1. Introduction
Bartonella constitutes a group of widely parasitic, aerobic, and microaerobic gram-negative bacteria found within animal cells. Taxonomically, it falls under subgroup α2 of the class Alphaproteobacteria, order Hyphomicrobiales, family
Bartonellaceae, genus
Bartonella. There are a total of 39 species and 3 subspecies with valid taxonomic status in this genus (
https://www.bacterio.net/genus/bartonella, assessed on 14 January 2024). Seventeen of these
Bartonella species or subspecies have been confirmed to be associated with human diseases [
1], with six transmitted by rodents recognized as human pathogens, including
Bartonella grahamii [
2],
Bartonella elizabethae [
3],
Bartonella tribocorum [
4],
Bartonella vinsonii subsp. arupensis [
5],
Bartonella washoensis [
6], and
Bartonella tamiae [
7]. These pathogens collectively cause bartonellosis, leading to various human illnesses such as cat-scratch disease, Carrion’s disease, chronic lymphadenopathy, endocarditis, trench fever, chronic bacteraemia, bacillary angiomatosis, bacillary peliosis, vasculitis, uveitis, and others [
1]. Globally, as of 2022, 24 cases of rodent-associated
Bartonella species in humans have been reported [
8].
Bartonella, as a zoonotic pathogen, is prevalent in both wild and domestic mammals, displaying a considerable degree of prevalence and genetic diversity [
9], a trait evolved to enhance evasion of host animal immunity [
10]. The initial documented case of
Bartonella spp. infecting a person was “trench fever” during World War I, attributed to the louse-borne
Bartonella quintana [
11]. Currently,
Bartonella is distributed worldwide, reported in all regions except the Middle East, Central Africa, and Latin America, where countries with low health coverage remain uninvestigated.
Bartonella infects a diverse array of host animals, primarily including mammals such as Rodentia [
12], Lagomorpha [
13], Carnivora [
14], Chiroptera [
15], Artiodactyla [
16,
17], as well as Primates (e.g., macaques) [
18], Insectivora (e.g., shrews) [
19], and certain birds and fish.
Since the 1980s, molecular technology has continually advanced the classification of
Bartonella, progressing from DNA-DNA hybridization technology to multi-locus sequence analysis (MLSA), and the use of single-gene detection technology. Detected genes encompass 16S rDNA, 16S-23S rRNA intergenic spacer region (ITS), citrate synthase (
gltA), genes encoding RNA polymerase subunits (
rpoB), riboflavin synthase gene (
ribC),
groEL, cytosolic protein gene (
ftsZ), cell division protein gene (
ftsZ), etc. Notably, the
rpoB gene has emerged as a reliable, reproducible, and accurate tool for bacterial detection and identification [
20]. The
rpoB gene, being a widespread single-copy gene in bacteria, is characterized by its susceptibility to synonymous substitutions and substantial conservation [
21,
22]. La Scola et al. conducted a comparative analysis of seven different loci in
Bartonella, revealing that the
rpoB and
gltA genes, utilized for intraspecific differentiation, proved to be the most effective [
10]. However, it is noteworthy that homologous recombination events have been observed within the
gltA gene. In conventional PCR, both the
rpoB and
gltA genes are commonly employed for the detection of
Bartonella sp. Despite the effectiveness of this approach, traditional PCR has its limitations. To overcome the drawbacks associated with traditional PCR, the detection of single-copy prokaryotic specific molecules, such as the
ssrA gene, has been facilitated through quantitative PCR (qPCR). This method offers heightened specificity and sensitivity in the
Bartonella assay, enabling a more precise and accurate assessment of the presence of
Bartonella species.
In this research, our focus was on assessing the prevalence of Bartonella species among small mammals in Yunnan, China. Recognizing the limitations associated with detecting Bartonella species primarily through a single gene and employing only one detection method, we implemented a comprehensive approach. Initially, real-time PCR was employed to detect samples, offering a rapid and efficient means of initial screening. Subsequently, conventional PCR was utilized to target different genes, allowing for a more nuanced analysis of Bartonella diversity. To augment our investigation, we conducted quantitative analysis on positive samples, assessing their prevalence in various tissues including the heart, lung, liver, spleen, kidney, intestine, and brain. This multifaceted approach aimed to provide a more comprehensive understanding of Bartonella species prevalence among small mammals in the specified region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
Small mammal samples were collected using live rat traps (20×12×10.5 cm, Xiangyun Hong Jin Mouse Cage factory, Dali City, Yunnan Province, China) baited with freshly deep-fried dough sticks in Heqing County and Gongshan County in Yunnan Province, from August 2020 to August 2022. A total of 200 cages were set every five meters during the evening and collected in the morning, with this process repeated for approximately 6 days in each habitat. Small animals were gently anesthetized in an induction chamber filled with cotton infused with isoflurane (1 ml of isoflurane per 500 ml of chamber volume). Following anesthesia, animals were compassionately sacrificed on a warming blanket to minimize distress. Dissections were performed to extract heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, brain, and intestinal tissues. These tissues were stored in 2 mL cryogenic vials (CORNING, Shanghai, China) at -80°C for subsequent analysis. Molecular biological identification involved the amplification of the mitochondrial cytochrome b (mt-Cytb) gene of liver tissue DNA using PCR as described previously [
23,
24,
25,
26].
2.2. DNA Extraction
Under aseptic conditions, approximately 1 g of heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, brain, and intestinal tissue samples were clipped into GeneReady Animal PIII pulverizing tubes (Life Real, Guangzhou, China). Following the addition of sterilized 600 μL of phosphate buffer solution (PBS), samples were ground using a GeneReady Ultimate grinder (Life Real, Guangzhou, China). Subsequently, 300 μL of supernatant from the ground tissue samples was extracted using the DNA extraction kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China) with a fully automated nucleic acid extraction and purification instrument (BIOER, Hangzhou, China). Extracted samples were stored at -80°C for subsequent analysis [
27,
28].
2.3. Bartonella sp. Detection
The species-specific primer
ssrA (
Bartonella’s non-coding RNA gene) was selected for fluorescence quantitative real-time PCR of nucleic acids extracted from spleen tissue samples (
ssrA-F: GCTATGGTAATAAATGGACAATGAAATAA;
ssrA-R: GCTTCTGTTGCCAGGTG;
ssrA-P: FAM-ACCCCGCTTAAACCTGCGACG-BHQ1) [
29]. The reaction system was as follows: HR qPCR Master Mix (10 μL),
ssrA-F and
ssrA-R (0.4 μM each), RNase-Free ddH
2O (7.8 μL), DNA template (1 μL), and
ssrA-P (0.4 μL, 10 µM). The amplification reaction took place using the Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The amplification conditions comprised 45 cycles with initial predenaturation at 95°C for 30 s, followed by denaturation at 95°C for 10 s, annealing at 53 °C for 1 min, and fluorescence signal acquisition times. To prevent contamination and false positives, sample processing, reaction system preparation, and PCR amplification were occurred out in separate areas. Controls included a blank control, a negative control (
Orientia tsutsugamushi, Seoul
Orthohantavirus), and a positive control (A synthetic plasmid). Plasmid standards were utilized to establish the standard curve, and results were interpreted based on the curve; a C
t value <35 was deemed positive, while a C
t value ≥35 was considered negative.
