Submitted:
30 March 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD), Gut-Brain Axis (GBA) Interactions and Neurodegeneration
Aim
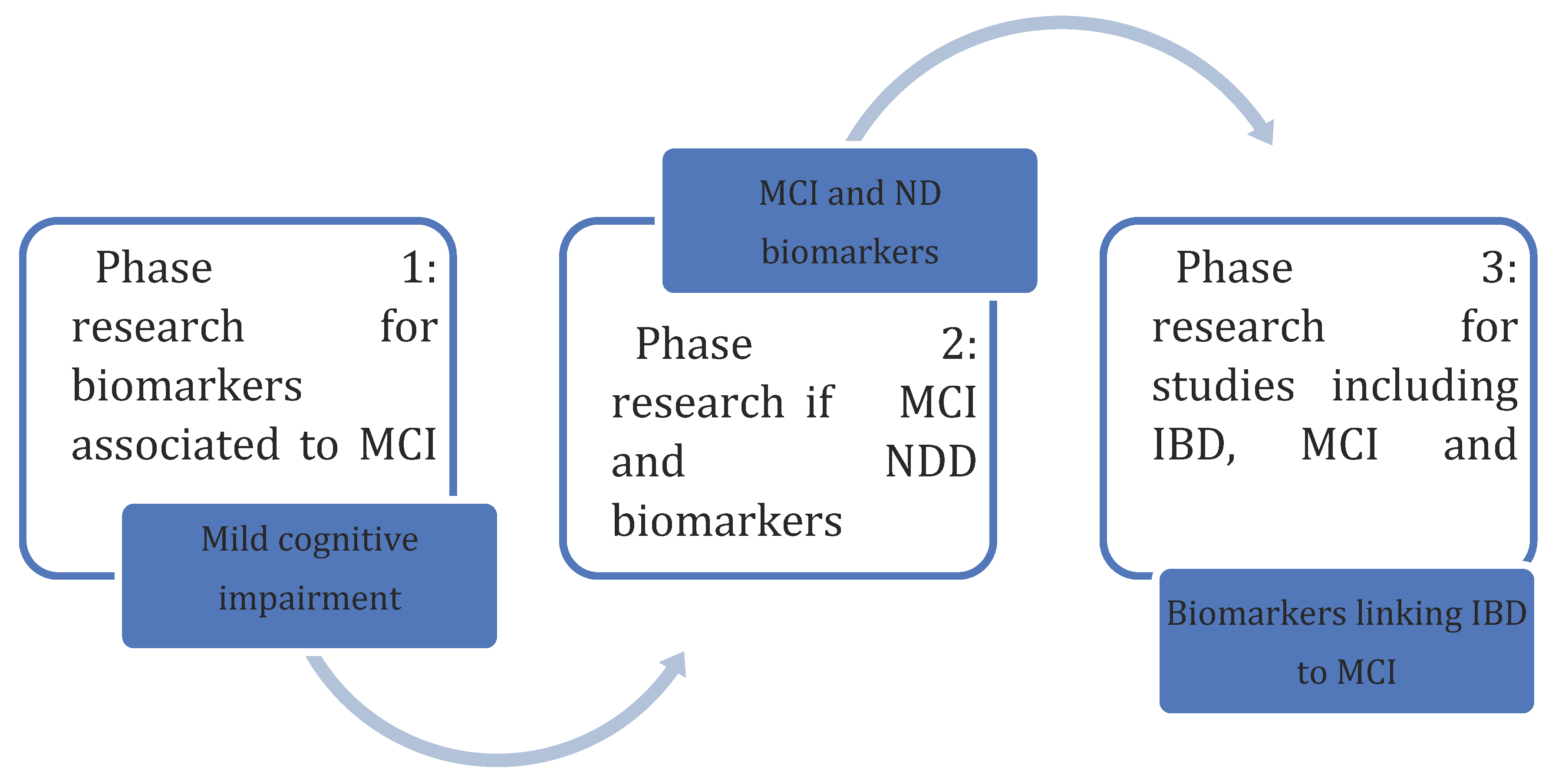
Methodology
Neurodegeneration as an Extraintestinal Manifestation of IBD
Mild Cognitive Impairment: Definition, Risk Factors and Diagnosis
The Presumed Link between IBD and MCI
Gut Microbiome Alterations and MCI
Serum Biomarkers as Predictors for MCI
Vitamin D3
C reactive Protein and High-Sensivity C Reactive Protein
Vitamin B12
Homocysteine
Serum Amyloid
Neuron Specific Enolase
Neurofilament Light Chain
S100 Proteins
Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor
IL-6
LP-2 Associated Phospholipase
Prostaglandin E2
IL-1β
TNF- ɑ
Conclusions
Abbreviation list
| AD | Alzheimer's Disease |
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BBB | Blood brain barrier |
| BDNF | Brain derived neurotrophic factor |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CRP | C reactive protein |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| ENS | Enteric nervous system |
| FTD | Fronto-temporal dementia |
| GBA | Gut-brain axis |
| HD | Huntignton’s Disease |
| HPAA | Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis |
| IBDs | Inflammatory bowel disease(s) |
| IBS | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| LBD | Lewy body dementia |
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| ND | Neurodegeneration |
| NDDs | Neurodegenerative disease(s) |
| NfL | Neurofilament light chain |
| NMO | Neuromielytis optica |
| NSE | Neuron specific enoloase |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| SAA | Serum amyloid A |
| SCFA | Short chain fatty acids |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
References
- McDowell C, Farooq U, Haseeb M. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. 2023 Aug 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B.L.; Bernstein, C.N. Brain-Gut Interactions in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gîlcă-Blanariu, G.-E.; Șchiopu, C.G.; Ștefănescu, G.; Mihai, C.; Diaconescu, S.; Afrăsânie, V.A.; Lupu, V.V.; Lupu, A.; Boloș, A.; Ștefănescu, C. The Intertwining Roads between Psychological Distress and Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abautret-Daly. ; Dempsey, E.; Parra-Blanco, A.; Medina, C.; Harkin, A. Gut–brain actions underlying comorbid anxiety and depression associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2017, 30, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q.X.; Soh, A.Y.S.; Loke, W.; Lim, D.Y.; Yeo, W.-S. The role of inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfi, D.; Moro, E.; Bosi, A.; Bistoletti, M.; Cerantola, S.; Crema, F.; Maggi, F.; Giron, M.C.; Giaroni, C.; Baj, A. Impact of Microbial Metabolites on Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, L. ‘All disease begins in the gut’: was Hippocrates right? Brain 2018, 141, e20–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, K.G. Changes in life expectancy 1900–1990. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 55, 1196S–1202S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Chen, M.-H.; Wang, H.E.; Lu, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-P.; Zhang, B. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Gut Liver 2023, 17, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.; Li, S.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X. Are neurodegenerative diseases associated with an increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease? A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 956005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, E.R.; Hong, S.N.; Chang, D.K.; Kim, Y.-H. Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Nationwide Population-based Cohort Study. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 16, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szandruk-Bender, M.; Wiatrak, B.; Szeląg, A. The Risk of Developing Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Chen, M.-H.; Wang, H.E.; Lu, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-P.; Zhang, B. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Gut Liver 2023, 17, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Lobbestael, E.; Vermeire, S.; Sabino, J.; Cleynen, I. Inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease: common pathophysiological links. Gut 2020, 70, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Wang, J.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, R.; Tong, S.; Wu, H.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, Q.; Leung, F.W.; Sha, W.; et al. Lack of Causal Associations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Parkinson's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, H.H. Mild Cognitive Impairment. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2005, 13, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.D. State of the science on mild cognitive impairment (MCI). CNS Spectrums 2019, 24, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnode, C.D.; Perdue, L.A.; Rossom, R.C.; Rushkin, M.C.; Redmond, N.; Thomas, R.G.; Lin, J.S. Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults. JAMA 2020, 323, 764–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, B. Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Geriatrics. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 34, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, C.W.; Powell, N.; Norton, C.; Dumbrill, J.L.; Hayee, B.; Moulton, C.D. Cognitive Impairment in Adult Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychosom. 2021, 62, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Dhiman, S.; Bodh, V.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, B. Cognitive dysfunction in ulcerative colitis patients in remission and its comparison with patients with irritable bowel syndrome and healthy controls. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 40, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Du, H. Inflammatory bowel disease: A potential pathogenic factor of Alzheimer's disease. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 119, 110610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, L.; Cantoni, C.; Rotondo, E.; Galimberti, D. The Gut Microbiome–Brain Crosstalk in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, A.R.L.; Monroy, G.R.; Salazar, F.E.; Lee, J.-Y.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H.; Borlongan, C.V. Gut–Brain Axis as a Pathological and Therapeutic Target for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yue, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, H.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interact With the Brain Through Systemic Chronic Inflammation: Implications on Neuroinflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Aging. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 796288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, W.; Ding, S.; Zheng, L.; Liang, X.; Luo, J.; Ding, D.; et al. Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Clinical Relevance in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Shanghai Aging Study and Shanghai Memory Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljumaah, M.R.; Bhatia, U.; Roach, J.; Gunstad, J.; Peril, M.A.A. The gut microbiome, mild cognitive impairment, and probiotics: A randomized clinical trial in middle-aged and older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, H.; Jegou, S.; McQuitty, C.; Straub, M.; Leducq, V.; Landman, C.; Kirchgesner, J.; Le Gall, G.; Bourrier, A.; Nion-Larmurier, I.; et al. Specificities of the intestinal microbiota in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and Clostridium difficile infection. Gut Microbes 2017, 9, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhan, S.; Tian, Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Zhuang, X. Alterations in Bile Acid Metabolism Associated With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 1525–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrad, J.E.; Chen, Z.; Devlin, J.; Ruggles, K.V.; Cadwell, K. Pathogen-Specific Alterations in the Gut Microbiota Predict Outcomes in Flare of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Complicated by Gastrointestinal Infection. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 14, e00550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, G.; Raimo, S.; Erro, R.; Picillo, M.; Amboni, M.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Pivonello, C.; Barone, P.; Vitale, C. Vitamin D as a possible biomarker of mild cognitive impairment in parkinsonians. Aging Ment. Heal. 2020, 25, 1998–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavoaca, D.; Birle, C.; Stan, A.; Tatomir, A.; Popa, O.; Rosu, P.; Vulcan, A.-M.; Chira, D.; Popa, L.L.; Dina, C.; et al. Prediction of Neurocognitive Outcome after Moderate-Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Using Serum Neuron-Specific Enolase and S100 biomarkers. J. Med. Life 2020, 13, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benussi, A.; Ashton, N.J.; Karikari, T.K.; Alberici, A.; Saraceno, C.; Ghidoni, R.; Benussi, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Borroni, B. Prodromal frontotemporal dementia: clinical features and predictors of progression. Alzheimer's Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Christakos, S. Mechanisms Underlying the Regulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by Vitamin D. