1. Introduction
A new era of multi-messenger astronomy has begun with the first detection of gravitational wave signals, also known as GW170817 or AT2017gfo for the electromagnetic emission originating from the kilonova formed by the binary neutron star merger [
1,
2]. This new astronomy emphasizes the crucial role of neutron stars (NSs), which are prototypes for the most extreme phases of matter where the strong, the weak, the gravitational and the electromagnetic interactions can be studied in regimes that cannot be explored on Earth. In this paper, we are analyzing the properties of the dense-matter equation of state (EOS) from microscopic calculations with a focus on the strong three-body interaction and we discuss the link with empirical energy density functionals (EDFs).
In recent years, the determination of nuclear EDFs incorporates more and more information deduced from microscopic calculations of nuclear matter. Usually, one specific or a very limited number of microscopic calculations are considered in the fitting protocoles. However, the impact of the choices of the bare nuclear interaction, the regularization scheme, the experimental error in the phase shift data, and of the many-body framework is important, and has been cautiously addressed in the chiral effective field theory (
-EFT) [
3] in order to theoretically predict the nuclear EOS including error estimates. There is however an upper limit on density (presently estimated to be (1–2)
with
[
4]), where the chiral EFT breaks down and also the error estimates become meaningless [
5,
6,
7].
At increasing density – and already around
– also the role of nuclear three-body forces (3BF) in nuclear matter cannot be ignored. For traditional meson-exchange potential models, the compatible 3BF correction at saturation density is of limited magnitude, a few MeV, which represents (15–20)% of the total energy, in order to reproduce the saturation of nuclear matter. With the advent of regularized soft-core nuclear interactions, such as
[
8] as well as chiral effective field theory (
-EFT) [
3], a new paradigm has emerged. In short, any modification of the two-body interaction, by applying a unitary transformation, generates many-body interactions. The 3BF cannot be viewed as independent of the two-body force (2BF), but instead, it contains a part of the repulsive hard-core interaction. Regularized soft-core interactions need stronger many-body interactions to saturate, compared to the hard-core ones.
Building bridges between EDFs for the in-medium nuclear interaction and microscopic approaches of the nuclear many-body problem is, therefore, fundamental for a consistent understanding of nuclei, neutron stars, core-collapse supernovae, and kilonovae. Microscopic approaches, on one hand, have the advantage of being based on realistic 2BFs that reproduce with high precision the scattering phase shifts and the deuteron properties, and include the isospin asymmetry dependence in a natural way. However, the direct implementation of microscopic approaches in finite nuclei is not an easy task. A realistic 2BF cannot be used directly in nuclei. Its hard-core repulsion requires a resummation as in uniform matter and 3BFs are required to describe both the energy and charge radii of finite nuclei. EDF models, on the other hand, are usually based on effective density-dependent interactions with parameters frequently fitted to reproduce global properties of nuclei and properties of symmetric and neutron matter [
9,
10,
11]. These effective interactions capture the essence of the in-medium nuclear interaction as well as the effect of the complex correlations. Their predictions at high densities and isospin asymmetries, however, should be taken with care and discussed in view of the considered constraints. Combining phenomenological models with microscopic approaches would, therefore, help in setting up a nuclear model based on realistic 2BFs and 3BFs that can simultaneously describe the properties of nuclei and those of infinite nuclear matter in a large range of densities and isospin asymmetries.
Two major sources of uncertainty arise, however, when trying to build links between EDFs and microscopic approaches. The first is that there is a fairly large number of realistic 2BFs that reproduce the scattering data and the deuteron properties with equivalent high accuracy. Predictions employing these interactions shall then be compared to estimate the uncertainty due to the nuclear interaction (leading to an estimate of systematic uncertainties). The second source of uncertainties is due to the different methods employed to solve the nuclear many-body problem (which also contributes to systematical uncertainties). A critical comparison of various microscopic approaches using the same 2BF has been performed in Ref. [
12]. The aim of this work is to find the sources of discrepancies, and ultimately to determine a “systematic uncertainty" associated with the different microscopic approaches of the nuclear-matter EOS. The approaches considered were the Brueckner–Hartree–Fock (BHF) [
13], the Brueckner–Bethe–Goldstone (BBG) expansion up to third order [
14], the self-consistent Green’s function (SCGF) [
15], the auxiliary field diffusion Monte Carlo (AFDMC) [
16], the Green’s function Monte Carlo (GFMC) [
17], and the Fermi hypernetted chain (FHNC) [
18]. The properties of pure neutron matter (NM) and symmetric nuclear matter (SM) were computed with simplified versions [
19] of the widely used Argonne Av18 potential [
20], and a careful comparison of the results obtained with the different approaches was performed. The results of this work confirmed that the tensor and spin-orbit components of the 2BF and their in-medium treatment are responsible for most of the observed discrepancies among these approaches [
12]. A very similar study has been performed recently in Refs. [
21,
22].
The EDF models adjusted to microscopic approaches shall incorporate these sources of uncertainties in the microscopic predictions for dense matter. Several authors have already determined EDF models from microscopic approaches (see, e.g., Refs. [
10,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]). The authors of Ref. [
23], for instance, constructed a Skyrme-type EDF based on BHF results for infinite matter and applied it to a set of isospin-symmetric and asymmetric nuclei through the mass table. Their results provided a microscopic basis for a link between nuclear surface behavior and the NM EOS, as previously observed with phenomenological effective forces. The same authors have also developed the so-called Barcelona-Catania-Paris-Madrid (BCPM) EDF [
24] obtained from BHF calculations of nuclear matter within an approximation inspired by the Kohn-Sham formulation of density functional theory [
29]. The BCPM EDF is built with a bulk part obtained directly from BHF results for NM and SM via a local-density approximation, and is supplemented by a phenomenological surface part together with the Coulomb, spin-orbit, and pairing contributions. The functional, with four adjustable parameters, is able to describe the ground-state properties of finite nuclei with an accuracy comparable to that of Skyrme and Gogny forces.