The three genes of
gltA,
rpoB, and
ssrA were amplified using conventional PCR (
gltA-F: GGGGACCAGCTCATGGTGG,
gltA-R: AATGCAAAAAGAACAGTAAACA;
rpoB-F: CGCATTGGCTTACTTCGTATG,
rpoB-R: GTAGACTGATTAAACGCTG;
ssrA-F: GCTATGGTAATAA ATGGACAATGAAATAA;
ssrA-R: GCTTCTGTTGCCAGGTG) [
29,
30,
31]. The
gltA amplification was carried out with the following conditions: pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 3 minutes, followed by 35 cycles at 94 °C for 15 seconds (denaturation), 48 °C for 15 seconds (annealing), and 72 °C for 30 seconds (extension), with a final extension at 72 °C for 5 minutes and a 1 minute cooling step at 10 °C. The length of the amplification product after PCR was approximately 379 bp (
gltA). The
rpoB amplification was conducted under the following conditions: pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 3 minutes, followed by 35 cycles at 94 °C for 15 seconds (denaturation), 48 °C for 15 seconds (annealing), and 72 °C for 30 seconds (extension), with a final extension at 72 °C for 5 minutes and a 1 minute cooling step at 10 °C. The length of the amplification product after PCR was approximately 866 bp (
rpoB). The
ssrA amplification was conducted under the following conditions: pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 3 minutes, followed by 35 cycles at 94 °C for 15 seconds (denaturation), 53 °C for 15 seconds (annealing), and 72 °C for 30 seconds (extension), with a final extension at 72 °C for 5 minutes and a 1 minute cooling step at 10 °C. The length of the amplification product after PCR was approximately 301 bp (
ssrA). The amplified products underwent agarose gel electrophoresis for identification. Positive amplicons, aligning with the expected size, were excised and purified from the gel (OMEGA Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, USA), then forwarded to Shenggong Bioengineering Co., Ltd.(Shanghai, China) for bidirectional sequencing. Utilizing BLASTn and BLASTp analyses, we determined nucleotide sequence similarity and translated amino acid similarity against sequences in the NCBI GenBank database (
https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 14 January 2024).
2.4. Sequence Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
The DNA sequences were assembled using the DNAstar Lasergene software package, employing manual editing and precision trimming to generate the definitive
Bartonella genome sequence. Subsequently, a thorough similarity analysis was conducted using the BLAST. The representative reference sequences for the
gltA,
rpoB, and
ssrA genes were obtained from the NCBI GenBank database. Sequence alignment was performed using ClustalX2, followed by DNA sequence analysis utilizing the maximum likelihood method in MEGAX 11.0 [
32]. The analysis incorporated 1000 bootstrap replicates for robustness. Evolutionary distances were computed using the Kimura 2-parameter method, with a self-spread value greater than 70% generally considered reliable for evolutionary branching. The results were visualized in iTOL (
https://itol.embl.de/, accessed on 14 January 2024). The present study utilized all sequences obtained from the three genes of
ssrA,
gltA, and
rpoB in GeneBank (Accession Numbers: OR993996-OR994040).
2.5. Construction of Plasmids and Determination of DNA Copy Number
The partial ssrA fragment of Bartonella was cloned into the pEASY-T1 vector (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China), and the resulting T-loaded construct was transformed into DH5α E. coli cells. Following bacterial liquid amplification, the presence of the inserted target gene was confirmed through sequencing analysis. A small quantity of plasmids carrying the cloned ssrA fragment were extracted using the Plasmid Mini Kit I (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, USA), and stored at -80°C for future use. Upon melting, the concentration of Bartonella plasmids extracted was determined by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Life Real, Hangzhou, China). The concentration was then converted into a copy number using the formula:
Copies/µL= Plasmid concentration (ng/µL) ×10−9×6.02×1023 / (660×DNA length)
The plasmid concentration was converted into a copy number, which was used for the establishment of a standard curve and quantitative analysis as the positive control.
2.6. qPCR Optimization
The positive standards, serving as templates for optimizing conditions, were diluted with RNase-Free ddH2O in a 10-fold gradient and stored at -20°C for future use. The optimization process involved fine-tuning the primers, probe concentration, and annealing temperature within the qPCR system through several trials to determine the optimal amplification conditions and reaction system.
For the qPCR experiments, the HiScript® II U+ One Step qRT-PCR Probe Kits were utilized. After multiple rounds of experimentation to optimize the conditions, the final reaction system for qPCR was as follows: ace Universal U+ probe: 10μL; primers (10μM): 0.4μL each; taq probe (10μM): 0.4μL; RNase-Free ddH2O: 7.8μL; DNA template: 1μL. The total reaction system for the assay was 20 µL, and the amplification reaction was carried out using the Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The amplification conditions included 45 cycles at 95°C with a 30 s pre-denaturation, followed by denaturation at 95°C for 10 s, annealing temperatures, and fluorescence signal acquisition times at 51°C for 34 s.
2.7. Standard Curves Plotting
To establish the standard curve for the qPCR assay, the positive standard was subjected to a 10-fold gradient dilution, with each concentration repeated three times. The average of the three repetitions was calculated. The logarithmic value of the positive standard’s copy number served as the horizontal coordinate, while the corresponding Ct value of the assay served as the vertical coordinate. The standard curve was plotted, and the slopes and correlation coefficients were determined.
2.8. qPCR Sensitivity and Specificity Evaluation
The detection limit of qPCR was assessed through serial dilution of Bartonella plasmid DNA, initially at a concentration of 356.828 ng/µL, converted to pre-dilution concentrations of 6.09 × 10¹⁰ copies/µL. This plasmid was successively diluted at 10-fold dilutions for 10 time with RNase-Free H₂O to serve as the qPCR template. The primer’s specificity was evaluated by referencing relevant literature. It demonstrated the ability to detect all types of Bartonella. This was confirmed by comparing results against blank controls and negative controls (Orientia tsutsugamushi, Seoul Orthohantavirus), along with positive controls.
2.9. qPCR Repeatability and Stability Evaluation
Six concentration gradients (1.00 × 10⁴ ~ 1.00 × 10⁹ copies/µL) of positive standards were utilized as templates. Intra-group repetitions were conducted with each concentration repeated thrice. This operation was performed once a week, totaling three inter-group repetitions. RNase-free ddH₂O served as the negative control group. Mean Ct values, standard deviation (SD), and coefficient of variation (CV) were computed to evaluate reproducibility and stability.
2.10. Comparison of qPCR and Conventional PCR Assays
Conventional PCR reactions were executed using serial 10-fold gradient dilutions of positive standards as positive templates, with RNase-free H₂O as the negative control. Amplified PCR products underwent agarose gel electrophoresis to compare the sensitivity of qPCR with conventional PCR methods.
2.11. qPCR for Small Mammal Samples
Small mammal samples underwent DNA extraction from tissues using the aforementioned method. Subsequently, all samples were subjected to Bartonella assay following optimized qPCR experimental conditions.
2.12. Tissue Tropism of Bartonella sp. in Small Mammals
The qPCR method was employed to detect positive samples and quantitatively analyze various tissues from small mammalian samples that tested positive for Bartonella. This approach aimed to investigate the tissue tropism of the pathogen.
