Submitted:
01 April 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of C. cardunculus Extracts
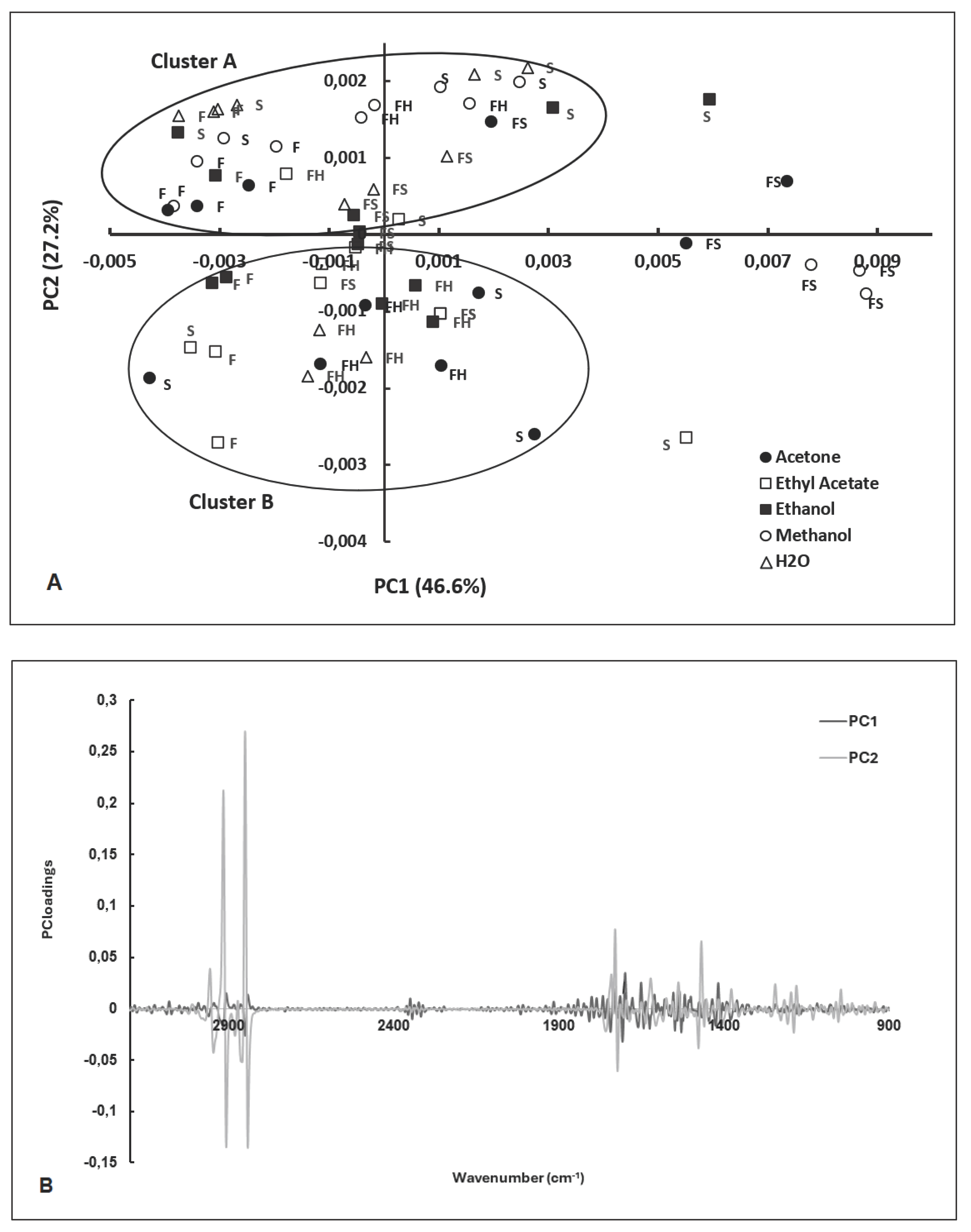
2.2. PCA of FT-MIR Spectra
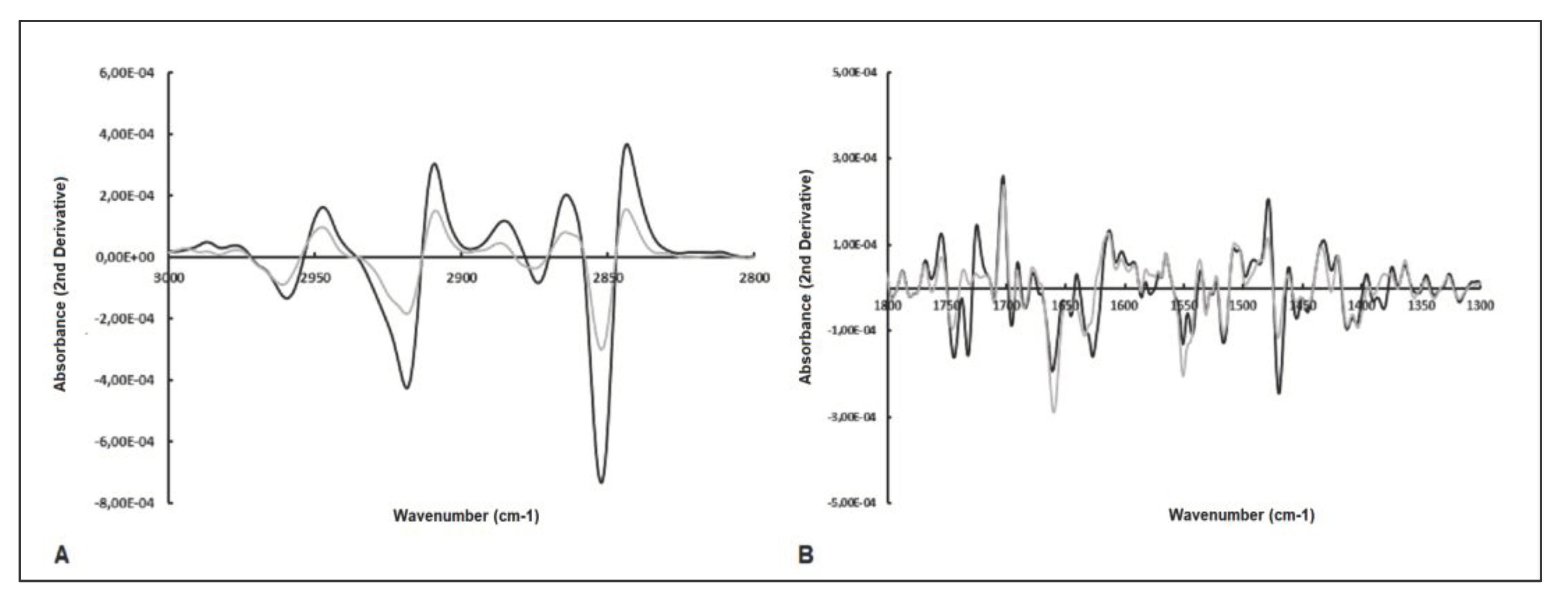
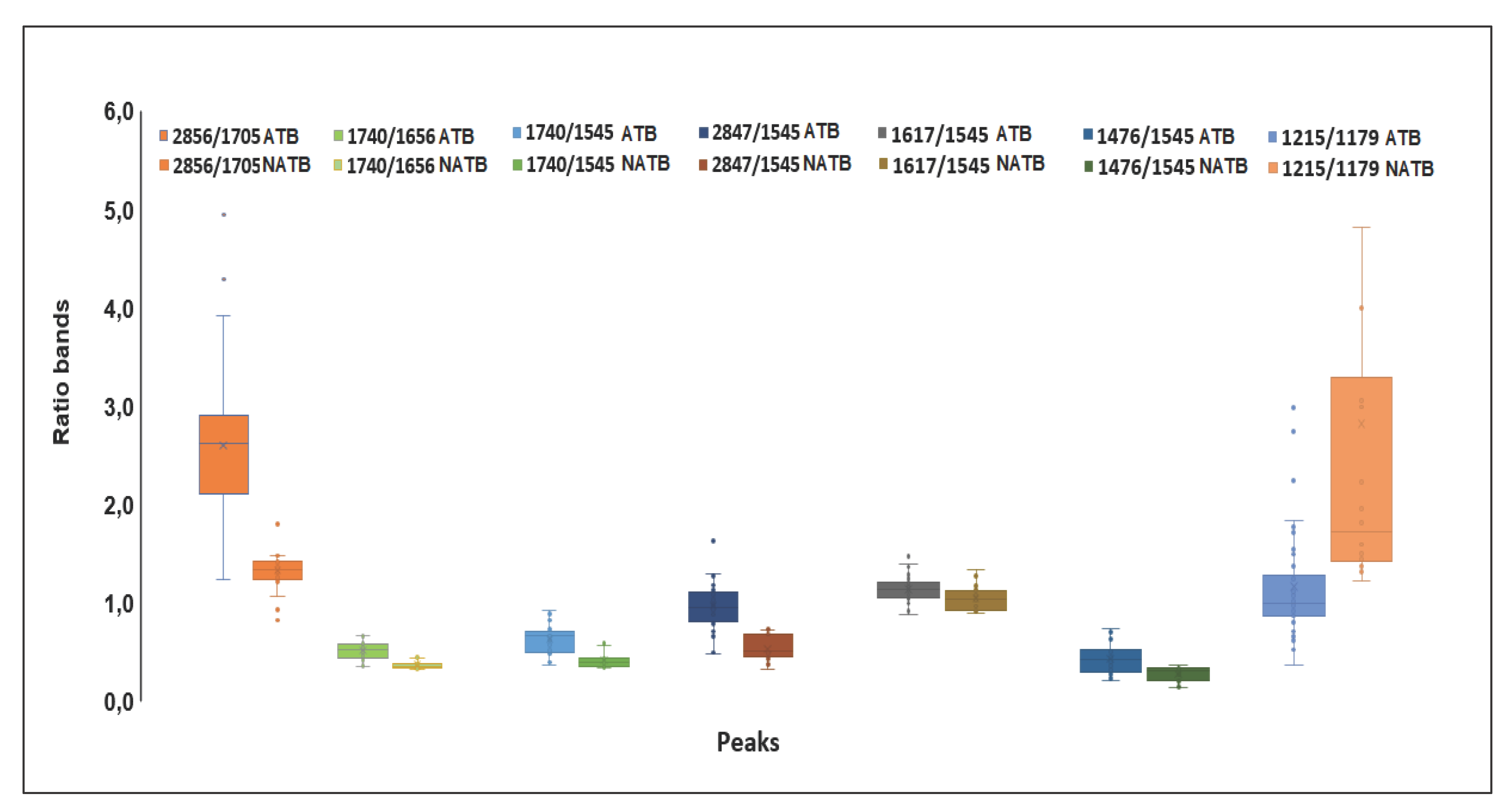
2.3. Analysis of Spectral Bands
2.4. Classification Models
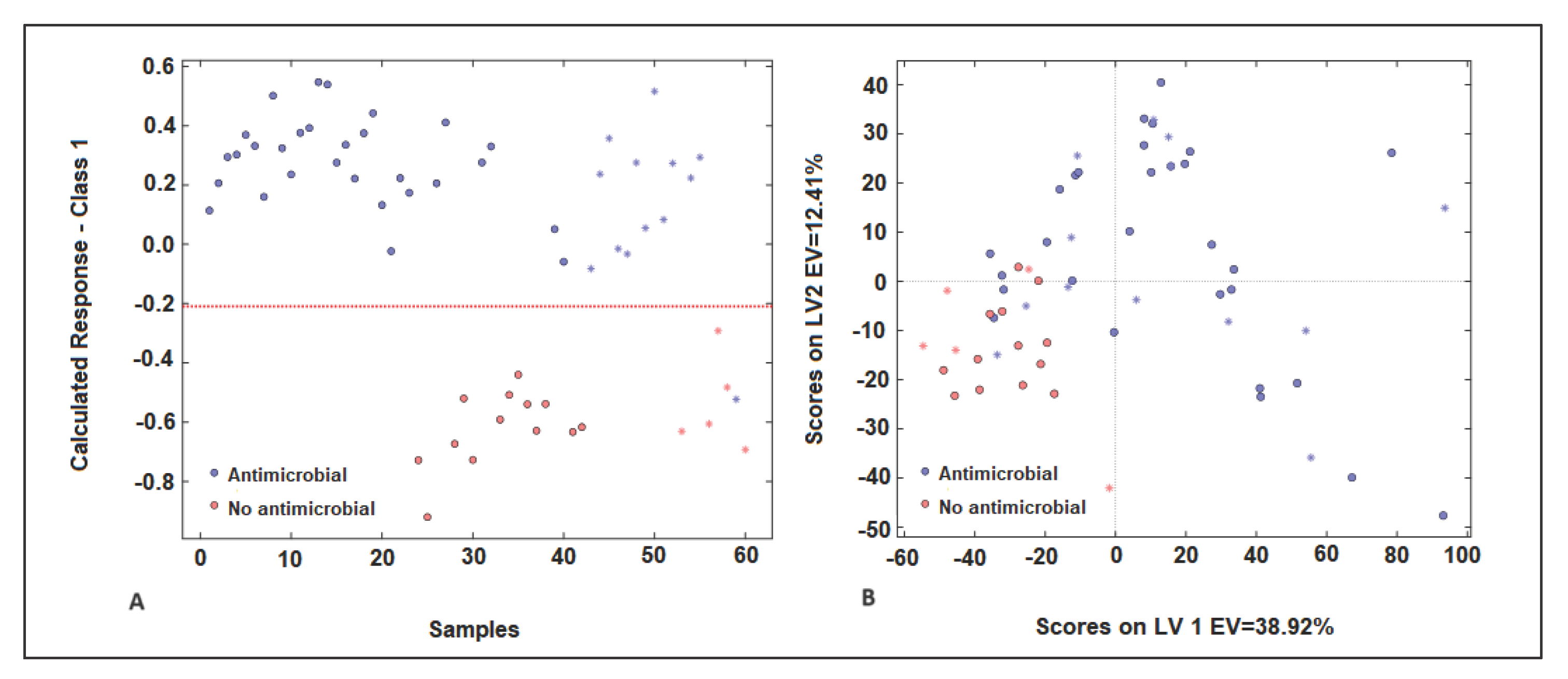
