Submitted:
02 April 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Plasma Medicine in the Clinic
2.1. Wound Healing
| CP device | Ref | Study design | Population and treatment groups | Primary results | |
| SteriPlas® plasma torch | [50] | RPCT (n = 37) |
Chronic non-healing wounds. SWC with 2 min CP 1×/week (group 1, n = 14), 3×/week (group 2, n = 13), or placebo (1×/week, n = 10). | Wound area significantly reduced > 60% with 1×/week treatment (p = 0.005). No additional benefit with 3×/week. | |
| kINPen® Med plasma jet | [51] | MC, RCT, NIT (n = 78) |
Chronic non-healing wounds. Equal groups CP treatment or SWC. CP treatment (30 s/cm2 wound) 3× 1st week, 2× 2nd week then 1×/week for 4 weeks. | Relative wound area significantly lower in CP treated group by 5th visit. Lower infection frequency and significantly faster time to infection healing. | |
| [32] | SB, RPCT (n = 45) |
DFU. Wound care with CP (n = 33) or placebo (n = 32) applied for 30 s/cm2 wound once daily for 5 days, followed by 3 treatments every 2nd day | CP treatment led to 26% greater wound closure in CP compared to placebo (p = 0.03). NSD in bacterial load. |
||
| Bioplasma Jet | [64] | RCT (n = 42) |
Patients with pressure ulcers. Wound care with 1 min/cm2 CP (n = 23) or without CP (n = 19). CP applied once weekly for 8 weeks. | Bacterial load reduced after 1 week of CP treatment. The wound size, wound base and exudate were significantly improved after two CP treatments. | |
| PlasmaDerm® VU-2010 DBD | [65] | Two-armed, open, RCT (n = 14) |
Chronic venous leg ulcers. CP (n = 7) or SWC (n = 7). CP (45 s/cm2) ulcer, 3 ×/week for 8 weeks + 4-week follow-up | NSD in ulcer lesion size between groups. Significant increase in bacteria free region (p = 0.0313) | |
| Housemade He plasma jet | [33] | DB, RCT (n = 44) |
DFU. Standard care with (n = 22) or without (n = 22) CP therapy. CP (5 min) 3×/week for 3 weeks | CP accelerated wound closure after 3 weeks compared to control (cf. 61% vs. 21%, respectively, p < 0.05). Bacterial load significantly reduced by CP, but recolonised before the next CP treatment. | |
| CPT®cube & CPT®patch | [52] | * MC, RCT (n = 47) |
Uninfected, chronic leg wounds. CP treatment (2 min) 3×/week for 4 weeks (n = 25) compared to SWC (n = 22). 3- and 6-month follow-up. | CP treatment resulted in ≥ 90% wound closure in 16% of participants, SWC alone only lead to ≥ 40% wound reduction in 18% of subjects. | |
| PlasmaDerm® FLEX9060 DBD | [56] | C, cohort (n = 20) |
Healthy volunteers with single 90 s application of CP to determine microvascular effects. | Oxygen saturation and perfusion significantly elevated in microcirculation up to 8 and 11 min after CP therapy, respectively. | |
| [58] | self-C, cohort (n = 10) |
Healthy volunteers with single 4.5 min CP application to determine microvascular effects. | Oxygen saturation and perfusion significantly elevated after CP exposure over 60 min follow-up | ||
| [59] | C, cohort (n = 20) |
Patients with chronic, infection-free leg wounds with single 1.5 min CP application to determine microvascular effects. | CP therapy significantly increased deep capillary perfusion after 11 min to end of 30 min follow-up. Superficial perfusion significantly elevated 1 – 6 min follow-up. | ||
| [60] | C, cohort (n = 20) |
Otherwise-healthy participants requiring skin grafting. CP treatment (90 s) at the skin donor site. | Deep capillary perfusion significantly increased entire 30 min follow-up to CP. Tissue oxygen significantly increased 1 – 5 min after CP therapy. |
2.2. Cancer
3. Cold Plasma on Redox-Mediated Modification of Cell Components
4. Cellular Responses to Cold Plasma through Redox-Responsive Intracellular Signalling Pathways
4.1. Keap1-Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Pathways
4.2. ERS and UPR Signalling Pathway
4.3. ERK1/2, JNK and P38 MAPK Pathways
4.3.1. MAPK Inducing Cancer Cell Death
4.3.2. MAPK in Wound Healing and Inflammation
4.4. PI3K/Akt Pathway
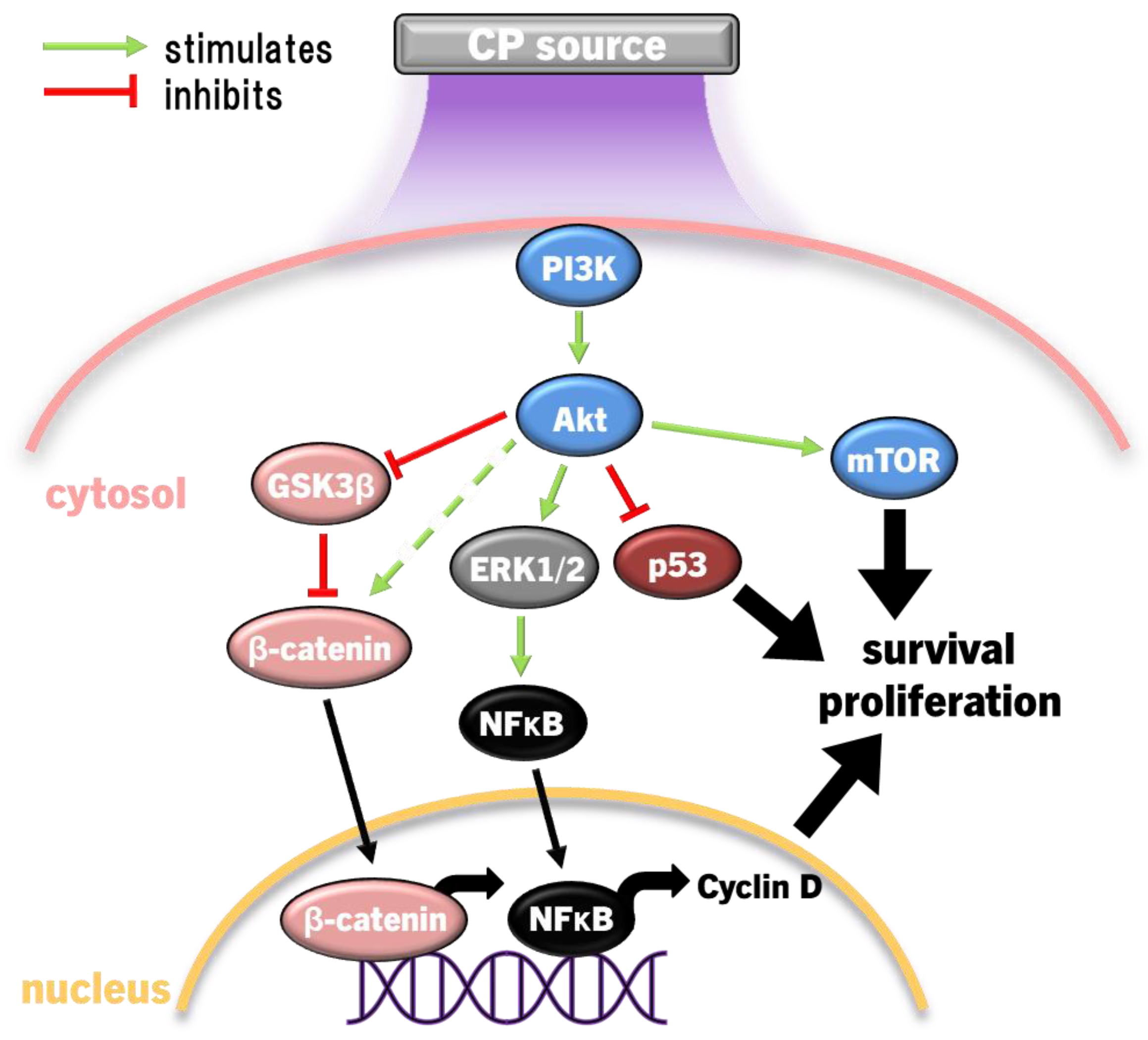
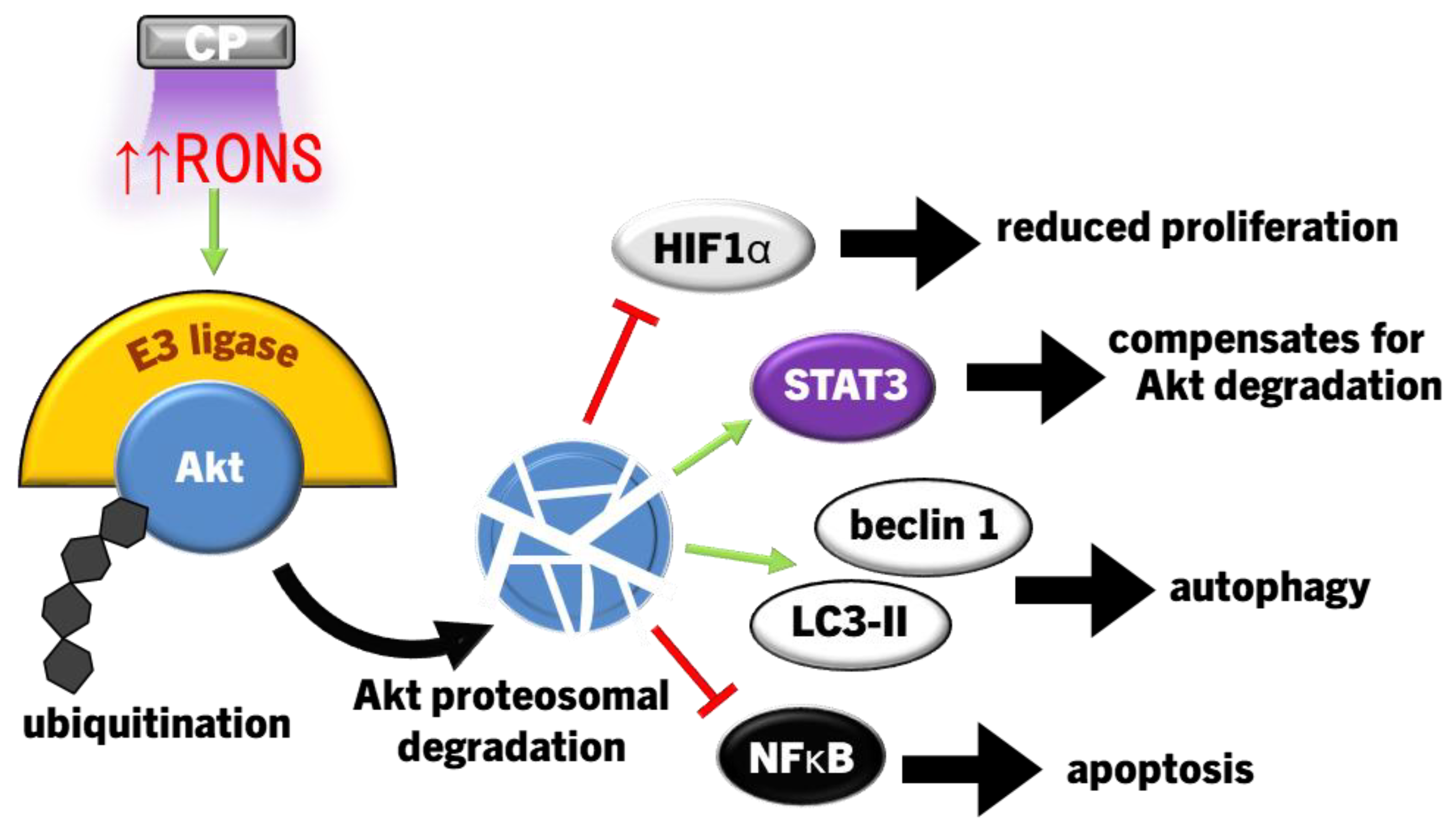
4.4.1. Suppressing PI3K/Akt Signalling in Cancer Cells
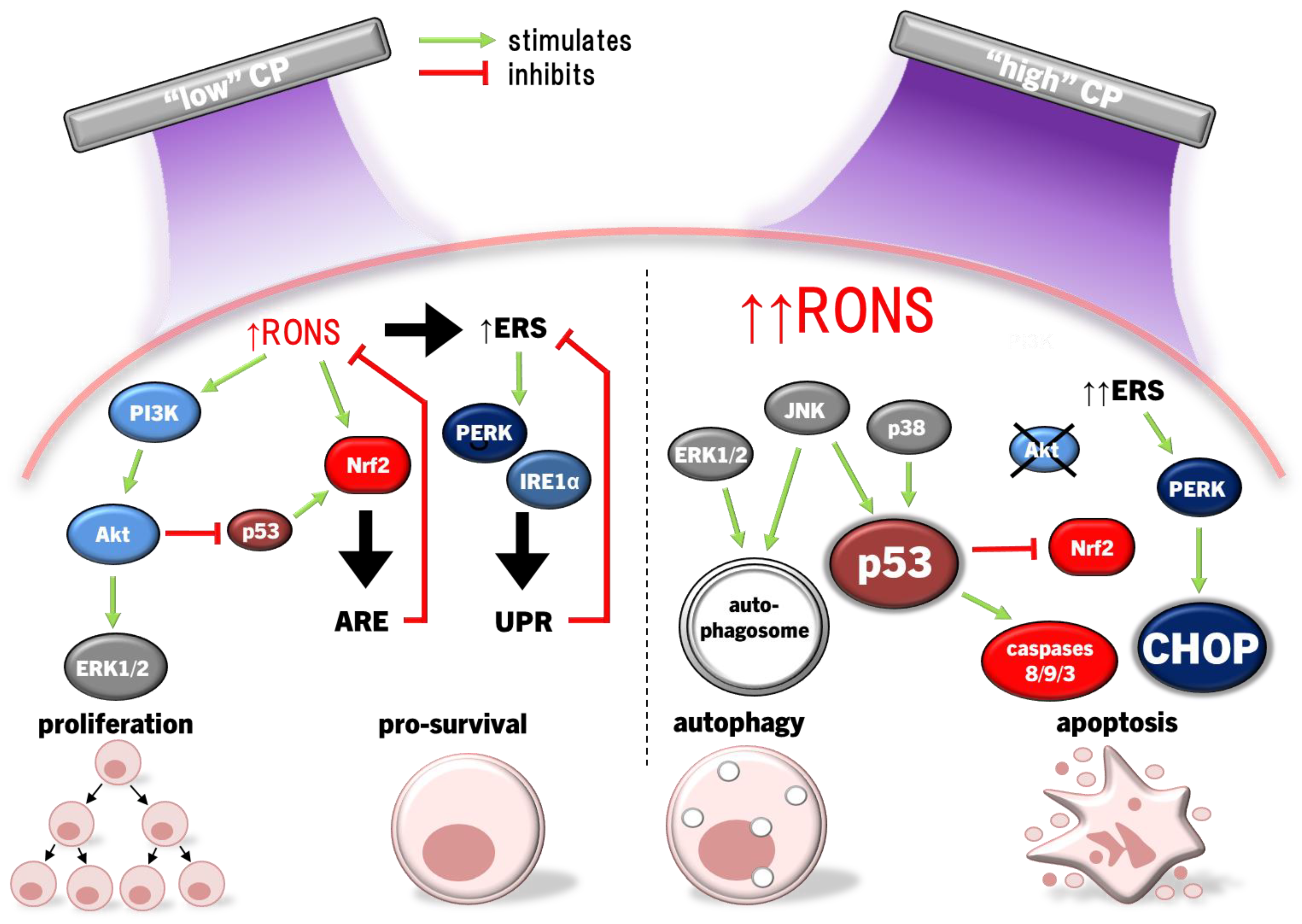
5. Discussions and Perspectives
5.1. Direct Comparisons between Malignant Cells and between Malignant and Non-Malignant Cells and Tissue
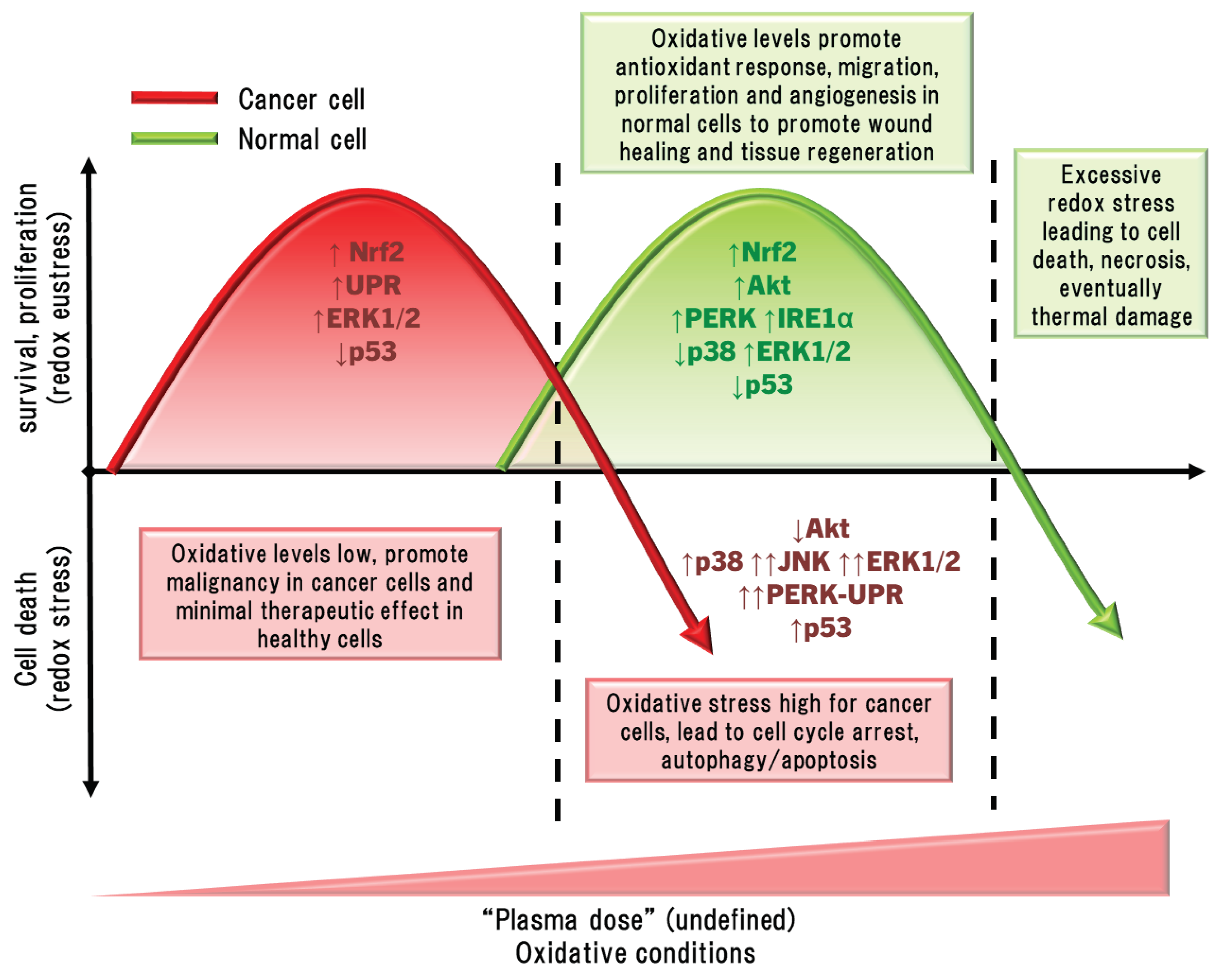
5.2. The Hormesis Principle to Plasma Medicine
5.3. Limitations and Challenges in Plasma Medicine
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tendero, C.; Tixier, C.; Tristant, P.; Desmaison, J.; Leprince, P. Atmospheric pressure plasmas: A review. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 2006, 61, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Woedtke, T.; Laroussi, M.; Gherardi, M. Foundations of plasmas for medical applications. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 2022, 31, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Woedtke, T.; Emmert, S.; Metelmann, H.-R.; Rupf, S.; Weltmann, K.-D. Perspectives on cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) applications in medicine. Phys Plasmas 2020, 27, 070601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, P.J.; Iza, F.; Brandenburg, R. Foundations of atmospheric pressure non-equilibrium plasmas. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzec, D.; Hoppenthaler, F.; Nettesheim, S. Piezoelectric Direct Discharge: Devices and Applications. Plasma 2020, 4, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Nie, Q.; Bayliss, D.L.; Walsh, J.L.; Ren, C.S.; Wang, D.Z.; Kong, M.G. Spatially extended atmospheric plasma arrays. Plasmas Sources Sci Technol 2010, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeva, N.Y.; Kushner, M.J. Interaction of multiple atmospheric-pressure micro-plasma jets in small arrays: He/O2into humid air. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 2014, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancampiano, A.; Selaković, N.; Gherardi, M.; Puač, N.; Petrović, Z.L.; Colombo, V. Characterisation of a multijet plasma device by means of mass spectrometric detection and iCCD imaging. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Nie, Q.; Huang, T.; Hou, C. Numerical studies on downstream uniformity of atmospheric pressure plasma jet array modulated by flow and electric multi-field coupling control. AIP Adv 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, Y.; Han, W.; Fan, L.; Guo, W.; Li, W.; Mu, H.; Zhang, G. In situ measurement of dynamic surface charge on dielectrics interacted with plasma jet arrays. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 2023, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Naidis, G.V.; Laroussi, M.; Reuter, S.; Graves, D.B.; Ostrikov, K. Reactive species in non-equilibrium atmospheric-pressure plasmas: Generation, transport, and biological effects. Phys Rep 2016, 630, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Ghimire, B.; Li, Y.; Adhikari, M.; Veerana, M.; Kaushik, N.; Jha, N.; Adhikari, B.; Lee, S.J.; Masur, K.; et al. Biological and medical applications of plasma-activated media, water and solutions. Biol Chem 2018, 400, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, D.; Curtin, J.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Hydrogen peroxide and beyond-the potential of high-voltage plasma-activated liquids against cancerous cells. Anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry 2018, 18, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Xian, Y.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Lu, X.; Cullen, P.J.; Ostrikov, K.; Bazaka, K. Plasma-activated water: generation, origin of reactive species and biological applications. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2020, 53, 303001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privat-Maldonado, A.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wende, K.; Bogaerts, A.; Bekeschus, S. ROS from Physical Plasmas: Redox Chemistry for Biomedical Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 9062098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, D.; Liu, D.; Cui, Q.; Cai, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Production of simplex RNS and ROS by nanosecond pulse N2/O2 plasma jets with homogeneous shielding gas for inducing myeloma cell apoptosis. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2017, 50, 195204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, M.L.; Bekeschus, S.; Schafer, M.; Bernhardt, T.; Fischer, T.; Witzke, K.; Seebauer, C.; Rebl, H.; Grambow, E.; Vollmar, B.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of the efficacy of cold atmospheric pressure plasma (CAP) in cancer treatment. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faramarzi, F.; Zafari, P.; Alimohammadi, M.; Moonesi, M.; Rafiei, A.; Bekeschus, S. Cold Physical Plasma in Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms, Signaling, and Immunity. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021, 2021, 9916796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Woedtke, T.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Plasma medicine: A field of applied redox biology. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Prasad, K.; Fang, Z.; Speight, R.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Cold atmospheric plasma activated water as a prospective disinfectant: the crucial role of peroxynitrite. Green Chem 2018, 20, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Feng, H.; Ma, R.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. A study of oxidative stress induced by non-thermal plasma-activated water for bacterial damage. Appl Phys Lett 2013, 102, 203701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Assessment of the physicochemical properties and biological effects of water activated by non-thermal plasma above and beneath the water surface. Plasma Process polym 2015, 12, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondeti, V.S.S.K.; Phan, C.Q.; Wende, K.; Jablonowski, H.; Gangal, U.; Granick, J.L.; Hunter, R.C.; Bruggeman, P.J. Long-lived and short-lived reactive species produced by a cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet for the inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Free Radic Biol Med 2018, 124, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Sun, F. The key reactive species in the bactericidal process of plasma activated water. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2020, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.I.; Schmitt-John, T.; Richter, K. Cold Plasma Therapy as a Physical Antibiofilm Approach. In Antibiofilm Strategies: Current and Future Applications to Prevent, Control and Eradicate Biofilms, Richter, K., Kragh, K.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 225–261. [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz, V.; Vankova, E.; Kasparova, P.; Premanath, R.; Karunasagar, I.; Julak, J. Non-thermal Plasma Treatment of ESKAPE Pathogens: A Review. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 737635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.; Marques, J.; da Cruz, M.B.; Luís, H.; Sério, S.; Mata, A. The applications of cold atmospheric plasma in dentistry. Plasma Process Polym 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schafer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma medicine: Applications of cold atmospheric pressure plasma in dermatology. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 3873928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Jiang, J.; Duan, J.W.; Wu, X.J.Z.; Zhang, S.; Duan, X.R.; Song, J.Q.; Chen, H.X. Cold atmospheric plasma applications in dermatology: A systematic review. J Biophotonics 2021, 14, e202000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.O.; Schulz, L.; Schleusser, S.; Matzkeit, N.; Stang, F.H.; Mailaender, P.; Kraemer, R.; Kleemann, M.; Deichmann, H.; Kisch, T. The repetitive application of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) improves microcirculation parameters in chronic wounds. Microvasc Res 2021, 138, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsavar, S.; Mahmoudi, H.; Shakouri, R.; Khani, M.R.; Molavi, B.; Moosavi, J.; Daneshpazhooh, M.; Etesami, I.; Shokri, B. The evaluation of efficacy of atmospheric pressure plasma in diabetic ulcers healing: A randomized clinical trial. Dermatol Ther 2021, 34, e15169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, B.; Costea, T.C.; Nolte, C.; Hiller, J.; Schmidt, J.; Reindel, J.; Masur, K.; Motz, W.; Timm, J.; Kerner, W.; et al. Effect of cold atmospheric plasma therapy vs. standard therapy placebo on wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3, e2010411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirpour, S.; Fathollah, S.; Mansouri, P.; Larijani, B.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Mohajeri Tehrani, M.; Amini, M.R. Cold atmospheric plasma as an effective method to treat diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized clinical trial. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, M.R.; Sheikh Hosseini, M.; Fatollah, S.; Mirpour, S.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Larijani, B.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.R.; Khorramizadeh, M.R. Beneficial effects of cold atmospheric plasma on inflammatory phase of diabetic foot ulcers; a randomized clinical trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2020, 19, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgeo, T.; Maconi, A.; Gardalini, M.; Gatti, D.; Di Matteo, R.; Lapidari, M.; Longhitano, Y.; Savioli, G.; Piccioni, A.; Zanza, C. The Role of Cold Atmospheric Plasma in Wound Healing Processes in Critically Ill Patients. J Pers Med 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.C.; Kostov, K.G.; Pessoa, R.S.; de Abreu, G.M.A.; Lima, G.d.M.G.; Figueira, L.W.; Koga-Ito, C.Y. Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Dentistry. Appl Sci 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhan, N.V.M.; Chiappim, W.; Sampaio, A.d.G.; Vegian, M.R.d.C.; Pessoa, R.S.; Koga-Ito, C.Y. Applications of Plasma-Activated Water in Dentistry: A Review. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, M.A.; Hussein, L.K.; Molina, E.A.; Keyloun, J.W.; McKnight, S.M.; Jimenez, L.M.; Moffatt, L.T.; Shupp, J.W.; Carney, B.C. Cold atmospheric plasma is bactericidal to wound-relevant pathogens and is compatible with burn wound healing. Burns 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; Patenall, B.L.; Ghimire, B.; Thet, N.T.; Gardiner, J.E.; Le Doare, K.E.; Ramage, G.; Short, B.; Heylen, R.A.; Williams, C.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Activated Composite Hydrogel for an Enhanced and On-Demand Delivery of Antimicrobials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2023, 15, 19989–19996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrin, S.; Hong, S.H.; Kc, S.K.; Oh, J.S.; Derrick-Roberts, A.L.K.; Karmokar, D.K.; Habibullah, H.; Short, R.D.; Ghimire, B.; Fitridge, R.; et al. Electrochemically Enhanced Antimicrobial Action of Plasma-Activated Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Hydrogel Dressings. Adv Funct Mater 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, S.; Doll, C.; Voss, J.O.; Hertel, M.; Preissner, S.; Raguse, J.D. Treatment of Wound Healing Disorders of Radial Forearm Free Flap Donor Sites Using Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Proof of Concept. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2017, 75, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, S.; Preissner, S.; Voss, J.O.; Hertel, M.; Doll, C.; Waluga, R.; Raguse, J.D. The feasibility of cold atmospheric plasma in the treatment of complicated wounds in cranio-maxillo-facial surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017, 45, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.K.; Parab, S.; Alexander, A.; Agrawal, M.; Achalla, V.P.K.; Pal, U.N.; Pandey, M.M.; Kesharwani, P. Cold atmospheric plasma therapy in wound healing. Process Biochem 2022, 112, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senneville, E.; Lipsky, B.A.; Abbas, Z.G.; Aragon-Sanchez, J.; Diggle, M.; Embil, J.M.; Kono, S.; Lavery, L.A.; Malone, M.; van Asten, S.A.; et al. Diagnosis of infection in the foot in diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2020, 36 Suppl 1, e3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence. N Engl J Med 2017, 376, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narres, M.; Kvitkina, T.; Claessen, H.; Droste, S.; Schuster, B.; Morbach, S.; Rumenapf, G.; Van Acker, K.; Icks, A. Incidence of lower extremity amputations in the diabetic compared with the non-diabetic population: A systematic review. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0182081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzatvar, Y.; Garcia-Hermoso, A. Global estimates of diabetes-related amputations incidence in 2010-2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023, 195, 110194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCosker, L.; Tulleners, R.; Cheng, Q.; Rohmer, S.; Pacella, T.; Graves, N.; Pacella, R. Chronic wounds in Australia: A systematic review of key epidemiological and clinical parameters. Int Wound J 2019, 16, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assadian, O.; Ousey, K.J.; Daeschlein, G.; Kramer, A.; Parker, C.; Tanner, J.; Leaper, D.J. Effects and safety of atmospheric low-temperature plasma on bacterial reduction in chronic wounds and wound size reduction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Wound J 2019, 16, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moelleken, M.; Jockenhofer, F.; Wiegand, C.; Buer, J.; Benson, S.; Dissemond, J. Pilot study on the influence of cold atmospheric plasma on bacterial contamination and healing tendency of chronic wounds. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2020, 18, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohal, R.; Dietrich, S.; Mittlbock, M.; Hammerle, G. Chronic wounds treated with cold atmospheric plasmajet versus best practice wound dressings: a multicenter, randomized, non-inferiority trial. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rached, N.A.; Kley, S.; Storck, M.; Meyer, T.; Stucker, M. Cold Plasma Therapy in Chronic Wounds-A Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial (Plasma on Chronic Wounds for Epidermal Regeneration Study): Preliminary Results. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalghatgi, S.U.; Fridman, G.; Cooper, M.; Nagaraj, G.; Peddinghaus, M.; Balasubramanian, M.; Vasilets, V.N.; Gutsol, A.F.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G. Mechanism of blood coagulation by nonthermal atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge plasma. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 2007, 35, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, G.; Robert, E.; Lenoir, A.; Vandamme, M.; Darny, T.; Dozias, S.; Kieda, C.; Pouvesle, J.M. Plasma jet-induced tissue oxygenation: potentialities for new therapeutic strategies. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 2014, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, K.; Hoffmanns, M.A.; Demir, E.; Baldus, S.; Volkmar, C.M.; Rohle, M.; Fuchs, P.C.; Awakowicz, P.; Suschek, C.V.; Oplander, C. The topical use of non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge (DBD): nitric oxide related effects on human skin. Nitric Oxide 2015, 44, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisch, T.; Helmke, A.; Schleusser, S.; Song, J.; Liodaki, E.; Stang, F.H.; Mailaender, P.; Kraemer, R. Improvement of cutaneous microcirculation by cold atmospheric plasma (CAP): Results of a controlled, prospective cohort study. Microvasc Res 2016, 104, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daeschlein, G.; Rutkowski, R.; Lutze, S.; von Podewils, S.; Sicher, C.; Wild, T.; H. -R., M.; von Woedkte, T.; Jünger, M. Hyperspectral imaging: innovative diagnostics to visualize hemodynamic effects of cold plasma in wound therapy. Biomed Eng 2018, 63, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchardt, T.; Helmke, A.; Ernst, J.; Emmert, S.; Schilling, A.F.; Felmerer, G.; Viol, W. Topically confined enhancement of cutaneous microcirculation by cold plasma. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 2022, 35, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleusser, S.; Schulz, L.; Song, J.; Deichmann, H.; Griesmann, A.C.; Stang, F.H.; Mailaender, P.; Kraemer, R.; Kleemann, M.; Kisch, T. A single application of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) improves blood flow parameters in chronic wounds. Microcirculation 2022, 29, e12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzkeit, N.; Schulz, L.; Schleusser, S.; Jensen, J.O.; Stang, F.H.; Mailaender, P.; Kramer, R.; Kisch, T. Cold atmospheric plasma improves cutaneous microcirculation in standardized acute wounds: Results of a controlled, prospective cohort study. Microvasc Res 2021, 138, 104211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchesne, C.; Banzet, S.; Lataillade, J.J.; Rousseau, A.; Frescaline, N. Cold atmospheric plasma modulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase signalling and enhances burn wound neovascularisation. J Pathol 2019, 249, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frescaline, N.; Duchesne, C.; Favier, M.; Onifarasoaniaina, R.; Guilbert, T.; Uzan, G.; Banzet, S.; Rousseau, A.; Lataillade, J.J. Physical plasma therapy accelerates wound re-epithelialisation and enhances extracellular matrix formation in cutaneous skin grafts. J Pathol 2020, 252, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, S.; Panariello, B.H.D. Comprehensive biomedical applications of low temperature plasmas. Arch Biochem Biophys 2020, 693, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuangsuwanich, A.; Assadamongkol, T.; Boonyawan, D. The healing effect of low-temperature atmospheric-pressure plasma in pressure ulcer: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 2016, 15, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehmer, F.; Haenssle, H.A.; Daeschlein, G.; Ahmed, R.; Pfeiffer, S.; Gorlitz, A.; Simon, D.; Schon, M.P.; Wandke, D.; Emmert, S. Alleviation of chronic venous leg ulcers with a hand-held dielectric barrier discharge plasma generator (PlasmaDerm((R)) VU-2010): results of a monocentric, two-armed, open, prospective, randomized and controlled trial (NCT01415622). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2015, 29, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metelmann, H.-R.; Seebauer, C.; Miller, V.; Fridman, A.; Bauer, G.; Graves, D.B.; Pouvesle, J.-M.; Rutkowski, R.; Schuster, M.; Bekeschus, S.; et al. Clinical experience with cold plasma in the treatment of locally advanced head and neck cancer. Clin Plasma Med 2018, 9, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canady, J.; Murthy, S.R.K.; Zhuang, T.; Gitelis, S.; Nissan, A.; Ly, L.; Jones, O.Z.; Cheng, X.; Adileh, M.; Blank, A.T.; et al. The First Cold Atmospheric Plasma Phase I Clinical Trial for the Treatment of Advanced Solid Tumors: A Novel Treatment Arm for Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, R.; Daeschlein, G.; von Woedtke, T.; Smeets, R.; Gosau, M.; Metelmann, H.R. Long-term Risk Assessment for Medical Application of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, J.; Stope, M.B.; Henes, M.; Koch, A.; Wenzel, T.; Holl, M.; Layland, S.L.; Neis, F.; Bosmuller, H.; Ruoff, F.; et al. Noninvasive Physical Plasma as Innovative and Tissue-Preserving Therapy for Women Positive for Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Cancers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Arnholdt, M.; Hissnauer, A.; Fischer, I.; Schonfisch, B.; Andress, J.; Gerstner, S.; Dannehl, D.; Bosmuller, H.; Staebler, A.; et al. Tissue-preserving treatment with non-invasive physical plasma of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia-a prospective controlled clinical trial. Frontiers in Medicine 2023, 10, 1242732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Utz, R.; Ackermann, M.; Taran, F.A.; Krämer, B.; Hahn, M.; Wallwiener, D.; Brucker, S.Y.; Haupt, M.; Barz, J.; et al. Characterization of a non-thermally operated electrosurgical argon plasma source by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Plasma Process Polym 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzke, K.; Seebauer, C.; Jesse, K.; Kwiatek, E.; Berner, J.; Semmler, M.L.; Boeckmann, L.; Emmert, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Metelmann, H.R.; et al. Plasma medical oncology: Immunological interpretation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Plasma Process Polym 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horr, C.; Buechler, S.A. Breast Cancer Consensus Subtypes: A system for subtyping breast cancer tumors based on gene expression. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collisson, E.A.; Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Biankin, A.V. Molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 16, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonnenmacher, L.; Fischer, M.; Haralambiev, L.; Bekeschus, S.; Schulze, F.; Wassilew, G.I.; Schoon, J.; Reichert, J.C. Orthopaedic applications of cold physical plasma. EFORT Open Rev 2023, 8, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golpour, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; Mohseni, A.; Zaboli, E.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Bekeschus, S.; Rafiei, A. Lack of Adverse Effects of Cold Physical Plasma-Treated Blood from Leukemia Patients: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Appl Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmark, P.; Tod, A.M. Ethical challenges in conducting clinical research in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2016, 5, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.; Spickett, C.M. Chemistry of phospholipid oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 1818, 2374–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.; Munoz, M.F.; Arguelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheux, S.; Frache, G.; Thomann, J.S.; Clément, F.; Penny, C.; Belmonte, T.; Duday, D. Small unilamellar liposomes as a membrane model for cell inactivation by cold atmospheric plasma treatment. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2016, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Honda, R.; Hokari, Y.; Takashima, K.; Kanzaki, M.; Kaneko, T. Characterization of plasma-induced cell membrane permeabilization: focus on OH radical distribution. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2016, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Paal, J.; Neyts, E.C.; Verlackt, C.C.W.; Bogaerts, A. Effect of lipid peroxidation on membrane permeability of cancer and normal cells subjected to oxidative stress. Chem Sci 2016, 7, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusupov, M.; Van der Paal, J.; Neyts, E.C.; Bogaerts, A. Synergistic effect of electric field and lipid oxidation on the permeability of cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 2017, 1861, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svarnas, P.; Asimakoulas, L.; Katsafadou, M.; Pachis, K.; Kostazos, N.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Liposomal membrane disruption by means of miniaturized dielectric-barrier discharge in air: liposome characterization. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2017, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Saito, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Sekine, A.; Noguchi, N.; Niki, E. 4-Hydroxynonenal induces adaptive response and enhances PC12 cell tolerance primarily through induction of thioredoxin reductase 1 via activation of Nrf2. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 41921–41927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sano, M.; Shinmura, K.; Tamaki, K.; Katsumata, Y.; Matsuhashi, T.; Morizane, S.; Ito, H.; Hishiki, T.; Endo, J.; et al. 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal protects against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury via the Nrf2-dependent pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2010, 49, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanan, R.; Oikawa, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Ohnishi, S.; Ma, N.; Pinlaor, S.; Yongvanit, P.; Kawanishi, S.; Murata, M. Oxidative stress and its significant roles in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2014, 16, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrom, L.M.; Guzman, M.L.; Rivella, S. Iron and reactive oxygen species: friends or foes of cancer cells? Antioxid Redox Signal 2014, 20, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Talbot, A.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Sherman, J.H.; Cheng, X.; Keidar, M. Toward understanding the selective anticancer capacity of cold atmospheric plasma--a model based on aquaporins (Review). Biointerphases 2015, 10, 040801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, C.M.; Kolb, J.F.; Weltmann, K.D.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S. Combination Treatment with Cold Physical Plasma and Pulsed Electric Fields Augments ROS Production and Cytotoxicity in Lymphoma. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Paal, J.; Verheyen, C.; Neyts, E.C.; Bogaerts, A. Hampering Effect of Cholesterol on the Permeation of Reactive Oxygen Species through Phospholipids Bilayer: Possible Explanation for Plasma Cancer Selectivity. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 39526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Liebelt, G.; Menz, J.; Berner, J.; Sagwal, S.K.