Later on, the so-called LNS Skyrme force was built in Ref. [
25] based also on BHF calculations of infinite nuclear matter with consistent 2BFs and 3BFs. It was further refined in Ref. [
27] to reproduce experimental binding energies and charge radii of some selected nuclei. A similar fitting procedure was also used in Ref. [
10], where various Skyrme forces were adjusted to the
decomposition of the results of two different BHF calculations [
30,
31]
1. The comparison of the two microscopic calculations provided a kind of theoretical uncertainty based on the 2BFs and 3BFs employed, and suggests that the associated differences should be carefully analyzed. In Ref. [
28] the tensor contribution to the
channels and different partial waves was analyzed. However, similarly to previous works, the uncertainty of the microscopic calculations was not included in the determination of the EDF. Finally let us mention the analysis of Quantum Monte Carlo (QMC) calculations of spin-polarized neutron matter, which have been compared to predictions of several Skyrme EDFs [
32]. Such analysis allowed to probe the time-odd part of the Skyrme EDFs independently of the time-even one and was found to be very constraining. Also here an estimate of the uncertainty of the microscopic calculation would be very valuable, in particular as the density of the medium increases.
In the present paper, we aim to provide an estimation of the uncertainty of the nuclear EOS predicted by the BHF approach up to about 0.4 based on several nuclear two- and three-body interactions. Special attention is paid to the impact of the latter ones for which we consider two different types: phenomenological and microscopical 3BF. We then determine the corresponding parameter ranges of Skyrme-type nuclear energy density functionals, and more importantly, we show that the BHF calculations in the different channels in SM and NM cannot be reproduced by the Skyrme EDF above , already from the 2BF results.
The paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2 a brief review of the BHF approach is presented. The
and partial-wave decomposition of the BHF correlation energy per particle for SM and NM is analysed in
Section 3. In
Section 4 this decomposition is employed to constrain the parameters of Skyrme-type forces. A summary and the main conclusions are given in
Section 5.
2. BHF Approach of Nuclear Matter
The BHF approach is the lowest-order realization of the BBG many-body theory of nuclear matter [
33]. In this theory, the ground-state energy of nuclear matter is evaluated in terms of the so-called hole-line expansion, where the perturbative diagrams are grouped according to the number of independent hole-lines. The expansion is derived by means of the in-medium two-body scattering matrix
G, which describes the effective interaction between two nucleons in the presence of a surrounding medium. The
G matrix is obtained by solving the well-known Bethe-Goldstone equation
where the multi-indices
indicate all the quantum numbers (momentum
k, spin
and isospin
projections) characterizing the two nucleons in the initial, intermediate, and final states,
V denotes the bare
interaction,
is the (large) volume enclosing the system,
with
is the Pauli operator taking into account the effect of the exclusion principle on the scattered holes, and
is the Fermi momentum for particle
i with density
defined in the ground state. The single-particle (s.p.) energy of a nucleon with momentum
and isospin
is
being
the mean field felt by the nucleon
i due to its interaction with the other nucleons of the medium. In the BHF approximation it is calculated through the “on-shell”
G-matrix,
where the matrix elements are meant to be properly antisymmetrized. Note that Eqs. (
1,
2,
3) should be solved self-consistently. The momentum dependence of the s.p. energy
can be characterized in terms of the effective mass [
34],
We consider in the following isospin-asymmetric nuclear matter and for clarity we shall specify the isospin index . However, since we will discuss only spin-symmetric matter, the spin up and down potentials are equal and we do not specify the spin index in the following. For simplicity we consider the same bare mass for neutrons and protons .
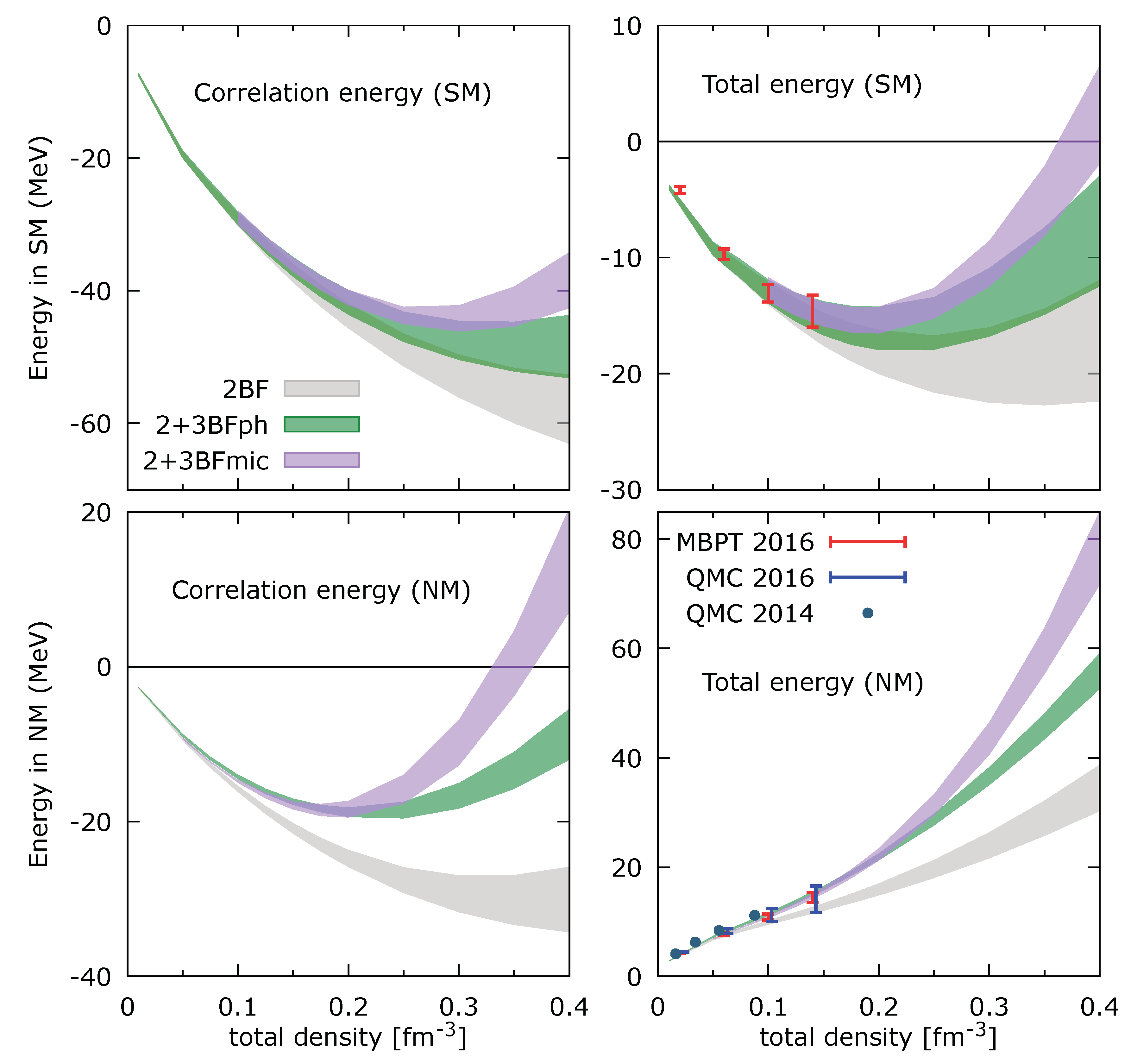
In the BHF approach, the total energy per particle of nuclear matter is given by the sum of only two-hole-line diagrams that include the effect of two-body correlations through the
G matrix,
where the first term on the right hand side is the energy of a free Fermi gas and the second one is the so-called BHF correlation energy,
. We note here that the latter is usually referred to as BHF potential energy.