2.4.1. PLS-DA Model
2.4.2. K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN)
2.4.3. Support Vector Machines (SVM)
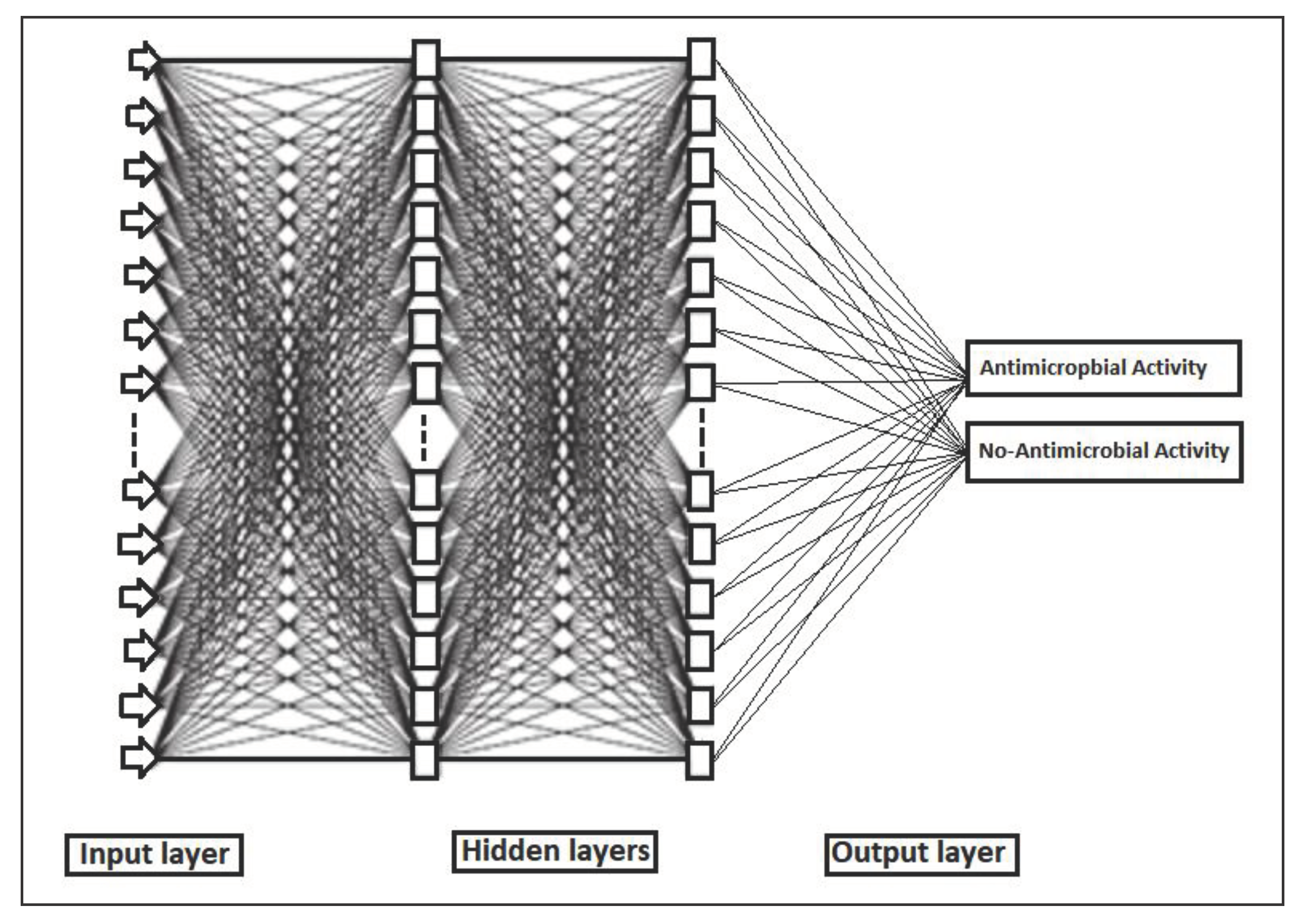
2.4.4. Backpropagation Network (BPN)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Extraction Process
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Total Phenols
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
3.5. FTIR Spectral Analysis
3.5.1. Acquisition of Spectra
3.5.2. Spectral Pre-Processing
3.6. Chemometric Methods
3.6.1. Principal Component Analysis
3.7. Classification Methods
3.7.1. Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
3.7.2. K-Nearest Neighbours
3.7.3. Support Vector Machine
3.7.4. Back Propagation Network (BPN)
3.8. Other Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nwobodo, D.C.; Ugwu, M.C.; Anie, C.O.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.S.; Ikem, J.C.; Chigozie, U.V.; Saki, M. Antibiotic resistance: The challenges and some emerging strategies for tackling a global menace. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. 2014.