2.13. Statistical Test
Data analysis was performed using a one-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) with GraphPad Prism software version 8.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). All results are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical significance was determined with p-values when p-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant, p-values less than 0.01 were deemed highly significant.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Collection and Testing
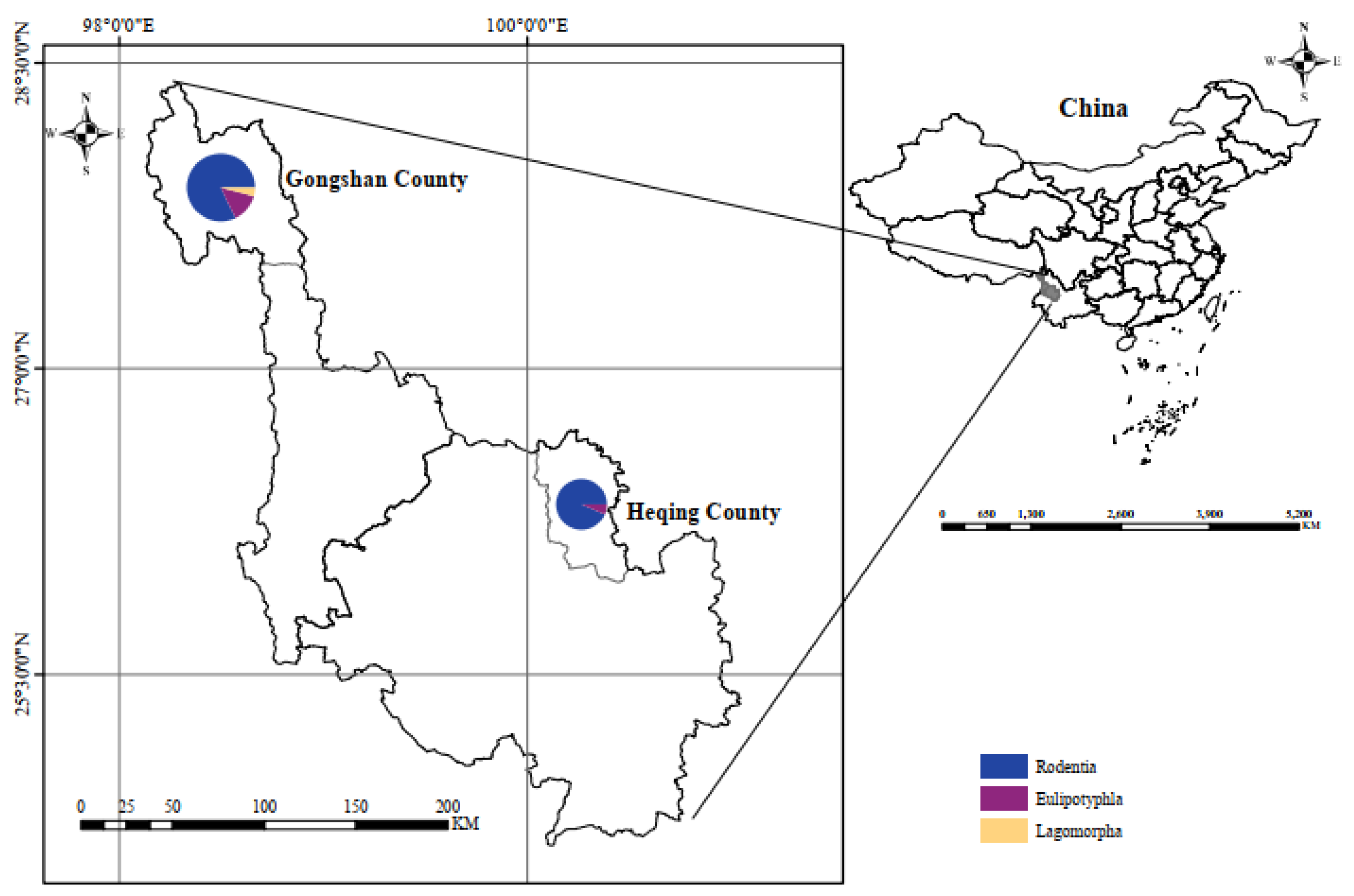
A total of 333 small mammals, comprising 13 species across 3 orders, 4 families, and 4 genera, were captured in Heqing County and Gongshan County in Yunnan Province (
Figure 1). Notably, Chevrier’s field mouse (
Apodemus chevrieri) and Small Oriental vole (
Eothenomys eleusis) emerged as the dominant species, constituting 27.4% (n=94) and 44.0% (n=151), respectively. The samples (n=333) underwent
Bartonella sp. testing via qPCR, revealing a natural infection rate of 31.5% (n=105, 95% CI: 27.7%-36.7%). The infection rates in Chevrier’s field mouse(
Apodemus chevrieri), Small Oriental vole (
Eothenomys eleusis), Chestnut white-bellied rat (
Niviventer fulvescens), Asian house rat (
Rattus tanezumi), Long-tailed red-toothed shrew (
Episoriculus leucops), Chinese mole shrew (
Anourosorex squamipes), and Titanium Pika (
Ochtona Thibetana) were 44.4% (67/151), 27.7% (26/94), 100.0% (1/1), 6.3% (2/32), 60.0% (3/5), 60.0% (3/5), and 22.2% (2/9), respectively (
Table 1). Additionally, the prevalence of
ssrA,
rpoB, and
gltA in small mammals was 9.0% (n=30), 2.9% (n=10), and 1.4% (n=5), respectively, as determined by conventional PCR. qPCR demonstrated significantly higher detection rates than conventional PCR (χ2=34.8, P<0.05), with
ssrA showing a higher detection rate than
rpoB and
gltA (P<0.05).
3.2. Comparison of Similarities among ssrA, rpoB, and gltA Genes in Bartonella sp.
In this study, 30 strains of
Bartonella sp. were identified based on the
ssrA gene. When compared with the nucleotide sequences of
Bartonella sp. in GenBank, the homology ranged from 96.0% to 99.5%. Notably, 9 strains from
A. chevreri and 4 strains from
E. eleusis exhibited a similarity of 96.0% to 97.0% with
B. tribocorum in Guangdong Province, China. Furthermore, 9 strains from
A. chevrieri demonstrated a similarity ranging from 96.3% to 99.3% to
Bartonella sp. Coyote22sub2 from blood samples of Coyotes (
Canis latrans) in California, USA. Additionally, 4 strains from
E. Eleusis showed up to 99.0% to 99.5% similarity to
Bartonella sp. AR 15-3 in Switzerland. Moreover, 3 strains from
Anourosorex. squamipes,
R. tanezumi, and
A. chevrieri were found to be 96.6%, 97.7%, and 98.0% similar, respectively, to
B. taylorii from blood samples of
Microtus sp. in France. Lastly, one strain from
N. fulvescens exhibited 97.7% similarity to uncultured
Bartonella sp. from Natal multimammate mouse (
Mastomys natalensis) in Tanzania (
Figure S1).
For the
rpoB gene of
Bartonella sp., 10 strains were obtained, and when compared with
Bartonella sp. sequences in GenBank, the nucleotide levels were homologous to a range of 95.8% to 100.0%. Notably, two strains from
A. chevrieri and two strains from
E. Eleusis showed a similarity of 86.7% to 100.0% to
B. grahamii from
A. chevrieri in Yunnan Province, China. Furthermore, one strain from
A. chevrieri exhibited the highest similarity of 96.4% to
B. rochalimae from the blood of a dog in Japan. Another strain from
A. chevrieri and one from
E. Eleusis demonstrated the highest similarity of 95.8% to 96.9% with B. Sendai from
Microtus montebelli in Japan. Additionally, two strains from
A. chevrieri and one from
E. Eleusis were 97% similar to
B. Koshimizu from the striped field mouse (
A. agrarius) in Japan, while one strain from
N. fulvescens showed 97.6% similarity to
B. phocinensis from
R. norvegicus in France (
Figure S2).
Concerning the
gltA gene of
Bartonella sp., 5 strains were obtained, and the nucleotide similarity with
Bartonella sp. sequences in GenBank ranged from 92.1% to 99.9%. Notably, two strains from
A. chevrieri had the highest similarity of 99.7% to 100.0% with
B. Koshimizu from
A. agrarius in Japan. Additionally, one strain from
A. chevrieri exhibited the highest similarity of 97.4% with
B. grahamii from the Social vole (
Microtus socialis) in Georgia. Furthermore, one strain from
E. leucops showed 96.3% similarity to uncultured
Bartonella sp. from the black-legged tick (
Ixodes. scapularis) in the USA. Interestingly, one strain (GS136) from the Long-tailed Shrew (
E. leucops) had the highest similarity of only 92.1% with uncultured
Bartonella sp. from fleas (
Ctenophthalmus lushuiensis) in China, potentially representing a new species of
Bartonella (
Figure S3, Table S1).
