1. Introduction
The Gut-Brain Axis (GBA) is a bidirectional communication system that connects the enteric nervous system (ENS) of the gastrointestinal tract to the central nervous system (CNS) of the brain [
1]. It includes a wide range of physiological processes such as digestion, metabolism, immune function, and even cognitive functions such as mood and behavior [
2]. Understanding the intricate workings of the GBA is critical for investigating the mechanisms of various neurological and gastrointestinal disorders. Neuromodulation refers to a medical approach that precisely targets and modulates nerve activity within the nervous system to enhance neurological functioning and patient quality of life. This field is rapidly advancing, propelled by breakthroughs in neuroscience and medical engineering technology [
3]. Different types of neuromodulation techniques are distinguished by their unique targets and methods of affecting the neurological system [
3]. In this review, we explored the current literature on the GBA, neuromodulation and the possible uses for neuromodulation for the management of GBA disorders covering indications, possible mechanisms of actions, outcomes, and adverse effects in an effort to spot the light on what we believe is a potentially promising field that could impact and improve the quality of life for millions of patients worldwide suffering from disease with not so many options for management and with many reports describing newer understanding of the role the GBA plays in them.
2. Methodology
Our search strategy involved conducting systematic searches through PubMed, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases using different combinations of the following search and Mesh terms (GBA, Neuromodulation, Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), sacral nerve modulation, Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS), Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), epidural motor cortex stimulation (EMCS), Occipital nerve stimulation (ONS), transcranial direct current stimulation(tDCS), transcutaneous direct current stimulation, remote electrical neuromodulation (REN), Gastrointestinal Diseases, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Gastroparesis, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Neurodegenerative disease, Parkinson’s disease (PD), neuropsychiatric disorders, benefits, outcomes, mechanism of action, pathophysiology, functional GI disorders, microbiota), in some instances and when search results seemed too wide , the search was limited to articles published in 2018 or after (i.e. last five years) to have a synthesis of more recent understanding in our review. Results were then screened by titles and abstracts for relevance, and 182 articles were reviewed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Gut-Brain-Axis:
3.1.1. Key Components of the Gut-Brain Axis:
a. Enteric Nervous System (ENS):
ENS constitutes an extensive network of intrinsic neurons distributed throughout the gastrointestinal tract [
4]. It functions independently of the CNS and is responsible for regulating essential gastrointestinal processes [
4]. These functions include peristalsis, nutrient absorption, and gut motility. The ENS acts as an autonomous control system for gastrointestinal functions [
4].
b. Vagus Nerve:
The Vagus Nerve (cranial nerve X) serves as the primary neural pathway connecting the gut and the brain [
5]. It consists of sensory and motor fibers that facilitate bidirectional communication [
5]. Sensory fibers transmit information from the gut to the brain, relaying signals related to satiety, nutrient availability, and gastrointestinal discomfort[
6]. Motor fibers convey instructions from the brain to modulate gut functions such as gastric secretion and motility [
6]. This dual communication allows for continuous feedback and regulation between the gut and the brain.
c. Gut Microbiota:
The gut microbiota comprises a diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and archaea, residing within the gastrointestinal tract [
7]. This microbial population exceeds the number of human cells in the body [
7].
The beneficial roles of gut microbiota are the facilitation of metabolism through metabolic pathways and enzymatic activity, the synthesis of vitamins and metabolites, and the inhibition of pathogens [
8]. Dysbiosis and subsequent illness may occur due to an imbalance between the microbial flora in the gut, characterized by disruption of both beneficial and harmful bacteria as well as decreased bacterial diversity [
9]. Dysbiosis can lead to a depletion of TJ proteins, and an increase in intestinal wall permeability due to the overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 6 [
10]. It is noteworthy that dysbiosis may also influence the onset and progression of several diseases, such as diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, autism, and PD as evidenced in a variety of studies in both human and animal models [
11,
12]. The gut microbiota actively participates in GBA communication by producing bioactive compounds and metabolites[
13]. These include neurotransmitters, short-chain fatty acids, and other signaling molecules that influence neural activity, immune responses, and physiological processes within the host organism[
13]. The gut microbiota's role is integral to shaping both gastrointestinal and neurological functions.
In humans, evidence of an interaction between gastrointestinal bacteria and brain cells was first shown more than 20 years ago in the observation that patients with hepatic encephalopathy often showed a dramatic improvement when they took oral antibiotics [
14].
In the meantime, emerging data support the role of microbiota in influencing anxiety and depressive-like behaviors [
15] and, more recently, dysbiosis in autism. In fact, according to the severity of the disease, certain changes in the microbiota are observed in patients with autism [
16]. Data have been provided that both brain-gut and gut-brain dysfunctions occur, the former being dominant, particularly in IBS [
17].
The damage to the GBA can determine changes in intestinal motility and secretion, cause visceral hypersensitization, and lead to cell modification of the enteroendocrine and immune systems.
Figure 1.
Gut-Brain-Axis key components and functions.
Figure 1.
Gut-Brain-Axis key components and functions.
3.1.2. Physiology of the Gut-Brain Axis:
a. Neurotransmitters:
GBA relies on a complex array of neurotransmitters to facilitate its communication pathways [
18]. These neurotransmitters act as molecular messengers that transmit signals between the gut and the brain, thereby influencing various physiological processes. Key neurotransmitters involved in GBA communication include serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) [
19]. Serotonin, primarily produced in the gut, is a critical player in regulating mood, cognition, and gastrointestinal functions [
19]. GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, can modulate stress responses and influence gut motility [
19]. The precise balance of these neurotransmitters is essential for maintaining homeostasis within the GBA.
b. Hormones:
Hormones are integral components of the GBA, exerting profound effects on both gut and brain functions [
20]. Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, plays a central role in the GBA by regulating stress responses. Elevated cortisol levels can impact gut permeability and mucosal function [
21]. Ghrelin, known as the hunger hormone, and leptin, which are responsible for appetite regulation and energy balance, are also featured prominently in GBA physiology. These hormones convey information about nutritional status to the brain, influencing food intake and energy expenditure [
22]. The intricate interplay between these hormones within the GBA contributes significantly to overall homeostasis.
3.1.3. Neural Communication between the Gut and the Brain:
The neural communication pathways within the GBA constitute a remarkable system of information exchange that impacts various aspects of physiology and cognition. Understanding these intricate pathways is essential to grasp how gut-related signals influence brain function and vice versa.
a. Sensory Information Transmission:
Sensory information originating from the gut travels along dedicated neural routes, with the vagus nerve playing a central role. This cranial nerve serves as the primary conduit for transmitting visceral sensations and signals from the gut to the brain. As sensory input from the gastrointestinal tract ascends through the vagus nerve, it eventually reaches the brain stem [
23]. Here, crucial processing occurs, enabling the relay of information to higher brain regions. The brainstem acts as a gateway for GBA signals, with connections to various brain areas that regulate autonomic functions, emotional responses, and homeostatic balance.
b. Brain Regions Influenced by GBA Signals:
Within the brain, the sensory information from the gut can impact several key regions, including:
Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus serves as a central hub for regulating autonomic functions, hormonal responses, and appetite. GBA signals can influence hypothalamic circuits, modulating processes like satiety, thermoregulation, and stress responses [
24].
Limbic System: The limbic system, particularly the amygdala and the hippocampus, plays a pivotal role in emotional and memory-related processes [
25]. GBA signals can influence emotional states and memory consolidation, contributing to the intricate link between gut health and mood disorders.
Pre-Frontal Cortex: The pre-frontal cortex, responsible for executive functions and decision-making, is susceptible to GBA influence. Altered GBA signaling has been associated with cognitive impairments and behavioral changes [
26].
3.1.4. Pathophysiological Involvement of Brain-Gut-Axis in Different Disorders
3.1.4.1. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
The disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBIs) are considered one of the most common gastrointestinal (GI) disorders. IBS is one of these disorders and is one of the most searched. IBS manifests as changes in bowel functions escorted by abdominal discomfort with a lack of detectable biochemical and structural anomalies [
27]. However, the etiology of IBS has not been fully described, but various factors are well-known to be associated with it. Uncovering the pathogenesis of IBS is imperative for the development of pharmacotherapeutic agents. The visceral hypersensitivity, gut-brain interactions, and microbiota dysbiosis are all factors that entail the pathogenesis of IBS [
28].
Unfortunately, there is no definitive treatment for IBS. It's usually controlled by the removal of factors that exacerbate it, such as certain medicines, stress, and dietary habits. Nonetheless, modulation of the GBA is under investigation as an attractive target for the development of novel treatments [
29].
Population studies have shown that IBS is very common [
30,
31]. For example, the Rome IV and III, IBS diagnostic questionnaires as well as 80 items of data were used in a recently conducted global study with 24 countries to assess indicators relating to DGBIs. The findings show that 40 % of the global population is affected by DGBIs which affect individual quality of life and healthcare use [
32]. In addition, the population of IBS is usually dominated by females in Western countries [
33].
IBS has usually been explained as a disorder of visceral hypersensitivity and GI motor disturbances, which can cause or lead to abdominal pain or discomfort and diarrhea or constipation [
30]. However, there is a lack of understanding of the pathophysiology of IBS. Pathogenetic factors can have contributed to this disorder, such as genetic susceptibility, GBA dysfunction, and innate immunity issues. In the meantime, it`s difficult to determine which of these factors can elicit or exacerbate IBS, in particular, because the symptoms are marked by significant interindividual differences [
34]. Therefore, for IBS, treatment often targets the patient’s primary or most troublesome symptom, as opposed to being based on the underlying pathophysiology as with other organic GI diseases [
35].
Studies showed that disturbance of the structural and functional GBA can cause alteration in CNS reflexes and perceptual responses, which can potentially instigate GI disorders, such as IBS [
36].
3.1.4.2. Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is considered a chronic and progressive disorder, characterized by the degeneration of midbrain dopaminergic neurons, leading to widespread alpha-synuclein (α-syn) accumulation [
37].
It has been established that the gut microbiota plays a role in affecting neurotrophic factors, controlling inflammation, and producing pro-inflammatory cytokines, T cells, or B cells thus playing an essential role in myelination processes and microglial activation [
38]. That's why it can affect behavior and cognition, which in turn increases the risk of developing diseases related to the nervous system and mental health [
39].
Movement symptoms that support the diagnosis of PD are usually preceded by other motor symptoms, in particular gastrointestinal symptoms, suggesting that the microbiome-intestine-brain axis plays an important role in the mechanisms leading to PD [
40]. Studies have shown that synucleinopathy may start in the enteric tissue and make its way to the brain with innervating autonomic fibers [
41]. Changes in the activity of bacterial metabolites and disruption of microbial balance dysbiosis in the gut are believed to have a significant influence on communication between the gut and the brain during the development of Parkinson's disease. Recent evidence suggests a significant role for gut-associated processes in the development of Parkinson's disease [
42].
Alterations of the colon's components have also been established to be related to Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases, according to a meta-analysis carried out by Gerhardt and colleagues that included 642 PD patients and 531 healthy controls [
43].
A microbiota with a stable composition consisting of high levels of Bifidobacteria and Bacteroides and low levels of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria is typically associated with low levels of lipopolysaccharide and is considered to be indicative of a healthy gut epithelium, despite large individual differences in the composition of the microbiota. However, there are often differences in the microbiota of patients with PD, which are similar to those observed in patients with inflammatory bowel disease [
44].
3.1.4.3. Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Changes in the composition of human gut microbiota seem to be associated with neuropsychiatric and mood disorders [
45] and neurotransmitter imbalances [
46]. Additionally, increasing evidence has linked the gut microbiota with symptoms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that are regularly affected by gastrointestinal problems and gut microbiota dysbiosis [
47]. In addition, many patients who experience gastrointestinal discomfort are more likely to present mental disorder comorbidities [
45].
Studies show that there is an association between diet, nutrition, anxiety, and depression, suggesting that dietary changes may be an alternate treatment or a preventative measure for anxiety and depression. The correlation between an unhealthy diet and the propensity to develop mental illnesses has received more attention in recent years [
48]. Dietary preferences, perceptions of sweetness and fatty foods as well as taste thresholds can also be influenced by stress and depression [
49]. A 10-year longitudinal research study conducted in France demonstrated a correlation between poor nutrition and depression incidence with healthy diet patterns being associated with lower depressive symptoms [
50]. To determine the direction of correlation, conflicting results have been seen in randomized control trials and prospective studies. A high-quality diet, independent of its form, with greater fish and vegetable consumption, was related to a decreased incidence of depression, with a dose-type association with compliance with the healthy diet, according to a meta-analysis of prospective studies. By contrast, the meta-analysis showed that a lack of nutrition was not associated with increased depression risk, and significant differences were observed from one study to another [
51].