- Mohr, K.I. History of Antibiotics Research. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016, 398, 237–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- David, L.; Brata, A.M.; Mogosan, C.; Pop, C.; Czako, Z.; Muresan, L.; Ismaiel, A.; Dumitrascu, D.I.; Leucuta, D.C.; Stanculete, M.F.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Antibiotic Discovery. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petropoulos, S.; Fernandes, Â.; Pereira, C.; Tzortzakis, N.; Vaz, J.; Soković, M.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Bioactivities, chemical composition and nutritional value of Cynara cardunculus L. seeds. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falleh, H.; Ksouri, R.; Chaieb, K.; Karray-Bouraoui, N.; Trabelsi, N.; Boulaaba, M.; Abdelly, C. Phenolic composition of Cynara cardunculus L. organs, and their biological activities. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2008, 331, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, R.R.; Moyse, H. Médicale Massons & Cie. Paris. Masson, 1971.
- Velez, Z.; Campinho, M.A.; Guerra, Â.R.; García, L.; Ramos, P.; Guerreiro, O.; Felício, L.; Schmitt, F.; Duarte, M. Biological characterization of Cynara cardunculus L. methanolic extracts: antioxidant, anti-proliferative, anti-migratory and anti-angiogenic activities. Agriculture 2012, 2, 472–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileo, A.M.; Di Venere, D.; Linsalata, V.; Fraioli, R.; Miccadei, S. Artichoke polyphenols induce apoptosis and decrease the invasive potential of the human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB231. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 227, 3301–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, M.S.; Sampaio, P.; Soares, R. Pharmaceutical composition containing the enzyme cyprosin B an aspartic peptidase from Cynara cardunculus and its inclusion in anti-tumorals formulations. WO 2009/040778 A2 (PT nº 103839) 2012.
- O’Connell, K.M.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; Sore, H.F.; Welch, M.; Salmond, G.P.; Spring, D.R. Combating multidrug-resistant bacteria: Current strategies for the discovery of novel antibacterials. Angew. Chem Int Ed Engl 2013, 20120, 10706–10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, F.; Sales, K.C.; Cunha, B.R.; Couto, A.; Lopes, M.B.; Calado, C.R.C. A comprehensive high-throughput FTIR spectroscopy-based method for evaluating the transfection event: estimating the transfection efficiency and extracting associated metabolic responses. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8097–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldauf, N.A.; Rodriguez-Romo, L.A.; Männig, A.; Yousef, A.E.; Rodriguez-Saona, L.E. Effect of selective growth media on the differentiation of Salmonella enterica serovars by Fourier-Transform Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 68, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamin, N.; Miller, L.; Moncuit, J.; Fridman, W.; Dumas, P.; Teillaud, J. Chemical heterogeneity in cell death: Combined synchrotron IR and fluorescence microscopy studies of single apoptotic and necrotic cells. Biopolym. 2003, 72, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.; Liew, M.; Sachdeva, A.; Bassan, P.; Dumas, P.; Hart, C.A.; Brown, M.D.; Clarke, N.W.; Gardner, P. SR-FTIR spectroscopy of renal epithelial carcinoma side population cells displaying stem cell-like characteristics. Anal. 2010, 135, 3133–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, T.; Lopes, V.V.; Calado, C.R.C. High-throughput analysis of the plasmid bioproduction process in Escherichia coli by FTIR spectroscopy. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, P.S.; Calado, C.R.C. Potential of FTIR-Spectroscopy for Drugs Screening against Helicobacter pylori. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, K.C.; Rosa, F.; Cunha, B.R.; Sampaio, P.N.; Lopes, M.B.; Calado, C.R.C. Metabolic profiling of recombinant Escherichia coli cultivations based on high-throughput FT-MIR spectroscopic analysis. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, P.N.; Sales, K.C.; Rosa, F.O.; Lopes, M.B.; Calado, C.R.C. High-throughput FTIR-based bioprocess analysis of recombinant cyprosin production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Carvajal, A.; Arguello, H.; Martínez-Lobo, F.; Naharro, G.; Rubio, P. Antibacterial activity and mode of action of a commercial citrus fruit extract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte, L.; Tiecco, M.; Roscini, L.; De Vincenzi, S.; Colabella, C.; Germani, R.; Tascini, C.; Cardinali, G. FTIR metabolomic fingerprint reveals different modes of action exerted by structural variants of N-alkyltropinium bromide surfactants on Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua cells. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moen, B.; Janbu, A.O.; Langsrud, S.; Langsrud, Ø.; Hobman, J.L.; Constantinidou, C.; Kohler, A.; Rudi, K. Global responses of Escherichia coli to adverse conditions determined by microarrays and FT-IR spectroscopy. Can J Microbiol. 2009, 55, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte, L.; Rellini, P.; Roscini, L.; Fatichenti, F.; Cardinali, G. Development of a novel, FTIR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) based, yeast bioassay for toxicity testing and stress response study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 659, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro da Cunha, B.; Fonseca, L.P.; Calado, C.R.C. A phenotypic screening bioassay for Escherichia coli stress and antibiotic responses based on Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J Appl Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1776–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamathevan, J.; Clark, D.; Czodrowski, P.; Dunham, I.; Ferran, E.; Lee, G.; Li, B.; Madabhushi, A.; Shah, P.