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
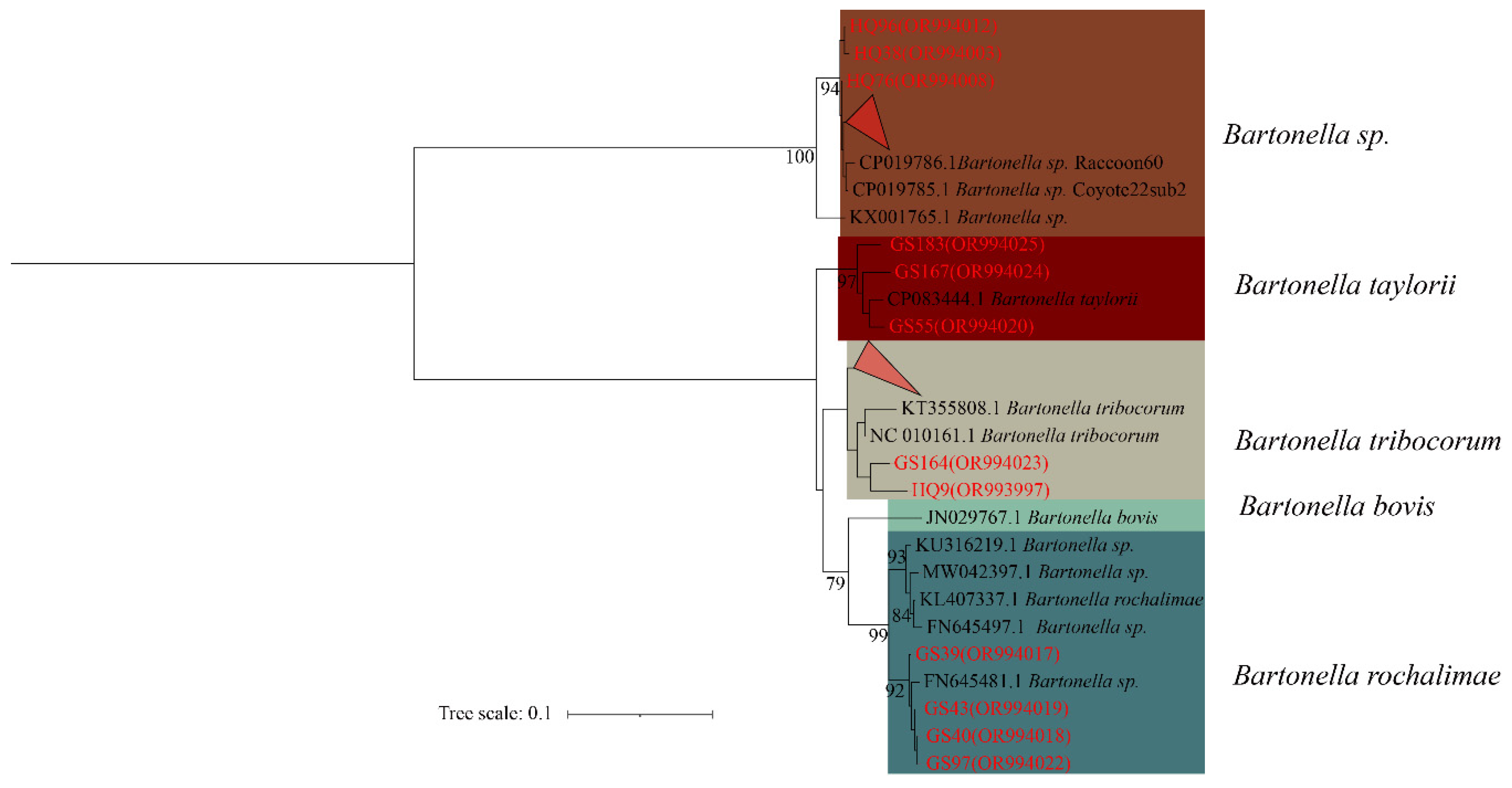
In the phylogenetic tree constructed based on the
ssrA gene, the 30 sequences are classified
Bartonella, forming four distinct categories. The first branch comprises HQ92, HQ38, HQ76 and the 6 folded sequences (HQ66, HQ72, HQ73, HQ77, HQ96, and HQ99) in unclassified
Bartonella sp. The second branch comprises GS183, GS167 and GS55 in
B. taylorii. The third branch comprises GS164, HQ9, and 12 fold sequences (HQ4, HQ18, HQ25, HQ32, HQ34, HQ35, HQ55, HQ80, GS29, GS35, GS37, GS60) in
B. tribocorum. The forth branch consists of GS39, GS40, GS43, and GS97 in
B. rochalimae (
Figure 2).
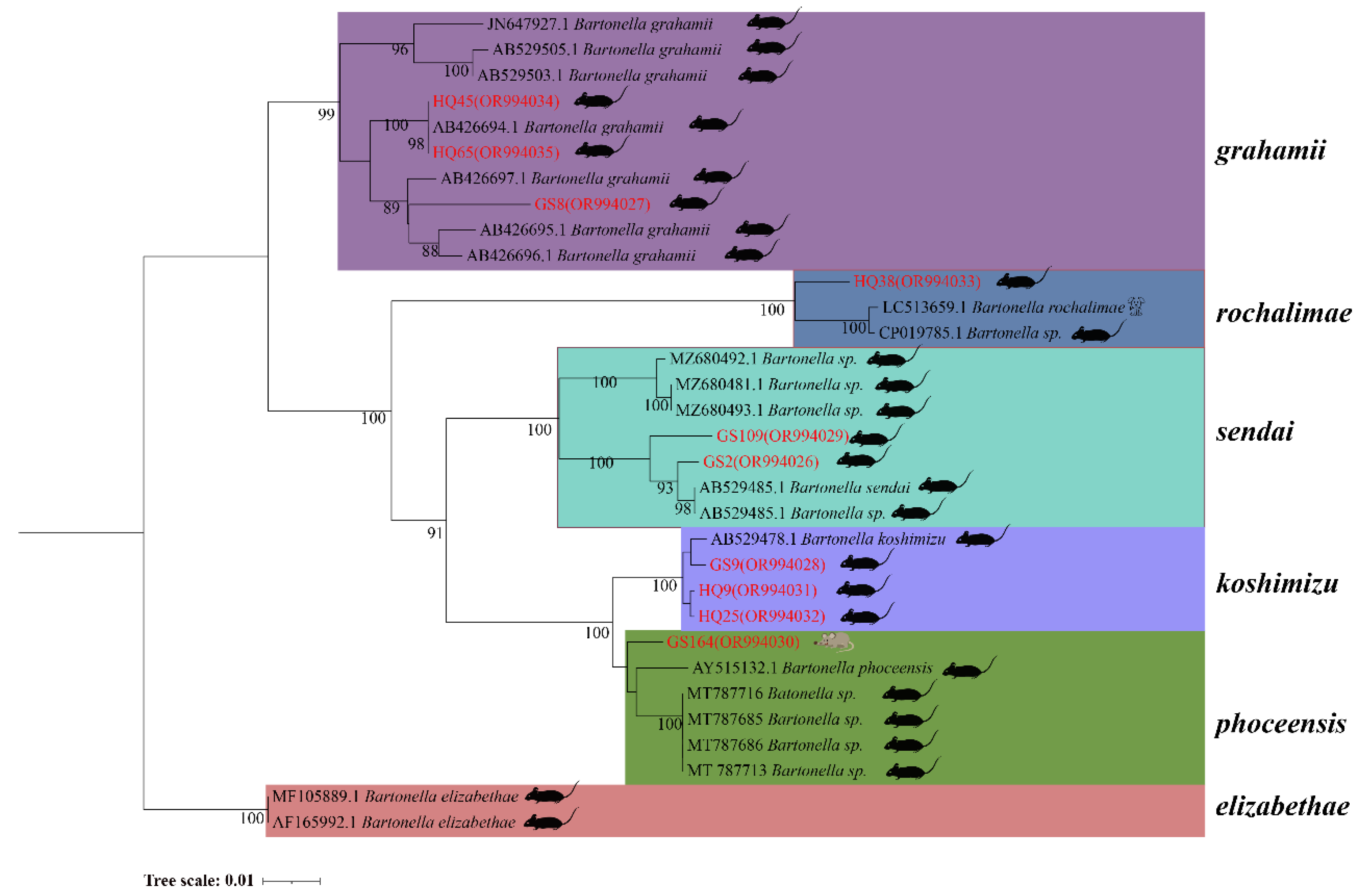
In the phylogenetic tree based on the
rpoB gene, 10 sequences form five distinct clades. HQ45 and HQ65 from
A. chevrieri and GS8 from
E. Eleusis cluster into
B. grahamii. HQ38 from
A. chevrieri forms a clade with
B. rochalimae. GS109 from
E. eleusis and GS2 from
A. chevrieri group together in
B. Sedai. GS9, HQ9, and HQ25 from
A. chevrieri cluster into
B. koshimizu. Finally, GS164 from
N. fulvescens groups into
B. phoceensis (
Figure 3).