Studies have been also performed to identify the relationship between gut microbiota and depression. The correlation between this mental disorder and the flora in the gut has been confirmed by Naseribafrouci et al. as they showed that individuals with major depressive disorder have higher levels of the genera Oscillibacter and Alistipes [
52].
3.2. Neuromodulation:
Neuromodulation is a medical technique that involves the focused delivery of signals to regulate the nerves in the nervous system. It's a technology that involves the modification of nervous activity to improve the patient’s neurological function and, thus, their quality of life. Neuromodulation has entered an accelerated phase of development, making use of the ongoing advances being made in neuroscience and medical engineering technology [
53]. Various neuromodulation modalities can be categorized according to their specific targets and methods of influencing the neurological system [
3]. The aforementioned categories include Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS), Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS), and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) [
54]. DBS encompasses a surgical procedure wherein a device is implanted to administer targeted electrical impulses to distinct regions of the brain. DBS is primarily designed to address neurological conditions that primarily affect the brain, such as Parkinson's disease and various movement problems [
55]. VNS is a therapeutic approach that specifically focuses on the vagus nerves located inside the neck region. The VNS device is commonly employed in the management of treatment-resistant depression and epilepsy. It functions by delivering periodic and gentle electrical energy pulses to the brain through the vagus nerve [
56]. SCS involves the utilization of a device that administers a low-level electric current to the spinal cord. The utilization of this treatment modality is commonly observed in cases of chronic pain syndromes, particularly those involving neuropathic pain [
57]. TMS is an emerging modality of brain stimulation that entails the application of an electromagnetic coil in direct contact with the scalp. TMS is often employed within the field of psychiatry, with a particular focus on its application in the treatment of depression [
58].
Additional types of neuromodulation encompass Sacral nerve stimulation, a technique that transmits impulses to the sacral nerve to enhance bladder control [
59]. Responsive nerve stimulation is a therapeutic approach that entails the continuous monitoring of neurological activity to administer personalized and immediate therapy [
60]. Epidural motor cortex stimulation is mostly employed for pain management, whilst Occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) is utilized to treat certain forms of headaches or migraines by targeting the occipital nerves [
61,
62]. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) are non-invasive methodologies developed to elicit brain and nerve stimulation, commonly employed in the domains of pain treatment and rehabilitation therapy [
63,
64]. Remote electrical neuromodulation (REN) is a nascent therapeutic modality that involves the remote administration of electrical pulses, typically employed to alleviate migraines or manage pain [
65].
3.3. Effects of Neuromodulation on Gut-Brain-Axis
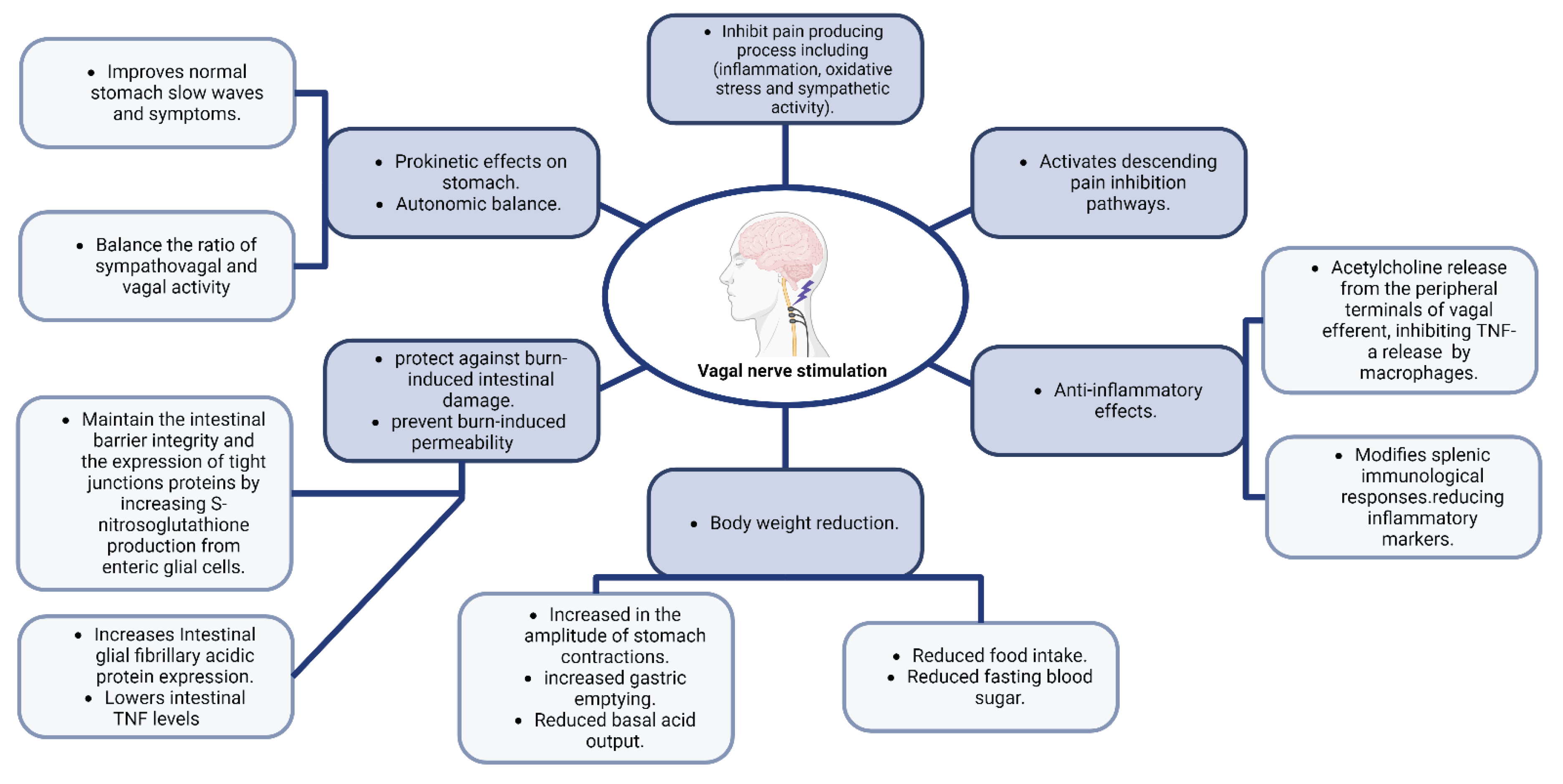
3.3.1. Physiological Changes in the Gut-Brain Axis after Neuromodulation Including Changes in GI Physiology
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 summarize key effects and changes in GBA physiology after neuromodulation.
3.3.1.1. Neuromodulation Effect on Pain
In a case report, results from the assessment of a 55-year-old lady who received bilateral DBS in the anterior limb of the internal capsule and who had obsessive-compulsive disorder and IBS are provided. Following the brain stimulation therapy, there was a reported significant reduction in IBS symptoms. This relief was dependent on certain stimulation settings, showed consistency over time, and wasn't directly related to reductions in the symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder. These findings imply that DBS has a positive effect on IBS [
66].
The vagus nerve (VN) is increasingly being shown to affect nociceptive processing in the spinal cord and brain. It has been demonstrated that nociceptive mechanical and chemical stimulus causes vagal afferents to respond, which in turn causes the brainstem to reflect nociceptive signals [
67,
68]. Patients who receive VNS for epilepsy and depression usually report feeling less pain. Evidence suggests a connection between pain and VN activity since the VN is known to decrease pain-causing processes such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and sympathetic activity. Additionally, it stimulates parts of the brain that can block the "pain matrix" in the brain, which in turn modifies the way opioids function as an analgesic [
69]. Nutrient content may influence the perception of painful visceral sensations in several gastrointestinal illnesses, including IBS, by enhancing the creation of aversive visceral memories via vagal afferent pathways [
70].
VNS activates vagal afferents that go to the Nucleus Tractus Solitarius (NTS), which suppresses experimentally produced pain. Descending pain inhibition pathways are then activated as a result of neurons in the NTS projecting to the Central Amygdala Nucleus (CAN), the Nucleus Raphe Magnus, and the Locus Coeruleus. Visceral pain is decreased by low-intensity VNS that particularly targets vagal afferent Ad fibers, indicating that a portion of the vagal afferents that innervate the viscera may have abilities to control visceral pain [
71].
3.3.1.2. Effects of Neuromodulation on GI Motility and Permeability
It has been shown that it is possible to achieve prokinetic effects by increasing vagal tone by VNS, deep breathing, moderate-pressure massage treatment, or other exercises that have a substantial impact on heart rate and heart rate variability [
72].
Four randomized sessions, comprising a control session, the conditioned stimulus (CS), CS paired with transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS), and CS mixed with sham-electrical stimulation (sham-ES), were carried out in research involving healthy individuals. Each session began with a period of fasting and ended with a test meal. While taVNS or sham-ES were given between 0 and 30 minutes after the meal, CS was delivered between 10 and 30 minutes after the meal. Assessing stomach slow waves and autonomic functioning involved recording the electrogastrogram and the electrocardiogram. The proportion of normal stomach slow waves and the symptom score were both considerably lowered by CS, and both were greatly improved by taVNS but not by sham-ES, according to the results. Additionally, CS raised the sympathovagal ratio and lowered vagal activity, while taVNS balanced these effects brought on by CS. These results imply that after exposure to a conditioned stimulus, taVNS has a prokinetic effect on stomach function and autonomic balance [
73].
By stimulating enteric glial cells (EGCs), Costantini et al. [
74] showed that VNS protects against burn-induced intestinal damage. Without altering systemic inflammation, this protection is achieved by controlling the reaction to damage inside the gut tissue itself, and the generation of cytokines in the spleen was shown to be not necessary for the maintenance of gut membrane integrity by VNS. Furthermore, S-nitrosoglutathione administration has been shown to produce outcomes that are comparable to those seen in animals that have received VNS, indicating that VNS may maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier and the expression of proteins related to TJs by increasing the ability of activated EGCs to produce S-nitrosoglutathione [
75].
Injuries that result in severe burns cause EGCS to become more activated, which increases the production of the mRNA for intestinal glial fibrillary acidic protein. When VNS is used alone, it increases intestinal glial fibrillary acidic protein expression and thus reduces burn-induced intestinal permeability, and lessens gut histological damage. In one experiment, animals who had vagotomies before receiving VNS showed intestinal permeability levels similar to those of animals that had just had burns, demonstrating the protective effect of efferent vagal nerve transmission. The intestinal TJ proteins myosin light chain kinase and phosphorylated myosin light chain, all of which are essential for maintaining TJ integrity, as well as the elevation in intestinal TNF caused by burn, were likewise avoided and reduced by VNS. These results provide insight into the mechanism through which VNS prevents the loss of the intestinal barrier and subsequent intestinal inflammation [
74].
Researchers found that VNS significantly lowers levels of intestinal TNF while successfully preventing trauma-induced intestinal permeability and intestinal damage in a mouse model modeling traumatic brain injury. Boosted levels of enteric glial fibrillary acidic protein also showed that VNS boosted the activity of EGCs in the same settings which shows that the CNS can directly affect intestinal barrier failure [
76].
Through the activation of myosin light chain kinase and subsequent phosphorylation of myosin II light chain, which results in the contraction of the actin-myosin ring, inflammation can compromise the epithelial barrier and change the expression of TJ proteins. There is a lot of gut inflammation after burn injuries, which raises myosin light chain kinase and amplifies myosin II light chain phosphorylation, leading to the separation of TJ proteins. A protective effect of VNS is seen on the gut epithelial barrier with a "therapeutic window" for VNS intervention since it can be used before or within 90 minutes after burn damage. When used during this window, VNS can either stop barrier breakdown or promote its recovery. In these circumstances, the gut's morphology, permeability, and protein expression are consistent. Similar to the sham-operated control group, VNS-treated mice in one study showed decreased inflammation and localized TNF production in the gut [
75].