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, N.; Tambe, S.S.; Kulkarn, B.D. Counter-propagation neural networks for fault detection and diagnosis. Comput Chem Eng 1997, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentão, P.; Fernandes, E.; Carvalho, F.; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.M.; Bastos, M.L. Antioxidative Properties of Cardoon (Cynara cardunculus L.) Infusion Against Superoxide Radical, Hydroxyl Radical, and Hypochlorous Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4989–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, A.; Knobloch, K. Inhibitory effects of essential oil components on growth of food-contaminating fungi. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 1987, 185, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikigai, H.; Nakae, T.; Hara, Y.; Shimamura, T. Bactericidal catechins damage the lipid bilayer. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Biomembr. 1993, 1147, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia Da Silva, T.B.; Souza, V.K.; Lyra, L. Determination of the phenolic content and antioxidant potential of crude extracts and isolated compounds from leaves of Cordia multispicata and Tournefortia bicolor. Pharm Biol. 2010, 48, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.; Lee, C.C.; Yenn, T.W.; Zakaria, L.; Sheh-Hong, L. Effect of the extract of endophytic fungus, Nigrospora sphaerica CL-OP 30, against the growth of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Klebsiella pneumonia cells. Trop J Pharm Res. 2015, 14, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Xu, B.T.; Xu, X.R.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, E.Q.; Li, H.B. Antioxidant capacities and total phenolic contents of 62 fruits. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V. Classification tools in chemistry. Part 1: linear models. PLS-DA. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.C.; Alonso-Salces, R.M.; Umpierrez, M.L.; Rossini, C.; Fuselli, S.R. Chemical Composition, Antimicrobial Activity, and Mode of Action of Essential Oils against Paenibacillus larvae, Etiological Agent of American Foulbrood on Apis mellifera. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakoc, E.; Cherkasov, A.; Sahinalp, S.C. Novel approaches for small biomolecule classification and structural similarity search. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2007, 9, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Leanse, L.G.; Feng, Y. Artificial intelligence and machine learning assisted drug delivery for effective treatment of infectious diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Molina, S.; Ruiz-Blanco, Y.B.; Harms, M.; Münch, J.; Sanchez-Garcia, E. PPI-detect: A Support Vector Machine Model for Sequence-based Prediction of Protein–Protein Interactions. J Comput Chem. 2019, 40, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-X.; Tong, X.; Yang, P.-P.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, J.-H.; Li, G.-H.; Liu, D.; Guan, D.-G.; Dai, S.-X. Screening of antibacterial compounds with novel structure from the FDA approved drugs using machine learning methods. Aging 2022, 14, 1448–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Mao, J.; Mohiuddin, K. Artificial neural networks: a tutorial. Computer 1996, 29, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badura, A.; Krysiński, J.; Nowaczyk, A.; Buciński, A. Prediction of the antimicrobial activity of quaternary ammonium salts against Staphylococcus aureus using artificial neural networks. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, A.C.; Prieto, J.M. Application of artificial neural networks to the prediction of the antioxidant activity of essential oils in two experimental in vitro models. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensor, L.L.; Menezes, F.S.; Leitão, G.G.; Reis, A.S.; dos Santos, T.C.; Coube, C.S.; Leitão, S.G. Screening of Brazilian plant extracts for antioxidant activity by the use of DPPH free radical method. Phytotherapy Res. 2001, 15, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slinkard, K.; Singleton, V.L. Total Phenol Analysis: automation and comparison with manual methods. Am J Enol Vitic 1977, 28, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V. Classification tools in chemistry. Part 1: linear models. PLS-DA. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.; Rayens, W. Partial least squares for discrimination. J Chemom 2003, 17, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deconinck, E.; Djiogo, C.S.; Courselle, P. Chemometrics and chromatographic fingerprints to classify plant food supplements according to the content of regulated plants. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerhuis, J.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Smit, S.; Vis, D.J.; Smilde, A.K.; van Velzen, E.J.; van Duijnhoven, J.P.M.; van Dorsten, F.A. Assessment of PLS-DA cross validation. Metabolomics 2008, 1, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.J.; Linoff, G. Data mining techniques: for marking, sales and customer support. Eds. 2001.