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8251–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivona, G.; Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. The immunological implication of the new vitamin D metabolism. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombash, S.E.; Lee, P.W.; Sawdai, E.; Lovett-Racke, A.E. Vitamin D as a Risk Factor for Multiple Sclerosis: Immunoregulatory or Neuroprotective? Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 796933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Ji, H.-F. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia: evidence from meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amin, M.; Bradford, D.; Sullivan, R.K.P.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Moon, Y.; Han, S.; Zalesky, A.; Burne, T.H.J. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with reduced hippocampal volume and disrupted structural connectivity in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 40, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Shah, J. Vitamin D3 supplementation ameliorates cognitive impairment and alters neurodegenerative and inflammatory markers in scopolamine induced rat model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 2653–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Michalski, E.S.; Tangpricha, V.; Chesdachai, S.; Kumar, A.; Prince, J.; Ziegler, T.R.; Suchdev, P.S.; Kugathasan, S. Vitamin D Status Is Associated with Hepcidin and Hemoglobin Concentrations in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviezel, D.; Maissen, S.; Niess, J.H.; Kiss, C.; Hruz, P. High Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2017, 2, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffler, H.; Schmidt, M.; Huth, A.; Reiner, J.; Glass. ; Lamprecht, G. Clinical factors are associated with vitamin D levels in IBD patients: A retrospective analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 19, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajettoab, A.; Bonaviaab, R.; Barberoab, S.; Florioa, T.; Schettiniab, G. Chemokines and Their Receptors in the Central Nervous System. Front. Neuroendocr. 2001, 22, 147–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Fritzer-Szekeres, M.; Szekeres, T.; Gehrig, T.; Gyöngyösi, M.; Bergler-Klein, J. Comparison of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein vs C-reactive Protein for Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in Chronic Cardiac Disease. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2022, 7, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mańkowska-Wierzbicka, D.; Karczewski, J.; Poniedziałek, B.; Grzymisławska, M.; Staszewski, R.; Królczyk, A.; Dobrowolska, A.; Grzymisławski, M. C-reactive protein as a diagnostic and prognostic factor in inflammatory bowel diseases. 70, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.G.; Stevens, B.W.; Guo, A.Y.; Russell, C.N.; Thornton, A.; Cohen, M.A.; Sturgeon, H.C.; Giallourakis, C.; Khalili, H.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. High C-Reactive Protein Is Associated with Poor Sleep Quality Independent of Nocturnal Symptoms in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinni, E. Alexithymic characteristics and interoceptive abilities are associated with disease severity and levels of C-reactive protein and cytokines in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2023, 36, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Xie, W. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and cognitive decline: the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Psychol. Med. 2017, 48, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Lewis, N.; E Knight, J. Longitudinal associations between C-reactive protein and cognitive performance in normative cognitive ageing and dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 50, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komulainen, P.; Lakka, T.A.; Kivipelto, M.; Hassinen, M.; Penttilä, I.M.; Helkala, E.-L.; Gylling, H.; Nissinen, A.; Rauramaa, R. Serum high sensitivity C-reactive protein and cognitive function in elderly women. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 36, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugaj, M.; Gerwig, M.; Wege, N.; Siegrist, J.; Mann, K.; Bröcker-Preuß, M.; Dragano, N.; Moebus, S.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Bokhof, B.; et al. Elevated Levels of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein are Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment and its Subtypes: Results of a Population-Based Case-Control Study. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2012, 28, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Ospina, C.A.; Nava-Mesa, M.O. B Vitamins in the nervous system: Current knowledge of the biochemical modes of action and synergies of thiamine, pyridoxine, and cobalamin. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 26, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbulut, S. An assessment of serum vitamin B12 and folate in patients with Crohn’s disease. Medicine 2022, 101, e31892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.G.; Kariyawasam, V.C.; Mogan, S.B.; Patel, K.V.; Pantelidou, M.; Sobczyńska-Malefora, A.; Porté, F.; Griffin, N.; Anderson, S.H.C.; Sanderson, J.D.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Functional Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Patients with Crohnʼs Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2839–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headstrom, P.D.; Rulyak, S.J.; Lee, S.D. Prevalence of and risk factors for vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with Crohnʼs disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.; Mander, A.; Ames, D.; Carne, R.; Sanders, K.; Watters, D. Cognitive impairment and vitamin B12: a review. Int. Psychogeriatrics 2012, 24, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jatoi, S.; Hafeez, A.; Riaz, S.U.; Ali, A.; Ghauri, M.I.; Zehra, M. Low Vitamin B12 Levels: An Underestimated Cause Of Minimal Cognitive Impairment And Dementia. Cureus 2020, 12, e6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilland, J.-C.; Favier, A.; de Courcy, G.P.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S. L’hyperhomocystéinémie : facteur de risque cardiovasculaire ou simple marqueur ?: 1. Données fondamentales. Pathol. Biol. 2003, 51, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, H.; Collins, G.; Pyle, R.; Deep-Dixit, V.; Taub, D.D. The immunoregulatory effects of homocysteine and its intermediates on T-lymphocyte function. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2004, 125, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ientile, R.; Curro', M.; Ferlazzo, N.; Condello, S.; Caccamo, D.; Pisani, F. Homocysteine vitamin determinants and neurological diseases. Front. Biosci. 2010, S2, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Sgambato, A.; Papa, A.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pola, R.; Sans, M.; Lovecchio, M.; Gasbarrini, G.; Cittadini, A.; Gasbarrini, A. Homocysteine Triggers Mucosal Microvascular Activation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, I.; Raijmakers, M.; Peters, W.; Hoensch, H.; Kirch, W. Homocysteine, Cysteine, and Glutathione in Human Colonic Mucosa: Elevated Levels of Homocysteine in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, A.J.; Karlinsky, H. Folate, vitamin B12 and cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1992, 86, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levels of Vitamins and Homocysteine in Older Adults with Alzheimer Disease or Mild Cognitive Impairment in Cuba. MEDICC Rev. 2020, 22, 40. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, R.-J. Homocysteine as a biomarker for cognitive dysfunction in the elderly. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, N.; Jernerén, F.; Turner, C.; Hart, K.; Tabet, N. Homocysteine concentrations in the cognitive progression of Alzheimer's disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 99, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.; Busse, S.; von Hoff, F.; Borucki, K.; Frodl, T.; Busse, M. Association Between Homocysteine and Vitamin Levels in Demented Patients. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2021, 81, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Song, A.; An, P.; Du, Y.; Xu, W.; Huang, G. Effects of Folic Acid and Vitamin B12, Alone and in Combination on Cognitive Function and Inflammatory Factors in the Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Single-blind Experimental Design. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.E.; Whitehead, A.S. Regulation of serum amyloid A protein expression during the acute-phase response. Biochem. J. 1998, 334, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokote, H.; Yagi, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Amino, T.; Kamata, T.; Mizusawa, H. Serum amyloid A level is increased in neuromyelitis optica and atypical multiple sclerosis with smaller T2 lesion volume in brain MRI. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 259, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarur, A.J.; Quintero, M.A.; Jain, A.; Czul, F.; Barkin, J.S.; Abreu, M.T. Serum Amyloid A as a Surrogate Marker for Mucosal and Histologic Inflammation in Patients with Crohnʼs Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 10.1186/s12876-020-01229-8. PMID: 32245401; PMCID: PMC7118889.