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.D.; Boeckmann, L.; von Woedtke, T.; Metelmann, H.R.; et al. Tumor cell metabolism correlates with resistance to gas plasma treatment: The evaluation of three dogmas. Free Radic Biol Med 2021, 167, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, G.; Sersenová, D.; Graves, D.B.; Machala, Z. Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Medium Trigger RONS-Based Tumor Cell Apoptosis. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 14210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornin, J.; Mateu-Sanz, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Labay, C.; Rodriguez, R.; Canal, C. Pyruvate Plays a Main Role in the Antitumoral Selectivity of Cold Atmospheric Plasma in Osteosarcoma. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, I.; Haigis, M.C. Metabolites and the tumour microenvironment: from cellular mechanisms to systemic metabolism. Nat Metab 2021, 3, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J. Protein oxidation and peroxidation. Biochem J 2016, 473, 805–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauerland, M.B.; Davies, M.J. Electrophile versus oxidant modification of cysteine residues: Kinetics as a key driver of protein modification. Arch Biochem Biophys 2022, 727, 109344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartesaghi, S.; Radi, R. Fundamentals on the biochemistry of peroxynitrite and protein tyrosine nitration. Redox Biol 2018, 14, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, T.; Kano, A.; Kamiya, T.; Hara, H.; Adachi, T. Enhanced ability of plasma-activated lactated Ringer's solution to induce A549 cell injury. Arch Biochem Biophys 2018, 656, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.N.; Guo, X.Y.; Xie, D.P.; Wang, X.M.; Ren, C.X.; Han, Y.H.; Yu, N.N.; Huang, Y.L.; Kwon, T. Knockdown of Peroxiredoxin V increased the cytotoxicity of non-thermal plasma-treated culture medium to A549 cells. Aging-US 2022, 14, 4000–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Pomicter, A.D.; Li, F.; Bhatt, S.; Chen, C.; Li, W.; Qi, M.; Huang, C.; Deininger, M.W.; Kong, M.G.; et al. Trident cold atmospheric plasma blocks three cancer survival pathways to overcome therapy resistance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Forman, H.J. Glutathione synthesis and its role in redox signaling. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2012, 23, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heusler, T.; Bruno, G.; Bekeschus, S.; Lackmann, J.-W.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. Can the effect of cold physical plasma-derived oxidants be transported via thiol group oxidation? Clin Plasma Med 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F.; Arcaro, A.; Pizzimenti, S.; Daga, M.; Cetrangolo, G.P.; Dianzani, C.; Lepore, A.; Graf, M.; Ames, P.R.J.; Barrera, G. DNA damage by lipid peroxidation products: implications in cancer, inflammation and autoimmunity. AIMS Genet 2017, 4, 103–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizdaroglu, M.; Jaruga, P. Mechanisms of free radical-induced damage to DNA. Free Radic Res 2012, 46, 382–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, K.N.; Ma, J.; Shen, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, F.; Cai, Z.; Han, W. Non-thermal plasma induces mitochondria-mediated apoptotic signaling pathway via ROS generation in HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 2017, 633, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.C.; Ruwan Kumara, M.H.S.; Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Oh, M.C.; Ryu, Y.S.; Jo, J.O.; Mok, Y.S.; Shin, J.H.; Park, Y.; et al. Exposure of keratinocytes to non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma increases the level of 8-oxoguanine via inhibition of its repair enzyme. Mol Med Rep 2017, 16, 6870–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, J.; Judee, F.; Vallette, M.; Decauchy, H.; Arbelaiz, A.; Aoudjehane, L.; Scatton, O.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Merabtene, F.; Augustin, J.; et al. Cold-Atmospheric Plasma Induces Tumor Cell Death in Preclinical In Vivo and In Vitro Models of Human Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Jeong, D.; Ham, J.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. ChIP-seq analysis reveals alteration of H3K4 trimethylation occupancy in cancer-related genes by cold atmospheric plasma. Free Radic Biol Med 2018, 126, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, K.; Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Jatsch, L.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T. Risk assessment of a cold argon plasma jet in respect to its mutagenicity. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 2016, 798-799, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxhammer, V.; Li, Y.F.; Koritzer, J.; Shimizu, T.; Maisch, T.; Thomas, H.M.; Schlegel, J.; Morfill, G.E.; Zimmermann, J.L. Investigation of the mutagenic potential of cold atmospheric plasma at bactericidal dosages. Mutat Res 2013, 753, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisch, T.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Unger, P.; Heider, J.; Shimizu, T.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Morfill, G.E.; Landthaler, M.; Karrer, S. Investigation of toxicity and mutagenicity of cold atmospheric argon plasma. Environ Mol Mutagen 2017, 58, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Kramer, A.; Metelmann, H.R.; Adler, F.; von Woedtke, T.; Niessner, F.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wende, K. High throughput image cytometry micronucleus assay to investigate the presence or absence of mutagenic effects of cold physical plasma. Environ Mol Mutagen 2018, 59, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Woedtke, T.V.; Stenzel, J.; Lindner, T.; Polei, S.; Vollmar, B.; Bekeschus, S. One Year Follow-Up Risk Assessment in SKH-1 Mice and Wounds Treated with an Argon Plasma Jet. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasse, S.; Duong Tran, T.; Hahn, O.; Kindler, S.; Metelmann, H.R.; von Woedtke, T.; Masur, K. Induction of proliferation of basal epidermal keratinocytes by cold atmospheric-pressure plasma. Clin Exp Dermatol 2016, 41, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackert, S.; Haertel, B.; Wende, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Influence of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma on cellular structures and processes in human keratinocytes (HaCaT). J Dermatol Sci 2013, 70, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wende, K.; Strassenburg, S.; Haertel, B.; Harms, M.; Holtz, S.; Barton, A.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment evokes transient oxidative stress in HaCaT keratinocytes and influences cell physiology. Cell Biol Int 2014, 38, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Park, H.J.; Yang, S.S.; Choi, K.S.; Lee, J.S. Anti-cancer efficacy of nonthermal plasma dissolved in a liquid, liquid plasma in heterogeneous cancer cells. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 29020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C.; Piao, M.J.; Hewage, S.R.K.M.; Han, X.I.A.; Kang, K.A.; Jo, J.O.; Mok, Y.S.; Shin, J.H.; Park, Y.; Yoo, S.J.; et al. Non-thermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma damages human keratinocytes by inducing oxidative stress. Int J Molec Med 2016, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, S.; Zhang, H.; Kong, X.; Ding, L.; Shen, J.; Lan, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhu, T.; Xia, W. Selective effects of non-thermal atmospheric plasma on triple-negative breast normal and carcinoma cells through different cell signaling pathways. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, K.N.; Cheng, C.; Ni, G.; Shen, J.; Han, W. Targeting Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 enhances non-thermal plasma-induced cell death in non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 2018, 658, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.; Ji, H.W.; Kim, H.W.; Yun, S.H.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Restores Paclitaxel Sensitivity to Paclitaxel-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells by Reversing Expression of Resistance-Related Genes. Cancers 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Nguyen, N.H.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, Y.; Kang, M.A.; Lee, J.S. Non-Thermal Plasma Couples Oxidative Stress to TRAIL Sensitization through DR5 Upregulation. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shome, D.; von Woedtke, T.; Riedel, K.; Masur, K. The HIPPO Transducer YAP and Its Targets CTGF and Cyr61 Drive a Paracrine Signalling in Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Mediated Wound Healing. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 4910280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, G.; Yu, K.N.; Yang, M.; Peng, S.; Ma, J.; Qin, F.; Cao, W.; Cui, S.; Nie, L.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma induces GSDME-dependent pyroptotic signaling pathway via ROS generation in tumor cells. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J.; Lu, T.; Song, W. Low-Dose Non-Thermal Atmospheric Plasma Promotes the Proliferation and Migration of Human Normal Skin Cells. Appl Sci 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, H.; Zakaly, H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Inhibits the Proliferation of CAL-62 Cells through the ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Sci Technol Nucl Install 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loenhout, J.; Freire Boullosa, L.; Quatannens, D.; De Waele, J.; Merlin, C.; Lambrechts, H.; Lau, H.W.; Hermans, C.; Lin, A.; Lardon, F.; et al. Auranofin and Cold Atmospheric Plasma Synergize to Trigger Distinct Cell Death Mechanisms and Immunogenic Responses in Glioblastoma. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Gumbel, D.; Hanschmann, E.M.; Mandelkow, R.; Gelbrich, N.; Zimmermann, U.; Walther, R.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Sckell, A.; Kramer, A.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment Induces Anti-Proliferative Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells by Redox and Apoptotic Signaling Pathways. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0130350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Peng, Y.; Utsumi, F.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Toyokuni, S.; Hori, M.; Kikkawa, F.; Kajiyama, H. Novel Intraperitoneal Treatment With Non-Thermal Plasma-Activated Medium Inhibits Metastatic Potential of Ovarian Cancer Cells. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yu, K.N.; Zhang, H.; Nie, L.; Cheng, C.; Cui, S.; Yang, M.; Chen, G.; Han, W. Non-thermal plasma induces apoptosis accompanied by protective autophagy via activating JNK/Sestrin2 pathway. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2020, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Sun, H.N.; Liu, R.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, D.S. Non-thermal Plasma-activated Medium Induces Apoptosis of Aspc1 Cells Through the ROS-dependent Autophagy Pathway. In Vivo 2020, 34, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.U.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, J.K.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.; Kim, C.H. Non-thermal plasma induces AKT degradation through turn-on the MUL1 E3 ligase in head and neck cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33382–33396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruwan Kumara, M.H.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Park, J.E.; Shilnikova, K.; Jo, J.O.; Mok, Y.S.; Shin, J.H.; Park, Y.; et al. Non-thermal gas plasma-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Oncol Rep 2016, 36, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.U.; Cho, J.H.; Chang, J.W.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, K.I.; Park, J.K.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, K.; et al. Nonthermal plasma induces head and neck cancer cell death: the potential involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Cell Death Dis 2014, 5, e1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.R.; Kang, S.U.; Kim, H.J.; Ji, E.J.; Yun, J.H.; Kim, S.; Jang, J.Y.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, C.H. Liquid plasma as a treatment for cutaneous wound healing through regulation of redox metabolism. Cell Death Dis 2023, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Sun, B.; Luo, S.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.; Rong, M.Z.; Kong, M.G. Fluid model of plasma–liquid interaction: The effect of interfacial boundary conditions and Henry’s law constants. AIP Adv 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Liu, D.X.; Chen, C.; Li, D.; Yang, A.J.; Rong, M.Z.; Chen, H.L.; Kong, M.G. Physicochemical processes in the indirect interaction between surface air plasma and deionized water. J Phys D: Appl Phys 2015, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbanev, Y.; O'Connell, D.; Chechik, V. Non-thermal plasma in contact with water: The origin of species. Chemistry 2016, 22, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Kothakota, A.; Annapure, U.; Siliveru, K.; Blundell, R.; Gatt, R.; Valdramidis, V.P. Plasma activated water (PAW): Chemistry, physico-chemical properties, applications in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci Technol 2018, 77, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Alborova, A.; Humme, D.; Patzelt, A.; Kramer, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; Hartmann, B.; Ottomann, C.; Fluhr, J.W.; et al. Risk assessment of the application of a plasma jet in dermatology. J Biomed Opt 2009, 14, 054025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Park, J.Y.; Choe, W. Origin of hydroxyl radicals in a weakly ionized plasma-facing liquid. Chem Eng J 2019, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, C.; Eymann, C.; Emicke, P.; Bernhardt, J.; Wilhelm, M.; Gorries, F.; Winter, J.; von Woedtke, T.; Darm, K.; Daeschlein, G.; et al. Improved Wound Healing of Airway Epithelial Cells Is Mediated by Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Time Course-Related Proteome Analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 7071536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Yoshida, T.; Tsujioka, M.; Arakawa, S. Autophagic cell death and cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2014, 15, 3145–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Hu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Wang, W. The Relationship of Redox With Hallmarks of Cancer: The Importance of Homeostasis and Context. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 862743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.C.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, S.; Song, K. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Efficiently Promotes the Proliferation of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells by Activating NO-Response Pathways. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 39298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Ma, J.; Yu, K.N.; Li, W.; Cheng, C.; Bao, L.; Han, W. Non-thermal plasma treatment altered gene expression profiling in non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, D.; Cai, D.; Ning, M.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, P.; Dai, X. Cold atmospheric plasma selectively induces G(0)/G(1) cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in AR-independent prostate cancer cells. J Cancer 2021, 12, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Song, H.; Bai, F.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z. Cold Atmospheric Plasma for Cancer Treatment: Molecular and Immunological Mechanisms. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci 2022, 6, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M. Molecular basis of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Radic Biol Med 2015, 88, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, H.C.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, C.; Surh, Y.J. Nitric oxide activates Nrf2 through S-nitrosylation of Keap1 in PC12 cells. Nitric Oxide 2011, 25, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Pi, J.; Zhang, Q. Signal amplification in the KEAP1-NRF2-ARE antioxidant response pathway. Redox Biol 2022, 54, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atayik, M.C.; Cakatay, U. Redox signaling in impaired cascades of wound healing: promising approach. Mol Biol Rep 2023, 50, 6927–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Dietrich, S.; Steuer, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; von Woedtke, T.; Masur, K.; Wende, K. Non-thermal plasma activates human keratinocytes by stimulation of antioxidant and phase II pathways. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 6731–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Jablonowski, H.; Barton, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wende, K. Role of Ambient Gas Composition on Cold Physical Plasma-Elicited Cell Signaling in Keratinocytes. Biophys J 2017, 112, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Schmidt, A.; Karrer, S.; von Woedtke, T. Comparing two different plasma devices kINPen and Adtec SteriPlas regarding their molecular and cellular effects on wound healing. Clin Plasma Med 2018, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.Z.; Stevenson, A.W.; Prele, C.M.; Fear, M.W.; Wood, F.M. The Role of IL-6 in Skin Fibrosis and Cutaneous Wound Healing. Biomedicines 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K.; Vollmar, B.; von Woedtke, T. A cold plasma jet accelerates wound healing in a murine model of full-thickness skin wounds. Exp Dermatol 2017, 26, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S. Redox for Repair: Cold Physical Plasmas and Nrf2 Signaling Promoting Wound Healing. Antioxidants 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacz, A.; Kloska, D.; Forman, H.J.; Jozkowicz, A.; Grochot-Przeczek, A. Beyond repression of Nrf2: An update on Keap1. Free Radic Biol Med 2020, 157, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; von Woedtke, T.; Vollmar, B.; Hasse, S.; Bekeschus, S. Nrf2 signaling and inflammation are key events in physical plasma-spurred wound healing. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1066–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Bethge, L.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S.; Wende, K. Redox Stimulation of Human THP-1 Monocytes in Response to Cold Physical Plasma. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 2016, 5910695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, I.; Odagiri, H.; Park, G.; Sanghavi, R.; Oshita, T.; Togi, A.; Yoshikawa, K.; Mizutani, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of cold atmospheric plasma irradiation on the THP-1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0292267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.H.; Cha, Y.N.; Surh, Y.J. Peroxynitrite induces HO-1 expression via PI3K/Akt-dependent activation of NF-E2-related factor 2 in PC12 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 2006, 41, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.W.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.G. Peroxynitrite activates NF-E2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element through the pathway of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: The role of nitric oxide synthase in rat glutathione S-transferase A2 induction. Nitric Oxide 2002, 7, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenhunen, R.; Marver, H.S.; Schmid, R. Microsomal Heme Oxygenase. J Biol Chem 1969, 244, 6388–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.K.; Fitzgerald, H.K.; Dunne, A. Regulation of inflammation by the antioxidant haem oxygenase 1. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, T.; Wang, H.; Tao, S.; Lau, A.; Fang, D.; Zhang, D.D. Does Nrf2 contribute to p53-mediated control of cell survival and death? Antioxid Redox Signal 2012, 17, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.H.; Tokheim, C.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Sengupta, S.; Bertrand, D.; Weerasinghe, A.; Colaprico, A.; Wendl, M.C.; Kim, J.; Reardon, B.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Cancer Driver Genes and Mutations. Cell 2018, 173, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, S.; Patinen, T.; Jawahar Deen, A.; Pitkanen, S.; Harkonen, J.; Kansanen, E.; Kublbeck, J.; Levonen, A.L. The KEAP1-NRF2 pathway: Targets for therapy and role in cancer. Redox Biol 2023, 63, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, Q.; Bao, L.; Li, M.; Chang, K.; Yi, X. Cytoprotective Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Cancer Chemoresistance: Focus on Antioxidant, Antiapoptotic, and Pro-Autophagy Properties. Antioxidants 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Golpur, M.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Hadavi, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Niaki, H.A.; Valadan, R.; Rafiei, A. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Is a Potent Tool to Improve Chemotherapy in Melanoma In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, J.; Boisvert, J.-S.; Glory, A.; Coulombe, S.; Wong, P. Synergy between Non-Thermal Plasma with Radiation Therapy and Olaparib in a Panel of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pefani-Antimisiari, K.; Athanasopoulos, D.K.; Marazioti, A.; Sklias, K.; Rodi, M.; de Lastic, A.L.; Mouzaki, A.; Svarnas, P.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Synergistic effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma and free or liposomal doxorubicin on melanoma cells. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornin, J.; Mateu-Sanz, M.; Rey, V.; Murillo, D.; Huergo, C.; Gallego, B.; Rodriguez, A.; Rodriguez, R.; Canal, C. Cold plasma and inhibition of STAT3 selectively target tumorigenicity in osteosarcoma. Redox Biol 2023, 62, 102685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Shin, Y.S.; Seo, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, K.; Kim, C.H. Combination of NTP with cetuximab inhibited invasion/migration of cetuximab-resistant OSCC cells: Involvement of NF-kappaB signaling. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 18208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tan, F. Cold atmospheric plasma sensitizes head and neck cancer to chemotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Redox Biol 2023, 69, 102991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezhpour, A.; Ghafouri, H.; Jafari, S.; Nilkar, M. Effects of cold atmospheric-pressure plasma in combination with doxorubicin drug against breast cancer cells in vitro and invivo. Free Radic Biol Med 2023, 209, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, O.G.; Brzozowski, J.S.; Skelding, K.A. Glioblastoma Multiforme: An Overview of Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Front Oncol 2019, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, S.; Jain, A.K.; Bloom, D.A.; Jaiswal, A.K. Bach1 competes with Nrf2 leading to negative regulation of the antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 gene expression and induction in response to antioxidants. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 16891–16900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenke-Kawasaki, Y.; Dohi, Y.; Katoh, Y.; Ikura, T.; Ikura, M.; Asahara, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Iwai, K.; Igarashi, K. Heme induces ubiquitination and degradation of the transcription factor Bach1. Mol Cell Biol 2007, 27, 6962–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lignitto, L.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Homer, H.; Jiang, S.; Askenazi, M.; Karakousi, T.R.; Pass, H.I.; Bhutkar, A.J.; Tsirigos, A.; Ueberheide, B.; et al. Nrf2 Activation Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting the Degradation of Bach1. Cell 2019, 178, 316–329.e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, J.; Lee, J. A Novel Therapeutic Target, BACH1, Regulates Cancer Metabolism. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, I.; Zeng, H.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Feedback Inhibition of the Unfolded Protein Response by GADD34-Mediated Dephosphorylation of eIF2α. J Cell Biol 2001, 153, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jousse, C.; Oyadomari, S.; Novoa, I.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Inhibition of a constitutive translation initiation factor 2α phosphatase, CReP, promotes survival of stressed cells. J Cell Biol 2003, 163, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.; Giresh, K.; Wrischnik, L.A.; Weiser, D.C. The PPP1R15 Family of eIF2-alpha Phosphatase Targeting Subunits (GADD34 and CReP). Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 17321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.M.; Abdelmalek, D.H.; Elfiky, A.A. GRP78: A cell's response to stress. Life Sci 2019, 226, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, X.; Hou, C.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Kong, L.; Liu, C.; Feng, L.; Wang, D.; et al. Cold Plasma Irradiation Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis via Enhancing HIF-1alpha-Induced MANF Transcription Expression. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 941219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.R.; Prescott, E.T.; Sylvester, C.F.; Higdon, A.N.; Shan, J.; Kilberg, M.S.; Mungrue, I.N. Human CHAC1 Protein Degrades Glutathione, and mRNA Induction Is Regulated by the Transcription Factors ATF4 and ATF3 and a Bipartite ATF/CRE Regulatory Element. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 15878–15891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungrue, I.N.; Pagnon, J.; Kohannim, O.; Gargalovic, P.S.; Lusis, A.J. CHAC1/MGC4504 is a novel proapoptotic component of the unfolded protein response, downstream of the ATF4-ATF3-CHOP cascade. J Immunol 2009, 182, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, G.; Berger, R.; Strasak, A.M.; Egle, D.; Muller-Holzner, E.; Schmidt, S.; Rainer, J.; Presul, E.; Parson, W.; Lang, S.; et al. Elevated mRNA expression of CHAC1 splicing variants is associated with poor outcome for breast and ovarian cancer patients. Br J Cancer 2012, 106, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, V.; Meena, J.; Kasana, H.; Munshi, A.; Chander, H. Prognostic significance of CHAC1 expression in breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep 2022, 49, 8517–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Yu, L.; Zou, F.; Hu, H.; Liu, K.; Lin, Z. Gene expression profiling and functional analysis reveals that p53 pathway-related gene expression is highly activated in cancer cells treated by cold atmospheric plasma-activated medium. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Katsumata, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Kondo, H.; Hashizume, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Toyokuni, S.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshikawa, N.; et al. Oxidative stress-dependent and -independent death of glioblastoma cells induced by non-thermal plasma-exposed solutions. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 13657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, T.; Staebler, S.; Taudte, R.V.; Unuvar, S.; Grosch, S.; Arndt, S.; Karrer, S.; Fromm, M.F.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Triggers Apoptosis via the Unfolded Protein Response in Melanoma Cells. Cancers 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motaln, H.; Cercek, U.; Recek, N.; Bajc Cesnik, A.; Mozetic, M.; Rogelj, B. Cold atmospheric plasma induces stress granule formation via an eIF2alpha-dependent pathway. Biomater Sci 2020, 8, 5293–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaul, Y.D.; Seger, R. The MEK/ERK cascade: from signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007, 1773, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Kong, N.; Ye, L.; Han, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Pan, H. p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett 2014, 344, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Mortezaee, K. Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling as a target for cancer therapy: an updated review. Cell Biol Int 2019, 43, 1206–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shain, A.H.; Joseph, N.M.; Yu, R.; Benhamida, J.; Liu, S.; Prow, T.; Ruben, B.; North, J.; Pincus, L.; Yeh, I.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Incremental Disruption of Key Signaling Pathways during Melanoma Evolution. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 45–55.e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yu, K.N.; Bao, L.; Shen, J.; Cheng, C.; Han, W. Non-thermal plasma inhibits human cervical cancer HeLa cells invasiveness by suppressing the MAPK pathway and decreasing matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 19720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronico, V.; Morelli, S.; Piscioneri, A.; Gristina, R.; Casiello, M.; Favia, P.; Armenise, V.; Fracassi, F.; De Bartolo, L.; Sardella, E. Anticancer Effects of Plasma-Treated Water Solutions from Clinically Approved Infusion Liquids Supplemented with Organic Molecules. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 33723–33736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Gao, W.; Shao, F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem Sci 2017, 42, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Gong, Y.; Rao, F.; Liu, R.; Danna, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; et al. A PLK1 kinase inhibitor enhances the chemosensitivity of cisplatin by inducing pyroptosis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Shi, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Wang, K.; Shao, F. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature 2017, 547, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, B.; Li, D.; Wang, G.; Han, X.; Sun, X. GSDME mediates caspase-3-dependent pyroptosis in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2018, 495, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, K.I.; Seo, S.J.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, K.; Kim, C.H. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma inhibits thyroid papillary cancer cell invasion via cytoskeletal modulation, altered MMP-2/-9/uPA activity. PLoS One 2014, 9, e92198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, H.; Ding, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Cold atmospheric plasma and iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles for synergetic lung cancer therapy. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 130, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, R.T.; Xu, L. Bcl-2:Beclin 1 complex: multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle switch. Am J Cancer Res 2012, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Ito, F.; Wang, Y.; Okazaki, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Hori, M.; Hirayama, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Richardson, D.R.; et al. Non-thermal plasma induces a stress response in mesothelioma cells resulting in increased endocytosis, lysosome biogenesis and autophagy. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 108, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Zeng, W.; Xia, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, D.; Liu, D.; Kong, M.G.; Dong, Y. Cold atmospheric plasma induces apoptosis of melanoma cells via Sestrin2-mediated nitric oxide synthase signaling. J Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderali, E.; Valipour, B.; Khaki, A.A.; Soleymani Rad, J.; Alihemmati, A.; Rahmati, M.; Nozad Charoudeh, H. Positive Effects of PI3K/Akt Signaling Inhibition on PTEN and P53 in Prevention of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Tumor Cells. Adv Pharm Bull 2019, 9, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, M.; Evans, M.M.; Ostrikov, K.K. Effect of atmospheric gas plasmas on cancer cell signaling. Int J Cancer 2014, 134, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, A.; Joh, H.M.; Chung, T.H.; Chung, J.W. Anticancer effects of plasma-activated medium produced by a microwave-excited atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 4205640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, G.; Graves, D.B. Mechanisms of Selective Antitumor Action of Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Derived Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Plasma Process Polym 2016, 13, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.; Sersenová, D.; Graves, D.B.; Machala, Z. Dynamics of Singlet Oxygen-Triggered, RONS-Based Apoptosis Induction after Treatment of Tumor Cells with Cold Atmospheric Plasma or Plasma-Activated Medium. Sci Rep 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Jangra, A.; Choi, S.A.; Choi, E.H.; Han, I. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Bio-Compatible Plasma Stimulates Apoptosis via p38/MAPK Mechanism in U87 Malignant Glioblastoma. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Jarick, K.; Hasse, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. Cold Physical Plasma Modulates p53 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Keratinocytes. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, L.C.; Billi, A.C.; Ward, N.L.; Harms, P.W.; Zeng, C.; Maverakis, E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Cytokinocytes: the diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Shen, L.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lan, L.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27 antagonizes TNF-alpha induced HeLa cell apoptosis via regulating TAK1 ubiquitination and activation of p38 and ERK signaling. Cell Signal 2014, 26, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, H.; Mashima, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsuruo, T. Modulation of heat-shock protein 27 (Hsp27) anti-apoptotic activity by methylglyoxal modification. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 45770–45775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundscherer, L.; Wende, K.; Ottmuller, K.; Barton, A.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Masur, K.; Lindequist, U. Impact of non-thermal plasma treatment on MAPK signaling pathways of human immune cell lines. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundscherer, L.; Nagel, S.; Hasse, S.; Tresp, H.; Wende, K.; Walther, R.; Reuter, S.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Masur, K.; Lindequist, U. Non-thermal plasma treatment induces MAPK signaling in human monocytes. Open Chem 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Clemen, R.; Haralambiev, L.; Niessner, F.; Grabarczyk, P.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Menz, J.; Stope, M.; von Woedtke, T.; Gandhirajan, R.; et al. The Plasma-Induced Leukemia Cell Death is Dictated by the ROS Chemistry and the HO-1/CXCL8 Axis. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci 2021, 5, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.B.; Seo, I.H.; Chae, M.W.; Park, J.W.; Choi, E.H.; Uhm, H.S.; Baik, K.Y. Anticancer Activity of Liquid Treated with Microwave Plasma-Generated Gas through Macrophage Activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 2946820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, B.S.; Hsieh, J.H.; Chen, C.M.; Hou, C.W.; Wu, H.Y.; Chou, P.Y.; Lai, C.H.; Lee, J.W. Helium/Argon-Generated Cold Atmospheric Plasma Facilitates Cutaneous Wound Healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Qi, M.; Feng, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Effects of Plasma-Activated Water on Skin Wound Healing in Mice. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haensel, D.; Dai, X. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cutaneous wound healing: Where we are and where we are heading. Dev Dyn 2018, 247, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Winterbourn, C.C.; Kolata, J.; Masur, K.; Hasse, S.; Bröker, B.M.; Parker, H.A. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation is elicited in response to cold physical plasma. JLB 2016, 100, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Herrmann, M.; Zhao, Y.; Munoz, L.E. Receptor-Mediated NETosis on Neutrophils. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 775267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Chang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Ma, Z.; Lin, H.; Fan, H. Streptococcus Suis Serotype 2 Stimulates Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Formation via Activation of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Ling, X.; Jin, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Miao, C.; et al. The emerging roles of neutrophil extracellular traps in wound healing. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchetti, L.; Boubaker, N.S.; Barba, M.; Vici, P.; Gurtner, A.; Piaggio, G. Neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer: not only catching microbes. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2021, 40, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Mei, W.; Zeng, C. PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway and Its Role in Cancer Therapeutics: Are We Making Headway? Front Oncol 2022, 12, 819128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squarize, C.H.; Castilho, R.M.; Bugge, T.H.; Gutkind, J.S. Accelerated wound healing by mTOR activation in genetically defined mouse models. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasowanjete, P.; Dhilip Kumar, S.S.; Houreld, N.N. A review of photobiomodulation on PI3K/AKT/mTOR in wound healing. J Photochem Thotobiol 2024, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jere, S.W.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. Role of the PI3K/AKT (mTOR and GSK3beta) signalling pathway and photobiomodulation in diabetic wound healing. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2019, 50, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongkolpobsin, K.; Sillapachaiyaporn, C.; Lertpatipanpong, P.; Boonruang, K.; Hwang, C.Y.; Tencomnao, T.; Baek, S.J. Cold atmospheric microwave plasma (CAMP) stimulates dermal papilla cell proliferation by inducing beta-catenin signaling. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Chung, K.B.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.; Song, K.; Kim, D.Y. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in dermal papilla cells. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimmeler, S.; Fleming, I.; Fisslthaler, B.; Hermann, C.; Busse, R.; Zeiher, A.M. Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature 1999, 399, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreira, B.P.; Morte, M.I.; Inacio, A.; Costa, G.; Rosmaninho-Salgado, J.; Agasse, F.; Carmo, A.; Couceiro, P.; Brundin, P.; Ambrosio, A.F.; et al. Nitric oxide stimulates the proliferation of neural stem cells bypassing the epidermal growth factor receptor. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holl, M.; Rasch, M.L.; Becker, L.; Keller, A.L.; Schultze-Rhonhof, L.; Ruoff, F.; Templin, M.; Keller, S.; Neis, F.; Kessler, F.; et al. Cell Type-Specific Anti-Adhesion Properties of Peritoneal Cell Treatment with Plasma-Activated Media (PAM). Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Liebelt, G.; Niessner, F.