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. 2003.
- Tu, J.V. Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ratio bands (cm-1) |
Average | Standard deviation | p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | No-Antimicrobial | Antimicrobial | No-Antimicrobial | ||
| A2912/2856 | 1,359 | 1,356 | 0,114 | 0,162 | 0,472 |
| A2912/1740 | 3,921 | 4,121 | 1,086 | 1,114 | 0,263 |
| A2856/1705 | 2,601 | 1,334 | 0,753 | 0,248 | 0,000 |
| A1740/1656 | 0,261 | 0,114 | 0,089 | 0,038 | 0,000 |
| A1740/1545 | 0,434 | 0,218 | 0,151 | 0,082 | 0,000 |
| A2847/1545 | 0,977 | 0,537 | 0,253 | 0,124 | 0,000 |
| A2847/1740 | 2,395 | 2,720 | 0,657 | 0,966 | 0,102 |
| A1617/1545 | 1,129 | 1,035 | 0,124 | 0,131 | 0,008 |
| A1476/1545 | 0,304 | 0,146 | 0,167 | 0,081 | 0,000 |
| A1215/1179 | 1,269 | 2,950 | 0,605 | 2,314 | 0,004 |
| A1215/1545 | 0,942 | 0,708 | 0,174 | 0,082 | 0,000 |
| A1244/1230 | 1,312 | 1,158 | 0,180 | 0,027 | 0,000 |
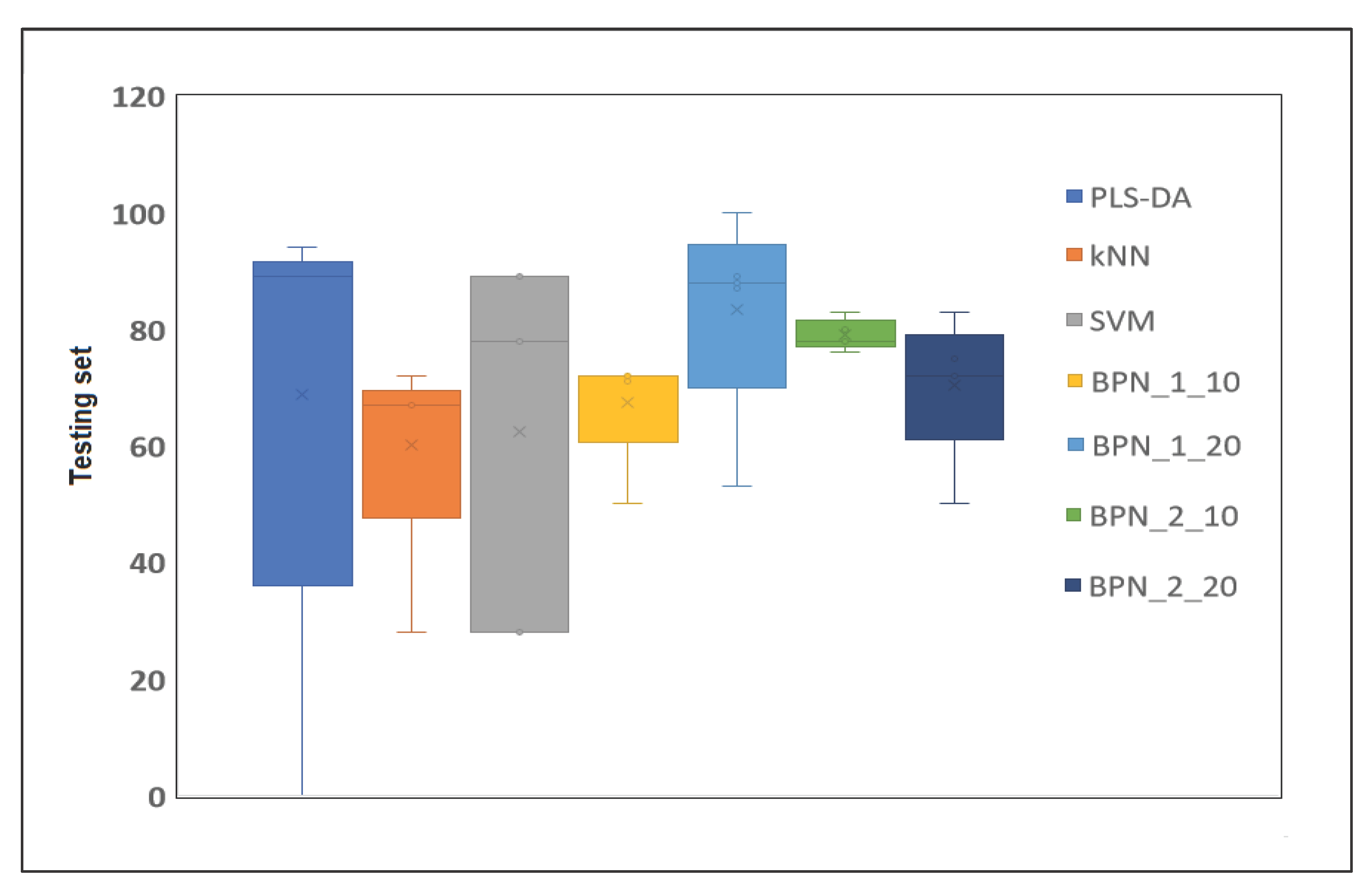
| Model | Calibration | Cross-Validation | Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NER | ER | Accuracy | NER | ER | Accuracy | NER | ER | Accuracy | |
| PLS-DA | 100 | 0 | 100 | 88 | 22 | 86 | 92 | 8 | 89 |
| PLS-DA msc | 100 | 0 | 100 | 89 | 11 | 88 | 96 | 4 | 94 |
| PLS-DA snv | 97 | 3 | 95 | 89 | 11 | 88 | 92 | 8 | 89 |
| PLS-DA 1st | 100 | 0 | 100 | 78 | 22 | 81 | 50 | 50 | 72 |
| PLS-DA 2nd | 100 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| kNN | 70 | 30 | 76 | 69 | 31 | 69 | 52 | 48 | 67 |
| kNN msc | 82 | 18 | 83 | 93 | 7 | 90 | 65 | 35 | 67 |
| kNN snv | 79 | 21 | 83 | 85 | 15 | 86 | 65 | 35 | 67 |
| kNN 1st | 87 | 13 | 88 | 91 | 9 | 90 | 50 | 50 | 72 |
| kNN 2nd | 74 | 26 | 76 | 69 | 31 | 71 | 50 | 50 | 28 |
