Submitted:
02 April 2024
Posted:
03 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
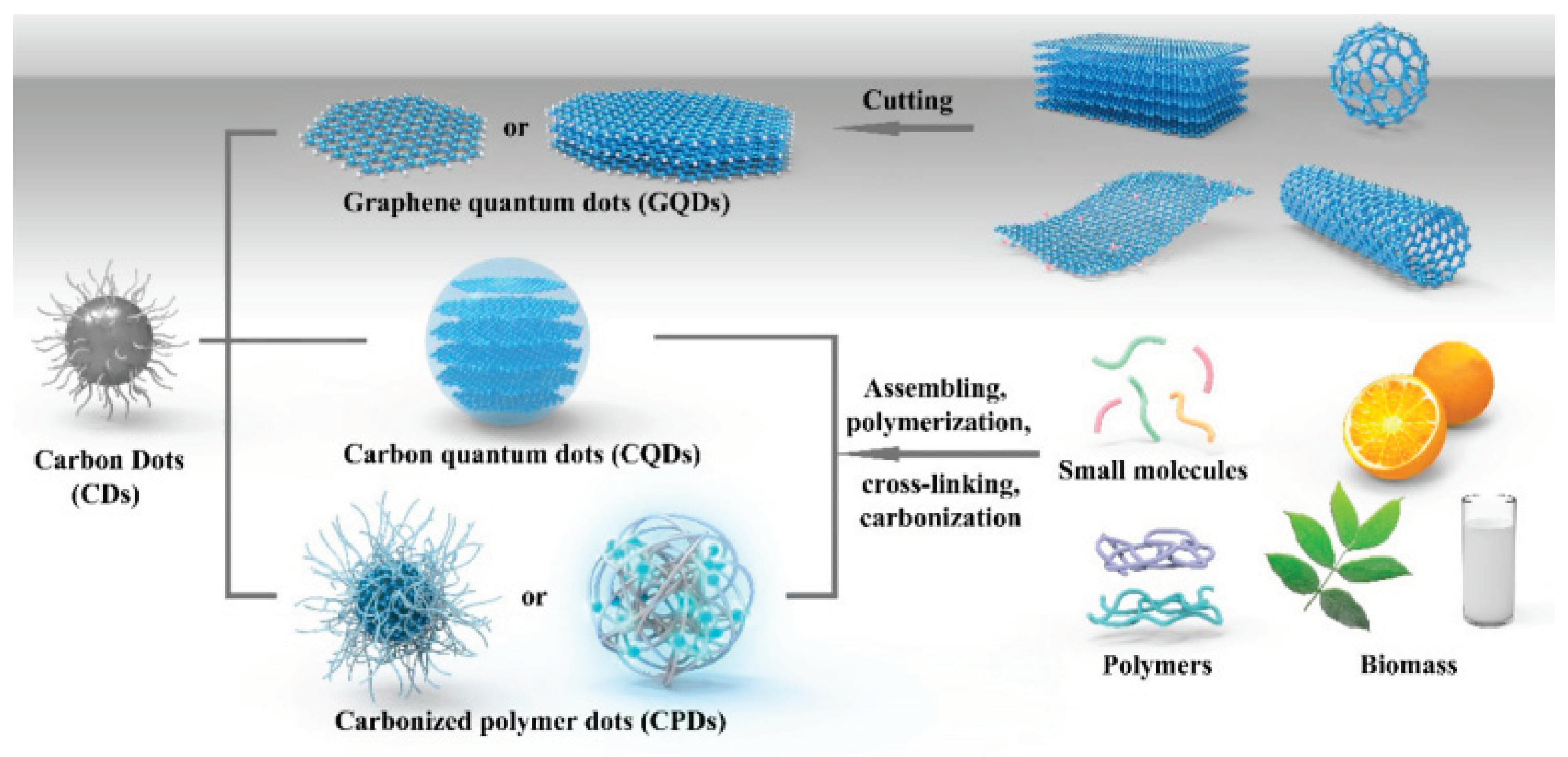
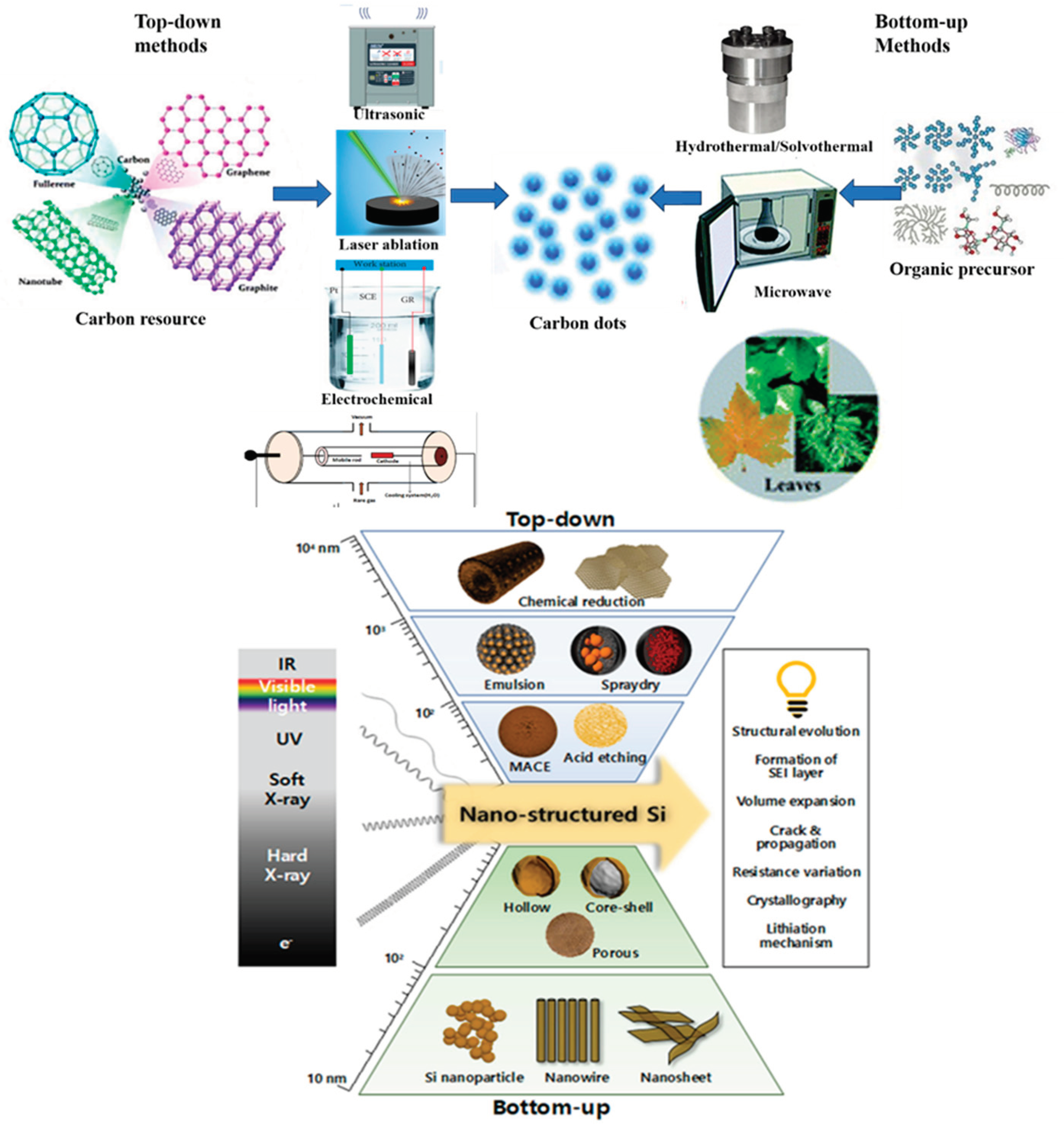
2. Synthesis Method for Carbon Dots
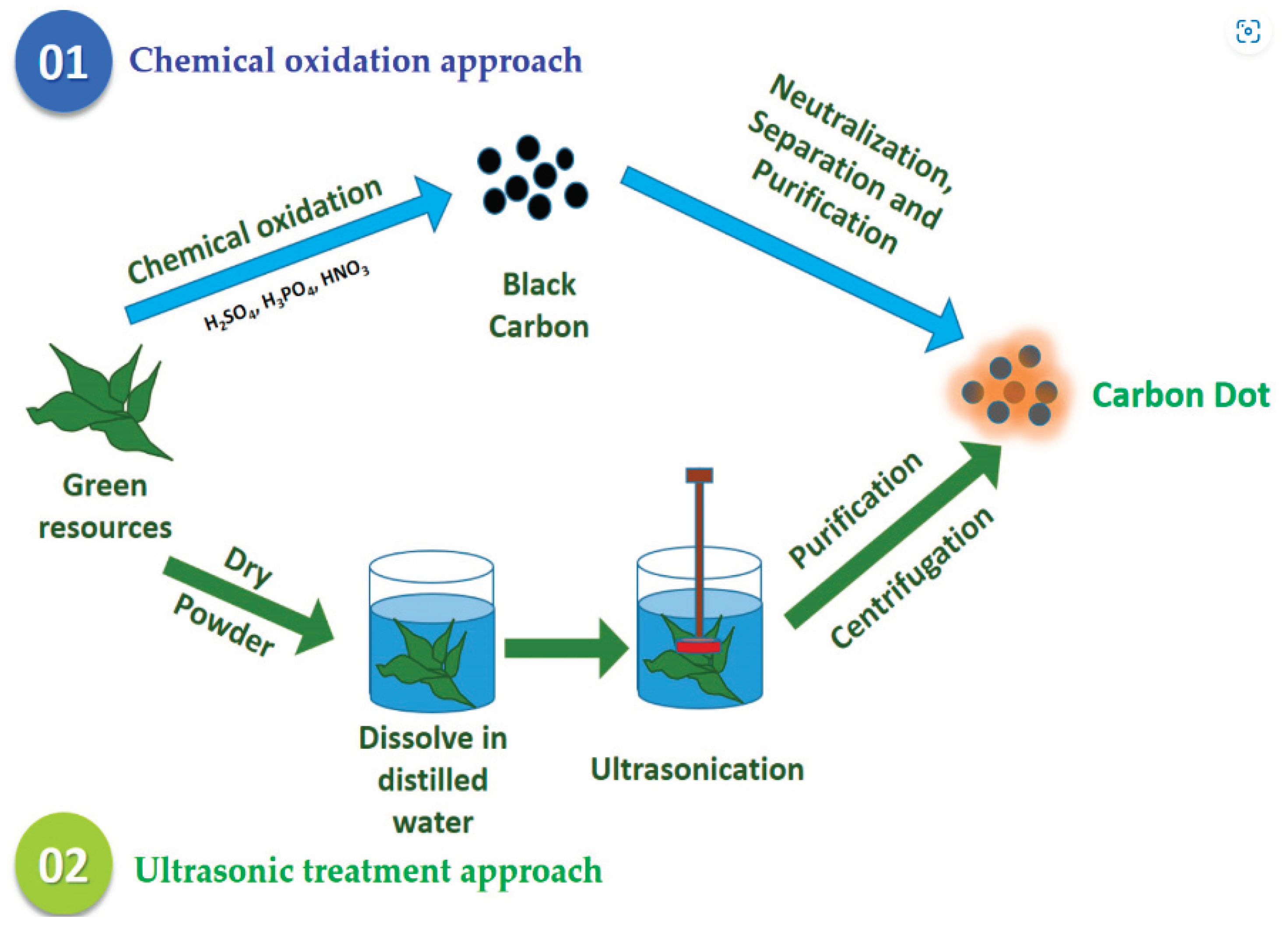
2.1. Ultrasonic Approaches
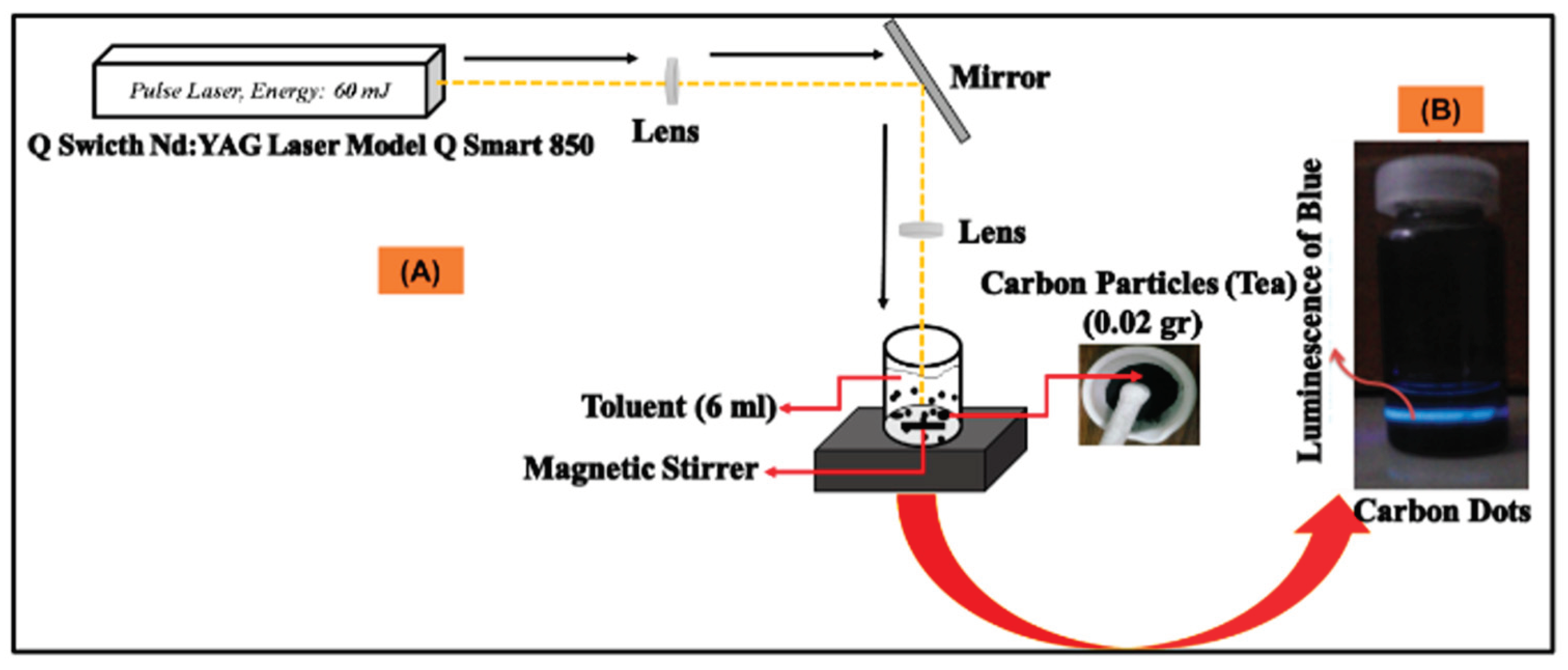
2.2. Laser Ablation
2.3. Electrochemical Oxidation
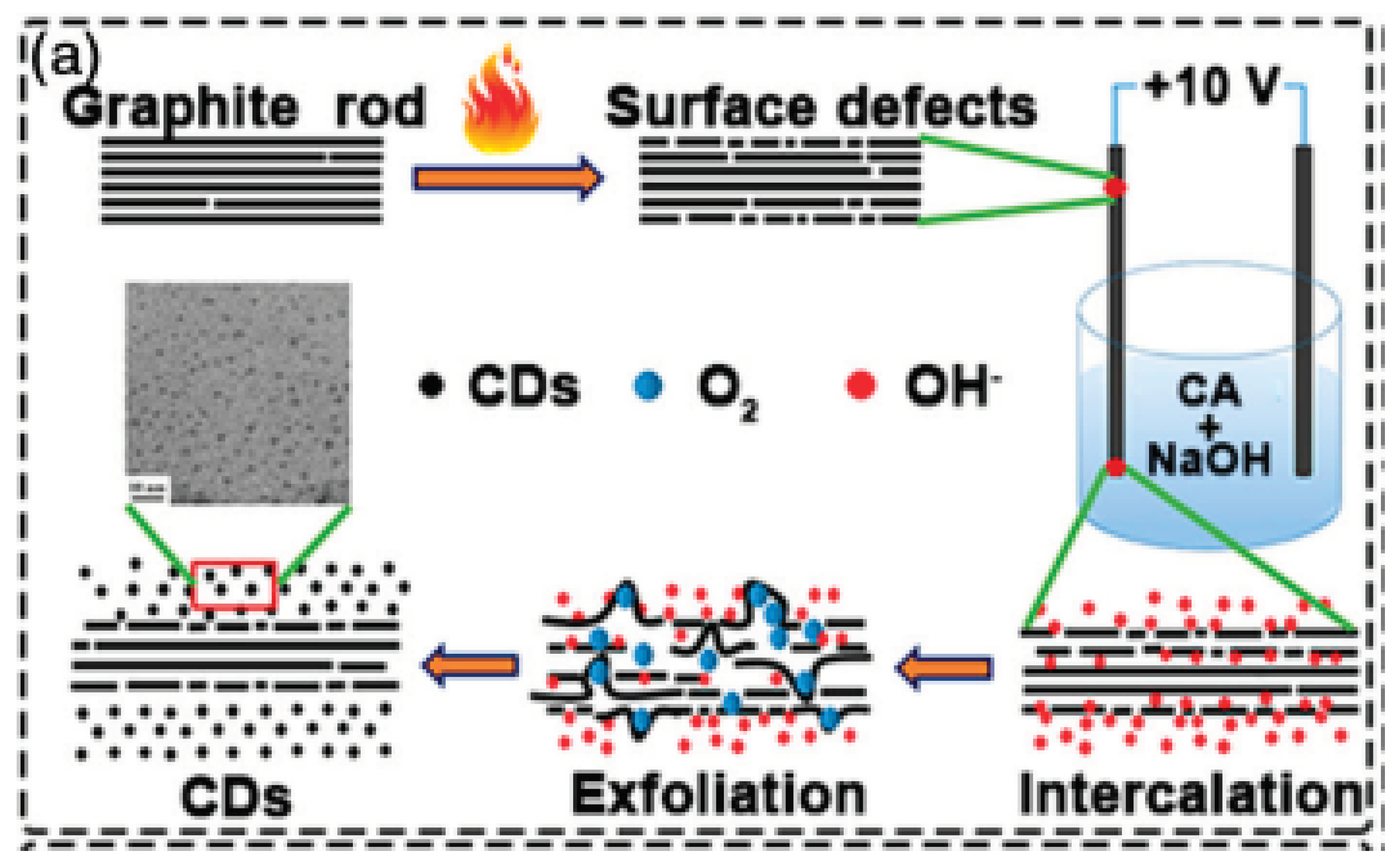
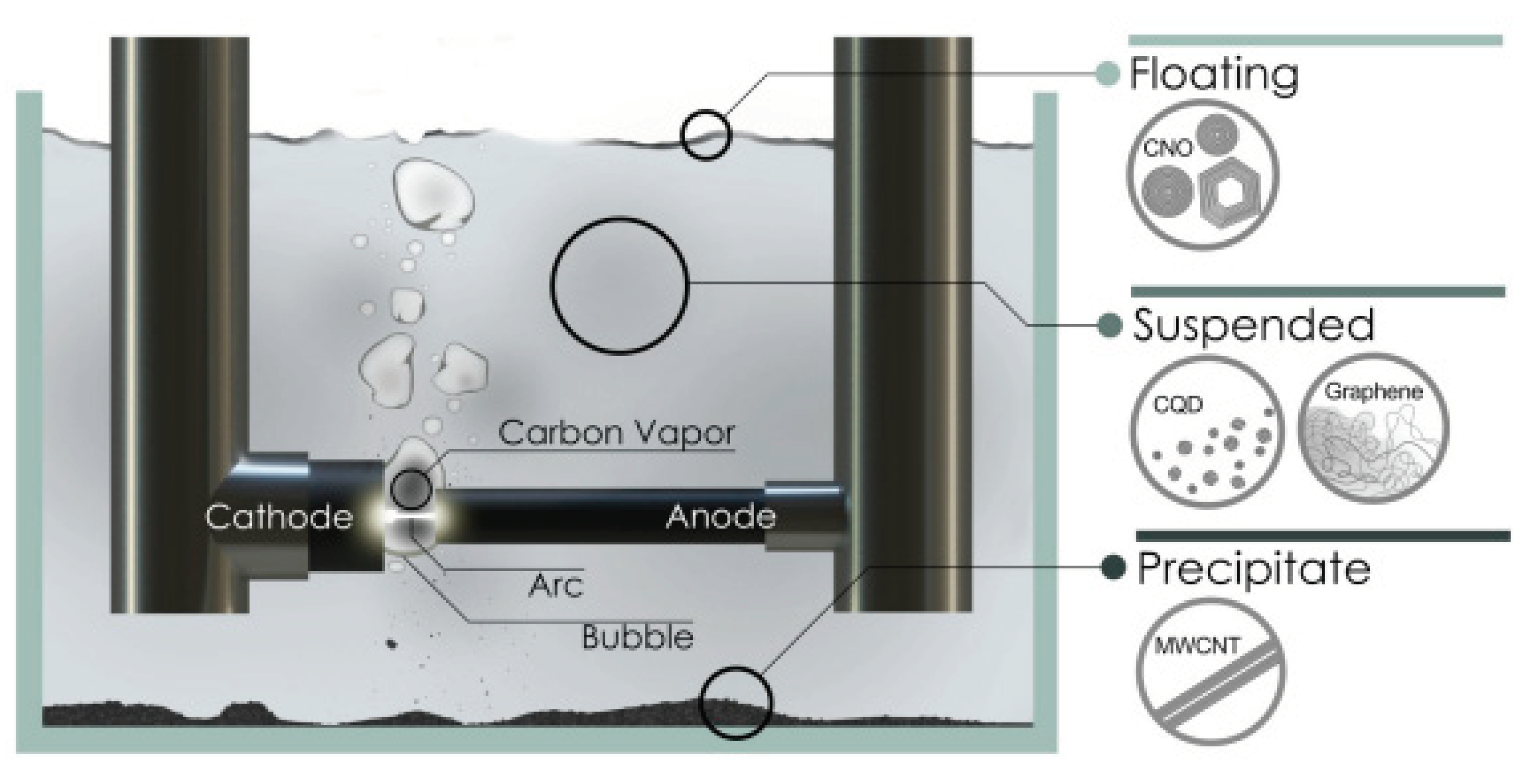
2.1.4. Arc Discharge
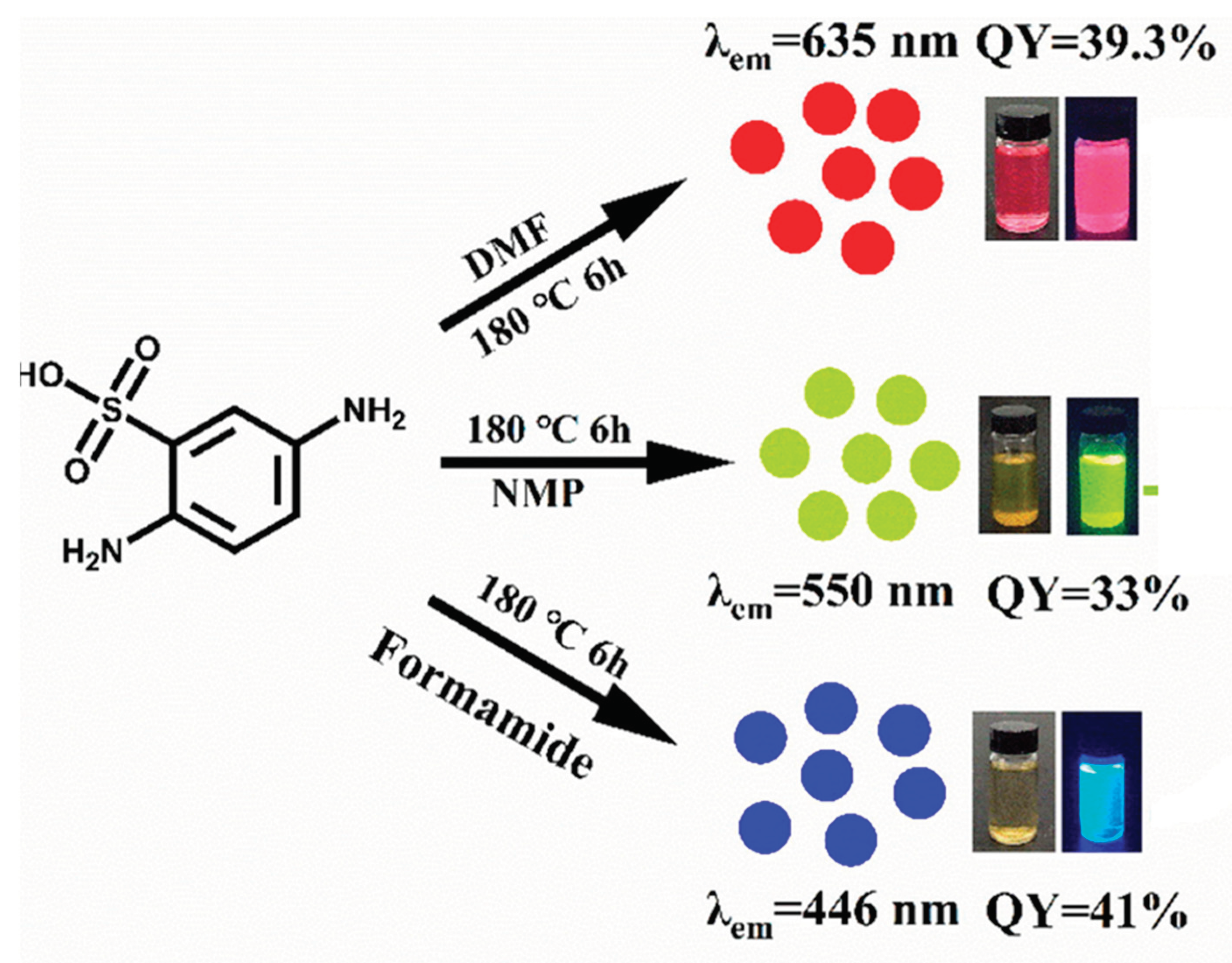
2.4. Hydrothermal Method
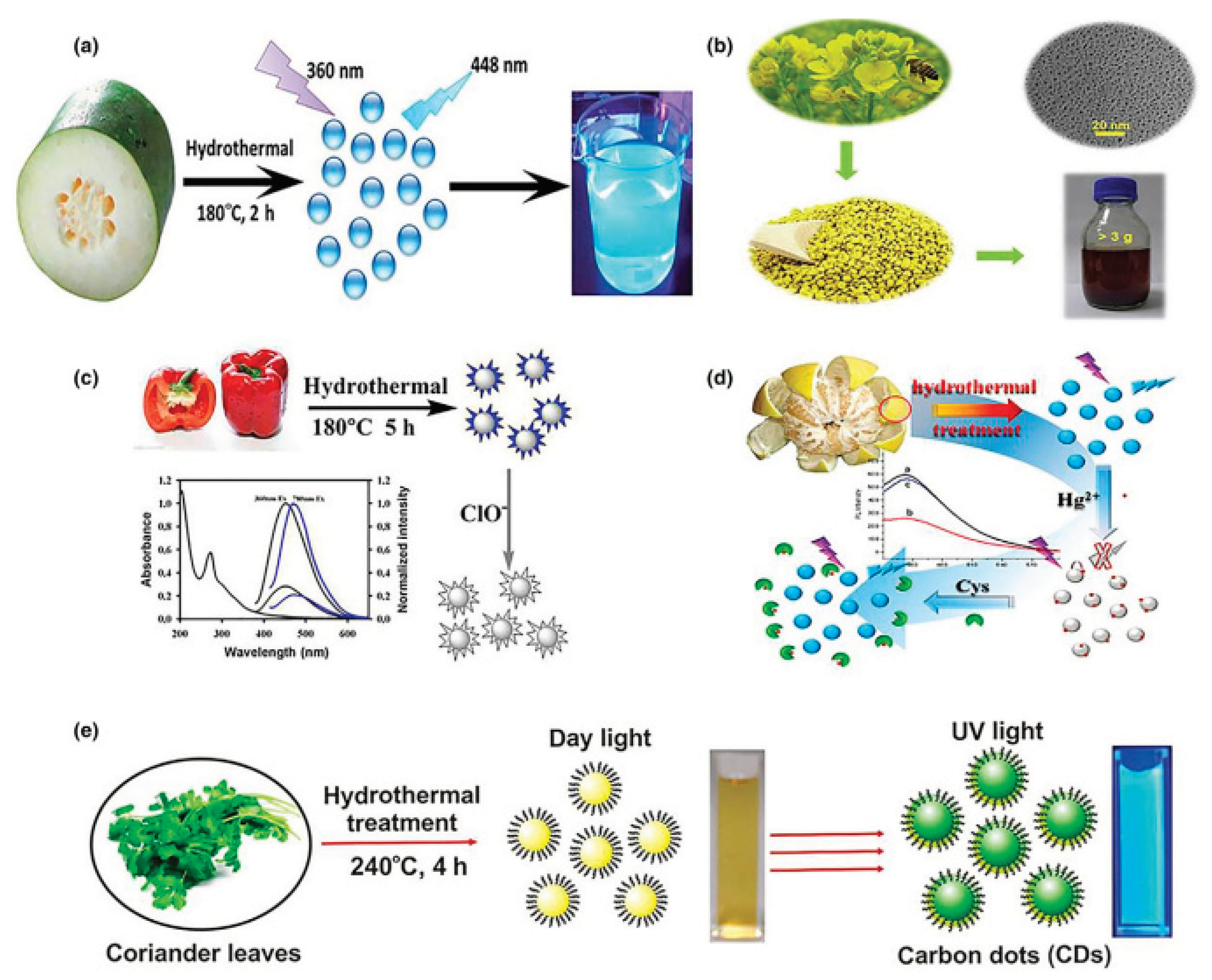
2.5. Microwave Synthesize Approach
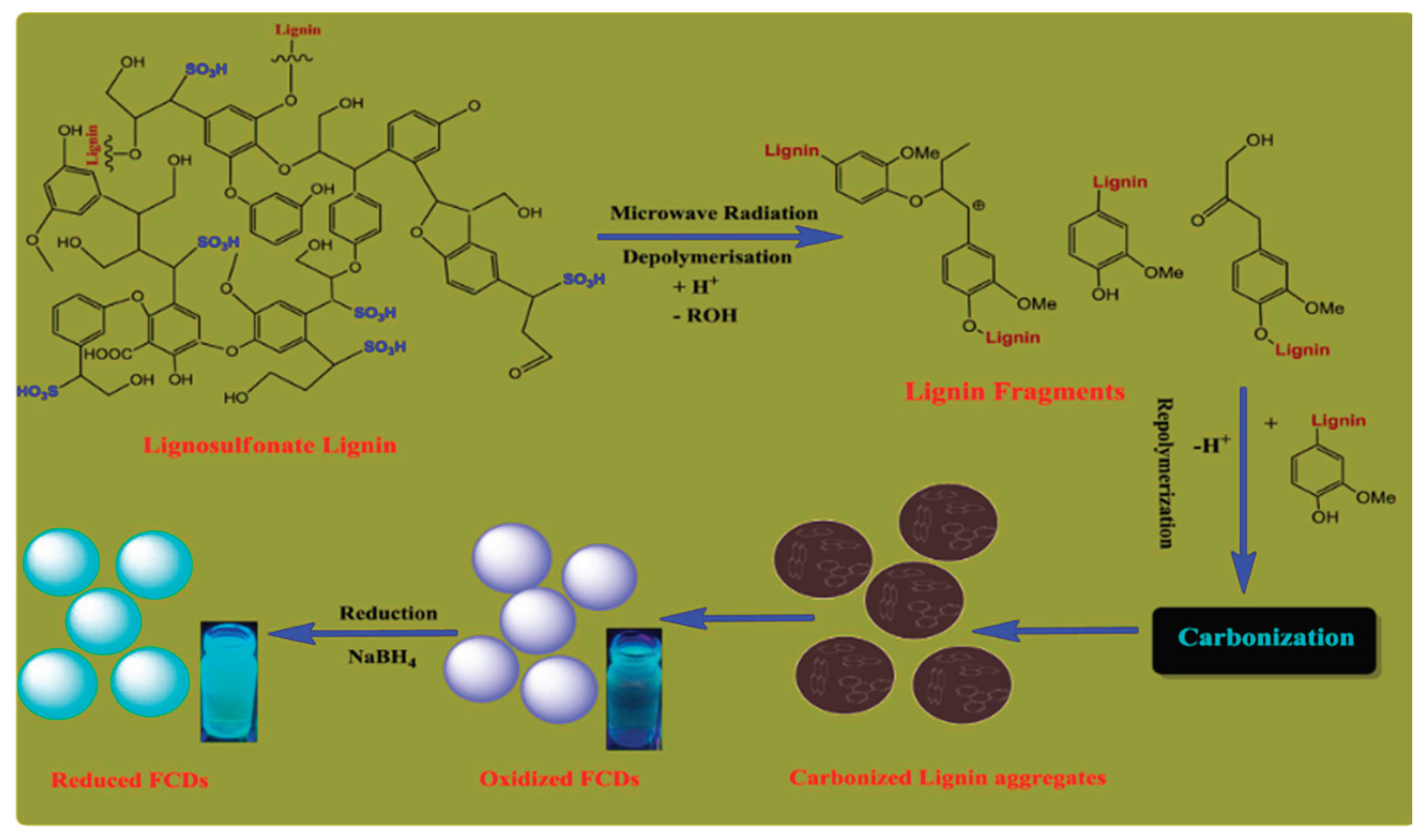
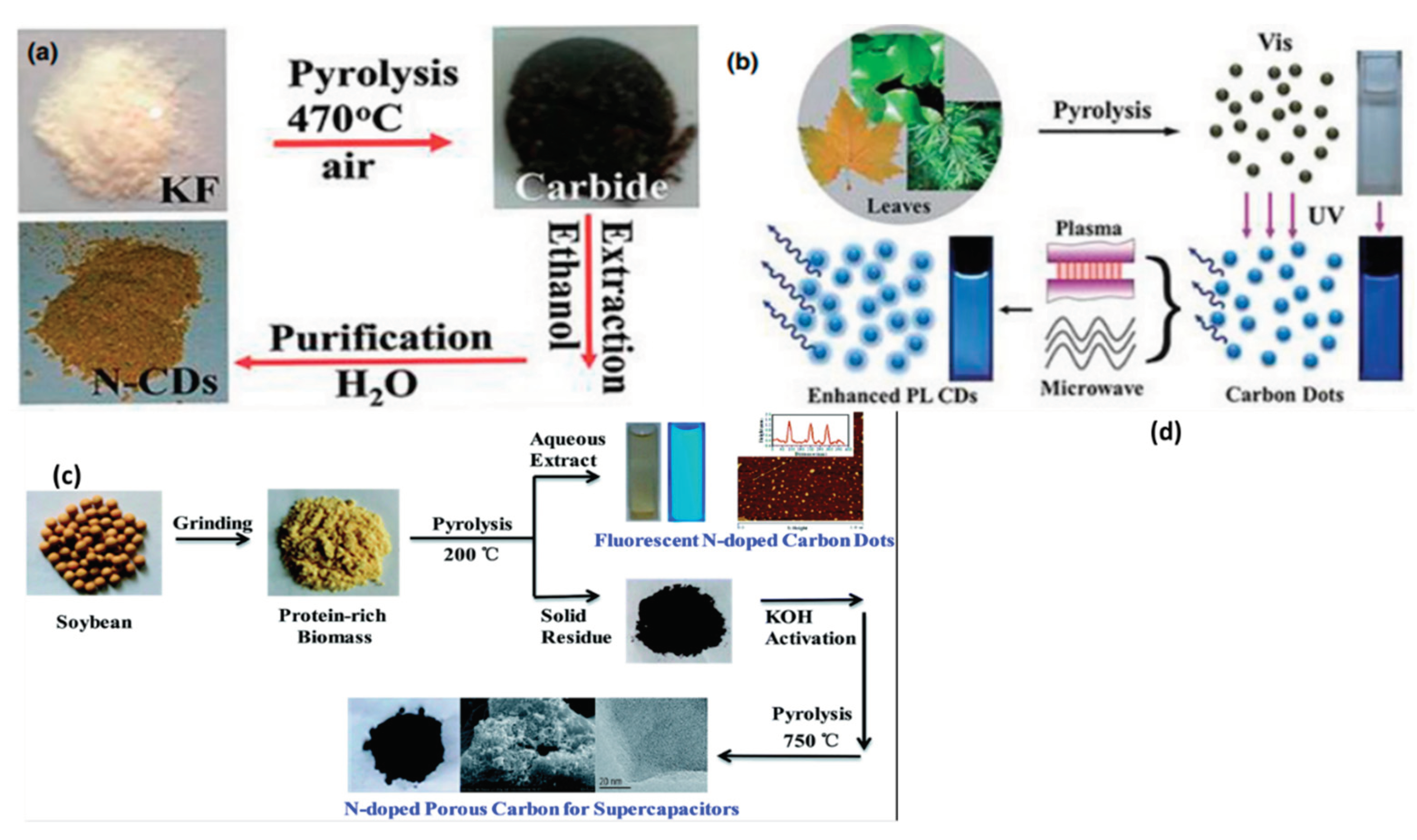
2.6. Pyrolysis Synthesis Approach
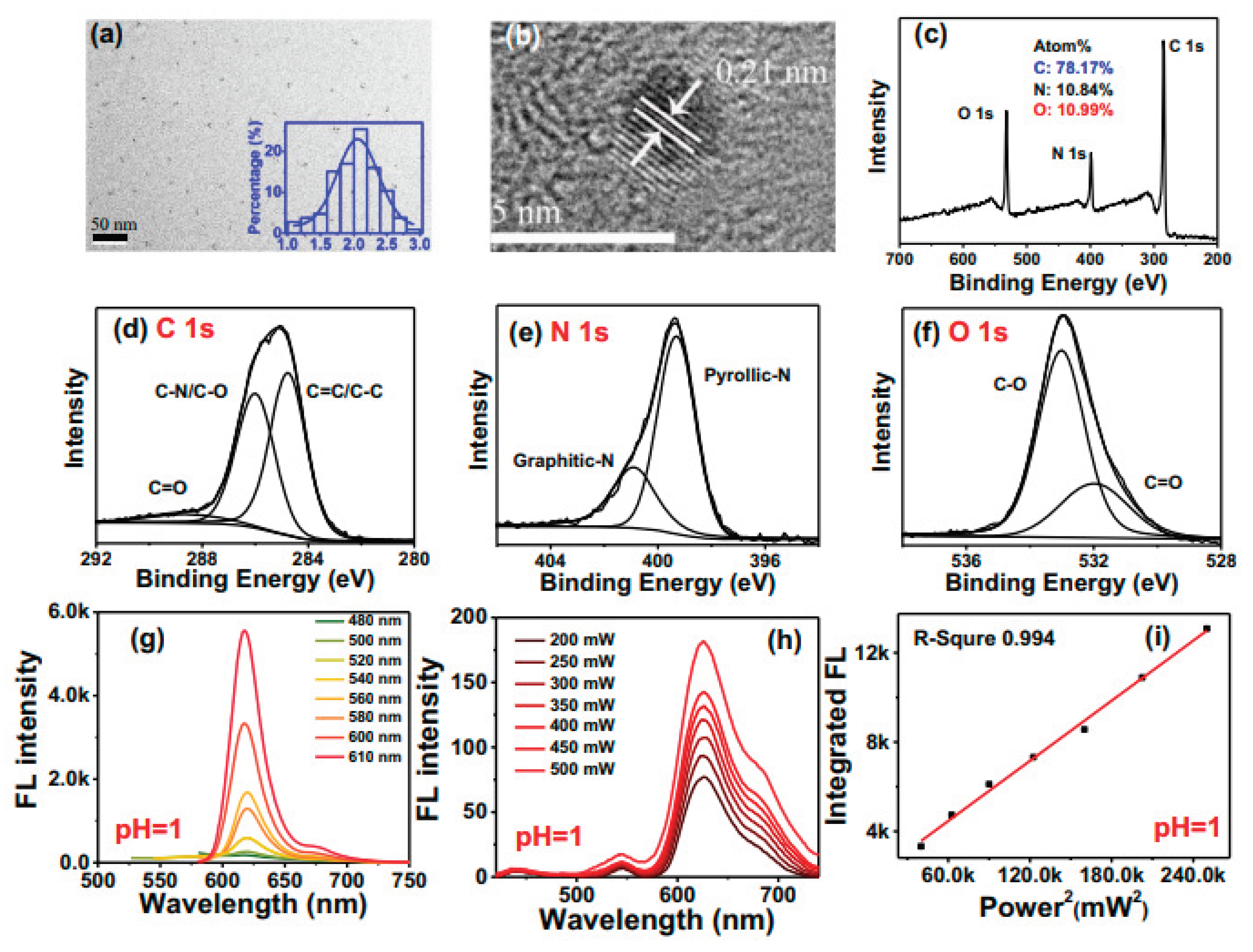
3. Characterizations Tools for Carbon Dots and Its Optical Properties
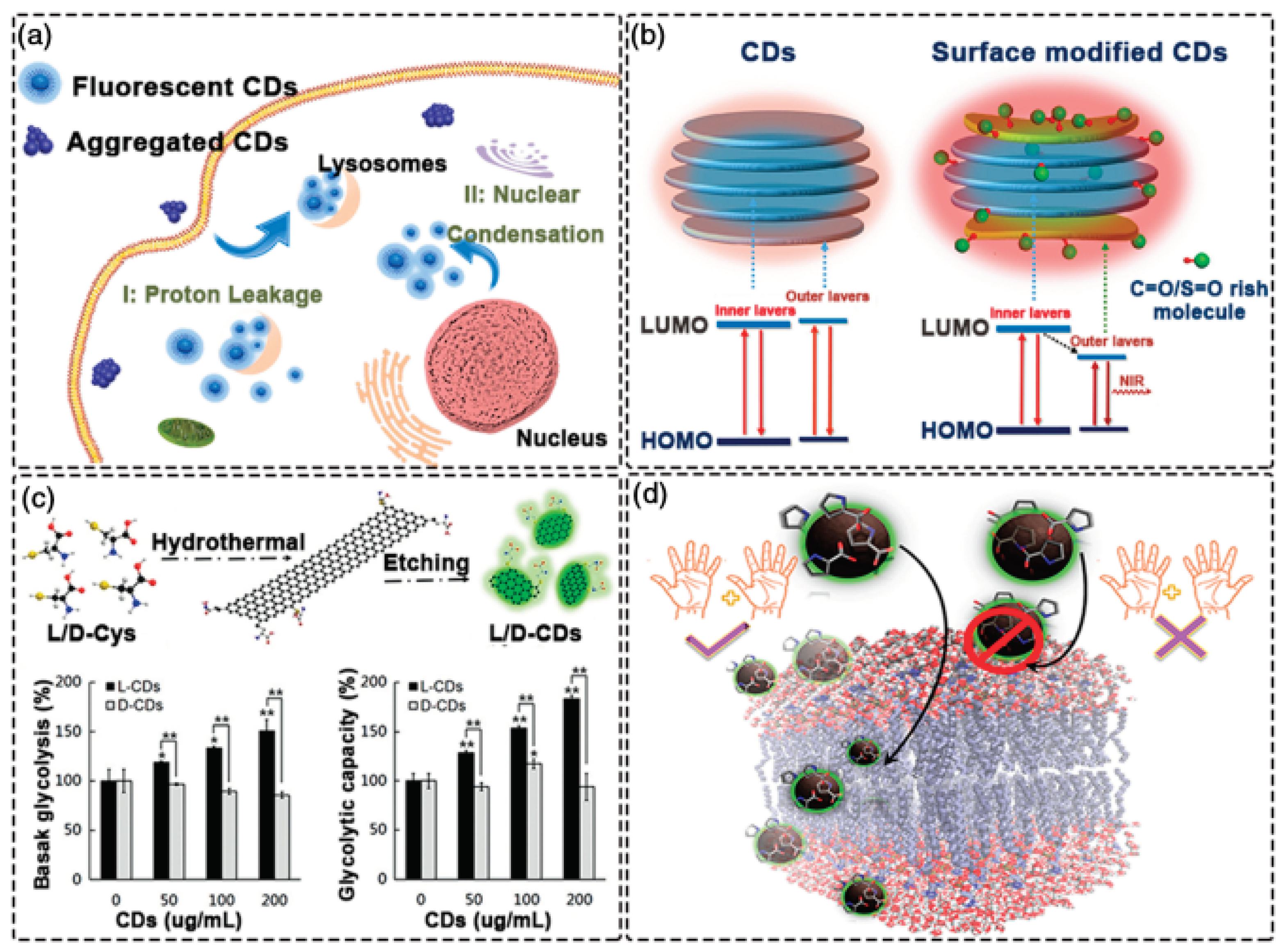
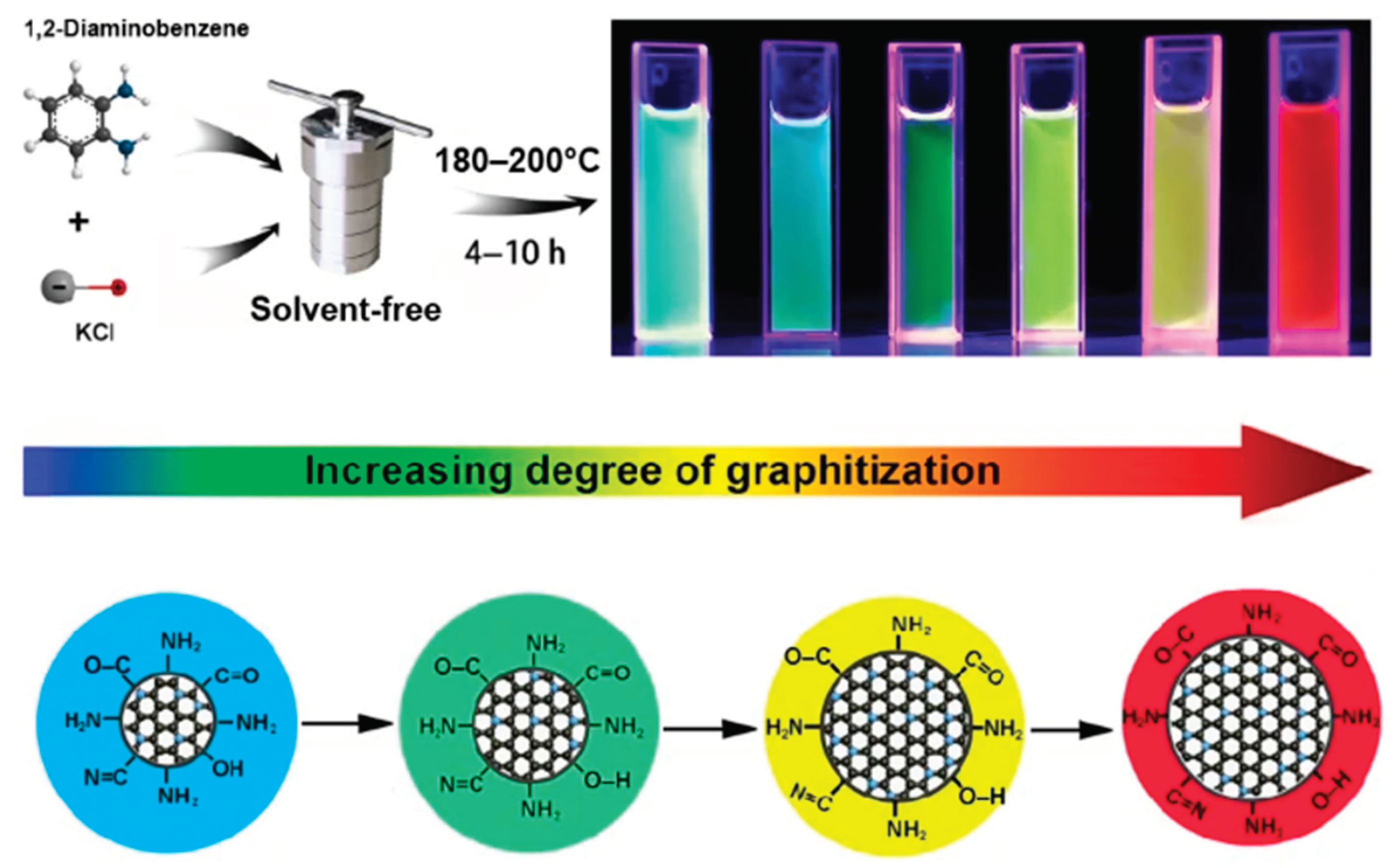
4. Application of Carbon Dots
4.1. Solar Cell

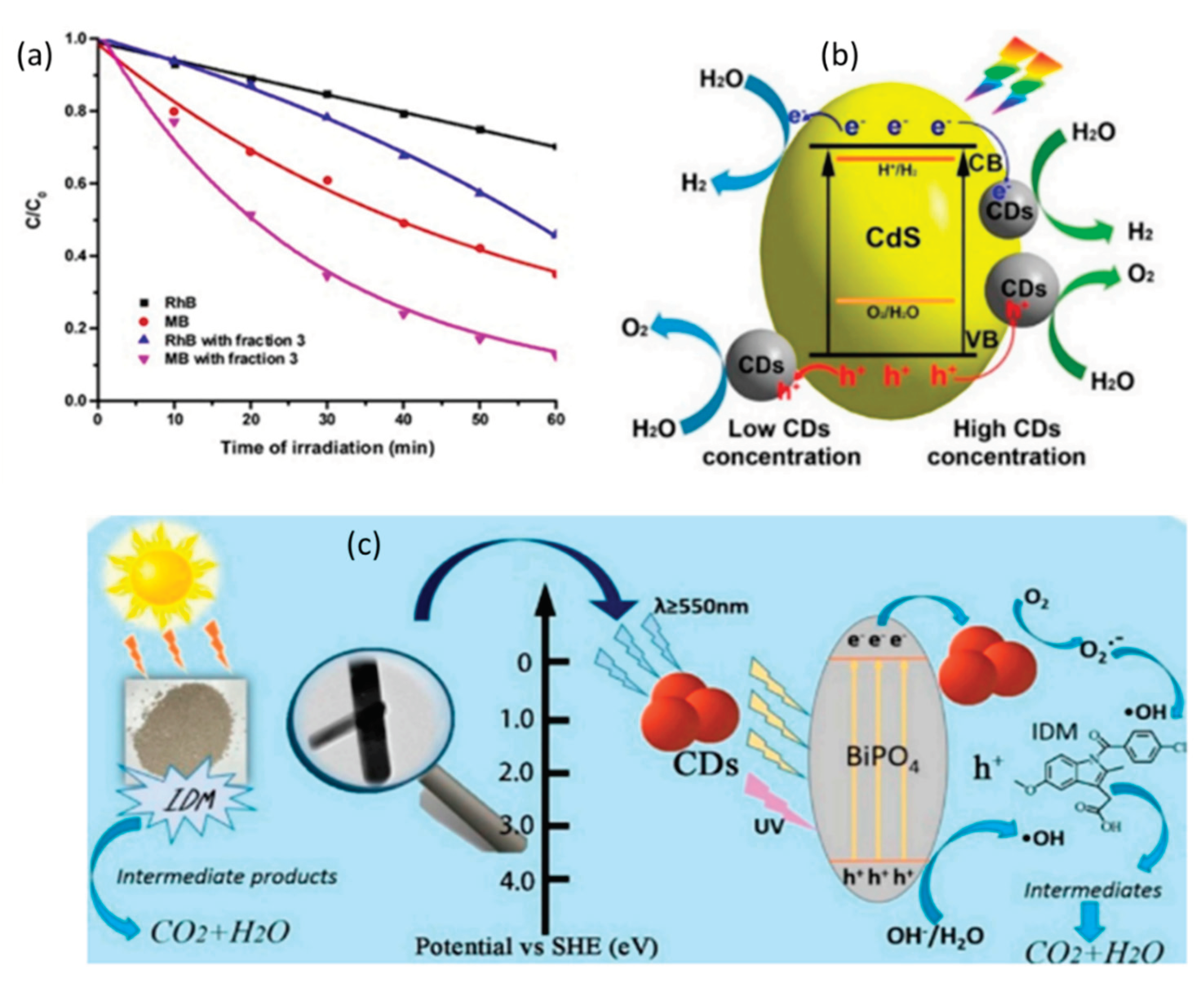
4.2. Photo Catalysis
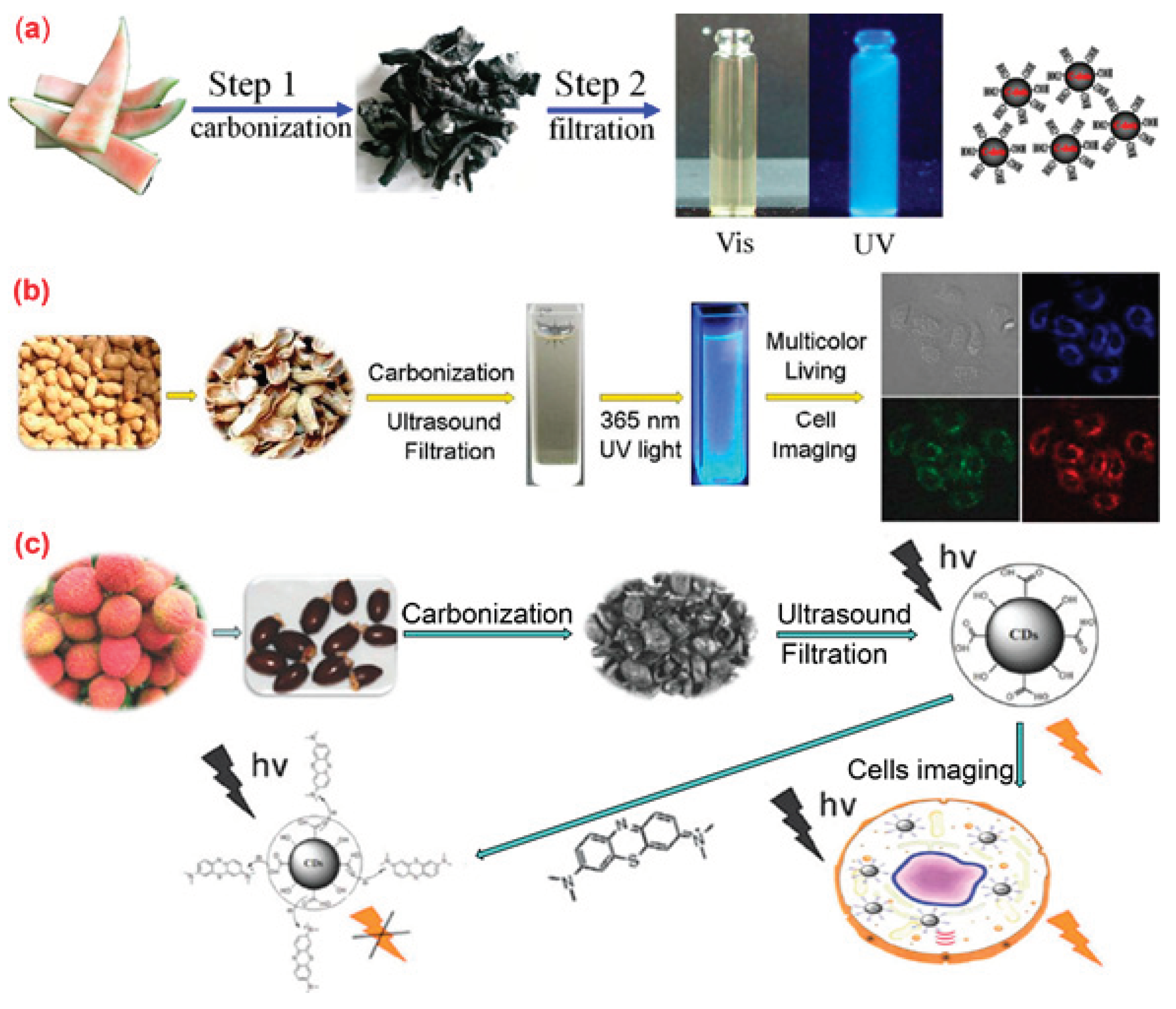
4.3. Biomass
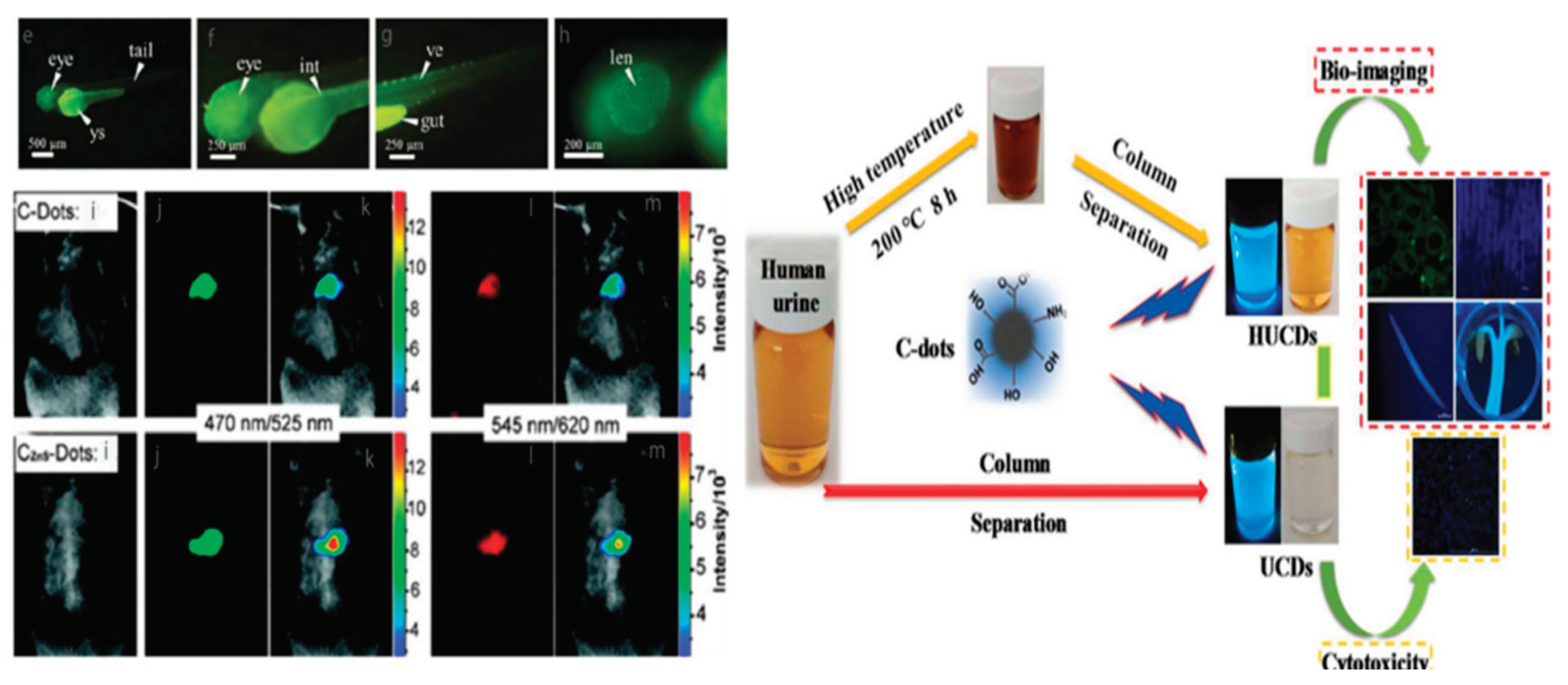
4.4. Biomedical
4.5. Antibacterial Applications of CDs
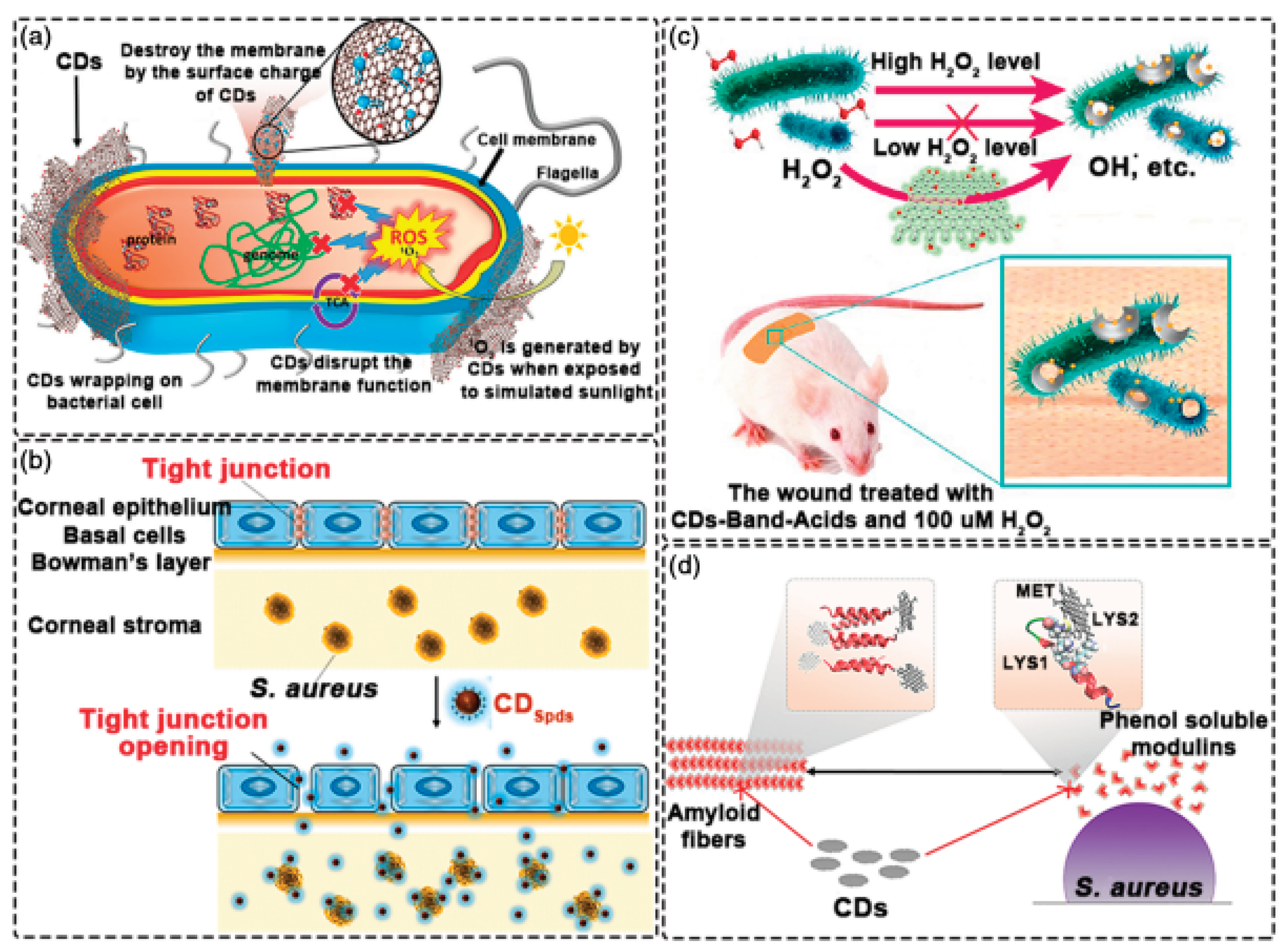
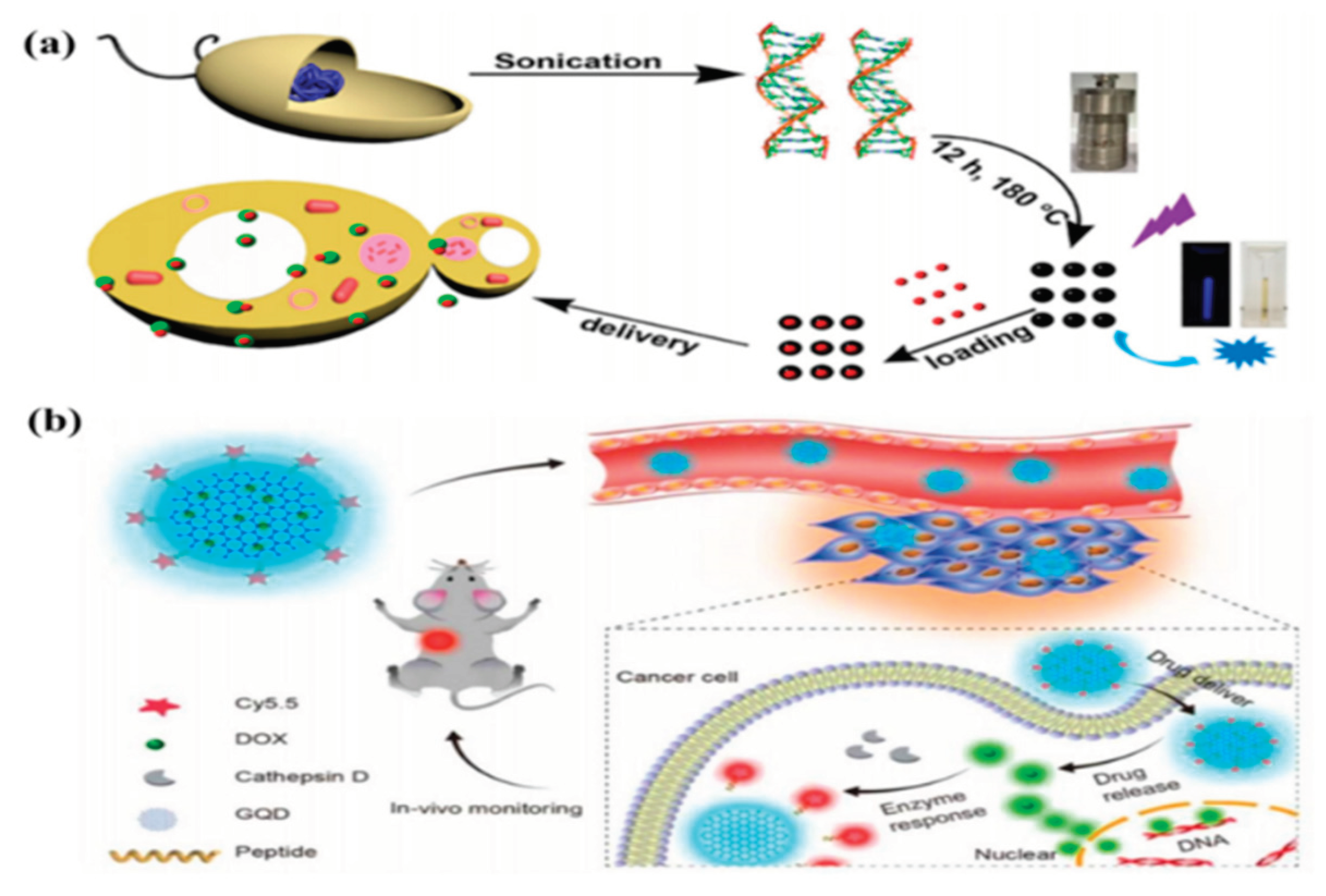
4.6. Drug Delivery
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A revolution in modern industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobokulova, M. THE ROLE OF NANOTECHNOLOGY IN MODERN PHYSICS. Development and innovations in science 2024, 3, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Asmatulu, E.; Andalib, M.N.; Subeshan, B.; Abedin, F. Impact of nanomaterials on human health: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2509–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, M.M.; Ansari, I.; Arora, C.; Rai, N.; Soni, S.; Verma, D.K.; Singh, P.; Mahmoud, A.E.D. Nanomaterials: A comprehensive review of applications, toxicity, impact, and fate to environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 121046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrajac, L.; Abbas, A.; Chrzanowski, W.; Dias, G.M.; Eggleton, B.J.; Maguire, S.; Maine, E.; Malloy, T.; Nathwani, J.; Nazar, L.; et al. Nanotechnology for a Sustainable Future: Addressing Global Challenges with the International Network4Sustainable Nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2022, 15, 18608–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, A.M. Carbon dots: Discovery, structure, fluorescent properties, and applications. Green Processing and Synthesis 2021, 10, 134–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, M.; Paul, A. Recent trends in the use of green sources for carbon dot synthesis–A short review. Carbon Trends 2021, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ngashangva, L.; Goswami, P. Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Macairan, J.-R.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N.; Naccache, R. Green synthesis of carbon dots and their applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25354–25363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Carbon Dots: Classification, properties, synthesis, characterization, and applications in health care—An updated review (2018–2021). Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, N.; Ali, M.N.; Khan, T.J. Carbon Quantum Dots for Biomedical Applications: Review and Analysis. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; et al. Double-pulse femtosecond laser ablation for synthesis of ultrasmall carbon nanodots. Materials Research Express 2020, 7, 015606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; et al. Progress in the Application of Nanozymes Compositing Carbon Dots. Frontiers in Chemistry 2021, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etefa, H.F.; Kumar, V.; Dejene, F.B.; Efa, M.T.; Jule, L.T. Modification of Flexible Electrodes for P-Type (Nickel Oxide) Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Performance Based on the Cellulose Nanofiber Film. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 15249–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armano, A.; Buscarino, G.; Messina, F.; Sciortino, A.; Cannas, M.; Gelardi, F.M.; Giannazzo, F.; Schilirò, E.; Agnello, S. Dynamic modification of Fermi energy in single-layer graphene by photoinduced electron transfer from carbon dots. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S. Carbon dots (CDs): basics, recent potential biomedical applications, challenges, and future perspectives. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2023, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhari, O.; Ntuli, T.D.; Coville, N.J.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Maubane-Nkadimeng, M.S. Supported carbon-dots: A review. J. Lumin. 