It has been shown in Ref. [
14] for the
, and recently confirmed in Ref. [
35] for several modern 2BFs, that the contribution to the total energy from three-hole-line diagrams (which account for the effect of three-body correlations) is minimized when the so-called continuous prescription [
34] is adopted for the BHF s.p. energy (
2). This is a strong indication of the convergence of the hole-line expansion around saturation density and above. We adopt this prescription in our calculations and limit the exploration to densities less than 0.4
, where the hole-line expansion parameter
(with
c the interaction range and
d the average distance between two nucleons) is still sufficiently small [
35,
36].
The present BHF calculations are carried out using a set of several phase-shift-equivalent
potentials, namely, Av18 [
37], NSC97a-f [
38], a non-relativistic version of the Bonn B potential (Bonn) [
39] and the charge-dependent Bonn potential (CD-Bonn) [
40]. The predictions for the nuclear EOS based on these 2BFs are grouped together under the name 2BF. The group 2+3BFph rassemble the predictions of the same 2BF interactions supplemented with a 3BF of Urbana type [
41] consisting of the sum of the attractive two-pion-exchange Fujita–Miyazawa force with excitation of an intermediate
-resonance [
42] plus a phenomenological repulsive term. The group 2+3BFmic is a set of microscopic potentials [
43] based on the Av18, Bonn B, or Nijmegen93 [
44] potentials, which are also used to calculate consistently a three-body potential including the virtual excitation of
(1232) and
(1440) resonances and anti-nucleons. In both cases, for the use in the BHF approach, these 3BF have been reduced to an effective two-nucleon density-dependent force by averaging over the coordinates of the third nucleon [
45]. The interested reader is referred to Refs. [
43,
46,
47,
48] for an extensive analysis of the use and effects of 3BF in nuclear matter.
4. Constraining the Skyrme Energy Density Functional
from BHF Calculations
The commonly called standard Skyrme interaction is a contact interaction with momentum-dependent terms, which is expressed in the following form,
where
,
,
is the relative momentum acting on the right,
its conjugate acting on the left, and