| SVM | 77 | 23 | 83 | 58 | 42 | 55 | 72 | 28 | 78 |
| SVM msc | 91 | 9 | 93 | 80 | 20 | 81 | 92 | 8 | 89 |
| SVM snv | 87 | 13 | 90 | 80 | 20 | 81 | 92 | 8 | 89 |
| SVM 1st | 92 | 8 | 95 | 79 | 21 | 83 | 50 | 50 | 28 |
| SVM 2nd | 100 | 0 | 100 | 68 | 32 | 79 | 50 | 50 | 28 |
| BPN:1:10 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 60 | 40 | 62 | 68 | 32 | 72 |
| BPN:1:10 msc | 96 | 4 | 95 | 90 | 10 | 90 | 81 | 19 | 71 |
| BPN:1:10 snv | 98 | 2 | 98 | 77 | 23 | 79 | 68 | 32 | 72 |
| BPN:1:10 1st | 100 | 0 | 100 | 73 | 27 | 80 | 62 | 38 | 72 |
| BPN:1:10 2nd | 85 | 15 | 87 | 51 | 49 | 52 | 47 | 53 | 50 |
| BPN:1:20 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 68 | 32 | 71 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| BPN:1:20 msc | 100 | 0 | 100 | 78 | 22 | 81 | 86 | 14 | 89 |
| BPN:1:20 snv | 100 | 0 | 100 | 86 | 14 | 86 | 81 | 19 | 87 |
| BPN:1:20 1st | 100 | 0 | 100 | 60 | 40 | 74 | 67 | 33 | 88 |
| BPN:1:20 2nd | 96 | 4 | 94 | 63 | 37 | 69 | 43 | 57 | 53 |
| BPN:2:10 | 98 | 2 | 97 | 74 | 26 | 79 | 82 | 18 | 83 |
| BPN:2:10 msc | 98 | 2 | 98 | 86 | 14 | 87 | 78 | 22 | 76 |
| BPN:2:10 snv | 100 | 0 | 100 | 77 | 23 | 80 | 72 | 28 | 78 |
| BPN:2:10 1st | 84 | 16 | 85 | 72 | 25 | 82 | 75 | 25 | 80 |
| BPN:2:10 2nd | 100 | 0 | 100 | 62 | 38 | 60 | 66 | 34 | 78 |
| BPN:2:20 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 60 | 40 | 64 | 50 | 50 | 72 |
| BPN:2:20 msc | 100 | 0 | 87 | 87 | 13 | 88 | 82 | 18 | 83 |
| BPN:2:20 snv | 100 | 0 | 100 | 72 | 28 | 78 | 68 | 32 | 72 |
| BPN:2:20 1st | 100 | 0 | 100 | 53 | 47 | 58 | 58 | 42 | 75 |
| BPN:2:20 2nd | 100 | 0 | 100 | 58 | 42 | 68 | 53 | 47 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