3.3.1.3. Effects of Neuromodulation on GI Inflammation and Immunity
Vagal efferents have been shown to have an anti-inflammatory activity by Tracey's team. In their study, they found that in a rat model of endotoxic shock, VNS causes the release of acetylcholine from the peripheral terminals of vagal efferents, which in turn inhibits the production of TNF-a by macrophages [
77].
According to a study [
78], low-frequency (5 Hz) VNS has been shown to treat colitis in rats. Additionally, VNS may have an anti-inflammatory impact on Crohn's disease patients who have autonomic instability [
79]. In one study, it was shown that in the majority (5 out of 7) of patients with mild to moderate active Crohn's disease, VNS resulted in clinical, biochemical, and endoscopic remission after 6 months. Additionally, VNS returned autonomic balance to levels comparable to those in healthy people [
80].
Endotoxin and intestinal inflammation have been proven to cause systemic inflammatory responses that can be reduced by VNS. Additionally, through interacting with the splenic sympathetic nerve, the Vagus nerve indirectly modifies immunological responses in the spleen. Daily VNS for three hours spread over five days significantly decreased inflammatory markers and improved colitis symptoms in another rat research that involved colonic inflammation [
6].
3.3.1.4. Effects of Neuromodulation on Gut Microbiota
According to a systematic review, Alterations in the relative abundances of the various bacterial species in the gut have been associated with the use of neuromodulation. The results also showed that neuromodulation therapies cause modest changes in the gut microbiome. However, it did not result in changes in the variety of species or the differences across microbial communities [
81].
Dynamic changes in microbial composition are seen in studies examining the links between the gut microbiota and device-assisted treatments (DATs) for PD. Specific changes in gut bacterial composition result from the acute use of DATs such as DBS and Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel (LCIG). Clostridium_XlVa and Parabacteroides are overrepresented in DBS samples, possibly as a result of antibiotic usage. On the other hand, Pseudoflavonifractor is overrepresented in LCIG treatment whereas Escherichia/Shigella and Gemmiger are underrepresented. With DBS, there is a rise in Euryarchaeota and Spirochaetes, whereas with LCIG, there is an overrepresentation of Prevotellaceae and Bacillus. Long-term usage of these treatments results in unique, diverse alterations. Notably, the microbiota's reaction to DAT exposure varies depending on how long it continues. Although the exact causes of these alterations are not entirely known, they may be brought on by changing physiological responses and reciprocal interactions between gut microbiota and DATs [
82].
In one research, electroacupuncture at certain acupoints, including DU20 and KI1, decreased pain and delirium-like symptoms in mice with a model of surgical pain and delirium brought on by a foot incision. Mice that experienced surgical pain and delirium-like behavior showed altered gut microbiota, spinal cord, somatosensory cortex, and hippocampus microglia activation, and increased dendritic spine removal in the cortex. In addition to reducing pain and delirium-like symptoms, electroacupuncture therapy also balanced the gut microbiota, reduced microglia activation, and stopped dendritic spine removal. This shows that through regulating gut-brain connections and microglial activity, electroacupuncture may have therapeutic promise for treating surgical pain and associated delirium-like symptoms [
83].
3.3.1.5. Effects of Neuromodulation on Weight Gain and Food Intake
In a study involving fifteen Large White pigs, they were divided into three groups (A, B, and C) and underwent implantation of a vagus nerve stimulator. Group A had stimulation deactivated, while groups B and C had it activated. Group C's purpose was solely to assess the impact of stimulation on heart rate, invasive arterial and venous pressures, and the bispectral index. Food intake showed no significant differences between A and B, but both groups exhibited a consistent increase in body weight. In group C, during VNS, arterial pressures significantly decreased, while heart rate and the bispectral index markedly increased. Ultimately, all animals were sacrificed to assess the effects of implantation and stimulation on the vagus nerve, and in both groups, the lesions were primarily localized in connective tissue rather than nervous tissue. All animals in groups A and B exhibited a thick fibrous capsule at the implantation site. Group B showed increased levels of fibrosis, inflammation, vascularization, and nervous fiber degeneration compared to group A. However, necrosis was more pronounced in group A. Analyzing all aspects of the lesions, inflammation seemed to be the most severe in group A, while group B exhibited more extensive fibrosis. Both groups demonstrated comparable levels of fiber degeneration [
84].
According to a review article, multiple studies seem to agree that during vagal stimulation, body weight is significantly reduced [
85].
One study looked at how conscious rats' long-term stomach motility, secretion, and weight management were affected by a neuromodulation surgery employing a microchip (MC). Within two weeks after MC implantation, the use of MC-induced neuromodulation caused rats' daily food intake to drop by 6% and their body weight increase to slow by 20%. Glucose levels in the fasting control group similarly dropped by 5.5%. When compared to the control group, the frequency of stomach contractions in the MC-treated rats remained consistent, but the amplitude of the contractions dramatically increased. In MC-treated rats, maximum acid output (MAO) did not change, while the basal acid output (BAO) dropped by 29.25% without affecting the H+ concentration, and gastric emptying increased by 10% [
86].
3.3.1.6. Special Consideration: Microbiota-Induced Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Cerebral Ischemia
A potentially effective treatment for cerebral ischemia involves controlling microglia to reduce neuroinflammation. In one study, the signals of the GBA were examined about berberine-modulated microglia polarization after cerebral ischemia. The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) metabolism, and stimulation of the vagus nerve were all included in the study. A test using metabolomics was performed to investigate the brain microenvironment. The results showed that berberine restored behavioral impairments in temporary middle cerebral artery blockage rats by modulating microglia polarization and reducing neuroinflammation via the microbiome. When given berberine, vagus nerve activity was increased, which could be inhibited by various antibiotic combinations, capsazepine, or sodium molybdate, respectively. VNS, accomplished by both assimilatory and dissimilatory sulfate reduction with enhanced synthetic enzymes, was linked to the synthesis of H2S generated by berberine. When berberine was supplied, the TRPV1 receptor's sulfation in turn caused the vagus nerve to become activated and encouraged the production of c-fos and ChAT in the nucleus tractus solitarius. Additionally, sphingolipid metabolism was disturbed by the major metabolic change brought on by berberine in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebral spinal fluid, which is a crucial feature that is altered by antibiotic therapy [
87].
3.3.2. Effects of Neuromodulation on the Gut-Brain-Axis Disorders
Functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) are frequent and have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. Although there are many approaches for distinct FGID symptoms, neuromodulation, a relatively recent treatment, has shown a favorable therapeutic impact on FGIDs.
3.3.2.1. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
The most prevalent functional gastrointestinal disorder, affecting up to 7-21% of the general population, is IBS [
88]. Visceral hypersensitivity (or changed pain perception), poor brain-gut connection, altered microbiota, and altered gastrointestinal motility are the core pathophysiology of IBS [
88]. Visceral hypersensitivity is thought to be the most common cause of stomach pain or discomfort; visceral hypersensitivity is thought to be caused by increased intestinal permeability and gut mucosal immune activation.
3.3.2.1.1. Tryptophan
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) 5-HT is a common gut-related transmitter, with enteroendocrine (EC) cells of the gut epithelium producing 90%-95% of the total 5-HT pool in the human body. Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) regulates 5-HT synthesis [
89]. By influencing EC cells, the gut microbiota also plays an important role in controlling 5-HT synthesis and release. In a post-infectious IBS model of rats, quercetin can lower the density of EC cells and the expression of TPH. As a consequence, quercetin lowers 5-HT levels and alleviates visceral pain sensations in IBS mice [
90].
3.3.2.1.2. Transcutaneous Auricular VNS (tVNS)
42 individuals with constipation-dominant IBS were given taVNS [
91]. The patients were randomly assigned to either undergo taVNS using silicon electrodes implanted at bilateral symba conchas or sham electrical stimulation (through the elbow). taVNS increased the weekly number of full spontaneous bowel movements, reduced abdominal discomfort, and improved overall IBS symptoms and quality of life. The improvement in rectal sensation and rectal distention-induced relaxation of the internal anal sphincter were noteworthy findings of this investigation, implying a vagal afferent and sacral efferent route. These effects were mediated through the vagal-sacral circuit in the following way: The NTS was stimulated, which then projected to other areas of the brain, resulting in increased sacral efferent activity, which acted on the rectum and anal sphincter [
92]. Auricular vagal nerve stimulation (aVNS) with identical stimulation parameters was also found to speed up the transit of the distal colon (not innervated by the vagus nerve) with a contemporaneous increase in activated neurons in the NTS in a mouse model of opioid-induced constipation [
93]. These findings imply that aVNS may influence colorectum motility and feeling via both the vago-vagal and vago-sacral pathways.
3.3.2.1.3. Tripolar Spinal Cord Stimulation
Coffin et al. have shown that hyperexcitability of spinal nociceptive pathways causes visceral hypersensitivity in IBS patients [
94]. The precise mechanism of action of SCS is unknown, however, based on animal research, one probable mechanism may be the suppression of pain pathways in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord [
95]. Palecek has highlighted the significance of the dorsal column route in the control of visceral pain by selectively suppressing the response to visceronoxious stimulus [
96]. The precise method through which SCS modulates intestinal motility and causes pain alleviation is unknown. Auli et al. studied the impact of direct electric stimulation on enteric motor neurons in human intestinal strips in vitro [
97]. They discovered that activation of inhibitory neurons causes the release of nitric oxide and purine, whereas stimulation of excitatory neurons causes the release of acetylcholine and tachykinins. Purine agonists and medicines that boost acetylcholine production and release, on the other hand, have been demonstrated in tests to have significant analgesic effects [
98].
3.3.2.2. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel illness, which includes Crohn's Disease (CD), Ulcerative Colitis (UC), and Microscopic Colitis (MC), is alarmingly frequent, affecting roughly 1% of the global population and growing in prevalence [
99]. IBD has a substantial influence on psychological well-being and social functioning as well. Both CD and UC involve significant inflammation and disruption of the gut immune system [
100]. The vagus nerve, pelvic nerves, sympathetic innervation of the stomach, and intrinsic neurons of the ENS all have an impact on inflammation.
Vagal nerve stimulation can reduce inflammation in the gut in at least three ways: by stimulating afferent neurons that signal to the brain to activate efferent pathways, which may include sympathetic outputs from the CNS [
101]; by activating vagal efferent pathways; and by stimulating vagal afferents to release transmitters from their peripheral ends. Evidence for the impact of vagal efferents on enteric neurons includes the fact that intestinal inflammation activates a vagally mediated circuit that leads to the activation of vagal motor neurons related to the inflamed gut [
102]. VNS decreased mechanically induced inflammation of the small intestine in normal mice, mice with denervated spleens, and T-cell deficient animals [
103]. In Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (7nAChR) knockout mice, VNS proved ineffective. Enteric neurons innervated 7nAChR-expressing macrophages, and 7nAChR activation lowered their excitability. According to the findings, resident macrophages are a target via which VNS mediates its anti-inflammatory activity.
3.3.2.3. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic condition in which the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus produces discomfort or difficulties. It is divided into three types: non-erosive reflux disease (NERD), erosive esophagitis, and Barrett's esophagus [
104]. Major GERD pathophysiologies include (a) impaired esophageal clearance due to impaired esophageal motility (e.g., weak esophageal peristalsis); (b) anti-reflux barrier dysfunction at the esophagogastric junction (EGJ) due to hypotensive lower esophageal sphincter (LES), transient LES relaxations (tLESRs), and/or dyssynergia between LES and the crural diaphragm (e.g. the presence of hiatal hernia); and c) downstream gastric factors: delayed gastric emptying and gastric acid pocket [
105,
106].
3.3.2.3.1. Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation (TEA)
Acute TEA at bilateral ST36 and bilateral PC6 acupoints has been shown to increase stomach accommodation and pace-making activity, as well as diminish postprandial dyspepsia symptoms in GERD patients [
107]. In patients with GERD, a 4-week TEA at bilateral ST36 and bilateral PC6 alleviated reflux symptoms, increased distal esophageal motility, decreased the incidence of inefficient esophageal contractions during wet swallows, and enhanced stomach accommodation and pace-making activity [
108]. The researchers concluded that the improvement in GERD symptoms was due to TEA's integrative effects on various gastric processes, which were mediated through the vagal mechanism. In another research, TEA at ST36 and PC6 was combined with deep breathing training in GERD patients [
109]. A 4-week therapy with this combination technique reduced acid reflux and GERD symptoms while simultaneously increasing LES pressure and vagal activity and decreasing serum nitric oxide.