is the spin-exchange operator. The last term, proportional to
, corresponds to the zero-range spin-orbit term. It does not contribute to the EOS in homogeneous systems and thus will be ignored for the rest of this article. In its standard form (
16) the Skyrme interaction contributes only in the
and
channels, which implies some limitations which will appear in the following discussion.
In the Hartree-Fock approximation, the total energy density of SM (
) and NM (
) is given respectively as
where the kinetic densities are
and
, and
for
. In this work, we employ the DFT coefficients, e.g.
,
, and
, which can be defined in terms of the Skyrme parameters
and
, see Ref. [
55], where they have been introduced.
Several authors (see, e.g., Refs. [
10,
25,
26,
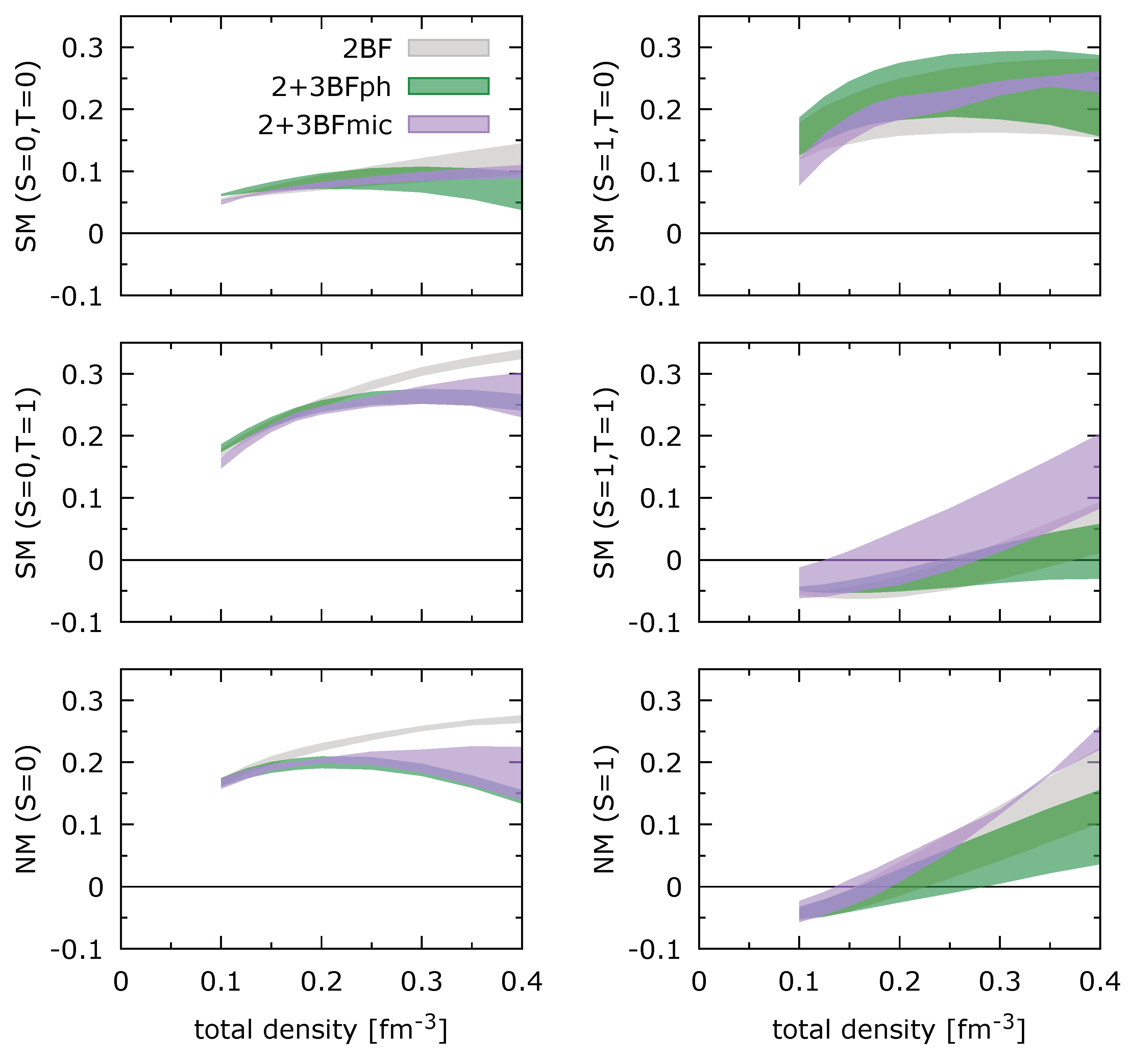
27]) have stressed the interest of using the spin-isospin decomposition of the BHF correlation energy as an additional constraint to better determine the parameters of energy density functionals based on effective interactions such as the Skyrme one. It indeed allows a more detailed determination of the parameters entering into the calculation of the energy per particle by increasing the number of equations to solve. From Equation (