- Crouch, P.J.; Harding, S.-M.E.; White, A.R.; Camakaris, J.; Bush, A.I.; Masters, C.L. Mechanisms of Aβ mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.H.; Kang, M.J.; Youn, Y.C.; An, S.S.A.; Kim, S. Alpha-synuclein: a pathological factor with Aβ and tau and biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer's Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirino, T.; Brightman, M.; Oertel, W.; Schmechel, D.; Marangos, P. Neuron-specific enolase as an index of neuronal regeneration and reinnervation. J. Neurosci. 1983, 3, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, A.J.; Reddy, K.; Mohammed, N.; Tandra, S.R.; Kandadai, R.M.; Kss, S.B. Neuron specific enolase as a marker of seizure related neuronal injury. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarna, H.; Delafosse, B.; Steinberg, R.; Debilly, G.; Mandrand, B.; Keller, A.; Pujol, J. Neuron-specific enolase as a marker of neuronal lesions during various comas in man. Neurochem. Int. 1982, 4, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busikova-Malenovska, P.; Danis, D.; Bencat, M.; Galfiova, P.; Kopani, M.; Labajova, V.; El Hassoun, O.; Porubsky, J.; Galatova, J. Neuron-specific enolase in the intestinal wall in Crohn´s disease. Bratisl. Med J. 2014, 115, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, A.; Polcyn, R.; Matzelle, D.; Banik, N.L. New Insights into the Role of Neuron-Specific Enolase in Neuro-Inflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Neuroprotection. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanacci, V.; Bassotti, G.; Nascimbeni, R.; Antonelli, E.; Cadei, M.; Fisogni, S.; Salerni, B.; Geboes, K.; Villanacci, V.; Bassotti, G.; et al. Enteric nervous system abnormalities in inflammatory bowel diseases. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, S.; Andriolo, M.; Boccagni, C.; Lucca, L.F.; De Tanti, A.; Pistarini, C.; Barone, T.; Galardi, G. Reduced Neuron-Specific Enolase Levels in Chronic Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancioiu, F.; Bogdan, R.; Dumitrescu, R. Neuron-Specific Enolase (NSE) as a Biomarker for Autistic Spectrum Disease (ASD). Life 2023, 13, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Li, J.-Q.; Hou, X.-H.; Ou, Y.-N.; Yu, J.-T.; Tan, L. Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood as a Biomarker for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2019, 72, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heizmann, C.W.; Fritz, G.; Schäfer, B.W. S100 proteins structure functions and pathology. Front. Biosci. 2002, 7, d1356–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss B, Ecsédi P, Simon M, Nyitray L. Isolation and Characterization of S100 Protein-Protein Complexes. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1929:325-338. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, R. Chromosomal mapping, differential origin and evolution of the S100 gene family. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2008, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, C. S100B protein in the gut: The evidence for enteroglial-sustained intestinal inflammation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1261–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michetti, F.; Di Sante, G.; Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Casalbore, P.; Volonté, C.; Spica, V.R.; Parnigotto, P.P.; Di Liddo, R.; Amadio, S.; et al. Growing role of S100B protein as a putative therapeutic target for neurological- and nonneurological-disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresnick, A.R. S100 proteins as therapeutic targets. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azman, K.F.; Zakaria, R. Recent Advances on the Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, C.; Cattaneo, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małczyńska, P.; Piotrowicz, Z.; Drabarek, D.; Langfort, J.; Chalimoniuk, M. Rola mózgowego czynnika neurotroficznego (BDNF) w procesach neurodegeneracji oraz w mechanizmach neuroregeneracji wywołanej wzmożoną aktywnością fizyczną. 65, 8. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Chauhan, L.; Bhardwaj, A.; Sharma, A.; Fayaz, F.; Kumar, B.; Alhashmi, M.; AlHajri, N.; Alam, S.; Pottoo, F.H. Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, T.J.; Martinez, C.; Niesler, B.; van der Voort, I.; Mönnikes, H.; Stengel, A.; Goebel-Stengel, M. The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-B.; Zuo, X.-L.; Zhao, Q.-J.; Chen, F.-X.; Yang, J.; Dong, Y.-Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.-Q. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2011, 61, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochal, M.; Ditmer, M.; Binienda, A.; Gabryelska, A.; Białasiewicz, P.; Talar-Wojnarowska, R.; Fichna, J.