.; Abrasheva, D.; Atanasov, V.; Kostandieva, R.; Mitev, M.; Petkova-Parlapanska, K.; et al. COVID-19 Complications: Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Mitochondrial and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, D.M.; Whettlock, E.M.; Liu, S.; Arachchillage, D.J.; Boyton, R.J. The immunology of long COVID. Nat Rev Immunol 2023, 23, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Andrade, B.; Siqueira, S.; de Assis Soares, W.R.; de Souza Rangel, F.; Santos, N.O.; Dos Santos Freitas, A.; Ribeiro da Silveira, P.; Tiwari, S.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Goes-Neto, A.; et al. Long-COVID and Post-COVID Health Complications: An Up-to-Date Review on Clinical Conditions and Their Possible Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awatade, N.T.; Wark, P.A.B.; Chan, A.S.L.; Mamun, S.; Mohd Esa, N.Y.; Matsunaga, K.; Rhee, C.K.; Hansbro, P.M.; Sohal, S.S.; On Behalf Of The Asian Pacific Society Of Respirology Apsr Copd, A. The Complex Association between COPD and COVID-19. J Clin Med 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J.; Scorza, F.A. Guillain-Barre syndrome in 220 patients with COVID-19. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg 2021, 57, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergantini, L.; Baldassarri, M.; d'Alessandro, M.; Brunelli, G.; Fabbri, G.; Zguro, K.; Degl'Innocenti, A.; study, G.-C.M.; Fallerini, C.; Bargagli, E.; et al. Ultra-rare RTEL1 gene variants associate with acute severity of COVID-19 and evolution to pulmonary fibrosis as a specific long COVID disorder. Respir Res 2023, 24, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, H.; Cui, G.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Chen, X.; Ren, H.; Sun, R.; Liu, W.; et al. Alterations in the human oral and gut microbiomes and lipidomics in COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, R.; Dai, W.; Zeng, R.; Luo, D.; Jiang, R.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Risks of digestive diseases in long COVID: evidence from a population-based cohort study. BMC Med 2024, 22, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Mu, M.; Yang, P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Yan, J.; Li, P.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Hu, C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study. Am J Gastroenterol 2020, 115, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.S.; Hung, I.F.N.; Chan, P.P.Y.; Lung, K.C.; Tso, E.; Liu, R.; Ng, Y.Y.; Chu, M.Y.; Chung, T.W.H.; Tam, A.R.; et al. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Virus Load in Fecal Samples From a Hong Kong Cohort: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, G.; Chu, H.; Wang, D.; Yan, H.H.; Poon, V.K.; Wen, L.; Wong, B.H.; Zhao, X.; et al. Human intestinal tract serves as an alternative infection route for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Sci Adv 2017, 3, eaao4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.; Young, B.E.; Ong, S. COVID-19 in gastroenterology: a clinical perspective. Gut 2020, 69, 1144–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Tang, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, H. Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1831–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Weng, S.; Xia, C.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, R.; Peng, L.; Sun, L.; et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms of long COVID-19 related to the ectopic colonization of specific bacteria that move between the upper and lower alimentary tract and alterations in serum metabolites. BMC Med 2023, 21, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekaev, N.N.; Zhukova, O.V.; Protsenko, D.N.; Demina, O.M.; Khlystova, E.A.; Bogin, V. Clinical characteristics of dermatologic manifestations of COVID-19 infection: case series of 15 patients, review of literature, and proposed etiological classification. Int J Dermatol 2020, 59, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandao, M.; Barros, L.M.; de Aquino Mendonca, J.; de Oliveira, A.R.; de Araujo, T.M.; Veras, V.S. Clinical and histopathological findings of cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 patients. Dermatol Ther 2020, 33, e13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Freeman, E.E. Viruses, Variants, and Vaccines: How COVID-19 Has Changed the Way We Look at Skin. Curr Dermatol Rep 2022, 11, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).