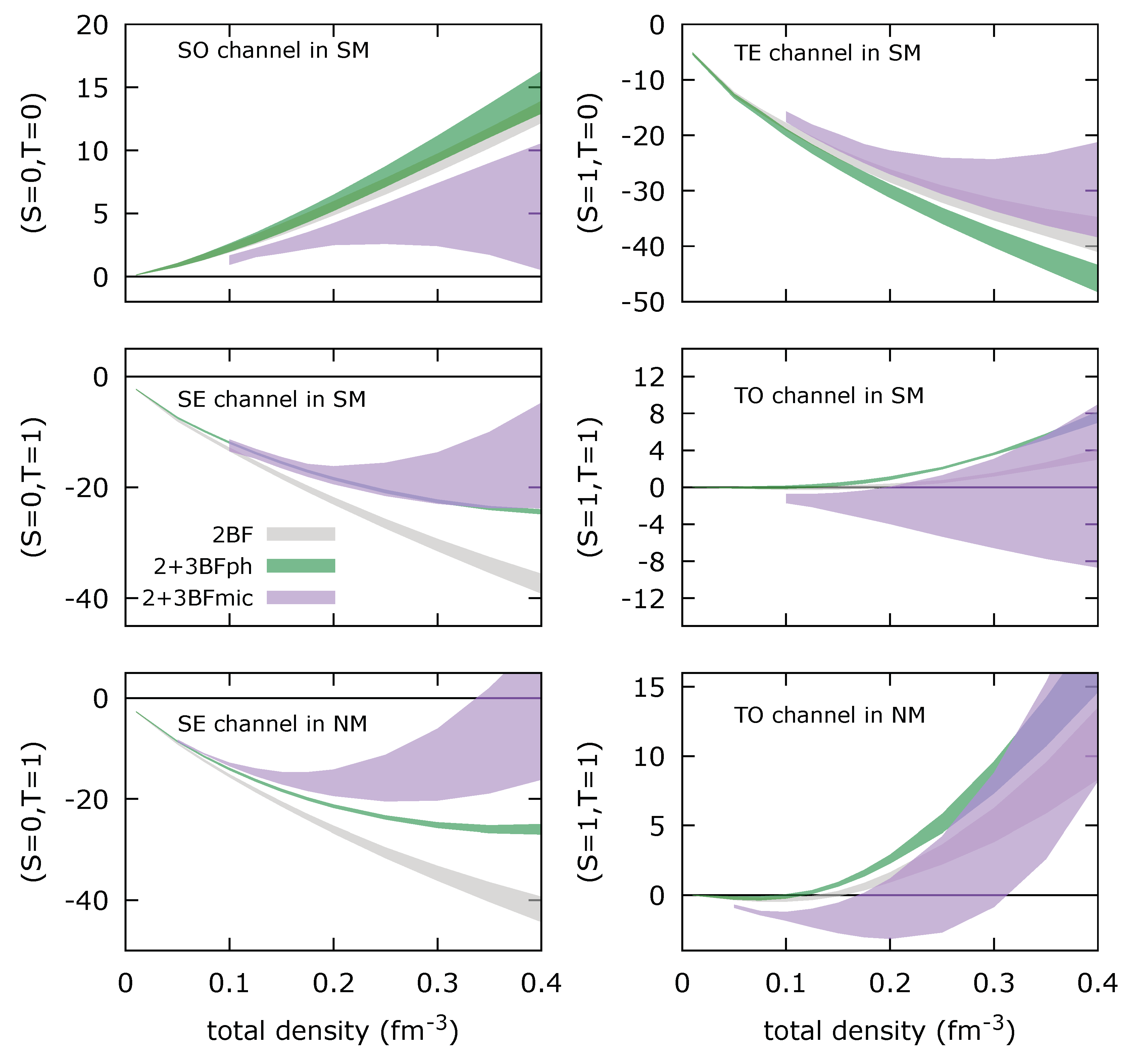
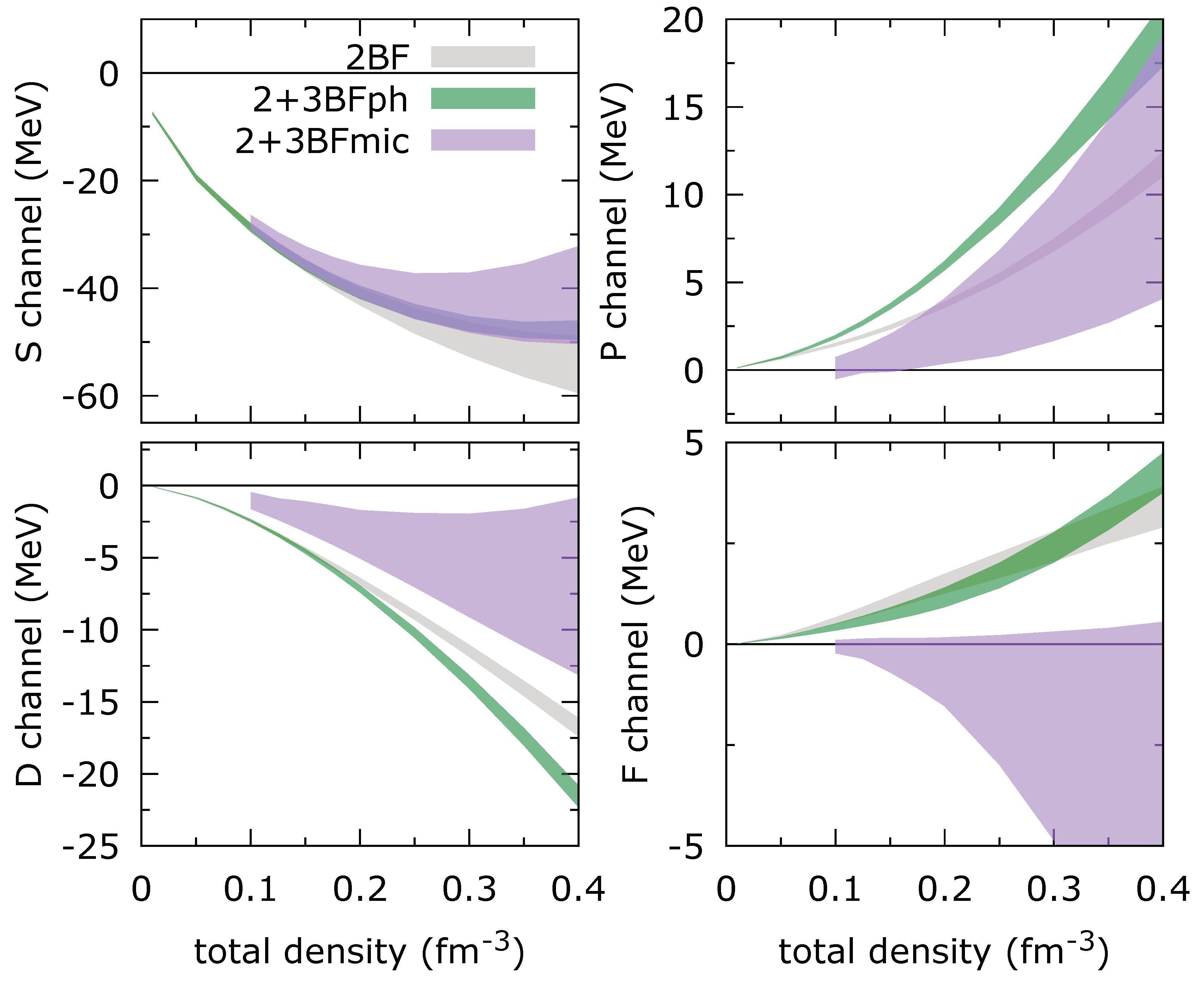
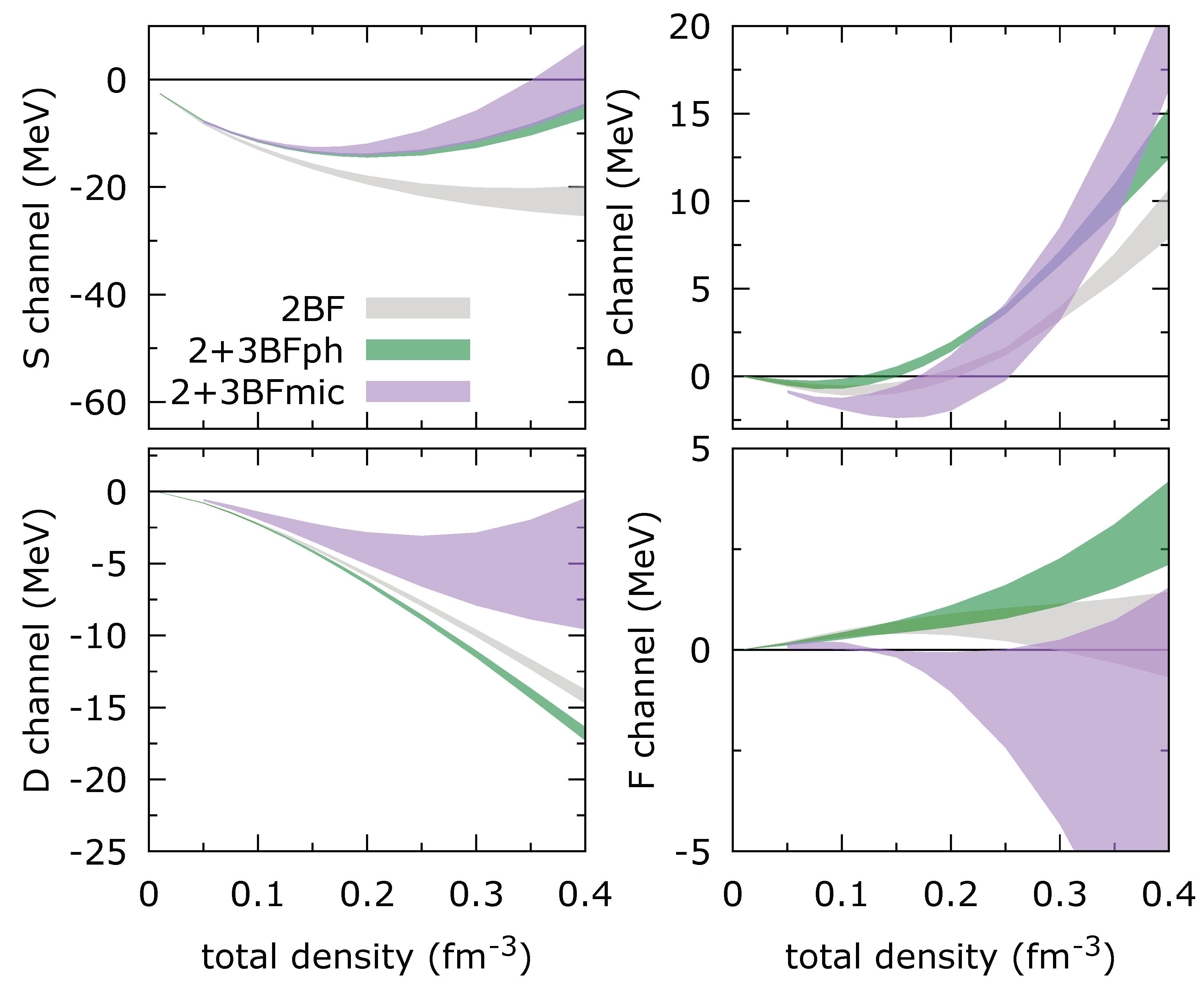
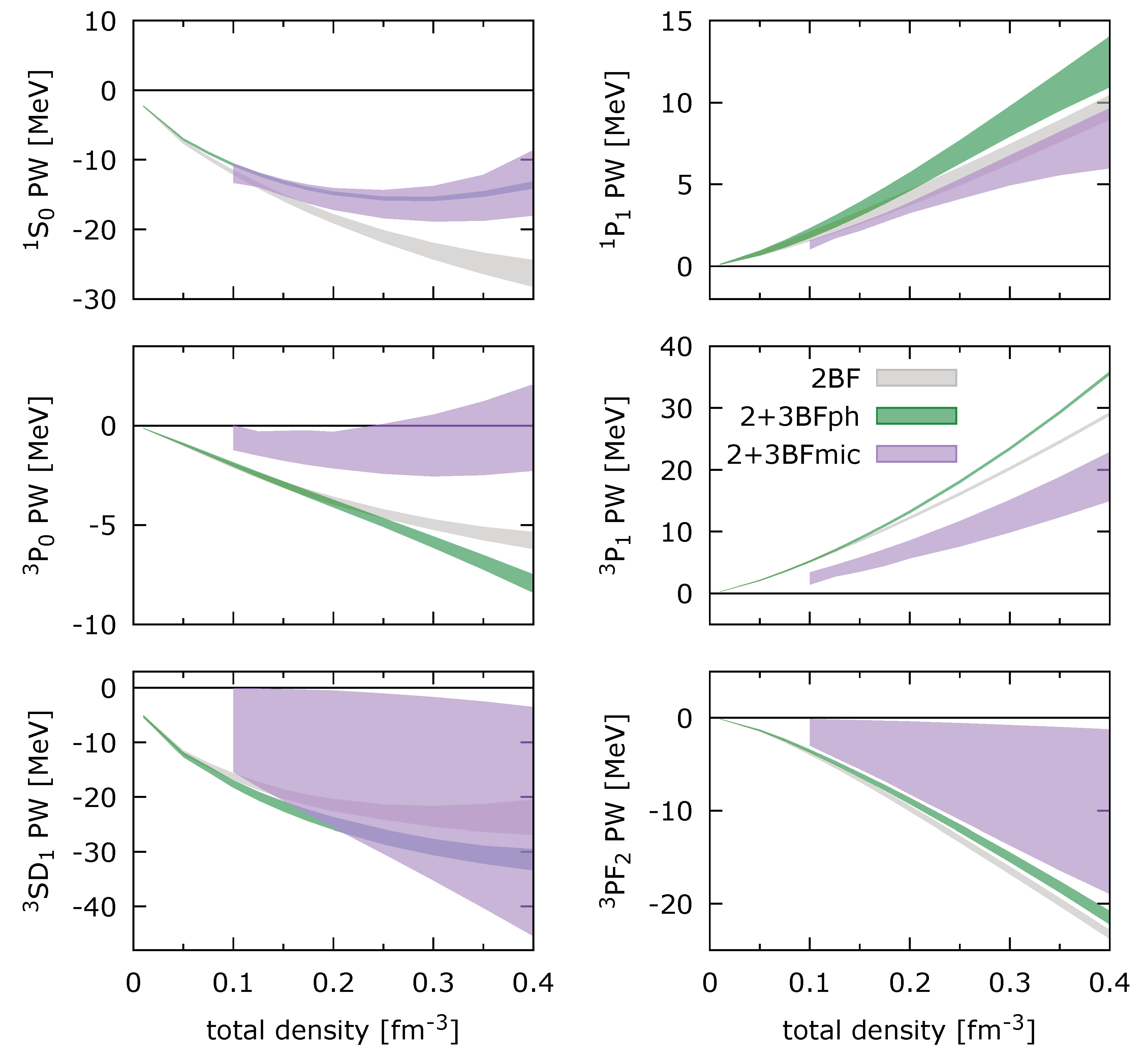
7), one can calculate the decomposition of the correlation energy density in terms of SE
, TE
, SO
, and TO
contributions as [
26]
in SM, and as
in NM. The correlation energy in the channels
and
in SM, and
in NM scales only with the kinetic energy,
and
, because only the angular momentum
can contribute in these channels. In the channels
and
in SM, and
in NM, there is also a term that scales with the density
n reflecting the
contribution of the Skyrme interaction. Depending on the sign of the combination of the coefficients, the energy per particle in the
channels can be positive or negative, in the channels
and
in SM, and
in NM, or can change its sign as a function of the density in the other channels. This is a clear limitation of the standard Skyrme interaction (
16), since BHF calculations predict a richer density dependence, see
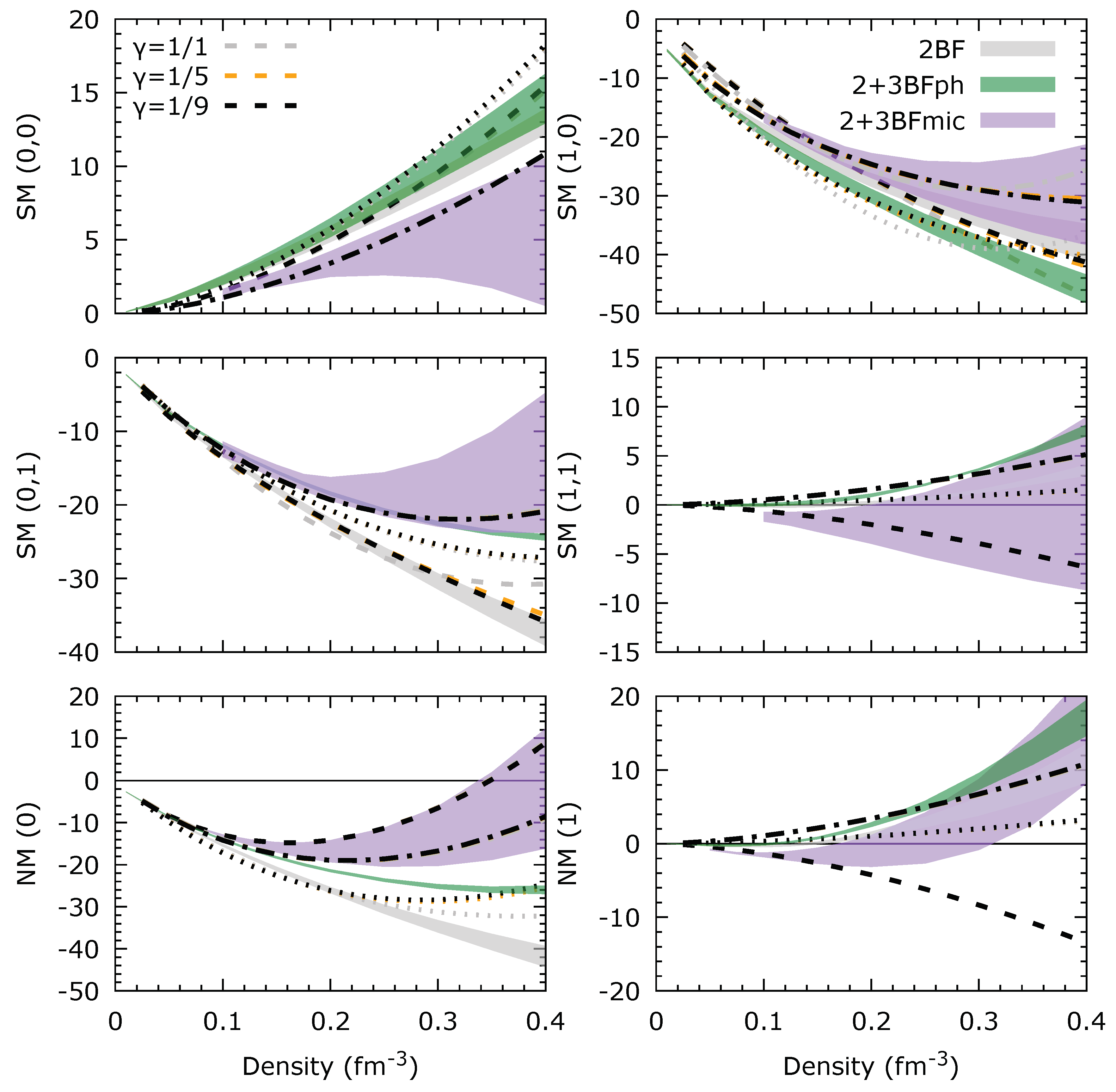
Figure 1 for instance.