3.3.2.3.2. Transcutaneous Abdominal Electrical Stimulation
Although the mechanism is unknown, it appears that transcutaneous abdominal electrical stimulation is intended to cause abdominal muscular contractions, hence increasing LES pressure. The LES pressure measured by esophageal manometry is known to be the combined pressure of the LES and crural diaphragm. This type of stimulation might raise the pressure in the crural diaphragm. However, there is no data to back up the idea. Transcutaneous abdominal electrical stimulation decreased acid exposure duration and the DeMeester score by more than 50% in GERD patients who were unresponsive to regular proton pump inhibitor treatment in a pilot open-label study [
110].
3.3.2.4. Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental illness with a wide range of symptoms, including social deficits and confined, repetitive activities [
111]. ASD therapy is notoriously difficult, and it may benefit from identifying underlying systems that overlap with those disrupted in other developmental disorders, which have more clear treatment choices. DBS in the prefrontal cortex, hypothalamic nucleus, and central thalamus have been proven in preclinical investigations to relieve VPA (Valproate acid)-induced autism-like symptoms [
112]. VNS is an FDA-approved therapy for reducing the severity of persistent epilepsy and depression, and it has emerged as a viable adjuvant therapy for people with autism [
113]. ASDs are usually associated with dysregulated parasympathetic nervous system and decreased vagal tone, which is linked to autistic behavioral and linguistic impairments [
114]. The use of VNS in children with epilepsy and ASD has yielded promising outcomes [
115]. Several studies have shown that gamma-band response (30-80 Hz) is highly dependent on cellular balance of excitation and inhibition (E/I) signal transduction [
116], mediating several basic neural functions such as sensorimotor integration, perceptual integration, working memory, network synchronization, and higher-order cognition [
117], all of which are disrupted in multiple ASD systems [
118].
3.3.2.4.1. Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Seizure reduction was comparable amongst persons with and without autism in the biggest research of VNS treatment in individuals with ASD to date [
115]. After 12 months of VNS therapy, 56% of people without autism had a 50% reduction in seizures, whereas 62% of those with autism had a 50% reduction in seizures. Individuals with and without autism had comparable gains in attentiveness, verbal communication, memory, and academic/professional success. Patients with autism, on the other hand, exhibited a considerably higher improvement in mood after 12 months of VNS therapy than persons without autism. Stimulation of the vagus nerve causes strong, phasic neuronal activity in the locus coeruleus, the principal source of norepinephrine in the CNS [
119]. VNS increases norepinephrine levels in the hippocampus and cortex, which is consistent with VNS-dependent noradrenergic system activation [
120]. Furthermore, VNS considerably raises levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a neurotrophin strongly associated with neural plasticity that is dysregulated in autistic people [
121].
3.3.2.4.2. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Consistent with the role of altered cortical development in ASD, regions of the frontal and prefrontal cortex related to language production and social skills have a spike in synaptogenesis and plasticity between years 1 and 3 [
122], when autistic symptoms related to these processes usually become apparent. TMS generates transitory, localized electrical fields in the cerebral cortex by electromagnetic induction, producing depolarization and firing of local neurons [
123]. Repetitive TMS (rTMS) produces patterns of numerous TMS pulses over a selected brain region at frequencies ranging from 0.5 to 20 Hz [
124]. At low frequencies, rTMS causes long-term suppression of cortical excitability on the target cortical tissue, but at higher frequencies, rTMS causes long-term stimulation of cortical excitability. rTMS could have clinical utility as an intervention in ASD. Some studies indicate that: low-frequency stimulation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) can reduce repetitive behaviors, improve neurophysiological markers of perception, and reduce irritability; low-frequency supplementary motor area (SMA) stimulation can improve movement-related cortical potentials; and low-frequency stimulation of the premotor cortex can improve sensorimotor integration [
125,
126,
127].
3.3.2.4.3. Transcranial Electric Stimulation (tES)
Transcranial electric stimulation modalities include tDCS, transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS), and transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS). tDCS employs a continuous mild electrical current to cause bidirectional, polarity-dependent changes in cortical areas, allowing for the measurement of effects at the cognitive, physiological, and motor levels [
128,
129]. The use of tDCS can be utilized to either raise or reduce cortical excitability and/or certain brain oscillations. Gamma activity can also be modulated by tDCS. tRNS is a low-intensity, randomly alternating biphasic current that is delivered directly to the scalp at frequencies ranging from 0.1 to 640 Hz [
130]. While both tDCS and tRNS are successful in modifying cortical excitability and plasticity processes, only tACS has been explicitly linked to frequency-specific regulation of oscillatory dynamics, with evidence of its influence on gamma activity in both animals and humans. tACS uses sinusoidal or biphasic currents at a predetermined frequency to interact with the brain's endogenous oscillatory activity to entrain huge populations of neurons [
131]. tACS works by synchronizing spiking activity to various driving frequencies, thereby entraining neuronal firing to the electrically applied field and exerting strong neuromodulatory effects. These gamma tACS-induced improvements were shown to be strongly associated with changes in blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) activity in the stimulated M1 area [
132]. Higher-order behavioral processes have also been targeted using tACS gamma-entrainment approaches. Hoy and colleagues discovered a selective improvement in working memory performance after gamma-tACS [
133]. Since there is an overall reduction of gamma activity in ASD, applying gamma-tACS to these regions might be able to entrain and restore, at least partially, neurotypical gamma activity in the ASD population.
3.3.2.5. Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a chronic, progressive illness characterized by the degeneration of a large number of dopaminergic neurons in the basal ganglia circuitry. The lack of dopamine contributes to clinical motor symptoms such as bradykinesia, tremor, stiffness, postural instability, and gait impairment [
134]. Recent epidemiological and clinical studies suggest that “mild cognitive impairment” (MCI) may be a complex typical of the early stages of PD [
135].
3.3.2.5.1. Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS is efficient in modulating abnormal basal ganglia motor circuit activity by acting on particular nuclei such as the subthalamic nucleus, the globus pallidus interna, and the thalamus. This method entails implanting pacing devices that provide constant high-frequency stimulation of the targeted region. The STN, a critical motor relay component whose failure has been related to Parkinson's disease symptoms, has been the most widely utilized target for DBS during the last decade [
136]. Numerous studies have also demonstrated that STN DBS gives lasting symptom relief even 5 or 10 years following surgery, but with worsening of cognition and gait because of the underlying degenerative disorder's unrelenting progression [
137]. In the case of DBS in the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson's disease, there is an enhanced firing rate in the globus pallidus despite the suppression of excitatory STN neurons that project to the globus pallidus [
138]. Furthermore, globus pallidus neurons have spike activity that is entrained to the stimulus pulses. DBS is hypothesized to segregate dendritic/somatic activity from axonal output activity, suppressing the former while driving the latter at or near the frequency of stimulation [
139].
3.3.2.5.2. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Shirota et al. explored the efficacy and stimulation frequency effect of rTMS over the SMA in PD. Results showed a decrease (improvement) of 6.84 points in the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) part III in the 1 Hz group at the last follow-up (12 weeks post-intervention) [
140]. Although the molecular mechanisms underlying these changes are not yet conclusive, several theories have been postulated. The initial alterations in neuronal ionic conductivity caused by electrolysis events caused by propagating electromagnetic currents appear to be associated with short-term consequences [
141]. The release of neurotransmitters is another potential mechanism for short-term effects. High-frequency rTMS administered to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex has been linked to tonic dopamine release in the ipsilateral caudate and orbitofrontal cortex [
142]. Meanwhile, the long-term effects of TMS are thought to be mediated via neuroplastic processes. The word "neuroplasticity" refers to the CNS's ability to respond to a wide range of external and internal stimuli via a functional, dynamic remodeling of its structures and connections [
134]. This is especially significant in patients with PD, because changes in cortical excitability and neuroplasticity are heavily influenced by dopamine bioavailability, and the implementation of dopaminergic therapy can influence the subsequent neurophysiologic and behavioral effects of stimulation [
143].
3.3.2.6. Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) affects roughly 3% of the population between the ages of 65 and 74 and more than 50% of the population over the age of 85 [
144]. Symptoms usually begin with issues with episodic memory, and as the disease develops, additional cognitive domains, such as language and executive function, are impaired [
145]. Pathologically, AD is distinguished by the presence of extracellular amyloid- (A) plaques and intra-neuronal tau neurofibrillary tangles (NFT).
3.3.2.6.1. Deep Brain Stimulation
In animals and/or humans, possible targets include the fornix, entorhinal cortex (EC), nucleus basalis of Meynert (NBM), anterior thalamic nuclei, mammillothalamic tract, hippocampus, and ventral capsule [
146,
147,
148]. EC stimulation reduced impairments in a variety of spatial and recognition memory tests in both young and old animals in the TgCRND8 and 3Tg mouse models of AD [
149]. Biological findings included increased neurogenesis as well as decreased plaque burden and A peptide concentration, albeit these effects on amyloid pathology may be age-dependent [
150]. In preliminary trials, activation of hippocampus outflow channels resulted in significant reversals of hypometabolism and stability of cognitive deterioration in certain individuals. To date, the majority of publications have been prospective, demonstrating that DBS in memory pathways can have physiological, network-wide metabolic changes and alter various elements of memory function.
3.3.2.6.2. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
rTMS for AD resulted in statistically significantly improved short-term cognitive function of participants (standard mean difference [SMD] for Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-Cog) = 0.42; 95% CI, 0.18 to 0.67, P = 0.0006 [
151]; mean pre-post MMSE change 1.08; 95% CI, 0.35 to 1.80) [
152], with high-frequency rTMS rated as the best short-term intervention for general cognitive function when compared to other electrical stimulation interventions. Furthermore, statistically significant effects on cognitive function were seen when multiple sites (SMD = 0.47; 95% CI, 0.14 to 0.79; P = 0.005) were stimulated compared to single-site stimulation (SMD = 0.24; 95% CI, –0.45 to 0.92; P = 0.50), with cognitive scores improving as patients received longer-term treatment (more than 10 sessions) and higher frequency (20 Hz versus 10 Hz or 1 Hz) [
151].
3.3.2.7. Depression
Major depression is a frequent and difficult disorder that can have a significant impact on quality of life, everyday functioning, and, ultimately, life expectancy [
153].
3.3.2.7.1. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
Transcranial direct current stimulation has also been studied as a therapy for serious depression, but its efficacy is still debated due to inconsistencies in published data. Some tDCS studies have found that anodic stimulation of the left DLPFC can significantly reduce depression scores for up to 30 days after treatment [
154], whereas a meta-analysis found no effect of cognition independent of mood improvement [
155], implying that identifying a specific effect of tDCS on cognition within a clinical trial design is difficult given general cognitive improvements in patients during a trial. Optimizing DLPFC stimulation in a subject-specific manner, as well as researching additional tDCS of other cortical areas implicated in mood and emotion, such as the parietal cortex [
156], may increase the efficacy of tDCS for depression therapy.
3.3.2.8. Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is frequently characterized by changes in cortical functional connectivity. Auditory verbal hallucinations are described in 50-70% of schizophrenia patients and are frequently resistant to pharmaceutical therapy [
157].
3.3.2.8.1. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
Transcranial direct current stimulation-anodal stimulation is thought to improve excitatory synaptic transmission by increasing glutamate neurotransmission [
129,
158] and inhibiting gamma-aminobutyric acid transmission in the cortex [
159]. On the other hand, it may control dopamine nervous system activity, increase serotonin neurotransmission [
160], and reduce acetylcholine neurotransmission [
161]. These ideas concerning tDCS's mechanism of action may explain why it helps with emotion detection in people with schizophrenia. Anodic (excitatory) stimulation of the left DLPFC in conjunction with cathodic (inhibitory) stimulation of the left temporal-parietal junction was found to significantly reduce the occurrence of auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia patients in a recent tDCS study [
157]. Importantly, the decrease in auditory verbal hallucinations lasted for three months after the tDCS therapy ended. Hypoactivity of the prefrontal cortex has also been linked to a variety of learning and memory impairments in schizophrenia, adding to its promise as a target for tDCS management. Anodic tDCS to the left DLPFC improved probabilistic association learning in a subset of schizophrenia patients [
162].