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E. Relation between Selected Sleep Parameters, Depression, Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy, and the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Pathway in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Metabolites 2023, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economos, A.; Wright, C.B.; Moon, Y.P.; Rundek, T.; Rabbani, L.; Paik, M.C.; Sacco, R.L.; Elkind, M.S. Interleukin 6 Plasma Concentration Associates with Cognitive Decline: The Northern Manhattan Study. Neuroepidemiology 2013, 40, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, T.; Kusugami, K.; Ina, K.; Ando, T.; Shinoda, M.; Imada, A.; Ohsuga, M.; Sakai, T.; Matsuura, T.; Ito, K.; et al. Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptor in the colonic mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1999, 14, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, M.M.; Alkhayyat, M.; Saleh, M.A.; Sarmini, M.T.; Singh, A.; Garg, R.; Garg, P.M.; Mansoor, E.; Padival, R.; Cohen, B.L.M. Alzheimer Disease Occurs More Frequently In Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.O.; Geda, Y.E.; Knopman, D.S.; Boeve, B.F.; Christianson, T.J.; Pankratz, V.S.; Kullo, I.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; Ivnik, R.J.; Petersen, R.C. Association of C-reactive protein with mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer's Dement. 2009, 5, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapamäki, M.M.; Grönroos, J.M.; Nurmi, H.; Söderlund, K.; Peuravuori, H.; Alanen, K.; Nevalainen, T.J. Elevated Group 11 Phospholipase A2 Mass Concentration in Serum and Colonic Mucosa in Crohn's Disease. cclm 1998, 36, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadou, E.G.; Katsipis, G.; Tsolaki, M.; Pantazaki, A.A. Involvement and relationship of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and cyclooxygenases levels in Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 357, 577561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Scherl, E.; Du, B.; Tai, H.-H.; Greifer, M.; Petrovic, L.; Daikoku, T.; Dey, S.K.; Subbaramaiah, K.; et al. Levels of NAD+-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase are reduced in inflammatory bowel disease: evidence for involvement of TNF-α. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G361–G368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.-L.; Shen, Y.-D.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Hu, X.-Y.; Lu, P.-L.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Roles of the prostaglandin E2 receptors EP subtypes in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2010, 26, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.P.; Sharkey, K.A.; Mawe, G.M. Effects of PGE2 in guinea pig colonic myenteric ganglia. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G1388–G1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Yan, H.; Bao, S.; Fei, J. Bioluminescence imaging for IL-1β expression in experimental colitis. J. Inflamm. 2013, 10, 16–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cominelli, F.; Nast, C.C.; Clark, B.D.; Schindler, R.; Lierena, R.; E Eysselein, V.; Thompson, R.C.; A Dinarello, C. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) gene expression, synthesis, and effect of specific IL-1 receptor blockade in rabbit immune complex colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin WS, Mrak RE. Interleukin-1 in the genesis and progression of and risk for development of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;72(2):233-238.
- Berrill, J.W.; Gallacher, J.; Hood, K.; Green, J.T.; Matthews, S.B.; Campbell, A.K.; Smith, A.; Berrill, J.W.; Gallacher, J.; Hood, K.; et al. An observational study of cognitive function in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 918–e704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.-B.; Sheng, G.-Q. 白介素1β 与学习和记忆. Neurosci. Bull. 2010, 26, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.C.; Ortigosa, L.C.; Benard, G. Anti-TNF-α agents in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: mechanisms of action and pitfalls. Immunotherapy 2010, 2, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M.A.; Chao, C.-Y.; Staudacher, H.M.; Kolosky, N.A.; Talley, N.J.; Holtmann, G. Anti-TNFα therapy in IBD alters brain activity reflecting visceral sensory function and cognitive-affective biases. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0193542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Dong, R.; Song, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, M.; Lv, C.; Wang, L.; Kou, J.; Xie, H.; et al. Mediation Effects of IL-1β and IL-18 on the Association Between Vitamin D Levels and Mild Cognitive Impairment Among Chinese Older Adults: A Case–Control Study in Taiyuan, China. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 836311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