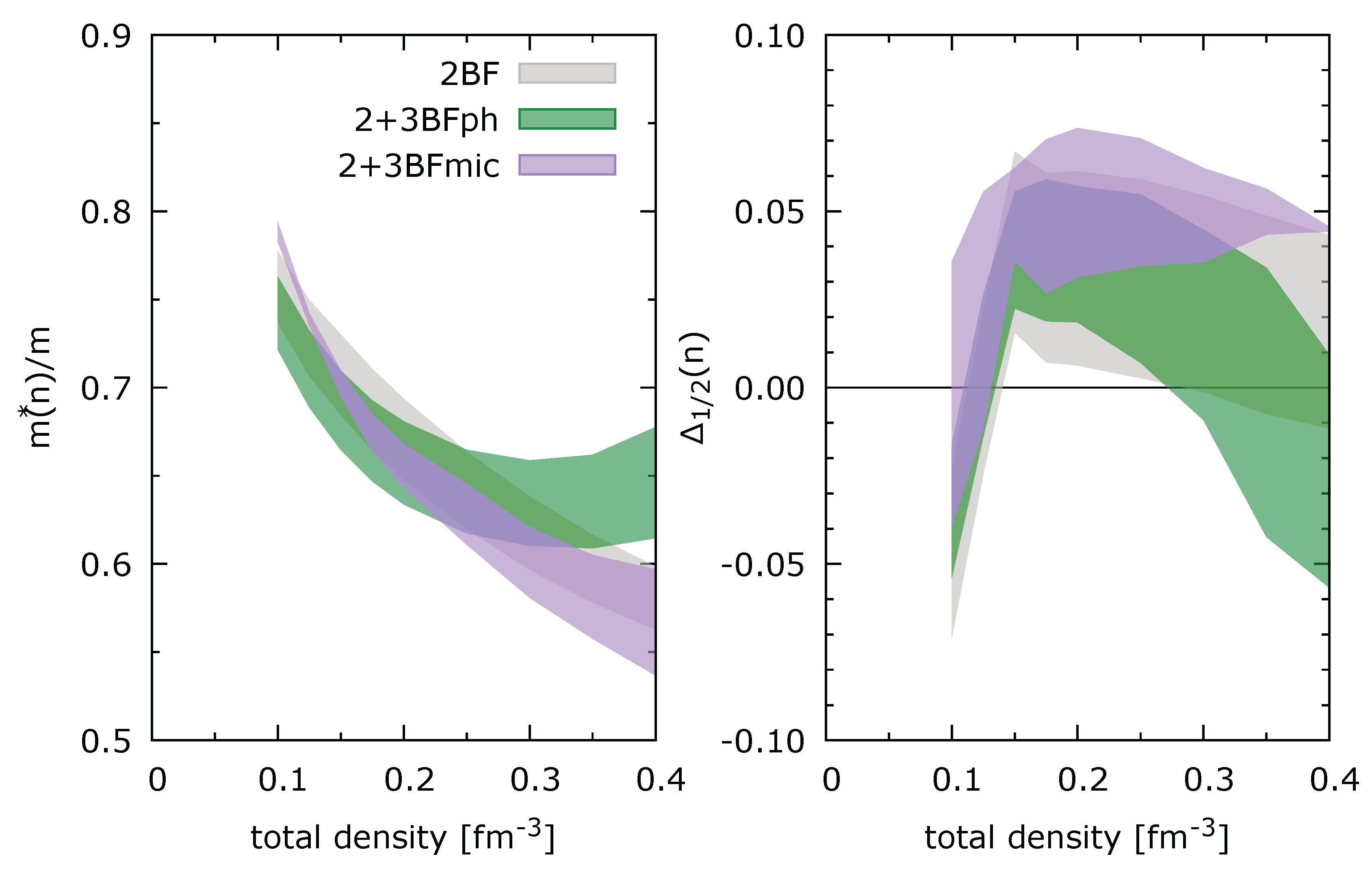
In nuclear matter, the Skyrme interaction is determined by 8 coefficients , , , and , as well as the exponent of the density dependence . We have 6 constraints in terms of the decomposition and we decide to fix the value of the parameter , see hereafter. We therefore need two additional constraints to determine unambiguously all Skyrme parameters. These two other constraints will be given by the effective mass in SM and the isospin splitting, namely from the BHF predictions we fix and for 2BF, 2+3BFph, and 2+3BFmic.
For the Skyrme interaction, the nucleon effective mass is expressed as [
26,
55]
The parameters
and
can therefore be obtained as
where the last approximation is valid for typical small values of
.