3.4. Implications
As neuromodulation plays a pivotal role in addressing gastrointestinal (GI) diseases by employing therapeutic strategies that modulate crucial neural pathways governing gut function, this intervention proved instrumental in managing a spectrum of conditions including IBS, gastroparesis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), showcasing its versatile applicability. Techniques like VNS and sacral nerve modulation stand at the forefront, offering effective modulation to regulate gut motility, mitigate symptoms, and significantly enhance the overall quality of life for individuals grappling with GI disorders. From a broader perspective, neuromodulation techniques encompass a diverse array of procedures precisely engineered to modify neural activity within targeted areas of the nervous system. Specifically within the realm of GI diseases, these techniques exert their influence on neural pathways intricately linked with the ENS and other vital components of the GBA. The overarching objective remains consistent: to finely regulate essential facets such as gut motility, visceral pain perception, and inflammation. By achieving this, patients experience noteworthy relief from distressing symptoms, marking a considerable enhancement in their quality of life while navigating the challenges posed by GI conditions. Focusing on the ENS, neuromodulation techniques such as VNS and sacral nerve modulation are carefully tailored to exert influence. Through this modulation of neural activity within the enteric system, these interventions effectively regulate gut motility. For example, in conditions characterized by disrupted motility like gastroparesis or intestinal pseudo-obstruction, neuromodulation steps in to restore coordinated contractions, facilitating the effective propulsion of digestive contents through the GI tract. Addressing chronic abdominal pain, a prevalent and debilitating symptom across numerous GI diseases like IBS and IBD is a hallmark achievement of neuromodulation techniques [
163,
164]. These interventions excel in managing visceral pain perception by strategically influencing pain pathways within the intricate nervous system [
165]. The targeted stimulation diminishes pain signals and elevates the pain threshold, providing substantial relief to patients burdened by persistent discomfort and abdominal pain. Furthermore, the profound impact of inflammatory processes in the pathology of several GI disorders, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, cannot be overstated [
166,
167]. The most widely used animal models of colitis involve the application of inflammatory agents such as dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) or 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonate (TNBS) through the luminal membrane. Electrical vagal stimulation has been shown in two studies to inhibit inflammation in such models, but neither of these studies investigated which vagal neurons are involved in this effect [
78,
168]. Seven patients with ileocolonic Crohn's disease were implanted with a cervical vagus nerve electrode and continuously stimulated for 6 months in a small pilot trial [
79]. The device was well tolerated, with only a few reports of throat pain and voice changes during the ON phases. Two patients with a more severe form of Crohn's disease dropped out due to symptoms worsening; however, the remaining five patients achieved clinical and endoscopic remission, including one who remained in remission for 42 months after surgery and no longer required azathioprine.
Ileus, also known as gut stasis, is a potentially fatal condition that occurs frequently following abdominal surgery or insult [
169]. Previously, drugs targeting inflammatory processes (for example, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), inhibitory neural pathways (antiadrenergic), or motility-stimulating mechanisms (for example, metoclopramide) were used to prevent and treat this condition [
170]. VNS is effective in preventing and treating ileus in a rat model caused by manipulation of the small intestine [
171,
172]. The efficacy of stimulating vagal pathways to treat ileus was also confirmed in a rat model in which the vagus nerve was activated via pharmacological stimulation (injection of a thyrotropin-releasing hormone agonist into the CNS) [
173]. Vagal stimulation prevented the slowing of gut transit, most likely by inhibiting inflammation. Another study, in which ileus was also induced in rats by intestinal manipulation, suggested that indirect electrical stimulation of vagal pathways could prevent ileus without suppressing inflammation [
174].
Gastroparesis is a chronic disorder characterized by delayed gastric emptying in the absence of obstruction, as well as postprandial distress, nausea, and vomiting [
175]. Pharmaceutical treatments are ineffective [
176,
177]. Electrical stimulation of the gastric corpus with parameters that stimulate vagal afferent fibers has been found to reduce nausea as well as postprandial satiety [
178,
179]. One review and one meta-analysis of Gastric Electrical Stimulation (GES) for the treatment of gastroparesis published in the last few years found benefit only in some trials [
176,
180]. The meta-analysis found that while 16 open-label, follow-up trials showed total symptom score reductions (nausea or nausea and vomiting, postprandial discomfort), 5 studies comparing symptoms with stimulation turned on or off randomly (the patients serving as their controls) found no difference between the on and off conditions[
181].
Neuromodulation interventions showcase significant potential in modulating inflammation within the gut [
182]. By exerting influence over immune responses and inflammatory pathways, these techniques contribute to a notable reduction in inflammation and its associated detrimental effects on GI tissues. This comprehensive approach offers a promising avenue for effectively managing these challenging conditions.
4. Conclusion and Future Trends
The exploration of neuromodulation techniques in the context of the GBA offers promising avenues for addressing a spectrum of neurological and gastrointestinal disorders. The bidirectional communication between the gastrointestinal tract and the CNS, orchestrated by the GBA, underscores the intricate interplay between physiological processes and cognitive functions. Neuromodulation emerges as a versatile and effective therapeutic approach, showing promise in the management of drug-resistant epilepsy, treatment-resistant depression, and FGIDs. The significance of VNS in influencing gastrointestinal motility, permeability, and protection against inflammatory damage signifies its role as a natural treatment for conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. While challenges and potential complications exist, the potential of neuromodulation to modulate abnormal circuit activity, alleviate chronic abdominal pain, and manage inflammatory processes in various GI disorders highlights its impactful role in improving the quality of life for individuals grappling with these challenging conditions. Looking ahead, the future of neuromodulation in tackling gastrointestinal disorders holds exciting prospects. Ongoing research suggests that the application of neuromagnetic therapies, device-assisted treatments (DATs), and electroacupuncture therapy could further refine our understanding of gut-brain connections and potentially open new avenues for therapeutic interventions. As the field continues to advance, it is anticipated that fine-tuned neuromodulation techniques, such as transcutaneous auricular VNS (tVNS) and tripolar SCS, will play an increasingly pivotal role in reducing inflammation, improving symptoms, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with FGIDs like IBS. Additionally, the ongoing exploration of DBS and TMS for modulating abnormal circuit activity and addressing chronic pain and inflammatory processes in gastrointestinal disorders suggests a continued evolution in the application of neuromodulation techniques for improved patient outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.A., D.K., A.S., M.R., Y.A., O,A., M.E., D.B., N.J., A.A. and M.W.; methodology, B.A., D.K., A.S., M.R., Y.A., O,A., M.E., D.B., N.J., A.A. and M.W.; validation, B.A., D.B., N.J., A.A. and M.W. ; investigation, B.A., D.K., A.S., M.R., Y.A., O,A., M.E. and D.B.; data curation, B.A., D.K., A.S., M.R., Y.A., O,A., M.E. and D.B.; writing—original draft preparation, B.A., D.K., A.S., M.R., Y.A., O,A., M.E. and D.B; writing—review and editing, B.A., D,B, N.J., A.A. and M.W.; visualization, D.B.; supervision, M.E., N.J., A.A. and M.W.; project administration, B.A. and A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- D’Antongiovanni, V.; Pellegrini, C.; Antonioli, L.; Ippolito, C.; Segnani, C.; Benvenuti, L.; D’Amati, A.; Errede, M.; Virgintino, D.; Fornai, M.; et al. Enteric Glia and Brain Astroglia: Complex Communication in Health and Disease along the Gut-Brain Axis. The Neuroscientist 2023, 107385842311634. [CrossRef]
- Tait, C.; Sayuk, G.S. The Brain-Gut-Microbiotal Axis: A Framework for Understanding Functional GI Illness and Their Therapeutic Interventions. Eur J Intern Med 2021, 84, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Rasche, D.; Rinaldi, P.C.; Young, R.F.; Tronnier, V.M. Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Various Chronic Pain Syndromes. Neurosurg Focus 2006, 21, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Fleming, M.A.; Ehsan, L.; Moore, S.R.; Levin, D.E. The Enteric Nervous System and Its Emerging Role as a Therapeutic Target. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2020, 2020, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Powley, T.L. Brain-Gut Communication: Vagovagal Reflexes Interconnect the Two “Brains.” American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2021, 321, G576–G587. [CrossRef]
- Breit, S.; Kupferberg, A.; Rogler, G.; Hasler, G. Vagus Nerve as Modulator of the Brain–Gut Axis in Psychiatric and Inflammatory Disorders. Front Psychiatry 2018, 9. [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An Insight into Gut Microbiota and Its Functionalities. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2019, 76, 473–493. [CrossRef]
- Belizário, J.E.; Faintuch, J.; Garay-Malpartida, M. Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Immunometabolism: New Frontiers for Treatment of Metabolic Diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2018, 2018, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Wallen, Z.D.; Demirkan, A.; Twa, G.; Cohen, G.; Dean, M.N.; Standaert, D.G.; Sampson, T.R.; Payami, H. Metagenomics of Parkinson’s Disease Implicates the Gut Microbiome in Multiple Disease Mechanisms. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 6958. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.; Le, W. Intestinal Permeability, Dysbiosis, Inflammation and Enteric Glia Cells: The Intestinal Etiology of Parkinson’s Disease. Aging Dis 2022, 13, 1381. [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.H.; Chong, C.W.; Lim, S.; Yap, I.K.S.; Teh, C.S.J.; Loke, M.F.; Song, S.; Tan, J.Y.; Ang, B.H.; Tan, Y.Q.; et al. Gut Microbial Ecosystem in Parkinson Disease: New Clinicobiological Insights from Multi-Omics. Ann Neurol 2021, 89, 546–559. [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, J.; Garces, L.; Quintero, M.A.; Pignac-Kobinger, J.; Santander, A.M.; Fernández, I.; Ban, Y.J.; Kwon, D.; Phillips, M.C.; Knight, K.; et al. Low-Fat, High-Fiber Diet Reduces Markers of Inflammation and Dysbiosis and Improves Quality of Life in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2021, 19, 1189-1199.e30. [CrossRef]
- Socała, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Zielińska, A.; Poleszak, E.; Fichna, J.; Wlaź, P. The Role of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatric and Neurological Disorders. Pharmacol Res 2021, 172, 105840. [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.Y. The Treatment of Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy. Hepatogastroenterology 1991, 38, 377–387.
- Foster, J.A.; McVey Neufeld, K.-A. Gut–Brain Axis: How the Microbiome Influences Anxiety and Depression. Trends Neurosci 2013, 36, 305–312. [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Padua, D.; Tillisch, K. Altered Brain-Gut Axis in Autism: Comorbidity or Causative Mechanisms? BioEssays 2014, 36, 933–939. [CrossRef]
- Koloski, N.A.; Jones, M.; Kalantar, J.; Weltman, M.; Zaguirre, J.; Talley, N.J. The Brain–Gut Pathway in Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Is Bidirectional: A 12-Year Prospective Population-Based Study. Gut 2012, 61, 1284–1290. [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A. Let the Gut Do the Guiding. Nat Rev Microbiol 2020, 18, 476–477. [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Debs, L.H.; Patel, A.P.; Nguyen, D.; Patel, K.; O’Connor, G.; Grati, M.; Mittal, J.; Yan, D.; Eshraghi, A.A.; et al. Neurotransmitters: The Critical Modulators Regulating Gut–Brain Axis. J Cell Physiol 2017, 232, 2359–2372. [CrossRef]
- Zac-Varghese, S.; Tan, T.; Bloom, S.R. Hormonal Interactions between Gut and Brain. Discov Med 2010, 10, 543–552.
- Mudd, A.T.; Berding, K.; Wang, M.; Donovan, S.M.; Dilger, R.N. Serum Cortisol Mediates the Relationship between Fecal Ruminococcus and Brain N-Acetylaspartate in the Young Pig. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 589–600. [CrossRef]
- Leeuwendaal, N.K.; Cryan, J.F.; Schellekens, H. Gut Peptides and the Microbiome: Focus on Ghrelin. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2021, 28, 243–252. [CrossRef]
- Farmer, A.D.; Ruffle, J.K.; Aziz, Q. Brain Processing of Gastrointestinal Sensory Signaling. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 373–385.
- Primeaux, S.D.; Harrison-Bernard, L.M.; Barnes, M.J. Neurophysiology of the Hypothalamus. In; 2021; pp. 33–52.