2023, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Hoffman, J.; Morgiel, J.; Mościcki, T.; Stobiński, L.; Szymański, Z.; Małolepszy, A. Luminescent carbon dots synthesized by the laser ablation of graphite in polyethylenimine and ethylenediamine. Materials 2021, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-T.; Wang, L.-N.; Xu, J.; Huang, K.-J.; Wu, X. Synthesis and modification of carbon dots for advanced biosensing application. Anal. 2021, 146, 4418–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasal, A.S.; Dehvari, K.; Getachew, G.; Korupalli, C.; Ghule, A.V.; Chang, J.-Y. Efficient quantum dot-sensitized solar cells through sulfur-rich carbon nitride modified electrolytes. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 5730–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; An, M.; Chen, X.; Zhao, D.; Li, J. The fluorescence mechanism of carbon dots based on the separation and identification of small molecular fluorophores. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11640–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Dash, J.K.; Kumar, P.; Patel, R. Carbon-based quantum dots for photovoltaic devices: a review. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 4, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleta, T.A.; Imae, T. Nanocomposite photoanodes consisting of p-NiO/n-ZnO heterojunction and carbon quantum dot additive for dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2021, 4, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; et al. Hybrid 1D Semiconducting ZnO and GaN Nanostructures for Light-Emitting Devices. 1D Semiconducting Hybrid Nanostructures: Synthesis and Applications in Gas Sensing and Optoelectronics 2023, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; et al. Mechanism, properties and applications of phosphors. In Phosphor Handbook; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Dash, J.K.; Kumar, P.; Patel, R. Carbon-Based Quantum Dots for Photovoltaic Devices: A Review. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 4, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ngashangva, L.; Goswami, P. Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 84, Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published ….. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.A.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, Z.; Ahmad, R.; Uddin, S.; Shahbaz, A.; Zahra, S.A.; Shaukat, M.; Kiran, F.; Kanwal, S.; et al. Phytofabrication of cobalt oxide nanoparticles from Rhamnus virgata leaves extract and investigation of different bioactivities. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon dots: a new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Central Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Feng, T.; Tao, S.; Zhu, S.; Yang, B. Precursor-dependent structural diversity in luminescent carbonized polymer dots (CPDs): the nomenclature. Light. Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Tan, Z.A. Fluorescent Carbon Dots: Fantastic Electroluminescent Materials for Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Abbas, K.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Bi, H. The application of carbon dots in tumor immunotherapy: Researches and prospects. Appl. Res. 2023, 2, e202300001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Tu, H.; Zhang, H.; Silvester, D.S.; Banks, C.E.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. The development of carbon dots: From the perspective of materials chemistry. Mater. Today 2021, 51, 188–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Karakoti, M.; Bhardwaj, D.; Tatrari, G.; Sharma, R.; Pandey, L.; Lee, M.-J.; Sahoo, N.G. Recent advances in carbon-based materials for high-performance perovskite solar cells: gaps, challenges and fulfillment. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 1492–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratre, P.; Nazeer, N.; Kumari, R.; Thareja, S.; Jain, B.; Tiwari, R.; Kamthan, A.; Srivastava, R.K.; Mishra, P.K. Carbon-Based Fluorescent Nano-Biosensors for the Detection of Cell-Free Circulating MicroRNAs. Biosensors 2023, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, B.; Dosso, J.; Prato, M. New trends in nonconventional carbon dot synthesis. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.K.; et al. Synthesis of nanomaterials using bottom-up methods. Advanced Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Renewable Energy 2022, 61–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorns, M.; Pappas, D. A review of fluorescent carbon dots, their synthesis, physical and chemical characteristics, and applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Naz, M.Y.; Shukrullah, S.; Shujah, M.A.; Akhtar, M.; Ullah, S.; Ali, S. One-pot sonochemical preparation of carbon dots, influence of process parameters and potential applications: a review. Carbon Lett. 2021, 32, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; et al. Properties of Carbon Dots versus Small Molecules from “Bottom-up” Synthesis. ACS nano 2023, 17, 22788–22799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, P.D.; et al. Bottom-up approaches for the preparation of carbon dots. In Carbon Dots in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.B.; El-Shahat, M.; Allayeh, A.K.; Emam, H.E. Maillard reaction for nucleation of polymer quantum dots from chitosan-glucose conjugate: Antagonistic for cancer and viral diseases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaka, K.; Jacob, M.V.; Ostrikov, K. Sustainable life cycles of natural-precursor-derived nanocarbons. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 163–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, B.; Lu, S. Efficient bottom-up synthesis of graphene quantum dots at an atomically precise level. Matter 2023, 6, 728–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Salehiyan, R.; Chauke, V.; Botlhoko, O.J.; Setshedi, K.; Scriba, M.; Masukume, M.; Ray, S.S. Top-down synthesis of graphene: A comprehensive review. FlatChem 2021, 27, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Chen, S. Facile Access to Fabricate Carbon Dots and Perspective of Large-Scale Applications. Small 2023, 19, e2206671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crista, D.M.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.; Pinto da Silva, L. Evaluation of different bottom-up routes for the fabrication of carbon dots. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Gangadharan, D.; Venkatanarasimhan, S. Synthetic strategies toward developing carbon dots via top-down approach. In Carbon Dots in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafeef, M.; Srivastava, I.; Aditya, T.; Pan, D. Carbon Dots: From Synthesis to Unraveling the Fluorescence Mechanism. Small 2023, 20, e2303937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareing, T.C.; Gentile, P.; Phan, A.N. Biomass-based carbon dots: current development and future perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15471–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, P.; Negahdari, B.; Eatemadi, A. Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of carbon-based quantum dots: An updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.; Meng, X.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Shining carbon dots: Synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Nano Today 2016, 11, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Bok, T.; Kim, S.; Park, S. Fundamental understanding of nanostructured Si electrodes: preparation and characterization. Chemnanomat 2018, 4, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Das, J.J.J.o.n. Small molecules derived carbon dots: synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. 2019, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, Q. Carbon dots based on natural resources: Synthesis and applications in sensors. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behi, M.; Gholami, L.; Naficy, S.; Palomba, S.; Dehghani, F. Carbon dots: a novel platform for biomedical applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, D.P.; Muñoz, R.; Amami, M.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V. Graphene-based materials for biotechnological and biomedical applications: Drug delivery, bioimaging and biosensing. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 33, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, D.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Hocking, R.K.; Fox, B. Properties, Synthesis, and Applications of Carbon Dots: A Review. Carbon Trends 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensminger, D.; Bond, L.J. Ultrasonics: fundamentals, technologies, and applications; CRC press, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, H.H.; et al. Green carbon dots: Synthesis, characterization, properties and biomedical applications. Journal of Functional Biomaterials 2023, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayal, A.; Dawane, V.; Amin, M.A.; Tirth, V.; Yadav, V.K.; Algahtani, A.; Khan, S.H.; Islam, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Jeon, B.-H. Advances in the methods for the synthesis of carbon dots and their emerging applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; et al. Preparation of carbon dots-metal nanoparticles nanocomposites and their application in heterogeneous catalysis. Nano Futures 2023, 7, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Molaei, R.; Kousheh, S.A.; Guimarães, J.T.; McClements, D.J. Carbon dots synthesized from microorganisms and food by-products: active and smart food packaging applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1943–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Luo, J.; Xu, W.; Zhai, Y.; Li, J.; Qu, T.; Fu, G. Experimental study on influence of particle shape on shockwave from collapse of cavitation bubble. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 101, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; et al. Carbon dots: Synthesis, properties and applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liccardo, L.; Moretti, E.; Zhao, H.; Vomiero, A. Synthesis, optical properties and applications of red/near-infrared carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 11827–11847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.; Karmaker, P.G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yang, X. Preparation and biomedical applications of multicolor carbon dots: recent advances and future challenges. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundi, A.; Chang, C.-J. Recent advances in synthesis, modification, characterization, and applications of carbon dots. Polymers 2022, 14, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, L.; Hallaj, S.; Hallaj, T.; Amjadi, M. Doped-carbon dots: Recent advances in their biosensing, bioimaging and therapy applications. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; et al. Progress in laser ablation and biological synthesis processes:“Top-Down” and “Bottom-Up” approaches for the green synthesis of Au/Ag nanoparticles. 2022, 23, 14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Hoffman, J.; Morgiel, J.; Mościcki, T.; Stobiński, L.; Szymański, Z.; Małolepszy, A. Luminescent carbon dots synthesized by the laser ablation of graphite in polyethylenimine and ethylenediamine. Materials 2021, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairol Anuar, N.K.; et al. A review on multifunctional carbon-dots synthesized from biomass waste: Design/fabrication, characterization and applications. 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumardin, J.; Maddu, A.; Santoso, K.; Isnaeni, I. Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots (CDs) Using Laser Ablation Method for Bioimaging Application. J. ILMU Fis. | Univ. Andalas 2023, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwar, S.; Mallick, S.; Bahadur, D. Electrochemical method to prepare graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide quantum dots. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8343–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M. Colloidal nanocrystals for optoelectronic devices optically controlled at the nanometric scale; Université Paris sciences et lettres, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Cai, H.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Qu, X.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Carbon dots in bioimaging, biosensing and therapeutics: A comprehensive review. Small Sci. 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Bhattacharjee, L.; Bhattacharjee, R.R. Synthesis of carbon quantum dots, in Carbon Quantum Dots for Sustainable Energy and Optoelectronics; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kurian, M.; Paul, A. Recent trends in the use of green sources for carbon dot synthesis–A short review. Carbon Trends 2021, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Mohan, A. Photoluminescent Carbon Dots: A New Generation Nanocarbon Material. In Handbook of Porous Carbon Materials; Springer, 2023; pp. 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.K.; Tripathi, A.; Taufeeq, A.; Dar, A.H.; Samrot, A.V.; Rustagi, S.; Malik, S.; Bhattacharya, T.; Kovacs, B.; Shaikh, A.M. Significance and applications of carbon dots in anti cancerous nanodrug conjugate development: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 19, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L. Synthesis of graphene nanosheets by the electrical explosion of graphite powder confined in a tube. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 21934–21942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigodanza, F.; Burian, M.; Arcudi, F.; Đorđević, L.; Amenitsch, H.; Prato, M. Snapshots into carbon dots formation through a combined spectroscopic approach. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Li, X.-H.; Chen, X.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Li, X.-B.; Xiong, H.-M. Surface states of carbon dots and their influences on luminescence. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullal, N.; Mehta, R.; Sunil, D. Separation and purification of fluorescent carbon dots – an unmet challenge. Anal. 2024, 149, 1680–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andres, F.; Rios, A. Carbon dots–separative techniques: tools-objective towards green analytical nanometrology focused on bioanalysis. Microchemical Journal 2021, 161, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhong, X.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. A review of carbon dots in synthesis strategy. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 498, 215468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, V.M.; Bhosale, S.V.; Kolekar, G.B. A brief review on the synthesis, characterisation and analytical applications of nitrogen doped carbon dots. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao-Mujica, F.J.; Garcia-Hernández, L.; Camacho-López, S.; Camacho-López, M.A.; Contreras, D.R.; Pérez-Rodríguez, A.; Peña-Caravaca, J.P.; Darias-Gonzalez, J.G.; Hernandez-Tabares, L.; de Fuentes, O.A.; et al. Carbon quantum dots by submerged arc discharge in water: Synthesis, characterization, and mechanism of formation. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 163301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasal, A.S.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, A.; Kashale, A.A.; Manjunatha, S.T.; Altaee, A.; Chang, J.-Y. Carbon quantum dots for energy applications: A review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 6515–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Cruz, A.; Ruiz-Hernández, A.R.; Vega-Clemente, J.F.; Luna-Gazcón, D.G.; Campos-Delgado, J. A review of top-down and bottom-up synthesis methods for the production of graphene, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 14543–14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, B. Synthesis of Coal-based Nanocarbon Advances and Applications. Pure and Functionalized Carbon Based Nanomaterials 2020, 52–79. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, T.; Mushtaq, A. Efficacy and challenges of carbon-based nanomaterials in water treatment: A review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 232–248. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, G.; et al. Carbon dots: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2021, 9, 6553–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahal, S.; Macairan, J.-R.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N.; Naccache, R. Green synthesis of carbon dots and their applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25354–25363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Lu, K.-Q.; Tang, Z.-R.; Xu, Y.-J. Recent progress in carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications in photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3717–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Song, H.; Liu, Z.; Lu, S.; Yang, B. Kilogram-scale synthesis of carbon quantum dots for hydrogen evolution, sensing and bioimaging. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 2323–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Ji, W.; Jing, P.; Han, D.; Liu, L.; Zeng, H.; Shen, D. Toward efficient orange emissive carbon nanodots through conjugated sp2-domain controlling and surface charges engineering. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3516–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis of trichromatic carbon dots from a single precursor by solvent effect and its versatile applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis of trichromatic carbon dots from a single precursor by solvent effect and its versatile applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwer, A.; Hamed, S.M.; Osman, A.I.; Jamil, F.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Alhajeri, N.S.; Rooney, D.W. Algal biomass valorization for biofuel production and carbon sequestration: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2797–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velvizhi, G.; Goswami, C.; Shetti, N.P.; Ahmad, E.; Pant, K.K.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Valorisation of lignocellulosic biomass to value-added products: Paving the pathway towards low-carbon footprint. Fuel 2022, 313, 122678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Bystrzejewski, M.; De Adhikari, A.; Huczko, A.; Wang, N. Methods for the conversion of biomass waste into value-added carbon nanomaterials: Recent progress and applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 92, 101023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elashal, M.H.; Yosri, N.; Du, M.; Musharraf, S.G.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D.; Guo, Z.; Cao, W.; Zou, X.; et al. Bee pollen: Current status and therapeutic potential. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anpalagan, K.K. Carbon quantum dots for bioimaging cells and tissues; Victoria University, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, K.; et al. Biomedical Applications of Biogenic Carbon-Based Fluorescent Nanoparticles. Biogenic Nanomaterial for Health and Environment 2024, 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Lu, S.; Yang, B. Biomass-derived carbon dots and their applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2019, 2, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavikutti, A.S.; et al. Advances in the synthesis approaches of carbon and graphene quantum dots. In Zero-Dimensional Carbon Nanomaterials; Elsevier, 2024; pp. 17–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemlou, M.; Pn, N.; Alexander, K.; Zavabeti, A.; Sherrell, P.C.; Ivanova, E.P.; Adhikari, B.; Naebe, M.; Bhargava, S.K. Fluorescent Nanocarbons: From Synthesis and Structure to Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2024, e2312474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, M.