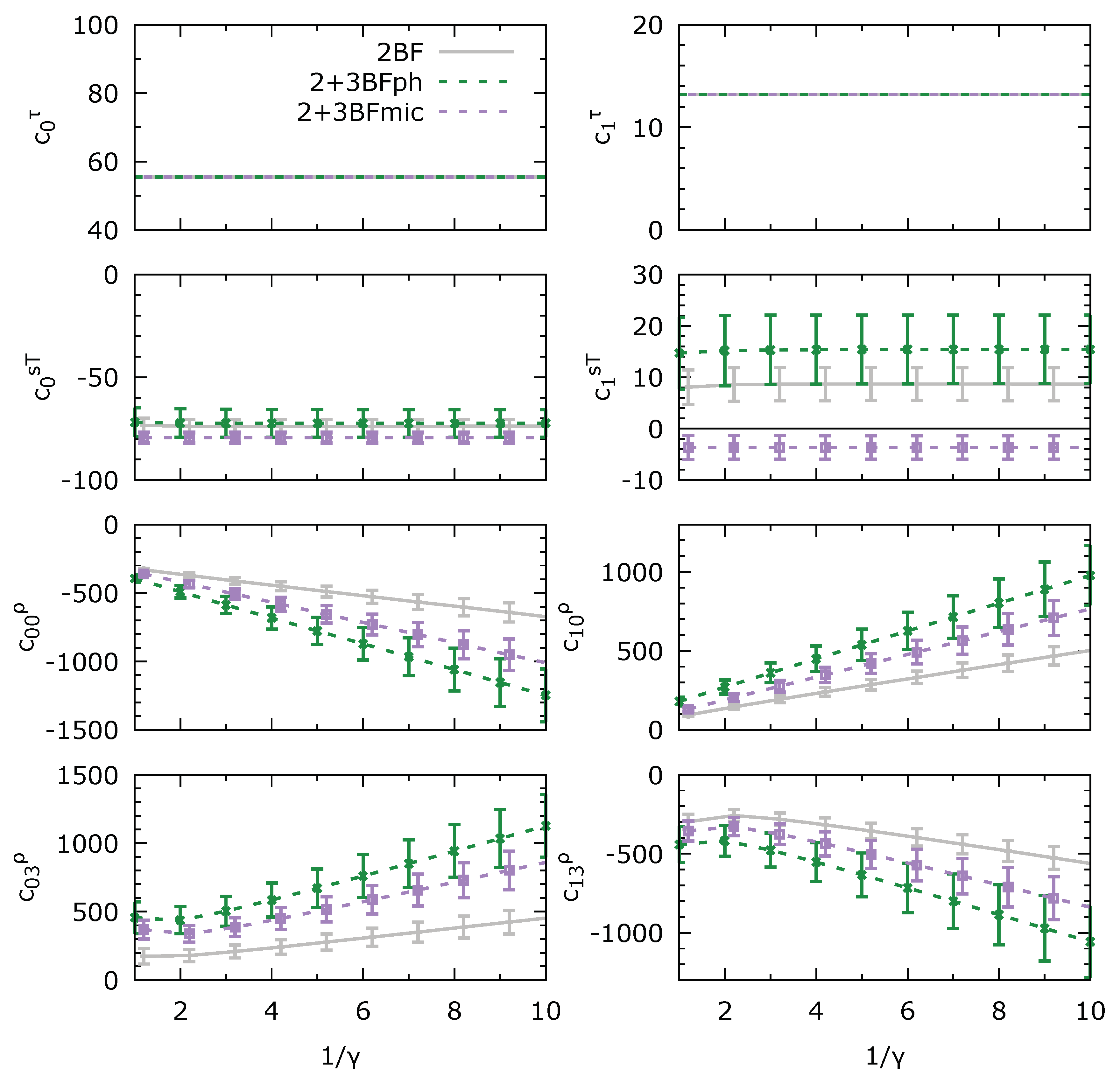
We determine the 8 Skyrme coefficients by imposing the global reproduction of the 6
channels predicted by the BHF calculations in the density range going from 0.01 up to 0.4
in SM and NM (including uncertainties), complemented by the effective mass
and its isospin splitting
. The fit is provided by the nonlinear least-squares Marquardt-Levenberg algorithm encoded in Gnuplot
2. The results are shown in
Figure 8, where the parameter
is explored from 1 to
. The error bars are estimated from the covariant matrix properties at the solution. There are 4 Skyrme coefficients
and
, with
, which are independent of
, and 4 other coefficients
and
, which depend on the value taken for
. We also observe a strong impact of the 3BF for the coefficient
, and a noticeable but less strong impact for the coefficients
and
.
In order to evaluate the quality of the fits, we compare in
Figure 9 the quantities targeted by our fits and the results provided by our fits. The Skyrme spin-isospin
channel decomposition of the correlation energy per particle in SM and NM are shown together with the constraints extracted from BHF calculations. We consider the centroid of the Skyrme coefficients obtained from
Figure 8 and vary the parameter
. The effect of
is very weak since it is absorbed in the values of the coefficients
and
, see
Figure 8. The other four coefficients
and
are independent of
. The quality of the fit is however not very good. This is particularly clear in the following channels:
,
in SM and
in NM. These channels are the ones where only the
contribution of the Skyrme interaction plays a role. The poor reproduction of the BHF results is therefore due to the lack of flexibility of the standard form (
16) of the Skyrme interaction, where higher values of
L are necessary.
Let us remark from
Figure 9 that the 2BF is quite well reproduced by the Skyrme model in SM and for the
,
and
channels. The
channel has a wrong sign in the Skyrme model, although the strength of the interaction in this channel is quite weak. In NM, however, the fit of the 2BF is poor above
. We, therefore, conclude that already at the 2BF level the Skyrme interaction could not reproduce well the BHF predictions in both SM and NM above
.
In Ref. [
10], a set of Skyrme interactions have been obtained by employing the
decomposition in SM for two BHF calculations and the NM channel was controlled globally by variational calculations. The difference with our approach are i) that our uncertainty estimate is based on a larger number of calculations, and ii) that we employ the
channel decomposition in NM to adjust Skyrme EDF. In Ref. [
27], only one BHF calculation is employed to fit the Skyrme EDF and only the
decomposition in SM is employed. In Refs. [
10,
27] data from finite nuclei, e.g. binding energies and charge radii, have been employed in addition to the BHF constraints. It is therefore difficult to perform detailed comparisons of our results with the ones presented in these papers. We however conclude from our analysis that the standard Skyrme EDF should be enriched, with higher
L terms for instance, in order to reproduce BHF calculations in
channel in SM and NM up to at least 0.4
. The results presented in this paper can be employed for such aim.