- Torsunova, Yu.P.; Afanasieva, N. V. Morphology and Functioning of Limbic System: Literature Review. Perm Medical Journal 2023, 40, 61–77. [CrossRef]
- Grčić, A.; Varljen, J.; Bedoić, E.; Kučić, N.; Detel, D.; Batičić, L. Gut-Brain Axis. Medicina Fluminensis 2022, 58, 4–19. [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: What’s New for Rome IV? Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016, 1, 6–8. [CrossRef]
- Occhipinti, K.; Smith, J. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Review and Update. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 2012, 25, 046–052. [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.L. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Clinical Review. World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 12144. [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A. The Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders and the Rome III Process. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1377–1390. [CrossRef]
- Boyce, P.M.; Talley, N.J.; Burke, C.; Koloski, N.A. Epidemiology of the Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Diagnosed According to Rome II Criteria: An Australian Population-Based Study. Intern Med J 2006, 36, 28–36. [CrossRef]
- Sperber, A.D.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Drossman, D.A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Simren, M.; Tack, J.; Whitehead, W.E.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Fang, X.; Fukudo, S.; et al. Worldwide Prevalence and Burden of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 99-114.e3. [CrossRef]
- Houghton, L.A.; Heitkemper, M.; Crowell, M.D.; Emmanuel, A.; Halpert, A.; McRoberts, J.A.; Toner, B. Age, Gender, and Women’s Health and the Patient. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1332-1343.e4. [CrossRef]
- Bellini, M.; Gambaccini, D.; Stasi, C.; Urbano, M.T.; Marchi, S.; Usai-Satta, P. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Disease Still Searching for Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 8807–8820. [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J.; Holtmann, G.; Walker, M.M. Therapeutic Strategies for Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on Pathophysiology. J Gastroenterol 2015, 50, 601–613. [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Towards Biomarker Identification. Trends Mol Med 2009, 15, 478–489. [CrossRef]
- Mavroeidi, P.; Xilouri, M. Neurons and Glia Interplay in α-Synucleinopathies. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 4994. [CrossRef]
- Lobo, B.; Tramullas, M.; Finger, B.-C.; Lomasney, K.W.; Beltran, C.; Clarke, G.; Santos, J.; Hyland, N.P.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The Stressed Gut: Region-Specific Immune and Neuroplasticity Changes in Response to Chronic Psychosocial Stress. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2023, 29, 72–84. [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Sandhu, K.; Peterson, V.; Dinan, T.G. The Gut Microbiome in Neurological Disorders. Lancet Neurol 2020, 19, 179–194. [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.-X.; Gulam, M.Y.; Chia, N.S.J.; Feng, L.; Rotzschke, O.; Tan, E.-K. Gut–Brain Axis: Potential Factors Involved in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. Front Neurol 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Challis, C.; Hori, A.; Sampson, T.R.; Yoo, B.B.; Challis, R.C.; Hamilton, A.M.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Gradinaru, V. Gut-Seeded α-Synuclein Fibrils Promote Gut Dysfunction and Brain Pathology Specifically in Aged Mice. Nat Neurosci 2020, 23, 327–336. [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.H.; Lim, S.-Y.; Chong, K.K.; Azhan A Manap, M.A.; Hor, J.W.; Lim, J.L.; Low, S.C.; Chong, C.W.; Mahadeva, S.; Lang, A.E. Probiotics for Constipation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. Neurology 2020, 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010998. [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, S.; Mohajeri, M. Changes of Colonic Bacterial Composition in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10, 708. [CrossRef]
- Baizabal-Carvallo, J.F.; Alonso-Juarez, M. The Link between Gut Dysbiosis and Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroscience 2020, 432, 160–173. [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-T.; Lai, J.-B.; Du, Y.-L.; Xu, Y.; Ruan, L.-M.; Hu, S.-H. Current Understanding of Gut Microbiota in Mood Disorders: An Update of Human Studies. Front Genet 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Frankiensztajn, L.M.; Elliott, E.; Koren, O. The Microbiota and the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenocortical (HPA) Axis, Implications for Anxiety and Stress Disorders. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2020, 62, 76–82. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Yang, B. Targeting Gut Microbiome: A Novel and Potential Therapy for Autism. Life Sci 2018, 194, 111–119. [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, S.A.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; González-Laredo, R.F.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A.; Moreno-Jiménez, M.R.; Bravo-Muñoz, M. Ancestral Food Sources Rich in Polyphenols, Their Metabolism, and the Potential Influence of Gut Microbiota in the Management of Depression and Anxiety. J Agric Food Chem 2022, 70, 944–956. [CrossRef]
- Platte, P.; Herbert, C.; Pauli, P.; Breslin, P.A.S. Oral Perceptions of Fat and Taste Stimuli Are Modulated by Affect and Mood Induction. PLoS One 2013, 8, e65006. [CrossRef]
- Le Port, A.; Gueguen, A.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Melchior, M.; Lemogne, C.; Nabi, H.; Goldberg, M.; Zins, M.; Czernichow, S. Association between Dietary Patterns and Depressive Symptoms Over Time: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study of the GAZEL Cohort. PLoS One 2012, 7, e51593. [CrossRef]
- Molendijk, M.; Molero, P.; Ortuño Sánchez-Pedreño, F.; Van der Does, W.; Angel Martínez-González, M. Diet Quality and Depression Risk: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. J Affect Disord 2018, 226, 346–354. [CrossRef]
- Naseribafrouei, A.; Hestad, K.; Avershina, E.; Sekelja, M.; Linløkken, A.; Wilson, R.; Rudi, K. Correlation between the Human Fecal Microbiota and Depression. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2014, 26, 1155–1162. [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.-T.; Zhang, J.-G. [Neuromodulation: Past, Present, and Future]. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2022, 53, 559–563. [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.; Ho, A.; Reddy, R.; Chen, J.; Castellanos, J. Narrative Review of Current Neuromodulation Modalities for Spinal Cord Injury. Frontiers in Pain Research 2023, 4. [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, J.M.; Tagliati, M.; Alterman, R.L.; Lozano, A.M.; Volkmann, J.; Stefani, A.; Horak, F.B.; Okun, M.S.; Foote, K.D.; Krack, P.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson Disease. Arch Neurol 2011, 68. [CrossRef]
- Aaronson, S.T.; Sears, P.; Ruvuna, F.; Bunker, M.; Conway, C.R.; Dougherty, D.D.; Reimherr, F.W.; Schwartz, T.L.; Zajecka, J.M. A 5-Year Observational Study of Patients With Treatment-Resistant Depression Treated With Vagus Nerve Stimulation or Treatment as Usual: Comparison of Response, Remission, and Suicidality. American Journal of Psychiatry 2017, 174, 640–648. [CrossRef]
- Deer, T.R.; Mekhail, N.; Provenzano, D.; Pope, J.; Krames, E.; Leong, M.; Levy, R.M.; Abejon, D.; Buchser, E.; Burton, A.; et al. The Appropriate Use of Neurostimulation of the Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nervous System for the Treatment of Chronic Pain and Ischemic Diseases: The Neuromodulation Appropriateness Consensus Committee. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface 2014, 17, 515–550. [CrossRef]
- George, M.S.; Taylor, J.J.; Short, E.B. The Expanding Evidence Base for RTMS Treatment of Depression. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2013, 26, 13–18. [CrossRef]
- Pires, M.; Severo, M.; Lopes, A.; Neves, S.; Matzel, K.; Povo, A. Sacral Neuromodulation for Low Anterior Resection Syndrome: Current Status—a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis 2023, 38, 189. [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.B.; Rao, V.R. Responsive Neurostimulation: Candidates and Considerations. Epilepsy & Behavior 2018, 88, 388–395. [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Fresnedo, A.; Perez-Vega, C.; Domingo, R.A.; Cheshire, W.P.; Middlebrooks, E.H.; Grewal, S.S. Motor Cortex Stimulation for Pain: A Narrative Review of Indications, Techniques, and Outcomes. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface 2022, 25, 211–221. [CrossRef]
- Staudt, M.D.; Hayek, S.M.; Rosenow, J.M.; Narouze, S.; Arle, J.E.; Pilitsis, J.G.; Schwalb, J.M.; Falowski, S.M.; Sweet, J.A. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines for Occipital Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Patients With Medically Refractory Occipital Neuralgia: Update. Neurosurgery 2023, 93, 493–495. [CrossRef]
- Byczynski, G.; Vanneste, S. Modulating Motor Learning with Brain Stimulation: Stage-Specific Perspectives for Transcranial and Transcutaneous Delivery. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2023, 125, 110766. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.M. Do; Cavalcanti, R.L.; Souza, C.G.; Chaves, G.; Macedo, L.B. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with Peripheral Stimulation in Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Expert Rev Med Devices 2023, 20, 121–140. [CrossRef]
- Nierenburg, H.; Stark-Inbar, A. Nerivio ® Remote Electrical Neuromodulation for Acute Treatment of Chronic Migraine. Pain Manag 2022, 12, 267–281. [CrossRef]
- Langguth, B.; Sturm, K.; Wetter, T.C.; Lange, M.; Gabriels, L.; Mayer, E.A.; Schlaier, J. Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Reduces Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in a Single Patient. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2015, 13, 1371-1374.e3. [CrossRef]
- Day, M. Sympathetic Blocks: The Evidence. Pain Practice 2008, 8, 98–109. [CrossRef]
- Randich, A.; Gebhart, G.F. Vagal Afferent Modulation of Nociception. Brain Res Rev 1992, 17, 77–99. [CrossRef]
- De Couck, M.; Nijs, J.; Gidron, Y. You May Need a Nerve to Treat Pain. Clin J Pain 2014, 30, 1099–1105. [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, X.; Yan, N.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Cholecystokinin Enhances Visceral Pain-Related Affective Memory via Vagal Afferent Pathway in Rats. Mol Brain 2012, 5, 19. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Cao, Z.J.; Fan, J.; Wang, M.; Owyang, C.; Li, Y. Subdiaphragmatic Vagal Afferent Nerves Modulate Visceral Pain. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2008, 294, G1441–G1449. [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Pellissier, S. Vagal Tone: Effects on Sensitivity, Motility, and Inflammation. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2016, 28, 455–462. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, F.; Sun, C.; Xu, W.; Li, M.; Gong, Y.; Rong, P.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.D.Z. Noninvasive Transcutaneous Auricular Vagal Nerve Stimulation Improves Gastric Slow Waves Impaired by Cold Stress in Healthy Subjects. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface 2022. [CrossRef]
- Costantini, T.W.; Bansal, V.; Krzyzaniak, M.; Putnam, J.G.; Peterson, C.Y.; Loomis, W.H.; Wolf, P.; Baird, A.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Coimbra, R. Vagal Nerve Stimulation Protects against Burn-Induced Intestinal Injury through Activation of Enteric Glia Cells. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2010, 299, G1308–G1318. [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Vagal Nerve Stimulation with a Special Attention to Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2022, 34. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Costantini, T.; Ryu, S.Y.; Peterson, C.; Loomis, W.; Putnam, J.; Elicieri, B.; Baird, A.; Coimbra, R. Stimulating the Central Nervous System to Prevent Intestinal Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury. Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection & Critical Care 2010, 68, 1059–1064. [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. Neural Circuitry and Immunity. Immunol Res 2015, 63, 38–57. [CrossRef]
- Meregnani, J.; Clarençon, D.; Vivier, M.; Peinnequin, A.; Mouret, C.; Sinniger, V.; Picq, C.; Job, A.; Canini, F.; Jacquier-Sarlin, M.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Autonomic Neuroscience 2011, 160, 82–89. [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Hoffmann, D.; Clarençon, D.; Mathieu, N.; Dantzer, C.; Vercueil, L.; Picq, C.; Trocmé, C.; Faure, P.; et al. Chronic Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Crohn’s Disease: A 6-Month Follow-up Pilot Study. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2016, 28, 948–953. [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, S.; Dantzer, C.; Canini, F.; Mathieu, N.; Bonaz, B. Psychological Adjustment and Autonomic Disturbances in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2010, 35, 653–662. [CrossRef]
- Korenblik, V.; Brouwer, M.E.; Korosi, A.; Denys, D.; Bockting, C.L.H.; Brul, S.; Lok, A. Are Neuromodulation Interventions Associated with Changes in the Gut Microbiota? A Systematic Review. Neuropharmacology 2023, 223, 109318. [CrossRef]
- Hey, G.; Nair, N.; Klann, E.; Gurrala, A.; Safarpour, D.; Mai, V.; Ramirez-Zamora, A.; Vedam-Mai, V. Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease and the Gut Microbiome: Evidence for Bidirectional Connection. Front Aging Neurosci 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ding, W.; Dong, Y.; Chen, C.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Gan, S.; You, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Surgical Pain-Induced Delirium-like Behavior in Mice via Remodeling Gut Microbiota and Dendritic Spine. Front Immunol 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Güemes, I.; Sánchez, F.M.; Luis, L.; Sun, F.; Pascual, S.; Usón, J. Continuous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Effects on the Gut-Brain Axis in Swine. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface 2007, 10, 52–58. [CrossRef]
- Sobocki, J.; Królczyk, G.; Herman, R.M.; Matyja, A.; Thor, P.J. Influence of Vagal Nerve Stimulation on Food Intake and Body Weight--Results of Experimental Studies. J Physiol Pharmacol 2005, 56 Suppl 6, 27–33.