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Synthesis, applications and biosafety evaluation of carbon dots derived from herbal medicine. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 18, 042004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagidi, S.; et al. One-Pot Synthesis of Deep Blue Hydrophobic Carbon Dots with Room Temperature Phosphorescence, White Light Emission, and Explosive Sensor. Advanced Electronic Materials 2022, 8, 2100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Thakkar, H.; Patel, D.; Thakore, S. Repurposing the domestic organic waste into green emissive carbon dots and carbonized adsorbent: A sustainable zero waste process for metal sensing and dye sequestration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansi, M.; Gaurav, S. Synthesis and applications of carbon dots from waste biomass. In Carbon Dots in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; et al. Simple microwave-assisted synthesis of amphiphilic carbon quantum dots from A3/B2 polyamidation monomer set. 2017, 9, 27883–27893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, S.; Singh, B.K.; Bhartiya, P.; Singh, A.; Kumar, H.; Dutta, P.; Mehrotra, G. Lignin derived reduced fluorescence carbon dots with theranostic approaches: Nano-drug-carrier and bioimaging. J. Lumin- 2017, 190, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Environmental Organic Chemistry for Engineers; Butterworth-Heinemann, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khayal, A.; Dawane, V.; Amin, M.A.; Tirth, V.; Yadav, V.K.; Algahtani, A.; Khan, S.H.; Islam, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Jeon, B.-H. Advances in the methods for the synthesis of carbon dots and their emerging applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, L.; Niu, W.; Wang, N.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, S.; Chen, S. A Hydrogen-Bonded Organic-Framework-Derived Mesoporous N-Doped Carbon for Efficient Electroreduction of Oxygen. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Huang, Q.; Sun, R.; Wang, X. Simultaneously obtaining fluorescent carbon dots and porous active carbon for supercapacitors from biomass. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88674–88682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Banerjee, S.L.; Khamrai, M.; Samanta, S.; Singh, S.; Kundu, P.P.; Ghosh, A.K. Hydrothermal synthesis of gelatin quantum dots for high-performance biological imaging applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2020, 212, 112014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, J. Preparation of fluorescent carbon dots composites and their potential applications in biomedicine and drug delivery—A review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, V.; Ansari, M.; Tewari, D.; Yadav, A.B.; Sharma, N.; Bawarig, S.; García-Betancourt, M.-L.; Karatutlu, A.; Bechelany, M.; Barhoum, A. Cutting-edge advances in tailoring size, shape, and functionality of nanoparticles and nanostructures: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.E.; Mohammad, A.; Yoon, T. State-of-the-art developments in carbon quantum dots (CQDs): Photo-catalysis, bio-imaging, and bio-sensing applications. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumardin, J.; Maddu, A.; Santoso, K.; Isnaeni, I. Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots (CDs) Using Laser Ablation Method for Bioimaging Application. J. ILMU Fis. | Univ. Andalas 2023, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Das, P. Are carbon dots worth the tremendous attention it is getting: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 26, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Roy, S.; Sarkar, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. A review of carbon dots and their composite materials for electrochemical energy technologies. Carbon Energy 2021, 3, 795–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Barba, D.; Cortese, M.; Martino, M.; Renda, S.; Meloni, E. Microwaves and heterogeneous catalysis: A review on selected catalytic processes. Catalysts 2020, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalloro, V.; et al. Microwave-assisted solid extraction from natural matrices, in Microwave Heating-Electromagnetic Fields Causing Thermal and Non-Thermal Effects; IntechOpen, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.; Tao, S.; Yue, D.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, W.; Yang, B. Recent advances in energy conversion applications of carbon dots: from optoelectronic devices to electrocatalysis. Small 2020, 16, e2001295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolai, S.; Bhunia, S.K.; Rajendran, S.; UshaVipinachandran, V.; Ray, S.C.; Kluson, P. Tunable fluorescent carbon dots: synthesis progress, fluorescence origin, selective and sensitive volatile organic compounds detection. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2021, 46, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Das, J. Small molecules derived carbon dots: synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Dong, C. One-pot synthesis of aqueous soluble and organic soluble carbon dots and their multi-functional applications. Talanta 2019, 202, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhan, X.; Du, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Xu, W. One-pot synthesis of dual carbon dots using only an N and S co-existed dopant for fluorescence detection of Ag+. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 208, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafeef, M.; Srivastava, I.; Aditya, T.; Pan, D. Carbon dots: from synthesis to unraveling the fluorescence mechanism. Small 2023, 20, e2303937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmartín-Matalobos, J.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Aboal-Somoza, M.; Fondo, M.; García-Deibe, A.M.; Corredoira-Vázquez, J.; Alves-Iglesias, Y. Semiconductor Quantum Dots as Target Analytes: Properties, Surface Chemistry and Detection. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, M.; Paloncýová, M.; Medveď, M.; Pykal, M.; Nachtigallová, D.; Shi, B.; Aquino, A.J.; Lischka, H.; Otyepka, M. Progress and challenges in understanding of photoluminescence properties of carbon dots based on theoretical computations. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 22, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, M.; Yi, Z.; Poursorkhabi, V.; Tjong, J.; Jaffer, S.; Lu, Z.-H.; Sain, M. Future perspectives and review on organic carbon dots in electronic applications. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6224–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Feng, B.; Zhong, X.; Ostrikov, K. Photoluminescence mechanism of carbon dots: triggering high-color-purity red fluorescence emission through edge amino protonation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; et al. Reversible “off–on” fluorescence of Zn2+-passivated carbon dots: mechanism and potential for the detection of EDTA and Zn2+. 2018, 34, 7767–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon dots: A new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Central Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshbaf, M.; Davaran, S.; Rahimi, F.; Annabi, N.; Salehi, R.; Akbarzadeh, A. Carbon quantum dots: recent progresses on synthesis, surface modification and applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1331–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, R.J.C.q.d.S.I.P., Cham, Carbon quantum dots. 2017: p. 29-46.
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Ruan, H.; Yin, K.; Li, H. Production of yellow-emitting carbon quantum dots from fullerene carbon soot. Sci. China Mater. 2017, 60, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, X.-X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Large scale synthesis of full-color emissive carbon dots from a single carbon source by a solvent-free method. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3548–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dua, S.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, M.; Bhatt, G. A review on advancements in carbon quantum dots and their application in photovoltaics. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 4714–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, M. Unprecedented chiral nanovaccines for significantly enhanced cancer immunotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39858–39865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efa, M.T.; Imae, T. Effects of carbon dots on ZnO nanoparticle-based dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochimica Acta 2019, 303, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etefa, H.F.; Imae, T.; Yanagida, M. Enhanced photosensitization by carbon dots Co-adsorbing with dye on ptype semiconductor (Nickel Oxide) solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18596–18608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.-W.; Lee, S.L.; Chang, C.-J.; Liu, L. Recent progress of carbon dot precursors and photocatalysis applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, K.; Nie, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Carbon dots based photocatalysis for environmental applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-X.; Zhao, D.-F.; Li, L.; Meng, Y.; Xie, Y.-H.; Feng, D.; Wu, F.; Xie, D.; Liu, Y.; Mei, Y. Unraveling fluorescent mechanism of biomass-sourced carbon dots based on three major components: Cellulose, lignin, and protein. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lyu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chmely, S.C.; Wu, Y.; Melcher, C.; Rajan, K.; Harper, D.P.