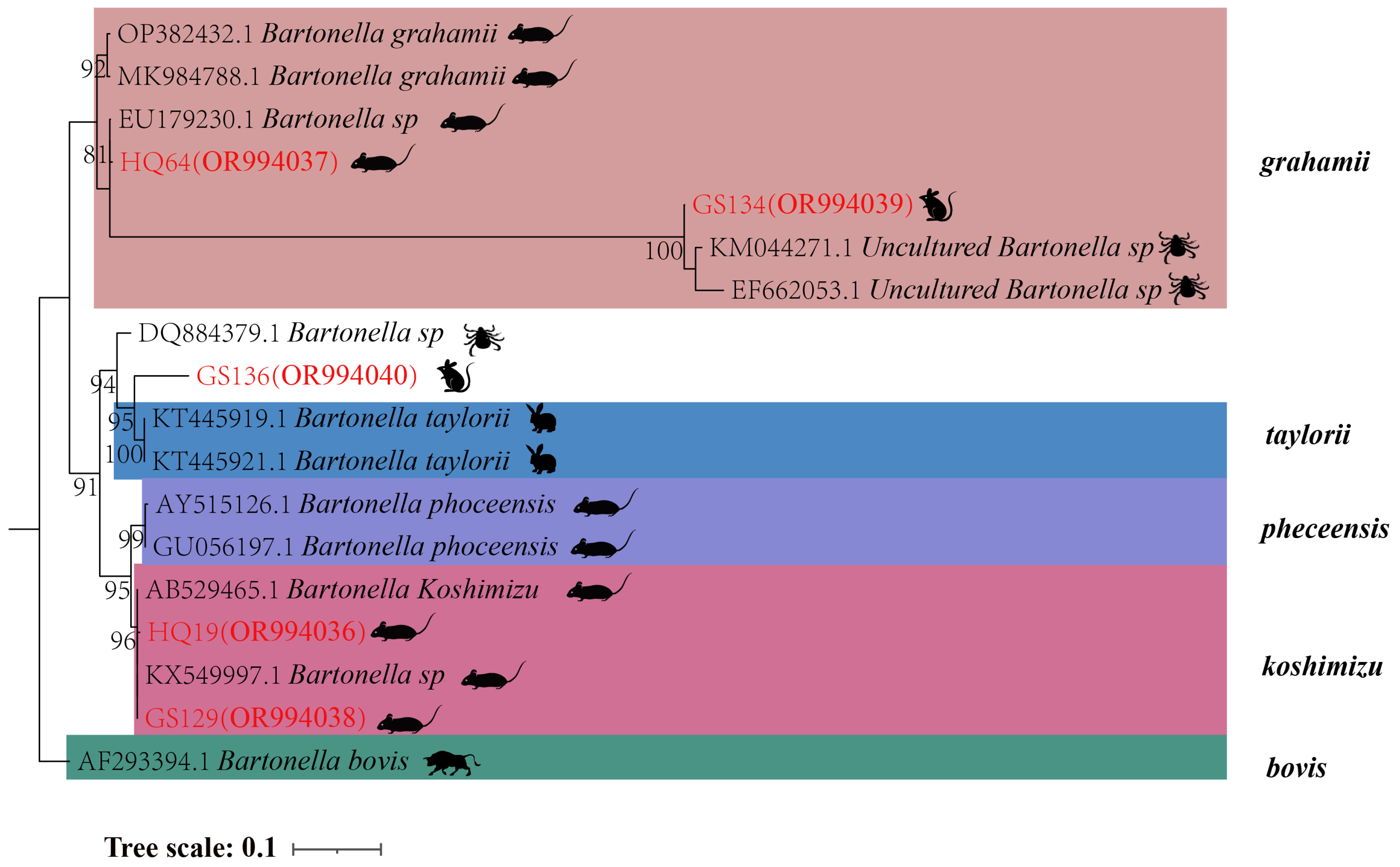
In the phylogenetic tree based on the
gltA gene, five sequences are categorized into three groups. The first branch includes GS134 from
E. leucops and HQ64 from
A. chevrieri, clustering with
B. grahamii. The second branch comprises GS136 from
E. leucops, aligning with
B. taylorii. The third branch consists of GS129 and HQ19 from
A. chevrieri, forming a clade with
B. koshimizu (
Figure 4).
3.4. Establishment of qPCR Standard Curve
To construct the qPCR standard curve, five pairs of
Bartonella standard products ranging from 1.00×10
4 to 1.00×10
8 copies/µL were selected for the X-axis, with the corresponding C
t values plotted on the Y-axis. The resulting graph demonstrates a robust linear relationship between the dilution templates and C
t values (
Figure S4).
3.5. Evaluation of qPCR Sensitivity and Specificity
The study revealed that the minimum detectable copy number of
Bartonella sp. positive standard was 1.00×10
2 copies/µL, indicating the excellent sensitivity of the established qPCR method (
Figure S5). In this investigation, testing was conducted with
Bartonella,
Orientia tsugamushi, and Seoul
Orthohantavirus. The primer employed could exclusively amplify
Bartonella.
3.6. Evaluation of qPCR Repeatability and Stability
Inter-group repeatability experiments demonstrated that the standard deviation of
Bartonella standard detection within each concentration group ranged from 0.06 to 0.40, and the coefficient of variation varied between 0.53 and 1.84. These results affirm the robust reproducibility of the established qPCR method (
Table S4). Intra-group repeatability experiments further revealed that the standard deviation of
Bartonella standard detection at various concentrations between groups ranged from 0.19 to 0.55, with a coefficient of variation between 0.82 and 1.92. These findings attest to the stability of the established qPCR method (
Table S5).
3.7. Comparison of Sensitivity between qPCR and Conventional PCR Methods
The experimental outcomes indicated that the lowest copy number for positive standard detection of
Bartonella by qPCR was 1.00×10
2 copies/µL. In contrast, the lowest copy number for
Bartonella positive standards detected by conventional PCR was 1.00×10
3 copies/µL (
Figure S6).
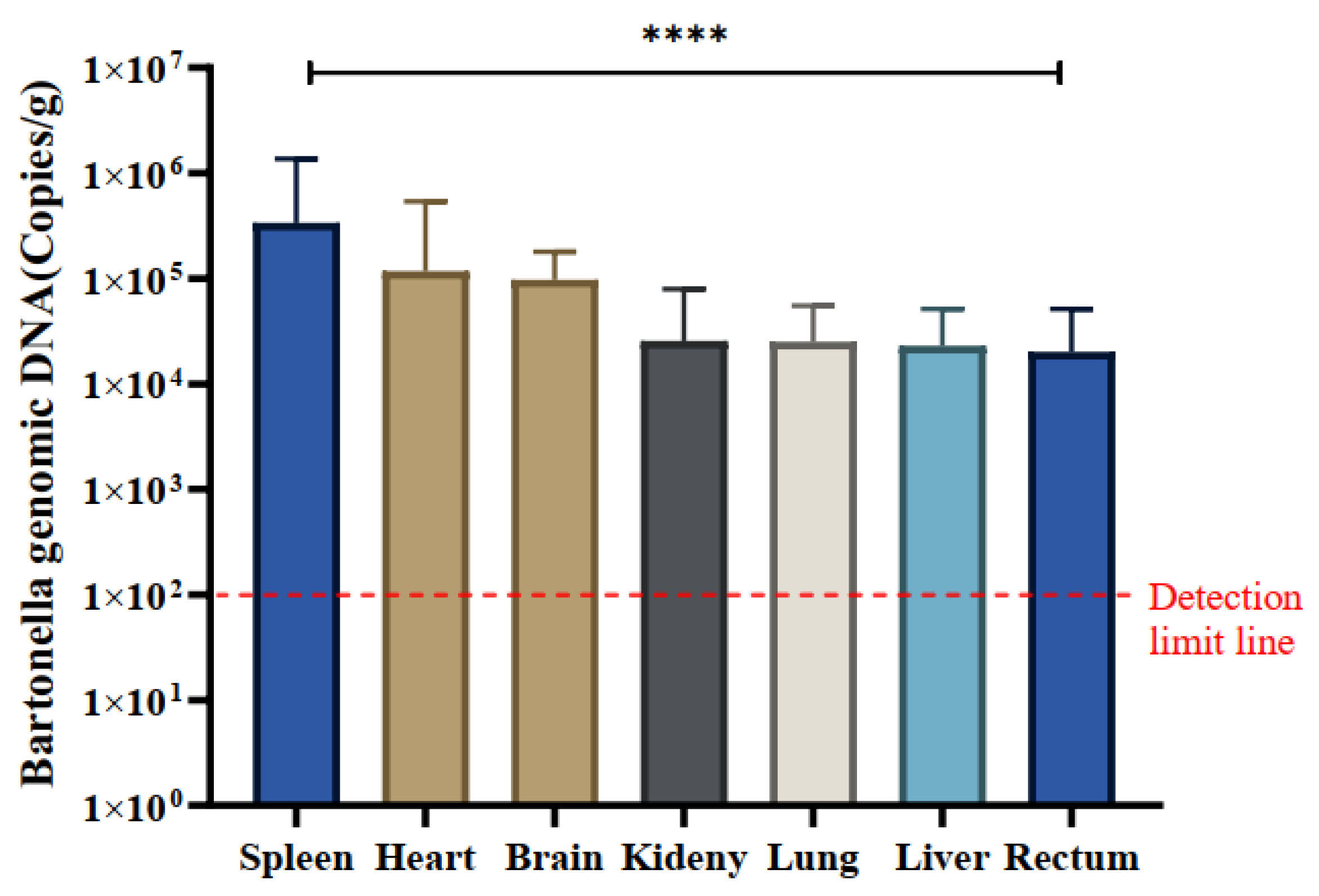
3.8. Tissue Tropism of Bartonella sp. in Small Mammals
A total of 30
Bartonella-positive samples were identified using the
ssrA gene. The quantitative analysis of naturally infected
Bartonella in various tissues, including the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, intestine, and brain, was conducted using the qPCR method. The mean copy number of
Bartonella was most pronounced in spleen tissue across all positive samples, registering at 3.37×10
5 copies/g, indicating a notably higher copy number of
Bartonella in the spleen. The mean copy numbers in other tissues were as follows: spleen (3.36×10
5), heart (1.17×10
5), brain (9.70×10
4), kidney (2.56×10
4), lung (2.50×10
4), liver (2.29×10
4), and intestine (2.00×10
4) copies/g, respectively (
Table 2).