- Krolczyk, G.; Zurowski, D.; Sobocki, J.; Słowiaczek, M.P.; Laskiewicz, J.; Matyja, A.; Zaraska, K.; Zaraska, W.; Thor, P.J. Effects of Continuous Microchip (MC) Vagal Neuromodulation on Gastrointestinal Function in Rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 2001, 52, 705–715.
- Ni, S.; Yao, Z.; Wei, X.; Heng, X.; Qu, S.; Zhao, X.; Qi, Y.; Ge, P.; Xu, C.; Yang, N.; et al. Vagus Nerve Stimulated by Microbiota-derived Hydrogen Sulfide Mediates the Regulation of Berberine on Microglia in Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Rats. Phytotherapy Research 2022, 36, 2964–2981. [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Kurlander, J.; Eswaran, S. Irritable Bowel Syndrome. JAMA 2015, 313, 949. [CrossRef]
- Mawe, G.; Spohn, S. Non-Conventional Features of Peripheral Serotonin Signalling — the Gut and Beyond.
- Qin, H.-Y.; Zang, K.-H.; Zuo, X.; Wu, X.-A.; Bian, Z.-X. Quercetin Attenuates Visceral Hypersensitivity and 5-Hydroxytryptamine Availability in Postinflammatory Irritable Bowel Syndrome Rats: Role of Enterochromaffin Cells in the Colon. J Med Food 2019, 22, 663–671. [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Chen, J.D.; Liu, F. Ameliorating Effects and Mechanisms of Transcutaneous Auricular Vagal Nerve Stimulation on Abdominal Pain and Constipation. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D. Parasympathetic Control of Gastrointestinal Motility and Cross-Branch Actions of Parasympathetic Neuromodulation. Chin Med J (Engl) 2023, 136, 53–55. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, T.; Meng, Y.; Maisiyiti, A.; Dong, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Yin, J.; Chen, J.D.Z. Auricular Vagal Nerve Stimulation Improves Constipation by Enhancing Colon Motility via the Central-Vagal Efferent Pathway in Opioid-Induced Constipated Rats. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface 2021, 24, 1258–1268. [CrossRef]
- Coffin, B. Alteration of the Spinal Modulation of Nociceptive Processing in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gut 2004, 53, 1465–1470. [CrossRef]
- Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Johnson, A.C.; Foreman, R.D.; Linderoth, B. Spinal Cord Stimulation Attenuates Visceromotor Reflexes in a Rat Model of Post-Inflammatory Colonic Hypersensitivity. Autonomic Neuroscience 2005, 122, 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Palecek, J. The Role of Dorsal Columns Pathway in Visceral Pain. Physiol Res 2004, 53 Suppl 1, S125-30.
- Aulí, M.; Martínez, E.; Gallego, D.; Opazo, A.; Espín, F.; Martí-Gallostra, M.; Jiménez, M.; Clavé, P. Effects of Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurotransmission on Motor Patterns of Human Sigmoid Colon in Vitro. Br J Pharmacol 2008, 155, 1043–1055. [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, A.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Ghelardini, C. Analgesic and Antineuropathic Drugs Acting Through Central Cholinergic Mechanisms. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 2011, 6, 119–140. [CrossRef]
- Molodecky, N.A.; Soon, I.S.; Rabi, D.M.; Ghali, W.A.; Ferris, M.; Chernoff, G.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Barkema, H.W.; et al. Increasing Incidence and Prevalence of the Inflammatory Bowel Diseases With Time, Based on Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 46-54.e42. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.T. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, 2652–2664. [CrossRef]
- Willemze, R.A.; Welting, O.; van Hamersveld, H.P.; Meijer, S.L.; Folgering, J.H.A.; Darwinkel, H.; Witherington, J.; Sridhar, A.; Vervoordeldonk, M.J.; Seppen, J.; et al. Neuronal Control of Experimental Colitis Occurs via Sympathetic Intestinal Innervation. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2018, 30. [CrossRef]
- Teratani, T.; Mikami, Y.; Nakamoto, N.; Suzuki, T.; Harada, Y.; Okabayashi, K.; Hagihara, Y.; Taniki, N.; Kohno, K.; Shibata, S.; et al. The Liver–Brain–Gut Neural Arc Maintains the Treg Cell Niche in the Gut. Nature 2020, 585, 591–596. [CrossRef]
- Matteoli, G.; Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Nemethova, A.; Di Giovangiulio, M.; Cailotto, C.; van Bree, S.H.; Michel, K.; Tracey, K.J.; Schemann, M.; Boesmans, W.; et al. A Distinct Vagal Anti-Inflammatory Pathway Modulates Intestinal Muscularis Resident Macrophages Independent of the Spleen. Gut 2014, 63, 938–948. [CrossRef]
- Katzka, D.A.; Pandolfino, J.E.; Kahrilas, P.J. Phenotypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Where Rome, Lyon, and Montreal Meet. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2020, 18, 767–776. [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Roman, S.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Fox, M.; Keller, J.; Pandolfino, J.E.; Sifrim, D.; Tatum, R.; Yadlapati, R.; Savarino, E. Classification of Esophageal Motor Findings in Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease: Conclusions from an International Consensus Group. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2017, 29. [CrossRef]
- Tack, J.; Pandolfino, J.E. Pathophysiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 277–288. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Shi, X.; Ning, B.; Shi, J.; Zeng, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.D.; Xie, W.-F. Ameliorating Effects and Autonomic Mechanisms of Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface 2020, 23, 1207–1214. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hu, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, W.; Zeng, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.D.Z.; Xie, W.-F. Integrative Effects and Vagal Mechanisms of Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation on Gastroesophageal Motility in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2021, 116, 1495–1505. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, R.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, C.; Chen, J.D.Z. Ameliorating Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation Combined With Deep Breathing Training on Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Mediated via the Autonomic Pathway. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface 2019, 22, 751–757. [CrossRef]
- Dickman, R.; Levy, S.; Perets, T.T.; Hazani-Pauker, M.; Boltin, D.; Schmilovitz-Weiss, H.; Nidal, I.; Siterman, M.; Carter, D.; Fass, R.; et al. Effect of the Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation System on Esophageal-Acid Exposure in Patients Non-Responsive to Once-Daily Proton-Pump Inhibitor: Proof-of-Concept Study. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf) 2021, 9, 323–328. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.R.; Gonda, X.; Tarazi, F.I. Autism Spectrum Disorder: Classification, Diagnosis and Therapy. Pharmacol Ther 2018, 190, 91–104. [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Lo, Y.C.; Lin, H.C.; Li, S.J.; Lin, S.H.; Wu, H.F.; Chu, M.C.; Lee, C.W.; Lin, I.C.; Chang, C.W.; et al. MR Imaging Central Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation Restored Autistic-like Social Deficits in the Rat. Brain Stimul 2019, 12, 1410–1420. [CrossRef]
- Engineer, C.T.; Hays, S.A.; Kilgard, M.P. Vagus Nerve Stimulation as a Potential Adjuvant to Behavioral Therapy for Autism and Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders. J Neurodev Disord 2017, 9, 20. [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, W.P. Highlights in Clinical Autonomic Neuroscience: New Insights into Autonomic Dysfunction in Autism. Autonomic Neuroscience 2012, 171, 4–7. [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.L.; Levy, K.M.; Hoff, D.; Amar, A.P.; Park, M.S.; Conklin, J.M.; Baird, L.; Apuzzo, M.L.J. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Intractable Epilepsy: Results from the Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy Patient Outcome Registry. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2010, 5, 595–602. [CrossRef]
- Yizhar, O.; Fenno, L.E.; Prigge, M.; Schneider, F.; Davidson, T.J.; O’Shea, D.J.; Sohal, V.S.; Goshen, I.; Finkelstein, J.; Paz, J.T.; et al. Neocortical Excitation/Inhibition Balance in Information Processing and Social Dysfunction. Nature 2011, 477, 171–178. [CrossRef]
- Buzsáki, G.; Wang, X.-J. Mechanisms of Gamma Oscillations. Annu Rev Neurosci 2012, 35, 203–225. [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Michmizos, K.; Tommerdahl, M.; Ganesan, S.; Kitzbichler, M.G.; Zetino, M.; Garel, K.-L.A.; Herbert, M.R.; Hämäläinen, M.S.; Kenet, T. Somatosensory Cortex Functional Connectivity Abnormalities in Autism Show Opposite Trends, Depending on Direction and Spatial Scale. Brain 2015, 138, 1394–1409. [CrossRef]
- Hulsey, D.R.; Riley, J.R.; Loerwald, K.W.; Rennaker, R.L.; Kilgard, M.P.; Hays, S.A. Parametric Characterization of Neural Activity in the Locus Coeruleus in Response to Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Exp Neurol 2017, 289, 21–30. [CrossRef]
- Follesa, P.; Biggio, F.; Gorini, G.; Caria, S.; Talani, G.; Dazzi, L.; Puligheddu, M.; Marrosu, F.; Biggio, G. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Increases Norepinephrine Concentration and the Gene Expression of BDNF and BFGF in the Rat Brain. Brain Res 2007, 1179, 28–34. [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Businaro, R.; Ippoliti, F.; Lo Vasco, V.R.; Massoni, F.; Onofri, E.; Troili, G.M.; Pontecorvi, V.; Morelli, M.; Rapp Ricciardi, M.; et al. Altered Cytokine and BDNF Levels in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurotox Res 2013, 24, 491–501. [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, P.R. Neural Plasticity; Harvard University Press, 2009; ISBN 9780674038936.
- Hallett, M. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and the Human Brain. Nature 2000 406:6792 2000, 406, 147–150. [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Tormos, J.M.; Keenan, J.; Tarazona, F.; Cañete, C.; Catalá, M.D. Study and Modulation of Human Cortical Excitability With Tra... : Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology Available online: https://journals.lww.com/clinicalneurophys/abstract/1998/07000/study_and_modulation_of_human_cortical.5.aspx (accessed on 5 October 2023).
- Barahona-Corrêa, J.B.; Velosa, A.; Chainho, A.; Lopes, R.; Oliveira-Maia, A.J. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Integr Neurosci 2018, 12. [CrossRef]
- Enticott, P.G.; Kirkovski, M.; Oberman, L.M. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurotechnology and Brain Stimulation in Pediatric Psychiatric and Neurodevelopmental Disorders 2019, 83–113. [CrossRef]
- Oberman, L.M.; Enticott, P.G.; Casanova, M.F.; Rotenberg, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; McCracken, J.T. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Challenges, Promise, and Roadmap for Future Research. Autism Research 2016, 9, 184–203. [CrossRef]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Nitsche, M.A.; Bolognini, N.; Bikson, M.; Wagner, T.; Merabet, L.; Edwards, D.J.; Valero-Cabre, A.; Rotenberg, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; et al. Clinical Research with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS): Challenges and Future Directions. Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation 2012, 5, 175–195. [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Paulus, W. Excitability Changes Induced in the Human Motor Cortex by Weak Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. J Physiol 2000, 527, 633. [CrossRef]
- Antal, A.; Herrmann, C.S. Transcranial Alternating Current and Random Noise Stimulation: Possible Mechanisms. Neural Plast 2016, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, A. V.; Yun, K. Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (TACS) Mechanisms and Protocols. Front Cell Neurosci 2017, 11, 280666. [CrossRef]
- Moisa, M.; Polania, R.; Grueschow, M.; Ruff, C.C. Brain Network Mechanisms Underlying Motor Enhancement by Transcranial Entrainment of Gamma Oscillations. The Journal of Neuroscience 2016, 36, 12053–12065. [CrossRef]
- Hoy, K.E.; Bailey, N.; Arnold, S.; Windsor, K.; John, J.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Fitzgerald, P.B. The Effect of γ-TACS on Working Memory Performance in Healthy Controls. Brain Cogn 2015, 101, 51–56. [CrossRef]
- Biagioni, M.C.; Sharma, K.; Migdadi, H.A.; Cucca, A. Non-Invasive Neuromodulation Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease. In Parkinson’s Disease - Understanding Pathophysiology and Developing Therapeutic Strategies; InTech, 2018.