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z. Recycling hot-water extractions of lignocellulosic biomass in bio-refinery for synthesis of carbon nanoparticles with amplified luminescence and its application in temperature sensing. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 145, 112066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azara, A.; Belbessai, S.; Abatzoglou, N. A review of filamentous carbon nanomaterial synthesis via catalytic conversion of waste plastic pyrolysis products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaku, B. Synthesis and Application of Boron-nitrogen Doped Carbon Nanoonions in Supercapacitors; University of the Witwatersrand, Faculty of Science, School of Chemistry, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, X.F.; Chen, Z.P. A review of carbon dots produced from biomass wastes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, A.; et al. Recent advances in green carbon dots (2015–2022): synthesis, metal ion sensing, and biological applications. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2022, 13, 1068–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots and their applications in drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Advances in carbon dots: from the perspective of traditional quantum dots. Materials Chemistry Frontiers 2020, 4, 1586–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.S.a.; et al. Natural, synthetic, and composite materials for industrial effluents treatment: a mini review on current practices, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering 2023, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Boora, A.; Thakur, A.; Gupta, T.K. Green and sustainable synthesis of nanomaterials: Recent advancements and limitations. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Thomas, S.; Gopi, S. Natural carbon-based quantum dots and their applications in drug delivery: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110834–110834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, Y.R.; Deshmukh, K.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Pasha, S.K.K. Graphene quantum dot based materials for sensing, bio-imaging and energy storage applications: a review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23861–23898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: a review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Long, W. The synthetic strategies, photoluminescence mechanisms and promising applications of carbon dots: Current state and future perspective. Carbon 2022, 186, 91–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ragib, A.; Al Amin, A.; Alanazi, Y.M.; Kormoker, T.; Uddin, M.; Siddique, A.B.; Barai, H.R. Multifunctional carbon dots in nanomaterial surface modification: a descriptive review. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, J.B.; Hu, M.Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, C.Z.; Liu, H. Controlled synthesis of multicolor carbon dots assisted by machine learning. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2210095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methods | Advantages | disadvantages | Applications | Ref. |
| Hydrothermal | Simple and cost-effective synthesis method | High reaction temperatures and long reaction times | Biomedical imaging, sensors, drug delivery | [120,121] |
| Arc discharge | High yield of CDs with good photoluminescence properties | Complex setup and requirement of a high-power arc discharge | Photovoltaics, optoelectronic devices | [50,122] |
| Laser ablation | Precise control over size and excellent photoluminescence | Expensive laser equipment and potential contamination | Bioimaging, photocatalysis | [123,124] |
| Chemical oxidation | Simple and versatile method | Harsh reaction conditions and potential toxic byproducts | Sensing, energy storage | [125,126] |
| Pyrolysis | Good stability and tunable properties | High temperatures and lack of control over size distribution | Photodetection, bioimaging | [56,127] |
| Microwave | Short reaction times and easy control of parameters | Potential overheating and non-uniform heating | Drug delivery, environmental remediation | [128,129] |
| Solvothermal | Controlled synthesis in a solvent medium | Requirement of specialized equipment and solvents | Optoelectronic devices, catalysis | [130,131] |
| Organic approach | Environmentally friendly synthesis | Limited control over size and properties | Sensing, bioimaging | [76,132] |
| ultrasonication | Simple and rapid synthesis method | Limited control over size and potential aggregation | Biosensing, antibacterial agents | [61,76] |
| One-Pot Synthesis | Convenient synthesis without additional purification steps | Potential variability in size and properties | Bioimaging, drug delivery | [133,134] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