Notably, spleen tissues exhibited significantly higher copy numbers of
Bartonella compared to kidney and intestinal tissues, and differences in
Bartonella copy numbers were observed across all tissues (P<0.0001). Specific variations in
Bartonella copy numbers were identified in certain tissues (
Figure 5).
4. Discussion
The current study detected Bartonella in seven species: A. chevrieri, E. eleusis, N. fulvescens, R. tanezumi, E. leucops, A. squamipes, and O. thibetana. Bartonella can infect a broad range of hosts. Among these, B. grahamii, B. rochalimae, and B. koshimizu were detected in A. chevrieri; B. grahamii, B. sendai, and B. koshimizu were detected in E. Eleusis, and B. phoceensis was detected in N. fulvescens. The Uncultured Bartonella sp. was detected in R. tanezumi and A. squamipes.
The study investigated the natural infection status and molecular characteristics of
Bartonella species carried by small mammals in two counties of Yunnan Province. This is the first reported survey of
Bartonella species in these areas. According to the results, the prevalence of
Bartonella is lower compared to certain regions in China, such as Yunnan Province (57.7%) [
33], Qinghai Province (38.61%) [
34], Heilongjiang Province (57.7%) [
35], and Shanxi Province (49.50%) [
36]. However, it is higher than in Zhejiang Province (31.4%) [
37] and Fujian Province (16.19%) [
38]. Regions at higher latitudes tend to have a higher infection rate of
Bartonella. The latitude of the area studied is relatively low, but there is a high density of rodents and a high species richness [
39]. This accounts for the relatively high infection rate in our study. In addition, compared to conventional PCR results, the infection rate obtained through qPCR detection is higher. It can detect samples with low copy numbers, providing a more accurate reflection of the infection situation. Using qPCR is recommended for investigating
Bartonella.
The
ssrA gene, along with the
gltA and
rpoB genes, possesses identical species identification functions [
29]. The
ssrA can also be employed for the swift detection and classification of
Bartonella. According to the DNA sequences determined by
gltA,
rpoB, and
ssrA genes, at least seven species of
Bartonella were detected in these small mammals through homology and phylogenetic analysis. These include
B. grahamii,
B. rochalimae,
B. Sendai,
B. koshimizu,
B. phoceensis,
B. taylorii,
B. koshimizu, and a newly isolated
Bartonella (GS136: the highest similarity of only 92.1% with Uncultured Bartonella sp.) that should be considered a new species based on the
gltA fragment of 327 bp having 96.0% sequence similarity to the validated species or the
rpoB fragment of 825 bp having 95.4% similarity to the sequence of the evidenced species [
40]. In addition,
B. grahamii, originally isolated from bank vole (
Myodes glareolus) in the UK and subsequently linked to retinitis and cat-scratch disease (CDS) [
2,
41,
42,
43], can infect humans. These results indicate the presence of diverse
Bartonella species among small mammals in the survey areas that can cause human disease.
The qPCR method demonstrates excellent sensitivity, specificity, stability, and repeatability. Quantitative studies have revealed that the copy number of Bartonella species in spleen tissues is significantly higher in infected small mammals (P < 0.0001), indicating the splenic tissue tropism of infected small mammals. Bartonella is extremely difficult to culture in vitro due to harsh nutritional conditions, but since Bartonella attacks endothelial cells to cause bacteremia, blood is used for in vitro culture. During sampling, blood is more difficult to collect, and tissue isolation is relatively simple, so the spleen tissue can be the organ of choice for tissue isolation. Variable DNA copy numbers were also detected in other tissues, suggesting that Bartonella species have broad tissue tropism.
Although we conducted quantitative analysis on tissues and organs such as heart, liver, lung, spleen, kidney, intestine, and brain for all amplified sequence samples, the majority of samples are well-preserved. Unfortunately, we lack blood samples, and only partial brain tissue samples are available. Nevertheless, we detected three unclassified
Bartonella in ten positive brain tissues, responding quantitatively to the presence of a large number of
Bartonella in brain tissues
B. henselae and
B. quintana have been reported to cause severe central nervous system disease [
44,
45]. The antibodies and DNA of
Bartonella have been found in the cerebrospinal fluid of cats and dogs, and
Bartonella has also been isolated from rodent brains [
34]. However, understanding how
Bartonella enters brain tissue and the mechanisms through which it affects the central nervous system requires further study.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study identified seven Bartonella species, namely B. grahamii, B. rochalimae, B. Sendai, B. koshimizu, B. phoceensis, B. Taylorii, and a newly isolated Bartonella (GS136), within seven small mammal species: Chevrier’s field mouse (A. chevrieri), Small Oriental vole (E. Eleusis), Chestnut white-bellied rat (N. fulvescens), Asian house rat (R. tanezumi), Long-tailed red-toothed shrew (E. leucops), Chinese mole shrew (A. squamipes), and Tibet Pika (O. thibetana). This finding underscores the species and host diversity of Bartonella, including species with zoonotic potential for human infection. Our study also highlighted the superior detection efficiency of qPCR compared to conventional PCR, with the qPCR method demonstrating higher sensitivity. Furthermore, the detection rate of Bartonella and the ssrA gene surpassed that of the rpoB gene and gltA gene, emphasizing the efficacy of utilizing the ssrA gene for rapid and accurate Bartonella detection and classification. Bartonella exhibited a natural ability to infect various tissues in small mammals, with brain tissue being among the affected organs. The broad tissue tropism observed, particularly with the highest load in spleen tissue, suggests the systemic nature of Bartonella infections. These findings contribute to our understanding of the diversity, prevalence, and tissue tropism of Bartonella, shedding light on the potential public health implications associated with these infections.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1. Identity comparisons of nucleotide sequence of Bartonella ssrA gene (301 bp) in small mammals from this study. Figure S2. Identity comparisons of nucleotide and amino acid sequence of Bartonella rpoB gene (866bp) in small mammals from this study. Figure S3. Identity comparisons of nucleotide and amino acid sequence of Bartonella gltA gene (375bp) in small mammals from this study. Figure S4. Standard curve. Figure S5. Sensitivity test results. Figure S6. Conventional PCR results. Table S1. Identity comparisons of nucleotide sequence of Bartonella ssrA gene (301 bp) in small mammals from this study. Table S2. Identity comparisons of nucleotide and amino acid sequence of Bartonella rpoB gene (866bp) in small mammals in this study. Table S3. Identity comparisons of nucleotide and amino acid sequence of Bartonella gltA gene (375bp) in small mammals from this study. Table S4: The results of intra-group repeatability. Table S5: The results of inter-group repeatability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.-Y.H. and Y.-Z.Z.; methodology, P.-Y.H, J.-W.T., and Y.-Z.Z.; software, P.-Y.H., Z.Y., B.W. and H.-M.Y.; validation, P.-Y.H., F.-H.X., Z.Y., L.-D.Z. and Y.-Z.Z.; formal analysis, P.-Y.H., F.-H.X., J.-Y.Z., W.K. and B.W.; investigation, P.-Y.H., F.-H.X., L.-D.Z., Z.Y., J.-Y.Z., L.-J.G. and W.K.; resources, P.-Y.H., J.-W.T., J.-Y.Z., W.K. and Y.-Z.Z.; data curation, P.-Y.H., B.W. and Y.-Z.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, P.-Y.H. and Y.-Z.Z.; writing—review and editing, B.W., P.-Y.H., J.-W.T., and Y.-Z.Z.; supervision, L.-J.G. and Y.-Z.Z.; project administration, P.-Y.H., L.-J.G. and Y.-Z.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.-Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U2002218, 81874274); Yunnan Health Training Project of High Level Talents (No. L-2017027); Doctoral Research Start-up Fee Project of Dali University (No. KYBS2018004); Project of Cross-border Control and Quarantine Innovation Group of Zoonosis of Dali University (No. ZKPY2019302).