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S. Gas plasma-spurred wound healing is accompanied by regulation of focal adhesion, matrix remodeling, and tissue oxygenation. Redox Biol 2021, 38, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, N.; Sajjadi, E.; Venetis, K.; Gaudioso, G.; Lopez, G.; Corti, C.; Rocco, E.G.; Criscitiello, C.; Malapelle, U.; Invernizzi, M. PTEN Alterations and Their Role in Cancer Management: Are We Making Headway on Precision Medicine? Genes 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemirli, N.; Pourcelot, M.; Ambroise, G.; Hatchi, E.; Vazquez, A.; Arnoult, D. Mitochondrial hyperfusion promotes NF-kappaB activation via the mitochondrial E3 ligase MULAN. FEBS J 2014, 281, 3095–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, S.; Bien-Moller, S.; Marx, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Schroeder, H.W.S.; Mustea, A.; Stope, M.B. Devitalization of Glioblastoma Cancer Cells by Non-invasive Physical Plasma: Modulation of Proliferative Signalling Cascades. Anticancer Res 2023, 43, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Guo, X.; Dong, Y.; Peng, P.; Huang, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Feedback activation of STAT3 limits the response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in PTEN-deficient cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, L.; Ma, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, G.-J. Helium low temperature plasma induced HepG2 cells autophagy through ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/P70s6k signaling pathway. AIP Adv 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Gu, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Cai, D. NF-kappaB-dependent MicroRNA-425 upregulation promotes gastric cancer cell growth by targeting PTEN upon IL-1β induction. Molec Cancer 2014, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wei, W.Z.; Wu, G.S. Activation of the Akt survival pathway contributes to TRAIL resistance in cancer cells. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, K.I.; Seo, S.J.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Baek, S.J.; Lee, K.; et al. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma induces apoptosis in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Involvement of DNA-damage-triggering sub-G(1) arrest via the ATM/p53 pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 2014, 545, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.B.; Lee, K.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Jang, I.T.; Gurmessa, S.K.; Choi, E.H.; Kaushik, N.K.; Kim, H.J. Non-Thermal Plasma Jet-Treated Medium Induces Selective Cytotoxicity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Infected Macrophages. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarakati, N.; Al-Shareeda, A.; Ramadan, M.; Al-Sowayan, B.; Negm, O.; Nedjadi, T. Interaction between HER2 and ATM predicts poor survival in bladder cancer patients. J Cell Mol Med 2022, 26, 4959–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Cheng, H.; Sun, F.; Lu, X.; He, G.; Laroussi, M. Differences in Cytotoxicity Induced by Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Exogenous RONS Solutions on Human Keratinocytes and Melanoma Cells. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci 2021, 5, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscop, E.; Lin, A.; Boxem, W.V.; Loenhout, J.V.; Backer, J.; Deben, C.; Dewilde, S.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A.A. Influence of Cell Type and Culture Medium on Determining Cancer Selectivity of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. Cancers 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasse, S.; Seebauer, C.; Wende, K.; Schmidt, A.; Metelmann, H.R.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S. Cold Argon Plasma as Adjuvant Tumour Therapy on Progressive Head and Neck Cancer: A Preclinical Study. Appl Sci 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, M.; Mehdian, H.; Hajisharifi, K.; Amini, E.; Ostrikov, K.; Robert, E. Plasma-activated medium induces apoptosis in chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer cells: High selectivity and synergy with carboplatin. Plasma Process Polym 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yan, C.; Kong, S.; Jia, T.; Chu, Z.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Geng, S.; Guo, K. Biosafety and differentially expressed genes analysis of melanoma cells treated with cold atmospheric plasma. J Biophotonics 2022, 15, e202100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Mohn, L.; Ambuhl, L.; Kanai, K.; Schmidt, I.; Kim, K.P.; Fraccaroli, A.; Feil, S.; Junge, H.J.; et al. Integrin-linked kinase controls retinal angiogenesis and is linked to Wnt signaling and exudative vitreoretinopathy. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Sherman, J.; Murphy, W.; Ratovitski, E.; Canady, J.; Keidar, M. The effect of tuning cold plasma composition on glioblastoma cell viability. PLoS One 2014, 9, e98652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasvani, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Rawtani, D. Hyaluronic acid: A review on its biology, aspects of drug delivery, route of administrations and a special emphasis on its approved marketed products and recent clinical studies. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 151, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golz, A.C.; Bergemann, C.; Hildebrandt, F.; Emmert, S.; Nebe, B.; Rebl, H. Selective adhesion inhibition and hyaluronan envelope reduction of dermal tumor cells by cold plasma-activated medium. Cell Adh Migr 2023, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, S.B.; Choi, E.H.; Han, I. Non-Thermal Bio-Compatible Plasma Induces Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells With ROS-Induced Activation of MAPK. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 36652–36663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.P.; Marttala, J.; Macarak, E.; Rosenbloom, J.; Uitto, J. Keloids: The paradigm of skin fibrosis - Pathomechanisms and treatment. Matrix Biol 2016, 51, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.U.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, J.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, H.Y.; Jang, J.W.; Ryeo, J.B.; Lee, Y.; Shin, Y.S.; et al. Opposite effects of non-thermal plasma on cell migration and collagen production in keloid and normal fibroblasts. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0187978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwanchinda, A.; Nararatwanchai, T. Efficacy and safety of the innovative cold atmospheric-pressure plasma technology in the treatment of keloid: A randomized controlled trial. J Cosmet Dermatol 2022, 21, 6788–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, W.; Lu, L.; Su, J.; Chen, X. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Lee, M.-H.; Kang, S.U.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, K. Development of an atmospheric nonthermal multineedle dielectric barrier discharge jet for large area treatment of skin diseases. Curr Appl Phys 2021, 24, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Kang, J.; Choi, Y.A.; Park, J.; Park, C.K.; Khang, D.; Kim, S.H. Portable Cold Atmospheric Plasma Patch-Mediated Skin Anti-Inflammatory Therapy. Advanced Science 2022, 9, e2202800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.-X.; He, T.; Dong, W.-W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, N.; Zou, Z.-F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A Novel Method for Estimating the Dosage of Cold Atmospheric Plasmas in Plasma Medical Applications. Appl Sci 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Lu, X. On the dose of plasma medicine: Equivalent total oxidation potential (ETOP). Phys Plasmas 2020, 27, 063514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Andrade, T.A.M.; Caetano, G.F.; Guimaraes, F.R.; Leite, M.N.; Leite, S.N.; Frade, M.A.C. Experimental models and methods for cutaneous wound healing assessment. Int J Exp Pathol 2020, 101, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronico, V.; Favia, P.; Fracassi, F.; Gristina, R.; Sardella, E. The active role of organic molecules in the formation of long-lived reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in plasma-treated water solutions. Plasma Process Polym 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
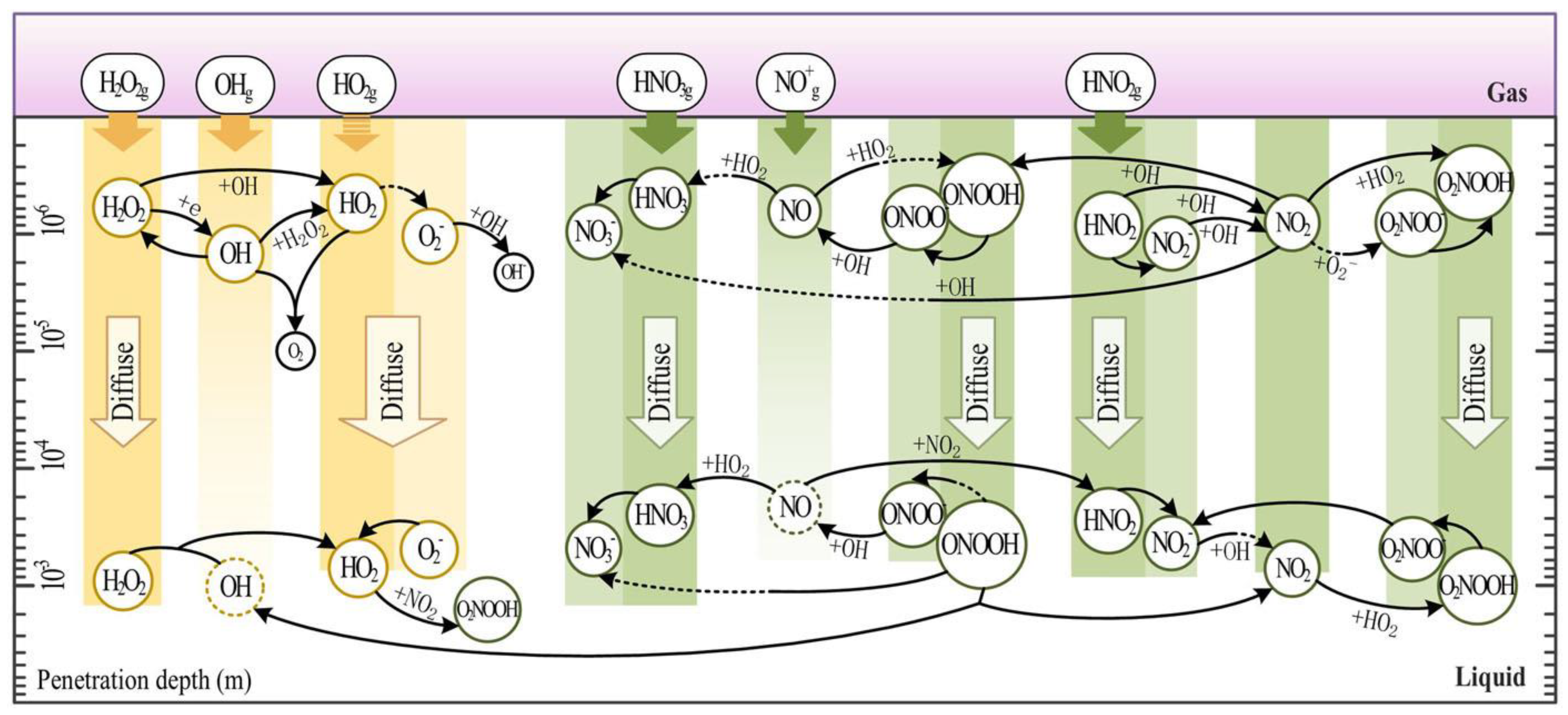
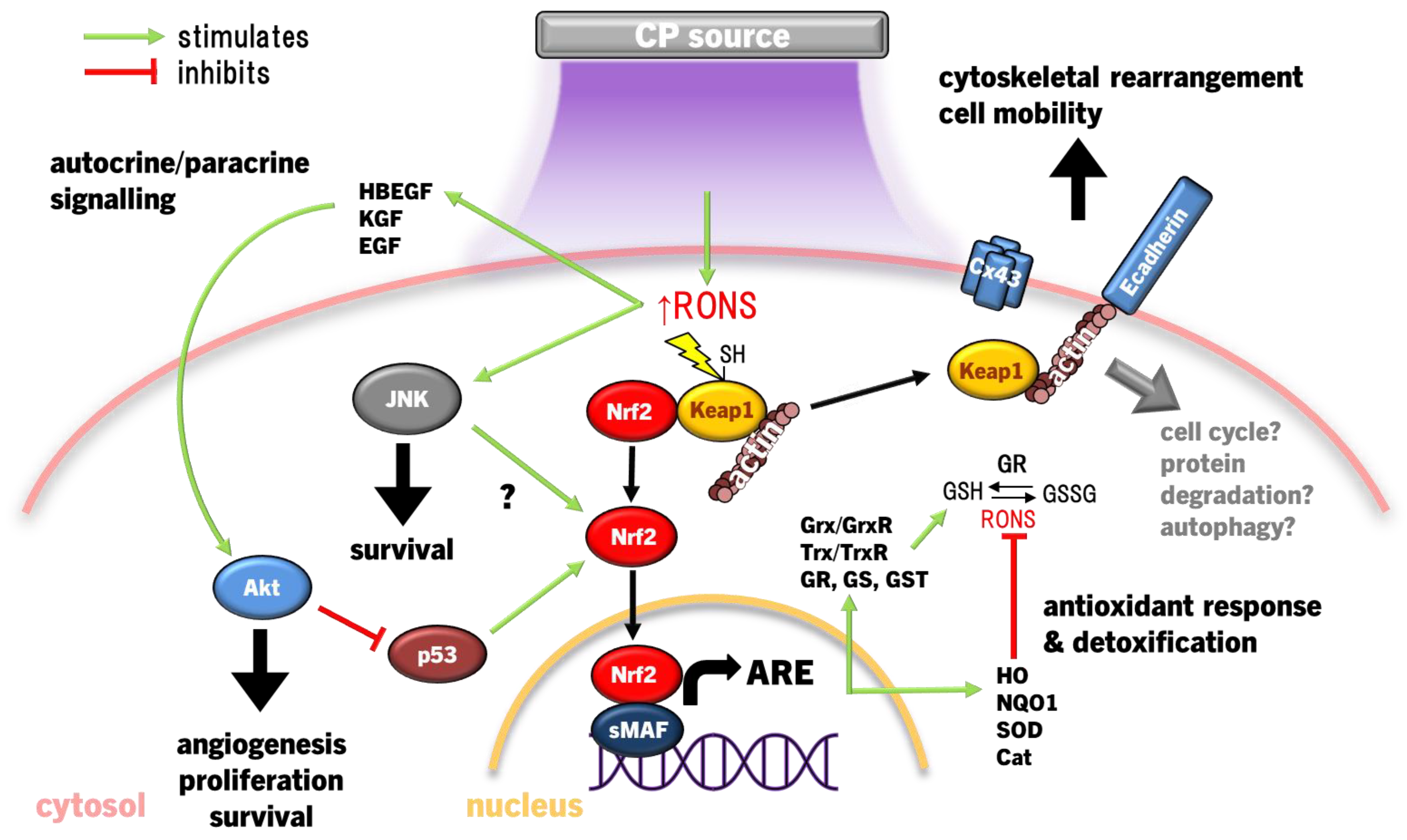
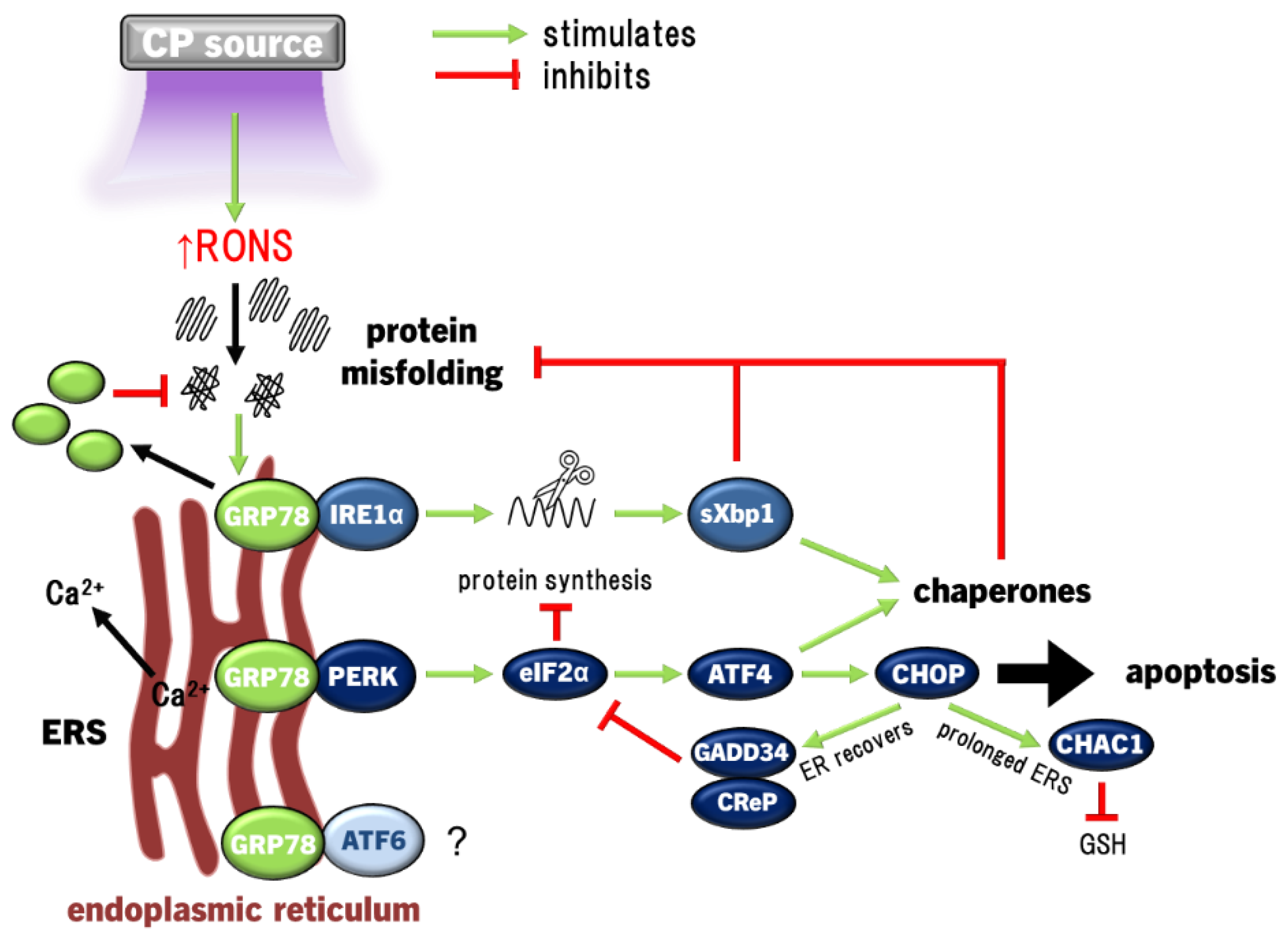
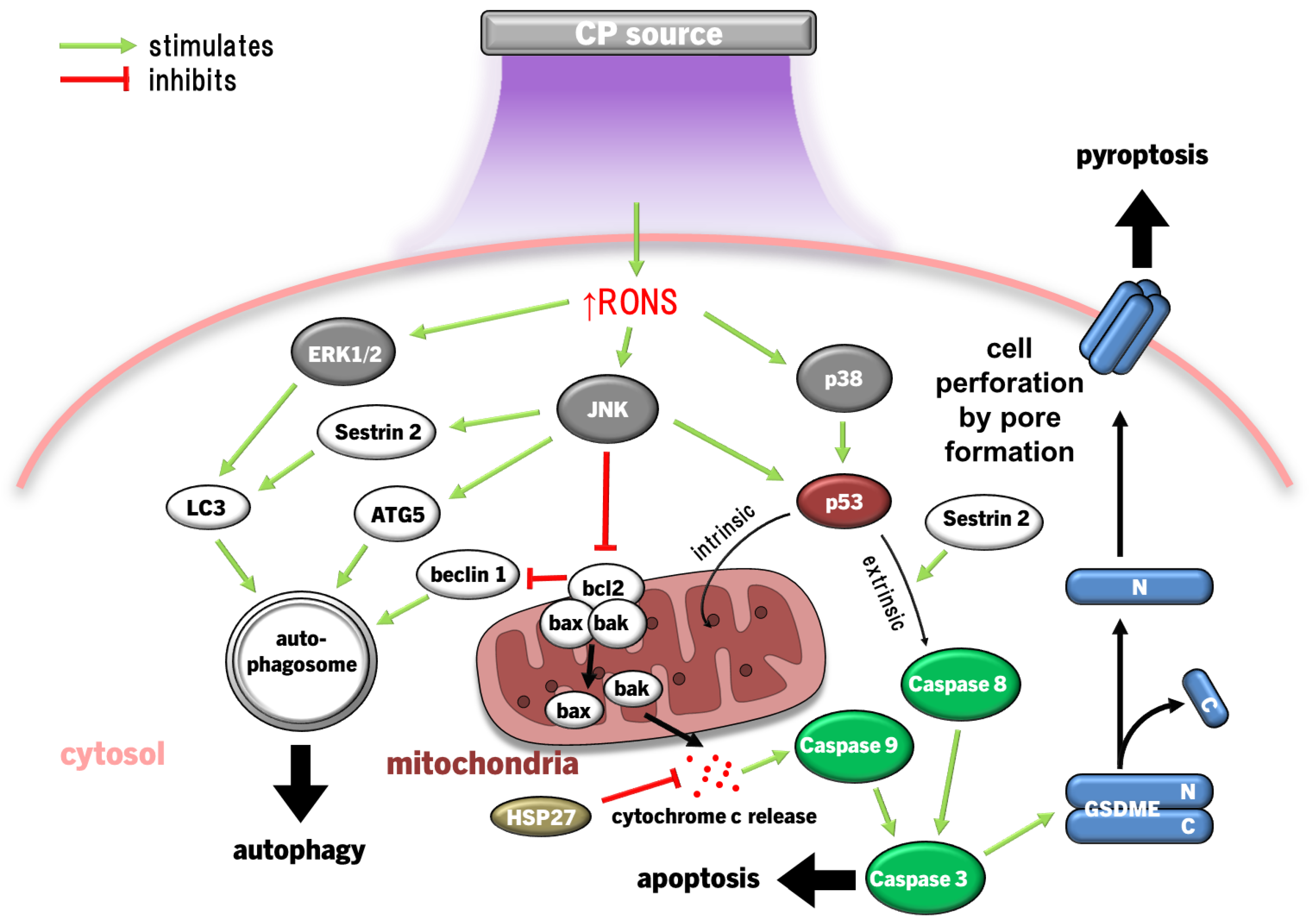
| CP device | Ref | Study design | Population and treatment groups | Primary results |
| kINPen® MED plasma jet | [66] | CS (n = 6) |
Patients with oropharyngeal cancer received 1 min CP exposure 3× within 1 week. | Significantly improved palliation/QOL with reduced infection load. Too few participants to conclude anti-tumour effects. |
| [68] | NCC, SB (n = 5) |
Subjects previously exposed to 10 – 30 s CP in wounds. Followed up for 5 years to monitor tumour formation. | No suspicious or malignant lesions found. No pathological signs of tissue modification detected. | |
| VIO3/APC3 electrosurgical plasma device | [69] | C, SA (n = 20) |
Patients with cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN) treated with CP 30 s/cm2 with up to 24-week follow-up. | 19/20 subjects exhibited normal cervical histopathology |
| [70] | C, SA (n = 63) |
CP treatment group showed approximately double histological and cytological CIN remission rate, but NSD to control. | ||
| Canady Helios® plasma jet | [67] | MC, C (n = 20) |
Patients with stage IV or recurrent solid tumour of mixed origins, with 21- to 32-month follow-up. CP treatment regime not disclosed. | No adverse effects or tumour recurrence. CP shows evidence of therapeutic effect as adjuvant to tumour resection. Evidence of pro-apoptotic protein expression induced by CP in cancer tissue biopsies. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