- Manenti, R.; Brambilla, M.; Benussi, A.; Rosini, S.; Cobelli, C.; Ferrari, C.; Petesi, M.; Orizio, I.; Padovani, A.; Borroni, B.; et al. <scp>M</Scp> Ild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease Is Improved by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with Physical Therapy. Movement Disorders 2016, 31, 715–724. [CrossRef]
- Deuschl, G.; Schüpbach, M.; Knudsen, K.; Pinsker, M.O.; Cornu, P.; Rau, J.; Agid, Y.; Schade-Brittinger, C. Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus at an Earlier Disease Stage of Parkinson’s Disease: Concept and Standards of the EARLYSTIM-Study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2013, 19, 56–61. [CrossRef]
- Rizzone, M.G.; Fasano, A.; Daniele, A.; Zibetti, M.; Merola, A.; Rizzi, L.; Piano, C.; Piccininni, C.; Romito, L.M.; Lopiano, L.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Subthalamic Nucleus DBS in Parkinson’s Disease: From the Advanced Phase towards the Late Stage of the Disease? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2014, 20, 376–381. [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Elder, C.M.; Okun, M.S.; Patrick, S.K.; Vitek, J.L. Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus Changes the Firing Pattern of Pallidal Neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience 2003, 23, 1916–1923. [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, C.C.; Grill, W.M.; Sherman, D.L.; Thakor, N. V. Cellular Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation: Model-Based Analysis of Activation and Inhibition. J Neurophysiol 2004, 91, 1457–1469. [CrossRef]
- Shirota, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Hamada, M.; Enomoto, H.; Ugawa, Y. Supplementary Motor Area Stimulation for Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2013, 80, 1400–1405. [CrossRef]
- Chervyakov, A. V.; Chernyavsky, A.Y.; Sinitsyn, D.O.; Piradov, M.A. Possible Mechanisms Underlying the Therapeutic Effects of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Front Hum Neurosci 2015, 9. [CrossRef]
- Strafella, A.P.; Paus, T.; Barrett, J.; Dagher, A. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Human Prefrontal Cortex Induces Dopamine Release in the Caudate Nucleus. J Neurosci 2001, 21. [CrossRef]
- Fregni, F.; Simon, D.K.; Wu, A.; Pascual-Leone, A. Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1614–1623. [CrossRef]
- Rajan, K.B.; Weuve, J.; Barnes, L.L.; Wilson, R.S.; Evans, D.A. Prevalence and Incidence of Clinically Diagnosed Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia from 1994 to 2012 in a Population Study. Alzheimers Dement 2019, 15, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Mantzavinos, V.; Alexiou, A. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis. Curr Alzheimer Res 2017, 14. [CrossRef]
- Laxton, A.W.; Lozano, A.M. Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Alzheimer Disease and Dementias. World Neurosurg 2013, 80, S28.e1-S28.e8. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Dai, C.; Huang, X.; Fang, L.; Ao, Q.; Huang, D. The Neuroprotective Effect of Deep Brain Stimulation at Nucleus Basalis of Meynert in Transgenic Mice with Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Stimul 2019, 12, 161–174. [CrossRef]
- Scharre, D.W.; Weichart, E.; Nielson, D.; Zhang, J.; Agrawal, P.; Sederberg, P.B.; Knopp, M. V.; Rezai, A.R. Deep Brain Stimulation of Frontal Lobe Networks to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2018, 62, 621–633. [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.; Gondard, E.; Tampellini, D.; Milsted, J.A.T.; Marillac, D.; Hamani, C.; Kalia, S.K.; Lozano, A.M. Chronic Deep Brain Stimulation in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model Enhances Memory and Reduces Pathological Hallmarks. Brain Stimul 2018, 11, 435–444. [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Yiu, A.; Stone, S.S.D.; Oh, S.; Lozano, A.M.; Josselyn, S.A.; Frankland, P.W. Entorhinal Cortical Deep Brain Stimulation Rescues Memory Deficits in Both Young and Old Mice Genetically Engineered to Model Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 2493–2503. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mao, Z.; Ling, Z.; Yu, X. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Neurol 2020, 267, 791–801. [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.S.; Li, C.T.; Brunoni, A.R.; Yang, F.C.; Tseng, P.T.; Tu, Y.K.; Stubbs, B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Thompson, T.; Rajji, T.K.; et al. Cognitive Effects and Acceptability of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation on Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Component Network Meta-Analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2021, 92, 195–203. [CrossRef]
- Whiteford, H.A.; Harris, M.G.; McKeon, G.; Baxter, A.; Pennell, C.; Barendregt, J.J.; Wang, J. Estimating Remission from Untreated Major Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol Med 2013, 43, 1569–1585. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fu, Y.; Liu, C.; Meng, Z. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex for Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front Behav Neurosci 2022, 16. [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.M.; Moffa, A.; Nikolin, S.; Bennabi, D.; Brunoni, A.R.; Flannery, W.; Haffen, E.; McClintock, S.M.; Moreno, M.L.; Padberg, F.; et al. Cognitive Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Treatment in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: An Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of Randomised, Sham-Controlled Trials. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2018, 90, 137–145. [CrossRef]
- Demirtas-Tatlidede, A.; Vahabzadeh-Hagh, A.M.; Pascual-Leone, A. Can Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Enhance Cognition in Neuropsychiatric Disorders? Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 566–578. [CrossRef]
- Brunelin, J.; Mondino, M.; Gassab, L.; Haesebaert, F.; Gaha, L.; Suaud-Chagny, M.F.; Saoud, M.; Mechri, A.; Poulet, E. Examining Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation (TDCS) as a Treatment for Hallucinations in Schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2012, 169, 719–724. [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Jaussi, W.; Liebetanz, D.; Lang, N.; Tergau, F.; Paulus, W. Consolidation of Human Motor Cortical Neuroplasticity by D-Cycloserine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004 29:8 2004, 29, 1573–1578. [CrossRef]
- Stagg, C.J.; Best, J.G.; Stephenson, M.C.; O’Shea, J.; Wylezinska, M.; Kineses, Z.T.; Morris, P.G.; Matthews, P.M.; Johansen-Berg, H. Polarity-Sensitive Modulation of Cortical Neurotransmitters by Transcranial Stimulation. Journal of Neuroscience 2009, 29, 5202–5206. [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Kuo, M.F.; Karrasch, R.; Wächter, B.; Liebetanz, D.; Paulus, W. Serotonin Affects Transcranial Direct Current-Induced Neuroplasticity in Humans. Biol Psychiatry 2009, 66, 503–508. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Inagawa, T.; Hirabayashi, N.; Sumiyoshi, T. Emotion Recognition Deficits in Psychiatric Disorders as a Target of Non-Invasive Neuromodulation: A Systematic Review. Clin EEG Neurosci 2022, 53, 506–512. [CrossRef]
- Vercammen, A.; Rushby, J.A.; Loo, C.; Short, B.; Weickert, C.S.; Weickert, T.W. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Influences Probabilistic Association Learning in Schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2011, 131, 198–205. [CrossRef]
- Mazurak, N.; Seredyuk, N.; Sauer, H.; Teufel, M.; Enck, P. Heart Rate Variability in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Review of the Literature. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2012, 24, 206–216. [CrossRef]
- cain, k. c.; jarrett, m. e.; burr, r. l.; hertig, v. l.; heitkemper, m. m. Heart Rate Variability Is Related to Pain Severity and Predominant Bowel Pattern in Women with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2007, 19, 110–118. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sarosiek, I.; McCallum, R.; Abell, T.; Sun, Y.; Moody, N. Chronic Transcutaneous Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Dyspeptic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetic Gastroparesis: A Placebo-Controlled Multicenter Clinical Trial Using a Newly Developed Microstimulator. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2012, 24, 43–190. [CrossRef]
- Drissi, F.; Bourreille, A.; Neunlist, M.; Meurette, G. Sacral Neuromodulation for Refractory Ulcerative Colitis: Safety and Efficacy in a Prospective Observational Series of Eight Patients. Tech Coloproctol 2023, 27, 501–505. [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B. Is-There a Place for Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Bioelectron Med 2018, 4, 4. [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhou, K.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Chen, S.; Lin, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T. Involvement of MAPK/NF-ΚB Signaling in the Activation of the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway in Experimental Colitis by Chronic Vagus Nerve Stimulation. PLoS One 2013, 8, e69424. [CrossRef]
- Vilz, T.O.; Stoffels, B.; Straßburg, C.; Schild, H.H.; Kalff, J.C. Ileus in Adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2017. [CrossRef]
- Luckey, A. Mechanisms and Treatment of Postoperative Ileus. Archives of Surgery 2003, 138, 206. [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, W.J.; van der Zanden, E.P.; The, F.O.; Bijlsma, M.F.; van Westerloo, D.J.; Bennink, R.J.; Berthoud, H.-R.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; et al. Stimulation of the Vagus Nerve Attenuates Macrophage Activation by Activating the Jak2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Nat Immunol 2005, 6, 844–851. [CrossRef]
- Stakenborg, N.; Wolthuis, A.M.; Gomez-Pinilla, P.J.; Farro, G.; Di Giovangiulio, M.; Bosmans, G.; Labeeuw, E.; Verhaegen, M.; Depoortere, I.; D’Hoore, A.; et al. Abdominal Vagus Nerve Stimulation as a New Therapeutic Approach to Prevent Postoperative Ileus. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2017, 29. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.-Q.; Taché, Y. Abdominal Surgery Induced Gastric Ileus and Activation of M1-like Macrophages in the Gastric Myenteric Plexus: Prevention by Central Vagal Activation in Rats. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2017, 313, G320–G329. [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Fang, J.; Shao, X.; Du, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z. Electroacupuncture Treatment Partly Promotes the Recovery Time of Postoperative Ileus by Activating the Vagus Nerve but Not Regulating Local Inflammation. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 39801. [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Chedid, V.; Ford, A.C.; Haruma, K.; Horowitz, M.; Jones, K.L.; Low, P.A.; Park, S.-Y.; Parkman, H.P.; Stanghellini, V. Gastroparesis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018, 4, 41. [CrossRef]
- Levinthal, D.J.; Bielefeldt, K. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Gastric Electrical Stimulation for Gastroparesis. Autonomic Neuroscience 2017, 202, 45–55. [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, P.J.; Camilleri, M.; Hasler, W.L.; Parkman, H.P. White Paper AGA: Gastroparesis: Clinical and Regulatory Insights for Clinical Trials. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2017, 15, 1184–1190. [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; De Z. Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Schirmer, B.D.; Williams, R.D.; Ross, R.A. Gastric Pacing Improves Emptying and Symptoms in Patients with Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 456–461. [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; Snape, W.; Brody, F.; Wo, J.; Parkman, H.P.; Nowak, T. Gastric Electrical Stimulation With Enterra Therapy Improves Symptoms From Diabetic Gastroparesis in a Prospective Study. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2010, 8, 947-954.e1. [CrossRef]
- Wo, J.M.; Nowak, T. V.; Waseem, S.; Ward, M.P. Gastric Electrical Stimulation for Gastroparesis and Chronic Unexplained Nausea and Vomiting. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 2016, 14, 386–400. [CrossRef]
- Levinthal, D.J.; Bielefeldt, K. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Gastric Electrical Stimulation for Gastroparesis. Autonomic Neuroscience 2017, 202, 45–55. [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, F.; Sahito, A.M.; Mir, S.L.; Khatri, G.; Shaikh, S.; Gul, A.; Hassan, S.A.; Koritala, T.; Surani, S. Electrical Neuromodulation Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2022, 13, 128–142. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).