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Dali University (DLDXLL2020007).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request. All the sequences in this manuscript can be obtained. from the NCBI database (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 20 Aug 2023).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of Heqing County and the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of Gongshan County for their help in sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cheslock, M.A.; Embers, M.E. Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhoff, F.T.; Bergmans, A.M.; van Der Zee, A.; Rothova, A. Demonstration of Bartonella grahamii DNA in ocular fluids of a patient with neuroretinitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 4034–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, J.S.; Worthington, M.G.; Brenner, D.J.; Moss, C.W.; Hollis, D.G.; Weyant, R.S.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Weaver, R.E.; Daneshvar, M.I.; O’Connor, S.P. Rochalimaea elizabethae sp. nov. isolated from a patient with endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Bai, Y.; Sheff, K.; Morway, C.; Baggett, H.; Maloney, S.A.; Boonmar, S.; Bhengsri, S.; Dowell, S.F.; Sitdhirasdr, A.; et al. Identification of Bartonella infections in febrile human patients from Thailand and their potential animal reservoirs. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, D.F.; Carroll, K.C.; Hofmeister, E.K.; Persing, D.H.; Robison, D.A.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Brenner, D.J. Isolation of a new subspecies, Bartonella vinsonii subsp. arupensis, from a cattle rancher: Identity with isolates found in conjunction with Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti among naturally infected mice. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2598–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Murray, M.; Gilmore, R.D., Jr.; Bai, Y.; Gage, K.L. Bartonella strains from ground squirrels are identical to Bartonella washoensis isolated from a human patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Morway, C.; Sheff, K.W.; Bai, Y.; Colborn, J.; Chalcraft, L.; Dowell, S.F.; Peruski, L.F.; Maloney, S.A.; Baggett, H.; et al. Bartonella tamiae sp. nov., a newly recognized pathogen isolated from three human patients from Thailand. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugel, M.; Krol, N.; Kempf, V.A.J.; Pfeffer, M.; Obiegala, A. Emerging rodent-associated Bartonella: A threat for human health? Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Kordick, D.L. Bartonella infection in animals: Carriership, reservoir potential, pathogenicity, and zoonotic potential for human infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, J.P.; Kosoy, M.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. Natural history of Bartonella-infecting rodents in light of new knowledge on genomics, diversity and evolution. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstead, G.M. The centenary of the discovery of trench fever, an emerging infectious disease of World War 1. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e164–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silaghi, C.; Pfeffer, M.; Kiefer, D.; Kiefer, M.; Obiegala, A. Bartonella, Rodents, Fleas and Ticks: A Molecular Field Study on Host-Vector-Pathogen Associations in Saxony, Eastern Germany. Microb Ecol 2016, 72, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, F.J. Detection of Bartonella alsatica in European wild rabbit and their fleas (Spilopsyllus cuniculi and Xenopsylla cunicularis) in Spain. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Carlos, E.T.; Kasten, R.W.; Yamamoto, K.; Chang, C.C.; Carlos, R.S.; Abenes, M.V.; Pajares, C.M. Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae infection in domestic cats from The Philippines. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilley, T.M.; Veikkolainen, V.; Pulliainen, A.T. Molecular Detection of Candidatus Bartonella hemsundetiensis in Bats. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antequera-Gomez, M.L.; Lozano-Almendral, L.; Barandika, J.F.; Gonzalez-Martin-Nino, R.M.; Rodriguez-Moreno, I.; Garcia-Perez, A.L.; Gil, H. Bartonella chomelii is the most frequent species infecting cattle grazing in communal mountain pastures in Spain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, R.; Riegel, P.; Barrat, F.; Bouillin, C.; Thibault, D.; Gandoin, C.; Halos, L.; Demanche, C.; Alliot, A.; Guillot, J.; et al. Bartonella chomelii sp. nov., isolated from French domestic cattle (Bos taurus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G.Z.; Sun, Z.Z.; Bai, J.Y.; Jiang, B.G.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.G.; Yang, H.; Tian, G.; et al. Transmission and maintenance cycle of Bartonella quintana among rhesus macaques, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediannikov, O.; El Karkouri, K.; Robert, C.; Fournier, P.E.; Raoult, D. Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Bartonella florenciae sp. nov. Stand. Genomic. Sci. 2013, 9, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekambi, T.; Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D. The rpoB gene as a tool for clinical microbiologists. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondoso, J.; Harder, J.; Lage, O.M. rpoB gene as a novel molecular marker to infer phylogeny in Planctomycetales. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volokhov, D.V.; Simonyan, V.; Davidson, M.K.; Chizhikov, V.E. RNA polymerase beta subunit (rpoB) gene and the 16S-23S rRNA intergenic transcribed spacer region (ITS) as complementary molecular markers in addition to the 16S rRNA gene for phylogenetic analysis and identification of the species of the family Mycoplasmataceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 62, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.M.; Kocher, T.D.; Wilson, A.C. Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 32, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cai, C.L.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.H.; Zhuo, F.; Shi, Z.L.; Yang, X.L. Detection and characterization of three zoonotic viruses in wild rodents and shrews from Shenzhen city, China. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.L.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, X.Y.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Bock, C.T.; Shi, Z.L. Detection and genome characterization of four novel bat hepadnaviruses and a hepevirus in China. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.H.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.H.; Pan, H.; Wang, L.X.; Bock, C.T.; Shi, Z.L.; et al. Chevrier’s Field Mouse (Apodemus chevrieri) and Pere David’s Vole (Eothenomys melanogaster) in China Carry Orthohepeviruses that form Two Putative Novel Genotypes Within the Species Orthohepevirus C. Virol. Sin. 2018, 33, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, B.; Han, P.; Dong, N.; Zhu, Y.; Li, F.; Si, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; et al. Identification of a Novel Hepacivirus in Southeast Asian Shrew (Crocidura fuliginosa) from Yunnan Province, China. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Fu, M.; Han, P.; Yin, H.; Yang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Ren, T.; Zhang, Y. Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome Caused by Orthohantaviruses in Xiangyun County, Dali Prefecture, Yunnan Province, China. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.H.; Bai, Y.; Malania, L.; Winchell, J.M.; Kosoy, M.Y. Development of a novel genus-specific real-time PCR assay for detection and differentiation of Bartonella species and genotypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.F.; Regnery, R.; Jameson, P.; Greene, C.; Krause, D.C. Differentiation of Bartonella-like isolates at the species level by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism in the citrate synthase gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renesto, P.; Gouvernet, J.; Drancourt, M.; Roux, V.; Raoult, D. Use of rpoB gene analysis for detection and identification of Bartonella species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.M.; Yu, D.Z.; Liu, Q.Y.; Gong, Z.D. Study on the prevalence of Bartonella species in rodent hosts from different enviromental areas in Yunnan. Chinese journal of Epidemiology 2004, 25, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Li, S.; Lu, L.; Wang, R.; Song, X.; Sun, K.; Shi, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, J. Genetic diversity of Bartonella species in small mammals in the Qaidam Basin, western China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong-mei, L.; Hou, Y.; Song, X.P.; Fu, Y.Q.; Li, G.C.; Li, M.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Wu, H.X.; Pang, B.; Yue, Y.J.; et al. High prevalence and genetic heterogeneity of rodent-borne Bartonella species on Heixiazi Island, China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7981–7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Cheng, H.B.; Li, D.M.; Rao, H.X. Molecular detection and genetic characterization of small rodents associated Bartonella species in Zhongtiao Mountain, China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Lu, L.; Fu, G.; Ding, G.; Song, X.; Meng, F.; Wu, H.; Yang, T.; Ren, Z.; et al. Detection of Bartonella species in small mammals from Zhejiang Province, China. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Inoue, K.; Kabeya, H.; Sato, S.; Takada, T.; Pangjai, D.; Chiu, S.H.; Fujita, H.; Kawabata, H.; Takada, N.; et al. Prevalence and Diversity of Bartonella Species in Wild Small Mammals in Asia. J Wildl Dis 2016, 52, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Scola, B.; Zeaiter, Z.; Khamis, A.; Raoult, D. Gene-sequence-based criteria for species definition in bacteriology: The Bartonella paradigm. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtles, R.J.; Harrison, T.G.; Saunders, N.A.; Molyneux, D.H. Proposals to unify the genera Grahamella and Bartonella, with descriptions of Bartonella talpae comb. nov., Bartonella peromysci comb. nov., and three new species, Bartonella grahamii sp. nov., Bartonella taylorii sp. nov., and Bartonella doshiae sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksi, J.; Rantala, S.; Kilpinen, S.; Silvennoinen, R.; Vornanen, M.; Veikkolainen, V.; Eerola, E.; Pulliainen, A.T. Cat scratch disease caused by Bartonella grahamii in an immunocompromised patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2781–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serratrice, J.; Rolain, J.M.; Granel, B.; Ene, N.; Conrath, J.; Avierinos, J.F.; Disdier, P.; Raoult, D.; Weiller, P.J. Bilateral retinal artery branch occlusions revealing Bartonella grahamii infection. Rev. Med. Interne. 2003, 24, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, J.H.; Dure, L.; Sullender, W.; Buraphacheep, W.; Frye, T.A.; Galliani, C.A.; Marston, E.; Jones, D.; Regnery, R. Central nervous system infection associated with Bartonella quintana: A report of two cases. Pediatrics. 1997, 100, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadly, E.; Chmielewski, T.; Tylewska-Wierzbanowska, S. Bartonella henselae and Borrelia burgdorferi infections of the central nervous system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 990, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Sampling locations. The right figure depicts a map of China, while the left figure illustrates maps of Heqing County and Gongshan County, located in Yunnan Province, China.
Figure 1.
Sampling locations. The right figure depicts a map of China, while the left figure illustrates maps of Heqing County and Gongshan County, located in Yunnan Province, China.
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree based on ssrA gene in small mammals from Yunnan Province, China. Note: The red triangle above represents: HQ66, HQ72, HQ73, HQ77, HQ92, HQ99; the red triangle below represents: HQ4, HQ18, HQ25, HQ32, HQ34, HQ35, HQ55, HQ80, GS29, GS35, GS37, GS60.
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree based on ssrA gene in small mammals from Yunnan Province, China. Note: The red triangle above represents: HQ66, HQ72, HQ73, HQ77, HQ92, HQ99; the red triangle below represents: HQ4, HQ18, HQ25, HQ32, HQ34, HQ35, HQ55, HQ80, GS29, GS35, GS37, GS60.
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree based on rpoB gene in small mammals from Yunnan Province, China.
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree based on rpoB gene in small mammals from Yunnan Province, China.
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree based on gltA gene in small mammals from Yunnan Province, China.
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree based on gltA gene in small mammals from Yunnan Province, China.
Figure 5.
Tissue distribution of Bartonella species in positive samples. The quantification (mean ± standard error) of Bartonella species in the spleen, heart, brain, kidney, lung, liver, and rectum of 30 positive samples was measured in copies/g. The significance test was performed using one-way ANOVA (**** p < 0.0001). The detection limit of qPCR is indicated by a red dashed line in this study.
Figure 5.
Tissue distribution of Bartonella species in positive samples. The quantification (mean ± standard error) of Bartonella species in the spleen, heart, brain, kidney, lung, liver, and rectum of 30 positive samples was measured in copies/g. The significance test was performed using one-way ANOVA (**** p < 0.0001). The detection limit of qPCR is indicated by a red dashed line in this study.
Table 1.
Molecular prevalence of Bartonella species in small mammals from Heqing County and Gongshan County, Yunnan Province.
Table 1.
Molecular prevalence of Bartonella species in small mammals from Heqing County and Gongshan County, Yunnan Province.
| Order |
Species |
Locations (County) |
Composition (%) |
Prevalence, % |
| qPCR |
Conventional PCR |
| ssrA |
rpoB |
gltA |
| Rodentia |
Chevrier’s field mouse (Apodemus chevrieri) |
Heqing, Gongshan |
45.4(151/333) |
44.4 (67/151) |
19.0(23/151) |
3.3 (5/151) |
1.9 (3/151) |
| Small oriental vole (Eothenomys Eleusis) |
Heqing, Gongshan |
28.2 (94/333) |
27.7 (26/94) |
4.2(4/94) |
4.2 (4/94) |
0.0 (0/94) |
Chestnut white-bellied rat
(Niviventer fulvescens) |
Heqing, Gongshan |
0.3(1/333) |
100.0 (1/1) |
100.0(1/1) |
100.0 (1/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
| Asian house rat (Rattus tanezumi) |
Heqing, Gongshan |
9.6 (32/333) |
6.3 (2/32) |
3.1(1/32) |
0.0 (0/32) |
0.0 (0/32) |
| Norway rat (Rattus norvegicus) |
Gongshan |
0.3 (1/333) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
White-footed Indochinese rat
(Rattus nitidus) |
Heqing |
0.3 (1/333) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
| Ryukyu mouse (Mus caroli) |
Heqing |
0.9 (3/333) |
0.0 (0/3) |
0.0 (0/3) |
0.0 (0/3) |
0.0 (0/3) |
| House moue (Mus musculu) |
Heqing |
0.6 (2/333) |
0.0 (0/2) |
0.0 (0/2) |
0.0 (0/2) |
0.0 (0/2) |
Swinhoe’s striped squirrel
(Tamiops swinhoei) |
Heqing |
0.3(1/333) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
0.0 (0/1) |
Smoke-bellied Niviventer
(Niviventer eha) |
Gongshan |
0.6(2/333) |
0.0 (0/2) |
0.0(0/2) |
0.0(0/2) |
0.0(0/2) |
| Eulipotyphla |
Long-tailed red-toothed shrew (Episoriculus leucops) |
Gongshan |
1.5 (5/333) |
60.0 (3/5) |
0.0 (0/5) |
0.0 (0/5) |
40.0 (2/5) |
| Asian gray Shrew (Crocidura attenuate) |
Gongshan |
4.2 (14/333) |
0.0 (0/14) |
0.0 (0/14) |
0.0 (0/14) |
0.0 (0/14) |
| Chinese mole shrew (Anourosorex squamipes) |
Gongshan |
5.1 (17/333) |
23.5 (4/17) |
16.7 (1/17) |
0.0 (0/17) |
0.0 (0/17) |
| Lagomorpha |
Tibet Pika (Ochtona Thibetana) |
Gongshan |
2.7 (9/333) |
22.2 (2/9) |
0.0 (0/9) |
0.0 (0/9) |
0.0 (0/9) |
| |
Total |
|
100.0 (333/333) |
31.5 (105/333) |
9.0 (30/33) |
2.9 (10/333) |
1.4 (5/333) |
Table 2.
Bartonella species copies in tissues of small mammals.
Table 2.
Bartonella species copies in tissues of small mammals.
| |
Spleen |
Heart |
Brain |
Kidney |
Lung |
Liver |
Rectum |
| Mean (Copies/g) |
3.3×105
|
1.1×105
|
9.7×104
|
2.5×104
|
2.5×104
|
2.2×104
|
2.0×104
|
| SEM (Copies/g) |
1.8×105
|
7.6×104
|
1.5×104
|
9.7×103
|
5.4×103
|
5.2×103
|
5.7×103
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).